Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Boyraz B, Roberts D. Chorangioma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/placentachorangioma.html. Accessed April 20th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Well demarcated placental mass composed of capillaries, stromal cells and surrounding trophoblast arising in a stem villus
Essential features
- Well circumscribed nodule(s) formed by proliferation of capillaries in a stem villus
- Most are asymptomatic and microscopic
- When large (> 4 cm), can cause fetal hemodynamic complications
Terminology
- Placental hemangioma
- Fibroangiomyxoma
ICD coding
- ICD-10: 043.89 - other placental disorders
Epidemiology
- Most common in multiple gestation pregnancies or pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia
- Most common placental tumor (in 0.5 - 1% of all placentas) (Fetal Pediatr Pathol 2010;29:199)
Sites
- Placenta
Pathophysiology
- Likely a hamartoma but may be a reactive process due to hypoxia
Etiology
- High altitude pregnancies (Placenta 2016;39:154)
- Increased maternal age
- Hypertension including preeclampsia
- Multiple gestation
- Rarely can recur in subsequent pregnancies (Pediatr Dev Pathol 1999;2:264)
- Co-occurrence with infantile hemangioma in 1 series at ~50% (Pathol Res Pract 2014;210:548, BMJ Open 2017;7:e015539)
Clinical features
- Most are small, incidental and asymptomatic
- Large (> 4 cm) chorangiomas are associated with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), polyhydramnios, preterm delivery, arteriovenous shunting (and fetal cardiomegaly or heart failure), hydrops, fetal thrombocytopenia and maternal mirror syndrome (J Perinat Med 2014;42:273, Indian Pediatr 1996;33:520)
Diagnosis
- Most are incidental and microscopic, rarely evident grossly as masses at the chorionic plate
- If large enough, diagnosis can be made antenatally by imaging
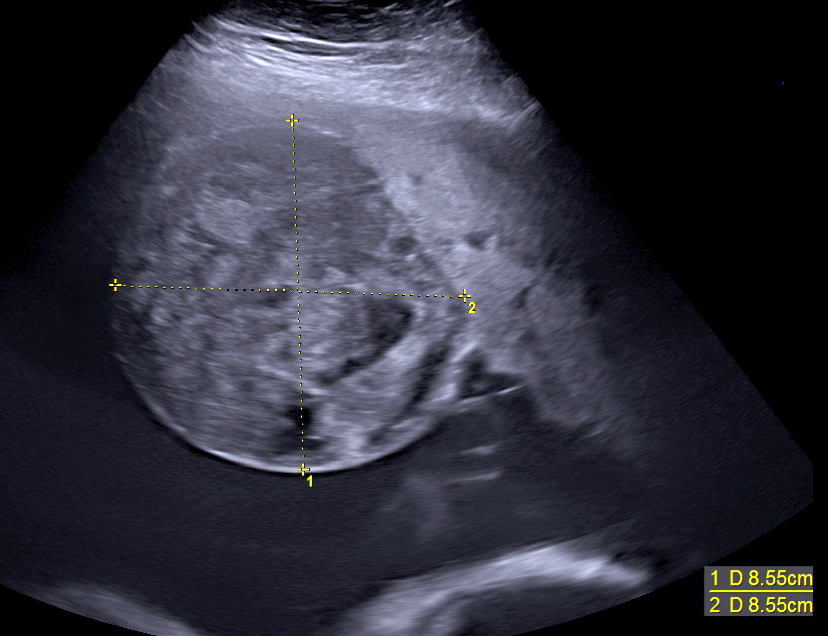
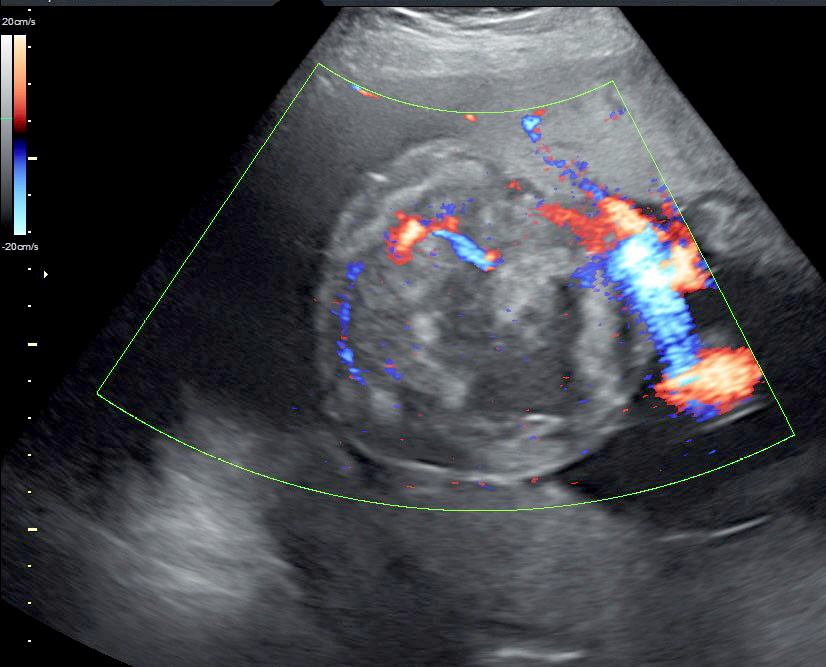
Radiology description
- Well circumscribed hypoechoic mass(es) by ultrasound imaging, vascular by color Doppler imaging or MRI
Prognostic factors
- Most small chorangiomas have no clinical relevance
- Large chorangiomas (> 4 cm) may be associated with perinatal morbidity and even mortality due to hemodynamic stresses on the fetus (see Clinical features)
Case reports
- 23 year old woman presents at 37 weeks in labor and delivers a live birth; the placenta was noted to have an 8 cm subchorionic mass (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2009;28:267)
- 27 year old woman presented at 27 weeks gestation with markedly enlarged placenta showing increased vascularity on color Doppler (JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc 2006;45:366)
- 27 year old woman presented at 32 weeks gestation with polyhydramnios, 12 cm well defined echogenic mass with ultrasound (Case Rep Obstet Gynecol 2012;2012:913878)
Treatment
- Careful monitoring for the development of hydrops if large
- Symptomatic treatment (intrauterine transfusions, amniodrainage)
- Interventions in rare cases (alcohol injection, microcoil embolization, endoscopic laser coagulation and interstitial laser therapy)
- Reference: Fetal Pediatr Pathol 2010;29:199
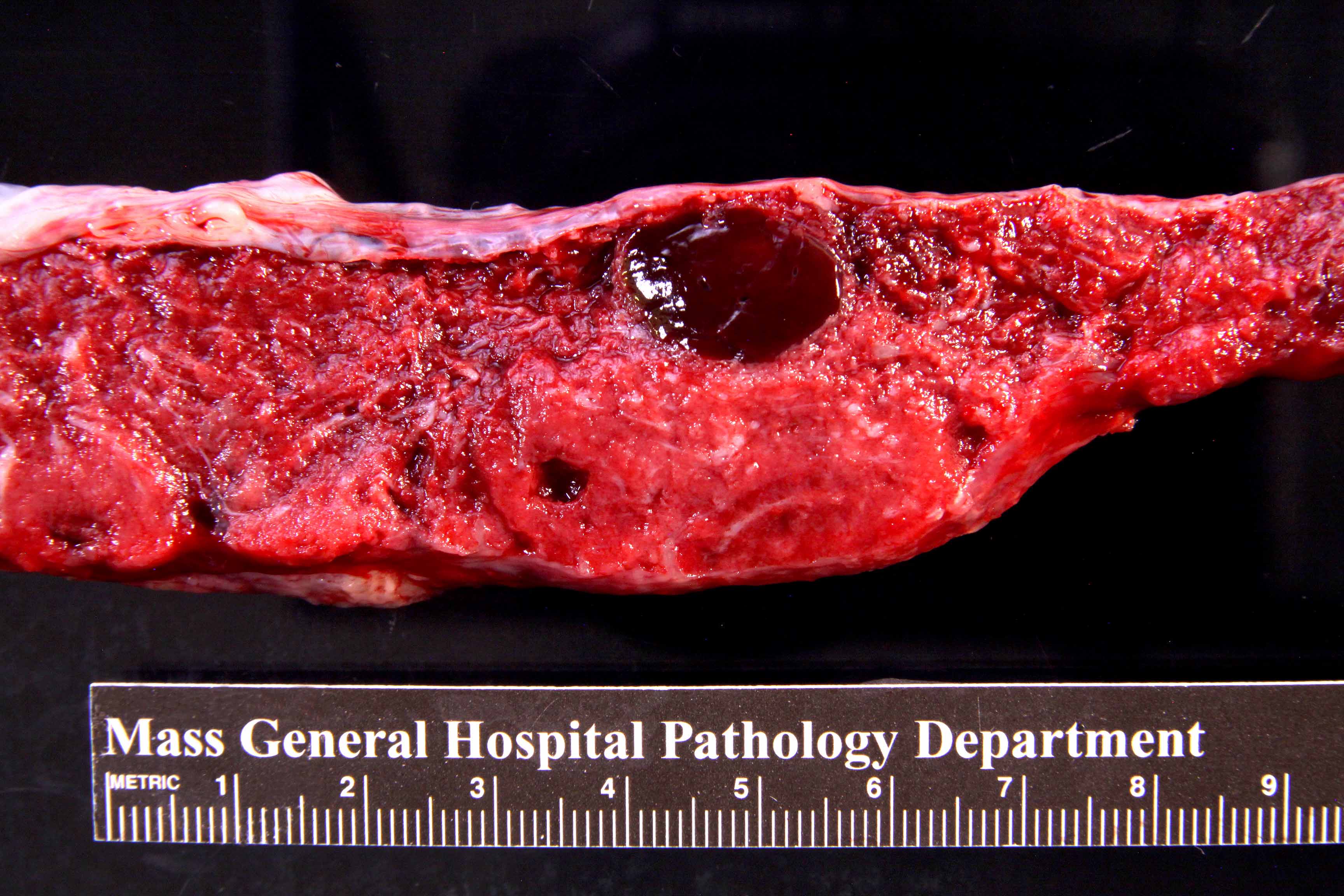
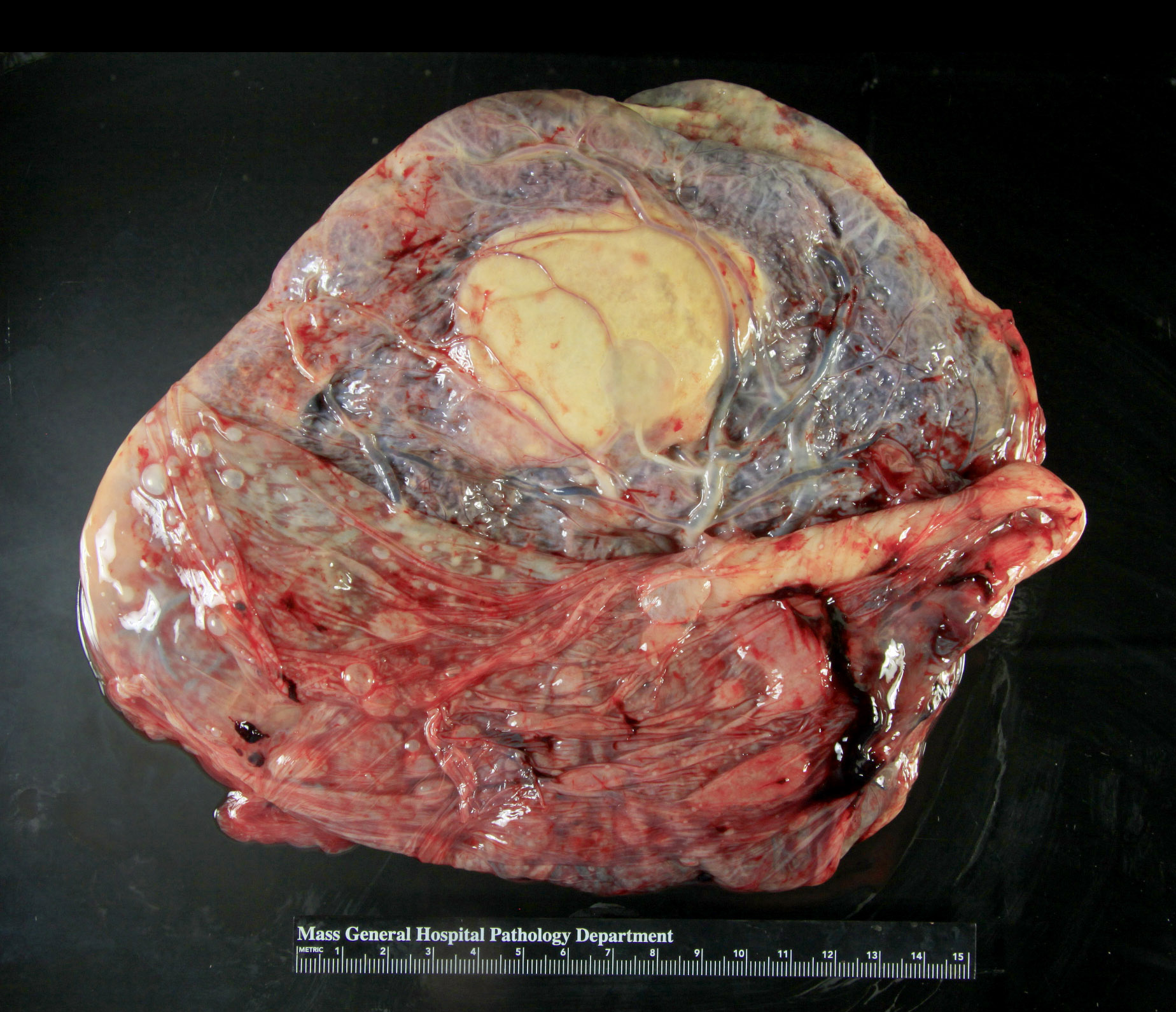
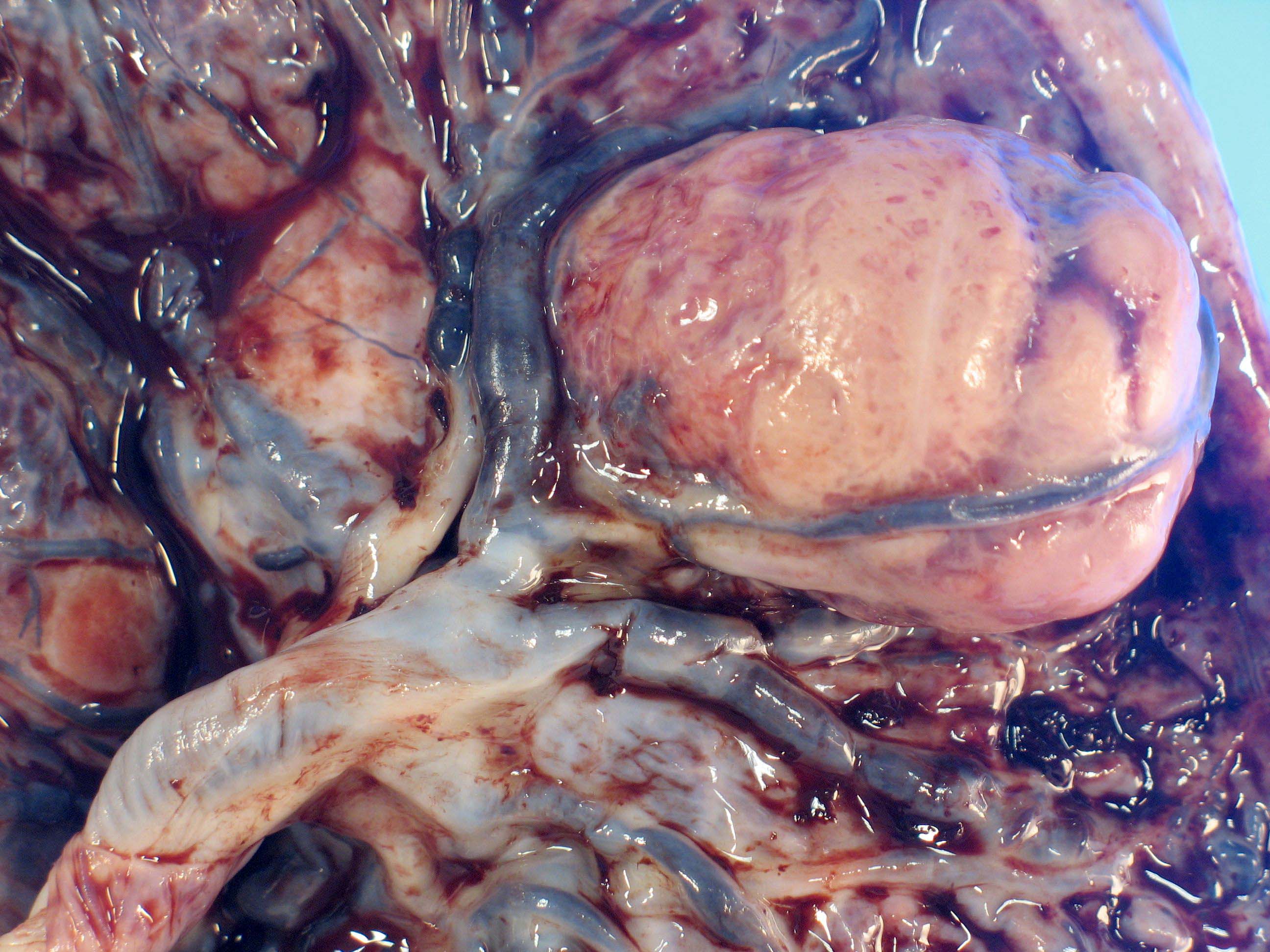
Gross description
- Single or multiple well circumscribed spherical / oval masses if large enough to be grossly identifiable
- Subchorionic or marginal
- Red-brown, fleshy
- Firm and tan-brown, if infarcted
- Range: 1 - 10 cm; most < 4 cm
- Reference: Fetal Pediatr Pathol 2010;29:199
Gross images
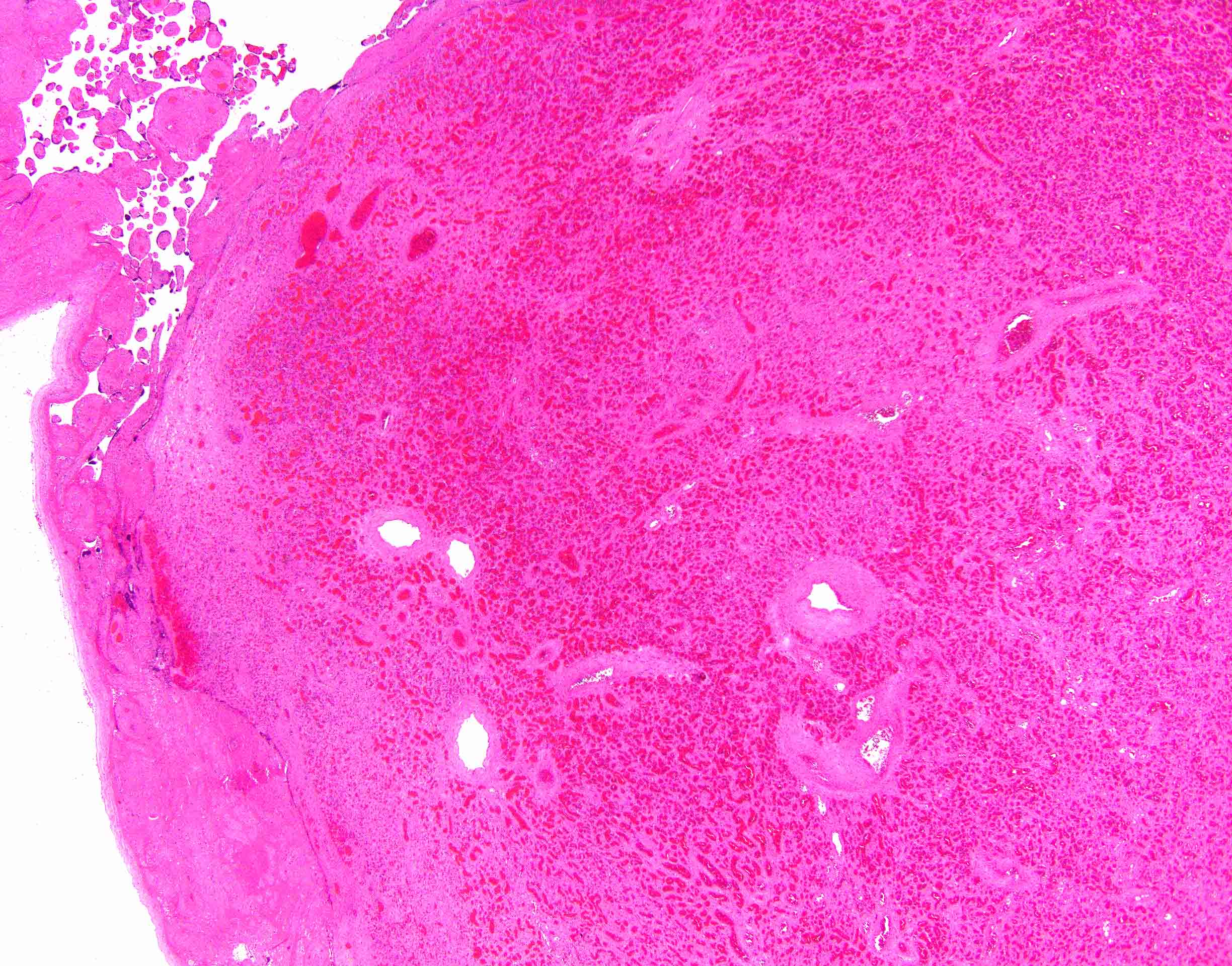
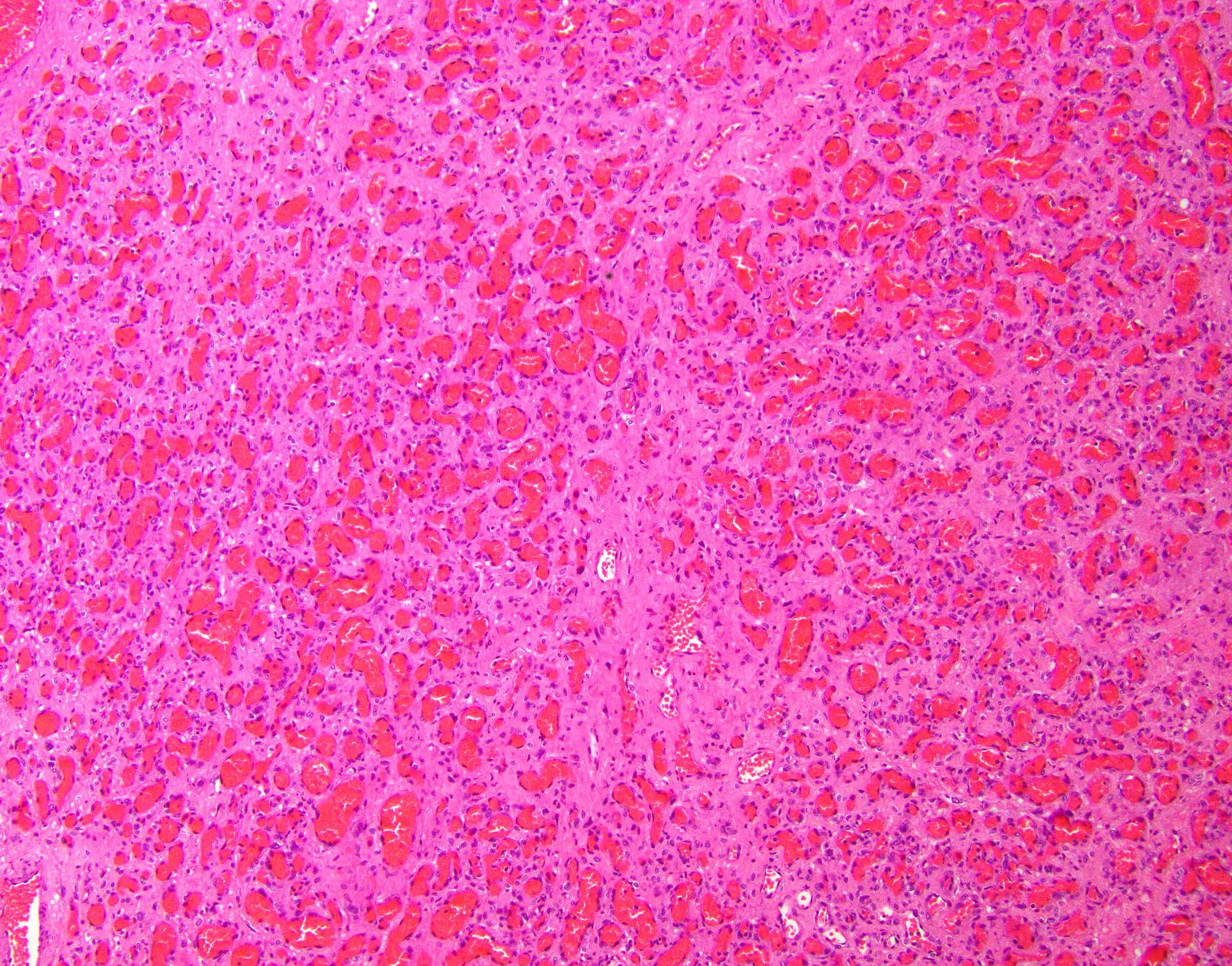
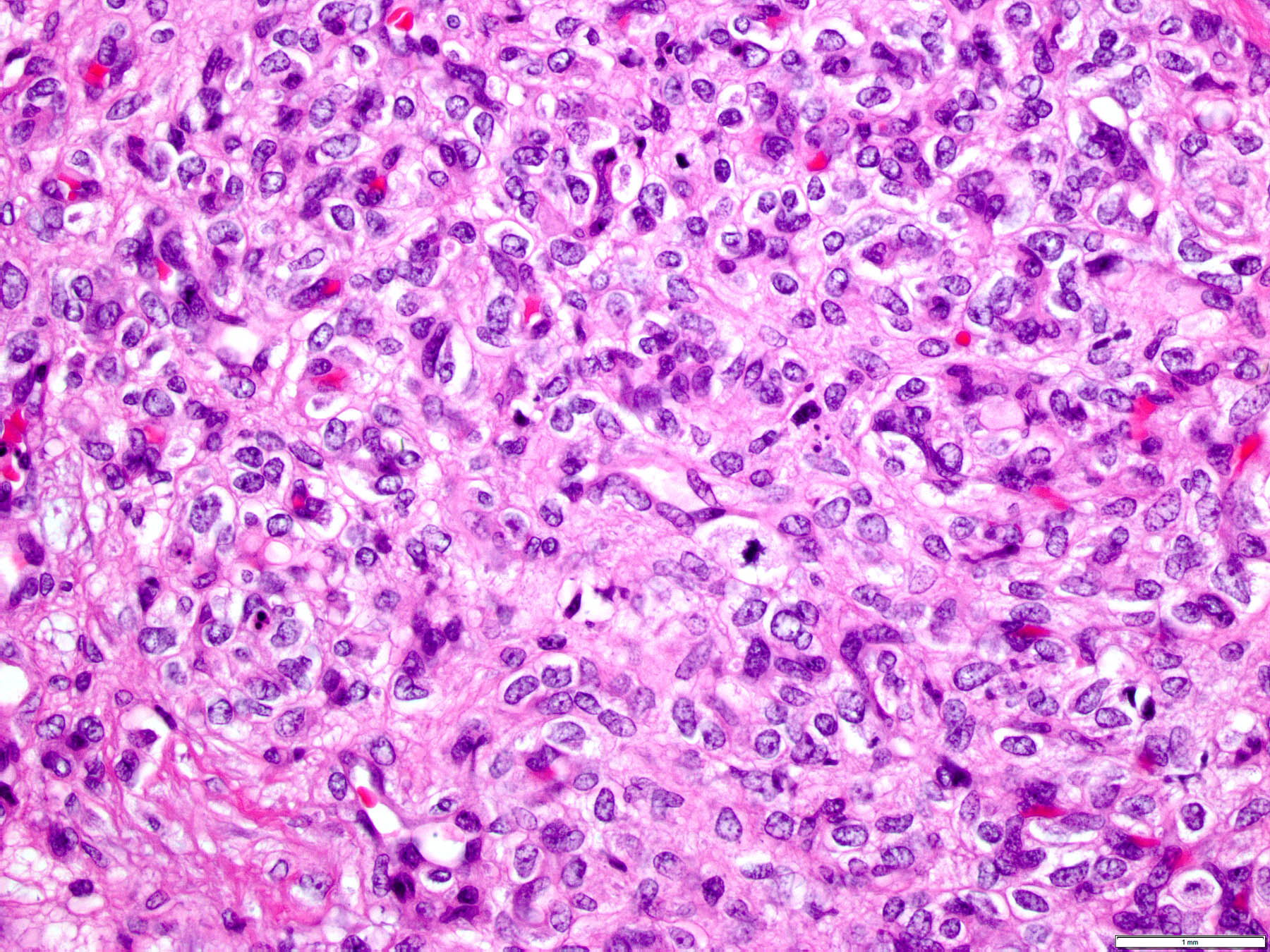
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Well circumscribed mass
- Fetal capillaries with surrounding stroma and trophoblast
- Infarction, fibrosis, hyalinization, calcification and hemosiderin deposition can be seen
- Rare myxoid degeneration reported (JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc 2006;45:366)
- Trophoblast proliferation can be present but should not show cytological atypia (Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8:16798, Virchows Arch 2000;436:167)
- Stroma can be cellular with increased mitoses and necrosis (atypical chorangioma) (Int J Surg Pathol 2015;23:364, Int J Gynecol Pathol 1983;1:403)
- No malignant transformation reported
Microscopic (histologic) images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- No copy number alteration identified (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2019;22:236)
Sample pathology report
- Placenta, term vaginal delivery:
- Mature placenta (530 g, ~50th percentile for 40 weeks gestational age); patchy villous edema; chorangioma (2 cm) (see comment)
- Comment: These are benign, usually incidental, placental masses, likely hamartomas, of no clinical significance when < 4 cm, as is this one. Some have noted an association with infantile hemangiomas; clinical correlation is necessary.
Differential diagnosis
- Chorangiosis and chorangiomatosis:
- No distinct mass
- Involves intermediate and terminal villi
- Chorangiocarcinoma:
- Controversial lesion of combined chorangioma and choriocarcinoma
- Extensive trophoblast proliferation, atypia and necrosis (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2009;28:267, Placenta 1988;9:607)
- Other placental masses:
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor:
- Rare circumscribed mass in the membranes or on the basal plate of the placenta
- Usually ALK1 positive (Hum Pathol 2020;106:62)
- References: Int J Gynecol Pathol 2015;34:419, Hum Pathol 2020;97:29, Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:970
- Leiomyoma:
- Rare circumscribed mass on the basal plate of the placenta (Clin Pathol 2020;13:2632010X20928328)
- Placental infarct:
- Common lesion often at the placental periphery
- Not well circumscribed, irregular in shape, gritty in texture
- Intervillous thrombus:
- Common lesion of either currant jelly or yellow / white laminated, irregularly shaped mass anywhere in the placenta
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor:
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
A. Chorangioma. Chorangiomas are likely hamartomas of the placental stem villi forming vascular masses nearly always peripheral and adjacent to the chorionic plate. They are well demarcated, firm masses when grossly identifiable and most are incidental and microscopic. Leiomyomas from the uterus can be adherent to the basal plate of the placenta and are extremely rare masses, extraneous to the placental parenchyma. Placental infarcts are typically firm and gritty triangular or rectangular masses at the maternal floor (not the chorionic plate). Intervillous thrombi are laminated irregularly shaped red or white soft masses anywhere in the placenta. Placental associated inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors are also unusual extrinsic masses that can be attached to the placenta basal plate or membranes.
Comment Here
Reference: Chorangioma
Comment Here
Reference: Chorangioma
Board review style question #2
What are complications associated with chorangioma?
- Fetal and maternal hydrops
- Malignant transformation
- Maternal visceral hemangiomas
- Obstructed labor and delivery
Board review style answer #2
A. Fetal and maternal hydrops. Vascular steal and heart failure due to fetal perfusion of a large chorangioma can lead to fetal hydrops. Maternal mirror syndrome is a rare but serious complication of hydrops fetalis. Malignant transformation does not occur in chorangiomas; if malignancy occurs, the diagnosis is likely an intraplacental choriocarcinoma, which can have associated hypervascular villi. Visceral hemangiomas in the mother are not associated with chorangiomas but fetal / neonatal hemangiomas of the skin have been reported. Chorangiomas rarely reach a size which could complicate delivery.
Comment Here
Reference: Chorangioma
Comment Here
Reference: Chorangioma