Table of Contents
Definition / general | Procedure | Sections to obtain | Tips | Gross description | Gross images | Sample gross description report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Ravishankar S. Grossing-products of conception. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/placentagrossingPOC.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- This topic describes how to gross specimens obtained from products of conception specimens (dilation and curettage or dilation and evacuation with or without fetal parts)
- Essential clinical history:
- Gestational age
- Ultrasound abnormalities
- Presence / absence of a fetus / fetal pole
- Abnormalities of beta hCG rise
- Antenatal genetic testing results (i.e., noninvasive prenatal screening [NIPS])
- Purpose of examination:
- Identify chorionic villi or implantation site to confirm the presence of intrauterine pregnancy
- If intrauterine pregnancy cannot be confirmed, this is a critical value and the clinician must be informed immediately, as there is risk for ectopic pregnancy
- Evaluate villous morphology and identify abnormalities, including gestational trophoblastic disease (i.e., molar pregnancy)
- If embryonic / fetal parts are identified, attempt to document:
- Sex (if possible)
- Whether growth is appropriate for gestational age
- Any dysmorphic features or congenital anomalies
- Collect fresh tissue for genetic / cytogenetic testing, if needed / requested
- If procedure is being done for retained products of conception, evaluate for retained placental tissue or subinvolution of implantation site (see Placental site subinvolution)
- Identify chorionic villi or implantation site to confirm the presence of intrauterine pregnancy
- References: Redline: Placental and Gestational Pathology Hardback, 1st Edition, 2018, Baergen: Manual of Pathology of the Human Placenta, 2nd Edition, 2011
Procedure
- Remove all tissue from the specimen container and measure in aggregate
- Separate blood clot from the soft tissue
- Examine the soft tissue and separate the different types of tissue
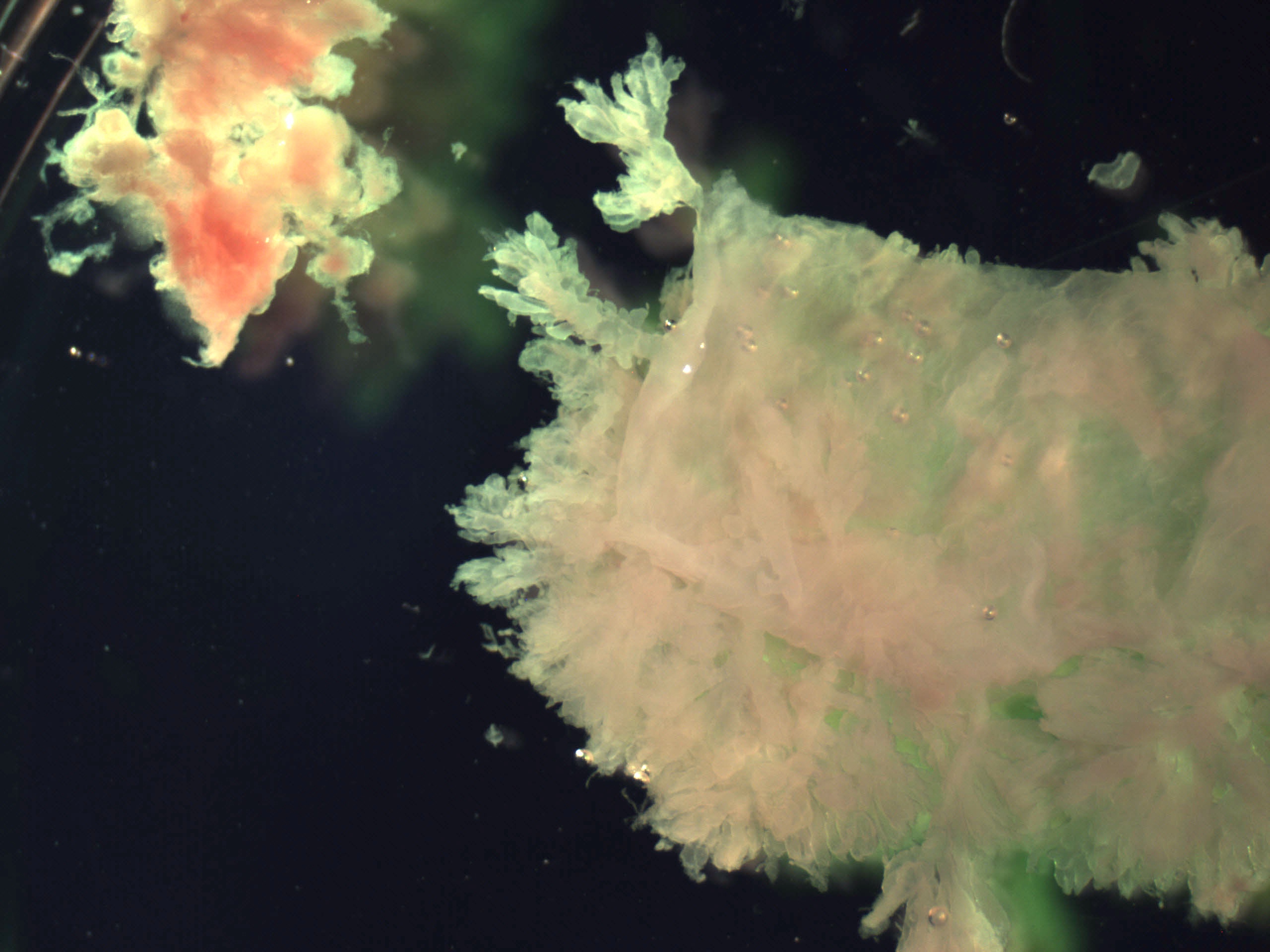
- Decidua: superficial part of the endometrium (maternal tissue)
- Usually a pale gray-white color and often looks like a sheet
- 1 side will be smooth while the other is rough
- Implantation site: decidua that contains the area where the placenta implanted
- Even if chorionic villi are absent, the presence of implantation site indicates an intrauterine pregnancy
- Looks similar to decidua but is more yellow and somewhat firmer
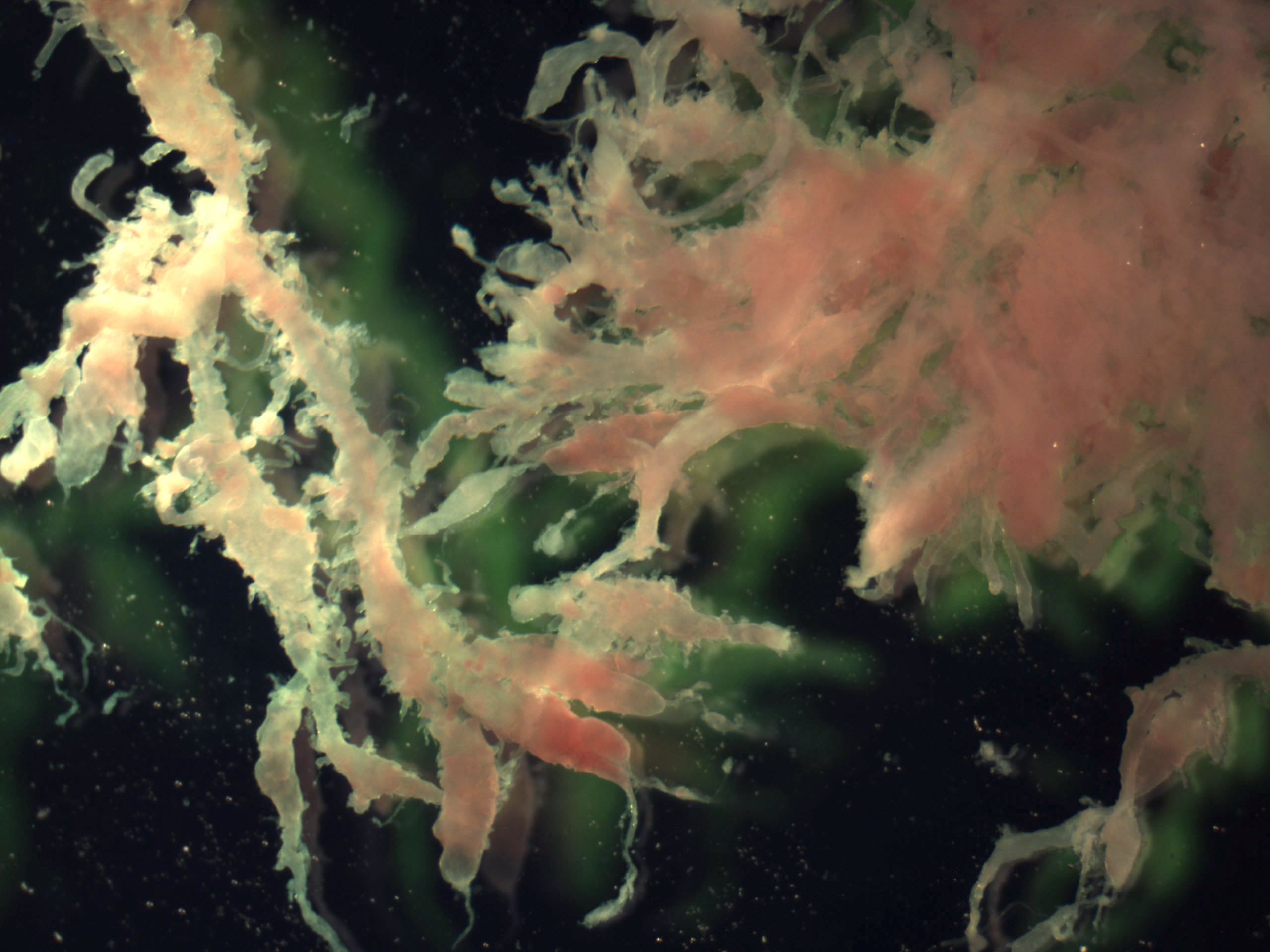
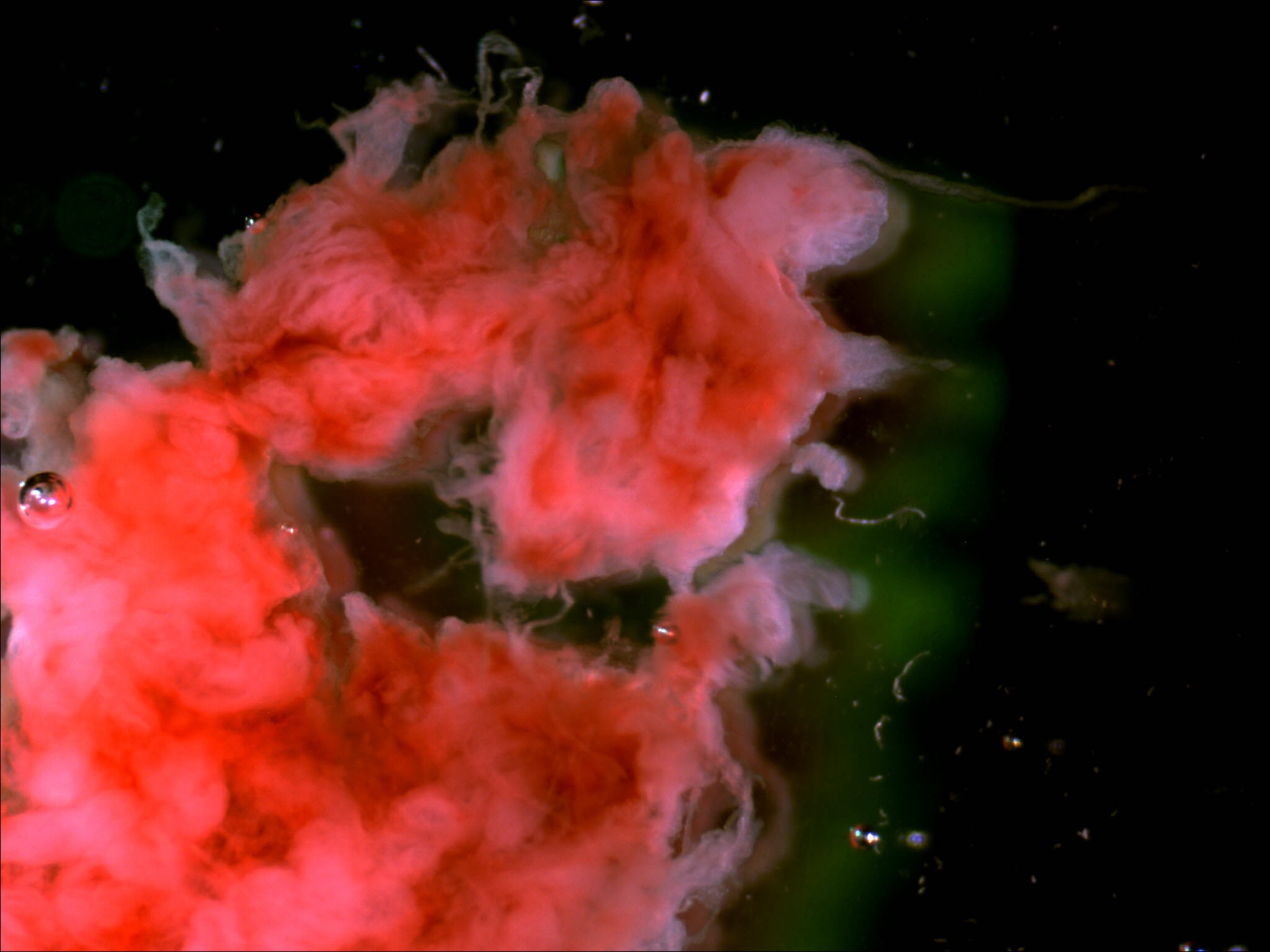
- Chorionic villi: placental tissue
- Usually white or pink-white in color and has long finger-like projections
- Membranes: placental tissue
- Looks similar to membranes in mature placentas but thinner and more translucent
- All of the above: may find an intact chorionic sac, which includes all of the above elements; may also contain umbilical cord, embryonic or fetal tissue
- Decidua: superficial part of the endometrium (maternal tissue)
- Measure the villous tissue in aggregate
- Examine the villous tissue to determine if there is hydropic change or vesicles (see Gross images)
- If vesicles are present, measure range of greatest dimension
- If an embryo (< 8 weeks gestation, < 27 mm crown rump length) or fetal parts are identified:
- Measure as many of the standard measurements as possible (crown to rump, crown to heel, head circumference, foot length)
- Attempt to evaluate the external genitalia
- Both male and female fetuses have an enlarged penile / clitoral swelling but females will have a vaginal orifice underneath, while males do not
- Perform external and internal examination to evaluate for any anomalies
- Correlation with prior ultrasound imaging can be very helpful
- Submit sections, as considered appropriate by your institution's general practice
- Reference: Obstet Gynecol 1986;67:79
Sections to obtain
- Submit representative chorionic villi, membranes, implantation site and decidua
- No grossly identifiable chorionic villi: submit entirely or up to 6 cassettes
- With chorionic villi but without fetal or embryonic tissue: submit 3 cassettes
- With hydropic change / vesicles: submit 6 cassettes
- With fetal / embryonic tissue: refer to your institution's policy
- Suggested sections: 3 - 5 sections of placental tissue, 2 cassettes of fetal tissue, 1 with gonads (wrap in Histowrap if needed) and 1 with lung, kidney, adrenal and liver
- References: Redline: Placental and Gestational Pathology Hardback, 1st Edition, 2018, Baergen: Manual of Pathology of the Human Placenta, 2nd Edition, 2011
Tips
- If you are having trouble determining whether a tissue fragment is decidua or villi, you can float it in a shallow container of saline or examine it under a dissecting microscope
- Villi will have longer and thinner projections, decidua appears more blunted (see Gross images)
- Sometimes the blood clot actually contains chorionic villi that can be difficult to identify grossly; if you do not find any villi in the soft tissue, consider submitting a few sections of blood clot and you may get lucky
- References: Redline: Placental and Gestational Pathology Hardback, 1st Edition, 2018, Baergen: Manual of Pathology of the Human Placenta, 2nd Edition, 2011
Gross description
- Early first trimester pregnancy loss:
- Most common scenario
- Mix of blood clot, decidua and villous tissue with no particular gross abnormalities
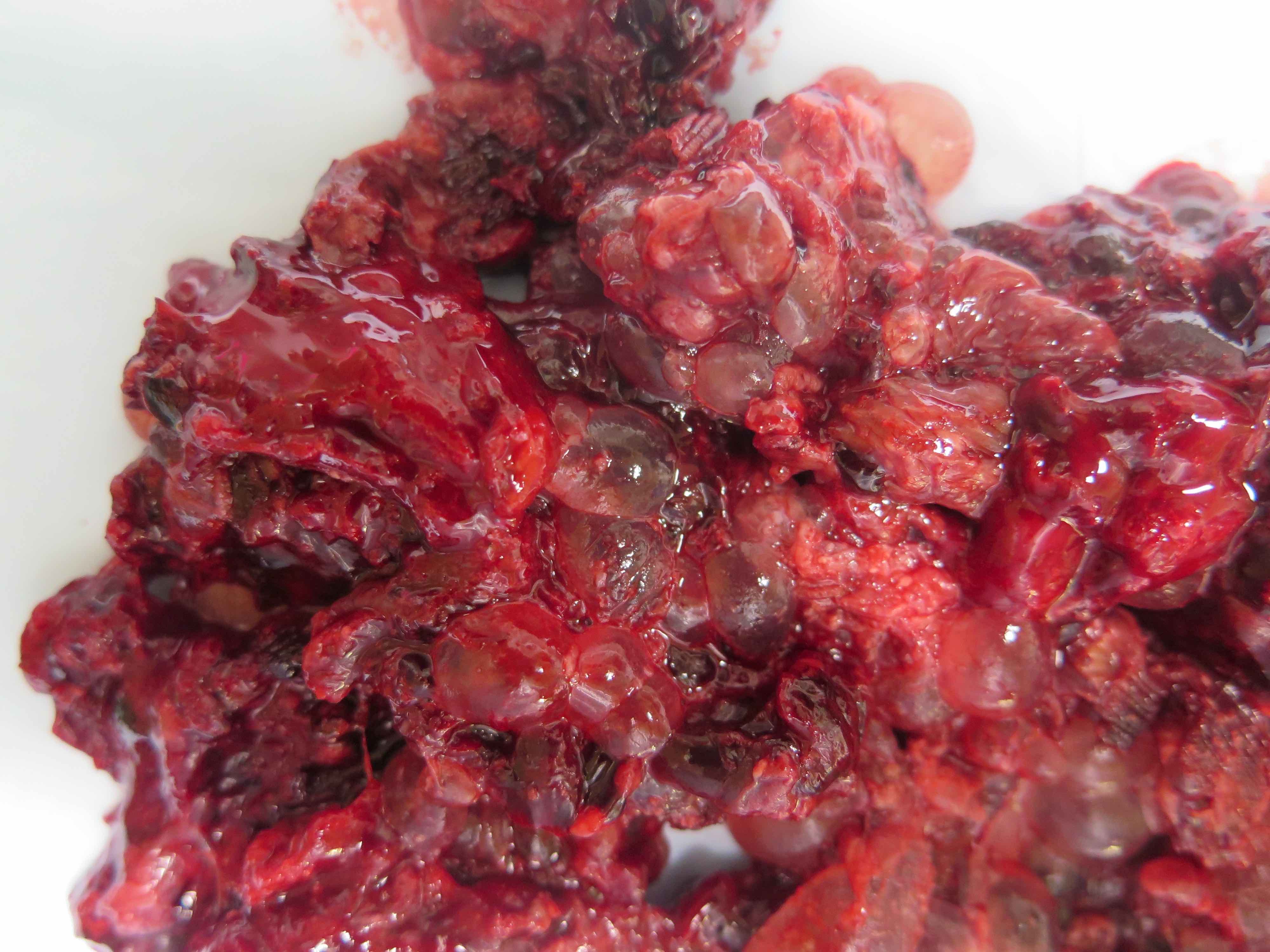
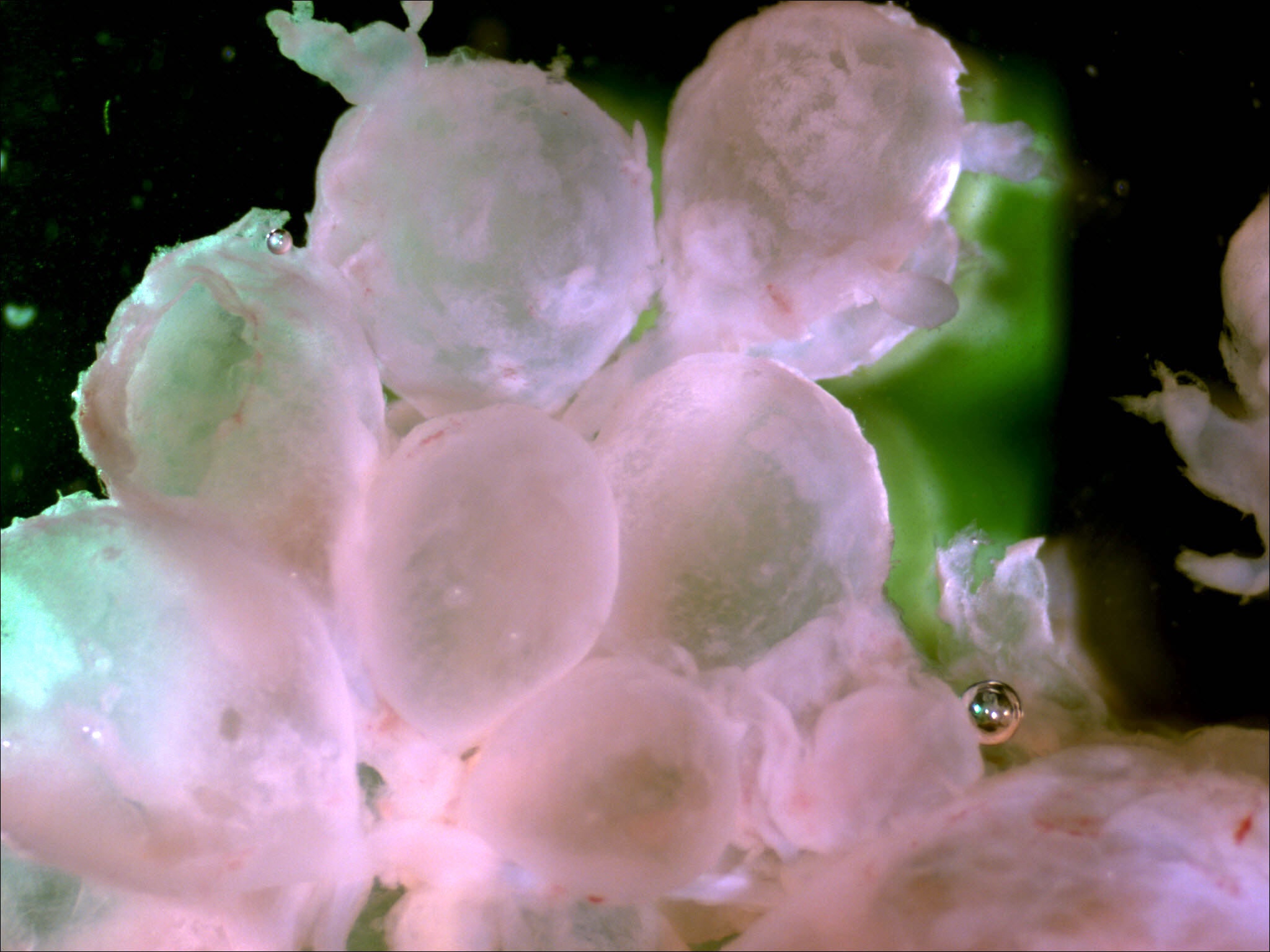
- Hydatidiform mole:
- Enlarged, hydropic villi or vesicles
- Partial hydatidiform mole: may contain fetal tissue
- References: Redline: Placental and Gestational Pathology Hardback, 1st Edition, 2018, Baergen: Manual of Pathology of the Human Placenta, 2nd Edition, 2011
Gross images
Sample gross description report
- Products of conception without chorionic villi:
- Received (fresh, in formalin), labeled with the patient's name and hospital number and "[ ]", are multiple fragments of (pale red soft tissue, dark red-brown friable tissue) and clotted blood, aggregating to [__ x __ x __ cm]. Chorionic villi are not grossly identified. The specimen is entirely submitted in [__] cassettes.
- Products of conception with chorionic villi:
- Received (fresh, in formalin), labeled with the patient's name and hospital number and "[ ]", are multiple fragments of (pale red soft tissue, dark red-brown friable tissue) and clotted blood, aggregating to [__ x __ x __ cm]. Possible villous tissue is identified, measuring [__ x __ x __ cm]. A portion of the specimen is submitted for genetic analysis. Representative sections are submitted in 3 cassettes.
- Summary of cassettes:
- A1: possible villous tissue
- A2: nonvillous tissue
- A3: additional villous and nonvillous tissue
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1