Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Case reports | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Garg S. Hepatocellular adenoma-like lesion of placenta. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/placentahepatocellularadenoma.html. Accessed April 18th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Extremely rare benign nontrophoblastic lesion (about 9 cases have been reported so far)
- May represent a liver heterotopia or specialized monodermal teratoma (Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:355)
Essential features
- Morphologic, immunophenotypic and ultrastructural features of fetal hepatocytes (Int J Surg Pathol 2016;24:640)
- Usually a benign incidental finding (Int J Surg Pathol 2016;24:640)
Sites
- Usually presents as a subchorionic intervillous mass or in the villous parenchyma of the placenta
Pathophysiology
- Exact pathophysiology of ectopic liver in the placenta is unknown
- Hypothesized that aberrant migration or displacement of cells from the developing hepatic buds leads to ectopic liver formation
- Groups of liver cells become entrapped in the foregut as the diaphragm closes (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2017 Jan 1 [Epub ahead of print])
- It may represent a specialized monodermal teratoma in the placenta
Clinical features
- Usually an incidental finding
Case reports
- Ectopic liver within the placental parenchyma of a stillborn fetus (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2017 Jan 1 [Epub ahead of print])
- Hepatic (hepatocellular) adenoma of the placenta (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2015;18:422)
- Coexistent chorangioma and hepatic adenoma in one twin placenta (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2015;18:422)
Gross description
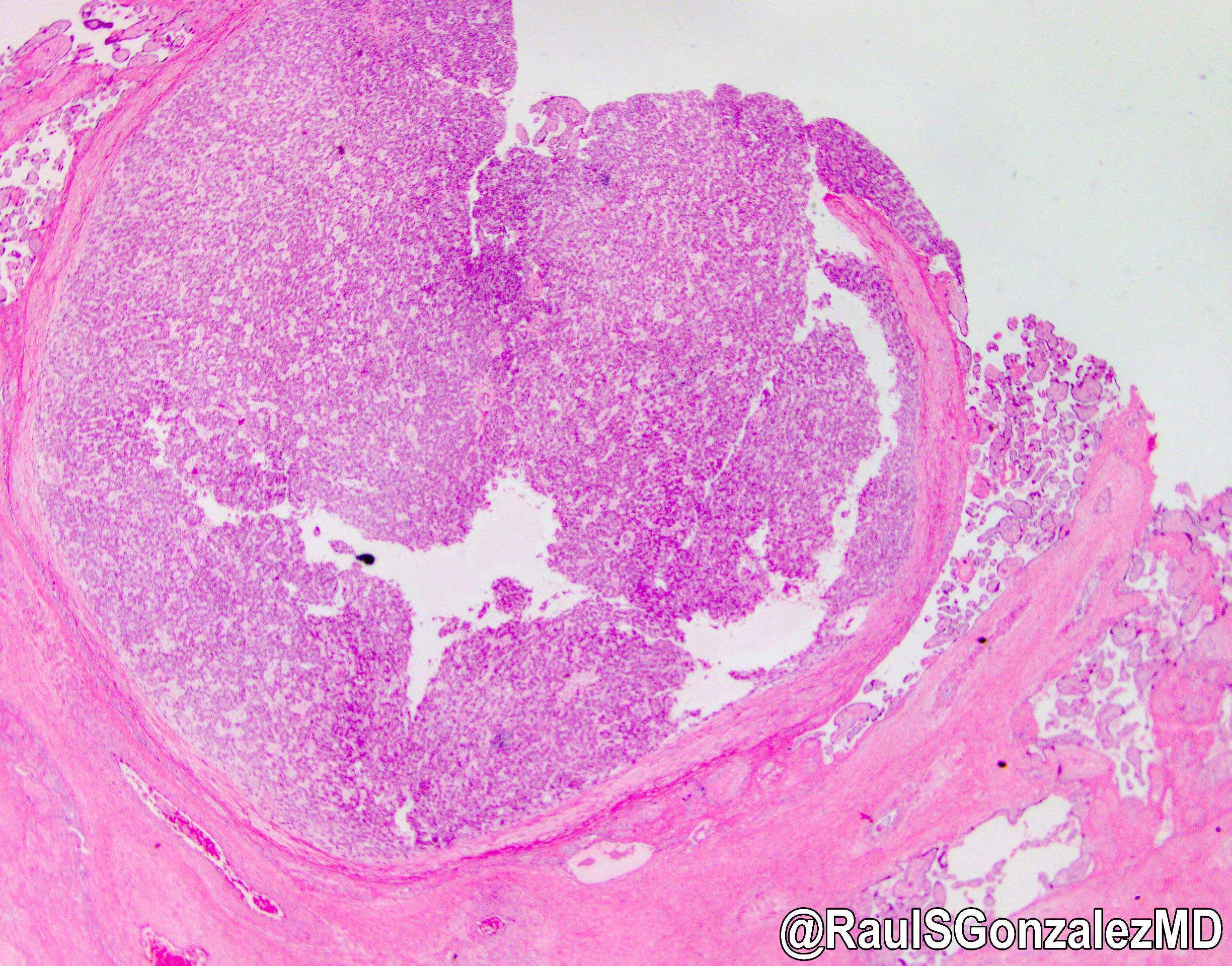
- Small (0.3 - 1.0 cm), well circumscribed tan to dark red nodules in the placental parenchyma
- May be encapsulated
- Without necrosis or hemorrhagic foci
- Sometimes may not be grossly visible
Microscopic (histologic) description
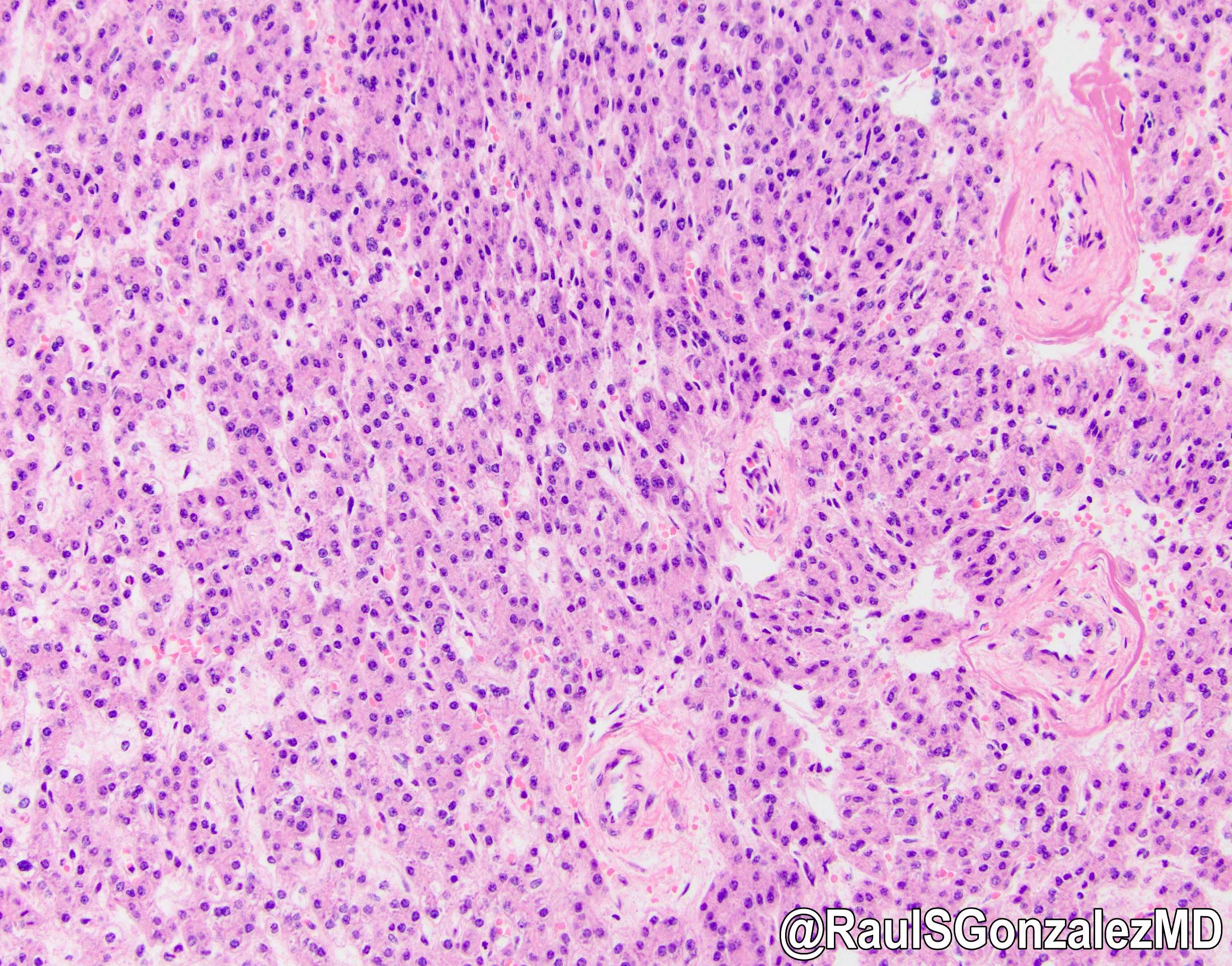
- Well circumscribed mass composed of semi distinct lobules of cords and nests of polygonal epithelial cells with pink and focally clear cytoplasm resembling fetal hepatocytes (Int J Gynecol Pathol 1998;17:241)
- No portal tracts, bile ducts or central veins are identified
- Extramedullary hematopoiesis is a constant feature
- Lesional cells contain glycogen
- No nuclear atypia, cellular pleomorphism or mitotic activity
- No globular cytoplasmic inclusions, intracytoplasmic hyaline or bile pigment
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Hep Par1, alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), polyclonal CEA in a canalicular pattern, AE1 / AE3 and CAM 5.2
Negative stains
- Beta catenin (no nuclear staining)
Electron microscopy description
- Tumor cells contain numerous glycogen granules, diffusely scattered endoplasmic reticulum and multiple mitochondria
- Cell membranes of adjacent cells are joined by desmosomes
- Structures resembling bile canaliculi are found (Am J Surg Pathol 1986;10:436)
Differential diagnosis
- Metastatic or primary hepatocellular carcinoma (reticulin stain shows increased plate thickness)
- Heterotopic adrenocortical nodule, chorangioma and placental metastasis of maternal and fetal malignancies
Board review style question #1
- Which of the following is true?
- Hepatocellular adenoma of the placenta is a benign and extremely rare lesion.
- Histologically, it presents as a well circumscribed mass composed of nests and cords of epithelial cells resembling fetal hepatocytes.
- It may actually represent liver heterotopia or a specialized monodermal teratoma in placenta.
- All of the above.
Board review style answer #1