Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Iczkowski KA. Prostatitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/prostateprostatitis.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Prostatitis is a clinical term only, so it should not be diagnosed on pathology reports
- Anatomic pathologists should simply diagnose chronic, acute or granulomatous inflammation
- Should be based on symptoms of pelvic pain and sexual dysfunction, with or without bacteria, based on quantitative bacterial cultures and microscopic examination of fractionated urine specimens (first 10 mL of urine is urethral, midstream urine is from bladder) and expressed prostatic secretions
Essential features
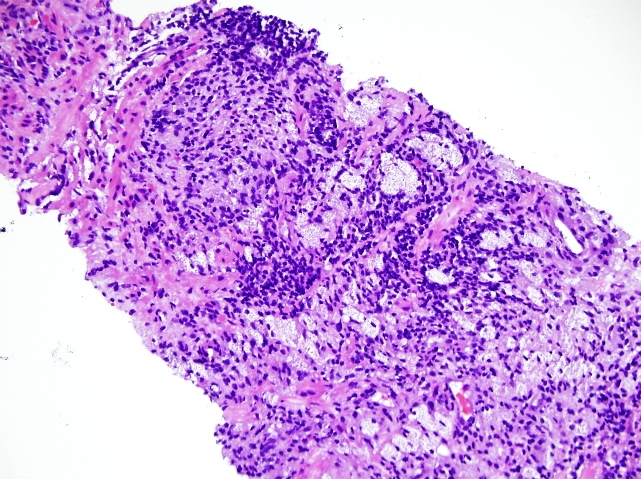
- Either lymphocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils or histiocytes
- When infectious, caused mainly by gram negative rods
Terminology
- Inflammatory disease of the prostate
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Chronic prostatitis / chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS), also known as NIH category III prostatitis, abacterial prostatitis or prostatodynia, is the most common urological diagnosis in men older than 50 years
- Current evidence suggests an inverse relationship between volume of atrophy (with or without inflammatory cells) and cancer (Hum Pathol 2014;45:54)
- Clinically diagnosed prostatitis may increase prostate cancer risk and may be race dependent; whereas histological prostatic inflammation can increase serum PSA and produce a false positive result that decreases the likelihood of cancer detection (PloS One 2021;16:e0252951, Mod Pathol 2012;25:1023)
Sites
- Can affect central and peripheral zones of the prostate (AJR Am J Roentgenol 1998;170:753)
Pathophysiology
- Histologic prostatitis, when present along with hyperplasia (BPH), correlates with greater lower urinary tract symptoms, prostate volume and risk of acute urinary retention; this suggests that prostatitis plays a role in progression of BPH (Aging Male 2022;25:88)
- Reflux of infected urinary contents into prostatic ducts is a postulated cause (Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 2011;22:298)
- Risk factors: indwelling catheter, underlying voiding dysfunction, poorly controlled diabetes, end stage renal disease (ESRD), cirrhosis, immunosuppression (Nat Rev Urol 2011;8:207)
Etiology
- Abacterial: this is a heterogeneous condition with many possible causes; however, aberrant cytokine function seems to be a final common pathway (J Urol 2010;184:1253)
- Newly recognized cause is IgG4 related prostatitis, which presents with obstruction and resolves with steroids and rituximab (BMC Urol 2022;22:35)
- Bacterial: Escherichia coli (accounts for > 70% of cases), Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Proteus, Enterobacter, Enterococcus species, Staphylococcus aureus (see Abscess)
Clinical features
- Systemic:
- Headache, fever, chills and general malaise, low back pain
- Prostate (local) (Korean J Urol 2012;53:860):
- Severely tender prostate with areas of fluctuation on digital rectal examination
- Perineal pain
- Dysuria, urinary urgency or frequency, hematuria, purulent urethral discharge
- Obstructive urinary symptoms
Diagnosis
- Overall, history and physical findings, complete blood count with differential, urine analysis, blood culture, urine culture and even PCR (detection of sexually transmitted organisms) may be used
- For specific types:
- Chronic abacterial prostatitis / chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS):
- Includes prostatodynia, category III or abacterial prostatitis
- Defined by the International Prostatitis Collaborative Network under the National Institute of Health, and diagnosis follows clinical, microbiological and laboratory criteria (JAMA 1999;282:236, Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2016;19:132)
- Histopathologic diagnosis is less crucial or may not be required for diagnosis
- Clinically similar to bacterial prostatitis, with persistent pain, especially after ejaculation; but no bacteria are cultured from expressed prostatic secretions (EPS)
- Excessive white blood cells (WBC) may be present or absent
- WBC number fluctuates within the same patient and does not correlate with symptom severity
- Essentially incurable
- Acute bacterial prostatitis:
- Same bacteria types as urinary tract infections (E. coli, gram negative rods, enterococci, staphylococci), usually due to reflux, also following surgical manipulation or sexually transmitted disease
- Usually localized, may cause obstruction, retention, abscess
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis:
- Symptoms of low back pain, dysuria, perineal and suprapubic discomfort
- Often have history of urinary tract infection by same organism
- May have no symptoms
- Granulomatous prostatitis:
- Necrotizing or nonnecrotizing granulomas may be seen in men who have undergone bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) treatment for bladder cancer
- Also occurs posttransurethral resection
- Otherwise, most cases are idiopathic and do not require acid fast stain
- Eosinophilic prostatitis:
- According to case reports, this is capable of increasing serum PSA levels (Br J Urol 1992;69:61)
- IgG4 related prostatitis:
- IgG4 related disease is a rare but under recognized type of chronic abacterial prostatitis that can cause urinary obstruction in young men (Case Rep Urol 2013;2013:295472)
- Elevated serum IgG4 levels are diagnostic; serum PSA should be normal
- There may be chronic sclerosing sialadenitis
- Biopsy shows prominent plasma cells; if the symptoms resolve following treatment with steroids, there is no need for prostate biopsy
- Chronic abacterial prostatitis / chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS):
Laboratory
- Bacterial: prostatic secretion cultures should have bacterial counts 10x higher than urethral / bladder cultures
- Nonbacterial: > 10 WBC/HPF in prostatic secretions without pyuria
- Can raise the serum PSA above normal (Hinyokika Kiyo 1993;39:445)
Radiology description
- Computed tomography (CT scan) of the abdomen and pelvis (AJR Am J Roentgenol 1987;148:899)
- Can better delineate the spread of infection to adjacent organs
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (Indian J Radiol Imaging 2011;21:46)
- Hypointense signal on T1 and hyperintense on T2 image
Prognostic factors
- Depends on the timely diagnosis and treatment and type of prostatitis
Case reports
- See case reports for specific types of prostatitis such as granulomatous, nonspecific granulomatous, malakoplakia and abscess
Treatment
- Difficult because antibiotics penetrate poorly into prostate
Microscopic (histologic) description
- WBCs in biopsied prostatic tissue do not correlate with the degree of pain in chronic prostatitis / CPPS
- Density of lymphocytes in the prostate is remarkably constant across age groups and races (Prostate 2003;55:187)
- Lymphoid aggregates are not specific for prostatitis but may be part of hyperplasia
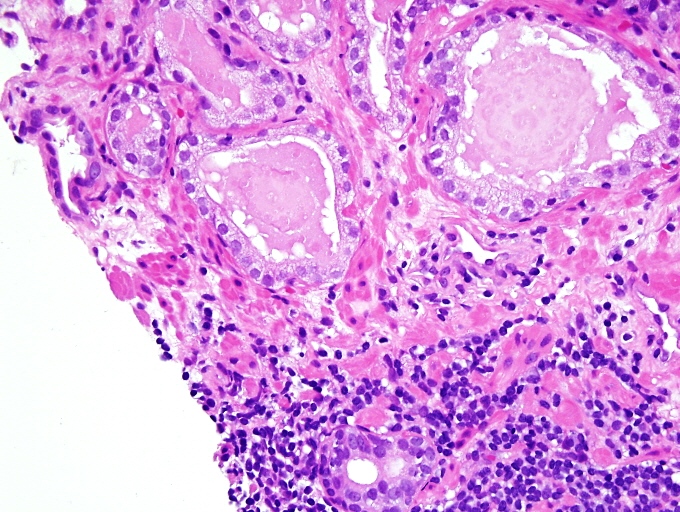
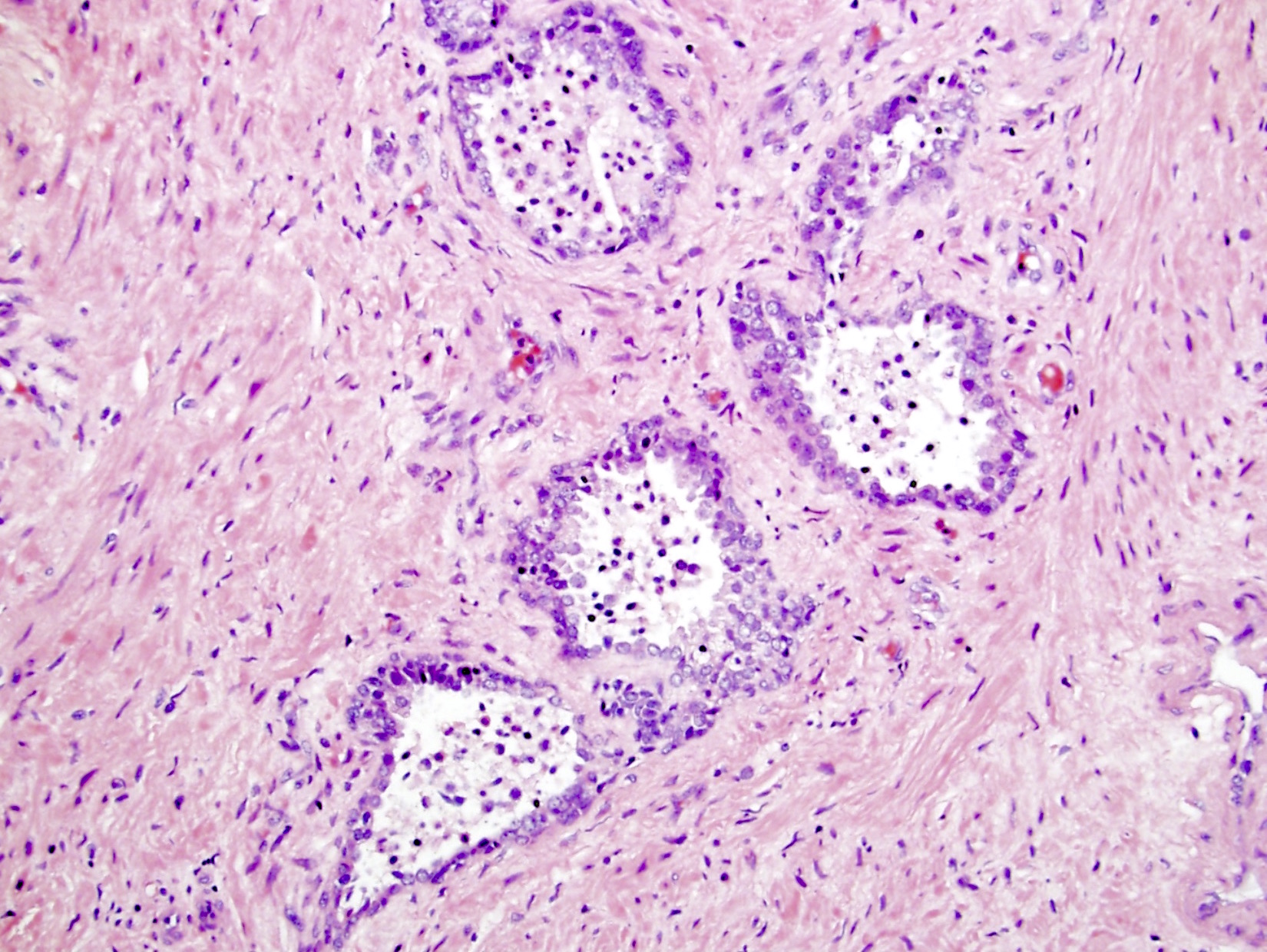
- Neutrophils tend to be in lumen spaces and macrophages in stroma; however, this is not specific for prostatitis
- Xanthoma cells
- Localized collection of cholesterol laden histiocytes, usually idiopathic
- Abundant vacuolated foamy cytoplasm; small, uniform, benign appearing nuclei, small inconspicuous nucleoli
- May have infiltration of prostatic stroma by cords and individual cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1225)
- No mitoses, rare / no necrosis
- May be interpreted as high grade prostate cancer or prostate cancer with treatment effect or foamy gland carcinoma, particularly in needle biopsies (Hum Pathol 1994;25:386, Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1225)
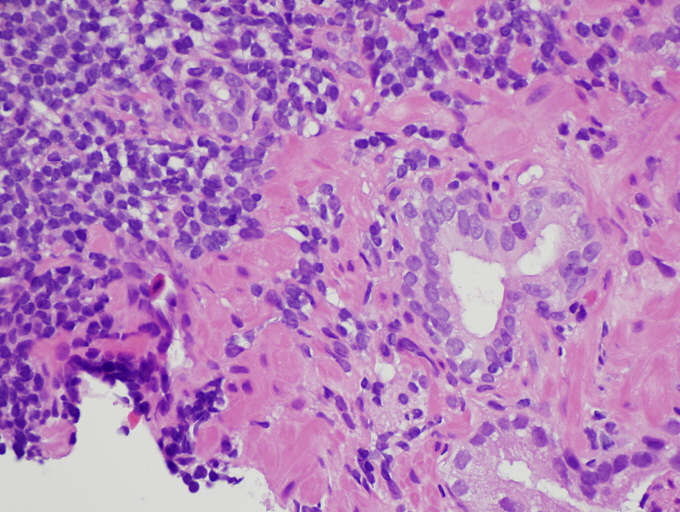
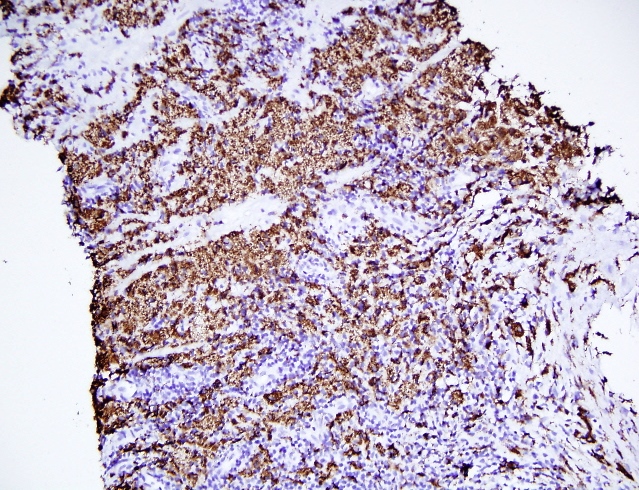
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- For bacterial type, bacteria may be visible on Gram stain
Sample pathology report
- Prostate, biopsy:
- Benign prostatic tissue with mild / moderate / severe chronic inflammation (with mild / moderate / severe acute inflammation, with mild / moderate / severe granulomatous inflammation)
Differential diagnosis
- Acute bacterial prostatitis:
- Clinically and histologically is similar (neutrophils are mostly in lumens and epithelium)
- No fluctuant mass during a rectal examination
- No hypoechoic areas on ultrasound
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis:
- Similar clinical symptoms but lower intensity
- Predominant lymphocytic infiltration (lymphocytes are mostly in the stroma)
- Granulomatous prostatitis:
- Fever and chills are common
- Irritative voiding symptoms of urgency, frequency
- May have history of bladder cancer BCG treatment
- Necrotizing or nonnecrotizing granulomas (cohesive clusters of histiocytes, usually with admixed lymphocytes, eosinophils, neutrophils)
- Prostate carcinoma:
- May mimic benign acini with reactive inflammatory atypia
- Typically lack background inflammation
- Small glands, sometimes medium to large glands, papillary or cribriform glands or solid growth or single cells
- Nucleomegaly, prominent and multiple nucleoli, lack basal cell layer
Board review style question #1
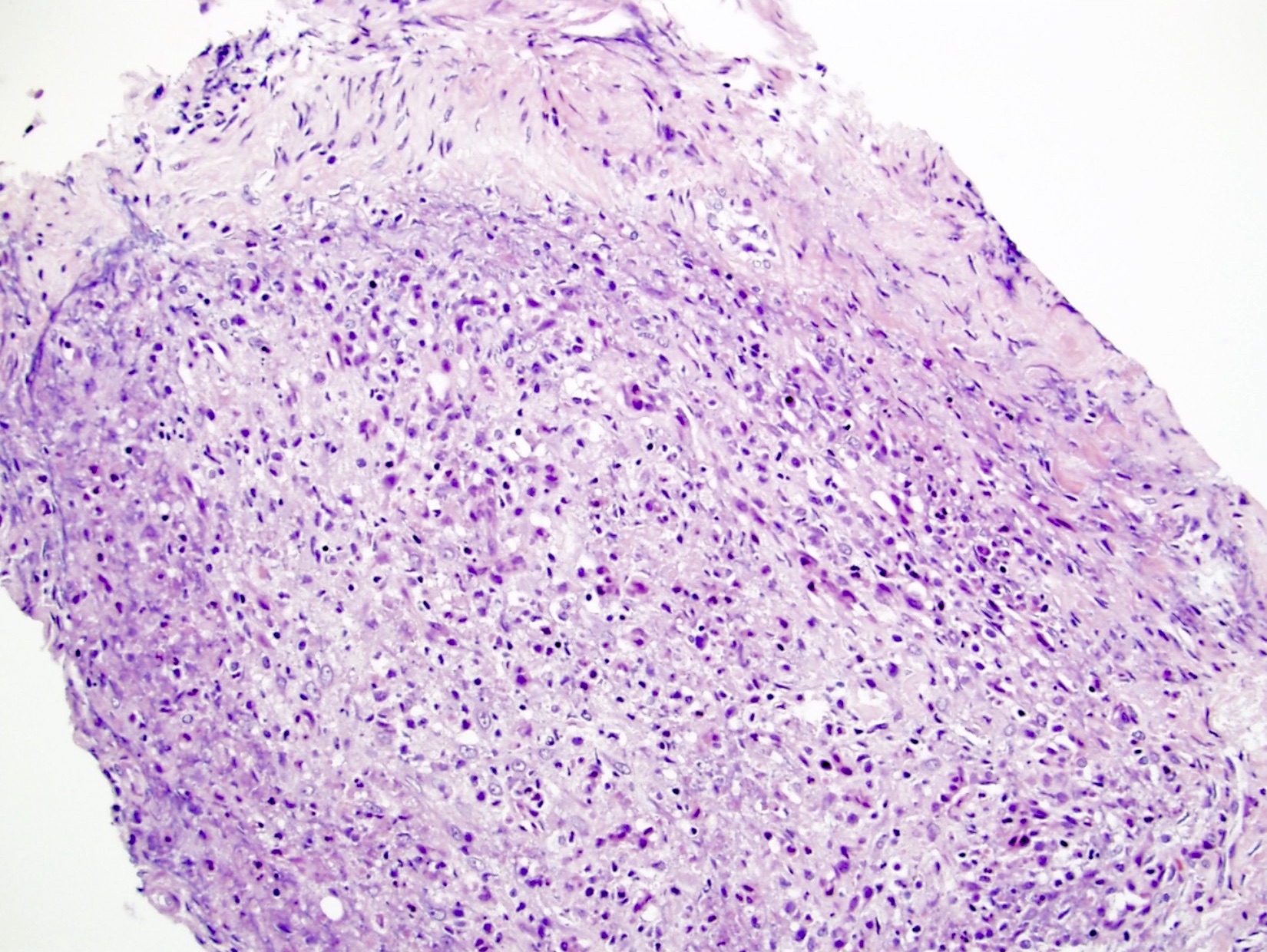
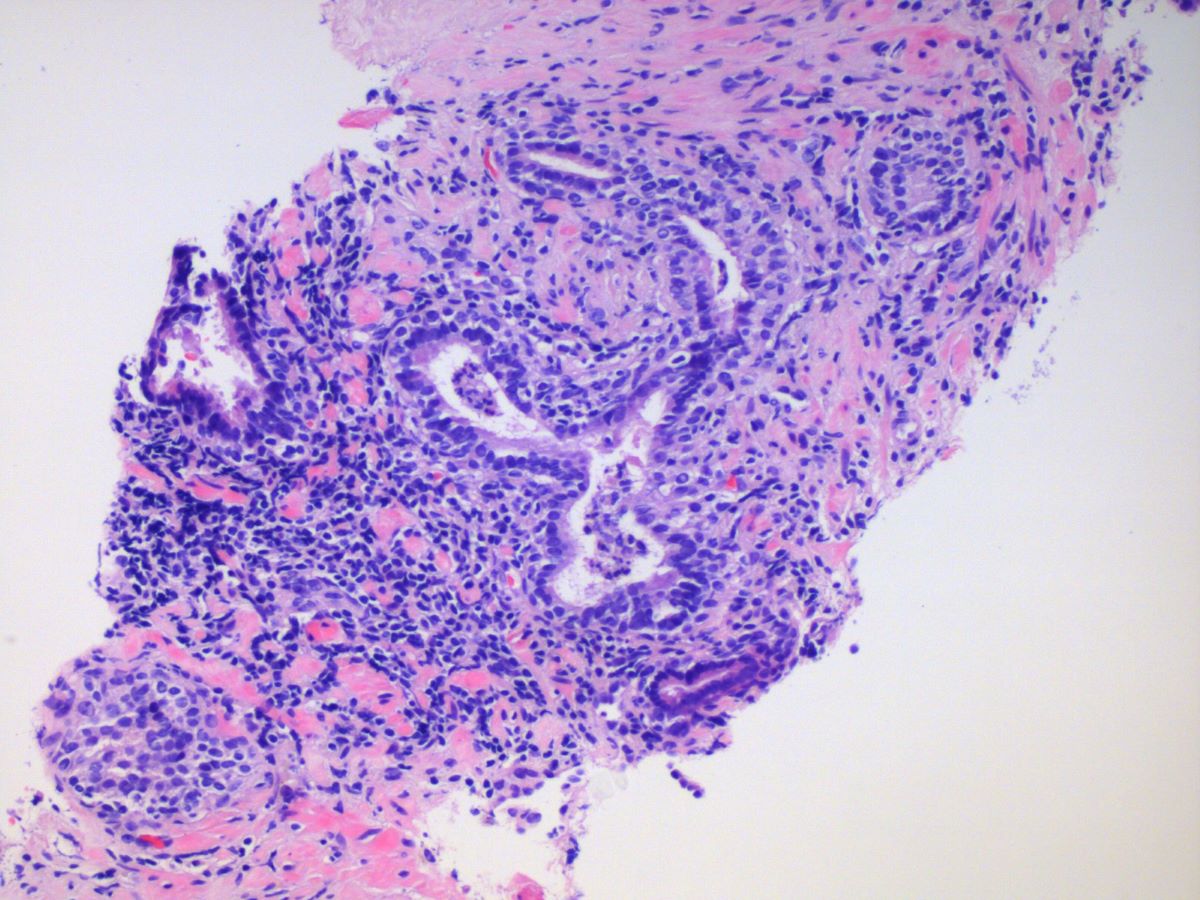
A 67 year old asymptomatic man underwent a prostate biopsy because of elevated serum prostate specific antigen (PSA) of 4.0. Findings of a representative biopsy core are shown above. In this setting, what are the findings most consistent with?
- Chronic abacterial prostatitis due to chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- Eosinophilic prostatitis
- IgG4 disease
- Nonnecrotizing granulomas
- Nonspecific acute and chronic inflammation
Board review style answer #1
E. Nonspecific acute and chronic inflammation. Stromal lymphocytes and a few luminal neutrophils are present. Answers D and B are incorrect because granulomas or eosinophils are not evident. Answer C is incorrect because plasma cells are not evident, which goes against IgG4 disease. Answer A is incorrect because the patient is asymptomatic, so CPPS is not consistent with the findings.
Comment Here
Reference: Prostatitis
Comment Here
Reference: Prostatitis