Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology images | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Videos | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2 | Board review style question #3 | Board review style answer #3Cite this page: Ullah AM, Lee L. Mycobacteria non-TB. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/microbiologymyconontb.html. Accessed April 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Mycobacteria other than Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) and Mycobacterium leprae
- Other terminologies: atypical mycobacteria, mycobacteria other than tuberculosis (MOTT)
- Gram positive, catalase positive, acid fast, rod shaped, aerobic, slow growing bacteria
Essential features
- Low virulence ubiquitous organisms affecting mostly patients with pre-existing lung disease or immunosuppression
- Different species need specific environments and time periods for optimal growth
- Culture is the gold standard for diagnosis; however, it cannot differentiate Mycobacterium tuberculosis from nontuberculous mycobacteria or its different subspecies
- Mycobacterium abscessus complex (MABC) has poor prognosis due to resistance to antibiotics
Epidemiology
- Generally low virulence but incidence of MOTT related lung disease increasing globally, especially in tropical weather (Front Immunol 2020;11:303)
- Ubiquitous organisms / environmental bacteria found in water, soil, dust and vegetation
- Infrequent person to person transmission, except with M. abscessus that has been discovered among cystic fibrosis patients (Indian J Med Res 2020;152:185)
- Commonly affects elderly people with pre-existing lung disease (Microbiol Spectr 2017;5)
- Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) is the most common species found in most areas, followed by M. abscessus complex and Mycobacterium kansasii, although variance occurs based on geography (Eur Respir J 2013;42:1604)
Sites
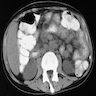
- Lung, most commonly involved organ (65 - 90%) (Adv Exp Med Biol 2017;944:19)
- Other sites that can be affected include lymph nodes, skin, soft tissues and rarely bones
- Disseminated nontuberculous mycobacterial disease is rare and occurs in individuals with congenital or acquired immune defects such as HIV / AIDS (Indian J Med Res 2020;152:185)
Pathophysiology
- Transmitted through inhalation of aerosol droplets, leading to phagocytosis by alveolar macrophages in the lungs, causing local destruction and eventual granuloma formation with varying degrees of necrosis
- M. abscessus can be transmitted by contaminated medical device and cause skin infections in healthcare settings (CDC: Mycobacterium abscessus in Healthcare Settings [Accessed 26 August 2022])
- Insidious onset of disease due to slow growth rates (J Biomed Sci 2020;27:74)
Clinical features
- Most commonly involves the lung, followed by skin and soft tissue (following surgery or trauma), local device associated infection (e.g., central line), lymph nodes and blood (disseminated in immunosuppressed patients) (CDC: Nontuberculous Mycobacteria (NTM) Infections [Accessed 26 August 2022])
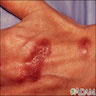
- Skin disorders (ulcerations, abscesses, rheumatoid-like nodules, histiocytic reactions, panniculitis), most commonly due to M. kansasii, M. marinum, M. ulcerans
- Lung manifestations: fibrocavitary disease, nodular bronchiectasis and hypersensitivity pneumonitis (Front Immunol 2020;11:303)
- Challenging to diagnose due to overlapping symptomatology with underlying lung disease and slow growth in culture
- Difficult to treat due to drug resistance
Diagnosis
- Nontuberculous mycobacteria exist naturally in the environment; therefore, isolation from a nonsterile respiratory specimen does not mean they are causative organisms of lung disease, which makes the diagnosis very challenging (Eur Respir J 2013;42:1604)
- The approach includes the integration of clinical, radiographic and microbiological data (with the latter being the gold standard) and including:
- At least 2 positive sputum cultures
- 1 positive culture in the case of bronchoscopic wash or lavage, or
- Transbronchial or other lung biopsy with a positive culture for nontuberculous mycobacteria or compatible histopathological features such as granulomatous inflammation or stainable acid fast bacilli (AFB) and 1 positive sputum or bronchial wash culture for nontuberculous mycobacteria, regardless of the mycobacterial strain (Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2007;175:367)
- Latest approaches in diagnosis include molecular methods such as line probe hybridization, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis, real time PCR and DNA sequencing
- Most accurate detection method includes gene sequencing; however, it is very cumbersome, expensive and not readily available (Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul) 2016;79:74)
Laboratory
- Nontuberculous mycobacteria can be cultured on:
- Solid growth media including Löwenstein-Jensen agar, Middlebrook 7H10 and 7H11 media
- Liquid media containing enriched Middlebrook 7H9 broth is more sensitive but prone to contamination (Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul) 2016;79:74)
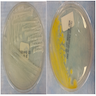
- Colonies on solid media differ for different subspecies (e.g., M. kansasii gives bright yellow colonies after exposure to light)
Case reports
- 17 year old boy with progressively worsening dyspnea (Respirol Case Rep 2020;8:e00682)
- 34 year old woman with right breast swelling (Clin Pract 2021;11:228)
- 40 year old immunocompetent man with nontuberculous mycobacterial pneumonia (Pan Afr Med J 2021;38:412)
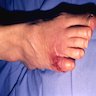
- 52 year old woman with foot infection (University of Pittsburgh: Case 80 [Accessed 18 October 2023])
- 61 year old woman with SLE and Sjögren syndrome (Dermatol Online J 2010;16:21)
- 62 year old man with productive cough (Lablogatory: Microbiology Case Study - A 62 Year Old Male with Productive Cough [Accessed 21 July 2022])
- 88 year old woman with a right lateral thoracic region tumor (BMC Infect Dis 2021;21:196)
- 97 year old woman with a ventriculoperitoneal shunt presenting with swelling and erythema on the right side of her neck (Cureus 2021;13:e16356)
Treatment
- Amikacin is an effective drug against most nontuberculous mycobacterial species
- Macrolides (clarithromycin and azithromycin) are the cornerstones of treatment for Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease (Clin Chest Med 2015;36:55)
- M. kansasii is easily treatable with sensitivity to standard anti-TB drugs, except for pyrazinamide (Future Microbiol 2014;9:1095)
- M. abscessus complex has poor outcomes due to its resistance to most known treatment modalities (Clin Chest Med 2015;36:67)
- Except for M. kansasii, nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease is difficult to control with antimicrobial therapy alone and may require surgical intervention; however, the role of adjunct surgical approaches remains unclear
- Current guidelines recommend that medical therapy should be continued until the patient has sputum cultures that are persistently negative for 12 months while undergoing treatments, including surgery (Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul) 2016;79:74)
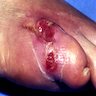
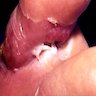
Clinical images
Gross description
- Granulomatous inflammation with varying degrees of necrosis; however, may vary depending on the organ involved and the stage of the disease (Semin Diagn Pathol 2017;34:518, J Biomed Sci 2020;27:74)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- M. tuberculosis and nontuberculous mycobacteria may share the same spectrum of histological findings; therefore, no reliable differentiation between them can be made microscopically (Semin Diagn Pathol 2017;34:518)
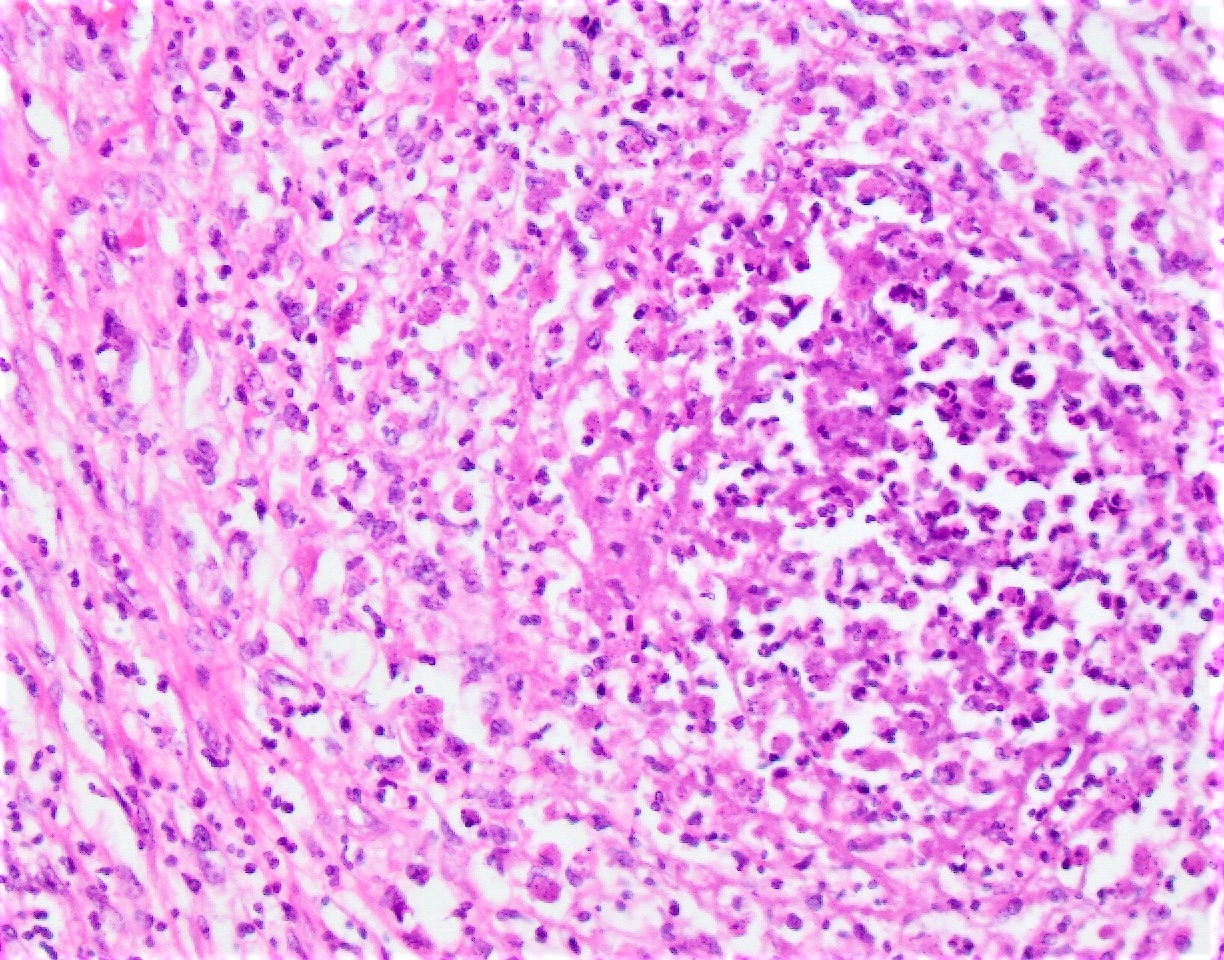
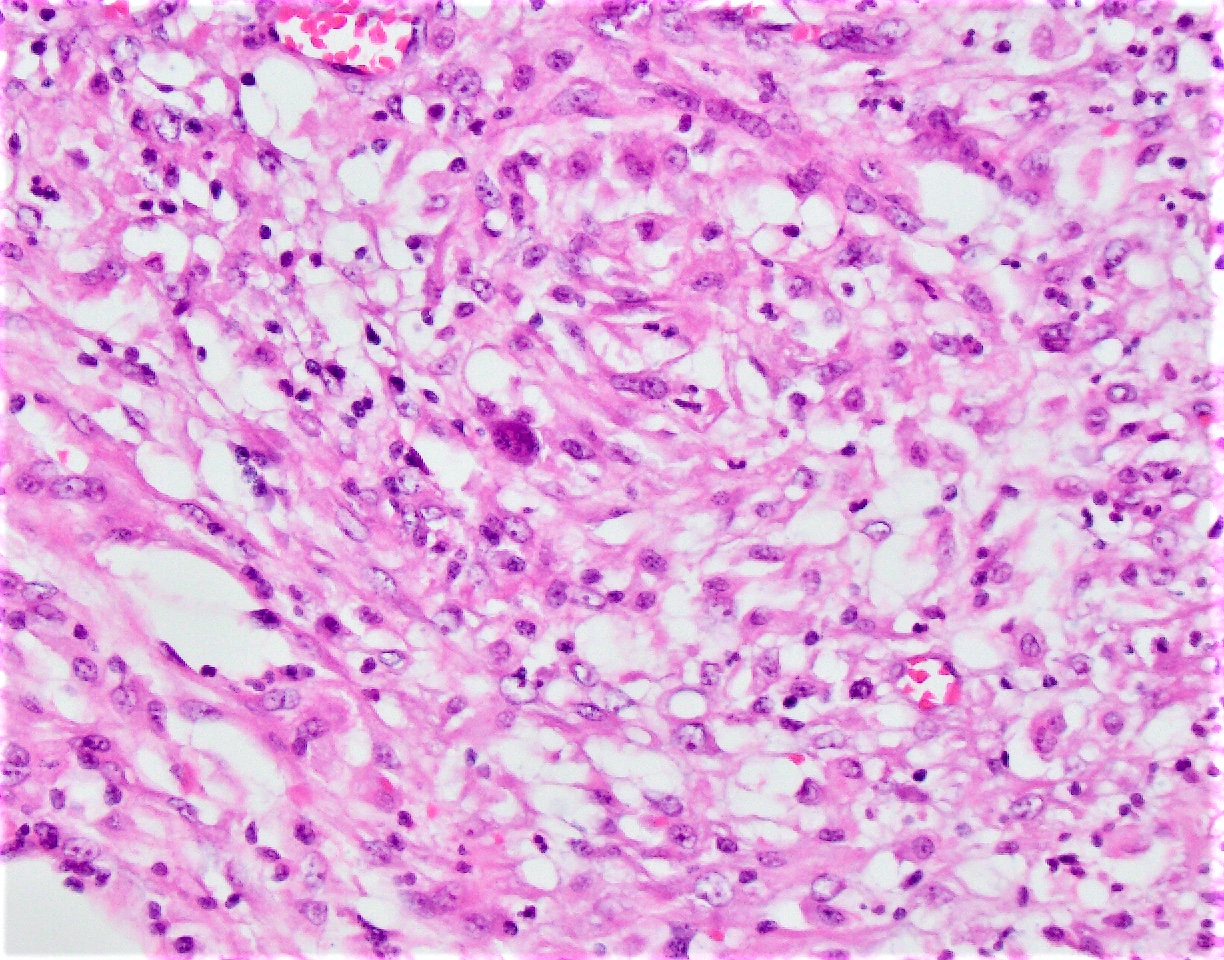
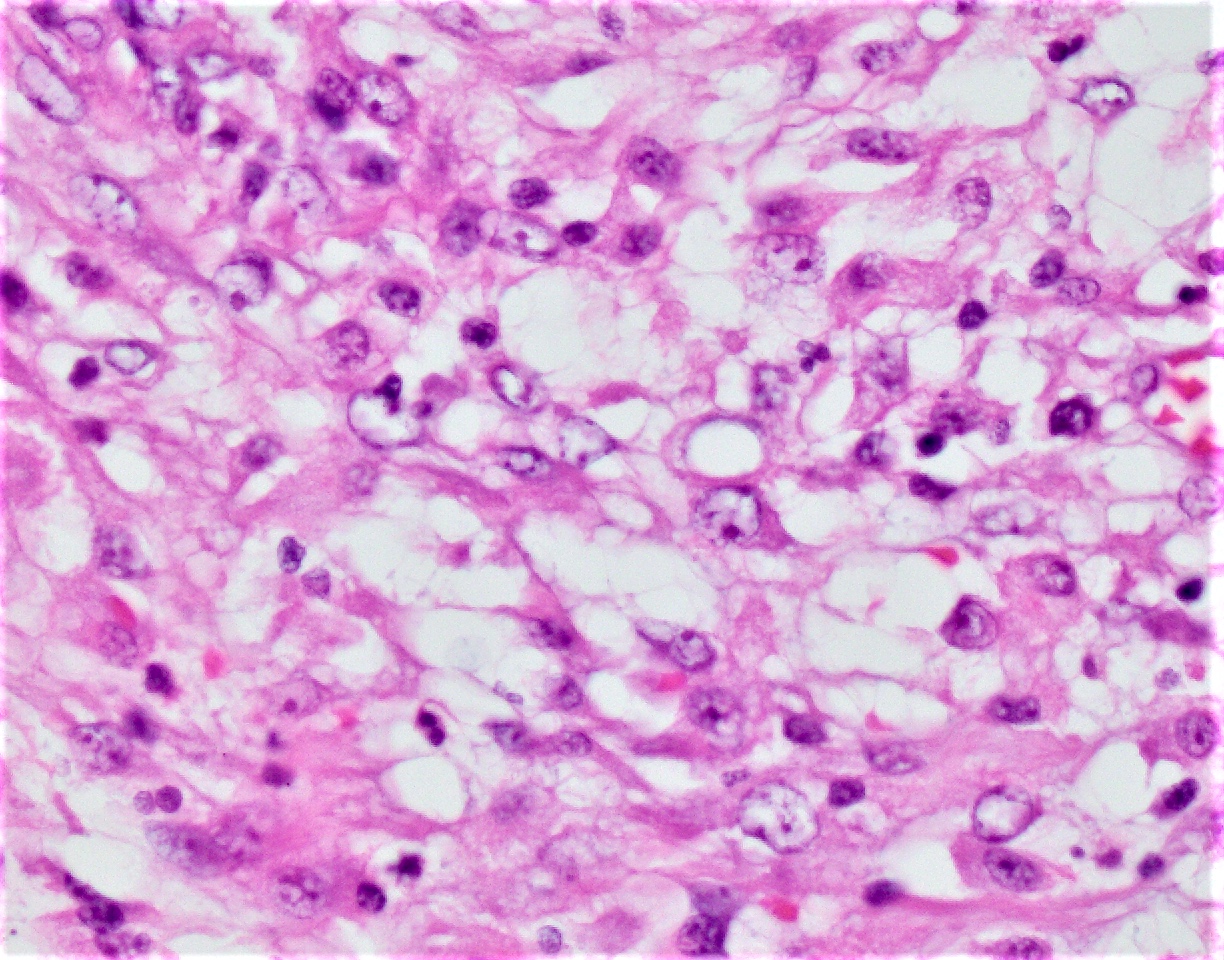
- Typically phagocytosed by foamy histiocytes that may form necrotizing or nonnecrotizing granulomas
- AIDS patients: histiocytes may contain abundant acid fast organisms; may lack well formed granulomata and lymphocytic response
Microscopic (histologic) images
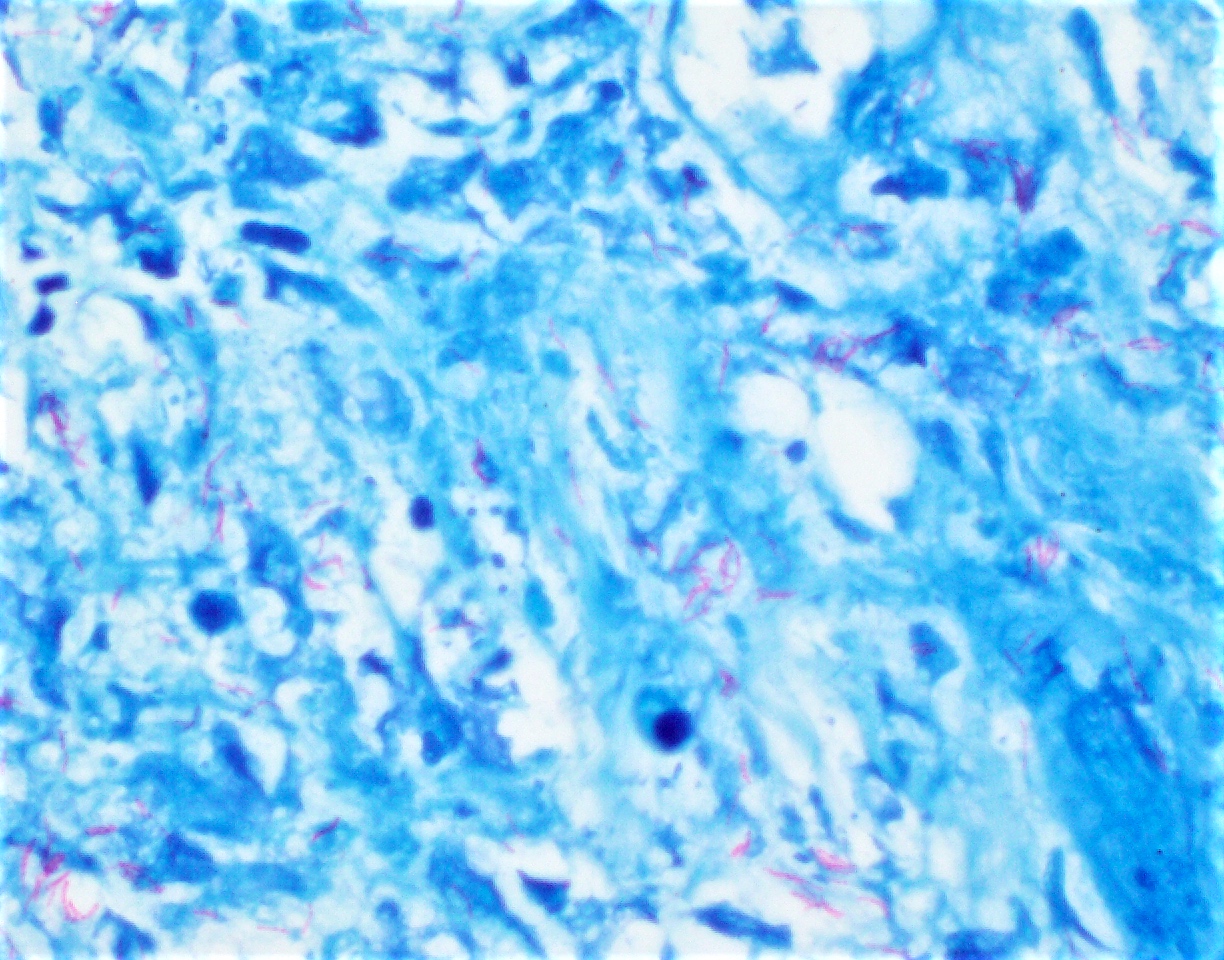
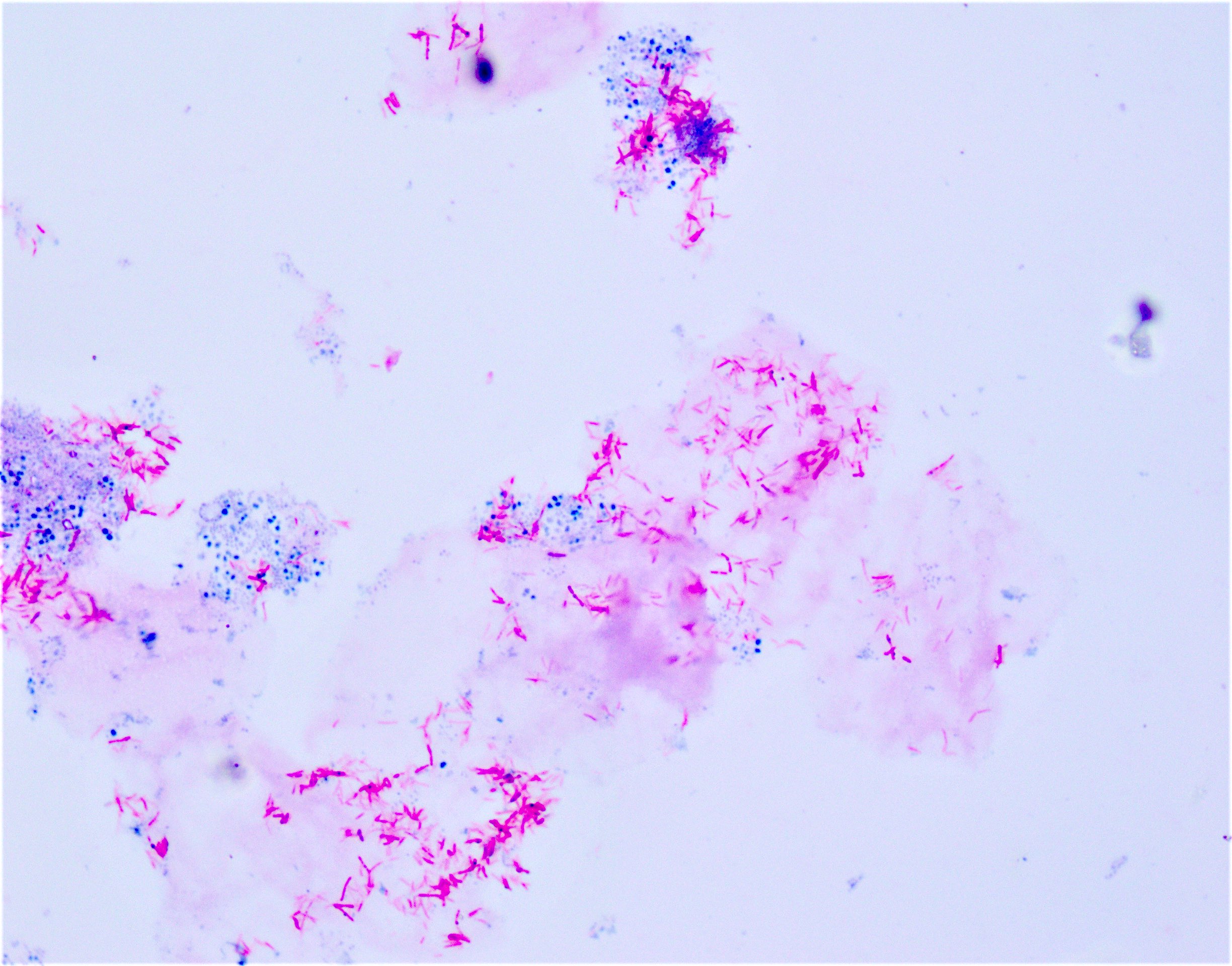
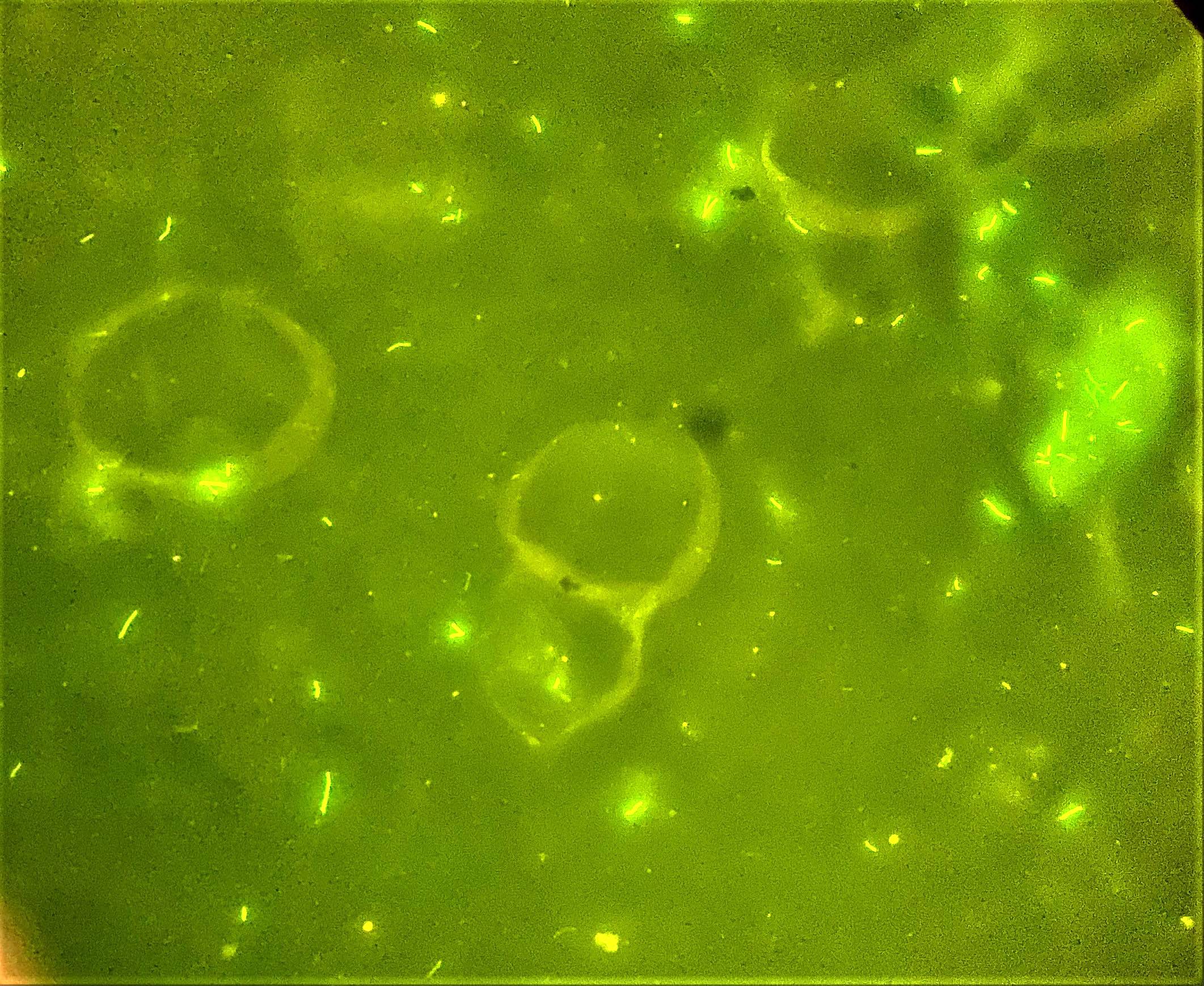
Positive stains
- Acid fast special stains including the classic Ziehl-Neelsen (ZN) stain and modified Kinyoun stain, also known as cold Ziehl-Neelsen technique
- Both stain mycobacteria as pink-red slender rods
- Auramine-rhodmaine fluorescent stain is more sensitive than acid fast stain under light microscopy (Wilmott: Kendig's Disorders of the Respiratory Tract in Children, 9th Edition, 2019)
- PAS positive
Videos
Quick revision of nontuberculous mycobacteria with mnemonics
Differential diagnosis
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis:
- Prevalence and epidemiology
- PCR based assays and nucleic acid amplification tests (J Clin Microbiol 2003;41:5121)
- Fungal lung diseases, including aspergillosis, cryptosporidiosis, pneumocystis pneumonia:
- Stain with Gomori methenamine silver (GMS) and periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) (Med Mycol 2015;53:470)
- Gram positive yeasts or pseudohyphae; yeasts or pseudohyphae also seen on KOH preparation
- Growth on Sabouraud agar
- Noninfectious granulomatous lung diseases (Internist (Berl) 2013;54:416, JAMA 1989;262:840):
- Autoimmune lung diseases, including sarcoidosis, rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis:
- Middle aged women with previous personal or family history
- Antinuclear antibody (ANA), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C reactive protein (CRP) levels are raised
- Occupational lung diseases, including hypersensitivity pneumonitis, silicosis, hard metal lung and chronic berylliosis:
- Strong, detailed occupational history
- Diffuse, bilateral disease
- Special stains and cultures negative for organisms
- Autoimmune lung diseases, including sarcoidosis, rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis:
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is the common setting of person to person transmission of a nontuberculous Mycobacterium species?
- Mycobacterium abscessus in cystic fibrosis patients
- Mycobacterium gordonae in HIV patients
- Mycobacterium kansasii in organ transplant patients
- Mycobacterium mucogenicum in patients on chemotherapy
- Mycobacterium scrofulaceum in individuals > 90 years old
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
A thin, immunocompetent 80 year old man presents with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and a chronic cough. Sputum smears were acid fast positive, with colorless colonies that grew from multiple specimens after culture at 32 °C and turned yellow after exposure to light. Which of the following is the most likely etiologic agent causing his infection?
- Mycobacterium abscessus
- Mycobacterium avium complex
- Mycobacterium gordonae
- Mycobacterium kansasii
- Mycobacterium scrofulaceum
Board review style answer #2
Board review style question #3
The most reliable method to differentiate M. tuberculosis from nontuberculous mycobacteria is
- Culture on liquid media
- Gene sequencing
- Histology
- Immunohistochemical or special stains
- PCR based assays
Board review style answer #3