Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Milani D, Warbasse E, Chen WS. Porokeratosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skinnontumorporokeratosis.html. Accessed April 20th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Skin disorder of abnormal clonal keratinization with various clinical expressions and subtypes
- Characterized by 1 or more variably sized lesions on the skin that are rimmed by a hyperkeratotic border
Essential features
- Keratinization disorder resulting from abnormal clonal expansion of keratinocytes
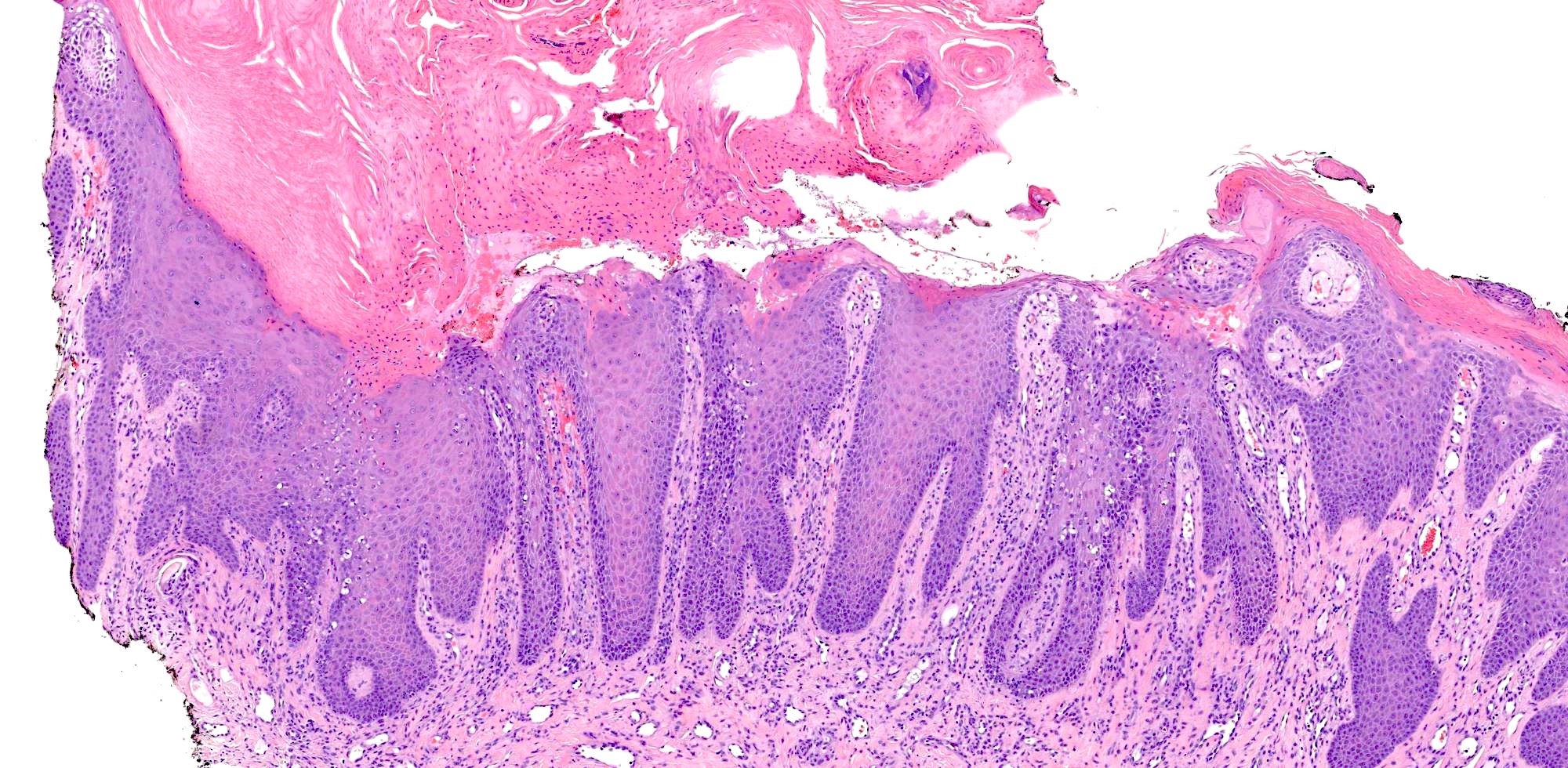
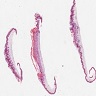
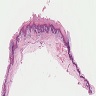
- Histologic hallmark is cornoid lamella, a column of parakeratosis with underlying dyskeratosis with reduction of keratohyalin granules (Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2022;88:291)
- Some subtypes premalignant
- Subtypes include
- Porokeratosis of Mibelli
- Disseminated actinic porokeratosis (DSAP)
- Disseminated superficial porokeratosis (DSP)
- Linear porokeratosis
- Eruptive disseminated porokeratosis (EDP)
- Porokeratosis palmaris et plantaris disseminate
- Punctate porokeratosis
- Porokeratosis ptychotropica
- Penoscrotal porokeratosis
- Follicular porokeratosis
Terminology
- Disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis
- Disseminated superficial porokeratosis
- Porokeratosis of Mibelli
- Linear porokeratosis
- Eruptive disseminated porokeratosis
- Porokeratosis palmaris et plantaris disseminata
- Punctate porokeratosis
- Porokeratosis ptychotropica
- Penoscrotal porokeratosis
- Follicular porokeratosis
- Porokeratoma
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Most common subtype is DSAP
- Third or fourth decades of life (Patterson: Weedon's Skin Pathology, 5th Edition, 2020)
- F > M, mostly on sun exposed skin (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- Porokeratosis of Mibelli, DSP and linear porokeratosis are seen in children (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- DSP resembles DSAP but occurs in younger patients and involves both sun exposed and non-sun exposed skin (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- Linear porokeratosis has a predilection for males (2 - 3:1) (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- EDP is associated with hepatic, digestive and hematologic malignancy in 33% of cases (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
Sites
- Varies per subtype
- DSAP: arms, legs, occasionally shoulders and back (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- Porokeratosis of Mibelli: trunk or limbs, 1 or more lesions (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- Linear porokeratosis: presents in a similar distribution to DSAP but with linear configuration (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- Porokeratosis palmaris et plantaris disseminata: palms or soles; may spread to trunk, limbs or mucous membranes (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- Punctate porokeratosis: palms and soles, with multiple seed-like keratotic papules (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- Porokeratosis ptychotropica: buttocks and perianal region (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- Penoscrotal porokeratosis: shaft of penis and anterior scrotum (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- Follicular porokeratosis: face (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- Porokeratoma: solitary lesions on limbs
Pathophysiology
- Abnormalities in the mevalonate pathway (Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2022;88:291)
- Affect sterol and cholesterol biosynthesis
- Results in abnormal differentiation of keratinocytes
- Immunosuppression may result in dysregulated proliferation of abnormal keratinocyte clones (Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2022;88:291)
- Malignant transformation if allelic loss associated with p53 overexpression (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
Etiology
- Unclear etiology
- Genetic factors (Am J Clin Dermatol 2017;18:435, Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2022;88:291)
- 5 loci have been identified on chromosomes 1, 12, 15, 16 and 18 for DSAP (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- Ultraviolet (UV) radiation or sun exposure (Am J Clin Dermatol 2017;18:435, Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2022;88:291)
- Immunosuppression
- Others: electron beam therapy, radiation therapy, transplant procedures, trauma, chronic renal failure, chronic liver disease, infections, hematological malignancies including lymphomas, HIV infection, hepatitis C infection, Crohn's disease and medications such as etanercept and adalimumab (Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2022;88:291)
- Genetic factors (Am J Clin Dermatol 2017;18:435, Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2022;88:291)
- Different subtypes may have different triggers
- DSAP and porokeratosis palmaris et plantaris disseminata: UV radiation (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- EDP: hepatotropic viruses and malignancies (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- DSP: immunosuppression (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- Porokeratosis ptychotropica and penoscrotal porokeratosis: trauma and scratching (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
Clinical features
- Commonly characterized by atrophic center, bordered by a peripheral, hyperkeratotic ridge (cornoid lamella)
- Slight increase in malignant transformation (basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma)
- DSAP
- Multiple, small, annular, skin colored to hyperpigmented papules surrounded by a hyperkeratotic ridge (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545, Patterson: Weedon's Skin Pathology, 5th Edition, 2020)
- Distributed symmetrically on the extremities > trunk in sun exposed areas (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- May worsen during summer months due to increased UV
- Porokeratosis of Mibelli
- Small papules with a keratotic ridge that evolve into larger plaques on the trunk and extremities (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- Most common subtype of childhood
- Occurs in adults in the setting of immunosuppression (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- Linear porokeratosis
- Distributed along Blaschko lines
- Strongest association with skin cancer (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- EDP
- Abrupt onset and progressive course (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- Intensely pruritic (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- Eruptive pruritic papular porokeratosis
- Inflammatory form of disseminated superficial porokeratosis
- Spontaneously resolves in most individuals (Dermatol Online J 2020;26:13030)
Diagnosis
- Clinical diagnosis
- Dermoscopy or biopsy helpful if atypical presentation (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545)
- Dermoscopy: blue-brown dots on homogenous central discoloration flanked by a 2 layered, raised, hyperkeratotic rim (double track sign) (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545, Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2022;88:291)
- Take biopsy from the edge of the peripheral rim to visualize the cornoid lamella
- Reflectance confocal microscopy to identify the cornoid lamella (Patterson: Weedon's Skin Pathology, 5th Edition, 2020)
- Iodine and self tanning lotions highlight lesions (Patterson: Weedon's Skin Pathology, 5th Edition, 2020)
Prognostic factors
- Prognosis varies depending on subtype and severity
- Often a chronic condition refractory to treatment
- Rarely, lesions may spontaneously resolve
- Malignant transformation is rare
- Greatest risk: large lesions, longstanding duration, linear subtype (Dermatol Surg 1996;22:339)
Case reports
- 8 year old Chinese boy with keratotic papules on the bottom of his foot (World J Clin Cases 2022;10:11585)
- 25 year old man with a single pruritic, ulcerated, indurated, nontender plaque on the buttocks (SAGE Open Med Case Rep 2022;10:2050313X221139559)
- 30 year old man with multiple pruritic, dark, raised skin lesions over the trunk, face and upper limbs (J Family Med Prim Care 2022;11:1195)
- 68 year old woman with diffuse, hyperkeratotic, scaly, lichenoid plaques on the buttocks (J Yeungnam Med Sci 2023;40:423)
- 89 year old Black woman with hyperkeratotic and filiform papules on the bilateral palms and soles (Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent) 2020;33:415)
Treatment
- No standard treatment
- Long term follow up
- Sun protection recommended for all patients
- Reported treatment options include excision, cryosurgery, electrocautery, carbon dioxide laser, topical 5-fluorouracil, keratolytics, imiquimod, vitamin D analogues and topical retinoids (Patterson: Weedon's Skin Pathology, 5th Edition, 2020)
- Topical cholesterol / lovastatin has been shown to be effective, particularly in DSAP (J Am Acad Dermatol 2020;82:123)
- Screen for hepatobiliary or hematologic malignancy in EDP
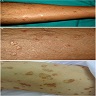
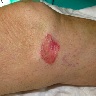
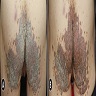
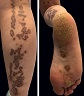
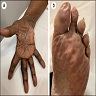
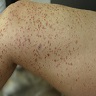
Clinical images
Images hosted on other servers:
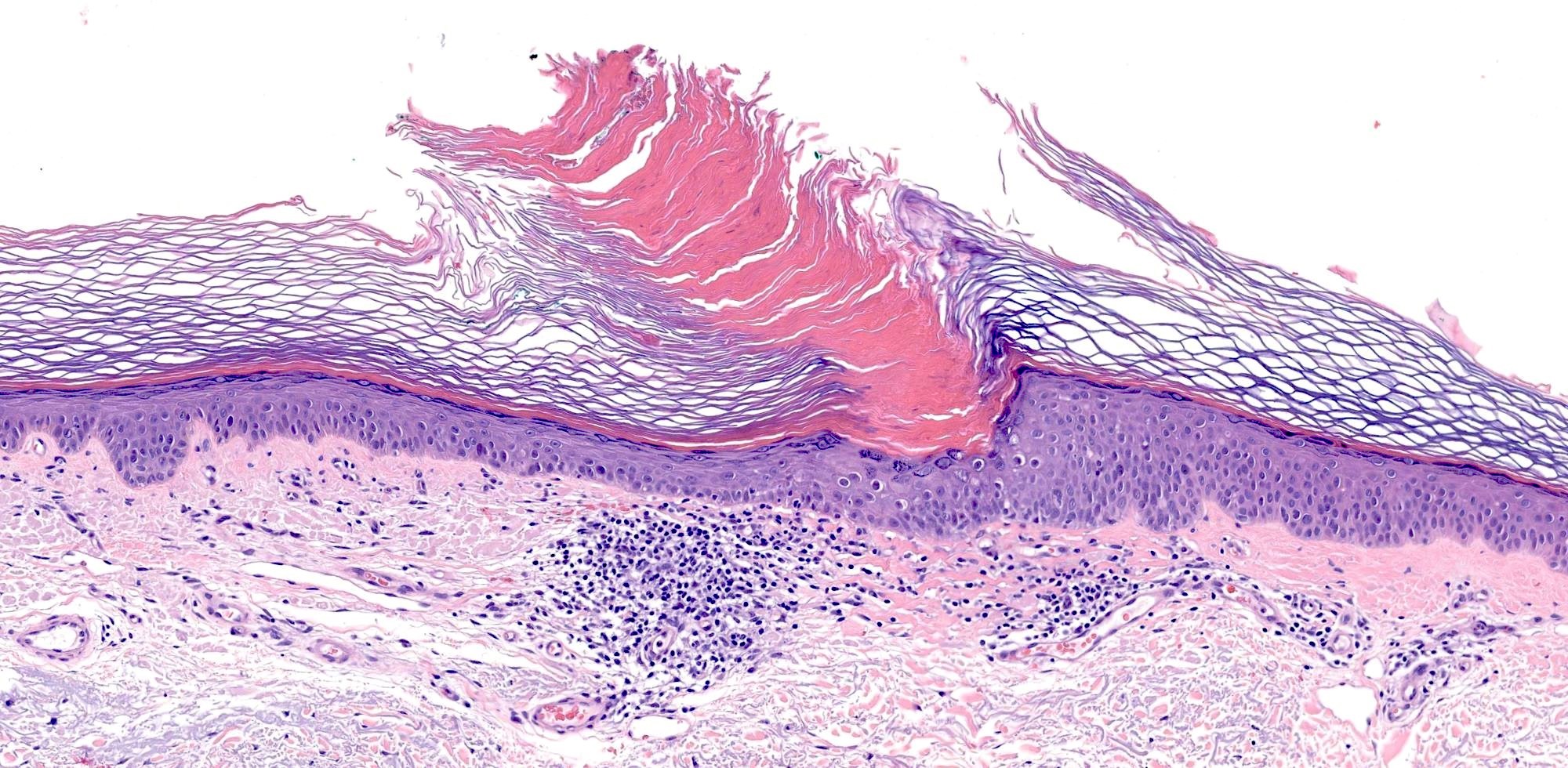
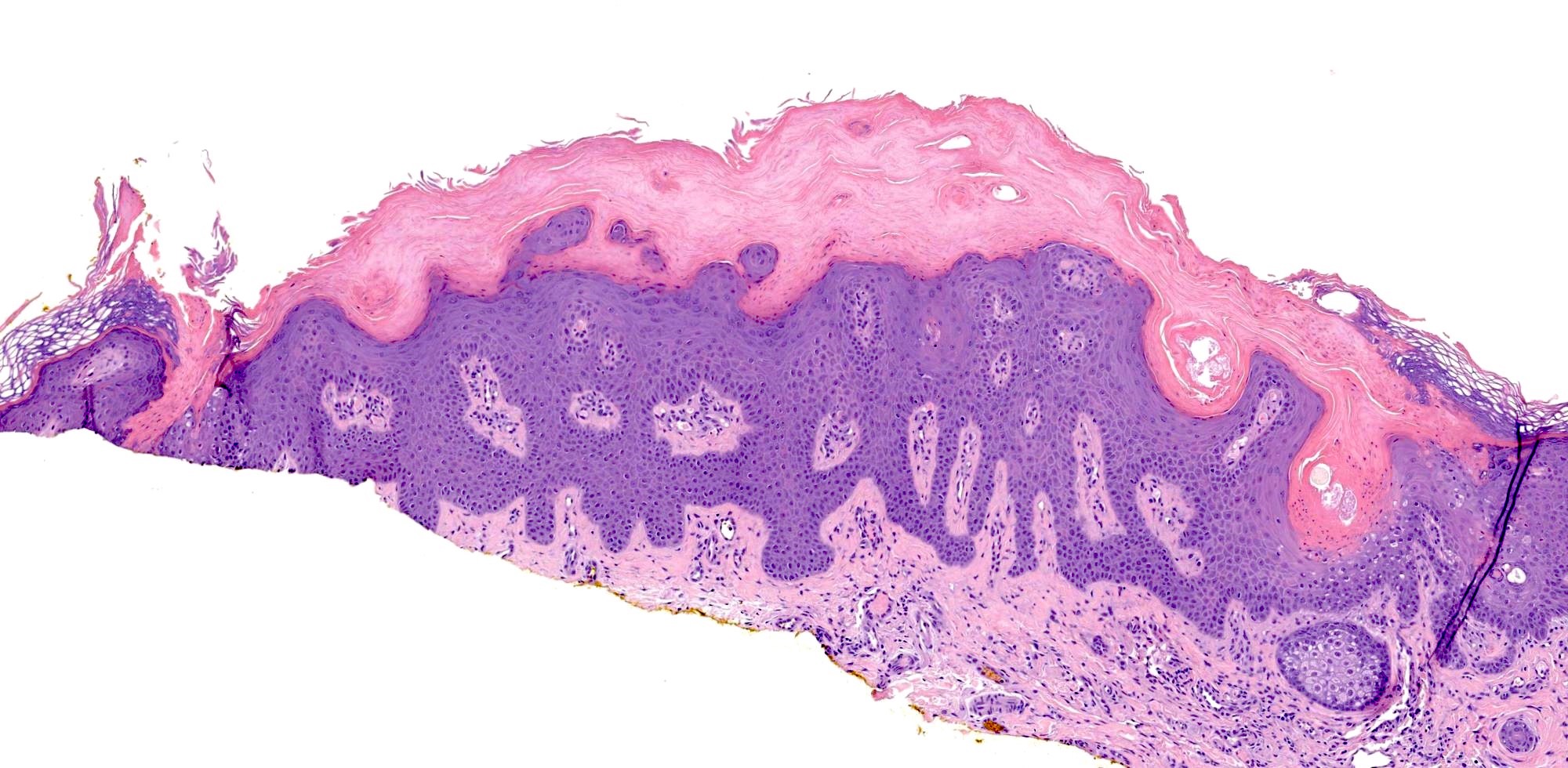
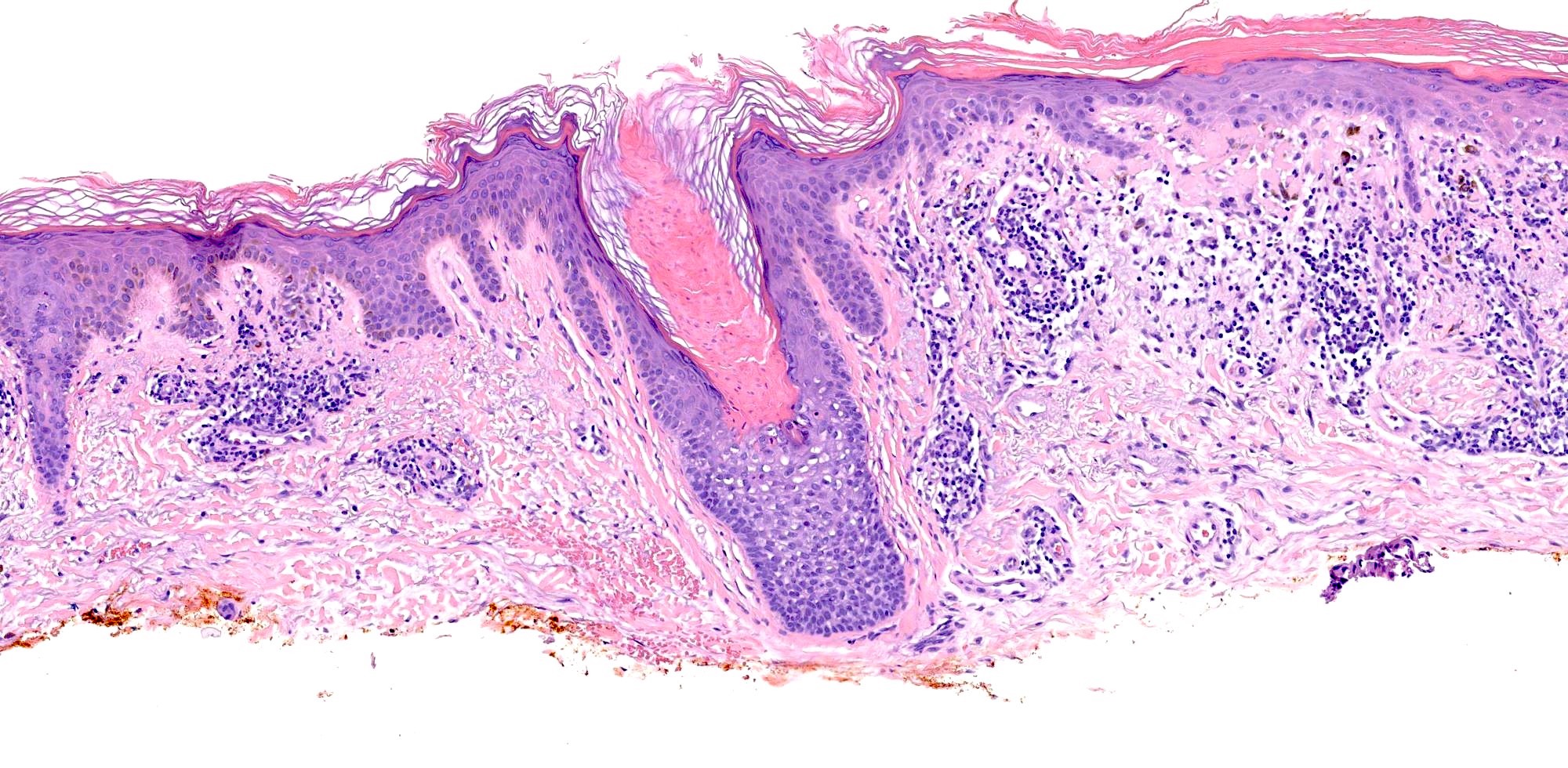
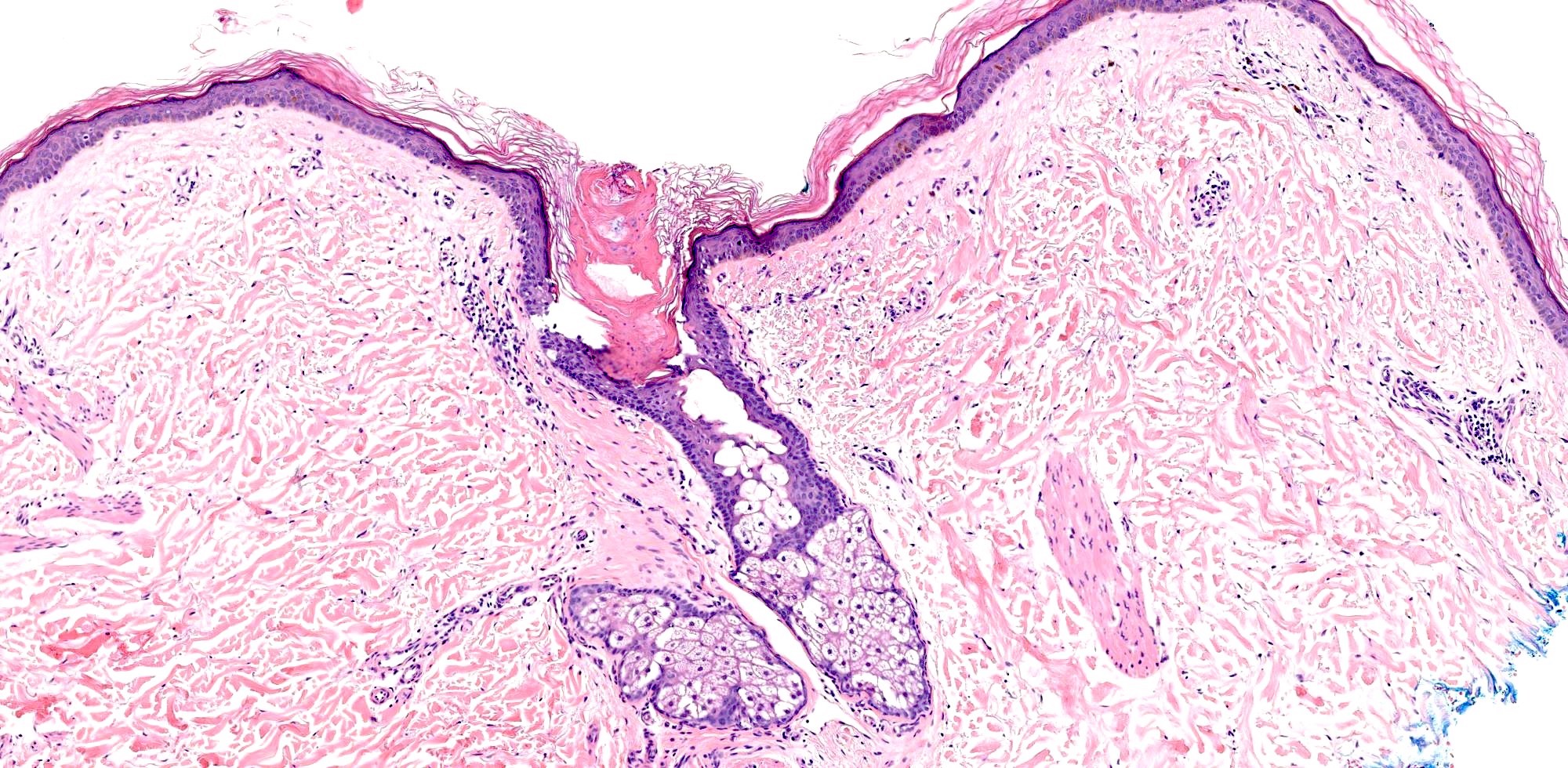
Microscopic (histologic) description
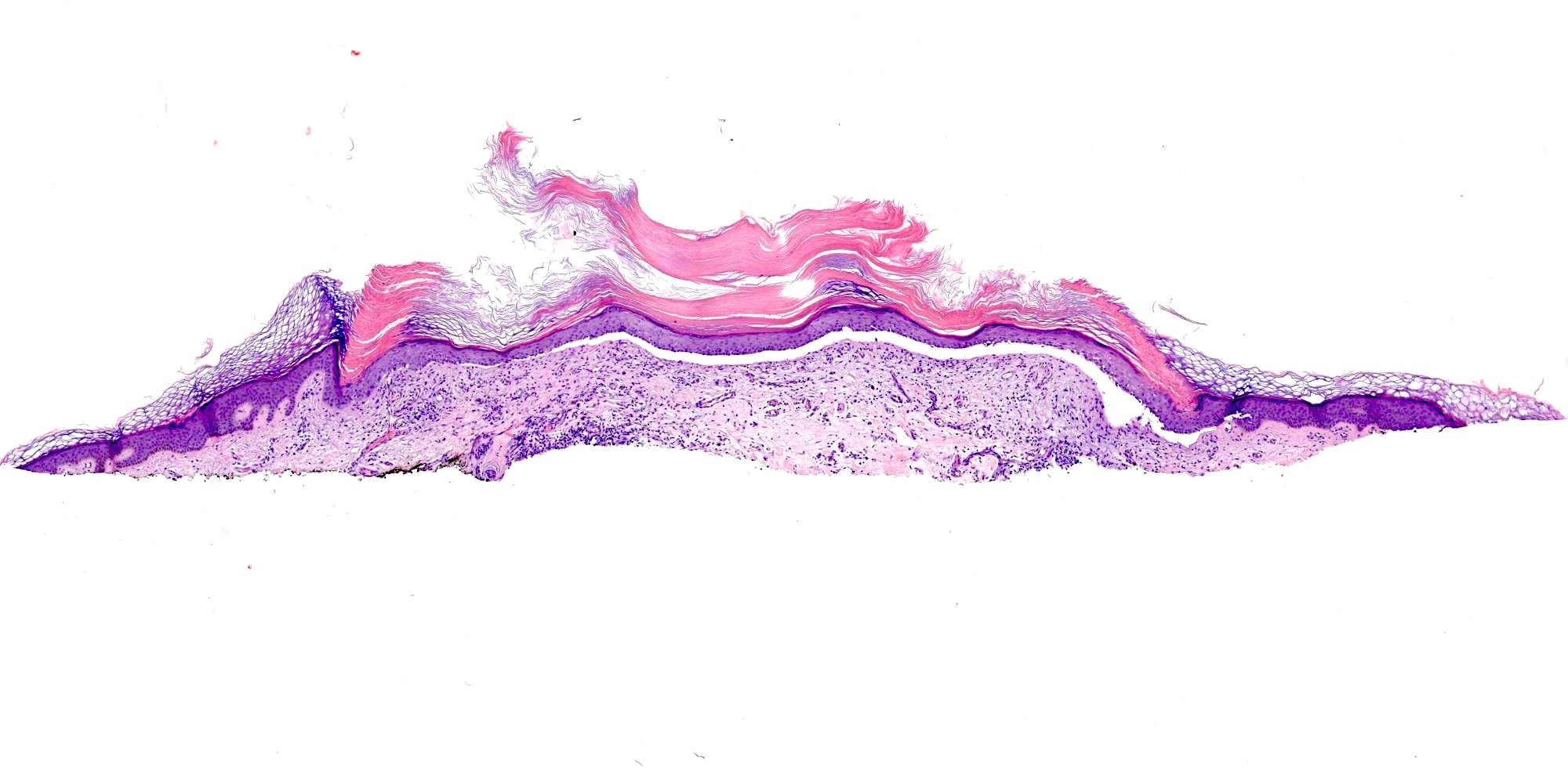
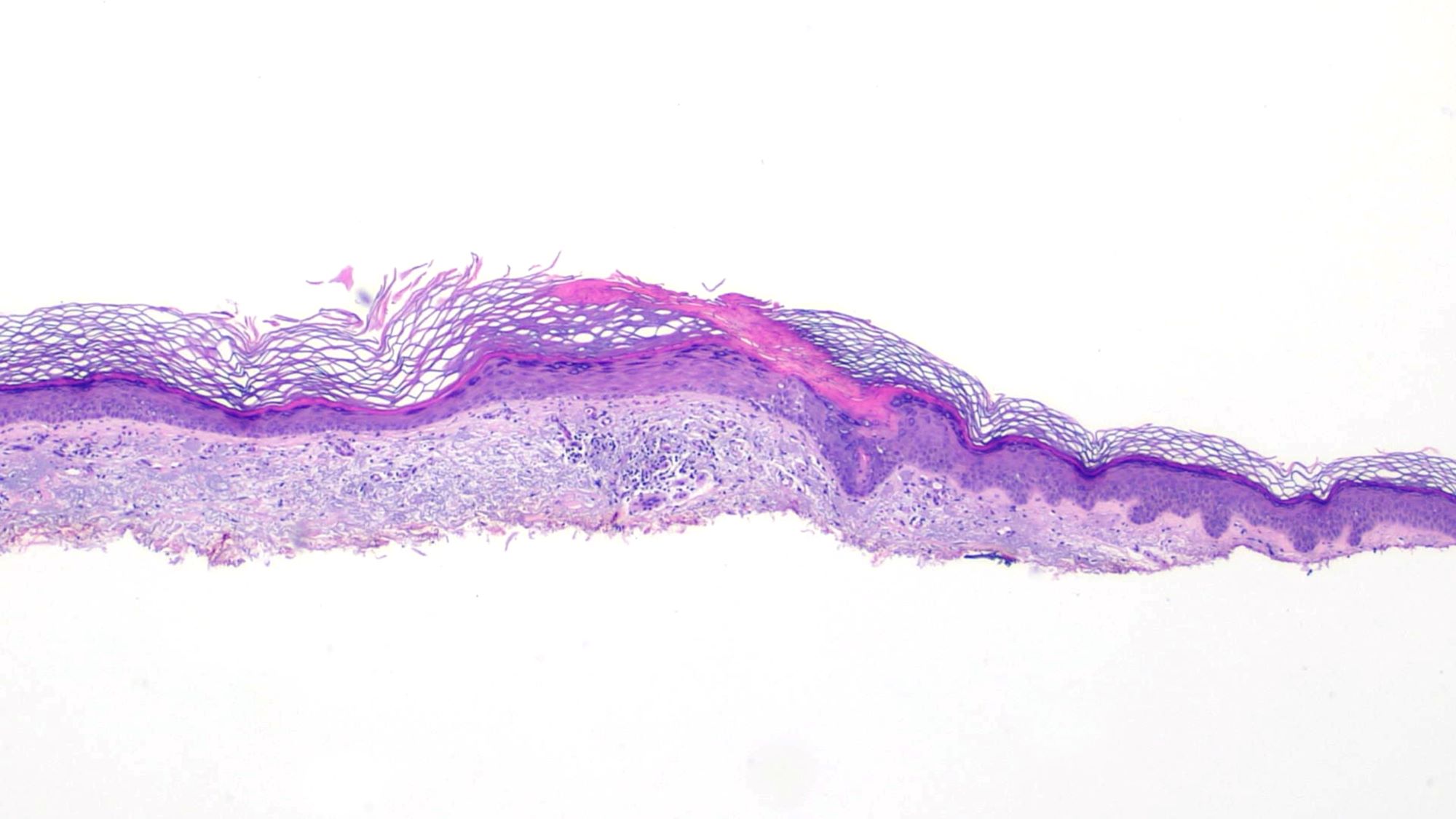
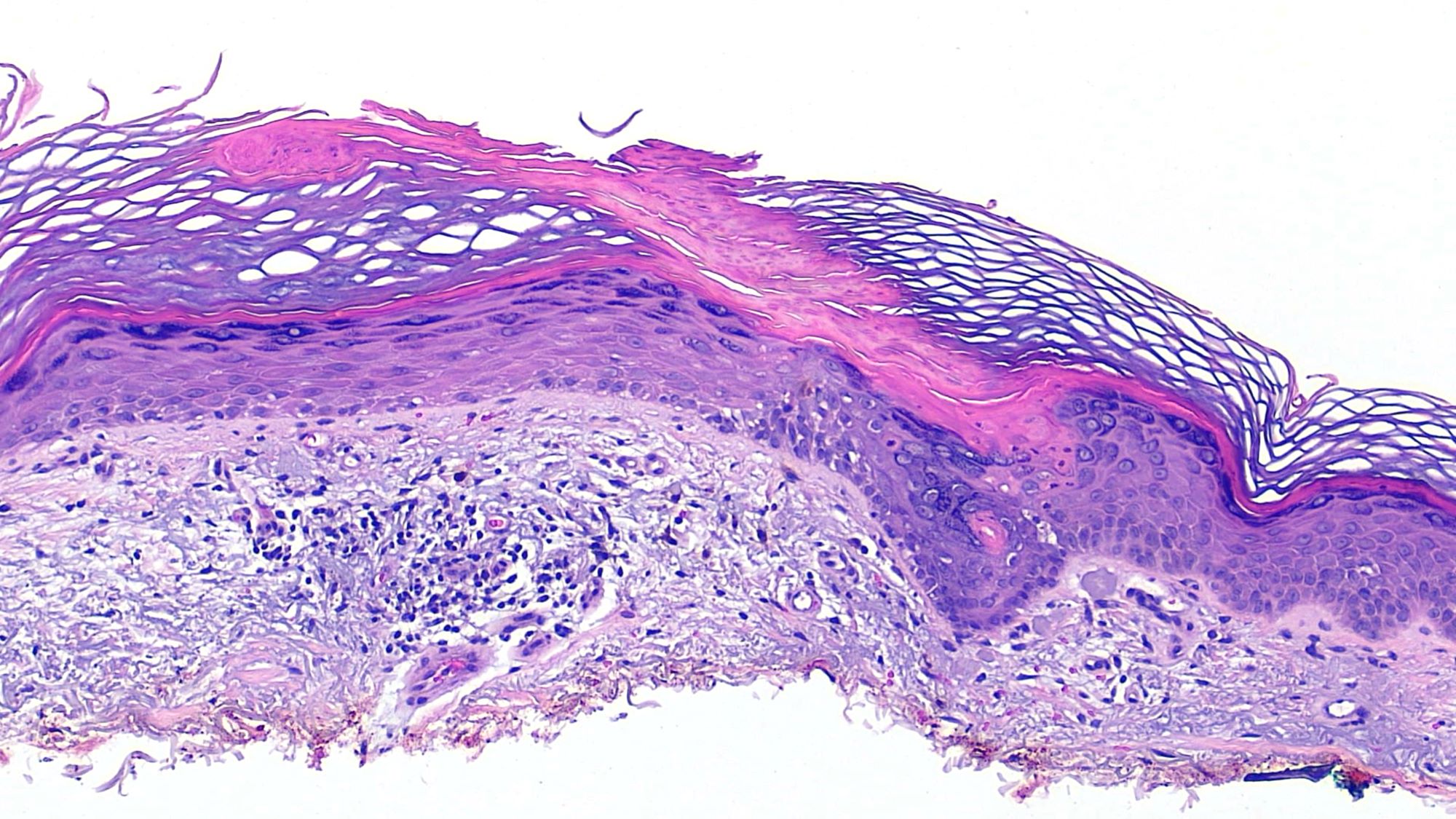
- Cornoid lamella (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2020;111:545, Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2022;88:291)
- Column of parakeratosis at 45 degree angle
- Underlying dyskeratosis with focal loss of granular layer
- Dilated capillaries in the papillary dermis are associated with a lymphocytic infiltrate (Patterson: Weedon's Skin Pathology, 5th Edition, 2020)
- Most prominent inflammatory changes are seen in DSAP
- Central to coronoid lamella, epidermis may be atrophic, normal thickness or acanthotic
- Central interface dermatitis or psoriasiform dermatitis possible
- Solar elastosis possible in DSAP
- Multiple cornoid lamellae can be seen in porokeratosis ptychotropica or penoscrotal porokeratosis
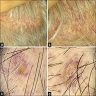
Microscopic (histologic) images
Virtual slides
Positive stains
- PAS special stain reportedly highlights granules within the corneocytes of the cornoid lamella, rarely required
Videos
Short video discussing porokeratosis (pathology pearls)
Sample pathology report
- Skin, right upper arm, skin shave:
- Porokeratosis (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show tiers of parakeratosis overlying dyskeratotic keratinocytes. If multiple lesions are present clinically, a diagnosis of DSAP should be considered.
- Skin, right scrotum, skin shave:
- Porokeratosis (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show acanthosis with multifocal columns of parakeratosis overlying dyskeratotic keratinocytes. At this anatomic site, the findings are consistent with a diagnosis of penoscrotal porokeratosis.
Differential diagnosis
- Porokeratoma:
- Benign acanthoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1897)
- Characterized by multiple cornoid lamellae embedded within a single verrucous lesion (Am J Dermatopathol 2022;44:748)
- Verrucae:
- Epidermal acanthosis, papillomatosis with tiers of parakeratosis and koilocytosis
- Actinic keratosis:
- Gritty papules in sun exposed sites
- Histology with lower keratinocyte atypia and disorder
- Cornoid lamella uncommonly seen
- Psoriasis:
- Regular acanthosis with parakeratosis and intracorneal neutrophils (Munro microabscesses)
- Porokeratotic eccrine ostial and dermal duct nervus:
- An eccrine hamartoma with punctate hyperkeratotic papules affecting the palms and soles
- Histologically and clinically could appear like punctate porokeratosis but cornoid lamellae are limited to eccrine ostia
- Tinea corporis (Am J Clin Dermatol 2022;23:37):
- Foci of parakeratosis with intracorneal hyphae
Board review style question #1
A 40 year old woman presented with an erythematous, annular macule with a thread-like, raised border on her arm. She had several similar lesions on her extensor arms. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis
- Guttate psoriasis
- Macular seborrheic keratoses
- Nummular eczema
- Tinea corporis
Board review style answer #1
A. Disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis. This patient has disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis, which classically presents as small, annular macules with thread-like raised borders. It usually presents more diffusely than other porokeratosis subtypes and frequently on sun exposed areas (posterior neck, extensor surfaces of arms, legs). The histological finding of cornoid lamella is characteristic of porokeratosis.
Answer B is incorrect because guttate psoriasis is a variant of psoriasis that presents in children and adolescents following streptococcal infection (StatPearls: Guttate Psoriasis [Accessed 7 August 2023]). Although guttate psoriasis may also present as lesions over the extensor surfaces, biopsy would reveal a psoriasiform reaction pattern. There is less acanthosis than seen in psoriasis vulgaris. Other features of psoriasis include dilated superficial blood vessels, parakeratosis and neutrophils in the stratum corneum (microabscesses of Munro) (StatPearls: Guttate Psoriasis [Accessed 7 August 2023]).
Answer C is incorrect because seborrheic keratoses are benign lesions that classically present as waxy papules or plaques with a stuck on appearance. Histologic features include hyperkeratosis, acanthosis and papillomatosis (Dermatol Online J 2019;25:13030).
Answer D is incorrect because nummular eczema is a chronic skin condition characterized by oval or coin shaped, erythematous, eczematous plaques. These lesions are usually symmetrically distributed with a predilection for the lower and upper extremities (Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov 2020;14:146). Predominant features of eczema are spongiosis, acanthosis and exocytosis of inflammatory cells.
Answer E is incorrect because tinea corporis is a superficial dermatophyte infection that may clinically resemble porokeratosis due to its annular appearance. Histopathology shows hyphal forms in the stratum corneum.
Comment Here
Reference: Porokeratosis
Answer B is incorrect because guttate psoriasis is a variant of psoriasis that presents in children and adolescents following streptococcal infection (StatPearls: Guttate Psoriasis [Accessed 7 August 2023]). Although guttate psoriasis may also present as lesions over the extensor surfaces, biopsy would reveal a psoriasiform reaction pattern. There is less acanthosis than seen in psoriasis vulgaris. Other features of psoriasis include dilated superficial blood vessels, parakeratosis and neutrophils in the stratum corneum (microabscesses of Munro) (StatPearls: Guttate Psoriasis [Accessed 7 August 2023]).
Answer C is incorrect because seborrheic keratoses are benign lesions that classically present as waxy papules or plaques with a stuck on appearance. Histologic features include hyperkeratosis, acanthosis and papillomatosis (Dermatol Online J 2019;25:13030).
Answer D is incorrect because nummular eczema is a chronic skin condition characterized by oval or coin shaped, erythematous, eczematous plaques. These lesions are usually symmetrically distributed with a predilection for the lower and upper extremities (Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov 2020;14:146). Predominant features of eczema are spongiosis, acanthosis and exocytosis of inflammatory cells.
Answer E is incorrect because tinea corporis is a superficial dermatophyte infection that may clinically resemble porokeratosis due to its annular appearance. Histopathology shows hyphal forms in the stratum corneum.
Comment Here
Reference: Porokeratosis
Board review style question #2
A 28 year old man presented with a 7 month history of a persistent rash over the scrotum and shaft of the penis associated with erythema, burning and pruritis. Clinical examination revealed a well circumscribed, erythematous plaque with a raised border and atrophic center. Poorly defined patches were also seen on the penile shaft. A punch biopsy revealed multiple cornoid lamellae. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Bowen disease
- Condyloma acuminatum
- Penoscrotal porokeratosis
- Verruciform xanthoma
- Zoon balanitis
Board review style answer #2
C. Penoscrotal porokeratosis. This patient's clinical pathologic presentation is consistent with a diagnosis of penoscrotal porokeratosis, a distinct variant of porokeratosis that is often self resolving. This variant is seen in young males typically during the third decade of life (Indian Dermatol Online J 2015;6:339). Histology demonstrates multiple cornoid lamellae involving a mildly hyperplastic epidermis.
Answer A is incorrect because Bowen disease is a form of in situ squamous cell carcinoma. Although Bowen disease may present similarly to porokeratosis, it is rare in patients younger than 30 years of age (Indian Dermatol Online J 2022;13:177). Histopathology would demonstrate full thickness keratinocyte atypia (Indian Dermatol Online J 2022;13:177).
Answer B is incorrect because condyloma acuminata are anogenital warts caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), most commonly HPV strains 6 and 11 (StatPearls: Condyloma Acuminata [Accessed 19 January 2024]). Similar to porokeratosis, condyloma acuminata display hyperkeratosis on histopathological evaluation. However, distinctive koilocytes are also expected. Additionally, condyloma acuminata lesions are usually found in groups that may coalesce into larger lesions and most often present as fleshy papules that range in size.
Answer D is incorrect because verruciform xanthoma is a rare mucocutaneous verrucopapillary lesion that is not associated with dyslipidemia. Histopathology demonstrates epithelial hyperplasia with prominent parakeratinization. The histological hallmark is the presence of foam cells or xanthoma cells confined to the connective tissue papillae (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2019;23:43).
Answer E is incorrect because Zoon balanitis is a nonvenereal condition that most commonly affects middle aged to older uncircumcised men. It most commonly presents as a single shiny erythematous plaque on the glans penis. Early cases will reveal thickening of the epidermis, parakeratosis and a patchy lichenoid infiltrate of lymphocytes and numerous plasma cells. Atrophy of the epidermis, superficial erosions, scattered neutrophils in the upper epidermis, scant spongiosis and a denser plasmacytic infiltrate may be seen in later stages (Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS 2016;37:129).
Comment Here
Reference: Porokeratosis
Answer A is incorrect because Bowen disease is a form of in situ squamous cell carcinoma. Although Bowen disease may present similarly to porokeratosis, it is rare in patients younger than 30 years of age (Indian Dermatol Online J 2022;13:177). Histopathology would demonstrate full thickness keratinocyte atypia (Indian Dermatol Online J 2022;13:177).
Answer B is incorrect because condyloma acuminata are anogenital warts caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), most commonly HPV strains 6 and 11 (StatPearls: Condyloma Acuminata [Accessed 19 January 2024]). Similar to porokeratosis, condyloma acuminata display hyperkeratosis on histopathological evaluation. However, distinctive koilocytes are also expected. Additionally, condyloma acuminata lesions are usually found in groups that may coalesce into larger lesions and most often present as fleshy papules that range in size.
Answer D is incorrect because verruciform xanthoma is a rare mucocutaneous verrucopapillary lesion that is not associated with dyslipidemia. Histopathology demonstrates epithelial hyperplasia with prominent parakeratinization. The histological hallmark is the presence of foam cells or xanthoma cells confined to the connective tissue papillae (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2019;23:43).
Answer E is incorrect because Zoon balanitis is a nonvenereal condition that most commonly affects middle aged to older uncircumcised men. It most commonly presents as a single shiny erythematous plaque on the glans penis. Early cases will reveal thickening of the epidermis, parakeratosis and a patchy lichenoid infiltrate of lymphocytes and numerous plasma cells. Atrophy of the epidermis, superficial erosions, scattered neutrophils in the upper epidermis, scant spongiosis and a denser plasmacytic infiltrate may be seen in later stages (Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS 2016;37:129).
Comment Here
Reference: Porokeratosis