Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Clinical features | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Ferrufino-Schmidt MC, Marques-Piubelli ML, Miranda RN. Primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticanaplasticlargecell.html. Accessed April 17th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Primary cutaneous lymphoma composed of large cells with an anaplastic, pleomorphic or immunoblastic cytomorphology with > 75% malignant cells positive for CD30 (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:877, Elder: WHO Classification of Skin Tumours, 4th Edition, 2018)
Essential features
- Primary cutaneous lymphoma composed of large cells with an anaplastic, pleomorphic or immunoblastic cytomorphology with > 75% malignant cells positive for CD30 (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:877, Elder: WHO Classification of Skin Tumours, 4th Edition, 2018)
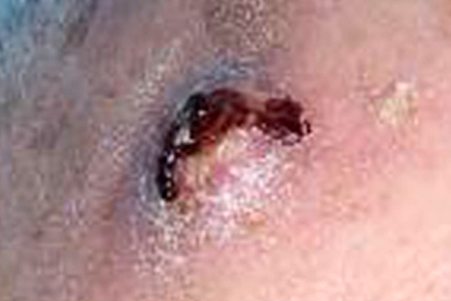
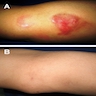
- 80% of cases present as a cutaneous localized nodule or papule with or without ulceration (Pathology 2020;52:100)
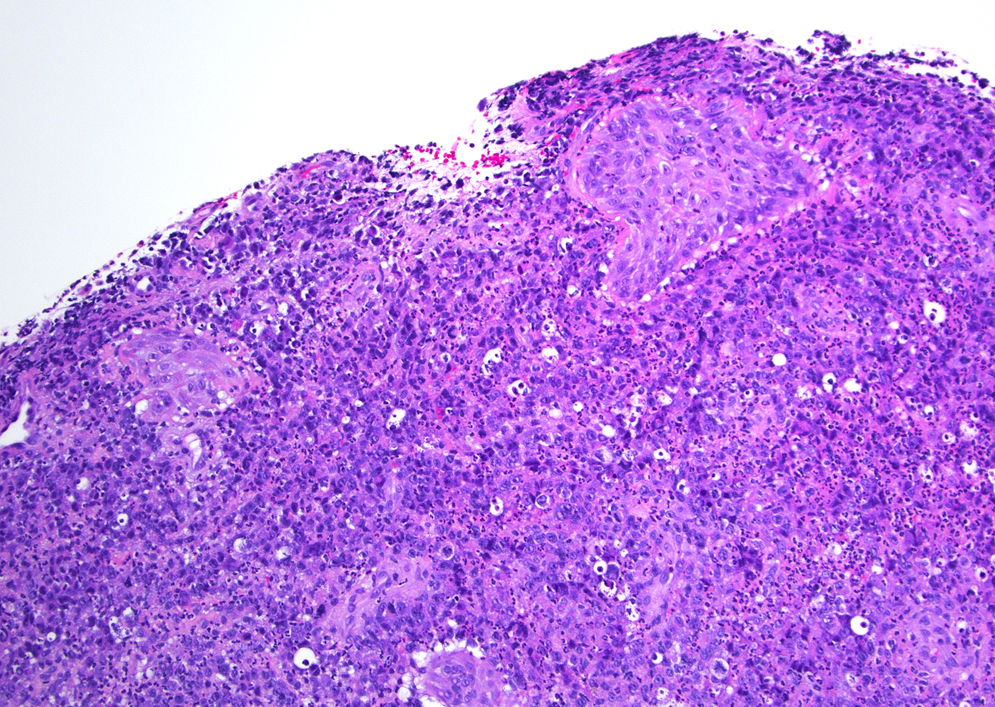
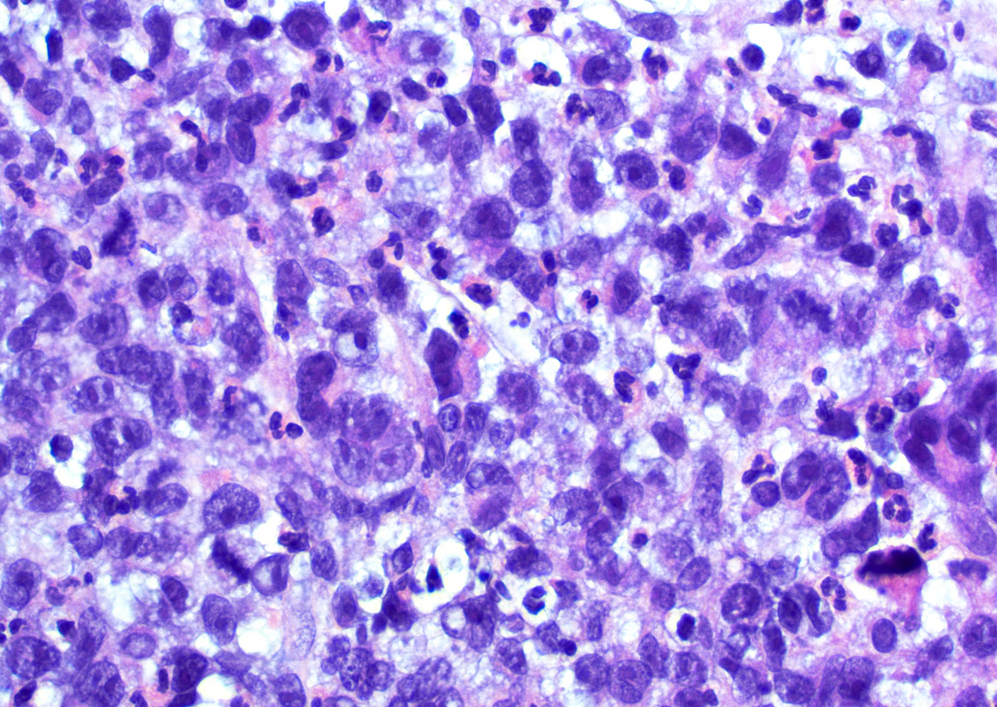
- Diffuse dermal infiltrates with cohesive sheets of tumor cells with anaplastic morphology (round to irregularly shaped nuclei, prominent eosinophilic nucleoli and abundant cytoplasm); nonanaplastic appearance (pleomorphic or immunoblastic) is seen in 20% of cases (Pathology 2020;52:100, Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:877)
Terminology
- Primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma is included under the umbrella term CD30+ T cell lymphoproliferative disorders (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:877)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9718/3 - primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma
Epidemiology
- 25 - 30% of primary cutaneous lymphomas; second most common type of cutaneous T cell lymphoma (J Cutan Pathol 2017;44:570)
- M:F = 2:1 - 3:1 (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:877, Elder: WHO Classification of Skin Tumours, 4th Edition, 2018)
- Median age: 60 years (J Cutan Pathol 2017;44:570)
- Pediatric and congenital cases are rare (Am J Dermatopathol 2015;37:398)
Sites
- Common sites: face, trunk and extremities (J Am Acad Dermatol 2016;74:1135, J Cutan Pathol 2017;44:570)
- Leg involvement is associated with extensive and multiple skin lesions
Clinical features
- 80% of cases present as a cutaneous localized nodule or papule with or without ulceration (Pathology 2020;52:100)
- Multifocal lesions in 20% of cases (Blood 2000;95:3653)
- Extra cutaneous dissemination (mainly to regional lymph nodes) in 10% of cases (Blood 2000;95:3653)
- Skin lesions can regress spontaneously or can progress or relapse (Blood 2000;95:3653)
Prognostic factors
- Prognosis is similar for patients with localized or multifocal skin lesions: 90% 10 year overall survival (Blood 2000;95:3653, J Am Acad Dermatol 2003;49:1049)
Case reports
- 10 day old neonate with congenital primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma (Am J Dermatopathol 2015;37:398)
- 18 year old man with primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma (J Cancer Res Ther 2015;11:656)
- 8 men, age 46 and older, with primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma small cell variant (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:877)
- 73 year old man with tumor in parotideomasseteric region initially diagnosed as discoid lupus (Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97:e9645)
- 81 year old cardiac transplant recipient with primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma (Am J Dermatopathol 2016;38:461)
Treatment
- Radiation or chemotherapy, alone or combined (Arch Craniofac Surg 2019;20:207)
- Excision plus radiotherapy for solitary nodules
- Low dose methotrexate (5 - 20 mg/wk) for multifocal lesions (Arch Craniofac Surg 2019;20:207)
- Brentuximab vedotin (anti-CD30) for refractory cases (Arch Craniofac Surg 2019;20:207)
Clinical images
Gross description
- Skin nodule with or without ulceration (J Am Acad Dermatol 2016;74:1135, J Cutan Pathol 2017;44:570)
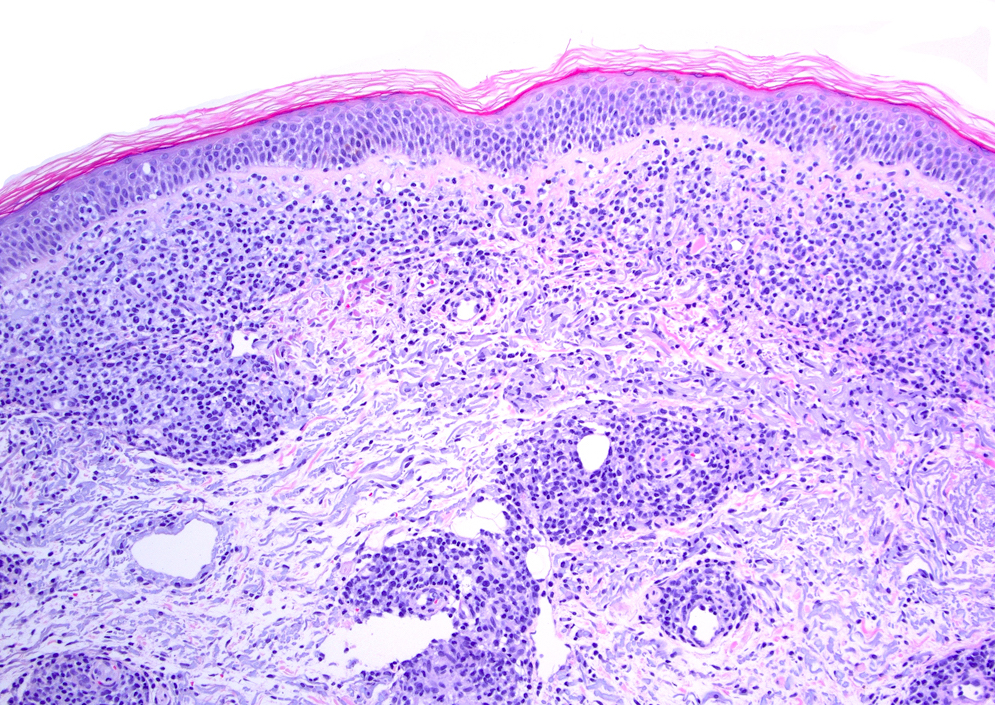
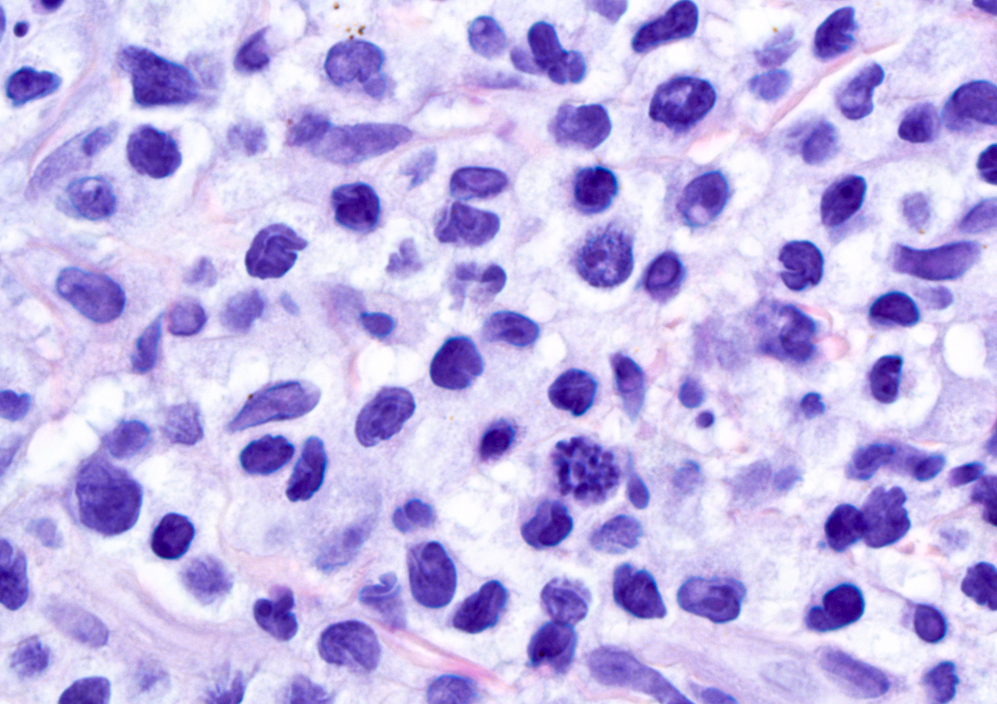
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Diffuse dermal infiltrates with cohesive sheets of tumor cells with anaplastic morphology (round to irregularly shaped nuclei, prominent eosinophilic nucleoli and abundant cytoplasm); nonanaplastic appearance (pleomorphic or immunoblastic) is seen in 20% of cases (Pathology 2020;52:100, Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:877)
- Epidermotropism is marked in cases with DUSP22-IRF4 rearrangement (Histopathology 2015;66:846)
- Cerebriform lymphocytes are not identified
- Variable degrees of inflammatory infiltrate, reactive lymphocytes are common in the periphery of the lesions (Br J Dermatol 2003;148:580)
- Ulcerated lesions may have lymphomatoid papulosis-like histology with abundant reactive T cells, histocytes, eosinophils, neutrophils and a low number of CD30+ cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:1203; J Cutan Pathol 2015;42:610)
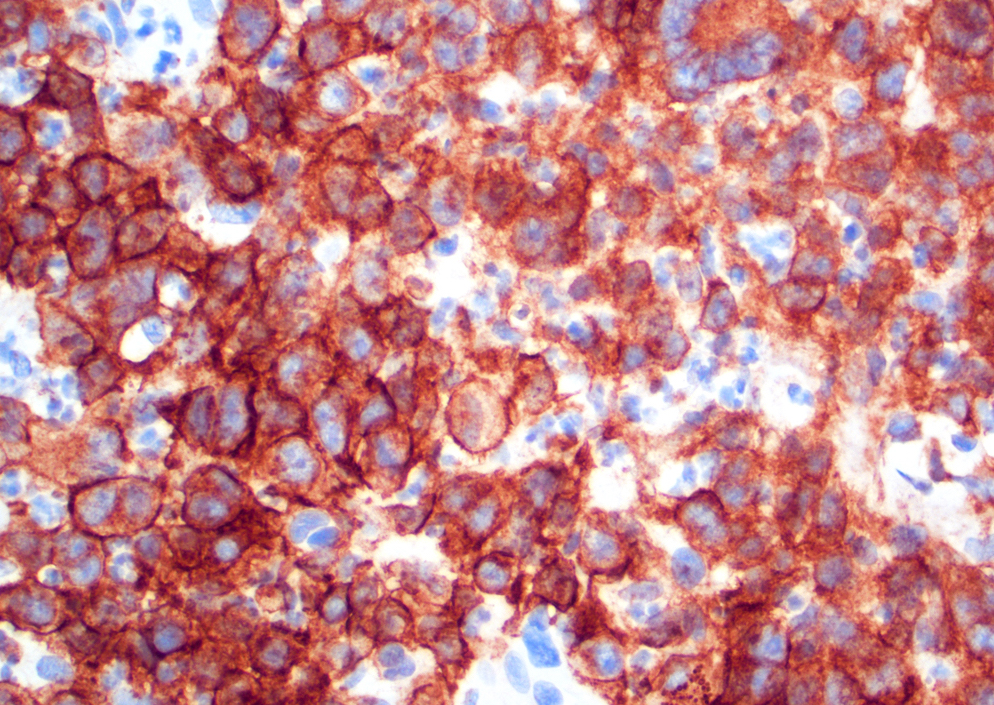
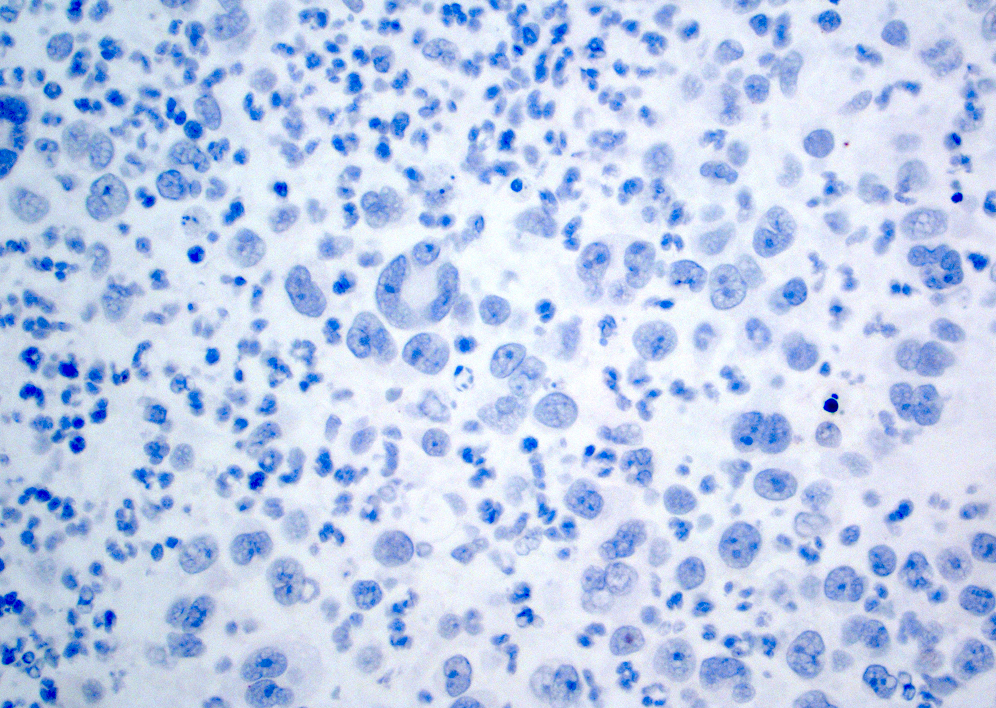
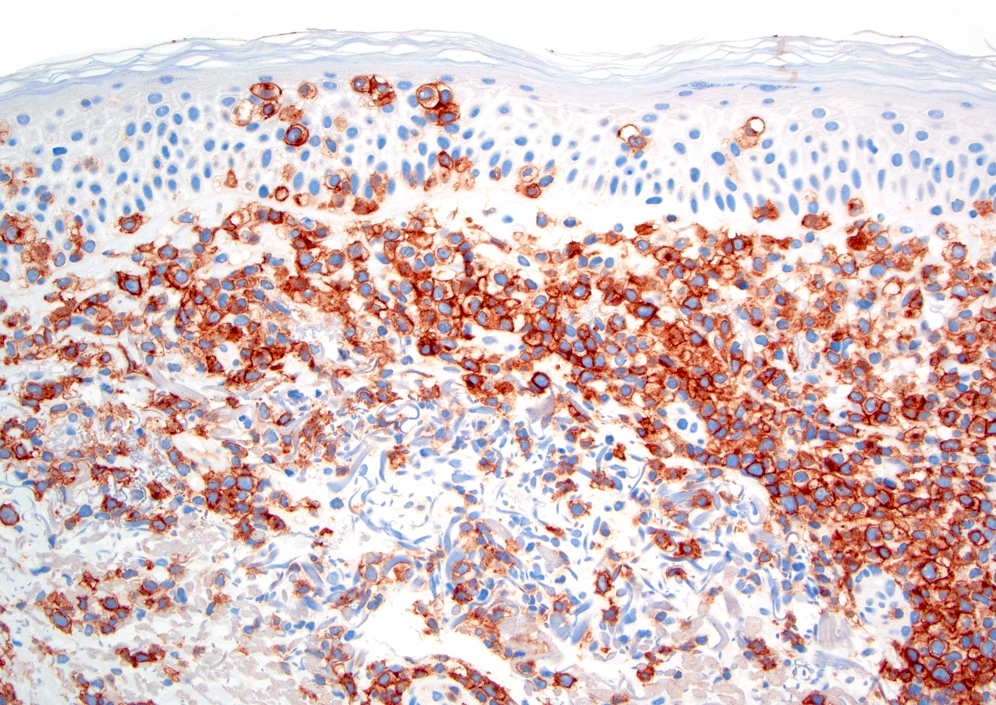
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- CD30 in more than 75% of neoplastic cells (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:877, Elder: WHO Classification of Skin Tumours, 4th Edition, 2018)
- Activated CD4 T cell immunophenotype (J Cutan Pathol 2017;44:570)
- CD45 (J Cutan Pathol 2017;44:570)
- Cytotoxic proteins: granzyme B, TIA1 and perforin (J Cutan Pathol 2017;44:570)
- CD15 (~40%) (Br J Dermatol 2009;161:121)
Negative stains
- Variable loss of CD2, CD5, CD7 and CD3 (J Invest Dermatol 1997;109:636)
- CD8 usually negative but can be CD4-/CD8+ or CD4+/CD8+ (Am J Dermatopathol 2014;36:153)
- EMA and ALK (J Clin Pathol 2000;53:445)
- CD56 (J Cutan Pathol 2000;27:392)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Clonal TRB or TRG rearrangements in > 90% (J Cutan Pathol 2017;44:570)
- Rearrangements of:
- DUSP22-IRF4 locus in 6p25.3 in 20 - 57% (J Invest Dermatol 2010;130:816)
- NPM1-TYK2 in ~5% (Blood 2014;124:3768)
- Rare case with translocations involving ALK gene at 2p23 (Histopathology 2015;66:846)
- Chromosomal imbalances (J Invest Dermatol 2010;130:563):
- Gains in 7q, 17q, 21
- Losses in 3p, 6q, 8p, 13q
Sample pathology report
- Skin, punch biopsy:
- CD30 lymphoproliferative disorder, mostly consistent with cutaneous ALK- anaplastic large cell lymphoma, in the appropriate clinical context (see comment)
- Comment: The section shows an extensive dermal infiltrate composed predominantly of medium to large sized lymphocytes and admixed neutrophils and histiocytes. Scattered mitotic figures are noted. There is epidermal ulceration and extensive neutrophilic serum crust that prevents the evaluation of epidermotropism. Immunohistochemical studies show that the large lymphoid cells are diffusely positive for CD30. CD3 and CD20 label a mixed population of T and B small lymphocytes in the background; the large cells are only focally positive for CD3 and are negative for CD20. The large cells are also partially positive for CD4, while CD8 highlights very rare background lymphocytes. TCR beta labels background lymphocytes while TCR gamma is essentially negative. CD56, EBER and ALK1 are negative.
Differential diagnosis
- Lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP) type C
- Multiple lesions arranged in crops < 10 mm with history of regression favor lymphomatoid papulosis
- Large cell transformation of mycosis fungoides
- Clinical history characteristic of mycosis fungoides: patches, plaques, tumors
- Look for typical features of mycosis fungoides at margins of lesion
- Often IHC positive for pan T cell antigens but negative for CD7
- Systemic ALK- anaplastic large cell lymphoma with cutaneous involvement
- Peripheral lymph nodes affected
- Systemic ALK+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma with cutaneous involvement
- Peripheral T cell lymphoma NOS with cutaneous involvement
- B symptoms and evidence of disseminated disease
- Usually spares epidermis
- IHC: CD30-, CLA-
- Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma
- Primary cutaneous gamma-delta T cell lymphoma
- Primary cutaneous CD8+ aggressive epidermotropic cytotoxic T cell lymphoma
- Primary cutaneous CD4+ small / medium T cell lymphoproliferative disorder
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2