Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2 | Practice question #3 | Practice answer #3 | Practice question #4 | Practice answer #4Cite this page: Hodgson A, Dickson BC. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticdfsp.html. Accessed September 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Locally aggressive, superficial mesenchymal neoplasm with fibroblastic differentiation
Essential features
- Locally aggressive, superficial mesenchymal neoplasm with fibroblastic differentiation
- Virtually all cases contain fusion genes; COL1A1::PDGFB is the most common fusion product, although others have recently been reported
- Fibrosarcomatous transformation imparts an increased risk of recurrence and metastasis
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Rare, though one of the most common sarcomas of the skin / subcutis
- Occurs over a wide age range but most commonly in early to mid adulthood (Cancer 1962;15:717, Am J Surg 1966;111:638)
- Both men and women affected, with some debate as to whether there is a slight male or female predilection (J Am Acad Dermatol 2007;56:968)
Sites
- Can ostensibly involve any area of skin but the trunk and extremities are the most common locations
Pathophysiology
- Tumors are generally presumed to occur sporadically
- Virtually all cases contain fusion genes; COL1A1::PDGFB is the most common fusion product, although others have been reported
- Possible association with adenosine deaminase deficient severe combined immunodeficiency (J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012;129:762)
Clinical features
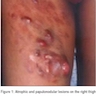
- Classically an exophytic, nodular cutaneous mass; however, often initially presents as a flat plaque (JAMA Netw Open 2019;2:e1910413)
- Initially may show persistent slow growth, often for many years, then sudden progression (Cancer 1962;15:717)
- Fibrosarcomatous transformation is associated with metastatic potential (Cancer 2000;88:2711)
Diagnosis
- Tumors are morphologically distinctive and frequently amenable to classification based on H&E
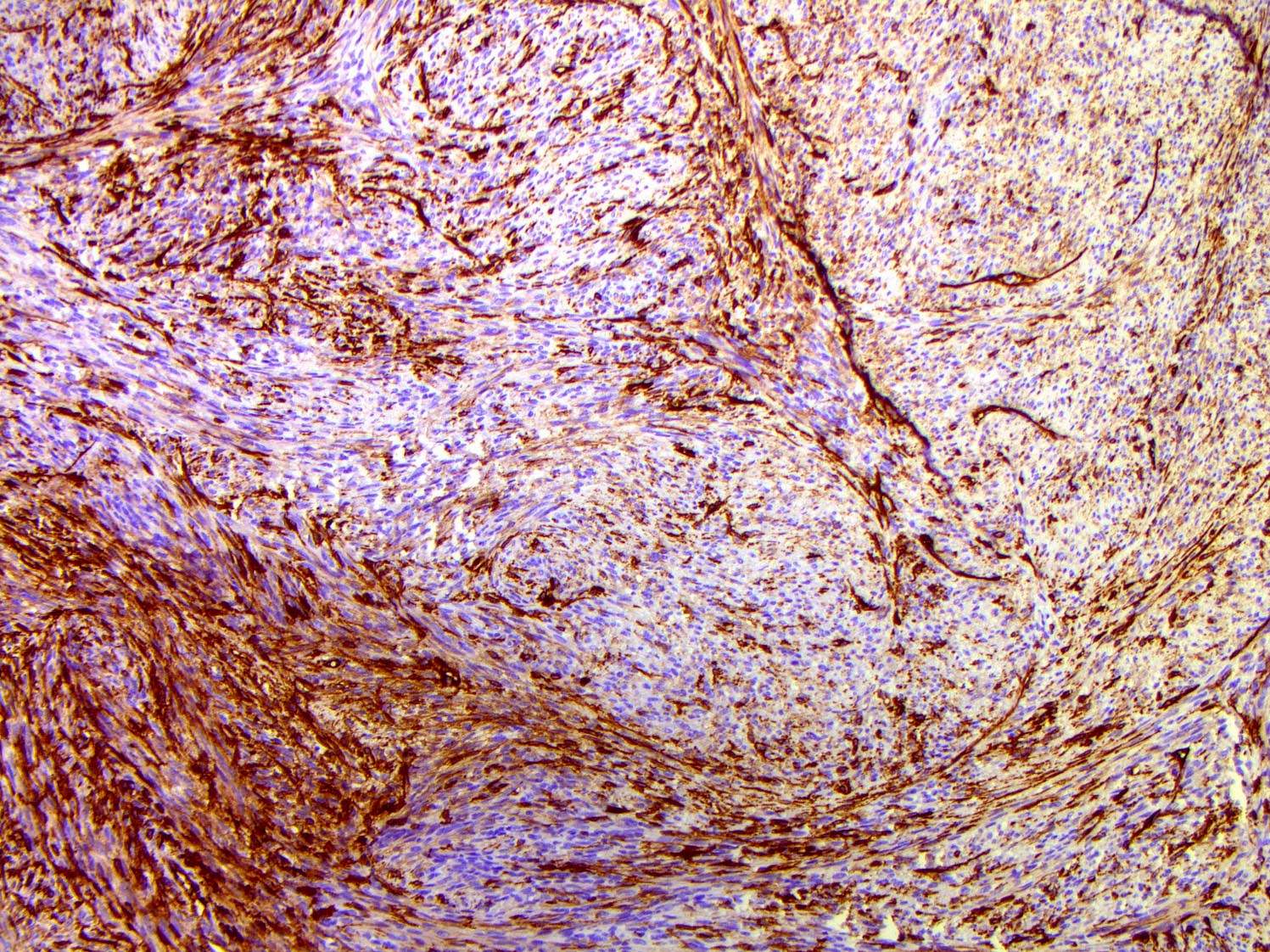
- Immunohistochemistry for CD34 is a useful adjunct since most cases are diffusely positive
- Molecular testing is helpful, particularly in the context of limited sampling or unusual morphology
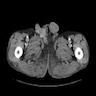
Radiology description
- Imaging findings are nonspecific but in general show a well defined, subcutaneous soft tissue mass with intermediate to marked enhancement on contrast enhanced CT and MRI (Medicine (Baltimore) 2015;94:e1001)
- So called claw sign may be seen in some cases (J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 2017;61:9)
Prognostic factors
- Incomplete resection is a risk factor for recurrence
- Fibrosarcomatous transformation (fibrosarcoma ex DFSP) imparts an increased risk of recurrence and metastasis (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:436)
- Metastases typically occur following multiple local recurrences
- Increased age, male sex and tumor size are associated with worse overall survival (JAMA Dermatol 2016;152:1365)
Case reports
- 21 year old man with history of Cowden syndrome and scalp tumor (Am J Dermatopathol 2016;38:e40)
- 23 year old man and 28 year old woman with fibrosarcomatous transformation occurring on the scalp (BMJ Case Rep 2016;2016:bcr2016215427)
- 30 year old woman with longstanding history of a small abdominal wall mass (Case #485)
- 37 year old man with recurrent dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, refractory to therapy (Onco Targets Ther 2018;11:2439)
- 44 year old woman with vulvar myxoid dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (Am J Dermatopathol 2016;38:226)
- 47 year old man with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans in the inguinal region (Ann Dermatol 2016;28:629)
- 60 year old man with metastatic fibrosarcomatous dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans treated with imatinib mesylate (Dermatol Ther 2022;35:e15736)
Treatment
- Wide local excision is considered the mainstay of treatment for localized disease (Cancer 2019;125:735)
- Advanced disease may also require consideration of imatinib or radiotherapy (Eur J Cancer 2015;51:2604, JAMA Dermatol 2019;155:361, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2016;30:1107)
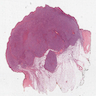
Clinical images
Gross description
- Initially, plaque-like dermal / subcutaneous thickening; progresses to raised firm multinodular mass (Cancer 1962;15:717)
- Tumor is usually centered in dermis with extension into subcutaneous tissue; occasionally, subcutaneous involvement only (Am J Dermatopathol 2008;30:327)
- Variable size (0.5 cm to > 10 cm) (Cancer 1962;15:717)
- Gray-white, firm; may be myxoid or gelatinous (Cancer 1962;15:717)
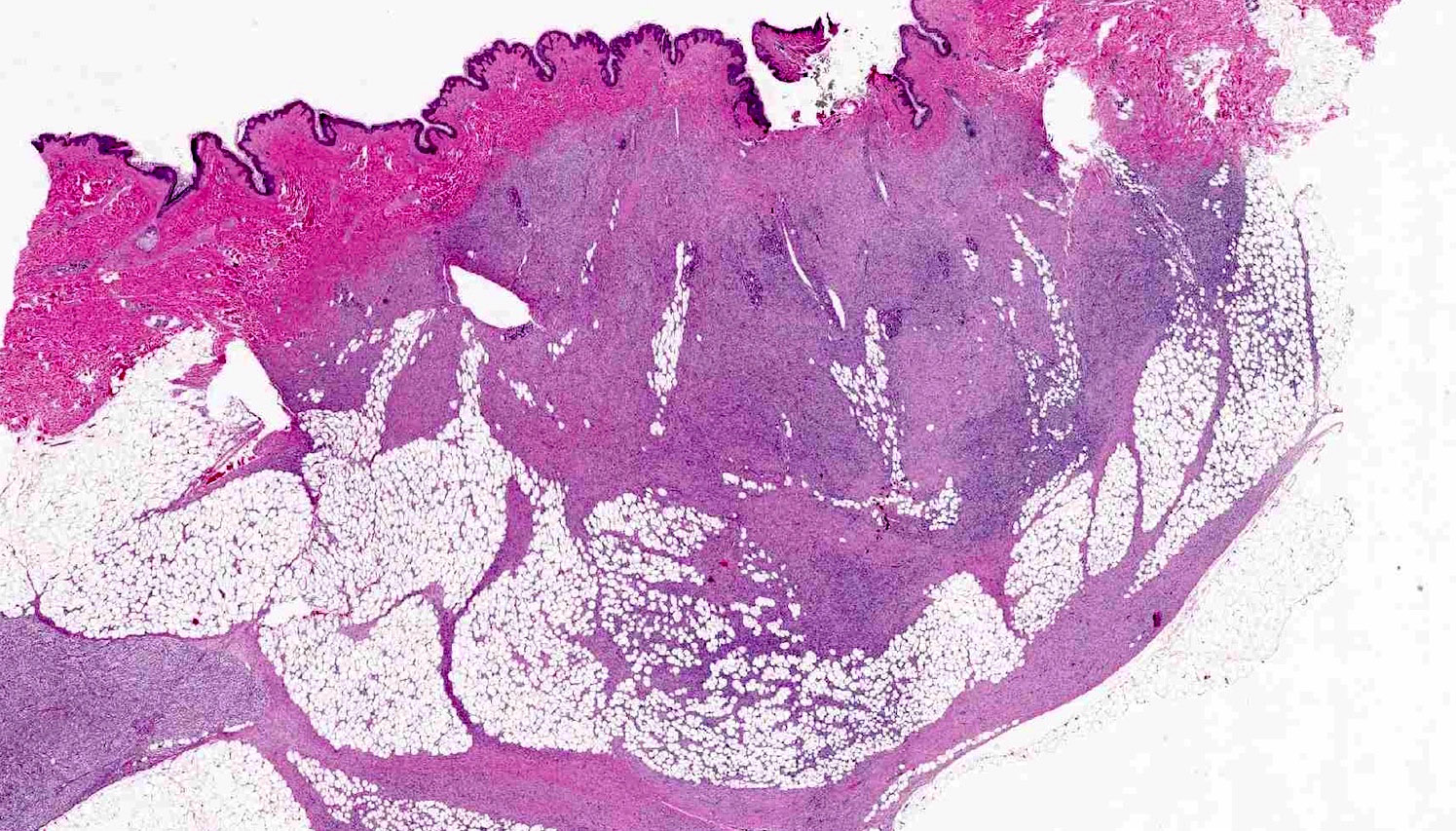
Microscopic (histologic) description
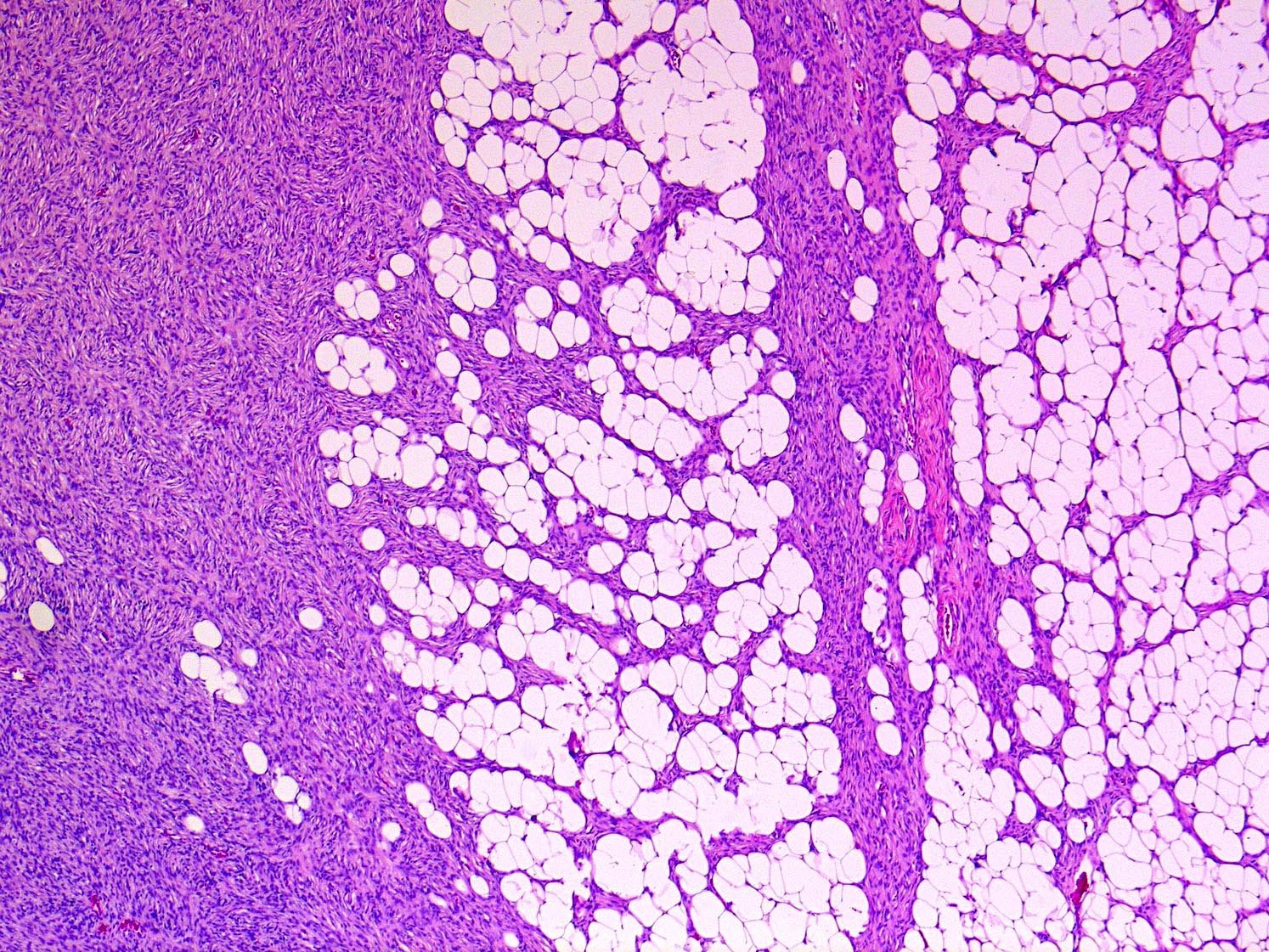
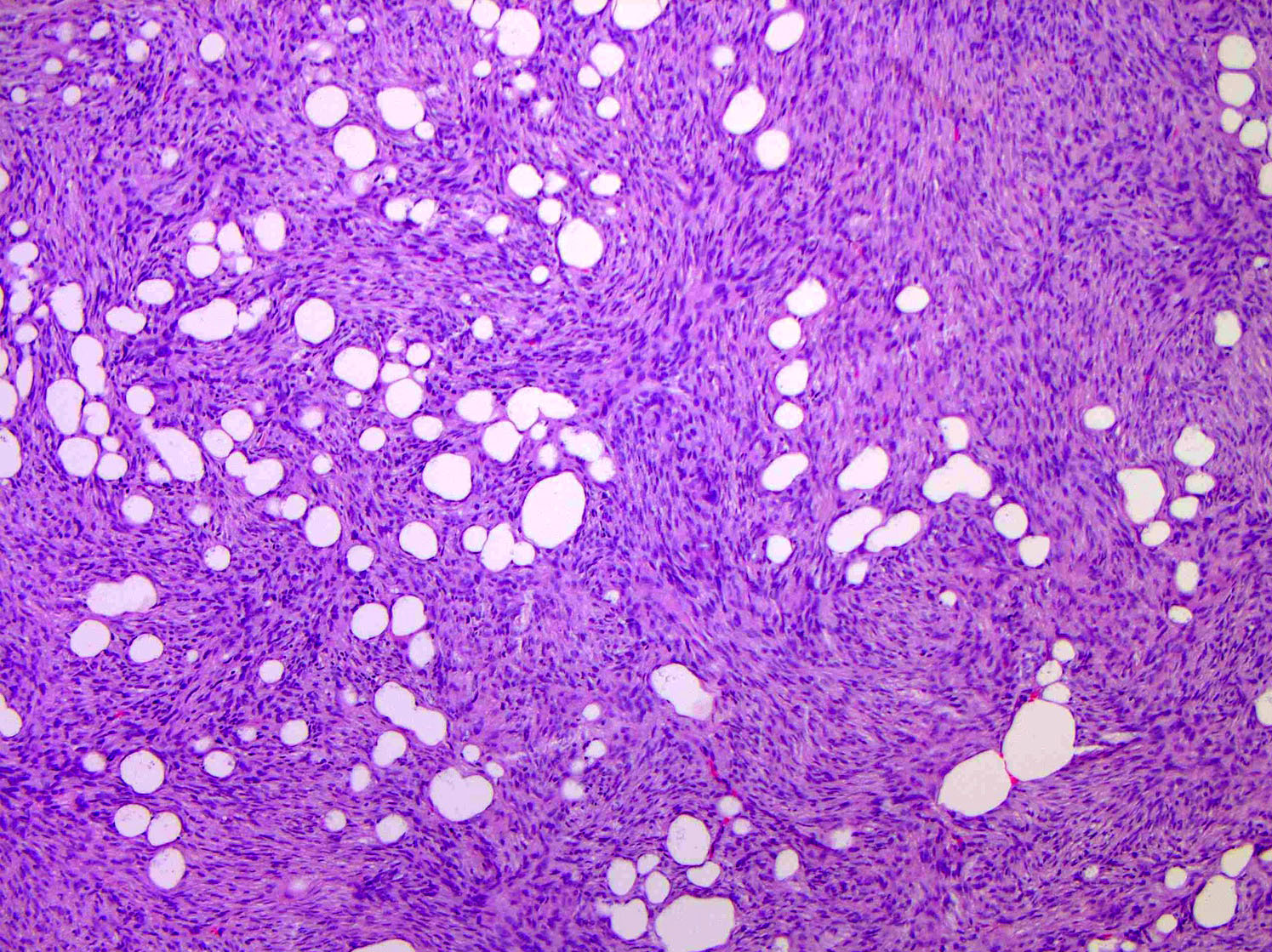
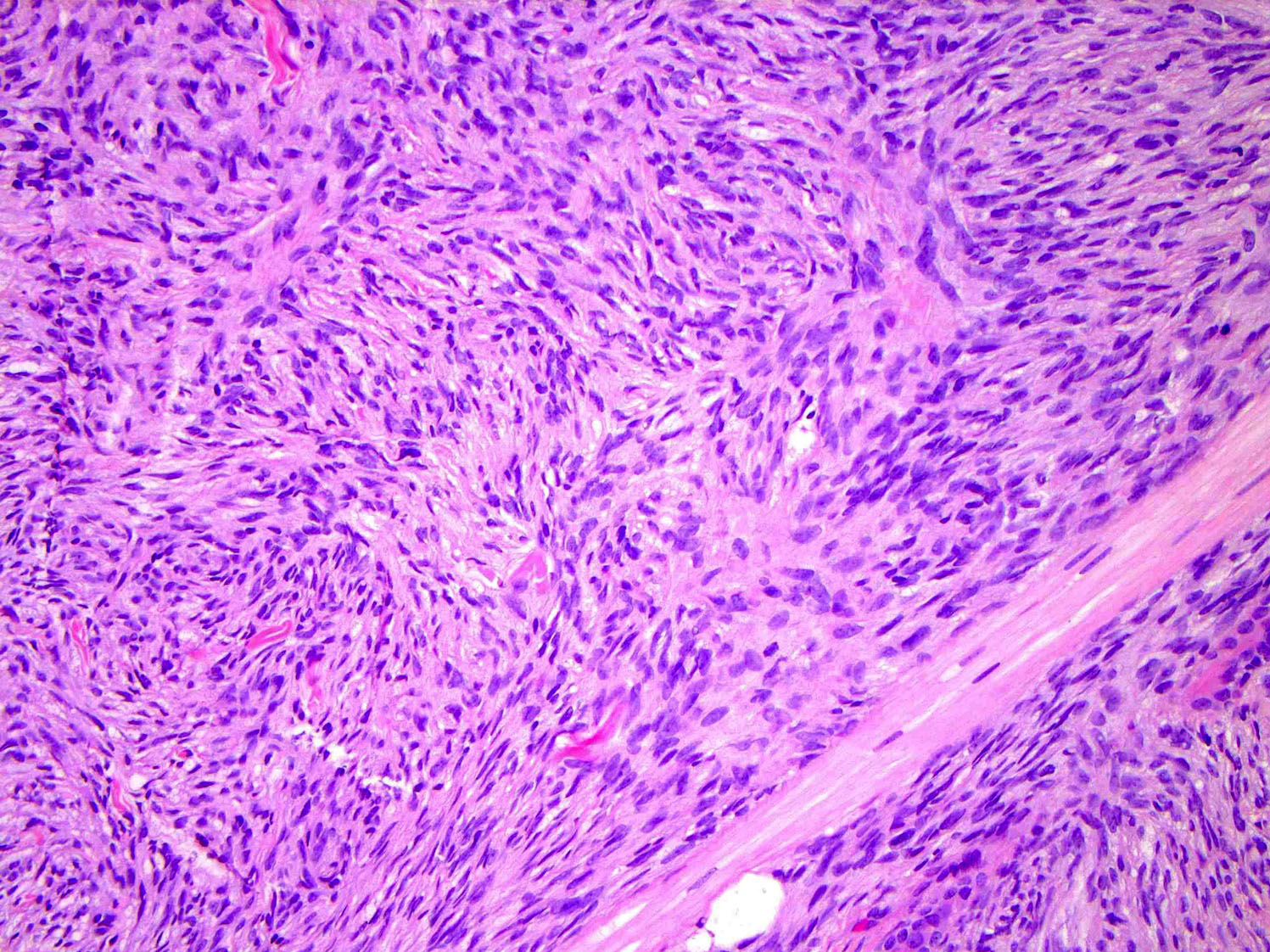
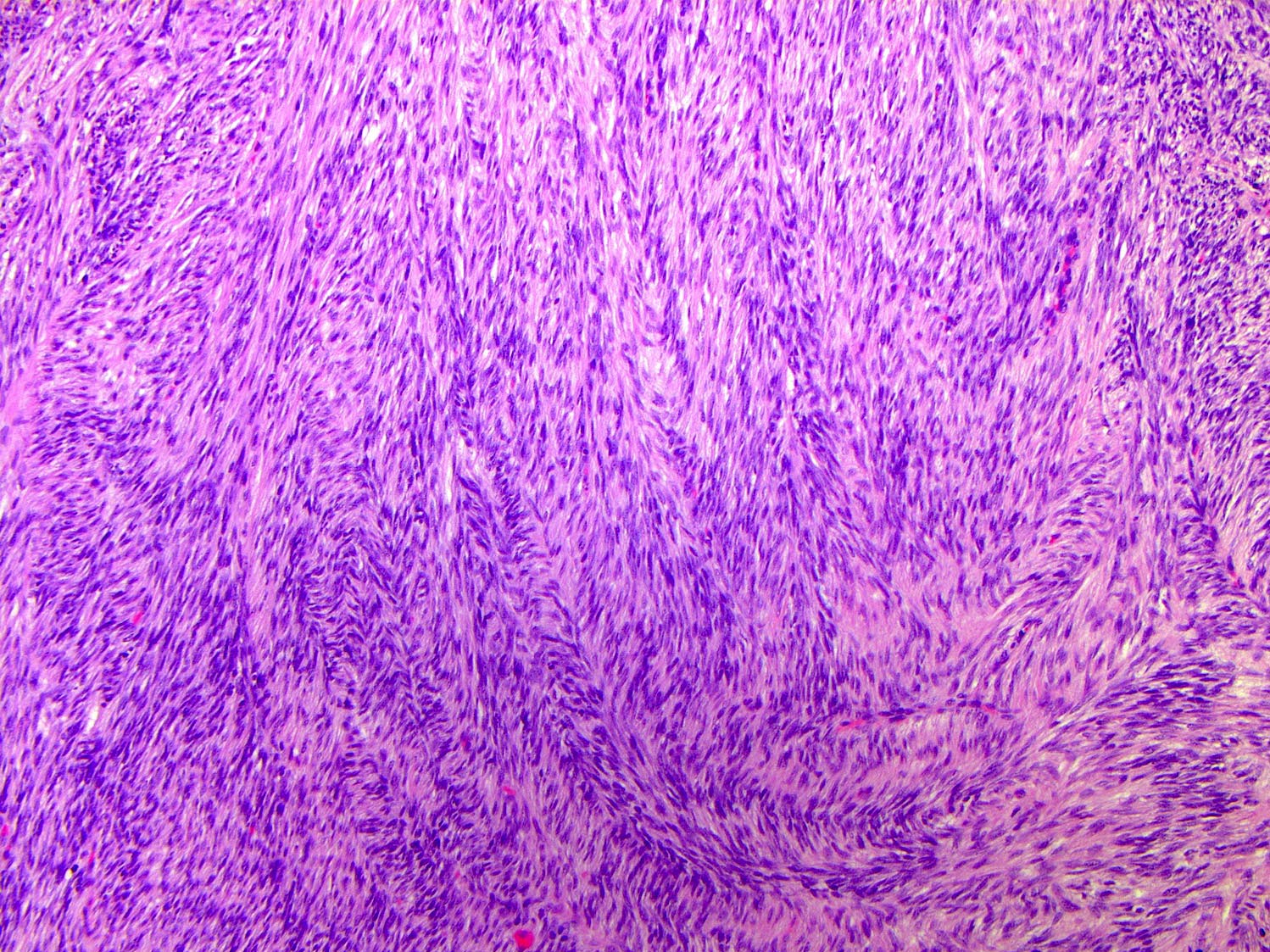
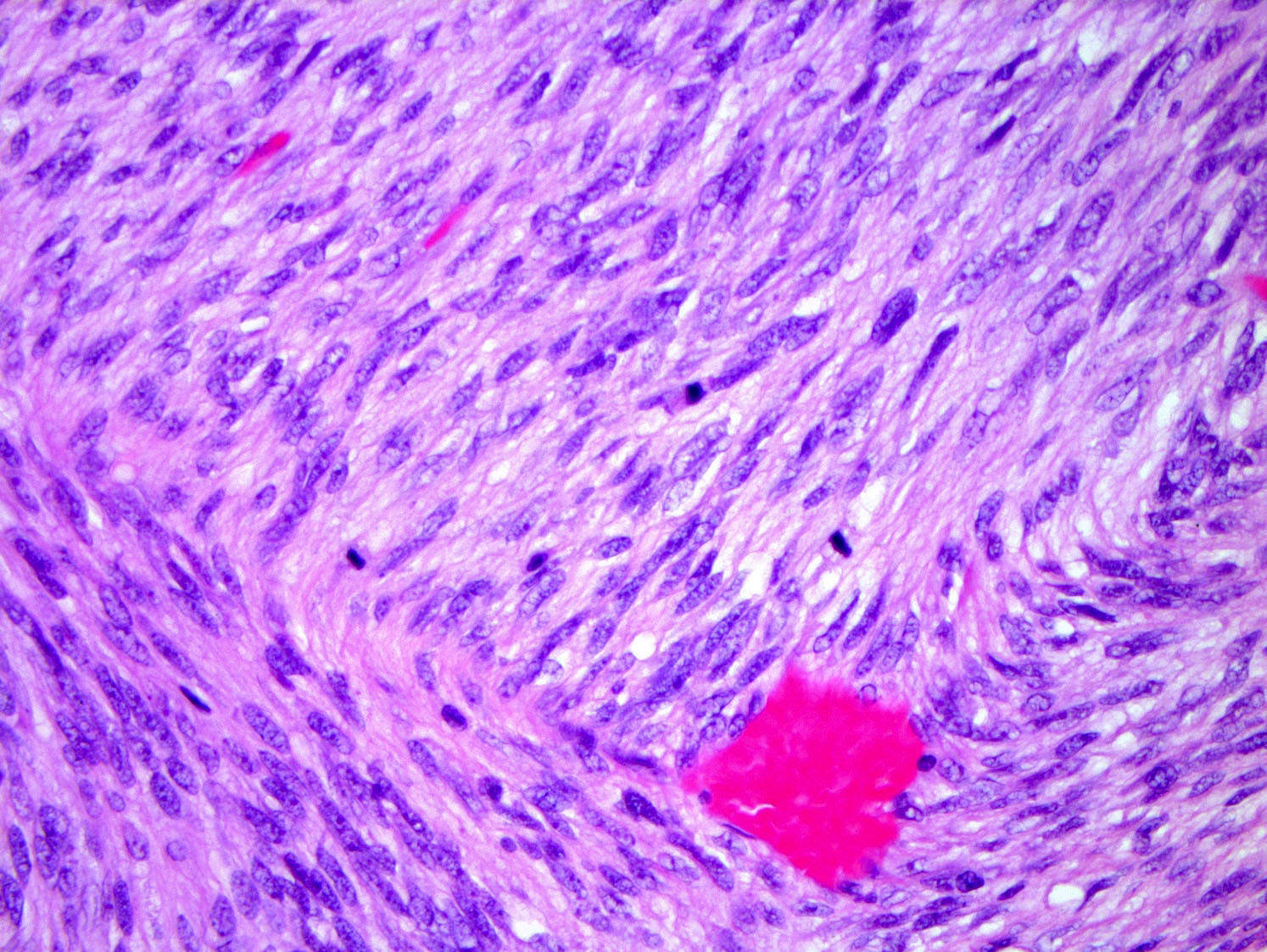
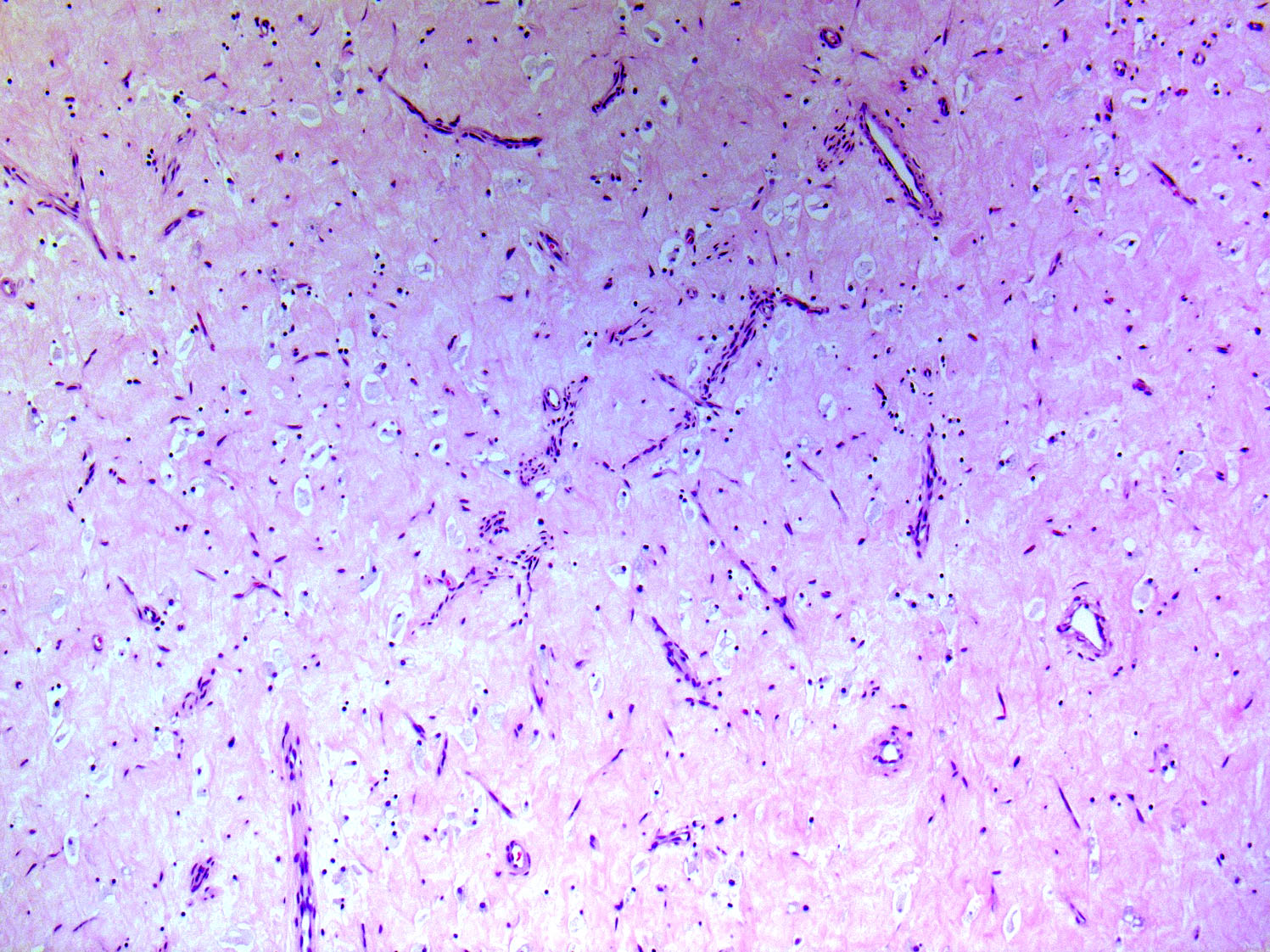
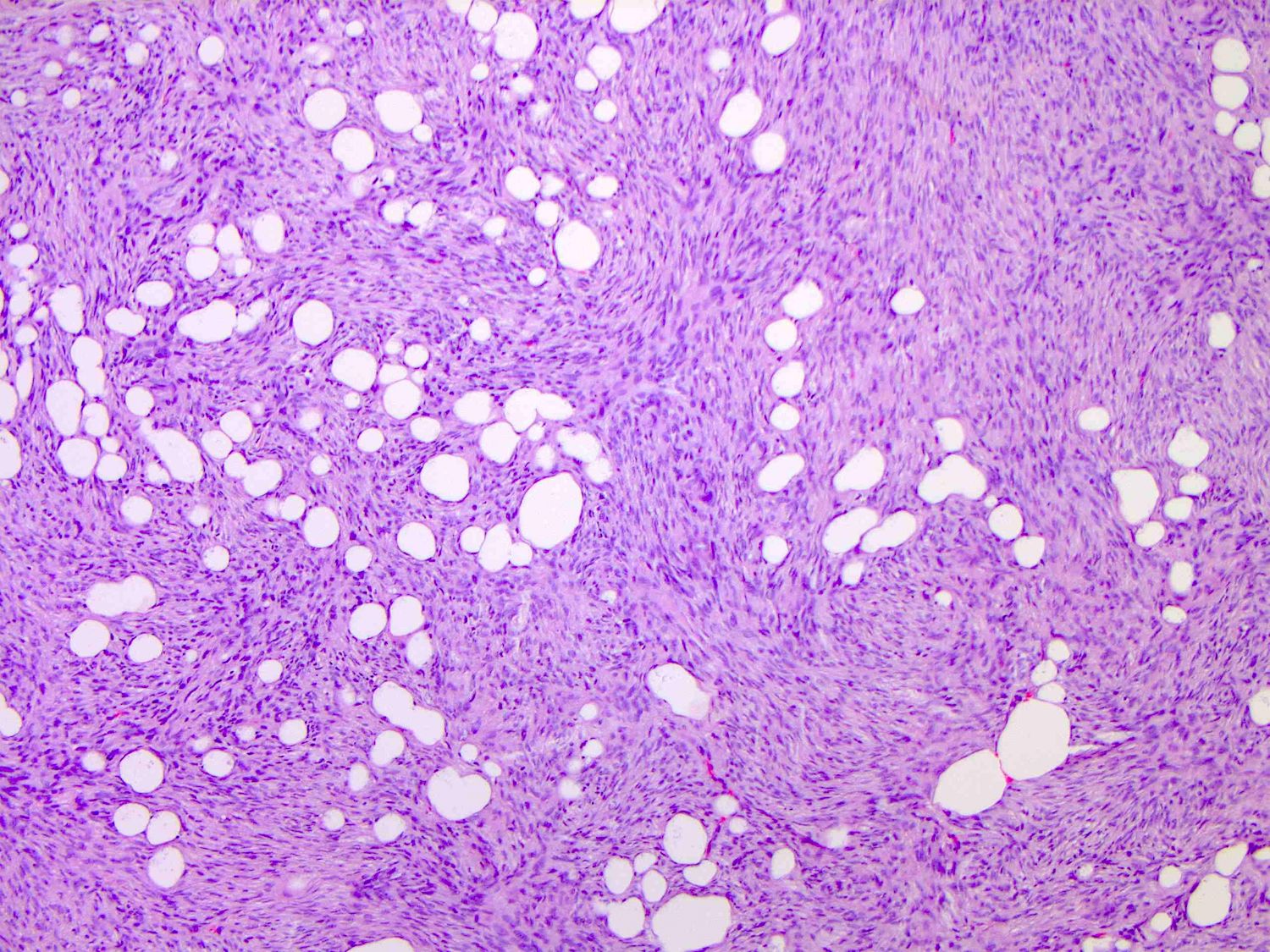
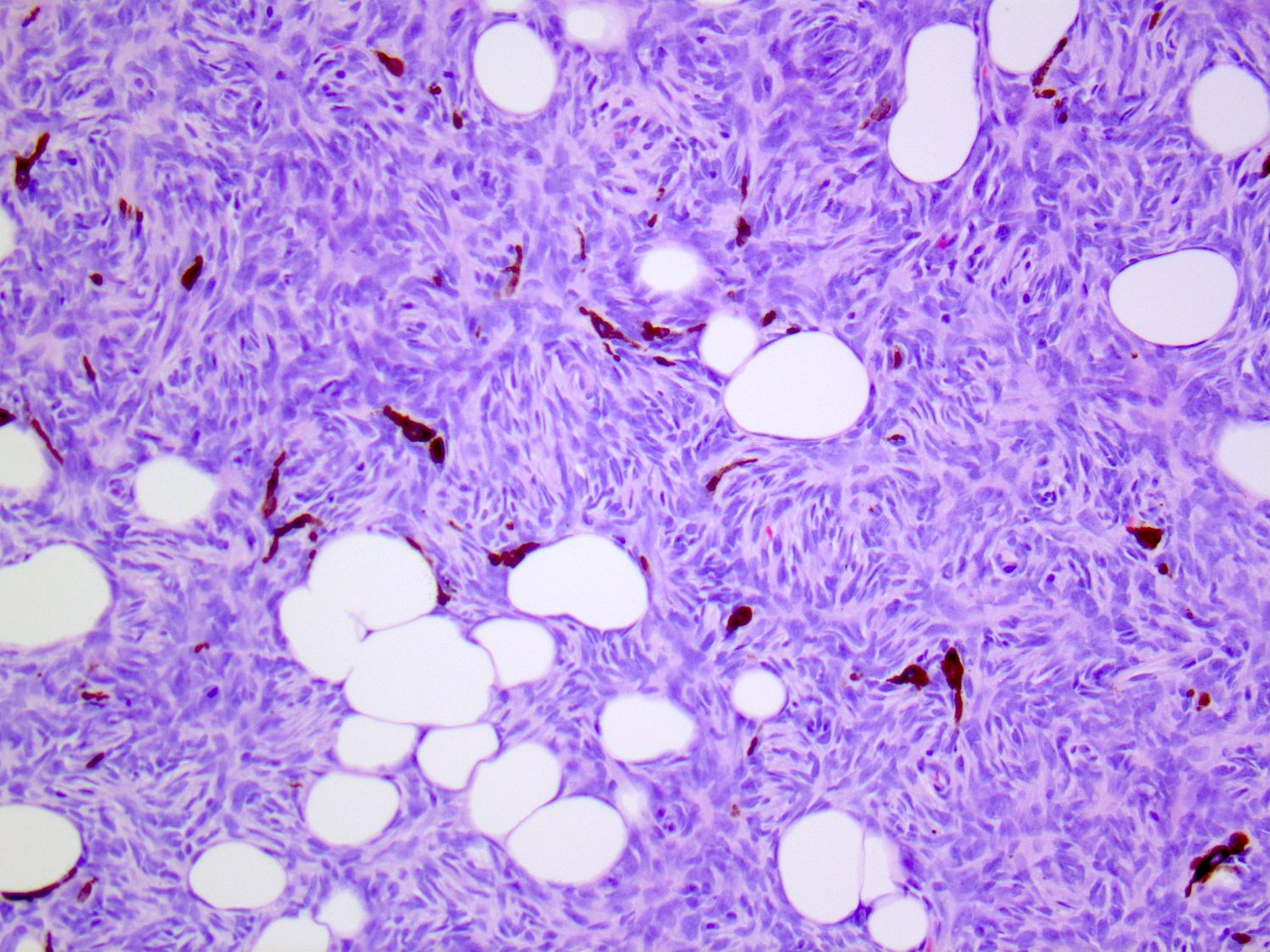
- Tumors are generally centered within the dermis or subcutis and characterized by spindle cells with a storiform to whorled pattern
- Cytoplasm is generally abundant and eosinophilic; nuclei are monomorphic and ovoid to elongated with variable mitotic activity
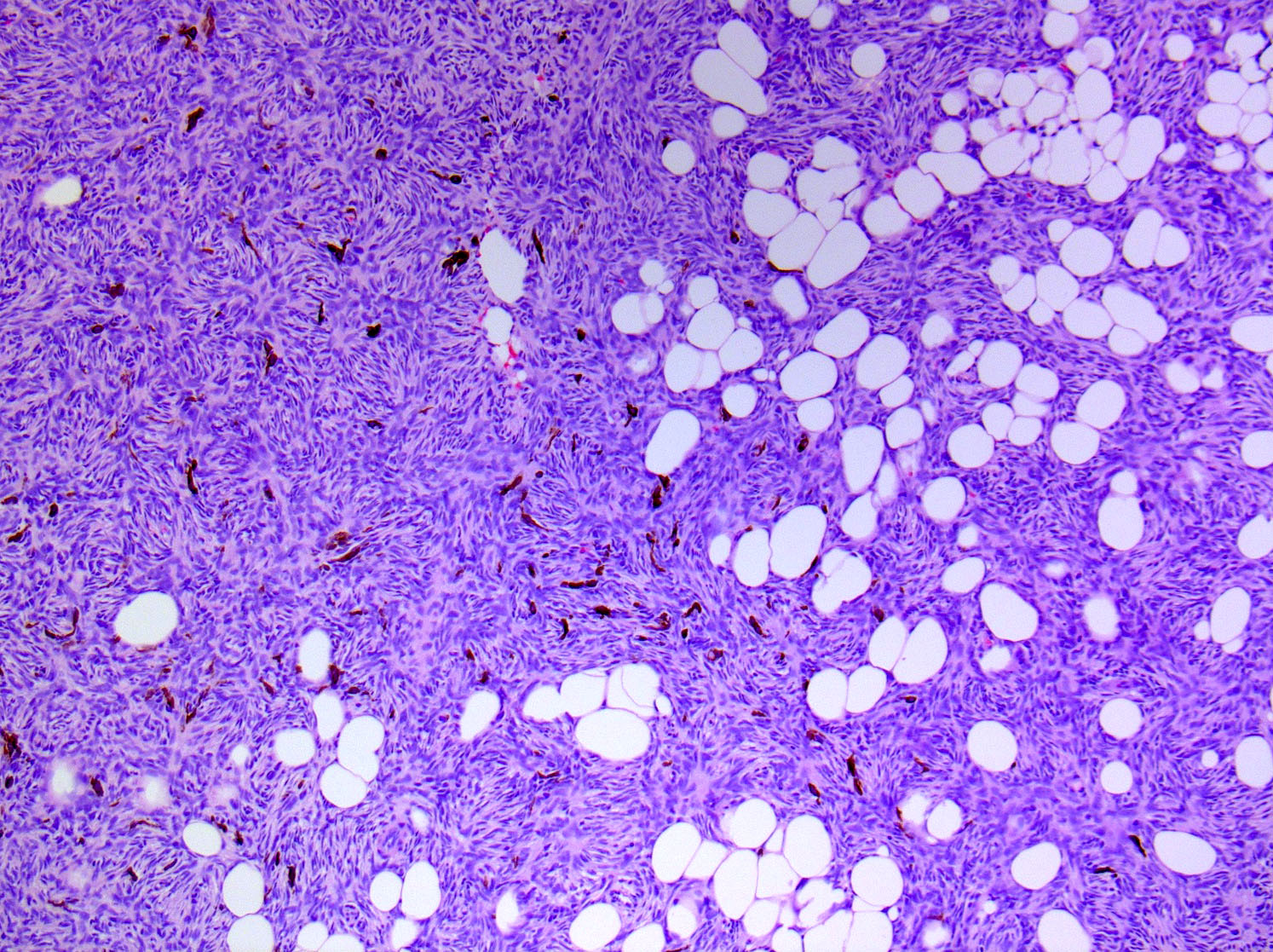
- Tumors infiltrate and expand fibrous septa; interdigitation among lobules of fat yields a honeycomb pattern
- Adnexal structures are typically spared
- Stroma may be collagenous, myxoid or microcystic
- Multiple variants exist, including those with
- Giant cells (Histopathology 1990;17:165)
- Melanin pigmentation (Bednar tumor) (Am J Surg Pathol 1985;9:630, Histopathology 1988;13:631)
- Myoid differentiation (J Cutan Pathol 1996;23:30)
- Myxoid stroma (Am J Surg Pathol 1983;7:445, Am J Dermatopathol 2007;29:443, Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1371)
- Pseudocystic change (J Cutan Pathol 2012;39:356)
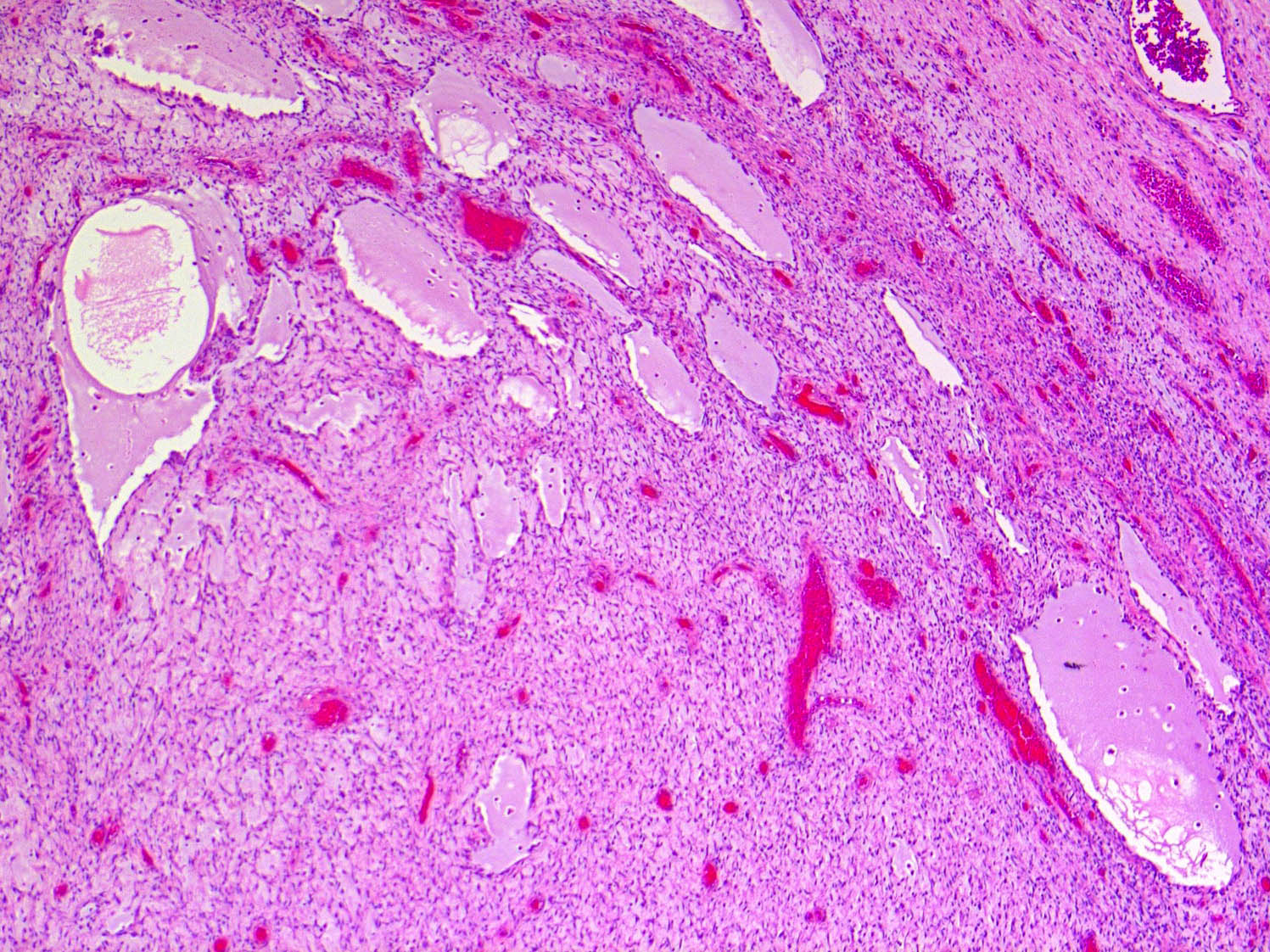
- So called sarcomatous transformation (mimics undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma) (Am J Dermatopathol 2011;33:354)
- Fibrosarcomatous transformation denotes those with cellular spindle cell fascicles or a herringbone pattern
- Generally with greater atypia and mitotic activity
- CD34 expression may be diminished / absent
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Brendan C. Dickson, M.D., M.Sc.
Virtual slides
Positive stains
- CD34: may be diminished / absent with fibrosarcomatous transformation
- Vimentin
- p53: with fibrosarcomatous transformation (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:436)
- Fontana-Masson (Bednar tumor)
Negative stains
- Factor XIIIa
- S100, HMB45, MelanA, Fontana-Masson: usually negative but positive in dendritic melanocytic cells in pigmented DFSP (Bednar tumor)
- Desmin
- Smooth muscle actin: positive in the context of myoid differentiation
- CD31
- ERG
- AE1 / AE3
- Prussian blue
- Reference: J Cutan Pathol 1996;23:30
Electron microscopy description
- Ultrastructural features are compatible with fibroblasts (J Cutan Pathol 1979;6:265, Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol 1981;391:165)
- Long ramified processes with primitive junctions (Ultrastruct Pathol 2006;30:283)
- Multivesicular buds (structures containing microvesicles abutting from the cell membrane) frequently present (Ultrastruct Pathol 2006;30:283)
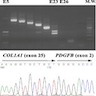
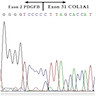
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Early cytogenetic studies identified a supernumerary ring chromosome in most cases; this led to the identification of t(17;22)(q22;q13) (Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1990;49:273, Am J Pathol 1995;147:1553, Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1996;89:88)
- Most common fusion is COL1A1::PDGFB (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1995;13:62, Nat Genet 1997;15:95)
- Less common fusions include
- COL1A2::PDGFB (JAMA Dermatol 2015;151:1330)
- COL6A3::PDGFD (Mod Pathol 2018;31:1683, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2018;57:437)
- EMILIN2::PDGFD (Mod Pathol 2018;31:1683)
- TNC::PDGFD (Diagn Pathol 2021;16:63)
- Of note: there is molecular pleiotropy with the COL1A1::PDGFB gene fusion, which has also been reported in a subset of uterine mesenchymal neoplasms (Mod Pathol 2019;32:1008, Gynecol Oncol Rep 2019;31:100523)
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Skin, back, biopsy:
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (see comment)
- Comment: Within the dermis and subcutis there is a spindle cell neoplasm with a storiform pattern. The cytoplasm is eosinophilic. The nuclei are ovoid and monomorphic with rare mitotic activity. There is sparing of adnexal structures and infiltration of the subcutaneous fat with a honeycomb pattern. The cells are diffusely positive for CD34; they are negative for desmin, smooth muscle actin, S100 and keratin (AE1 / AE3).
Differential diagnosis
- Cellular fibrous histiocytoma:
- Plump spindle cells with peripheral collagen entrapment
- Inflammation is often present, including foamy macrophages, lymphocytes and plasma cells; occasionally multinucleated giant cells (J Cutan Pathol 2012;39:747)
- Immunohistochemistry for CD34 may highlight peripheral dermal fibroblasts; rarely, tumors may be positive (J Cutan Pathol 2012;39:747)
- Cutaneous leiomyosarcoma:
- Plump spindle cells with a fascicular architecture
- Ovoid / cigar shaped nuclei, atypical mitoses may be identified
- Immunohistochemistry typically positive for desmin and h-caldesmon and negative for CD34
- Solitary fibrous tumor:
- Spindle cells with a patternless distribution; prominent branching vasculature
- Keloid-like collagen bundles
- Immunohistochemistry will also be positive for STAT6
Additional references
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
A. CD34 is typically diffusely positive in cases of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans while desmin, HMB45, pankeratin and S100 are not expressed.
Comment Here
Reference:Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)
Comment Here
Reference:Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)
Practice question #2
The presence of which of the following fusion genes can be used to support a diagnosis of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans in a primary dermal spindle cell neoplasm?
- COL1A1::PDGFB
- EWSR1::FLI1
- FUS::DDIT3
- JAZF1::SUZ12
- MYB::NFIB
Practice answer #2
A. COL1A1::PDGFB fusion product is present in most cases of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. It is important to note that additional fusion genes are possible but are missed by FISH or reverse transcription PCR assays that are restricted to PDGFB. It is also important to note that other tumors may harbor this fusion product (e.g., uterus, cervix). The other fusion gene options do not occur in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans and are characteristic of other neoplasms:
Comment Here
Reference: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)
- EWSR1::FLI1: Ewing sarcoma
- FUS::DDIT3: myxoid liposarcoma
- JAZF1::SUZ12: low grade endometrial stromal sarcoma
- MYB::NFIB: adenoid cystic carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)
Practice question #3
Practice answer #3
A. Positive for Fontana-Masson and CD34. This is an example of pigmented dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (Bednar tumor). The pigment is melanin, which is positive with the Fontana-Masson stain but not Prussian blue. The tumor cells are typically diffusely positive for CD34 but negative for factor XIIIa.
Comment Here
Reference: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)
Comment Here
Reference: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)
Practice question #4
The molecular pathogenesis of most cases of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is characterized by which of the following fusion gene products?
- COL6A3::CSF1
- COL1A1::PDGFB
- COL6A3::PDGFD
- COL1A1::USP6
Practice answer #4
B. COL1A1::PDGFB. COL6A3::CSF1 is found in a subset of tenosynovial giant cell tumors. COL6A3::PDGFD is only rarely encountered in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. COL1A1::USP6 may be present in myositis ossificans, a fibro-osseous pseudotumor of the digits and aneurysmal bone cyst.
Comment Here
Reference: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)
Comment Here
Reference: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)