Table of Contents
Definition / general | Sites | Pathophysiology / etiology | Diagnosis | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Tranesh GA, Qu H. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticmuc.html. Accessed April 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- Very rare in skin (~30 cases reported)
- Probable sweat gland origin
- Resembles similar tumor of salivary gland
- Usually low to intermediate grade, some higher grade tumors perhaps better classified as adenosquamous carcinoma
- Adenosquamous carcinoma
- Adenosquamous carcinoma (ASC) is rare malignancy of squamous and glandular differentiation
- Usually men with lesions on face, scalp or upper extremities (Arch Dermatol 2009;145:1152)
- Aggressive behavior (Oncol Lett 2014;7:1941)
- Tumor thickness, perineural invasion and patient immunosuppression are associated with more aggressive local disease (Arch Dermatol 2009;145:1152)
Sites
- Adenosquamous carcinoma
- Frequent confusion in the literature regarding this entity in the head and neck and high grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7:1809)
- More common in organs where adenocarcinoma arises frequently, including stomach, intestines and uterus (Oncol Lett 2014;7:1941)
Pathophysiology / etiology
- Adenosquamous carcinoma
- Although its pathogenesis is largely unknown, 4 hypotheses have been proposed:
- Malignant transformation of both squamous and glandular-like cells originating from pleiotropic epithelial stem cells
- Tumorigenesis of squamous metaplasia in columnar epithelium
- Transdifferentiation of adenocarcinoma to squamous cell carcinoma
- Coexistence of both carcinomas (World J Surg Oncol 2013;11:124)
- Although its pathogenesis is largely unknown, 4 hypotheses have been proposed:
Diagnosis
- Adenosquamous carcinoma
- Neoplasm composed of an admixture or separate areas of squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma
- Criteria for squamous cell carcinoma component are 2 or more of these features:
- Intercellular bridging
- Keratin pearl formation
- Parakeratotic differentiation
- Individual cell keratinization
- Cellular arrangement showing a pavementing or mosaic pattern
- Criterion for adenocarcinoma component is demonstration of intracytoplasmic mucin
- World Health Organization Classification does not require intracytoplasmic mucin for diagnosis of adenocarcinoma in the presence of true glandular formation (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7:1809)
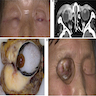
Case reports
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- 66 year old man with ear tumor (J Cutan Pathol 1991;18:56)
- 72 year old man with tumor arising within nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn on forehead (J Cutan Pathol 2003;30:652)
- 76 and 79 year old men (Int J Surg Pathol 2015;23:161, Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:131) with tumors of cheek and axilla
- 81 year old man with tumor infiltrating parotid gland (Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2012;16:26)
- Adenosquamous carcinoma
- 71 year old woman with adenosquamous carcinoma of tongue (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7:1809)
- 76 year old woman with adenosquamous carcinoma of conjunctiva (Oncol Lett 2014;7:1941)
Treatment
- Adenosquamous carcinoma
- Surgical excision or Mohs microsurgery are common treatment options (Head Neck Pathol 2011;5:108)
- Locoregional recurrence is not uncommon
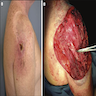
Gross description
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- Up to 0.6 cm, ulcerated and nonencapsulated
- Flesh colored nodules, painless
- Adenosquamous carcinoma
- White nodular infiltrate into subcutaneous tissue
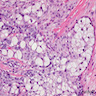
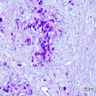
Microscopic (histologic) description
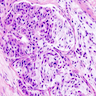
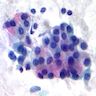
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- Circumscribed tumor, may not be attached to surface
- Multilobulated nodulocystic tumor extending throughout dermis, exhibiting glandular and squamoid differentiation
- Dermal lobules or cystic growth of low grade epidermoid, intermediate, mucinous cells and clear cells
- Cribiform nests of epidermoid cells contain glandular spaces with mucin
- Nuclei are mildly atypical and contain scattered mitotic figures
- Peritumoral fibrosis is common
- May have focal perineural invasion
- Adenosquamous carcinoma
- Infiltrative islands of squamous cell carcinoma with admixed mucin containing glandular structures, adenomatous changes and acinar formation
- Glandular structures lined by low columnar epithelium, sometimes lined by an eosinophilic cuticle (ductular differentiation)
- Perineural invasion relatively common (Arch Dermatol 2009;145:1152)
Microscopic (histologic) images
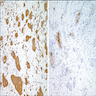
Positive stains
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- Adenosquamous carcinoma
- CK7, CEA and CA19-9 in adenocarcinoma component
- Alcian blue (pH 2.5), mucicarmine or PAS will identify the epithelial mucin
- p63 and p40 in squamous component (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7:1809)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- CRTC1 rearrangements have been detected in cutaneous MEC (like salivary gland MEC) but translocation t(11,19) or MAML2 rearrangements not seen (unlike salivary gland MEC) (Br J Dermatol 2009;161:925)
Differential diagnosis
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Adenosquamous carcinoma
- Adenosquamous carcinoma:
- High grade tumor, often involves epidermis, adenocarcinoma component is well differentiated
- Metastatic salivary gland tumor:
- Usually high grade
- Mucinous metaplasia
Adenosquamous carcinoma
- Adenocarcinoma (primary versus metastatic)
- Acantholytic squamous cell carcinoma
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma