Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Mazahery C, Rohr BR. Steatocystoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticsteatocystoma.html. Accessed September 6th, 2025.
Definition / general
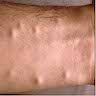
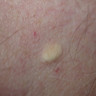
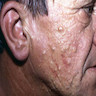
- Benign cysts with squamous epithelial lining and associated sebaceous glands
- Can present as single or multiple flesh colored papules
Essential features
- Benign, sebaceous gland associated cysts, with a characteristic hyaline cuticle and jagged squamous epithelial lining
- Can occur as sporadic lesions or in an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern
- Keratin 17 (KRT17) is the most common mutation
Terminology
- Steatocystoma simplex (single lesion clinically)
- Steatocystoma multiplex (multiple lesions clinically)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: L72.2 - steatocystoma multiplex
Epidemiology
- No gender predominance
Sites
- Face and neck, chest, arms, axillae
Etiology
- Sporadic (simplex and multiplex) (J Dermatol 2002;29:152)
- Autosomal dominant mutation in keratin 17 (multiplex)
Clinical features
- Missense mutations in the first exon of keratin 17 in steatocystoma multiplex patients (J Pathol 2019;247:158)
- Subtypes of pachyonychia congenita are caused by keratin 17 mutations and there are reports of the disease co-occurring with steatocystoma multiplex (J Pathol 2019;247:158, J Dermatol 2006;33:161, J Dermatol 1999;26:677, J Am Acad Dermatol 1994;30:275)
Diagnosis
- Generally a clinical diagnosis aided by histopathology
- May be incidentally found on imaging
Radiology description
- Not required for diagnosis
- Well circumscribed, subepidermal fat signals, generally found incidentally on ultrasound, mammogram or noncontrast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (Breast J 2021;27:389, Cureus 2022;14:e27756)
Prognostic factors
- High rate of recurrence (J Cutan Aesthet Surg 2010;3:25)
Case reports
- 22 and 58 year old transgender men with cutaneous nodules developing while on testosterone therapy (JAAD Case Rep 2022:26:70)
- 28 year old man with asymptomatic nodules on the face and scalp (Dermatopathology (Basel) 2018;5:58)
- 28 year old man with skin colored nodules that occasionally drain (Case Rep Dermatol 2019;11:71)
- Man in his 40s with nasal swelling and right sided nasal blockage (JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2022;148:380)
- 47 year old woman with recurrent skin infections and oil cysts on mammography (Cureus 2022;14:e27756)
Treatment
- Isotretinoin (Can Fam Physician 2018;64:892, Australas J Dermatol 2000;41:98)
- Aspiration (Can Fam Physician 2018;64:892, Arch Dermatol 1993;129:35)
- Cryotherapy (Can Fam Physician 2018;64:892, Australas J Dermatol 2000;41:98)
- Carbon dioxide laser (Can Fam Physician 2018;64:892, J Cosmet Laser Ther 2016;18:364)
- Surgical removal (Can Fam Physician 2018;64:892, J Cosmet Laser Ther 2019;21:1, JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2022;148:380, Plast Reconstr Surg 1997;99:1142, Arch Dermatol 1993;129:35)
Clinical images
Microscopic (histologic) description
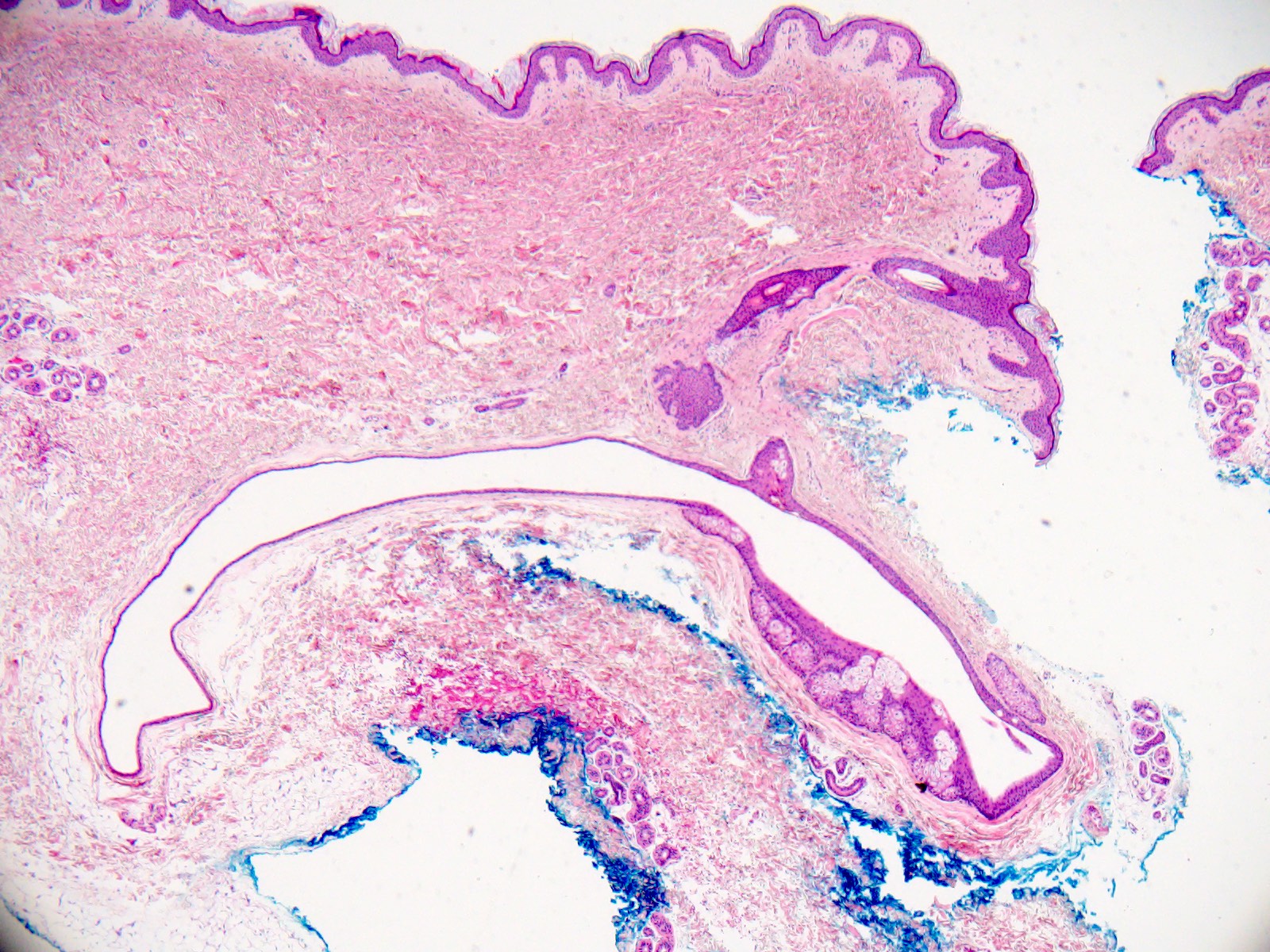
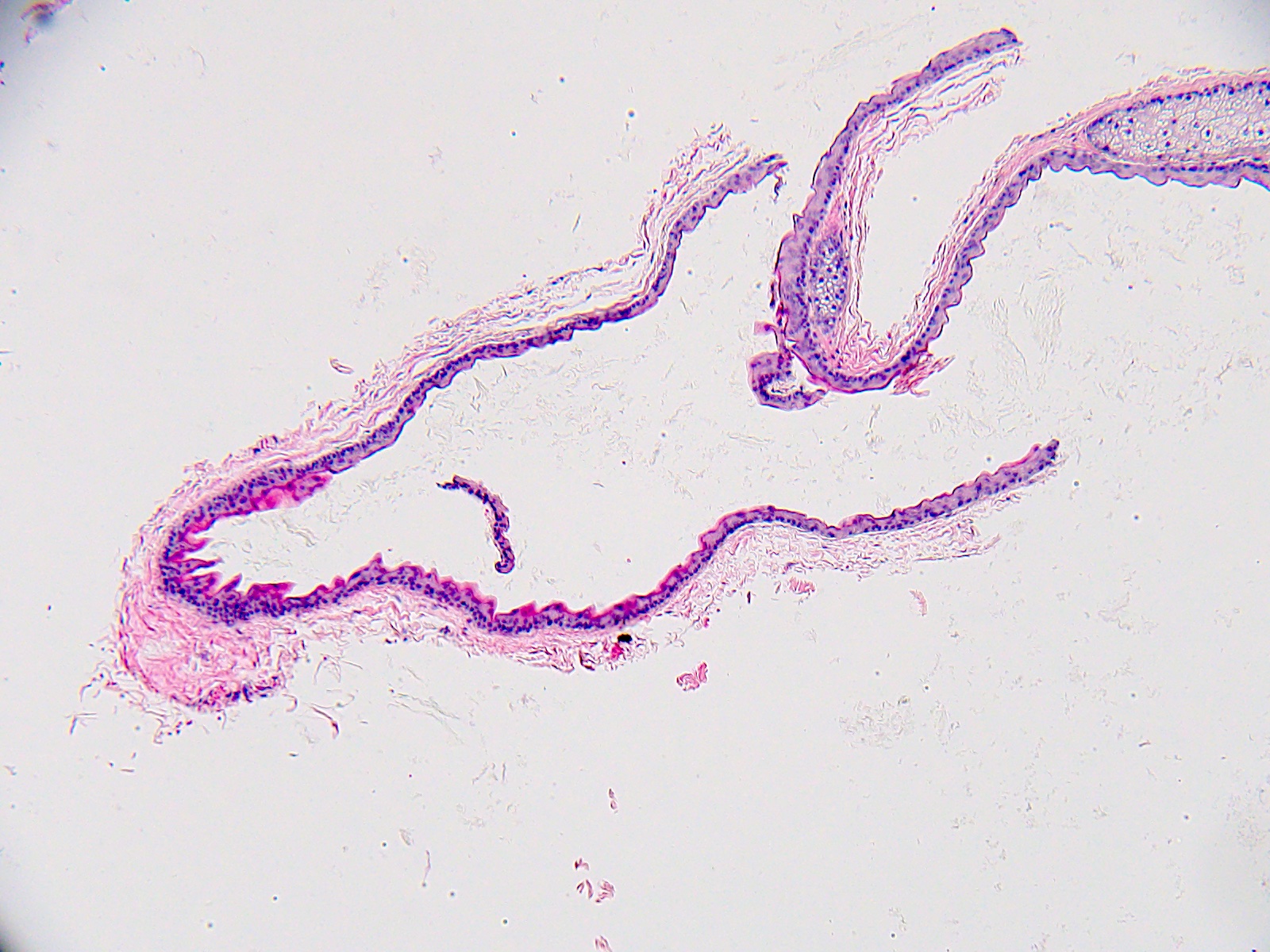
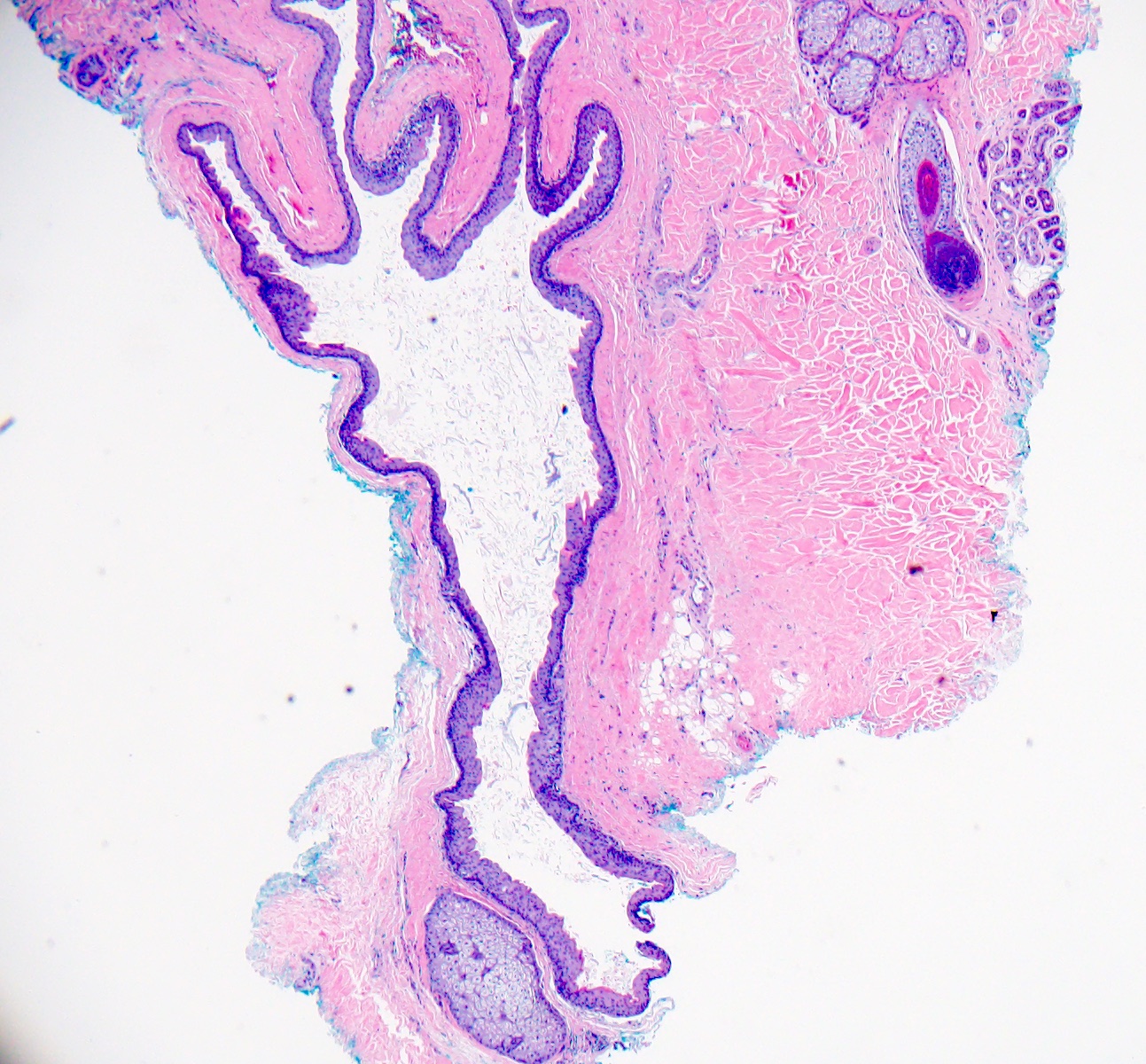
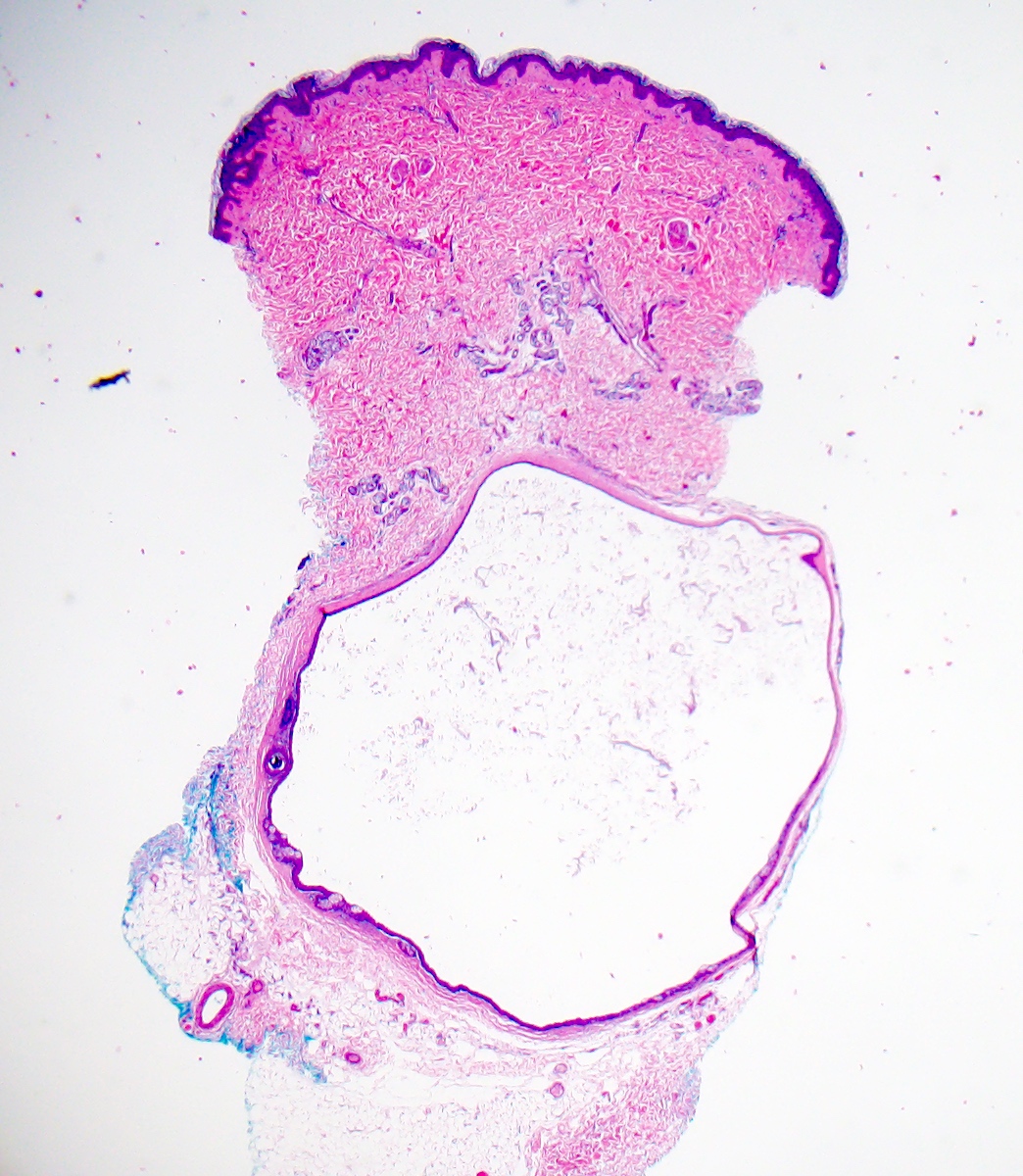
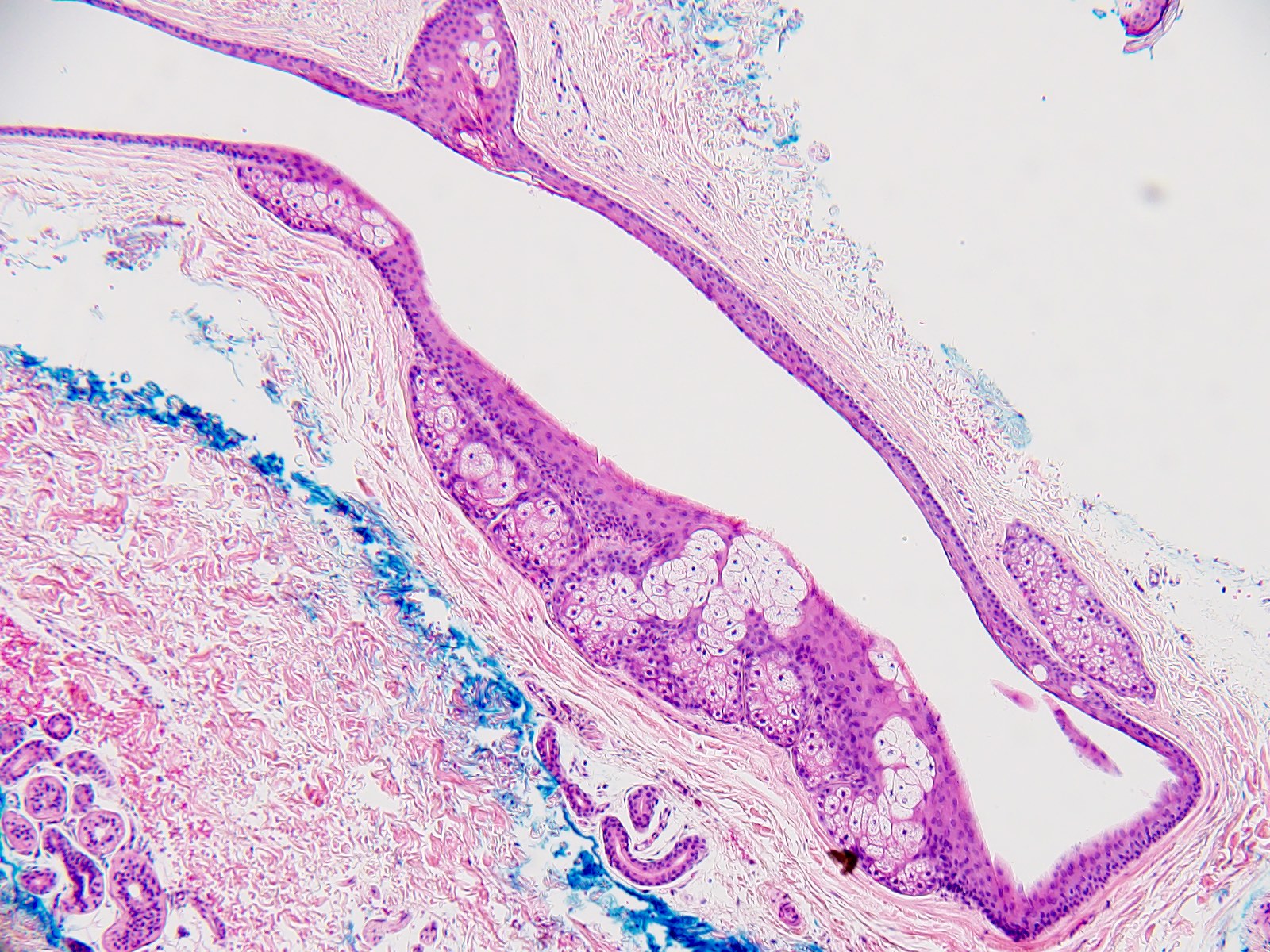
- Dermal cyst lined with stratified squamous epithelium
- Cyst epithelium lacks a granular layer
- Characteristic hyaline cuticle giving the lining a wavy, jagged or sawtooth appearance
- Sebaceous glands present in the cyst lining
- May see vellus hairs and adjacent hair follicles
- Can be part of follicular hybrid cysts in combination with other cysts of the pilosebaceous unit
- References: Calonje: McKee's Pathology of the Skin, 5th Edition, 2019, Am J Dermatopathol 1991;13:228, J Dermatol 2002;29:152
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Not required for diagnosis
- Keratin 10 and keratin 17 positive (Am J Dermatopathol 1997;19:250)
- Adipophilin positive in the sebaceous components
Videos
Steatocystoma: 5 minute pathology pearls by Dr. Jerad Gardner
Sample pathology report
- Skin, left proximal forearm, shave biopsy:
- Steatocystoma (see comment)
- Comment: In the dermis, there is a cyst with a stratified squamous epithelial lining lacking a granular layer. There is a sawtoothed pattern cuticle and scattered sebaceous glands in the cyst lining.
Differential diagnosis
- Cutaneous keratocyst (Am J Dermatopathol 2005;27:177):
- Sporadic or part of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (Grolin syndrome)
- Corrugated surface
- Lined by stratified squamous epithelium with absent granular layer
- Dense eosinophilic cuticle
- No pilar structures
- Epidermal inclusion cyst (Int J Trichology 2017;9:108):
- Dome shaped, commonly have central puncta on exam
- Stratified squamous epithelial lining with a granular layer
- Dermoid cyst (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:376, Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:286):
- Lined by fibrous layer and stratified squamous epithelium with granular layer
- 1 or more types of associated adnexal structures
- Vellus hair cyst (Int J Trichology 2018;10:31, J Am Acad Dermatol 1980;3:425):
- Red, brown or black, soft, smooth surfaced papules
- Lined by 2 - 3 layers of stratified squamous epithelium, focal areas with granular layer
- Wall may contain hair follicle or arrector pili
- Cavity contains keratin and transected vellus hair
Practice question #1
A 30 year old woman presented with a flesh colored papule on the arm. A biopsy was performed. What is the predominant inheritance pattern of the familial form of this entity?
- Autosomal dominant mutations in keratin 17
- Autosomal dominant mutations in keratin 18
- Autosomal recessive mutations in keratin 17
- Sporadic lesions only
Practice answer #1
A. Autosomal dominant mutations in keratin 17. The solitary lesion in the question above is steatocystoma simplex. Steatocystoma multiplex can be seen as a sporadic or an autosomal dominant disease presenting with multiple steatocystomas. The heritable form is thought to be due to mutations in keratin 17. Answer D is incorrect because although the patient in the question stem has a single lesion (steatocystoma simplex, which is sporadic), steatocystoma multiplex has identical lesions on histology. Answer C is incorrect because steatocystoma multiplex is an autosomal dominant (not recessive) mutation in keratin 17. Answer B is incorrect because the mutated gene is keratin 17, not keratin 18.
Comment Here
Reference: Steatocystoma
Comment Here
Reference: Steatocystoma
Practice question #2
A 40 year old man presents with a longstanding history of multiple asymptomatic, firm, flesh colored papules across the chest and upper back. He notes several family members with similar skin lesions. A close physical examination revealed thickened nails that he says have been a source of embarrassment since childhood. What adnexal structure is associated with his skin lesions?
- Apocrine glands
- Eccrine glands
- Follicular structures
- Sebaceous glands
Practice answer #2
D. Sebaceous glands. The patient's nail changes present since early life are suggestive of pachyonychia congenita, which can co-occur with familial steatocystoma multiplex (keratin 17 mutations present in both diseases), accounting for the skin findings in this patient and his family members. The cysts of steatocystoma multiplex are associated with sebaceous glands. Answers A and B are incorrect because these may be seen in hidrocystoma. Answer C is incorrect because these are found in follicular based cysts (such as pilar cyst, vellus cyst or epidermal inclusion cyst).
Comment Here
Reference: Steatocystoma
Comment Here
Reference: Steatocystoma