Table of Contents
Definition / general | Symptoms associated with specific deficiencies | Physiologic classification of malabsorption | Abetalipoproteinemia | Celiac sprue | Collagenous sprue | Microvillus inclusion disease | Tropical sprue | Tufting enteropathyCite this page: Gulwani H. Malabsorption-general. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/smallbowelmalabsorptiongen.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Standard site for biopsies is proximal jejunum, just distal to ligament of Treitz
- Mount specimen mucosal side up on solid substance, then embed perpendicular to mounting material, then step section or serial section
- Small bowel is important for absorption of fats, fat soluble vitamins, proteins, carbohydrates, electrolytes, minerals, water
- In U.S., most common malabsorption disorders are celiac sprue, pancreatic insufficiency and Crohn's disease
- Steatorrhea: bulky, greasy stools associated with weight loss, anorexia, muscle wasting
Symptoms associated with specific deficiencies
- Diarrhea, flatus, abdominal pain, weight loss, mucositis, anemia (iron, folate, vitamins B6, B12)
- Bleeding / purpura (vitamin K)
- Osteopenia, tetany (calcium, magnesium, vitamin D)
- Amenorrhea / impotence / infertility (generalized malnutrition)
- Hyperparathyroidism (calcium, vitamin D)
- Edema (albumin)
- Dermatitis (zinc, vitamin A, fatty acids, niacin)
- Peripheral neuropathy (vitamins A, B12)
Physiologic classification of malabsorption
- Disturbances related to:
- Intraluminal digestion: saliva, gastric peptic digestion, small bowel, bile salts
- Terminal digestion: hydrolysis of carbohydrates and peptides by disaccharidases and peptidases in brush border of small bowel
- Transepithelial transport: across small bowel epithelium to intestinal vasculature; fatty acids to triglycerides, cholesterol to chylomicrons
- Causes of defective intraluminal digestion:
- Digestion of fats / proteins: pancreatic insufficiency due to pancreatitis or cystic fibrosis, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
- Defective bile secretion (fat solubilization): ileal dysfunction or resection with decreased bile salt uptake, cessation of bile flow (obstruction, hepatic dysfunction), nutrient preabsorption or modification by bacterial overgrowth
- Causes of abnormalities in terminal digestion or transepithelial transport:
- Disaccharidase deficiency (lactose intolerance), bacterial overgrowth, abetalipoproteinemia, defects in ileal bile acid transporter
Abetalipoproteinemia
Definition / general
Laboratory
Microscopic (histologic) description
Positive stains
Differential diagnosis
- Rare; due to mutations in MTP gene encoding microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP); autosomal recessive (Ann Hepatol 2011;10:221)
- Causes defect in synthesis and export of apoprotein B from intestinal mucosal cells
- As a result, free fatty acids and monoglycerides cannot be assembled into chylomicrons and become triglycerides stored within cells, causing lipid vacuolization
- Symptoms: failure to thrive, diarrhea, steatorrhea
Laboratory
- Lipid profile shows no chylomicrons, no VLDL, no LDL
- CBC smear shows acantholytic red blood cells (burr cells) due to lipid membrane abnormalities
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Marked fat vacuoles in apical villous cytoplasm, normal villi
Positive stains
- Fat stains highlight lipid vacuoles
Differential diagnosis
Celiac sprue
- See Celiac sprue
Collagenous sprue
Definition / general
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Subtype of refractory sprue with patchy, excessive subepithelial collagen deposits (5 of 10 patients in one study, Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:676)
- May eventually respond to gluten free diet but disease may also be fatal (Mod Pathol 2010;23:12)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Small intestinal villous and crypt atrophy, subepithelial collagen deposit thicker than 12 μm that entraps lamina propria cellular elements (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2011;135:803)
Microvillus inclusion disease
Definition / general
Treatment
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
Electron microscopy description
- Also called congenital or familial microvillous atrophy
- Disorder of intestinal brush border that causes intractable watery diarrhea with steatorrhea in infants
- Patients require total parental nutrition and rarely live beyond age 2 years
- Villous atrophy may be due to apoptotic cell loss (Hum Pathol 2000;31:1404)
Treatment
- Small bowel transplant
Microscopic (histologic) description
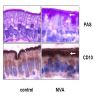
- Severe villous abnormality with crypt hypoplasia, resembling celiac sprue but without lymphocytosis
- Increased enterocyte apoptosis and proliferation, bubbly vacuolated apical cytoplasm with extensive or patchy absence of brush border, absence of inflammation (Ultrastruct Pathol 2010;34:327)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
- CD10 (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:902), PAS, polyclonal CEA, alkaline phosphatase (cytoplasmic staining versus linear brush border staining in normals)
- Vacuoles - PAS, CEA
- Cytoplasmic CD10 staining of absorptive colonocytes can aid in the diagnosis in situations where only colonic biopsy could be obtained (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:970)
Electron microscopy description
- Abnormal microvillus structures at luminal border of enterocytes
- Apical intracytoplasmic inclusions lined by microvilli
Tropical sprue
Definition / general
Treatment
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Hanni Gulwani, M.B.B.S.

Images hosted on other servers:
Additional references
- Also called postinfectious sprue
- Affects people living in or visiting the tropics, particularly Caribbean (not Jamaica), Africa, India, Southeast Asia, Central / South America (Case Rep Gastroenterol 2010;4:168)
- Has endemic and epidemic features
- May be due to E. coli or Haemophilus
- Symptoms: malabsorption within weeks of acute diarrheal enteric infection
Treatment
- Broad spectrum antibiotics (tetracycline), folic acid, vitamin B12
- No increased risk of intestinal lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Variable villous atrophy (none, partial, total)
- Injury to entire small bowel (not proximal as in celiac sprue), inflammatory infiltrate, crypt hyperplasia
Microscopic (histologic) images
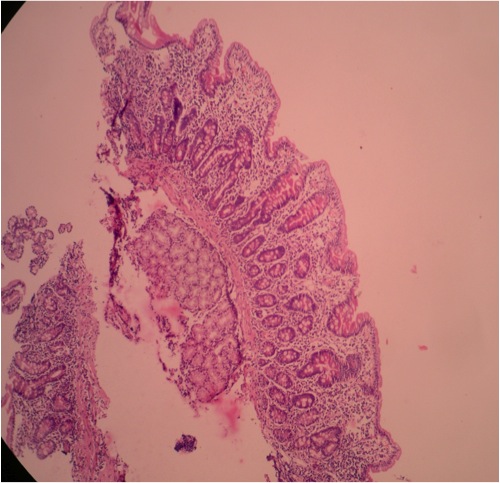
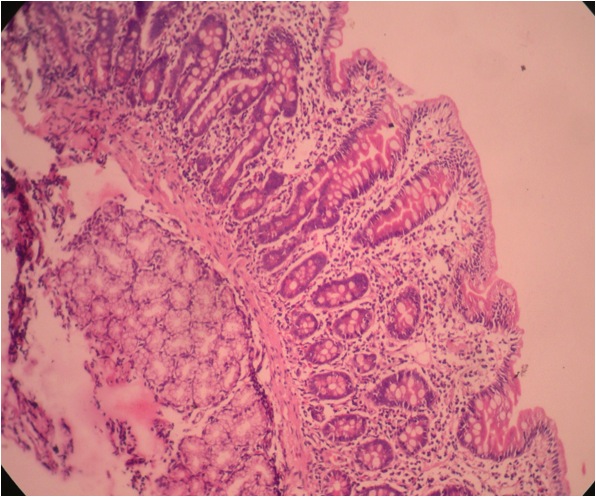
Contributed by Hanni Gulwani, M.B.B.S.



40 year old man with chronic diarrhea who improved after antibiotics; marked villous atrophy in duodenal biopsy but no increase in intraepithelial lymphocytes
Images hosted on other servers:
Additional references
Tufting enteropathy
Definition / general
Treatment
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Electron microscopy description
Electron microscopy images
Images hosted on other servers:
- Intractable diarrhea syndrome, sometimes familial, beginning in neonates
- Also called intestinal epithelial dysplasia (Orphanet J Rare Dis 2007;2:20)
- Due to epithelial cell adhesion molecule gene (EpCAM) (Gastroenterology 2008;135:429, Gut Liver 2010;4:407)
Treatment
- Total parental nutrition
Microscopic (histologic) description
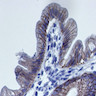
- Variable villus abnormality, epithelial crowding, disorganization and focal tufting
- No epithelial lymphocytosis
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Electron microscopy description
- Basement membrane abnormalities; increase in desmosome length and number; decreased number of microvilli of surface enterocytes with structural disorganization
Electron microscopy images
Images hosted on other servers: