Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Neurofibromatosis type 1 | Neurofibromatosis type 2 | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Videos | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Abdellatif E, Kamel D. Neurofibroma-general. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissueneurofibroma.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Benign peripheral nerve sheath tumor with classic identifiable features including the presence of a neuronal component comprising transformed Schwann cells and a nonneoplastic fibrous component that includes fibroblasts
Essential features
- Interlacing bundles of elongated cells with wavy darkly stained nuclei
- Interspersed variably sized collagen bundles
- Interspersed mast cells
- Stroma contains variable mucin and collagen
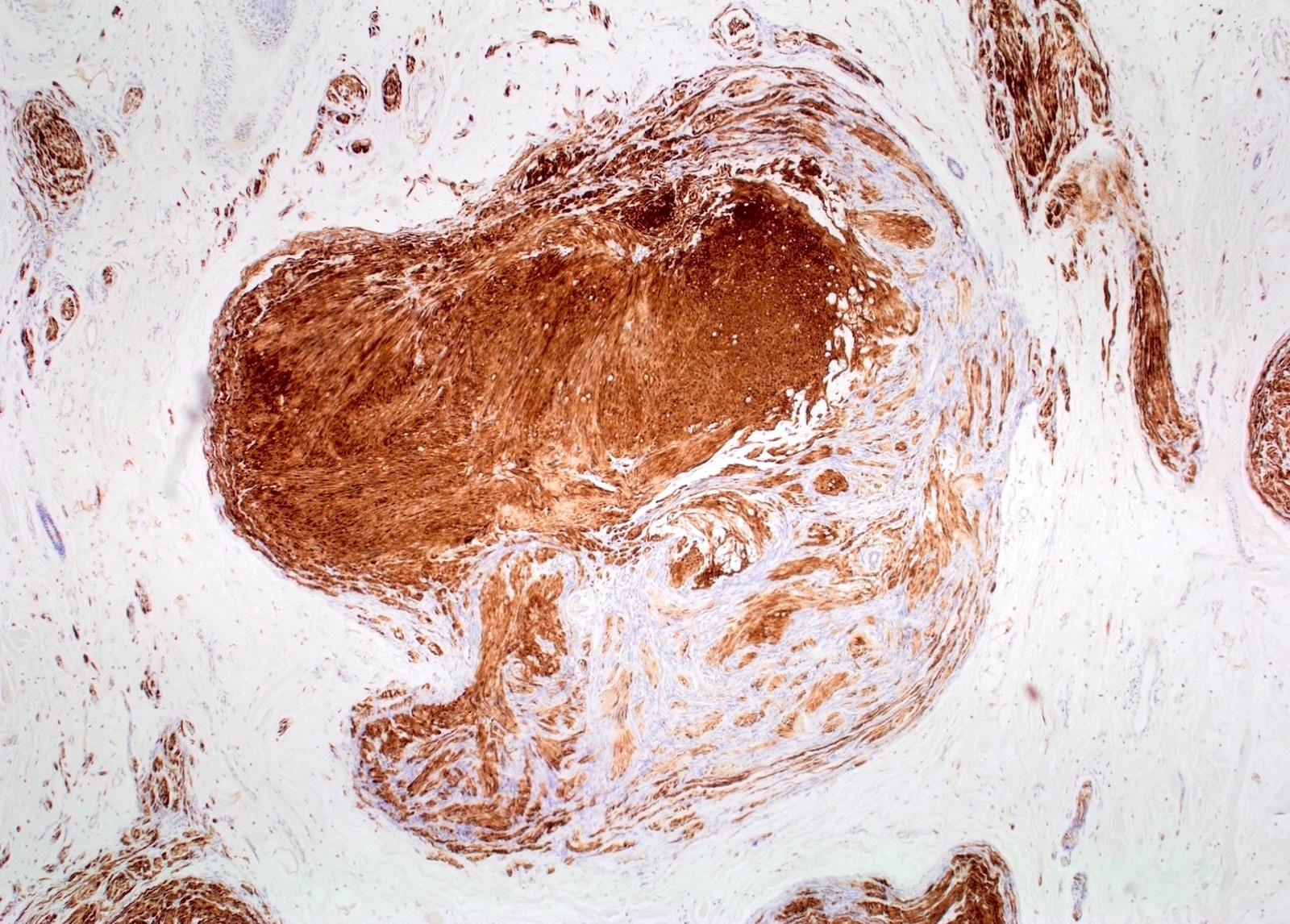
- CD34 positivity in cells of unclear histogenesis
- S100 positivity in neural cells
- Monomorphic comma shaped nuclei
- Divergent differentiation, including melanin pigmented cells, may occur rarely
Terminology
- Pacinian:
- Rare neurofibroma with proliferation of structures resembling Pacinian (Vater-Pacini) corpuscles
- Pacinian corpuscle is also called Vater-Pacini corpuscle (Wikipedia: Abraham Vater [Accessed 29 December 2022])
- It is a skin mechanoreceptor responsible for sensitivity to pain and pressure (Wikipedia: Lamellar Corpuscle [Accessed 29 December 2022])
- Pigmented:
- Rare tumor of scattered melanin laden cells and benign neural cells
- 1 - 5% of neurofibromas (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:331)
Epidemiology
- Occurs during the second or third decades of life
- All ethnic groups can be affected (StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf: Neurofibroma [Accessed 15 April 2019])
- M:F = 1:1
- Sporadic or as a part of neurofibromatosis type 1
- 90% of the solitary neurofibromas are sporadic and 10% are inherited
- Incidence of inherited neurofibromas is 1 in 2,600 to 3,000 individuals (Arch Dermatol 2005;141:71, Am J Med Genet A 2010;152A:327)
- Superficial neurofibromas are more common than deep neurofibromas (AJR Am J Roentgenol 2005;184:962)
Sites
- Localized neurofibromas are superficial and evenly disturbed over the body surface
- Diffuse neurofibromas are usually in the head and neck region (Int J Trichology 2010;2:60)
- Plexiform neurofibromas are localized to a major nerve trunk
Etiology
- Neurofibromas are caused by a biallelic inactivation of the tumor suppressor gene neurofibromatosis type 1 which is located on 17q11.2
- Non myelinating p75+ Schwann cell progenitors are the candidate cell for neurofibromatosis type 1 loss in plexiform neurofibroma (Cancer Cell 2008;13:117)
- Dermal neurofibromas may have a non Schwannian precursor of a neural stem cell / progenitor
Clinical features
- Sporadic (localized variant)
- Occurs in individuals who do not have neurofibromatosis type 1
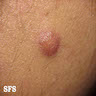
- Painless, slowly growing, solitary, skin colored, soft, flaccid, rubbery to firm papule or nodule with a smooth surface measuring up to 2 cm
- Lesion invaginates with pressure
- Cutaneous and subcutaneous
- Almost all patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 (Cell Stem Cell 2009;4:453)
- Inherited (diffuse and plexiform variants)
- Close associations with neurofibromatosis type 1
- Symptoms in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 include chronic pain, disfigurement, stigma and anxiety (Am J Med Genet A 2017;173:79)
- Rarely, neurofibromatous neuropathy can occur due to endoneurial fibrosis due to an altered relationship between Schwann cells and collagen fibrils (Ultrastruct Pathol 2018;42:312)
- Diagnostic criteria of neurofibromatosis type 1 are met if 2 or more of the following are present:
- ≥ 6 café au lait patches > 0.5 cm in prepubertal individuals or > 1.5 cm in postpubertal individuals
- ≥ 2 neurofibromas of any type or 1 plexiform neurofibroma
- Axillary or inguinal freckling
- ≥ 2 Lisch nodules
- Optic glioma
- Sphenoid dysplasia or thinning of long bone cortex with or without pseudoarthrosis
- First degree relative diagnosed with neurofibromatosis type 1
Neurofibromatosis type 1
Definition / general
Clinical features
Clinical images
Images hosted on other servers:
Differential diagnosis
- Also called von Recklinghausen disease, NF1
- Defect in neurofibromin gene at 17q11.2; protein is widely expressed tumor suppressor gene that downregulates p21 ras oncoprotein; highest levels in neural tissue; gene has numerous sites of mutation; variable phenotypic expression
- 1 per 3,000 individuals, 50% from autosomal dominant inheritance, 50% are new mutations
- Adrenomedullin (ADM) is serum biomarker of NF1 (Clin Cancer Res 2010;16:5048)
Clinical features
- Multiple neurofibromas (plexiform, solitary); plexiform are relatively specific
- ≥ 6 cafe au lait spots over nerve trunks, ≥ 1.5 cm (cafe au lait spot: increase in melanin in epidermal basal layer, may overlie a neurofibroma, smooth delicate margins; solitary café au lait spots are normal)
- Lisch nodules (pigmented iris hamartomas, 94% by age 6)
- 2 - 4x increased risk of other tumors (childhood CML, ganglioneuroma, meningioma, pheochromocytoma, rhabdomyosarcoma); 5 - 13% develop MPNST; also acoustic neuroma (schwannoma), astrocytoma, gastric carcinoid, GIST, glomus tumor, lipoma, optic nerve glioma, Wilm tumor (Hum Genomics 2011;5:623)
- Nontumors: congenital malformations, fibrosing alveolitis, megacolon, skeletal lesions (30% have spinal deformities [kyphoscoliosis], bone cysts)
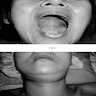
Clinical images
Images hosted on other servers:
Differential diagnosis
- Albright syndrome:
- Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia of bone, patchy dermal pigmentation, endocrine dysfunction
Neurofibromatosis type 2
- Also known as NF2, acoustic neurofibromatosis
- Autosomal dominant, incidence of 1 per 40,000
- Mutation in merlin gene at 22q12; function unknown but widely distributed and similar to cytoskeletal protein
- Nonsense mutations usually more severe than missense mutations
- Signs / symptoms: bilateral acoustic neuromas or multiple meningiomas, spinal cord ependymomas; also schwannosis (ingrowth of Schwann cells into cord), meningioangiomatosis (meningeal cells and blood vessel proliferation into the brain), glial hamartia (microscopic nodular collections of glial cells in cerebral cortex); cafe au lait spots but no Lisch nodules
- Reference: Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp 2010;61:306
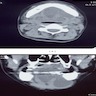
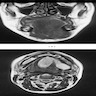
Radiology description
- On CT, appears as a well defined hypodense mass with minimal or no contrast enhancement
- On MRI, appears as a T1 hypointense and T2 hyperintense lesion with heterogeneous contrast enhancement
- On MRI of a superficial neurofibroma, the signal characteristics are usually homogeneous or heterogeneous without targets (AJR Am J Roentgenol 2005;184:962)
- Hybrid PET / MRI for the whole body of neurofibromatosis type 1 patients may be used for the detection of malignant transformation to malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (World J Nucl Med 2018;17:241)
- Does not reliably differentiate between neurofibroma and schwannoma (Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 2019;23:76)
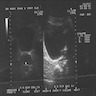
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Malignant transformation to malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor in deeply seated neurofibromas in a subset of neurofibromatosis type 1 patients
- Nuclear atypia (focal or diffuse) are accepted in neurofibromas
- Low grade malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor may be diagnosed if there is diffuse nuclear atypia, high cellularity and low level of mitotic activity
- Nuclear atypia includes nuclear enlargement (nuclear size ≥ 3 times normal Schwann cells) and hyperchromasia
- p16 can help to differentiate neurofibroma with atypical features from low grade malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (Am J Pathol 1999;155:1879)
Case reports
- 15 month old girl presenting with clitoromegaly and a chest mass (Semin Pediatr Neurol 2018;26:128)
- 18 year old man with pigmented (melanotic) diffuse neurofibroma of the back in neurofibromatosis type 1 (GMS Interdiscip Plast Reconstr Surg DGPW 2018;7:Doc04)
- 24 year old woman with neurofibroma discharged in stool (World J Clin Cases 2018;6:455)
- 62 year old man with appendiceal neurofibroma with low grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasm (Int J Surg Case Rep 2018;53:377)
- 73 year old woman with life threatening giant esophageal neurofibroma (Surg Case Rep 2018;4:107)
Treatment
- Sporadic lesions not associated with neurofibromatosis type 1
- Superficial neurofibromas respond well to marginal excision and deep-seated neurofibromas are treated conservatively
- Sometimes it is difficult to be separated from the parent nerve, which may require sacrificing of the parent nerve to ensure complete excision
- Inherited lesions associated with neurofibromatosis type 1
- Management includes early detection and risk assessment and is often non surgical (Nat Rev Dis Primers 2017;3:17004)
- Selumetinib has been used in children (GeneReviews 1998;NBK1109)
- Plexiform neurofibromas are particularly difficult to resect, often leading to incomplete resection with frequent recurrence
- Imatinib is used in affected patients with clinically significant plexiform neurofibromas (Lancet Oncol 2012;13:1218)
- Interferon-α can be used for unresectable progressive and symptomatic plexiform neurofibromas (J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2013;35:e115)
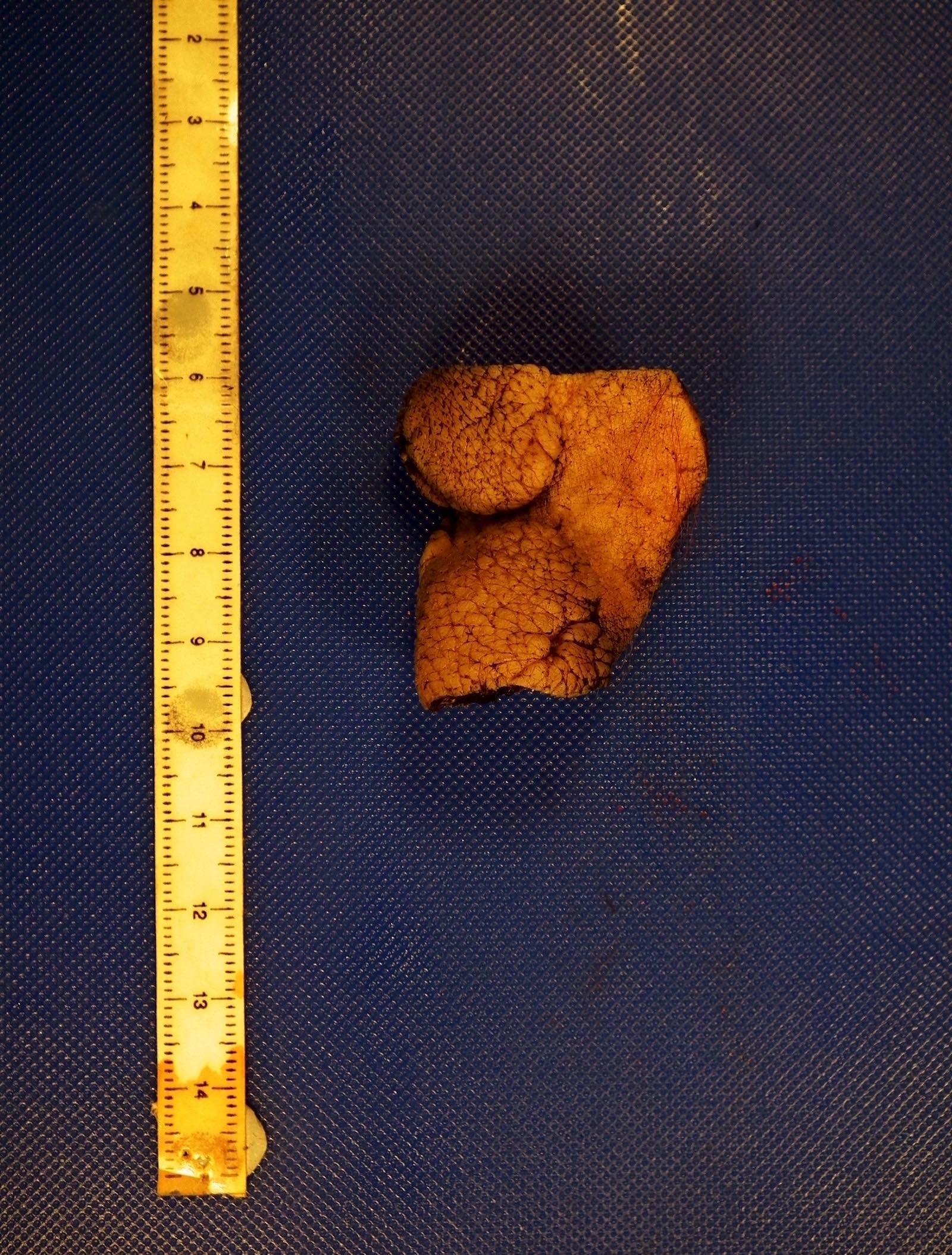
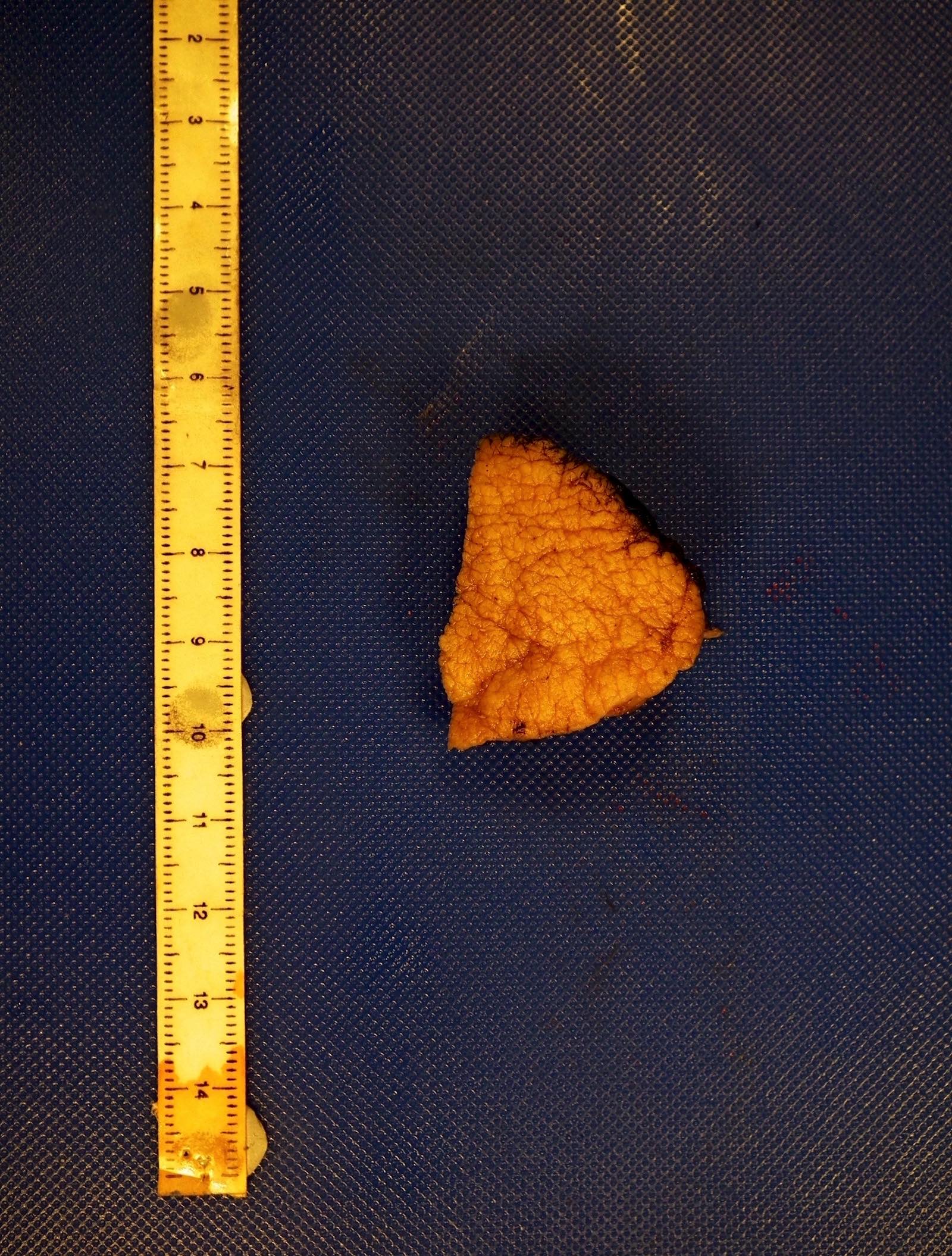
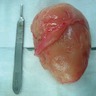
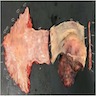
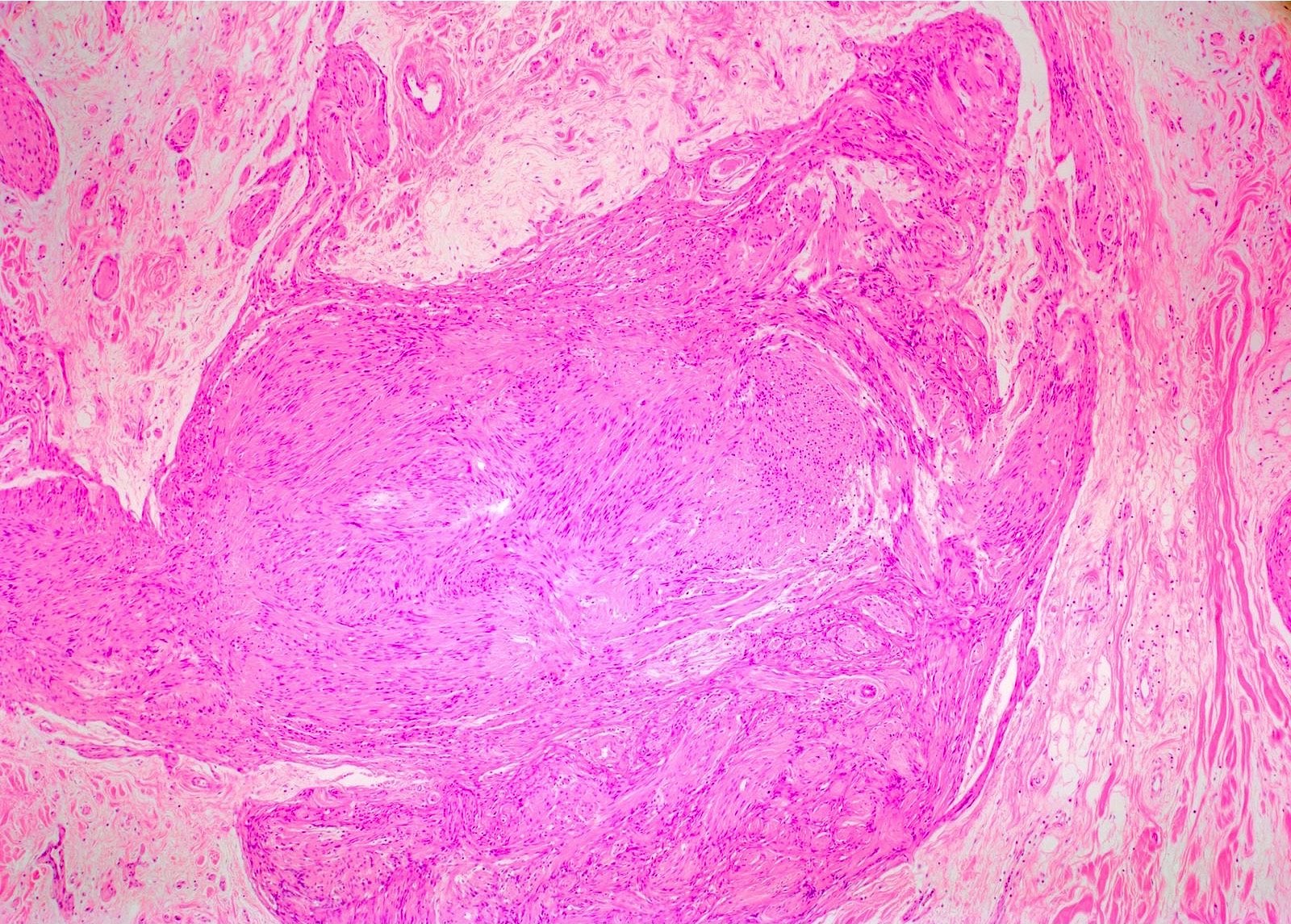
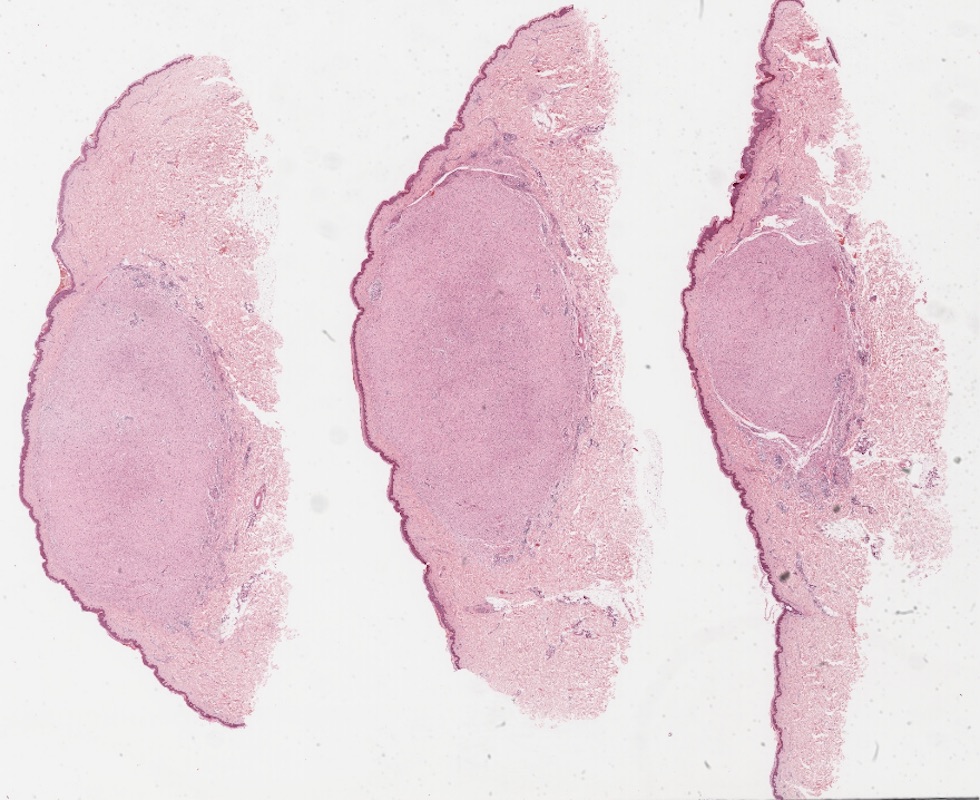
Gross description
- Skin colored with glistening tan-white cut section
- Localized neurofibroma can appear as a fusiform growth with myxoid and cystic areas (J Neurosci Rural Pract 2016;7:346)
- Those arising from major nerves show fusiform expansion of the affected nerves and may appear encapsulated
- Those arising from small nerves are well circumscribed but not encapsulated
- Deeper tumors may cause tortuous enlargement of peripheral nerves (plexiform neurofibromas) (Acta Neuropathol 2012;123:295, Am J Med Genet 1999;89:23)
Gross images
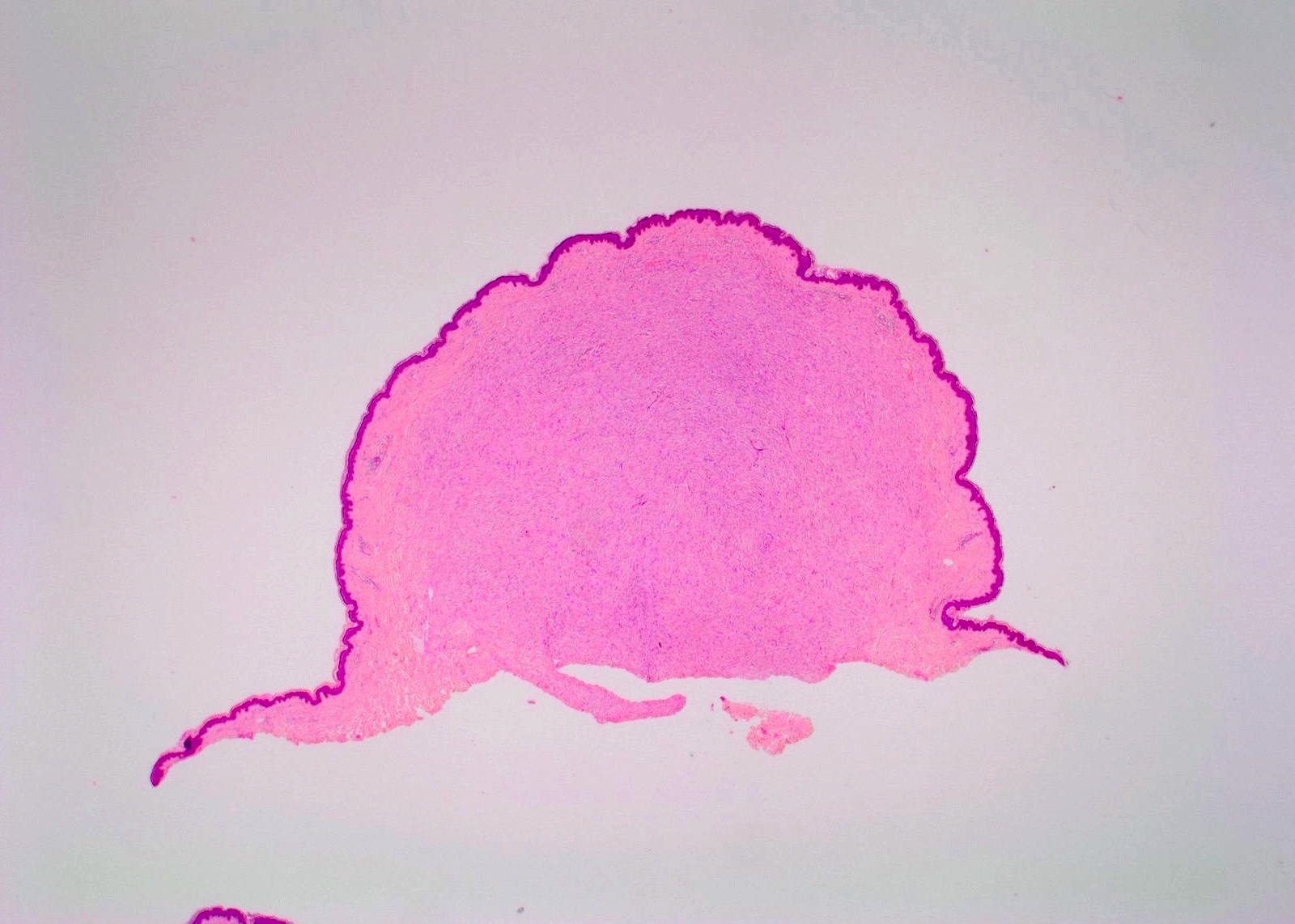
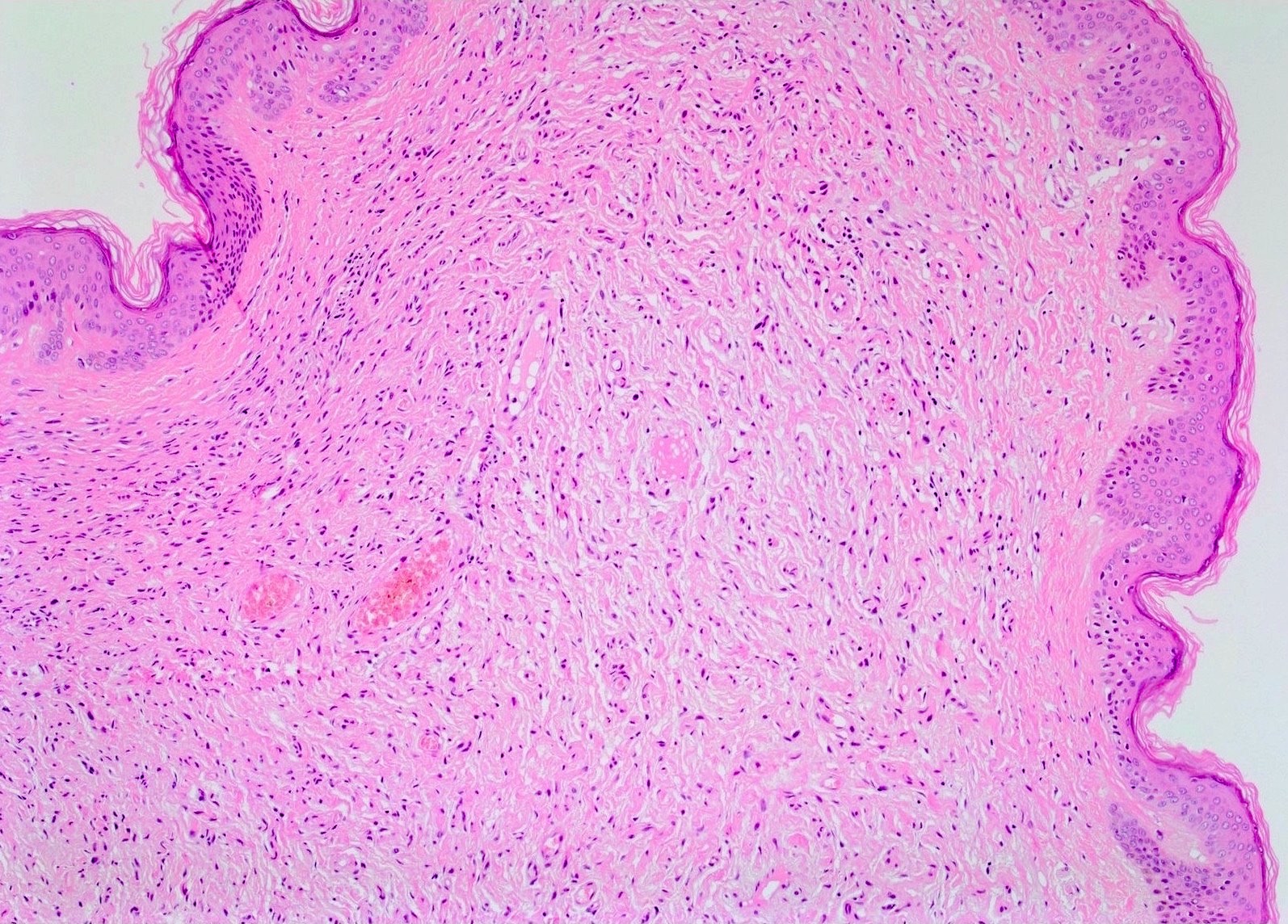
Microscopic (histologic) description
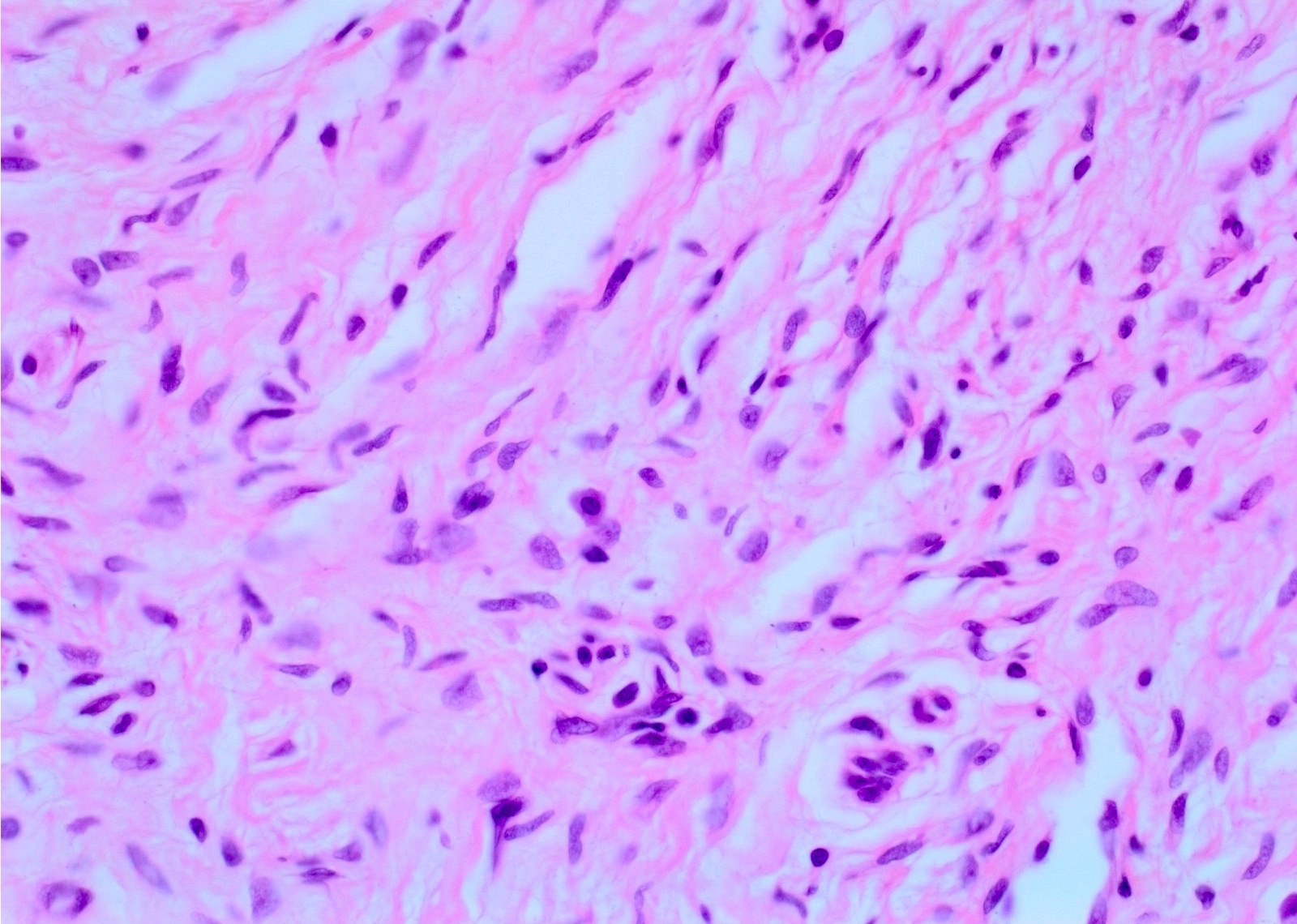
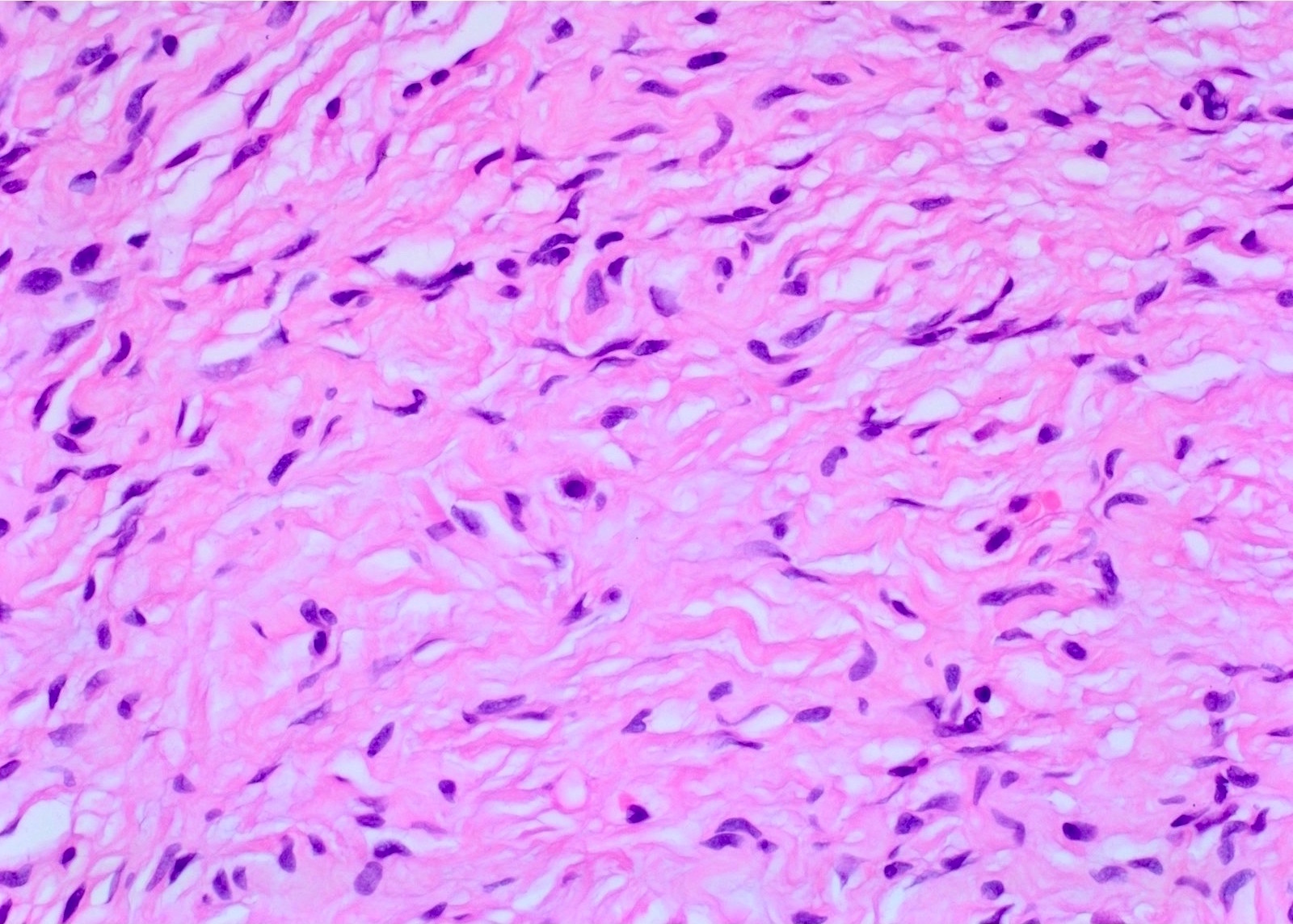
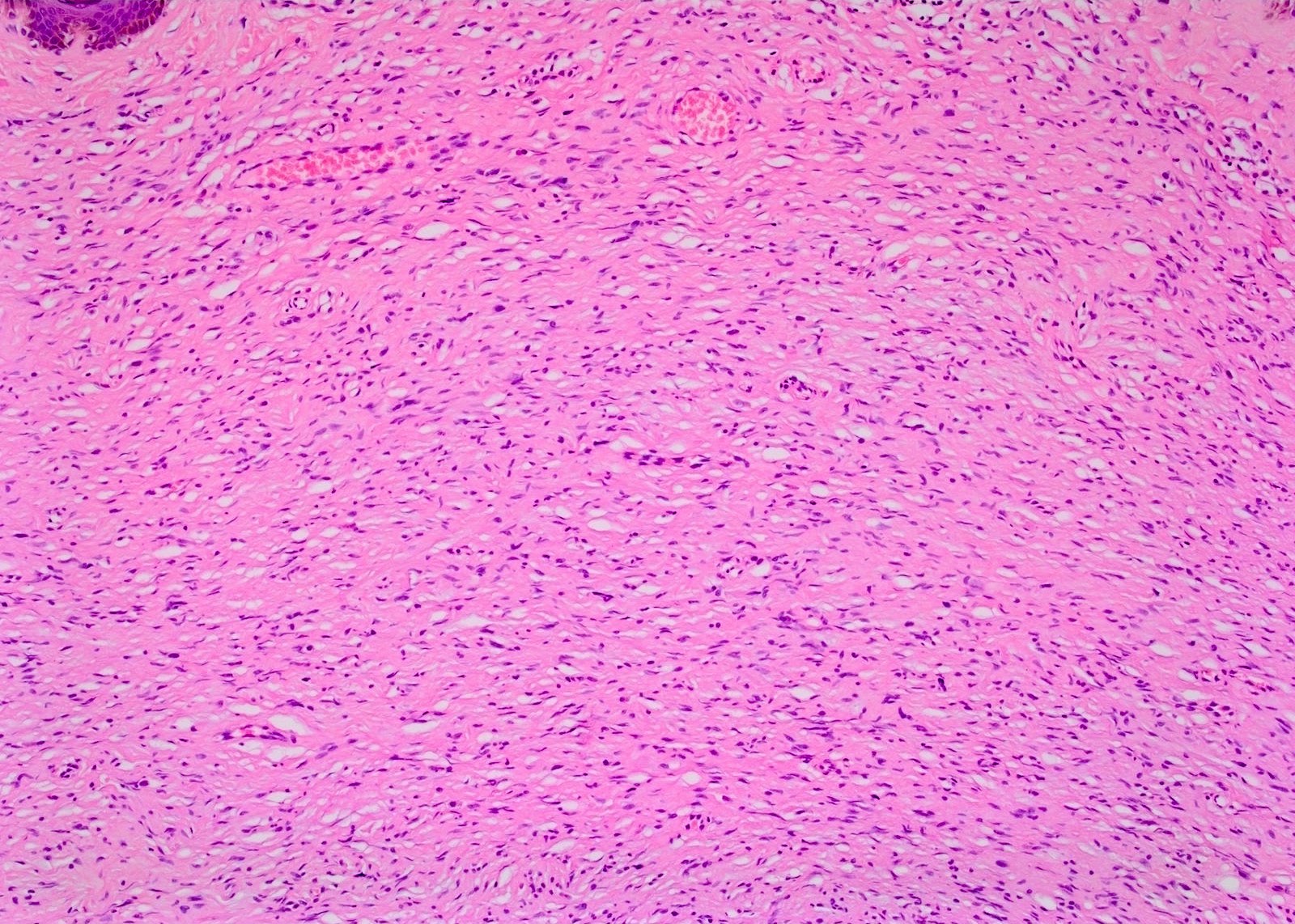
- Proliferation of all elements of peripheral nerves
- Schwann cells with wire-like collagen fibrils (wavy serpentine nuclei and pointed ends), stromal mucosubstances, mast cells, Wagner-Meissner corpuscles, Pacinian corpuscles, axons (highlight with silver or acetylcholinesterase stain, NSE, neurofilament), fibroblasts and collagen
- Perineurial cells in plexiform types, mitotic figures are rare
- May be infiltrative, have myxoid areas, contain melanin pigment, have epithelioid morphology
- Rarely has skeletal differentiation
- No Verocay bodies, no nuclear palisading, no hyalinized thickening of vessel walls (Acta Neuropathol 2012;123:295, Am J Med Genet 1999;89:23)
- Subtypes
- Plexiform: irregularly expanded nerve bundles with nodular appearance, prominent myxoid matrix; associated with neurofibromatosis type 1
- Diffuse cutaneous: traps adnexa, infiltrates into fat
- Focal cutaneous
- Intraneural
Microscopic (histologic) images
Virtual slides
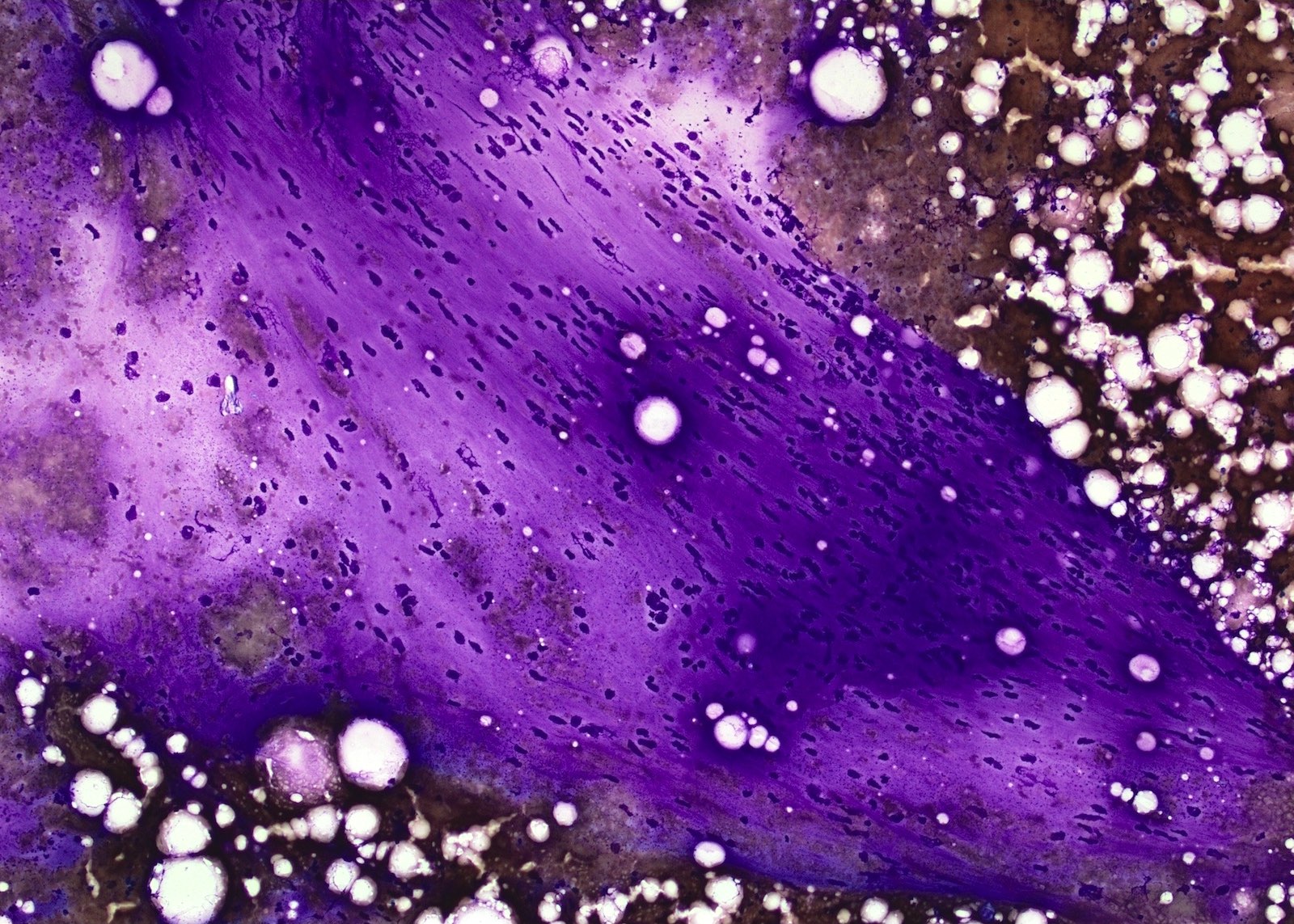
Cytology description
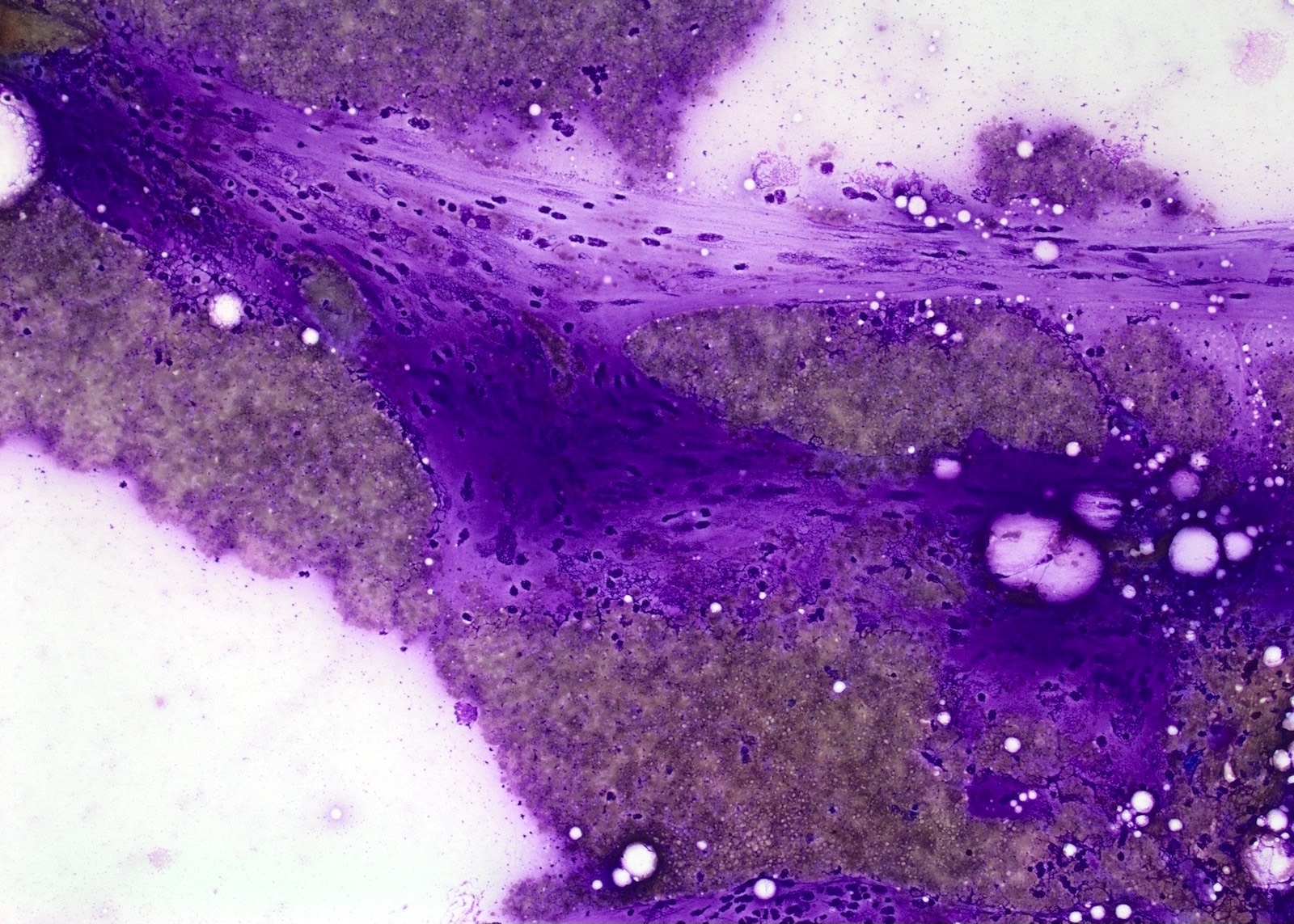
- Loosely arranged small groups of spindle cells
- Cells have scant cytoplasm and oval elongated and regular nuclei
- Nucleoli are not seen
Positive stains
- S100 shows strong positivity, CD34 shows fingerprints-like positivity, SOX10 shows strong positivity, factor XIIIa is useful to differentiate neurofibroma from neurotized neavi, calretinin shows focal positivity, EMA shows weak positivity, podoplanin shows weak positivity, neurofilaments stains entrapped axons, collagen type IV shows strong positivity, low Ki67 (J Craniofac Surg 2017;28:1780)
Negative stains
- EMA (except in plexiform neurofibromas)
- Cytokeratin, SMA and desmin
Electron microscopy description
- Schwann cells enclose axons in plasmalemmal invaginations (mesaxons) (J Cell Biol 1967;32:439)
Videos
Different types of neurofibroma
Differential diagnosis
| Schwannoma | Neurofibroma | |
| Epidemiology | Age 20 - 50 | Age 20 - 40 May occur in younger age |
| Etiology | Sporadic but may occur in neurofibromatosis type 2 > neurofibromatosis type 1 |
Sporadic, some in neurofibromatosis type 1 |
| Macroscopic | Encapsulated | Softer, usually lacks capsule |
| Microscopic | Antoni A and Antoni B Alternating hypercellular and hypocellular areas |
Spindle cells, shredded carrot collagen, mast cells, hypocellular, myxoid areas without hypercellular areas |
| Plexiform variant | Less common | More common |
| Immunohistochemistry | S100: almost diffuse Calretinin: stronger CD34: scattered (Korean J Pathol 2011;45:30) Factor XIIIa: negative / focal |
S100: weaker Calretinin: focal CD34: stronger (Korean J Pathol 2011;45:30) Factor XIIIa: stronger |
| Malignant transformation | Extremely rare | Rare but can occur in 2 - 3% of neurofibromatosis type 1 patients |
- Desmoplastic malignant melanoma (Acta Neuropathol 2012;123:295)
- Occurs in sun damaged skin
- Atypical junctional melanocytic hyperplasia or melanoma in situ
- Very long, hyperchromatic cells, "packeted" pattern of growth, dense fibrosis and deep nodular lymphoid aggregates
- Negative for melanocytic markers (e.g., HMB45, melanA, tyrosinase)
- CD34 is rarely positive and is often patchy when it is
- Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (Acta Neuropathol 2012;123:295)
| Neurofibroma | Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor |
|
| Microscopic features |
Smaller nuclear size, minimal hyperchromasia, wavy nuclei, abundant shredded carrot type collagen, rare fascicular growth pattern, no necrosis and rare mitosis |
Larger nuclear size, marked hyperchromasia, less evident wavy nuclei, rare shredded carrot type collagen, obvious fascicular growth pattern, shows necrosis and conspicuous mitosis |
| S100 | ++/+++ | +/++ |
| Collagen type IV | ++/+++ | +/++ |
| EMA | + | - |
| CD34 | +++ | ++ |
| Neurofilament protein | ++ | +/+++ |
| Podoplanin | + | + |
| SOX10 | +++ | +/++ |
| Hyaluronan | Lower levels | Higher levels (Clin Exp Metastasi 2014;31:715) |
This table was modified from (Acta Neuropathol 2012;123:295)
- Neurothekeoma
- Palisaded encapsulated neuroma: moderately cellular lesion with delicate EMA peripheral positivity
- Neurotized nevus: both are S100: positive but nevi tend to stain positive with MelanA and negative with Factor XIIIa (Arch Dermatol 1990;126:472)
- Nerve sheath myxoma hypocellular with abundant mucopolysaccharides
Additional references
- Case Rep Otolaryngol 2018;2018:8768472, Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila) 2018 Nov 2 [Epub ahead of print], Goldblum: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 6th Edition, 2013, Kransdorf: Imaging of Soft Tissue Tumors, 2nd Edition, 2006, IARC: WHO Classification of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone (Medicine), 4th Edition, 2013, OMIM #162200
Board review style question #1
- How can you differentiate between desmoplastic melanoma and neurofibroma using IHC?
- CD34
- EMA
- HMB45
- MelanA
- S100
Board review style answer #1
A. CD34 is rarely positive in desmoplastic melanoma and is often patchy when it is.
Comment Here
Reference: Neurofibroma-general
Comment Here
Reference: Neurofibroma-general
Board review style question #2
- Which one of the following immunohistochemical stains is positive in neurofibroma?
- CD34
- CK5 / 6
- EMA
- HMB45
- MelanA
Board review style answer #2