Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Sites | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosisCite this page: John I, Stuart LN. Anastomosing hemangioma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissueanastomosinghemangioma.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Benign vascular tumor that can simulate angiosarcoma
- Originally described in the genitourinary (GU) tract (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1364)
- Recently (2016) described in soft tissue, showing a predilection to paraspinal areas (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1084)
Essential features
- Benign vascular tumor which displays overlapping features with well differentiated forms of angiosarcoma
- Recently described in soft tissue, showing a predilection to the paraspinal areas (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1084)
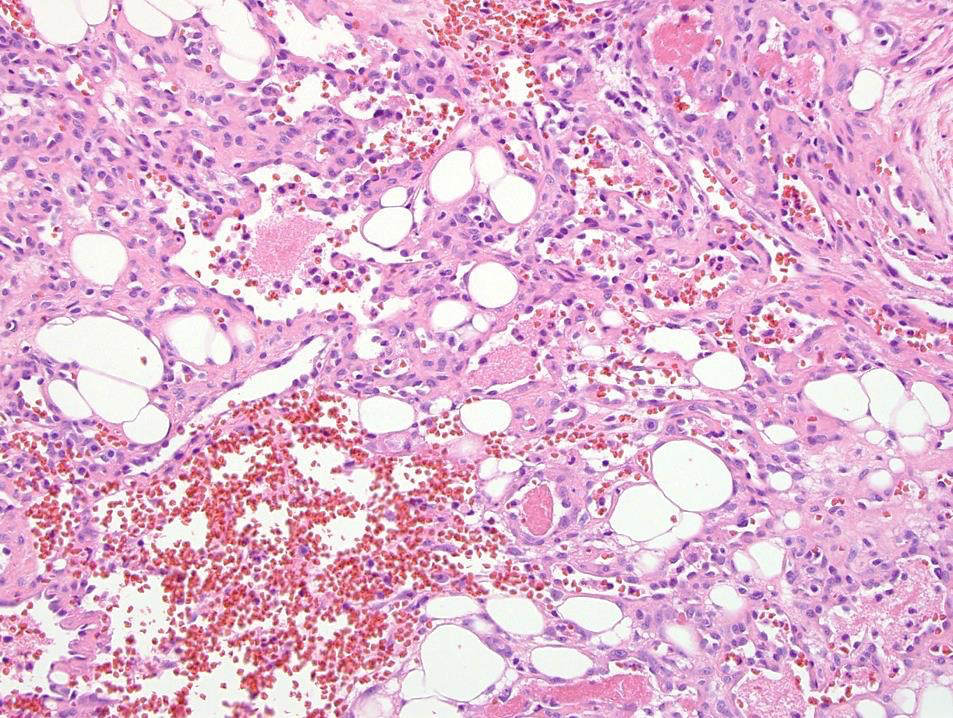
- Composed of anastomosing sinusoidal capillary sized vessels with mild endothelial nuclear variability and scattered hobnailed endothelial cells
- Cured by simple excision
Sites
- Soft tissue, GU tract, gastrointestinal tract / liver (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1761)
Gross description
- Well demarcated with a hemorrhagic mahogany spongy cut surface
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Nonlobular architecture
- Anastomosing proliferation of capillary sized vessels, reminiscent of splenic sinusoids (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:942), within a framework of nonendothelial supporting cells
- Rare to absent mitotic activity
- Mild endothelial nuclear variability and scattered hobnailed endothelial cells
- Fibrin thrombi are typical
- Extramedullary hematopoiesis and mature fat in roughly 50% of cases
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
- Angiosarcoma: diffusely infiltrative growth pattern; prominent cytological alterations, including high grade cytologic atypia, multilayering of endothelial cells and mitotic activity
- Retiform hemangioendothelioma: predilection for the distal extremities; usually involves the skin; similar appearance to normal rete testis
- Hobnail hemangioma: usually involves the skin; wedge shaped vascular proliferation with dilated vascular channels superficially and less conspicuous vessels in the deep aspect of the lesion
- Splenic tissue:
- Accessory spleen: encapsulated
- Splenosis: positive for CD8