Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Ashfaq Z, Chundriger Q, Ud Din N. Elastofibroma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissueelastofibroma.html. Accessed September 10th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign, ill defined proliferation of fibroelastic tissue with excessive abnormal degenerated elastic fibers
Essential features
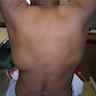
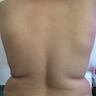
- Mostly asymptomatic mass at infrascapular region, incidentally found on radiological examination for other causes
- Well circumscribed lesion, comprised of mature fat, fibrous tissue and characteristic abnormal eosinophilic looking elastic fibers
- Surgical excision is curative, required mostly in symptomatic cases, with very rare local recurrence
Terminology
- Acceptable: elastofibroma dorsi
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8820/0 - elastofibroma
- ICD-11: FB51.Y & XH3BQ8 - other specified fibroblastic disorders & elastofibroma
Epidemiology
- Exact prevalence is unknown as most are detected incidentally
- Arises almost exclusively in the elderly, with peak incidence between the seventh and eighth decades of life
- F > M (Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2020;102:84)
Sites
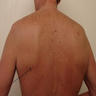
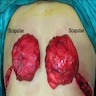
- Mostly arises in the deep soft tissue between the lower scapula and the thoracic wall
- Other (rare) sites include
- Thigh (Cureus 2023;15:e42174)
- Pancreas (Case Rep Gastrointest Med 2016;2016:2697187)
- Arm / hand (Am J Case Rep 2022;23:e937787)
- Umbilicus (Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2020;102:84)
- Greater omentum (Rom J Morphol Embryol 2020;61:841)
- Aortic valve (Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2020;102:84)
- Gluteal region (BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2020;21:16)
- Face (J Dent (Shiraz) 2015;16:73)
- Neck (West Indian Med J 2014;63:189)
Pathophysiology
- Elastotic degeneration of collagen or abnormal elastotic fibrogenesis may underlie the pathogenesis of elastofibroma and active neovascularization or endothelial mesenchymal transition plays a potential pathogenetic role (Eur J Histochem 2015;59:2459)
- Most recently, chromosomal abnormalities have been described in a few cases, including those for chromosome 1, suggesting a neoplastic nature for this tumor (Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2001;126:68)
- Traditionally, it was thought to be associated with microtrauma, being reported more commonly in laborers
- Case reports show positive relationship with a patient's dominant hand side (Turk Gogus Kalp Damar Cerrahisi Derg 2022;30:250)
Etiology
- Unknown at this time
Clinical features
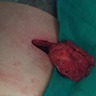
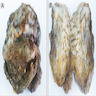
- Lesion usually presents as a slow growing, asymptomatic mass or rarely causes stiffness, pain, scapular snapping and impingement
Diagnosis
- Radiology is characteristic, particularly if the tumor arises at the typical subscapular location
- Most asymptomatic cases do not require a biopsy unless there is a need to rule out malignancy
- Symptomatic ones are excised and histopathology confirms the diagnosis suggested on imaging
- Reference: Saudi Med J 2022;43:156
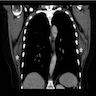
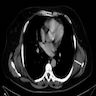
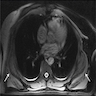
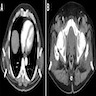
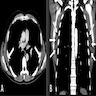
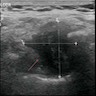
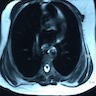
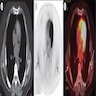
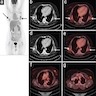
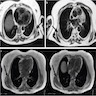
Radiology description
- Ultrasound: complex hypoechoic lesion
- CT scan: attenuation appears similar to skeletal muscle
- MRI: heterogeneous masses with internal fatty areas
- Diffusion MRI (Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul 2020;54:103)
- Newly proposed technique
- Lesions appear heterogeneous with hyperintensity on T2 weighted images
- More sensitive than conventional MRI in differentiating malignant lesions
- PET CT: moderate increased uptake, symmetrical in bilateral lesions (Indian J Nucl Med 2019;34:258)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Benign lesion cured by simple excision
- Local recurrence is extremely rare with only occasional case reports (J Orthop 2014;12:S133)
Case reports
- 48 year old woman with incidental bilateral subcapsular masses (Indian J Nucl Med 2019;34:258)
- 55 year old woman with painful thigh mass (Cureus 2023;15:e42174)
- 66 year old woman with mass arising at subcapsular port site after lung cancer surgery (Surg Case Rep 2017;3:121)
Treatment
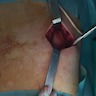
- Most asymptomatic cases do not require any treatment
- Complete excision is curative
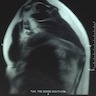
Clinical images
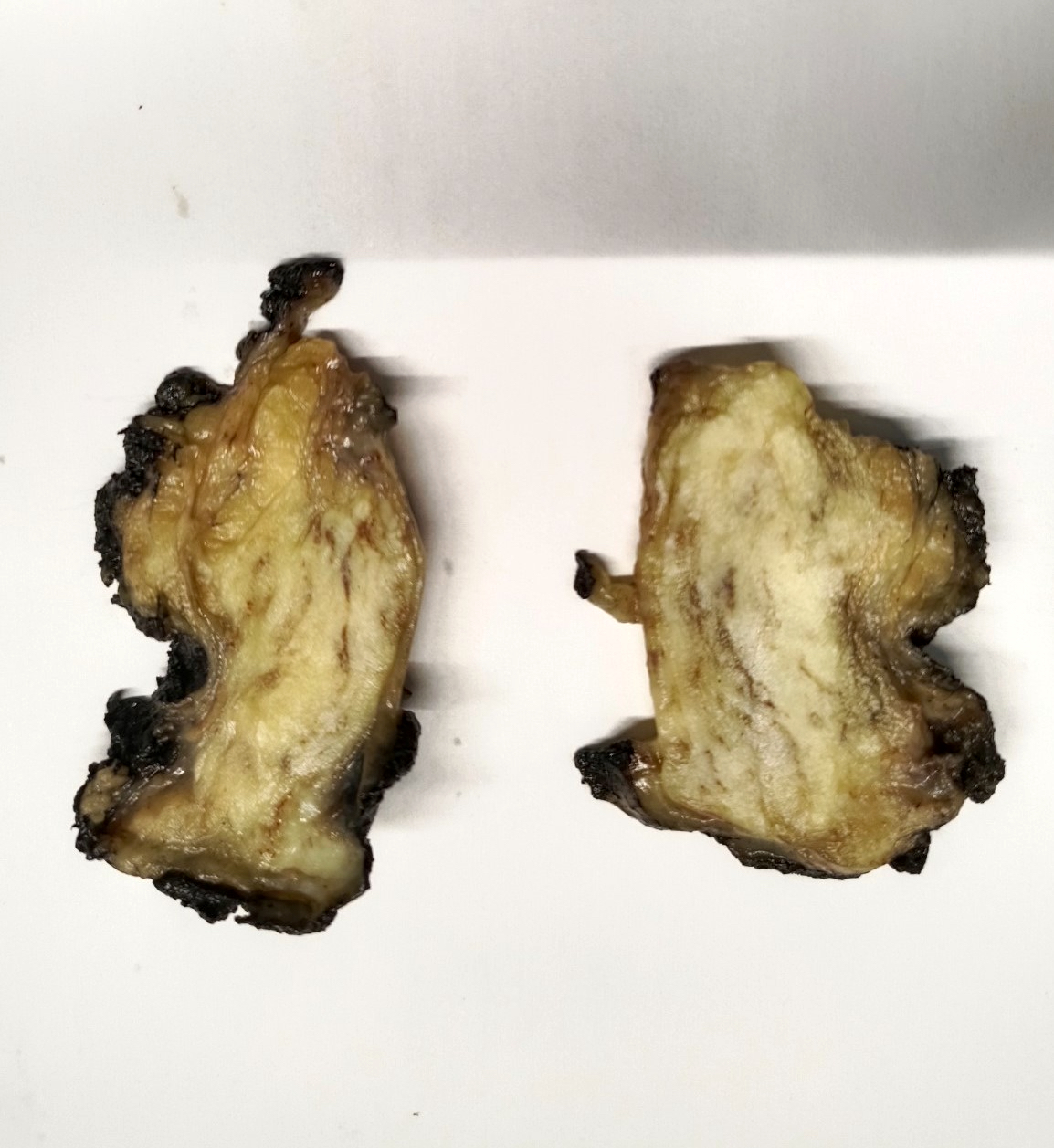
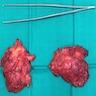
Gross description
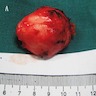
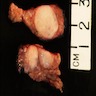
- May or may not be well circumscribed lesion, without a definite capsule
- Cut surface is firm to rubbery and shows fibrous and fatty areas
Gross images
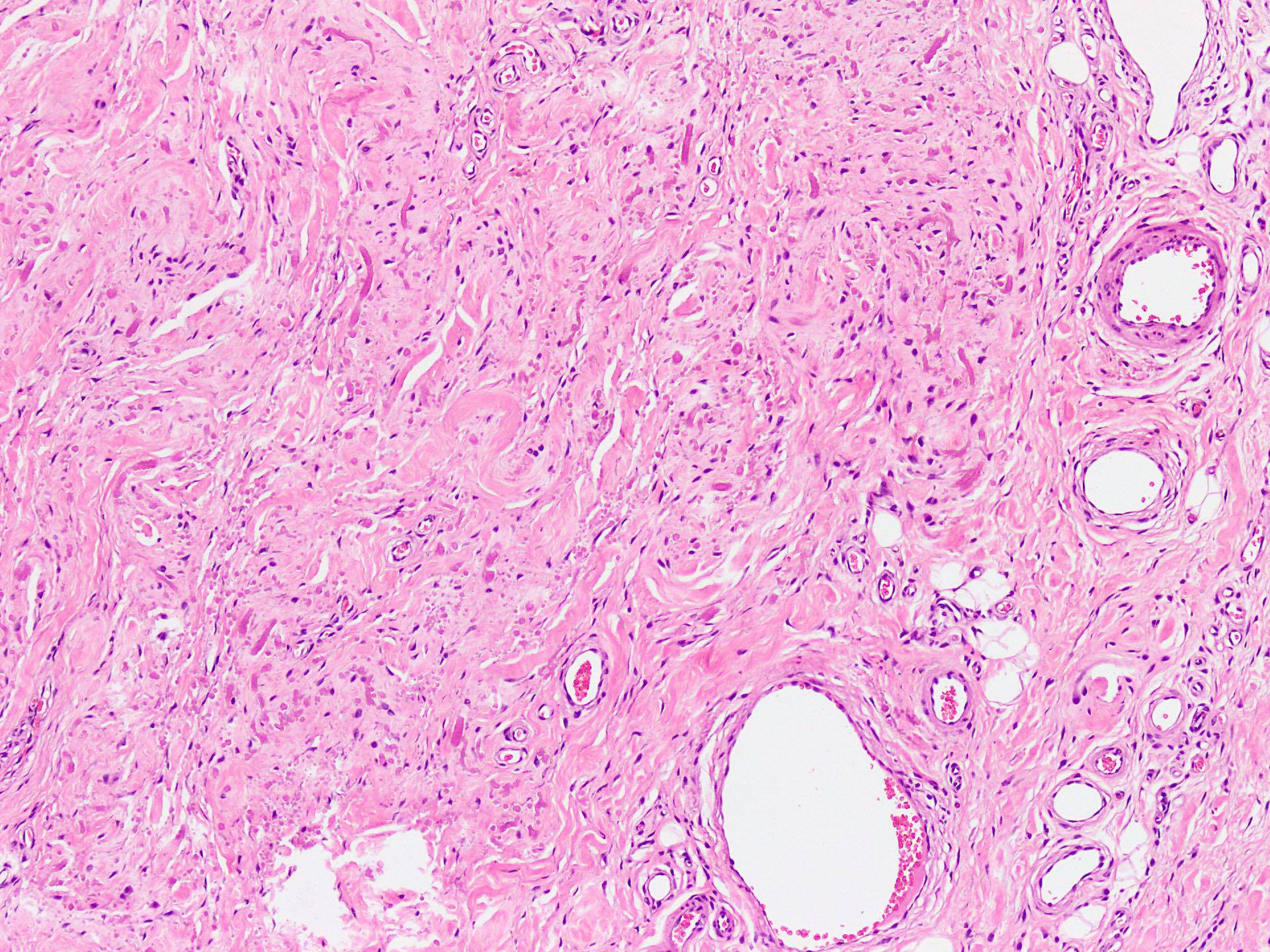
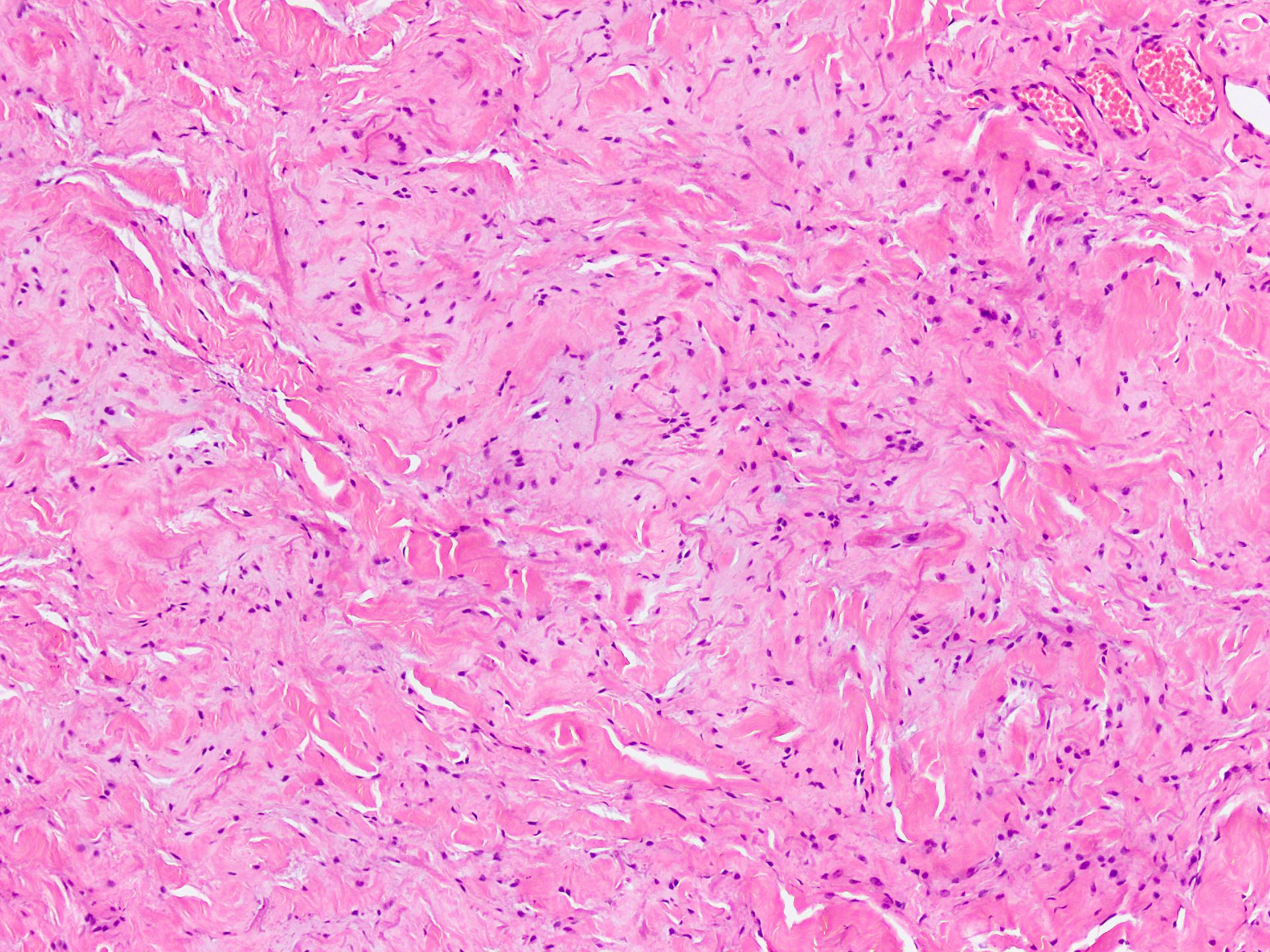
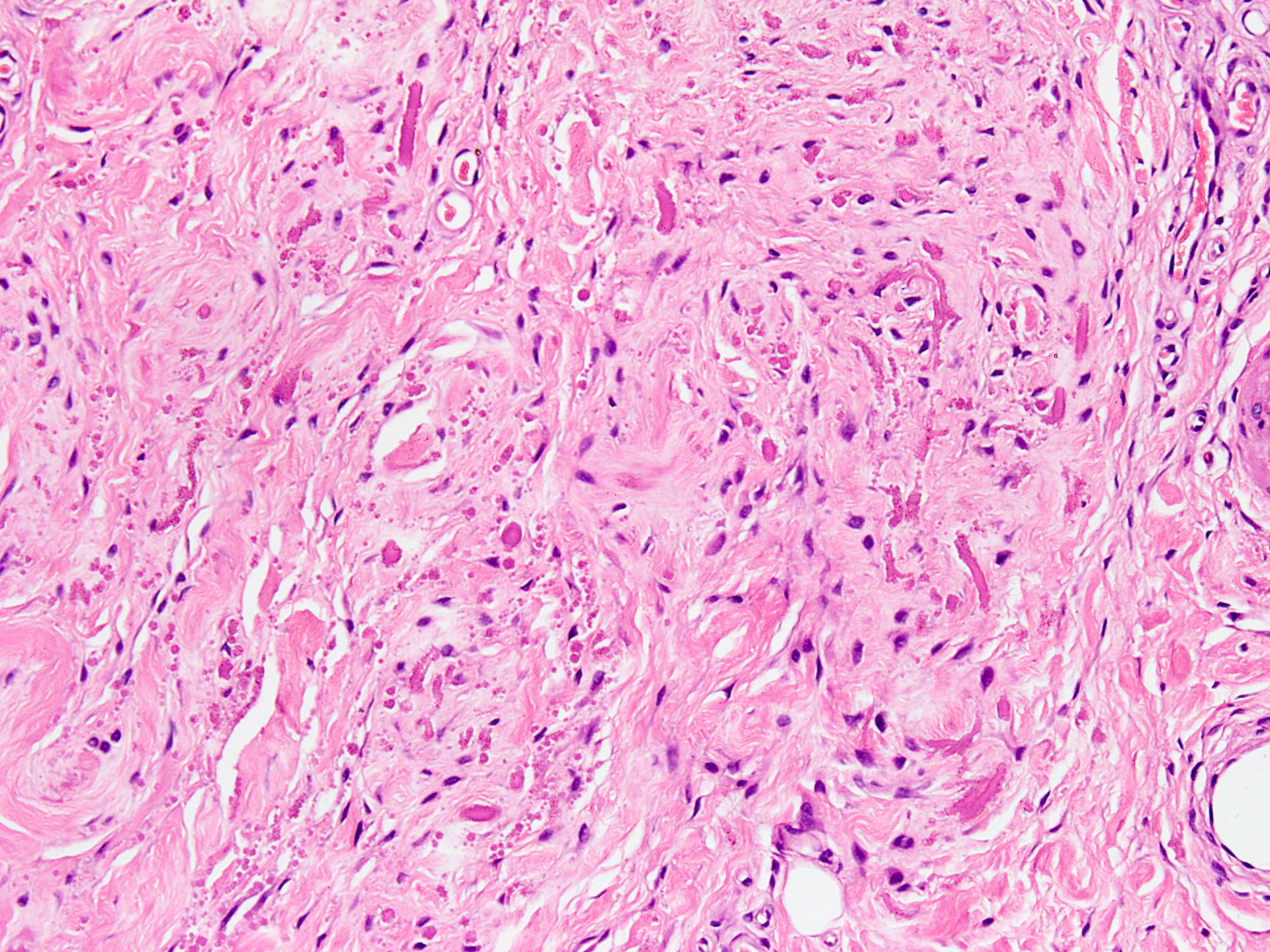
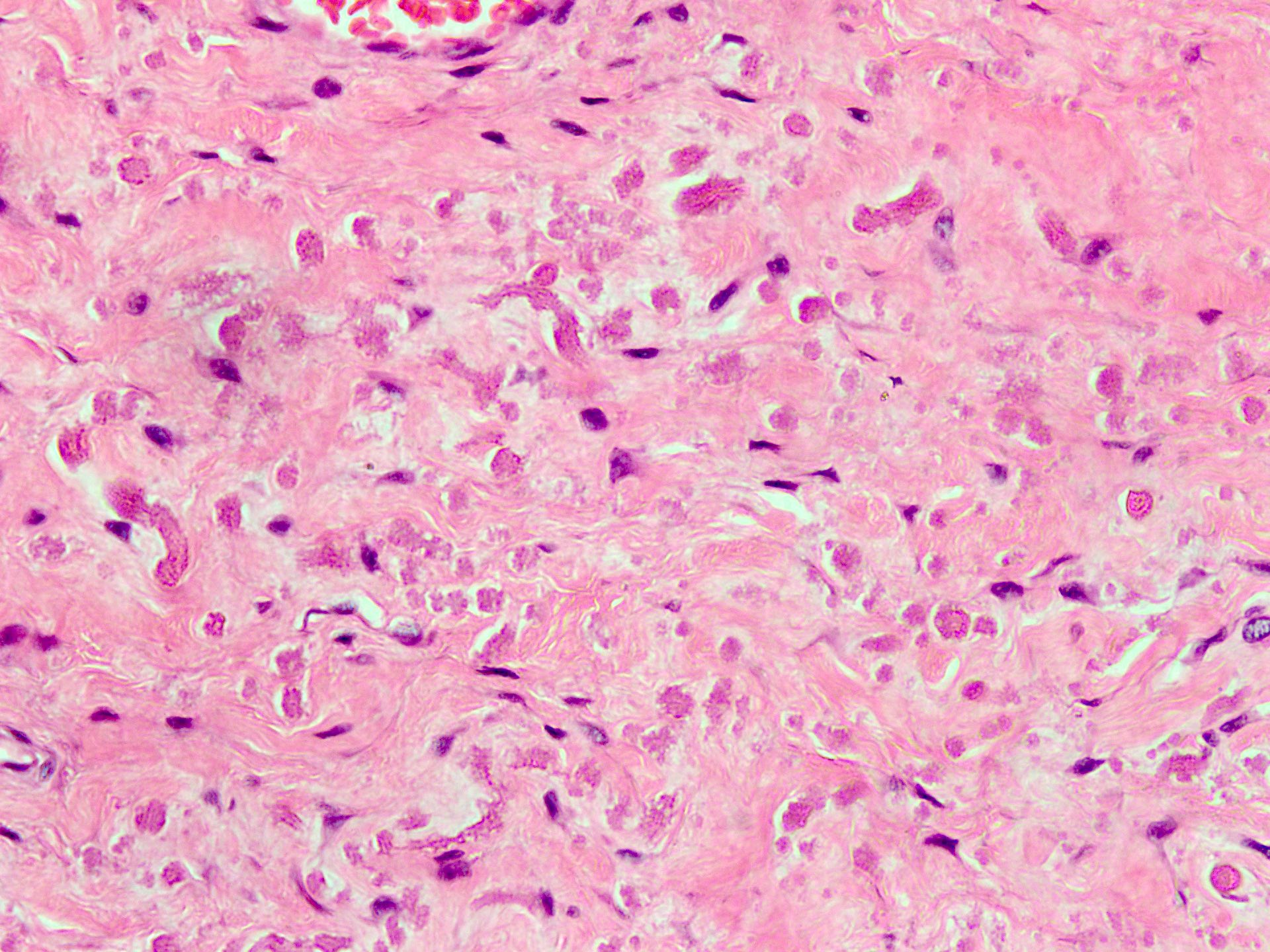
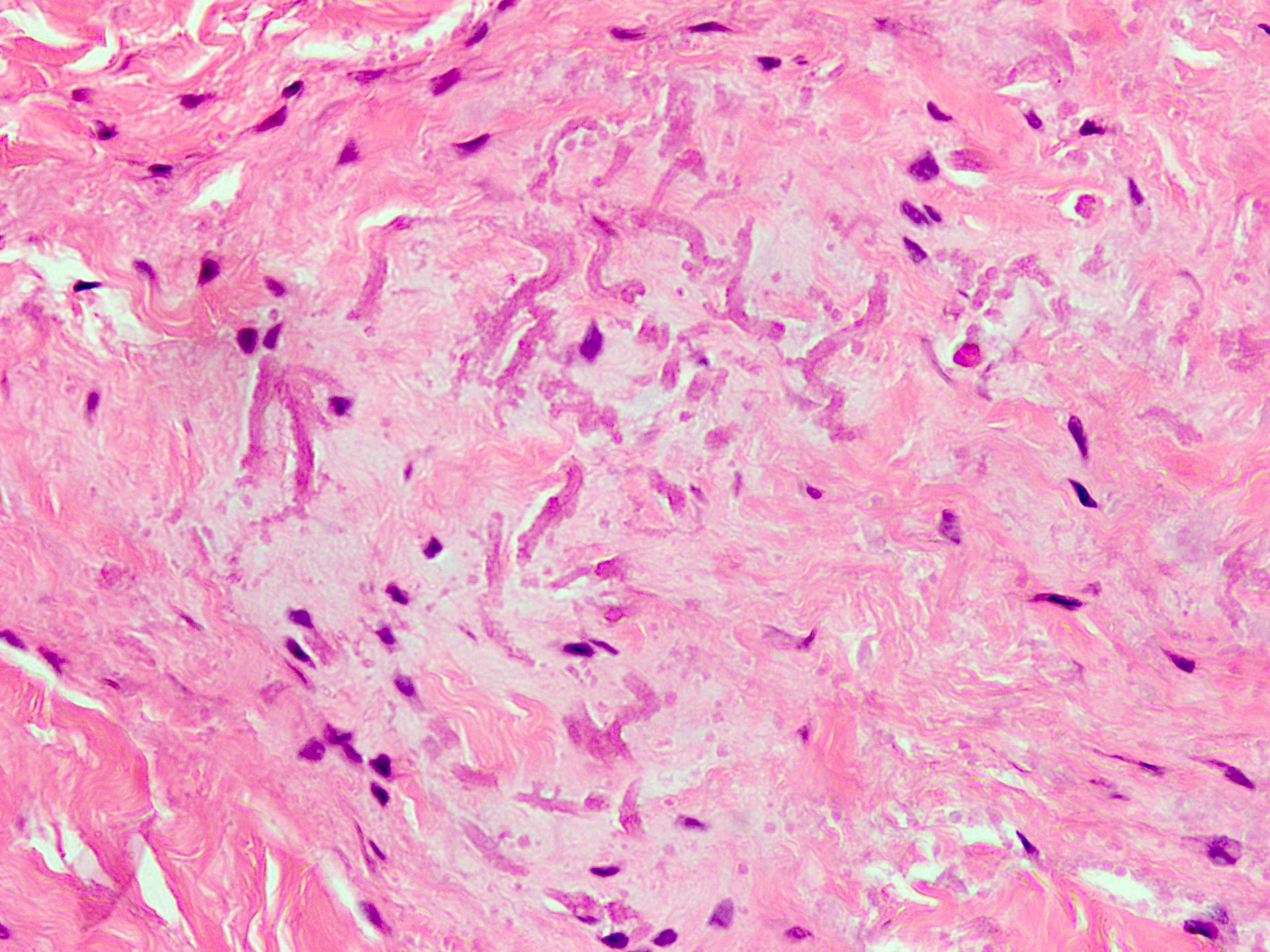
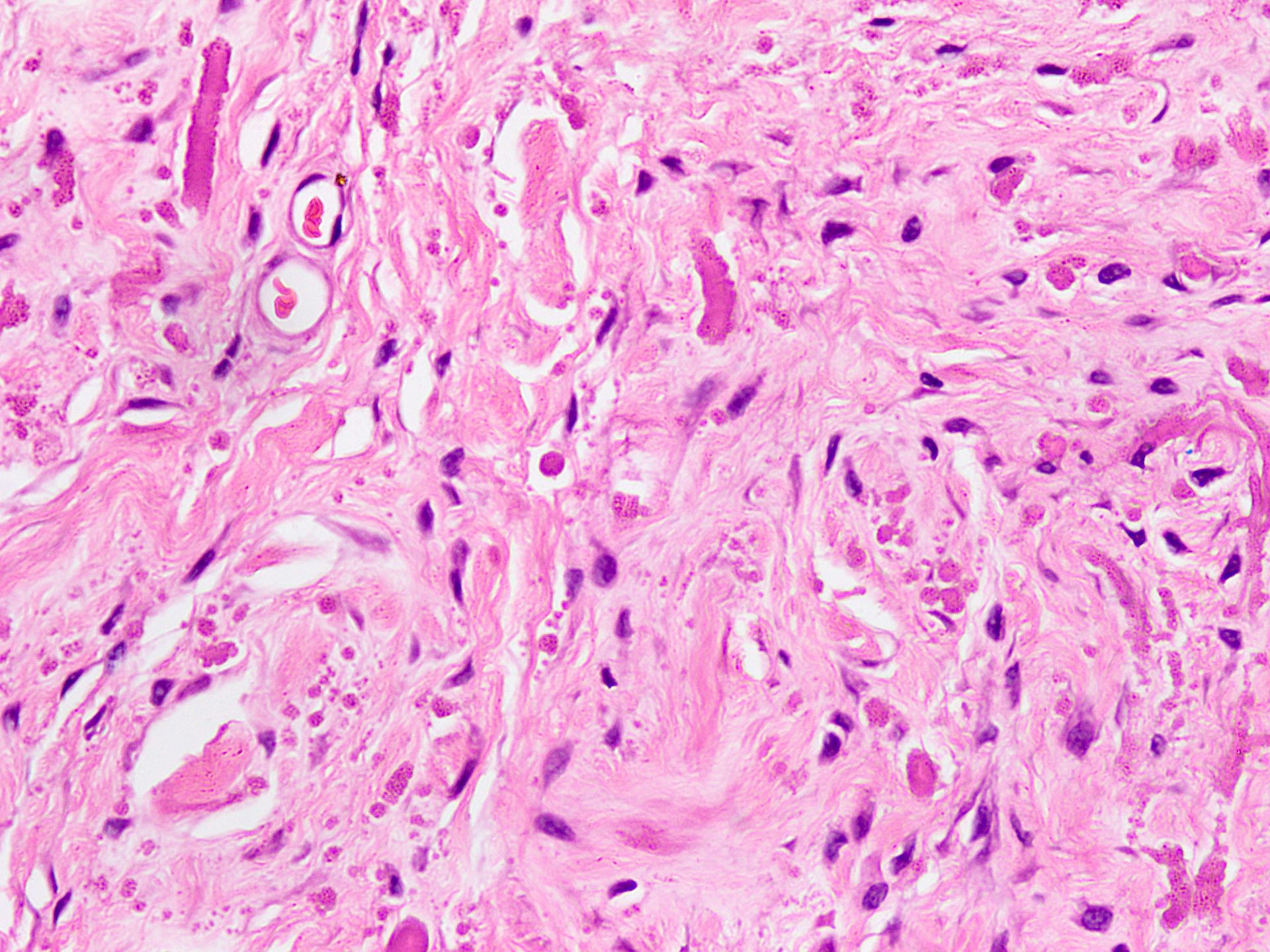
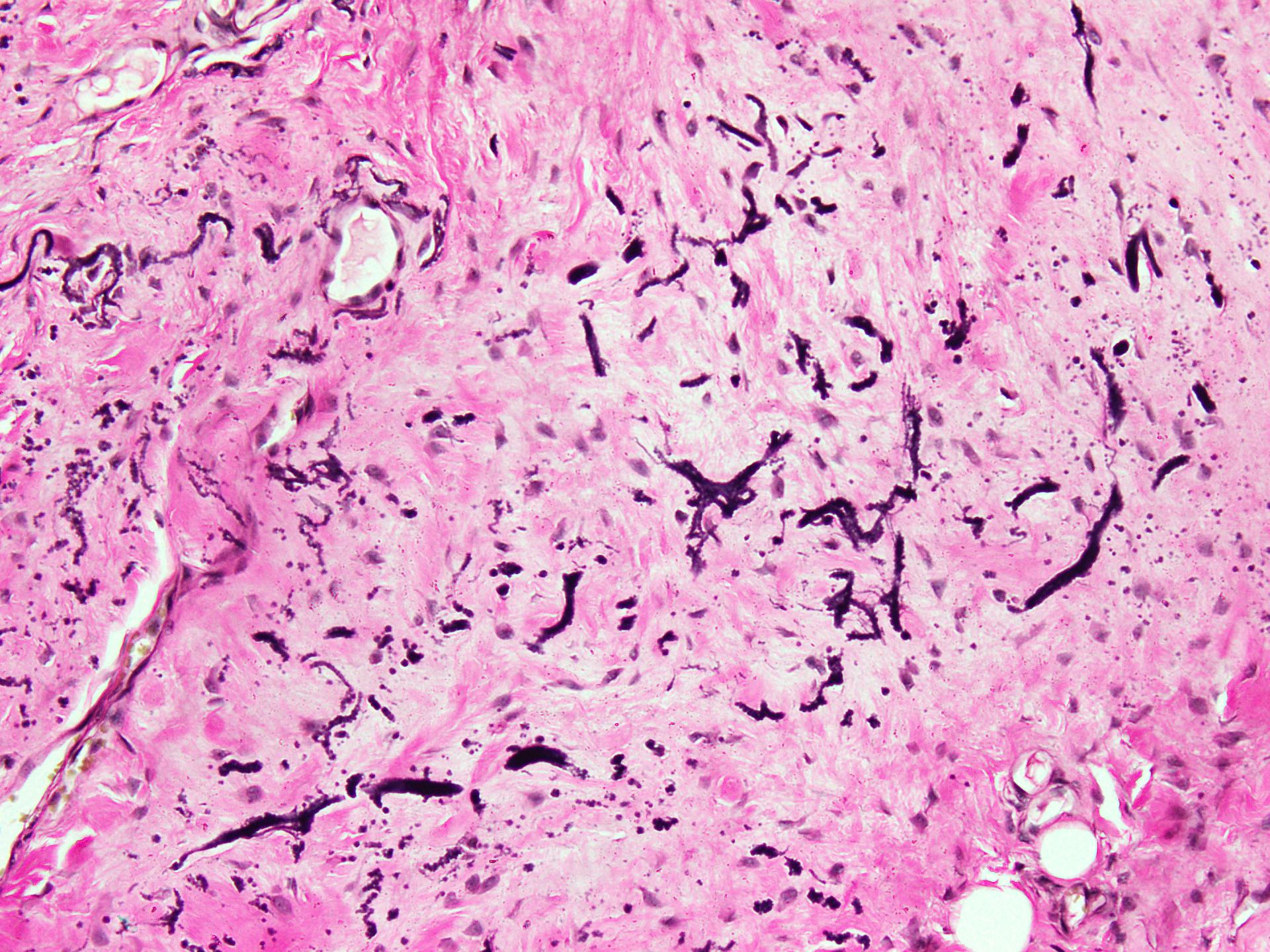
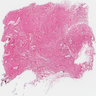
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Essential diagnostic criteria: bland appearing fibrofatty tumor with abnormal elastic fibers
- Infiltrative, ill defined, unencapsulated hypocellular lesion, which may entrap skeletal muscle fibers at the periphery or invade periosteum
- Collagenized stroma with variable hypocellular myxoid to edematous areas
- Admixed mature adipocytes present
- Scattered abnormal elastic fibers appear as densely eosinophilic, round to irregular, variably sized globules, elongated structures with irregular fuzzy outlines or beaded cords
- Scattered spindle to stellate, bland looking fibroblasts are seen
- Lacks significant nuclear atypia or foci of necrosis
- Reference: Anticancer Res 2021;41:2211
Microscopic (histologic) images
Virtual slides
Cytology description
- Cytological smears show degenerated abnormal elastic fibers in the form of globules, braids and elongated fibers
- Altered elastic fibers have green-yellow autofluorescence with ultraviolet light (Diagn Cytopathol 2002;26:310)
Positive stains
- Elastic (Verhoeff van Gieson): intense black staining of abnormal elastic fibers (J Dent (Shiraz) 2015;16:73)
- Alcian blue: stains mucopolysaccharide component of stromal connective tissue (Eur J Histochem 2015;59:2459)
- CD34: membranous positivity in a patchy manner seen in the fibroblasts (Cureus 2023;15:e42174)
- Periostin: cytoplasmic staining of cells around lesional blood vessels (Cureus 2023;15:e42174)
- Tenascin C: cytoplasmic staining of stromal cells; not specific as most human connective tissue cells also stain with this marker (Cureus 2023;15:e42174)
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
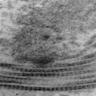
- Abnormal elastic fibers appear as electron dense masses of 3 - 5 micron diameter, removed by elastase digestion
- Some areas may show homogeneous, extremely dense core surrounded by dense, irregular fibers of diameter 350 A to 400 A with an indistinct outline (J Clin Pathol 1968;21:463)
Electron microscopy images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Pathognomonic cytogenetic abnormalities have not been described to date
- Recent studies have described DNA copy number changes in a few cases, particularly involving chromosome 1 and X chromosome (Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2001;126:68)
Videos
Elastofibroma pathology
Elastofibroma radiology
Sample pathology report
- Right subscapular mass, excision:
- Benign soft tissue lesion, consistent with elastofibroma (see comment)
- Comment: An ill defined, hypocellular lesion showing spindle cells and collagenized stroma in the background, with entrapment of fat and skeletal muscle at the periphery. Scattered abnormal elastic fibers appear as densely eosinophilic, round to irregular, variably sized globules to beaded structures. These tumors follow a benign course with complete excision being curative. Recurrence is extremely rare.
Differential diagnosis
- Desmoid fibromatosis:
- More cellular as compared with elastofibroma
- Prominent collagenous background
- Nuclear beta catenin positivity in most cases
- Fibrolipoma:
- Mixture of fibrous connective tissue and adipocytes
- Arises at anatomic sites other than those characteristic for elastofibroma
- Lacks abnormal elastic fibers
- Gardner / nuchal type fibroma:
- Densely collagenous lesions with cracking artifact
- Adipocytic component is minimal to absent
- Abnormal elastic fibers are not seen
- Differs in anatomic distribution
- Atypical lipomatous tumor / well differentiated liposarcoma:
- Characteristically shows atypical stromal cells or lipoblasts
- Adipocytes show variation in size as well as atypia
- Lacks abnormal elastic fibers
- Chest wall elastofibroma protruding into thoracic cavity may mimic liposarcoma on imaging (Acta Radiol Open 2022;11:20584601221080514)
- Elastofibromatosis / elastofibromatous change:
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 60 year old man undergoes MRI for staging of biopsy proven lung cancer. Imaging shows bilateral subscapular masses with attenuation similar to adjacent skeletal muscle. Surgical excision is performed and light microscopic appearance is shown in the photomicrograph. What is the most likely diagnosis in this case?
- Elastofibroma
- Metastatic carcinoma
- Neurofibroma
- Nodular fasciitis
- Spindle cell lipoma
Practice answer #1
A. Elastofibroma. The photomicrograph shows a fibrous tumor with loose background, few thin walled vessels and scattered abnormally shaped eosinophilic fibers. Admixed elements of adipose tissue are also seen. These are characteristic features of elastofibroma. There is no abnormal epithelial population. Answer C is incorrect because neurofibroma shows spindle cells with a background of characteristic small collagen fibers (shredded carrot-like). Answer D is incorrect because in nodular fasciitis, a tissue culture-like growth pattern, is seen with a myxoid background. Answer E is incorrect because spindle cell lipoma contains both fibrous and adipocytic components but the spindle cells are more elongated and there is an absence of abnormal elastic fibers in any of these lesions. Answer B is incorrect as elastofibromas are benign tumors.
Comment Here
Reference: Elastofibroma
Comment Here
Reference: Elastofibroma
Practice question #2
A 60 year old man undergoes MRI for staging of biopsy proven lung cancer. Imaging shows bilateral subscapular masses with attenuation similar to adjacent skeletal muscle. Surgical excision is performed and light microscopic appearance is shown in the photomicrograph. Which of the following special stains will help the most in reaching the correct diagnosis?
- Alcian blue
- Elastic stain
- Reticulin stain
- Schiff
- Trichrome
Practice answer #2
B. Elastic stain. The abnormal elastic fibers stain black with Verhoeff van Gieson elastic stain. Answer A is incorrect because Alcian blue may be positive in the background stroma but it is not specific for this entity and may be seen in a variety of soft tissue lesions. Answers C and D are incorrect because similarly, reticulin fibers are not a feature of this entity nor is Schiff positivity. Answer E is incorrect because trichrome stains the background collagen but not the elastic fibers.
Comment Here
Reference: Elastofibroma
Comment Here
Reference: Elastofibroma