Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Brčić I, Liegl-Atzwanger B. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissuehemangioendotheliomaepithelioid.html. Accessed April 26th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Malignant endothelial neoplasm that most commonly involves soft tissue, bone, lung, skin and liver; can be locally aggressive and has metastatic potential
- 2 subtypes defined by WWTR1-CAMTA1 or YAP1-TFE3 rearrangement; former expressing CAMTA1 and latter TFE3 (less specific)
Essential features
- Endothelial neoplasm that most commonly involves soft tissue, bone, lung, skin and liver
- Locally aggressive tumor with metastatic potential
- WWTR1-CAMTA1 rearranged tumors: composed of cords or small nests of large endothelial cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm embedded in a myxohyaline stroma; CAMTA1 positive staining
- YAP1-TFE3 rearranged tumors: composed of solid nests or pseudo alveolar formations of epithelioid cells enmeshed in a fibrous stroma; TFE3 positive staining
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9133/3 - epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, malignant
- ICD-10: D18.0 - hemangioma
- ICD-11: 2B5Y & XH9GF8 - epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Wide age range (0 - 93 years)
- Usually adults, 60% women (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:924)
Sites
- Any location
- Most commonly: soft tissue, bone, lung, skin and liver
- Often multifocal: bone and visceral lesions (Diagn Pathol 2014;9:131, Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:363)
- In up to 50% of cases, closely associated with or arising from a vein
Pathophysiology
- Gene fusion driven (see Molecular / cytogenetics description)
Etiology
- Unclear
Clinical features
- Clinical presentation depends on the tumor location, most frequently pain
- If arising from a vein, occurring symptoms caused by vascular occlusion, such as edema or thrombophlebitis
- Recurs locally, may metastasize (usually to lymph nodes and lungs) (Diagn Pathol 2014;9:131, Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:363)
Diagnosis
- Diagnostic workup includes radiology, histology (biopsy, resection) with immunohistochemistry and molecular analysis
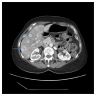
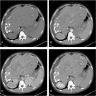
Radiology description
- CT scan: poorly circumscribed lesion with ground glass appearance
Prognostic factors
- 13% recur, 20 - 30% metastasize (lung, lymph nodes), 13% die of disease; for lung, mortality is 65% (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:363)
- High risk (> 3 mitotic figures per 50 high power fields and size > 3 cm) have 5 year disease specific survival of 59% versus 100% for low risk (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:924)
Case reports
- 43 year old woman with a 6 year history of severe Crohn's disease (Int J Surg Pathol 2019;27:423)
- 46 year old woman with a 2 month history of right shoulder and arm pain (Am J Case Rep 2019;20:864)
- 55 year old man with thigh mass (Case #77)
- 65 year old woman with multiple liver masses (Case Rep Gastrointest Med 2019;2019:7530845)
Treatment
- Wide local excision
Gross description
- Poorly circumscribed, firm, white-tan mass (Diagn Pathol 2014;9:131)
- Variable size, up to 18 cm
Frozen section description
- Hypercellular tumor composed of groups of epithelioid cells embedded in a myxohyaline stroma
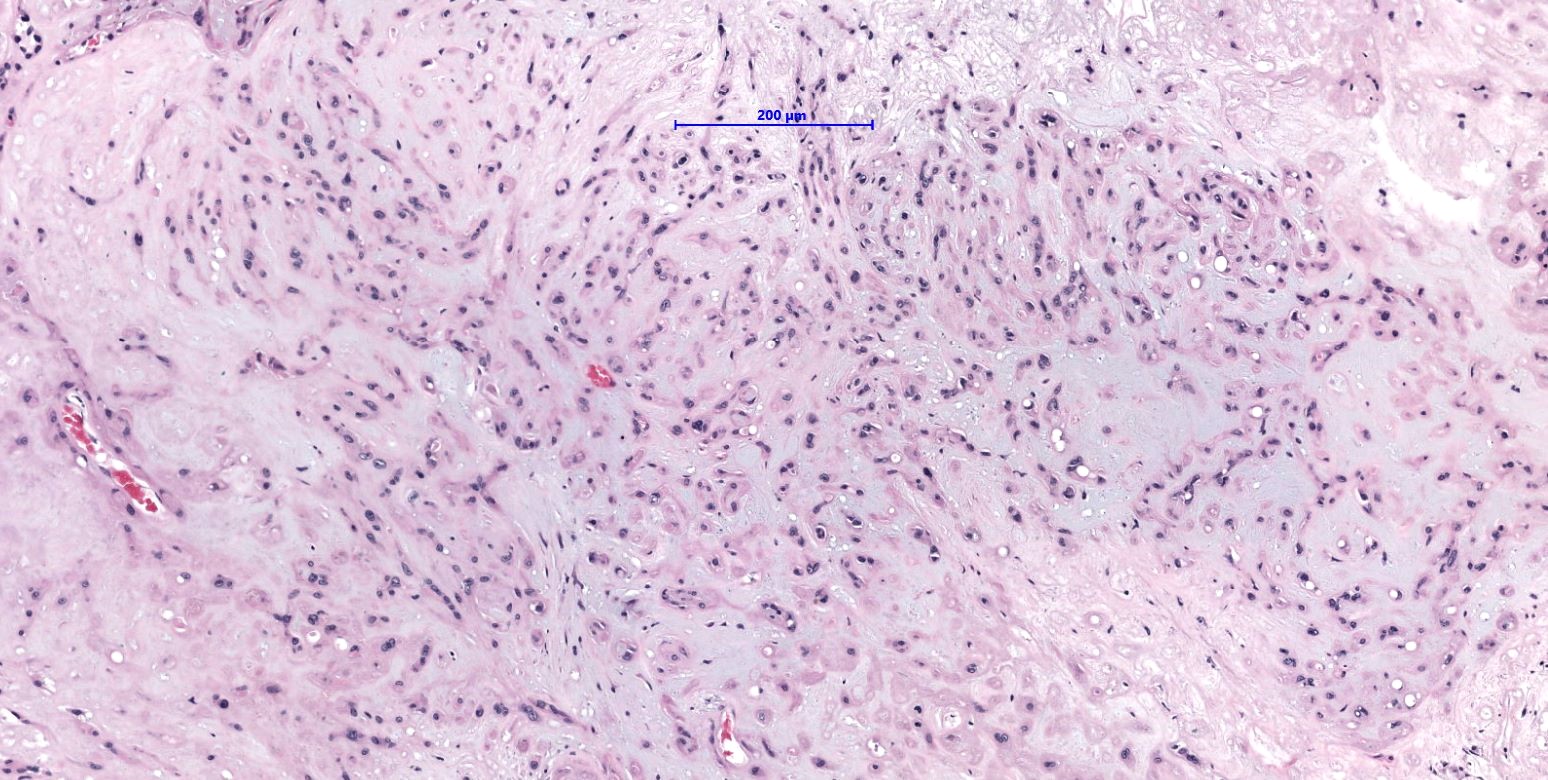
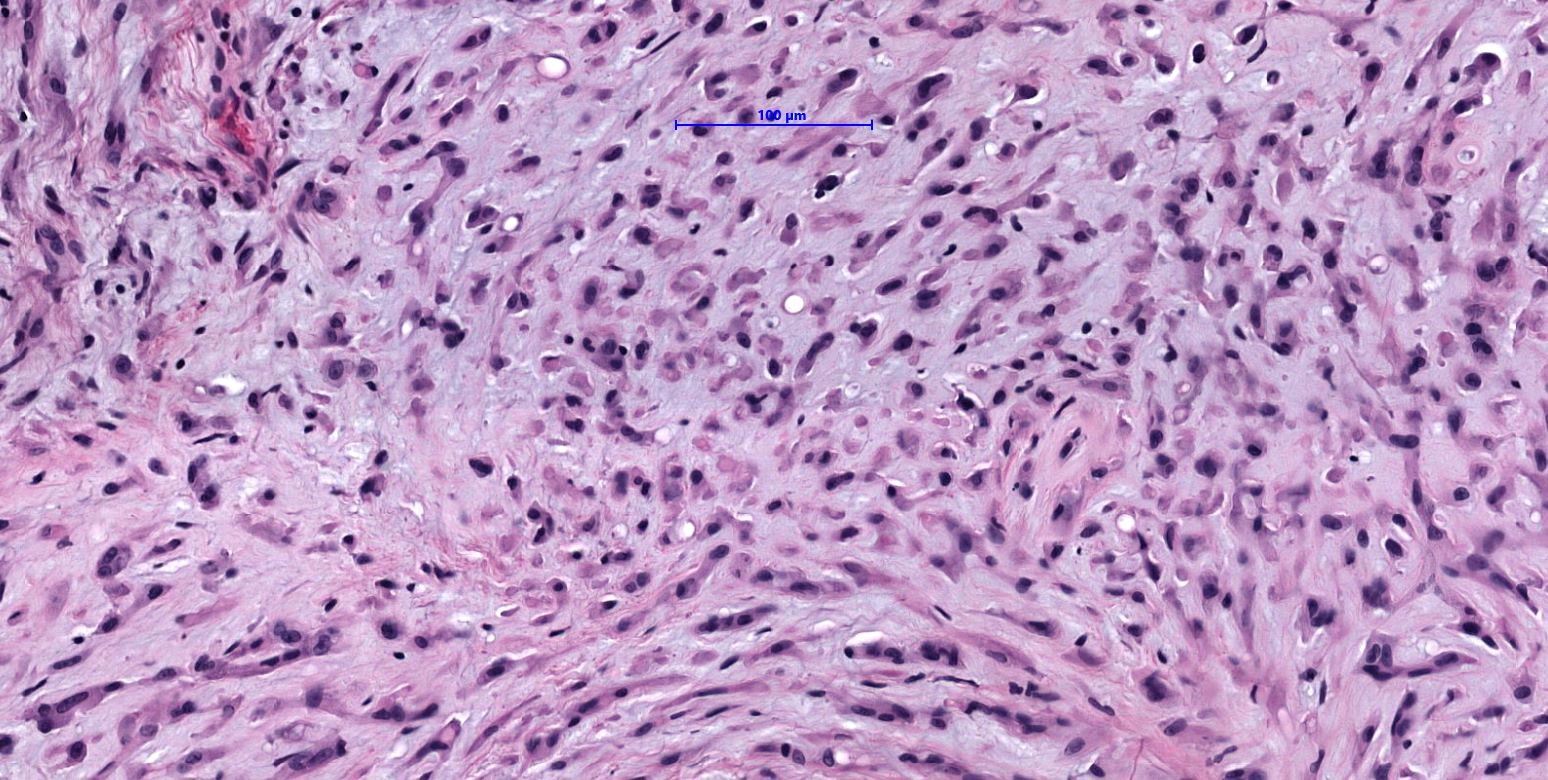
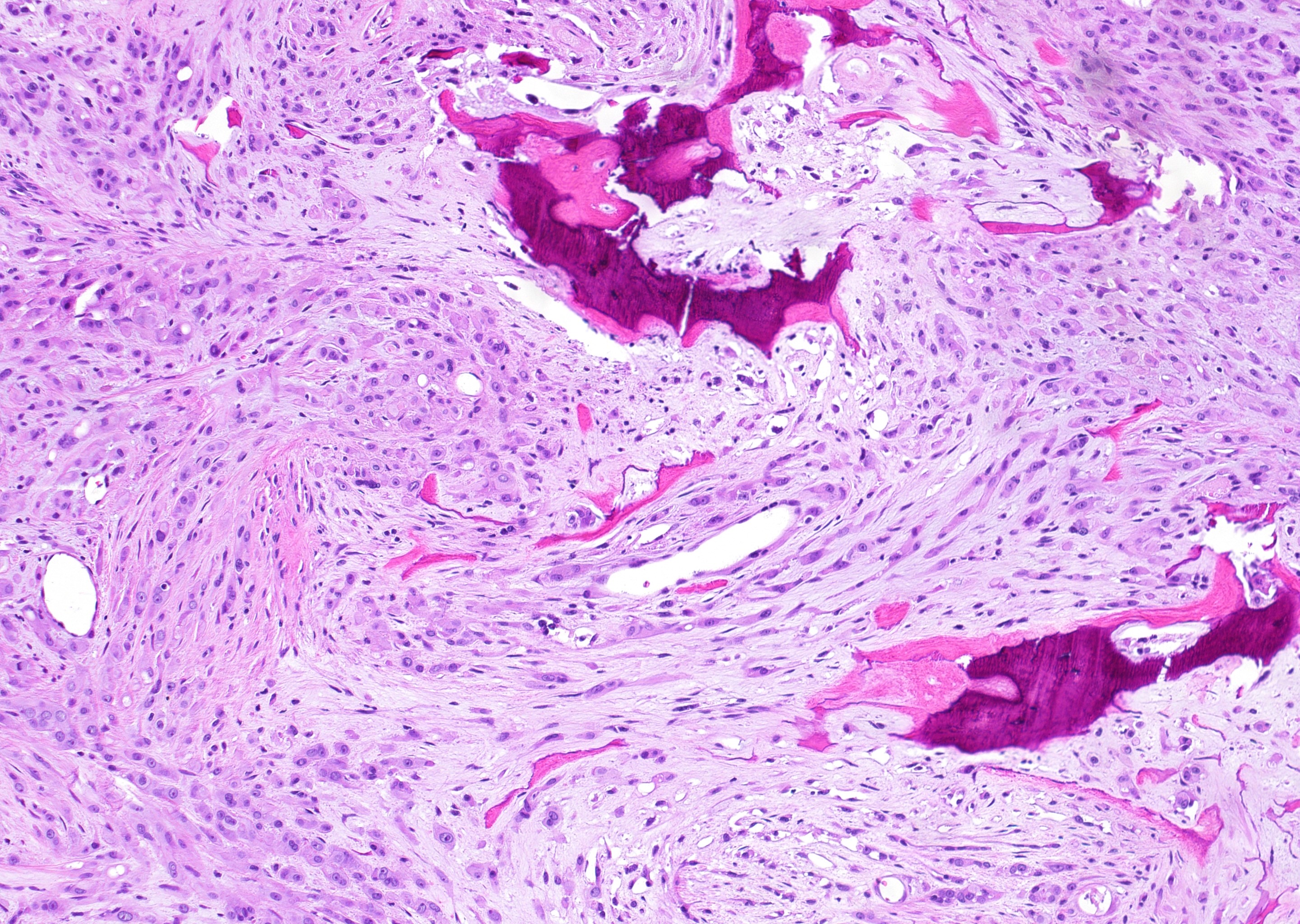
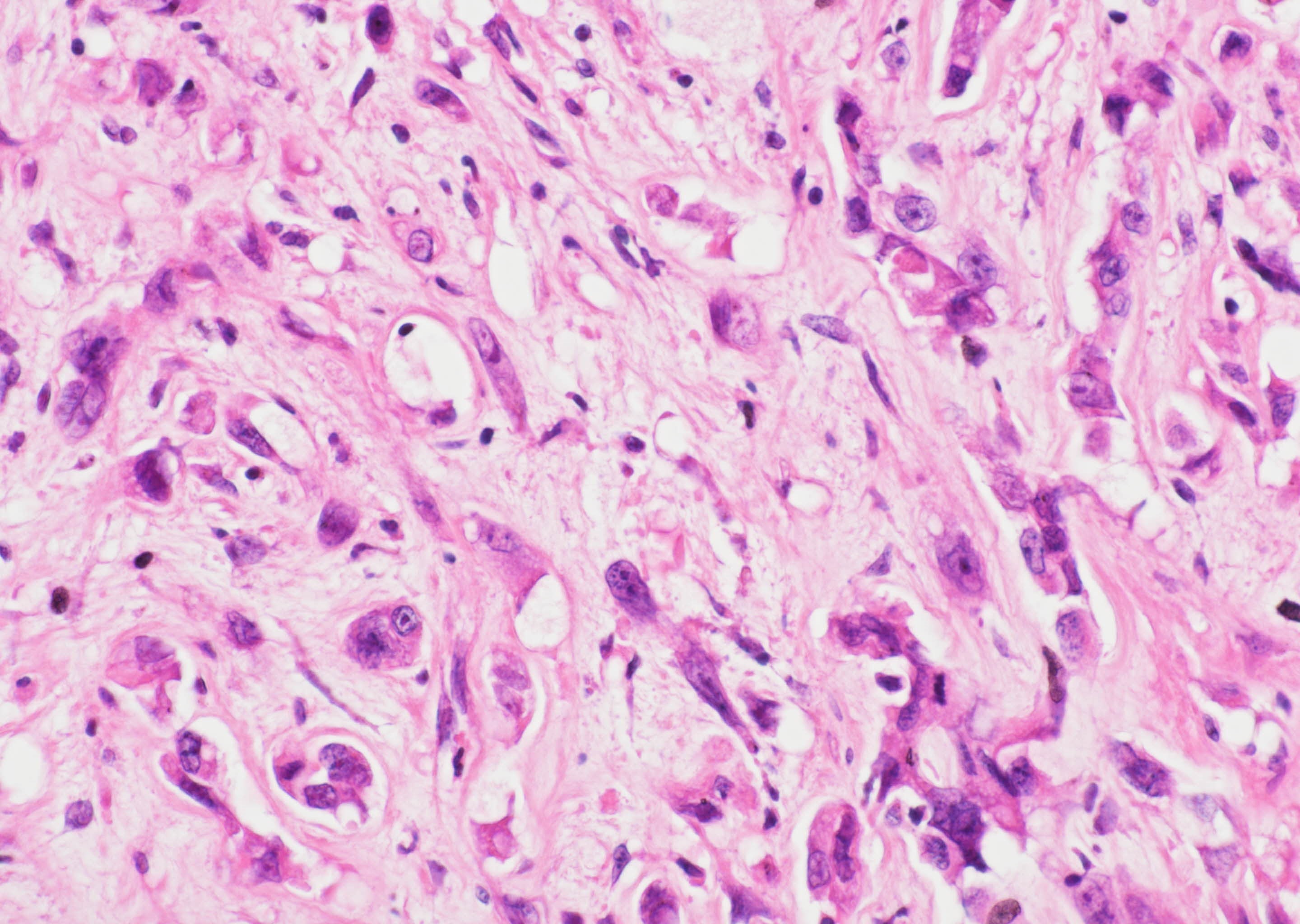
Microscopic (histologic) description
- WWTR1-CAMTA1 subtype (classic EHE):
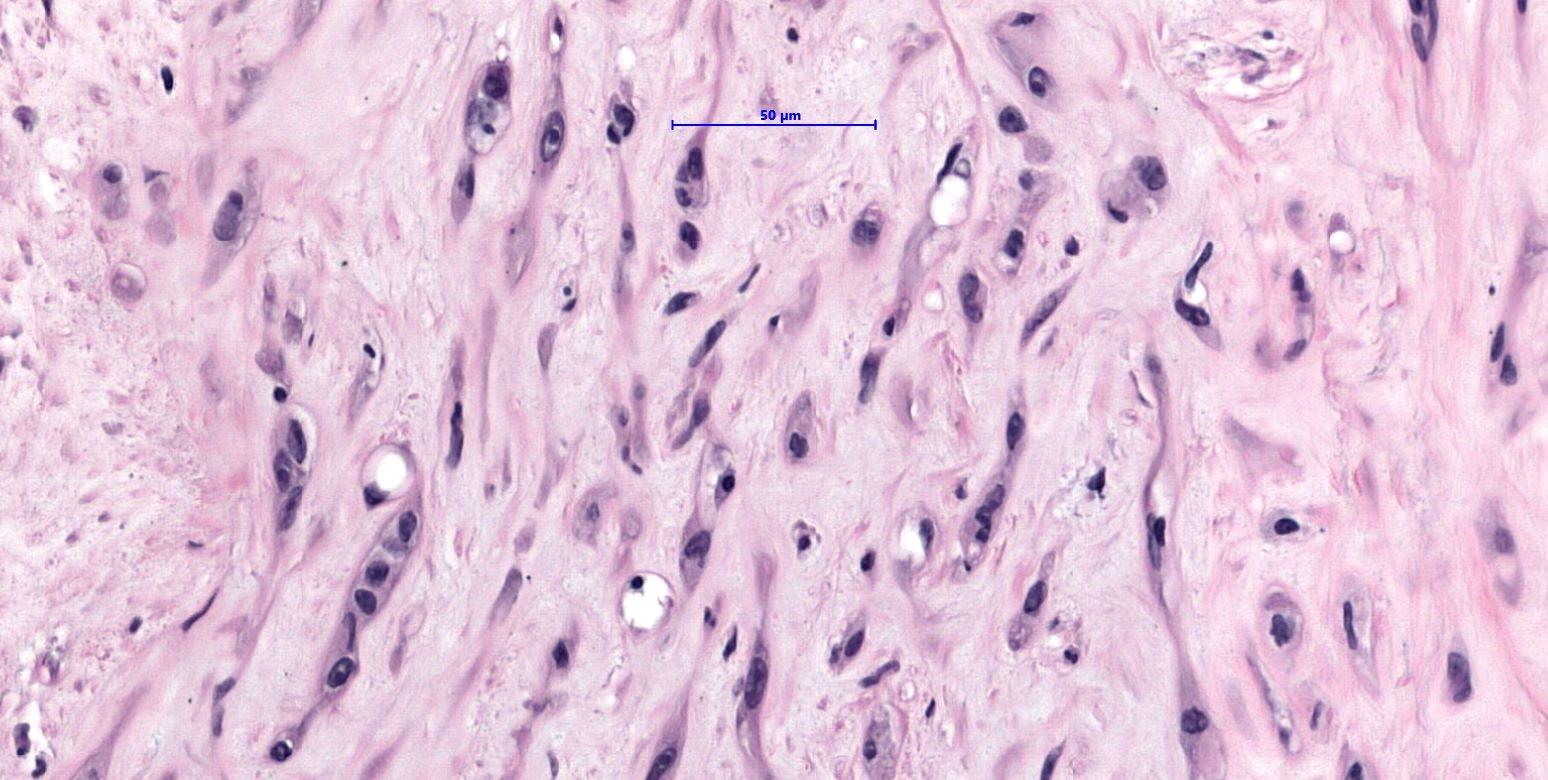
- Cords, strands or small nests of large endothelial cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm embedded in a myxohyaline stroma
- Tumor cells have vesicular, round to oval, sometimes indented nuclei
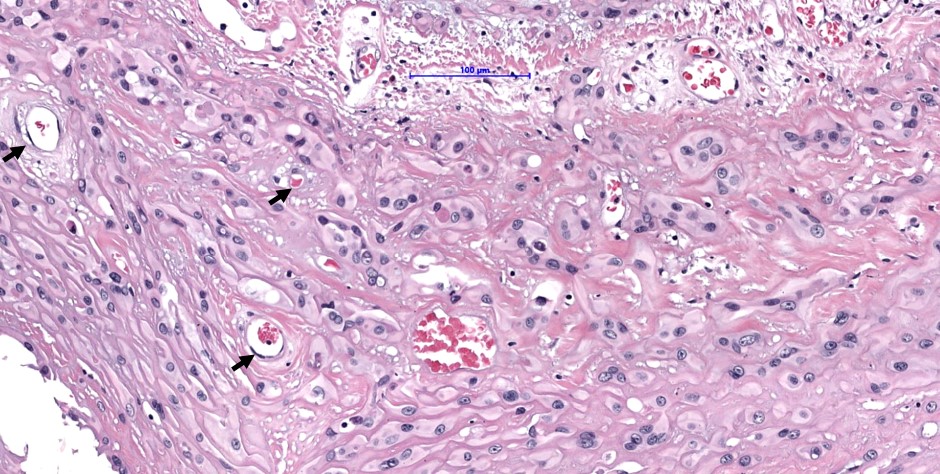
- Some tumor cells have intracytoplasmic, round, clear vacuoles representing small vascular lumina, which may contain erythrocytes
- YAP-TFE3 subtype:
- Solid nests or pseudo alveolar arrangement of epithelioid cells enmeshed in a fibrous stroma
- Tumor cells have abundant, densely eosinophilic cytoplasm and can form vascular spaces
- Intracytoplasmic vacuoles are rare
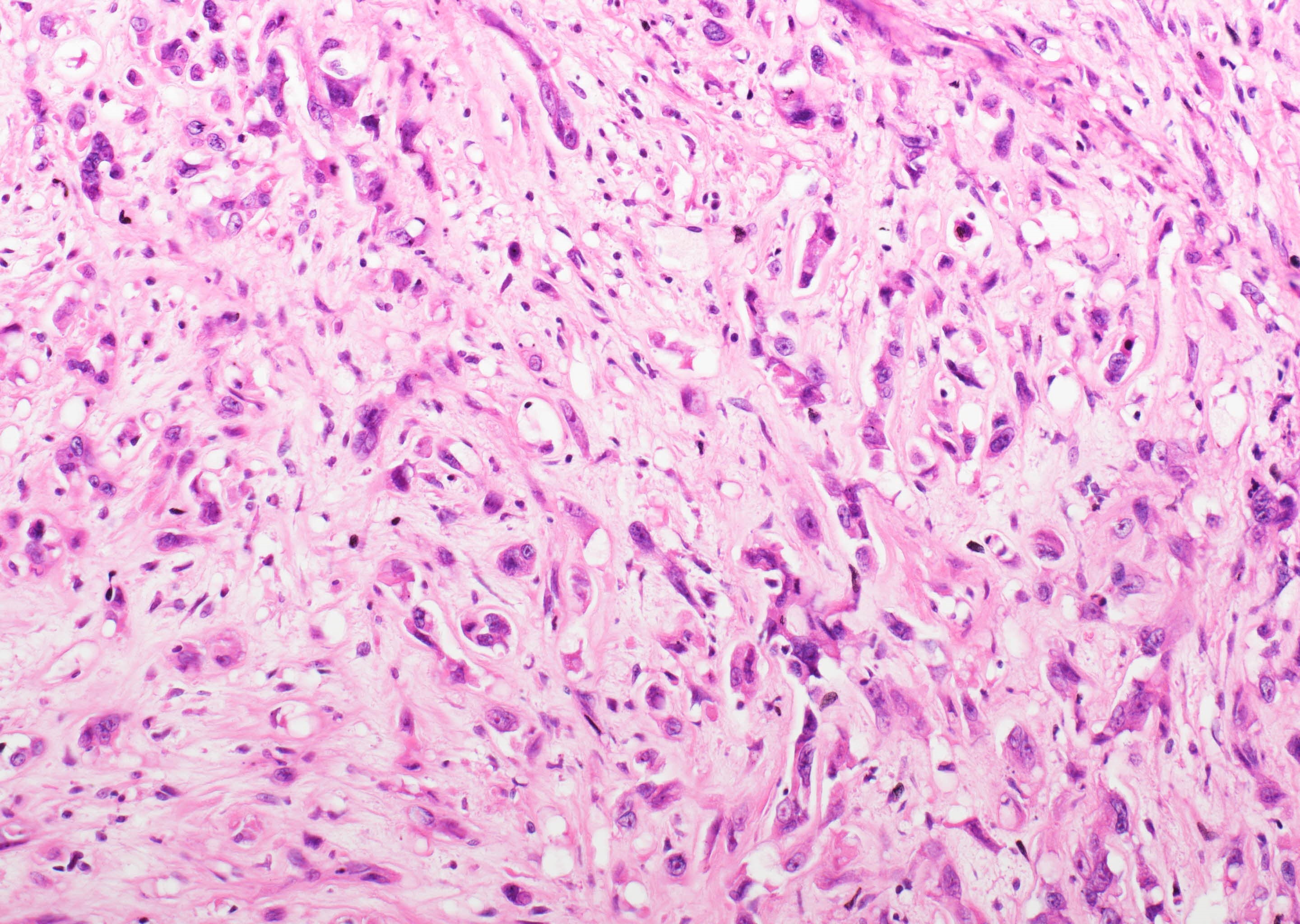
- Usually minimal mitotic activity, atypia or necrosis
- Up to 10% of cases exhibit frank malignant features of prominent nuclear pleomorphism, increased mitotic activity, solid growth or necrosis; these tumors resemble epithelioid angiosarcoma and have a more aggressive behavior (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:924)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Clusters of polygonal cells with moderate nuclear atypia (J Cytol 2012;29:89)
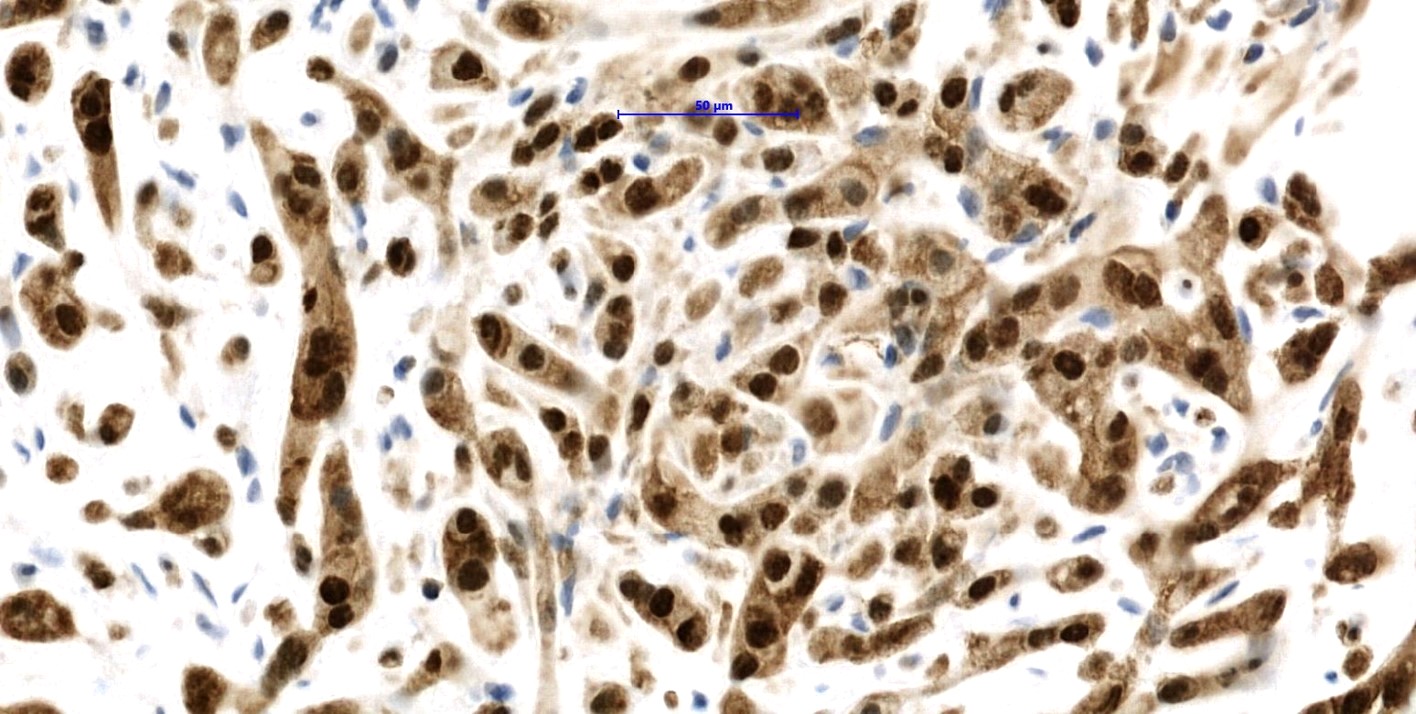
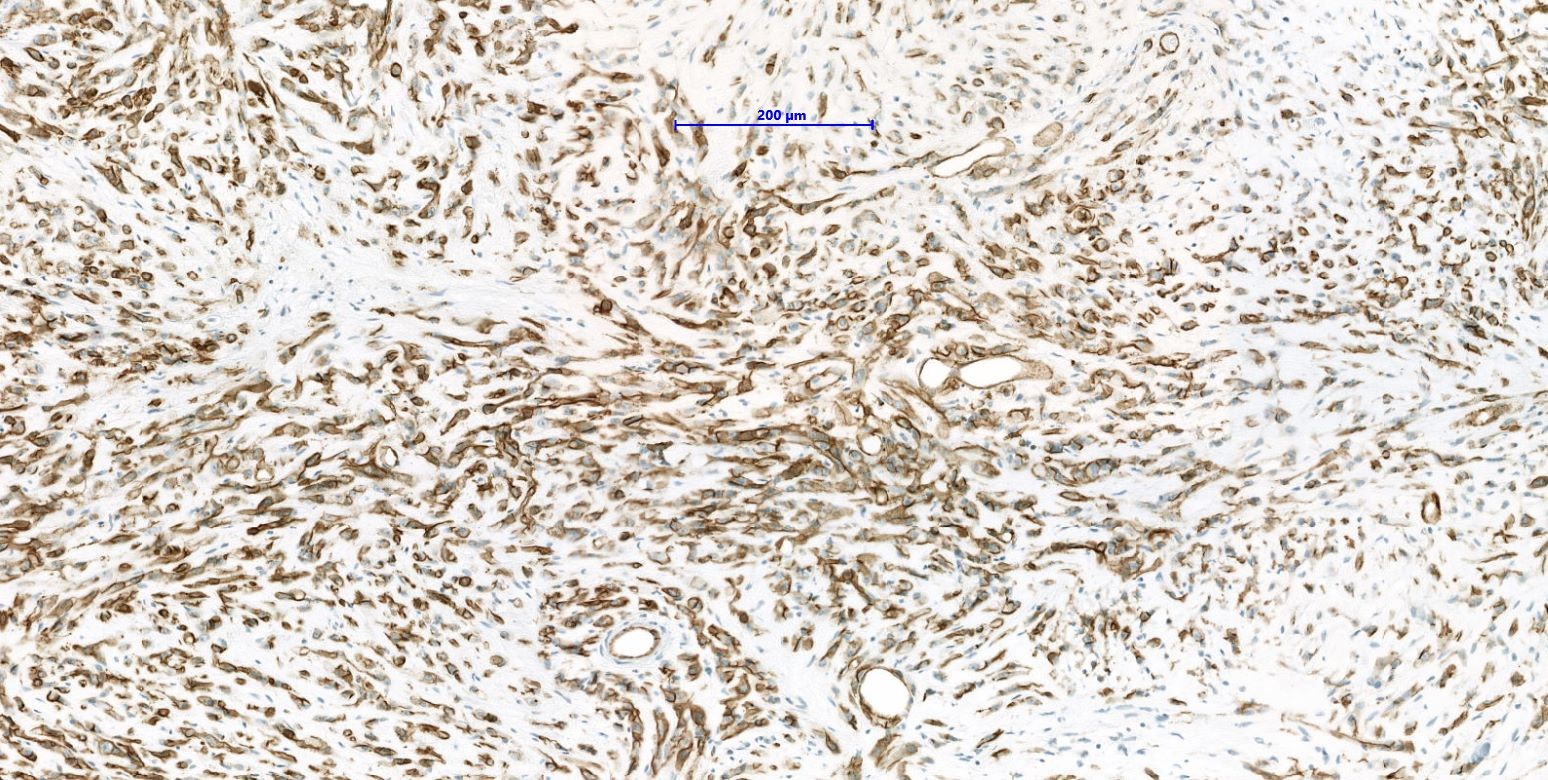
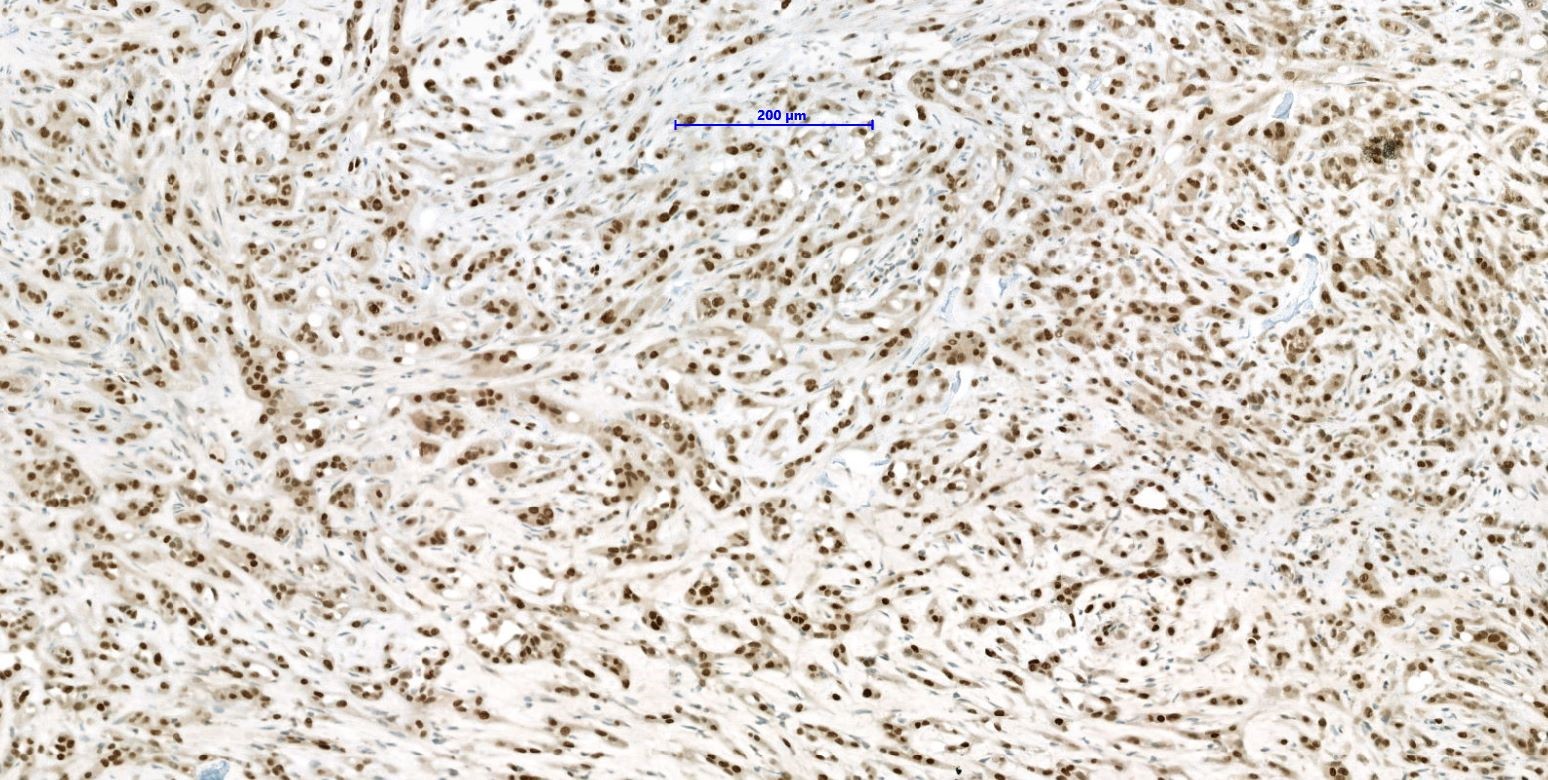
Positive stains
- ERG, CD31, CD34 (can be negative), podoplanin (D2-40), FLI1, von Willebrand factor (Diagn Pathol 2014;9:131, Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:363)
- CAMTA1 in WWTR1-CAMTA1 rearranged tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:94)
- TFE3 in YAP-TFE3 rearranged (less specific) (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2013;52:775)
Negative stains
- S100, SOX10, desmin, EMA (usually negative) (Diagn Pathol 2014;9:131)
- Keratin (positive up to 40%) (Diagn Pathol 2014;9:131, Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:363)
- SMA (positive up to 45%) (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:363)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Defined by recurrent WWTR1-CAMTA1 or YAP1-TFE3 gene fusion (Histopathology 2015;67:699, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2013;52:775)
- Translocations result in:
- Fusion of CAMTA1 on 1p36.23 to WWTR1 on 3q25.1
- Fusion of exon 1 of YAP1 and exon 4 of TFE3
Sample pathology report
- Right thigh, excision:
- WWTR1-CAMTA1 rearranged epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (see comment)
- Comment: Tumor is composed of cords and small nests of large endothelial cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm embedded in a myxohyaline stroma. Immunohistochemically, the tumor cells are positive for ERG, CD31, CAMTA1, focally positive for keratin and are negative for CD34 and TFE3. The morphology and immunoprofile strongly support the diagnosis of WWTR1-CAMTA1 rearranged epithelioid hemangioendothelioma.
Differential diagnosis
- Epithelioid angiosarcoma:
- Epithelioid sarcoma:
- Distal extremities of young adults
- Composed of nodules of medium sized epithelioid cells with epithelioid cytoplasm that merge with collagenous stroma
- Frequent mitosis, central necrosis and hemorrhage
- Keratin+ (strong), CD31-, CD34-, INI1 lost (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:542)
- Melanoma:
- Carcinoma / metastatic carcinoma:
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is true regarding epithelioid hemangioendothelioma?
- Cut surface is white with myxoid areas
- It is a benign neoplasm with vascular differentiation
- Most of the cases are negative for CAMTA1
- Tumor cells stain positive for ERG
- Tumor consists of spindle cells embedded in hyalinized stroma
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
A 30 year old woman presented with a mass of the trunk. Immunohistochemistry shows positive staining with CD31, CD34, ERG and CAMTA1 and focal positivity with keratin. Which of the following is most likely the correct diagnosis?
- Epithelioid angiosarcoma
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
- Epithelioid hemangioma
- Malignant melanoma
- Myoepithelioma of soft tissue
Board review style answer #2