Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Sebenik M. Intimal sarcoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissueintimalsarcoma.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Undifferentiated mesenchymal tumors arising from the inner lining (intima) of large arteries are classified as intimal sarcomas (ISA) with MDM2 amplification as their molecular hallmark (Mod Pathol 2021;34:2122)
- The defining feature is predominantly intraluminal growth with obstruction of the lumen of the vessels of origin and seeding of emboli to the peripheral organs (WHO 5th edition)
- ~67% of intimal sarcomas arise in the pulmonary circulation, almost always in the pulmonary artery; these are covered at Pulmonary artery intimal sarcoma
Essential features
- Occurrence within the lumen of a large vessel of the pulmonary or systemic circulation or within the heart cavities (WHO 5th edition)
- Primary high grade sarcoma, with or without heterologous elements
- MDM2 amplification strongly supports the diagnosis of intimal sarcoma (Cardiovasc Pathol 2019:43:107142, Virchows Arch 2001;438:57, Cancer Res 2010;70:7304)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9137/3 - intimal sarcoma
- ICD-11: 2B5F.2 & XH36H7 - sarcoma, not elsewhere classified of other specified sites & intimal sarcoma
Epidemiology
- Rare tumor
- Estimated prevalence: 0.0003 - 0.001%
- M = F
- Median age at diagnosis: 60 years (Intern Med 2016;55:3191)
Sites
- Medline search on intimal sarcoma performed on September 20, 2023, revealed 411 papers published in the last 50 years describing 716 cases
- Systemic circulation
- Arteries
- Aorta: 140 cases (19.56%)
- Ascending: 5 cases (0.70%)
- Arch: 15 cases (2.09%)
- Descending: 6 cases (0.84%)
- Thoracic: 29 cases (4.05%)
- Abdominal: 44 cases (6.15%)
- Not known: 41 cases (5.73%)
- Other arteries: 21 cases (2.93%)
- Aorta: 140 cases (19.56%)
- Veins: 14 cases (1.94%)
- Inferior vena cava: 7 cases (0.97%)
- Other veins: 7 cases (0.97%)
- Arteries
- Pulmonary circulation: 338 cases (47.21%)
- Pulmonary artery: 336 cases (46.93%)
- Pulmonary vein: 2 cases (0.28%)
- Heart: 203 cases (28.36%)
- Left heart: 128 cases (17.89%)
- Right heart: 75 cases (10.47%)
- Systemic circulation
Pathophysiology
- Frequent high level (co)amplifications / gains of MDM2, PDGFRA and EGFR (Cancer Res 2010;70:7304)
- MDM4 and CDK6 amplifications in intimal sarcomas, lacking MDM2 amplification (Mod Pathol 2021;34:2122)
Etiology
- Not known
- 5 - 10% of tumors occur at sites of remote Dacron graft placement
- In up to 20% of patients, the tumor is an incidental finding during aortic aneurysm repair (Pathology 2014;46:596)
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Clinical and radiological findings of intimal sarcoma are often similar to those of thromboembolic disease, leading to delays in establishing diagnosis
- Aortic intimal sarcoma mimics embolic phenom, such as claudication, skin necrosis and abdominal angina, due to the bulky intravascular component and friability
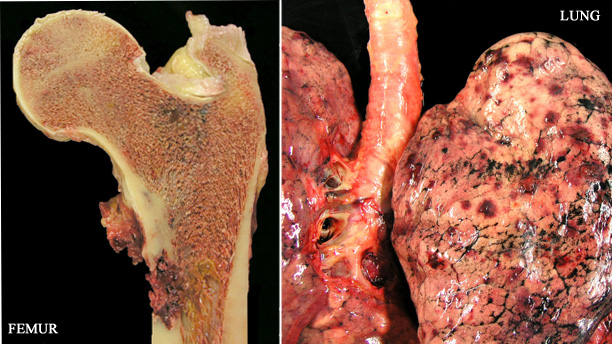
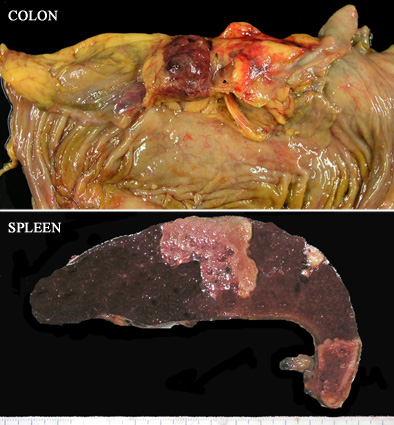
- In case reports, more than 50% of patients had metastatic disease at the time of presentation; common sites include bone, lung, liver, lymph nodes, extremities, kidneys, skin and adrenal glands
- Embolization to the brain is usually limited to tumors that involve the aortic arch and occurs in ~25% of patients
- Additional symptoms are nonspecific and include chest, back or abdominal pain, nausea, dyspnea and systemic hypertension (Radiographics 2021;41:361)
Diagnosis
- In some cases, the diagnosis of aortic neoplasia is made after endarterectomy for presumed thromboembolus in the systemic circulation (Pathology 2014;46:596)
- More often, diagnosis of aortic intimal sarcoma (AIS) is delayed or even postmortem because these neoplasms are frequently misdiagnosed as more common nonneoplastic conditions, such as atheroma
- Diagnosis is made by histology on resection specimens or during autopsy; biopsies of aorta are usually not performed
- More prompt recognition is essential for timely initiation of aggressive treatment (Radiographics 2021;41:361)
Laboratory
- D dimer might be elevated (mimics thromboembolism) (Med Clin (Barc) 2022;158:265)
- Clinical findings of vasculitis and other inflammatory conditions, including elevated C reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), dilated aorta or symptoms of claudication, may also manifest in aortic intimal sarcoma, increasing the diagnostic challenge (Semin Ultrasound CT MR 2011;32:377)
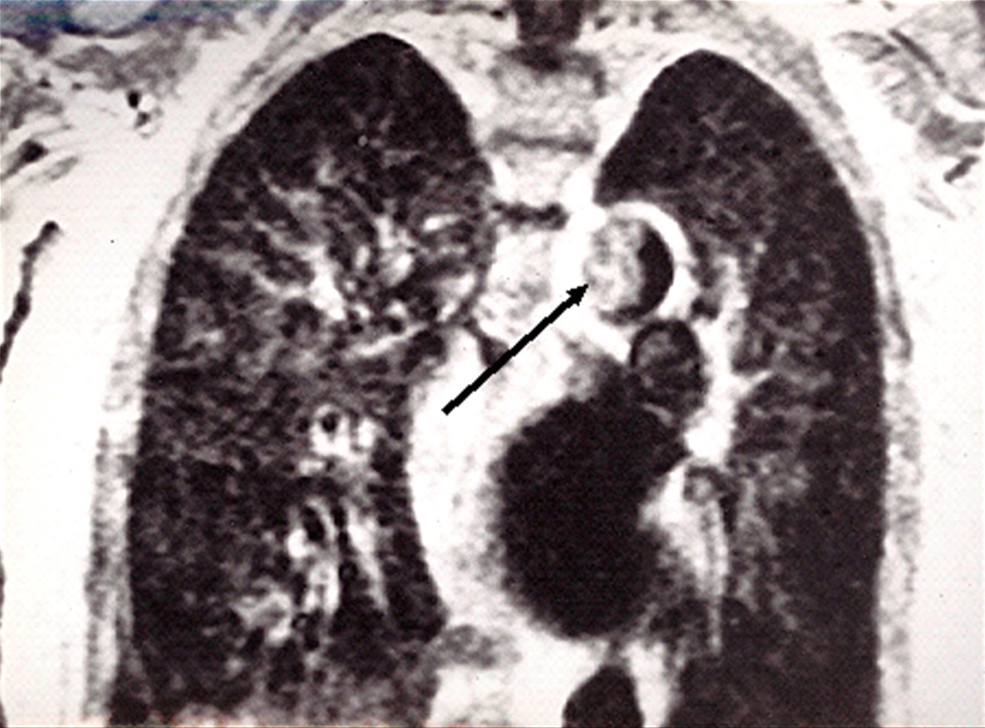
Radiology description
- Great vessel sarcomas are often misdiagnosed at initial clinical presentation, due to their extreme rarity and their imaging appearance, which can overlap with those of much more common entities
- Aortic intimal sarcomas are often misdiagnosed as protuberant atherosclerotic disease or intimal thrombus
- Localized, near occlusive, lobulated or frond-like, endoluminal aortic lesion of low attenuation lining the vessel wall, evident anywhere in the thoracoabdominal aorta, is suspicious for aortic intimal sarcoma
- Most useful imaging modalities for assessment of a suspected intimal sarcoma include computed tomography (CT) angiography, fluorine 18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- None of the above modalities, however, reliably differentiate between a thrombus and a malignancy; the ultimate diagnosis must be based on tissue examination (Radiographics 2021;41:361)
Prognostic factors
- While median survival in patients without metastatic disease at the time of diagnosis is 20 months, it is only 6 months when metastases are present (Ann Vasc Surg 2014;28:515)
- Even in the absence of metastatic disease, outcomes remain poor unless the tumor can be entirely excised (Radiographics 2021;41:361)
- Age does not appear to be a prognostic factor (Oncol Res Treat 2017;40:353)
Case reports
- 48 year old man with a history of chronic cardiac disease presented with 3 months of persistent back pain; CT and MRI both revealed a solid fusiform lesion of the descending aorta (Aorta (Stamford) 2019;7:169)
- 49 year old woman with atherosclerotic plaque and thrombus (Open Med (Wars) 2021;16:1306)
- 59 year old man with a tumor involving all segments of the thoracic aorta and a large floating thrombus causing acute mesenteric ischemia, treated successfully with embolectomy (Vasc Specialist Int 2021;37:46)
- 71 year old woman with abdominal angina and an intra-aortic mass at the thoracoabdominal aorta that restricted blood supply to the organs (Ann Vasc Dis 2019;12:225)
- 74 year old woman with aortic mass in the thoracoabdominal aorta masquerading as a mycotic aneurysm (J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Tech 2019;5:593)
Treatment
- Treatment of aortic intimal sarcoma depends on the extent of aortic involvement and the presence or absence of metastatic disease
- Radical surgical resection is the mainstay of treatment but complete surgical resection is rarely an option (Oncol Res Treat 2017;40:353)
- Neoadjuvant therapy might shrink the tumor and thereby facilitate more efficient surgery; however, patients are often highly symptomatic at diagnosis requiring immediate surgery for symptomatic relief, leaving no time for neoadjuvant chemotherapy (Tex Heart Inst J 2014;41:518)
- Role of adjuvant therapy is not yet proven, although some authors suggested better outcomes in patients receiving multimodality treatment compared to patients undergoing single modality treatment (Tex Heart Inst J 2009;36:451)
- If adjuvant chemotherapy is initiated, there is no consensus on which agent or combination of agents could be effective
- Palliative chemotherapy should be considered for inoperable, advanced cases but the quality and quantity of responses to available systemic agents is poor (Oncol Res Treat 2017;40:353)
- MDM2, studied extensively in intimal sarcoma of pulmonary artery and heart, has become an area of focus in cancer treatment because anti-MDM2 therapy has become a reality
- Small molecule inhibitors that block the MDM2 - p53 interaction and thus, reestablish wild type p53 activity, are available
- First generation small molecule inhibitors of MDM2, nutlins, were identified in 2004
- Nutlin 3A, a pharmacological inhibitor of the MDM2 - p53 interaction, stabilizes p53; however, its clinical efficacy is very low and severe thrombocytopenia represents a dose limiting toxicity
- Recent novel second generation molecules that interfere with MDM2 or the MDM2 - p53 interaction, seem to be more promising (Diagnostics (Basel) 2021;11:496)
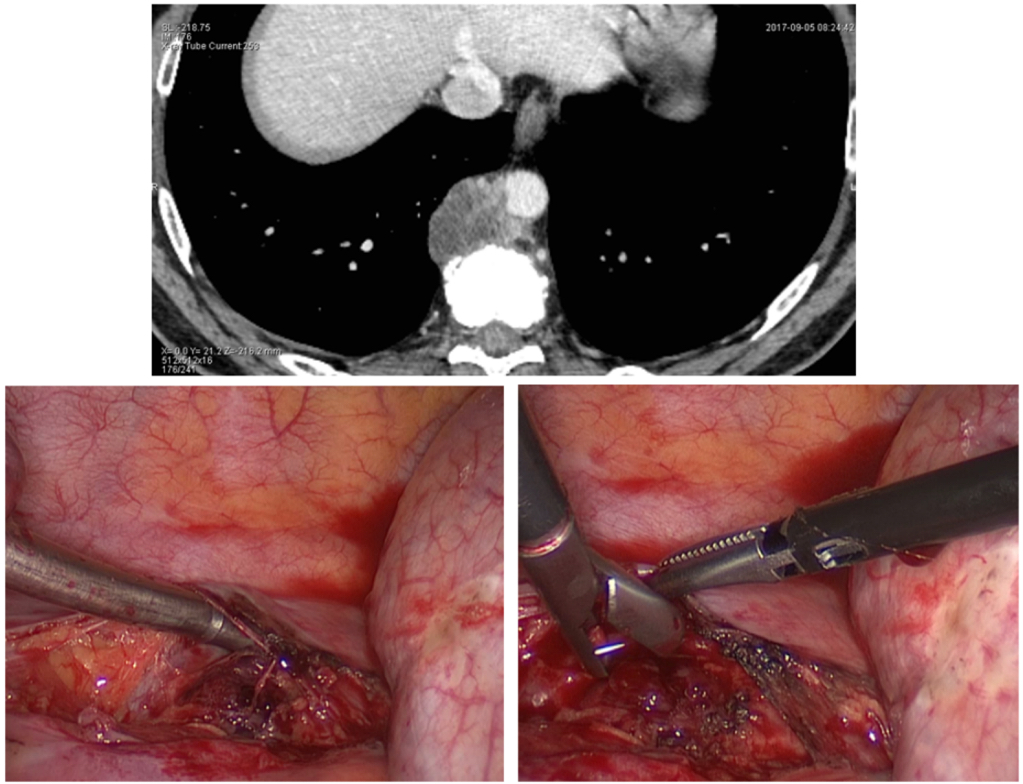
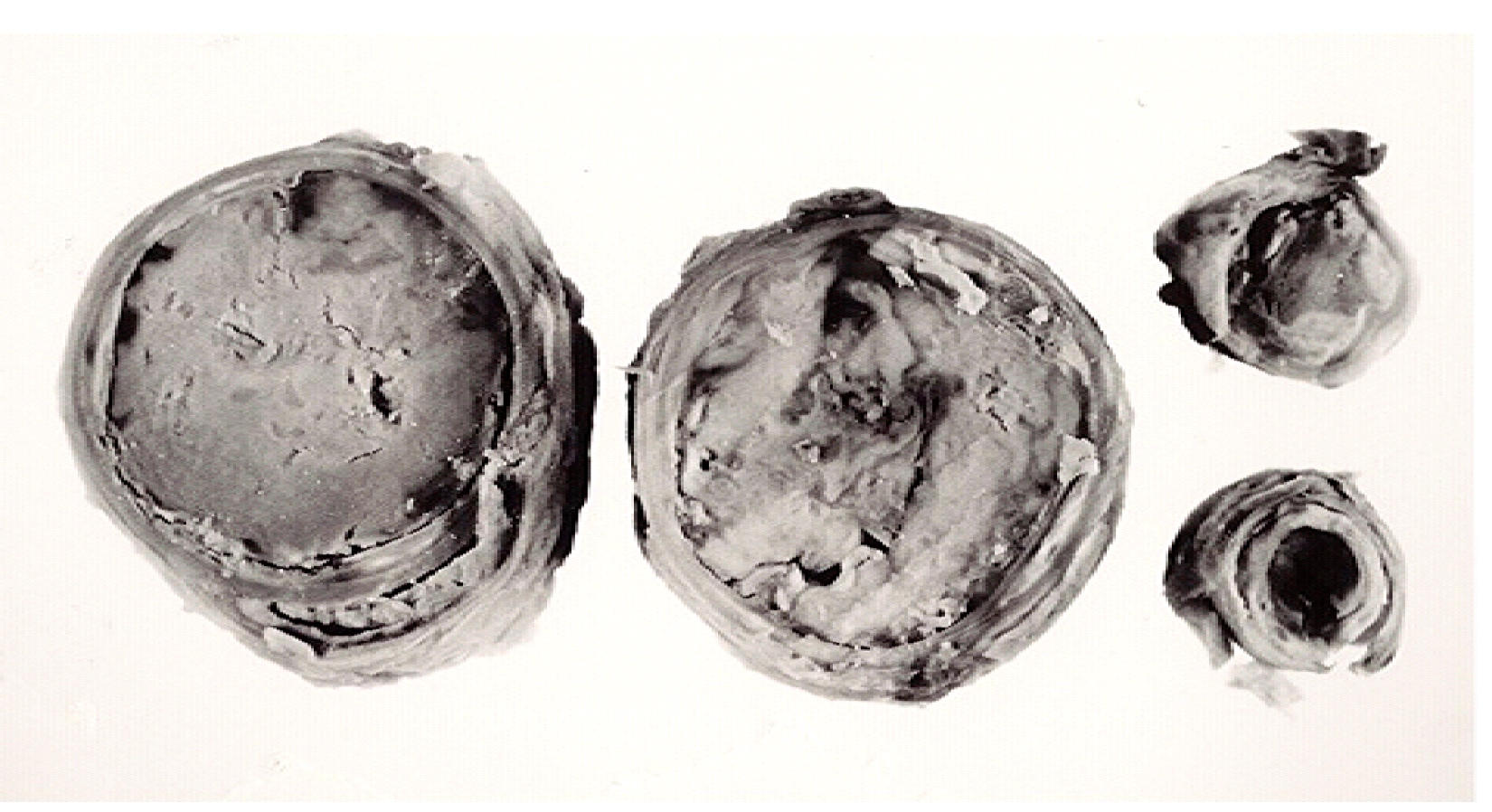
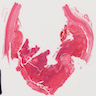
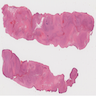
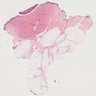
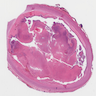
Gross description
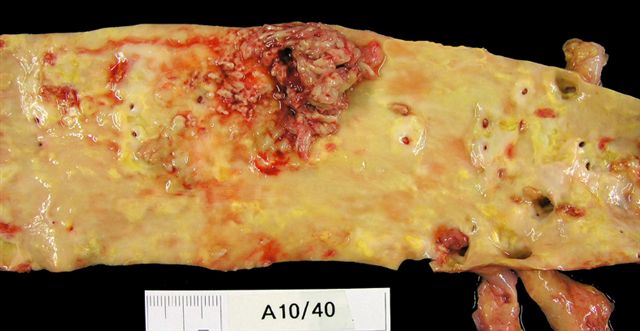
- Macroscopically, intimal sarcomas are predominantly intravascular polypoid masses bound to the vessel wall, resembling thrombi (Radiographics 2021;41:361)
- Section shows rubbery, gray, hemorrhagic, necrotic cut surface often associated with thrombus and atherosclerotic plaque material
- Sizes ranged from 1 cm to very large tumors exceeding 10 cm (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1184)
Gross images
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Surgical specimens
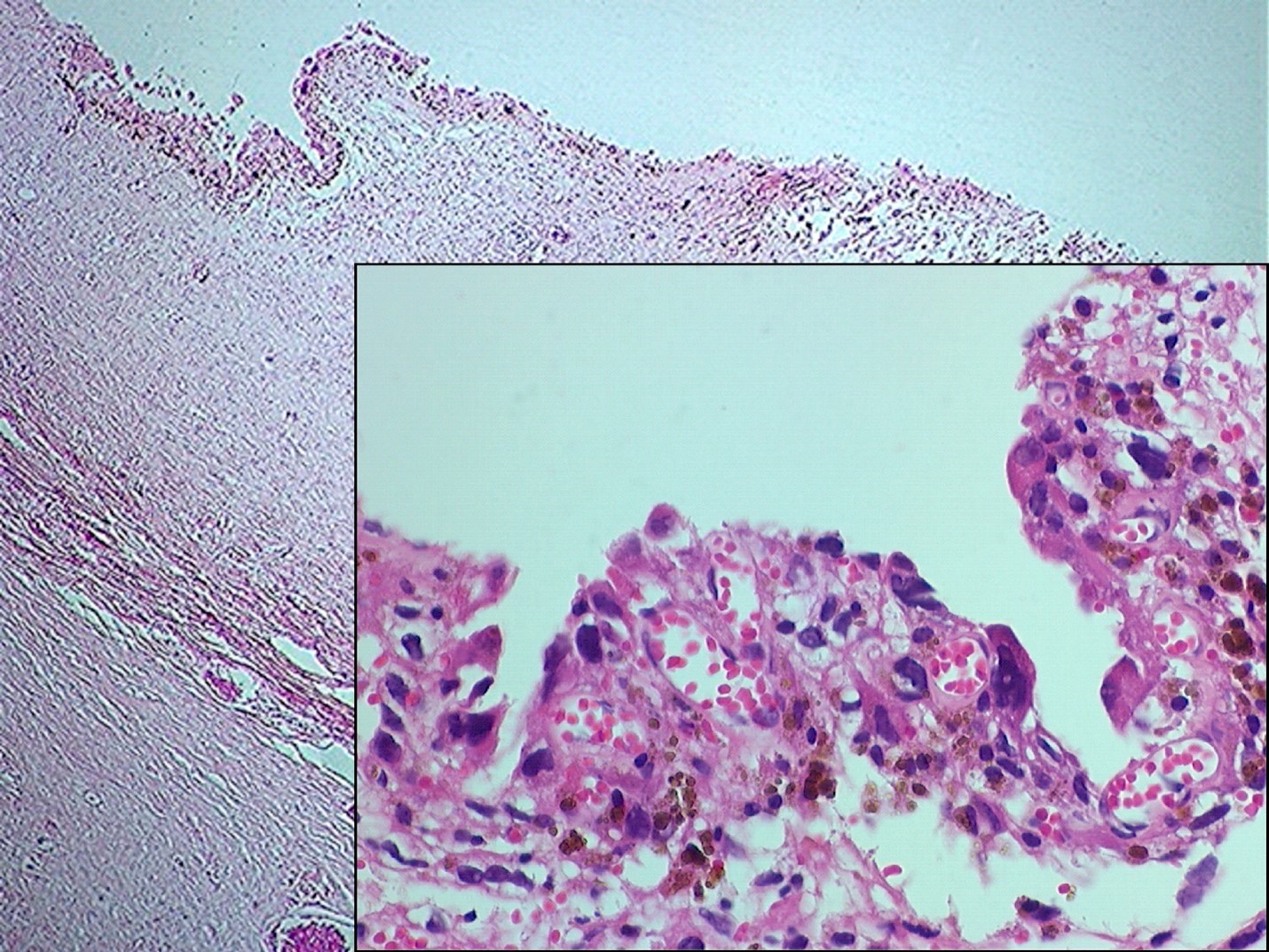
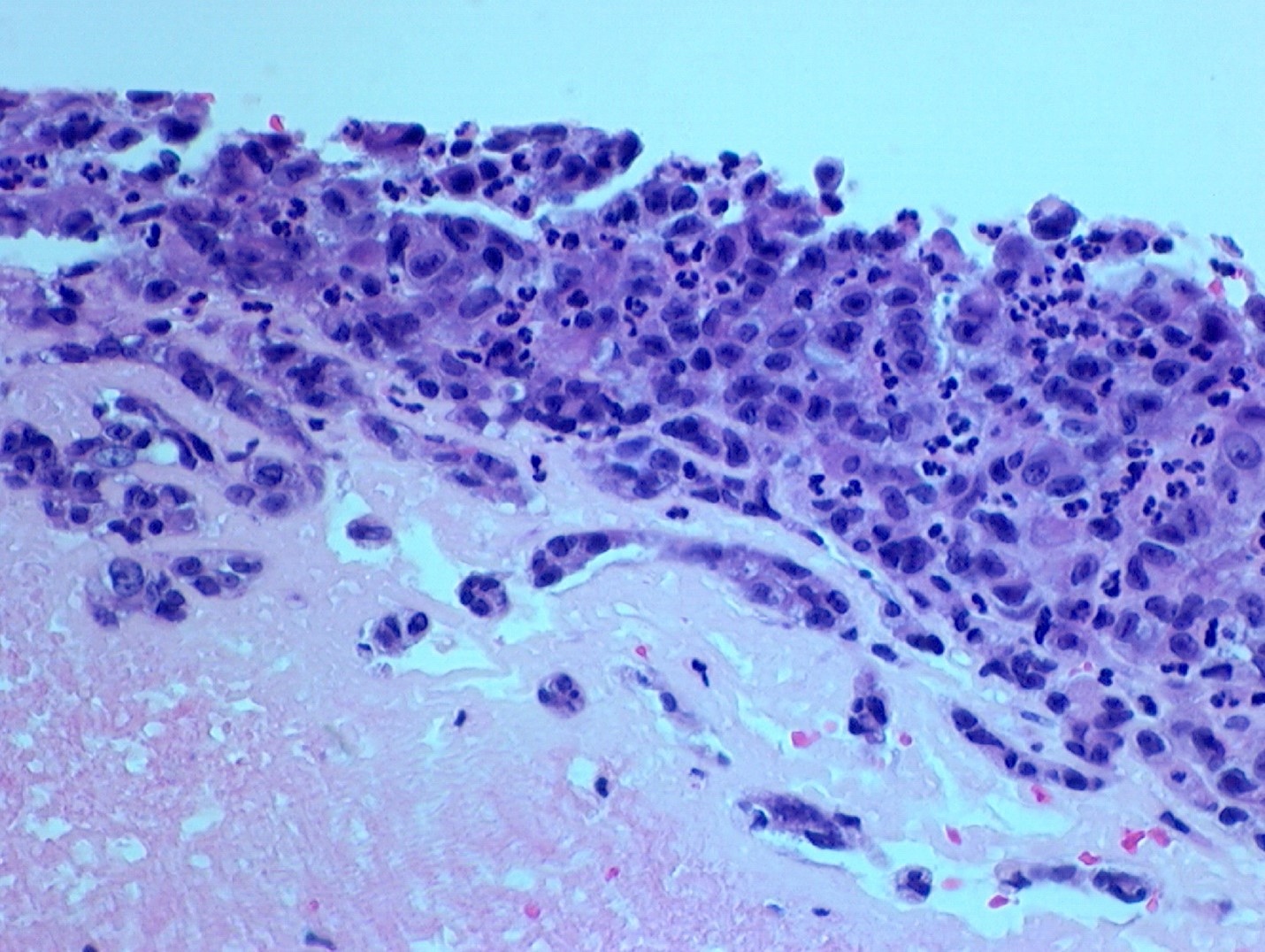
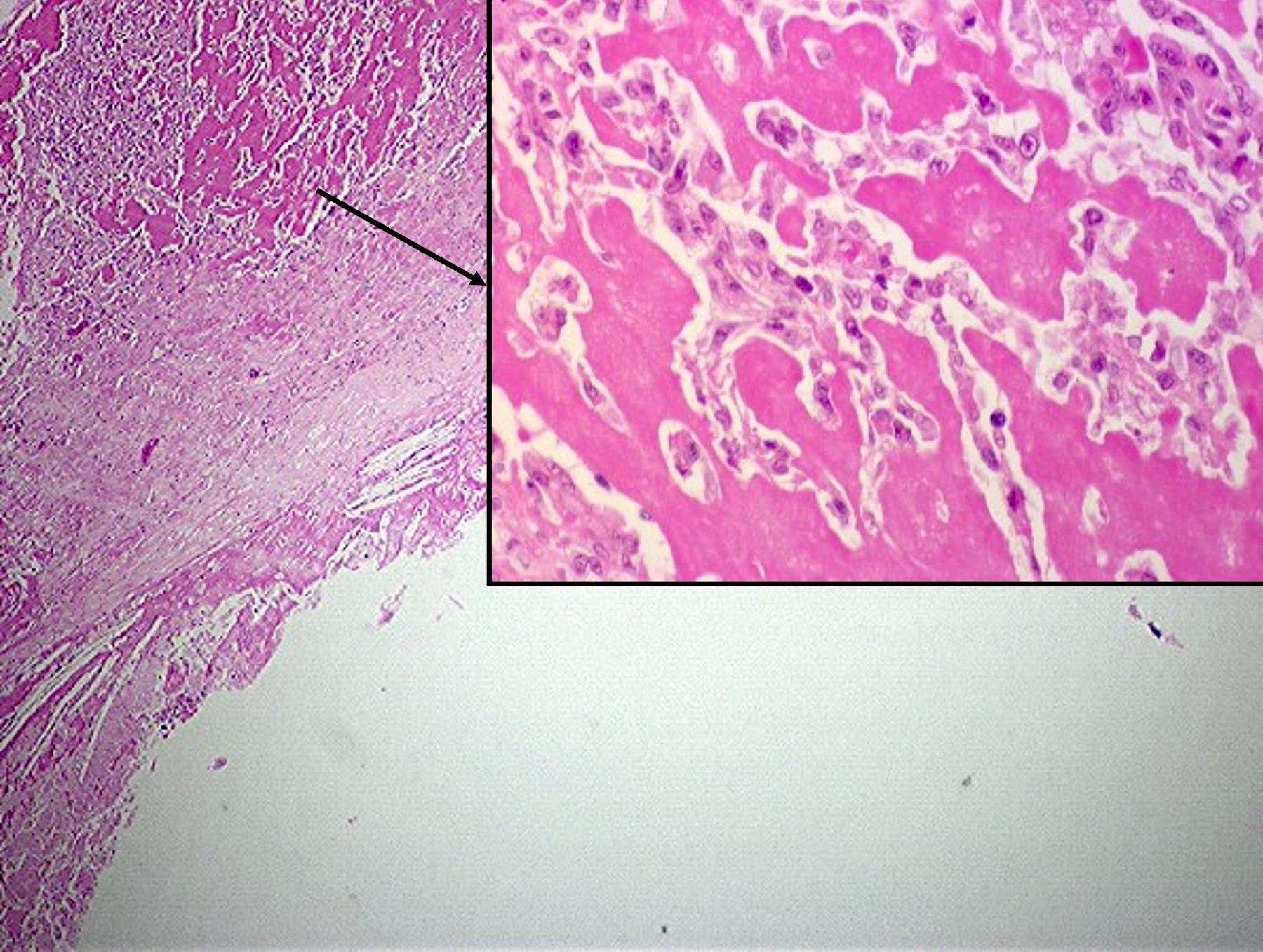
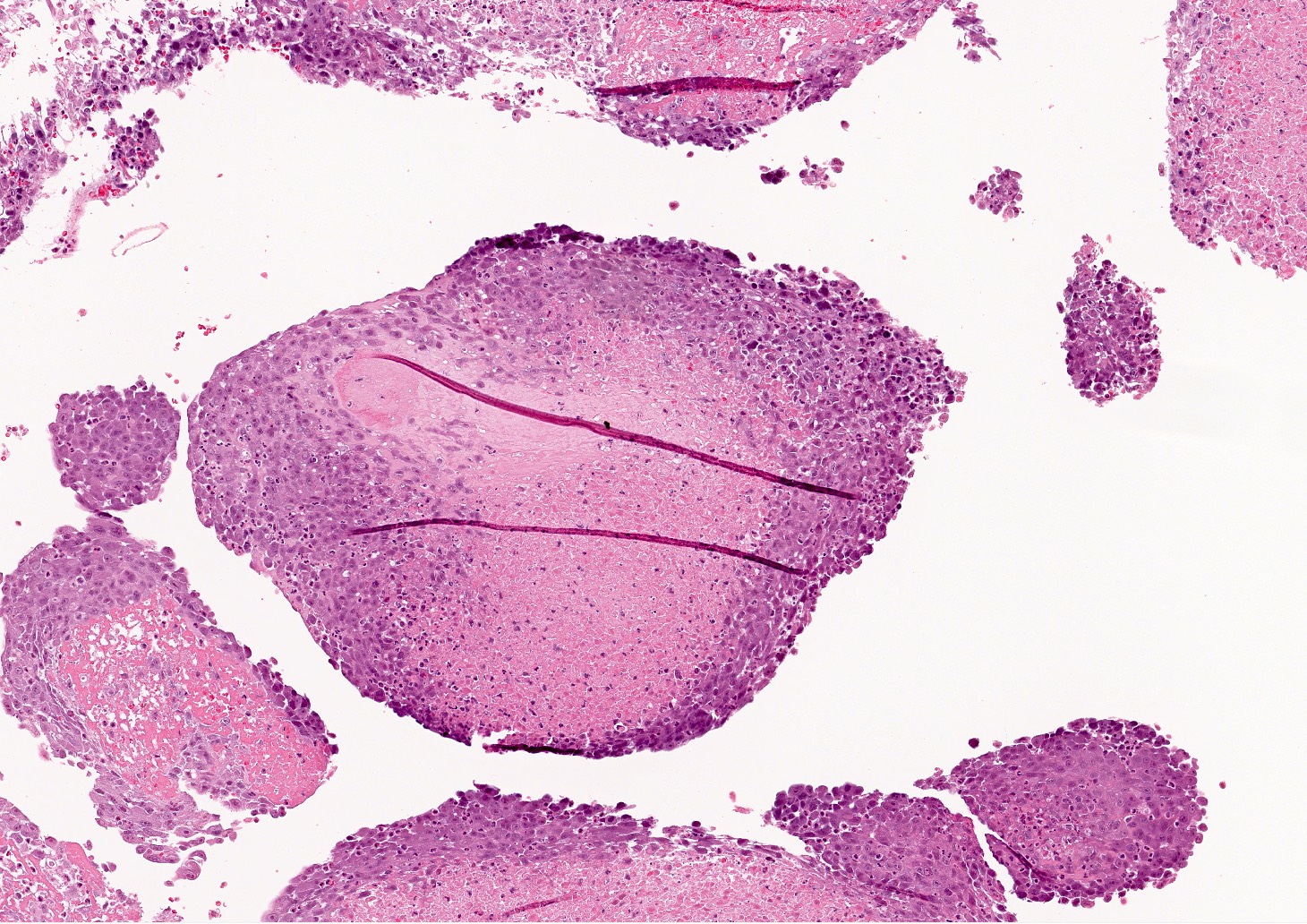
- Intraluminal tumors are largely necrotic, with a narrow layer or rind of preserved cells limited to the luminal surface of a large thrombus or the intimal aspect of the affected vessel (see figures 1 - 6)
- Low power appearance is often reminiscent of a complex atheroma with extensive fibrin thrombus
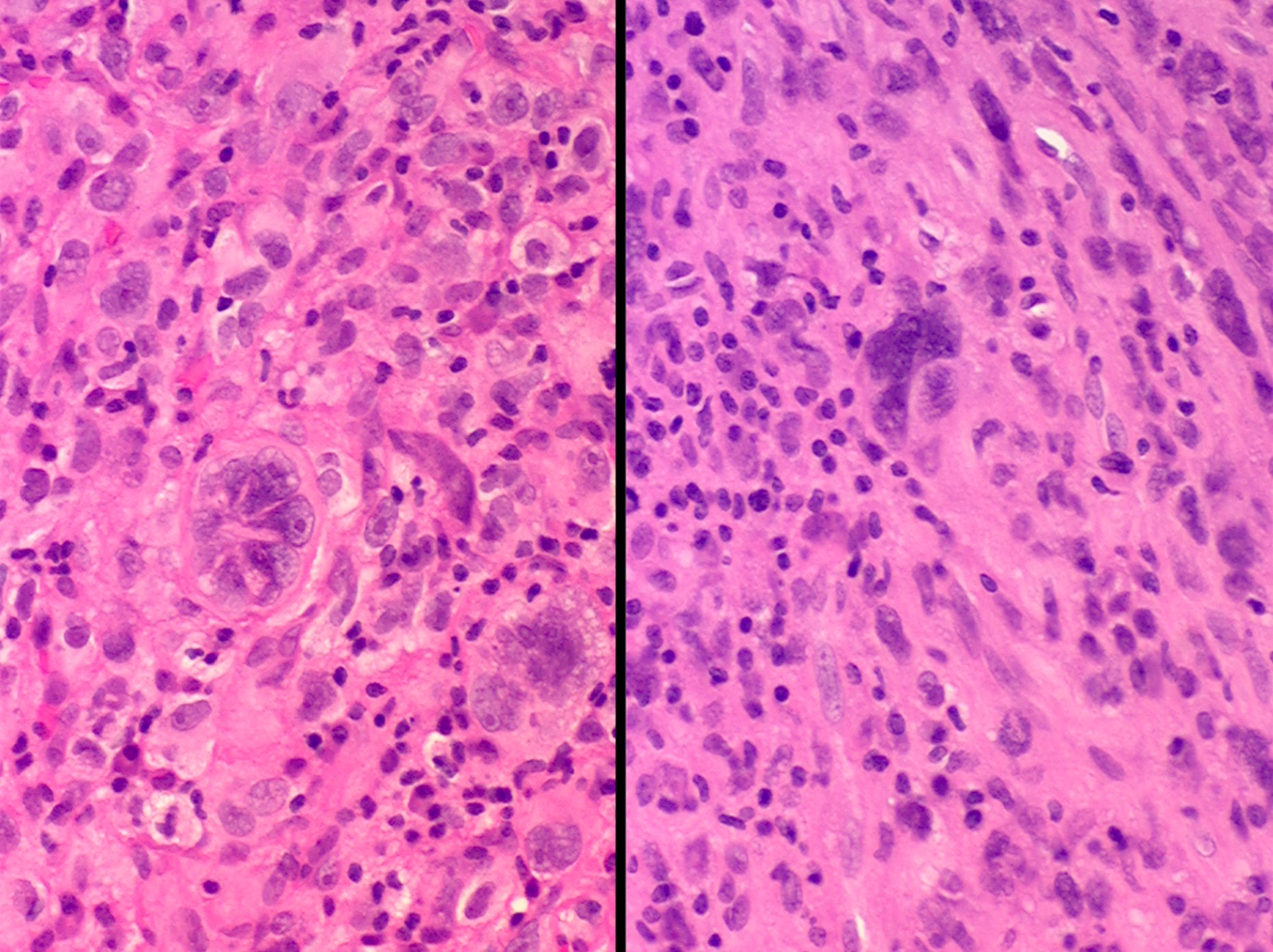
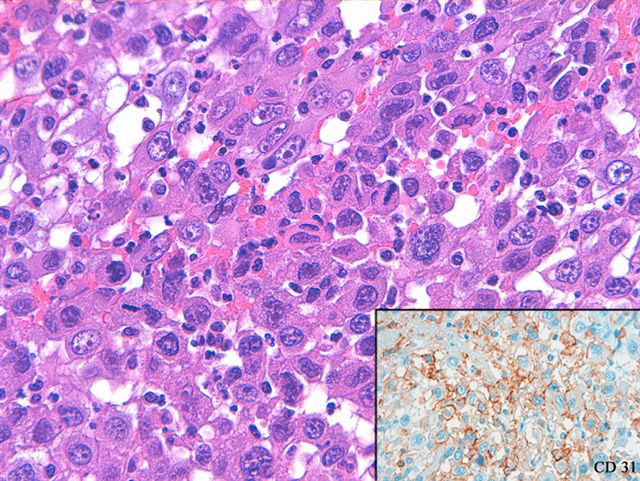
- Tumors are composed of large epithelioid or histiocytoid cells that are poorly cohesive exhibiting a high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio
- Nuclei are pleomorphic with macronucleoli and numerous mitotic figures, including abnormal forms; the cytology of individual tumor cells most closely resembles amelanotic malignant melanoma or an anaplastic lymphoma and multinucleated giant tumor cells are infrequent
- Cytoplasm is sparse and occasionally vacuolated but tumor cells neither exhibit intracytoplasmic lumina nor do they line capillary-like spaces in the primary tumors (see figure 4)
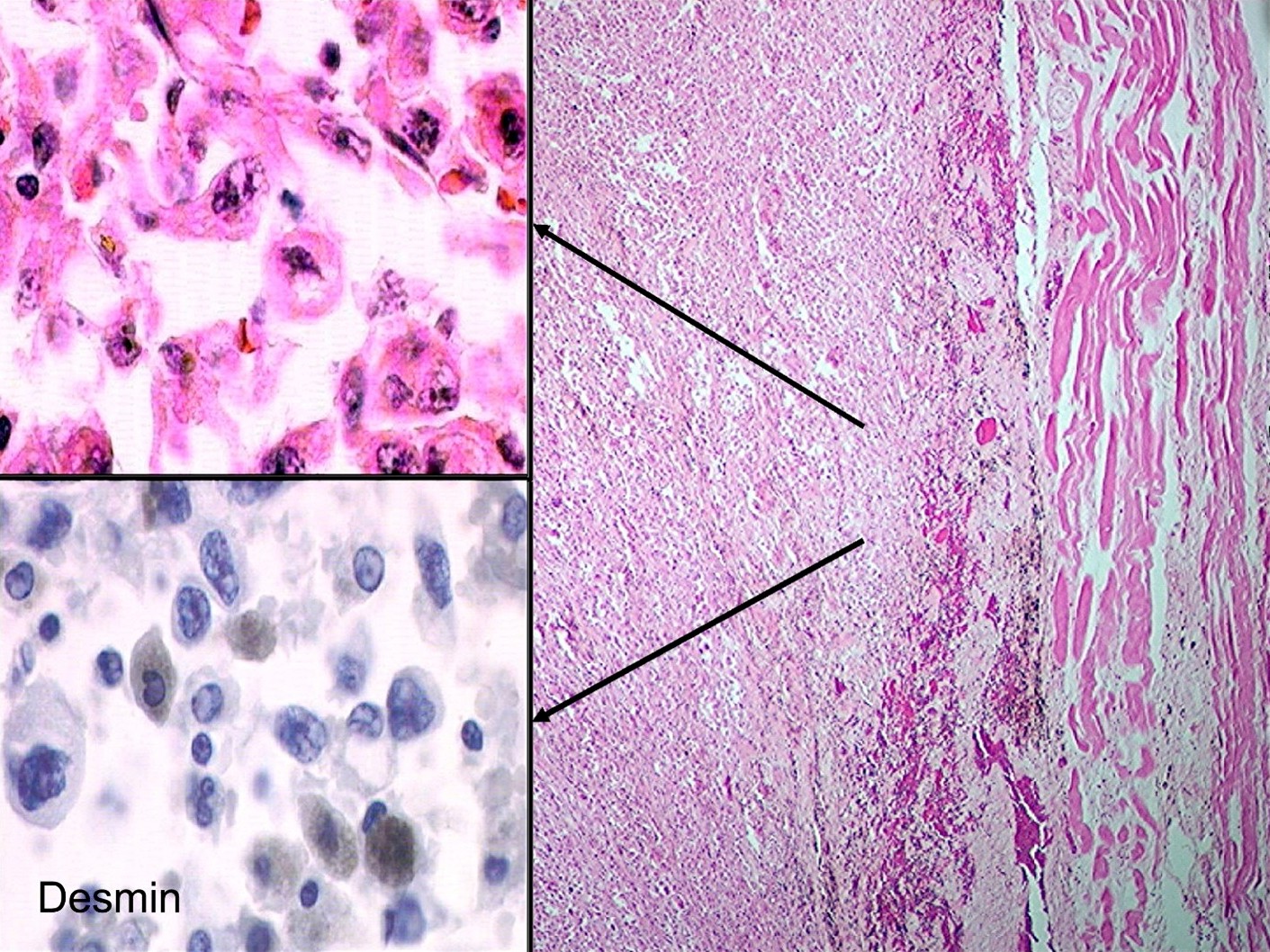
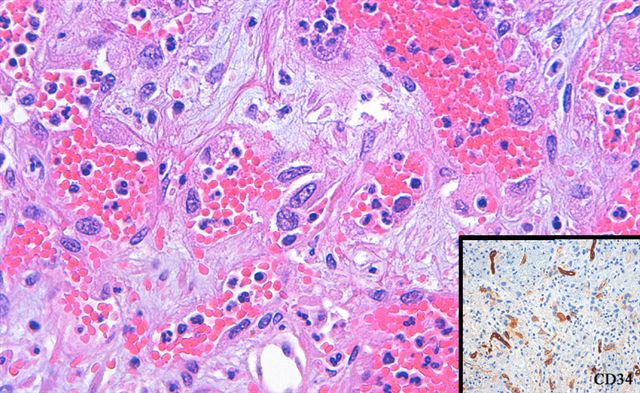
- In all metastatic sites, the tumor’s appearance is altered and can have a wide variety of histologic patterns; these alterations included classic angiosarcoma (figure 9), pleomorphic tumor resembling undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (UPS) (malignant fibrous histiocytoma [MFH]) (figures 10 - 11) or pleomorphic tumor resembling liposarcoma (figure 12) (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1184)
- Autopsies
- In all cases where autopsy material or records were available for review, the tumor had recurred at the primary site
- Widespread metastases were found in all cases, involving the lung, liver, vertebral bone, pancreas, small bowel, kidney, adrenal glands, diaphragm and skin
- In local extravascular soft tissue recurrences and in distant metastatic sites, the tumors no longer showed the characteristic histology described in the luminal lesions; similar to the surgical pathology material, extravascular tumors took on the appearance of differentiated sarcomas, such as rhabdomyosarcoma (figure 7), osteosarcoma (figure 8), angiosarcoma (figure 9) and liposarcoma (figure 12)
- Multiple patterns were seen in a single case and even in a single metastatic site (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1184)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Virtual slides
Contributed by Matjaz Sebenik, M.D.
- All cases are from Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1184
- A: case #3
- B: case #9
- C: case #11
- D: case #12
- E: case #14
Positive stains
- Diffusely positive
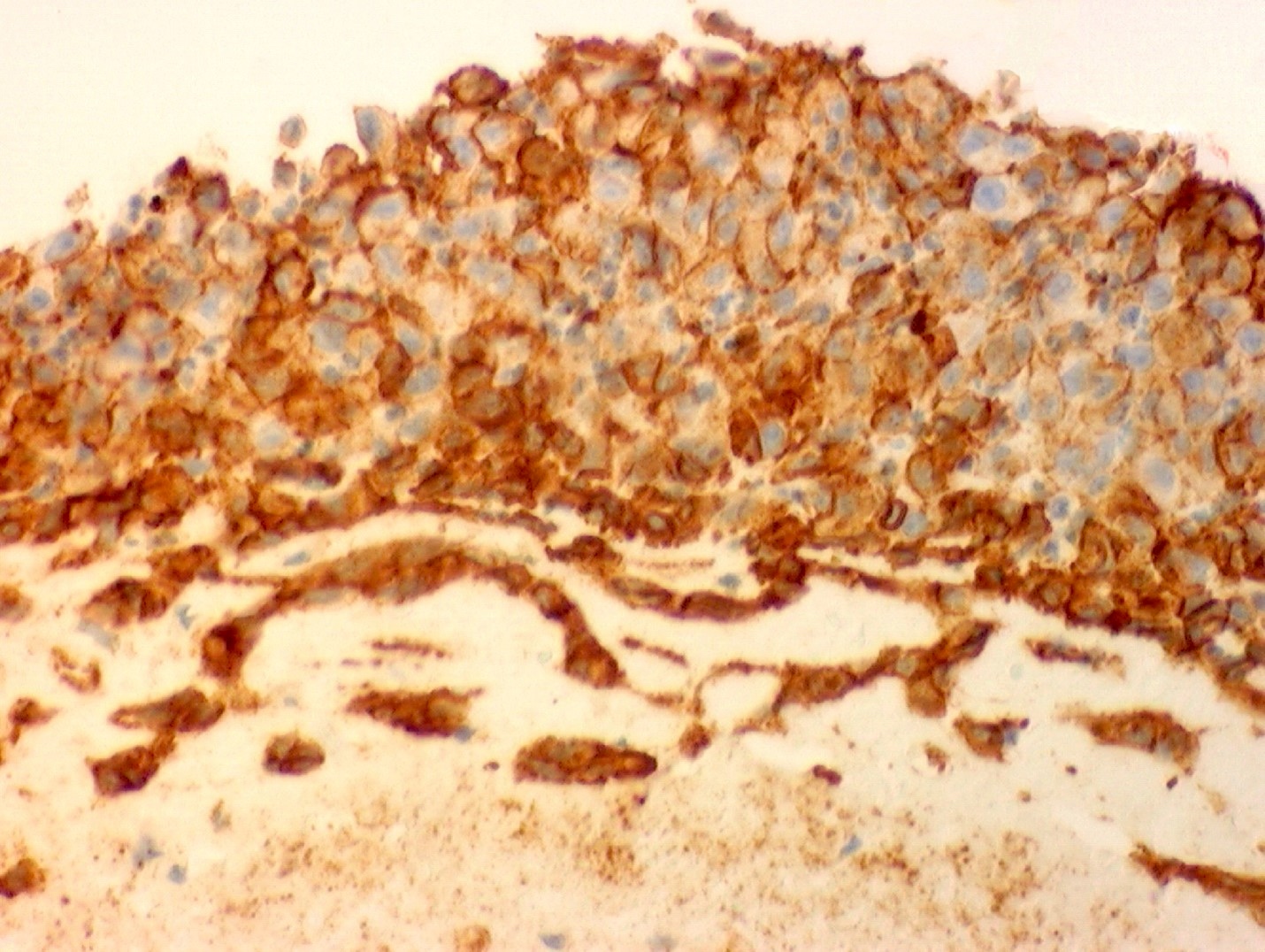
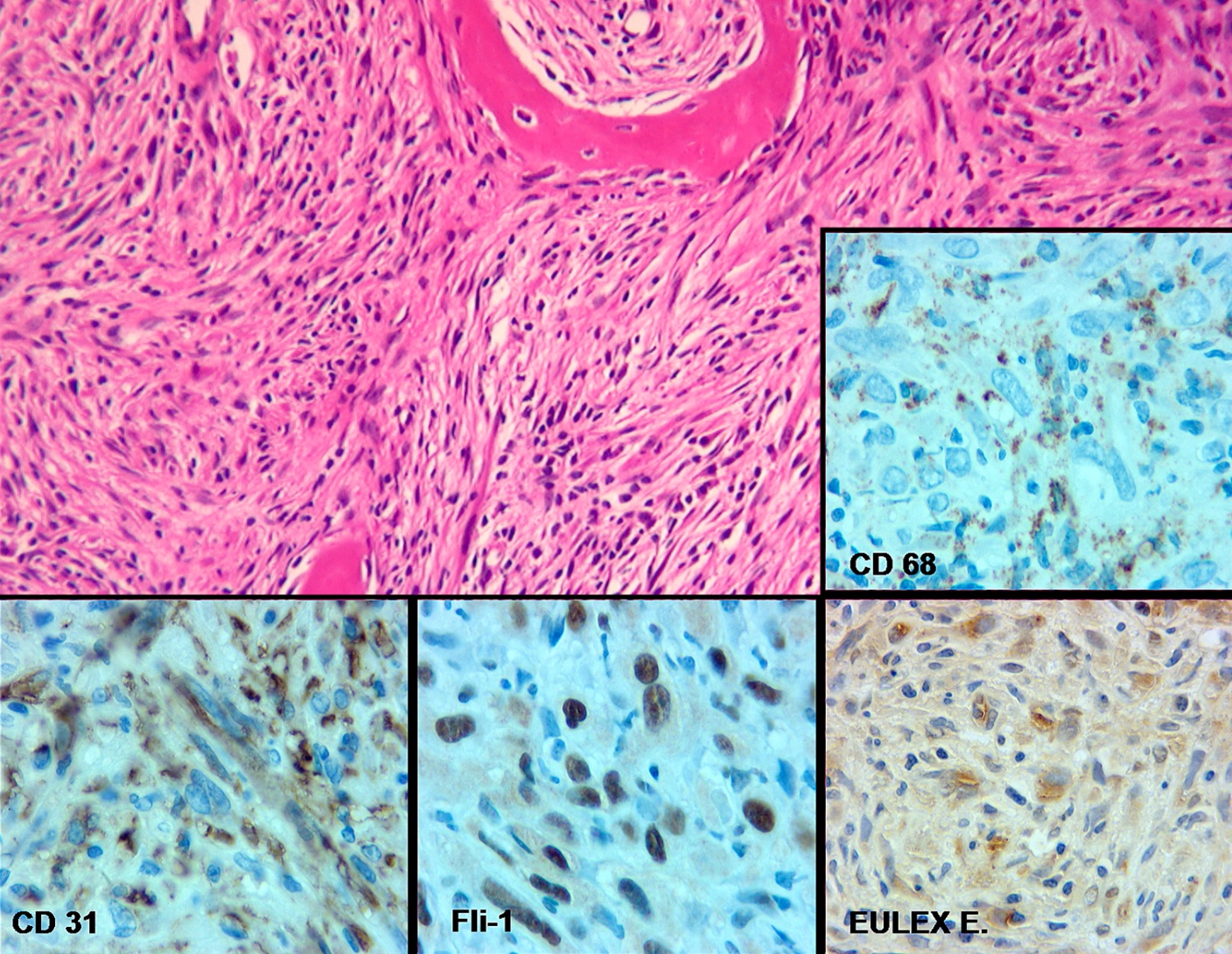
- CD31 shows strong membranous and moderate cytoplasmic staining outlining cellular ghosts forming a chicken wire-like pattern in areas of necrotic tumor (see figure 5)
- FLI1 generally shows strong nuclear staining occasionally associated with faint nonspecific cytoplasmic staining (see figure 6)
- Note: endothelial markers (CD31, FLI1, CD68, factor VIII and ulex europaeus) were preserved in the phenotypically altered tumors, like undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (see figure 11) and liposarcoma (see figure 12) (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1184)
- Strong immunoexpression for MDM2, CDK4, CD117, c-myc, PDGFRA and p16 (Int J Mol Sci 2023;24:7535)
Negative stains
- S100
- SOX10
- LCA
- CD68
- Predominantly negative stains
- Cytokeratin was identified in 2 of 14 tumors that were otherwise characteristic of undifferentiated intimal sarcoma, including reactivity to CD31 and FLI1
- Focal equivocal desmin staining in a metastatic tumor involving diaphragm was present in cells of 1 tumor that had some rhabdoid features (see figure 7) (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1184)
- CD34 is positive in 5% of cases of IS of systemic vessels (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1184, Cancer 1993;71:1761, Cardiovasc Pathol 2019:43:107142)
Electron microscopy description
- Fine structure is nonspecific (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1184)
- Viable appearing cells are ovoid with a high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio
- Nuclei are irregular and deeply convoluted with marginated condensed heterochromatin
- About 33% of cases show focal perinuclear intermediate filaments
- Cytoplasm is devoid of specific organelles like melanosomes or Weibel-Palade bodies
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- High level amplification of MDM2 was detected by both FISH and DISH (Cardiovasc Pathol 2019:43:107142, Mod Pathol 2021;34:2122)
- MDM4 and CDK6 amplifications in intimal sarcomas, lacking MDM2 amplification (Mod Pathol 2021;34:2122)
- Recurrent coamplifications in PDGFRA, CDK4, TERT, HDAC9, KIT and CCND1 (Mod Pathol 2021;34:2122, Int J Mol Sci 2023;24:7535)
- DNA methylation profiling (t-SNE) revealed an overlap of intimal sarcoma and cardiac undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (Mod Pathol 2021;34:2122)
Sample pathology report
- Mass, aorta, excision:
- Intimal sarcoma (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show proliferation of oval to round cells covering thrombus. Nuclei are hyperchromatic, nucleoli are prominent. Cells are predominantly limited to intima (supported by elastic stain) and only very focally invade media. Tumor cells are diffusely positive for CD31 and FLI1, focally positive for factor VIII and CD34, and negative for AE1 / AE3, SOX10 and HMB45. MDM2 immunohistochemistry shows positivity in the tumor nuclei. FISH study shows MDM2 and CDK4 amplification. The histologic, immunohistochemical and molecular findings are consistent with a diagnosis of intimal sarcoma.
Differential diagnosis
- Intravascular lymphoma:
- Most common in capillaries to medium sized vessels, especially in brain and skin; occasionally seen in larger systemic vessels, such as aorta
- Most cases are of B lineage, occasionally of T lineage
- T cell cases should generally be considered a different disease
- Positive for LCA and B cell markers; negative for CD31 and FLI1 (BMC Nephrol 2018;19:300)
- Metastatic carcinoma:
- Secondary (metastatic) aortic malignant neoplasms are more commonly seen than primary tumors and are more readily diagnosed, possibly owing to the knowledge of a pre-existing primary tumor
- There appears to be no age predilection (J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Tech 2018;4:160)
- In the thoracic region, invasion from the lungs, esophagus and thymoma is the usual scenario (Semin Ultrasound CT MR 2012;33:265)
- Retroperitoneal sarcomas and germ cell tumors are the most common malignant neoplasms invading the abdominal aorta, potentially with resultant aneurysm or pseudoaneurysm formation and rupture (Ann Vasc Surg 2008;22:568)
- Usually present in vasa vasorum and adventitia, not in the tunica intima (Discoveries (Craiova) 2020;8:e106)
- Positive for carcinoma markers; negative for CD31 and FLI1
- Leiomyoma / leiomyosarcoma (LMS):
- Originates from smooth muscles of tunica media
- 5 times more common in veins than in arteries
- 50% of venous LMS originate in inferior vena cava, 25% in saphenous vein, the rest in femoral vein, internal jugular vein or iliac vein
- Majority of the extremity venous LMS arise from lower extremity
- Histologically are indistinguishable from their soft tissue counterpart diagnosis (Ann Vasc Surg 2019;57:274.e5)
- Positive for smooth muscle markers; negative for endothelial markers
- Angiosarcoma:
- In theory, primary angiosarcomas of aorta should feature intima based vasoformative histologic pattern typical of soft tissue angiosarcomas
- To date, no vasoformative cases have been described in the aortic intima
- Published cases of primary angiosarcoma of the aorta are actually intimal sarcomas, which were called angiosarcomas because of positive staining for endothelial markers or because they featured vasoformative structures outside of tunica intima (i.e., within the native vessel wrap) (J Vasc Surg 1991;14:87)
- Metastatic melanoma:
- Melanoma cells are most frequently found embedded in the fibrinous blood clot
- Positive for melanoma markers; negative for CD31 and FLI1 (J Vasc Surg 2002;36:191)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 45 year old woman presented with a hypertensive crisis. Computed tomography (CT) revealed a thoracic aortic tumor and tissues obtained via endovascular biopsy revealed a thrombus rimmed by atypical cells, which were positive for CD31 and FLI1 and negative for LCA, CD20, SOX10 and HMB45. Despite undergoing surgical resection followed by adjuvant chemotherapy, the patient died from progressive multiple metastasis and severe sepsis only 3 months later. What is the diagnosis?
- High grade sarcoma, consistent with intimal sarcoma
- Intravascular lymphoma
- Metastatic carcinoma
- Metastatic melanoma
- Thromboembolus
Board review style answer #1
A. High grade sarcoma, consistent with intimal sarcoma. Answer A is correct because malignant cells covering the thrombus are positive for CD31 and FLI1 and negative for LCA, CD20, SOX10 and HMB45. Answer B is incorrect because intravascular lymphoma is stained with endothelial, not lymphatic markers. Answer D is incorrect because metastatic melanoma is stained with endothelial, not melanoma markers. Answer C is incorrect because metastatic carcinoma is stained with endothelial (not carcinoma) markers and because it was intimal (metastatic carcinomas involve adventitia and vasa vasorum, not intima). Answer E is incorrect because the thrombus in this case is covered by malignant cells.
Comment Here
Reference: Intimal sarcoma
Comment Here
Reference: Intimal sarcoma
Board review style question #2
What is the most common location of intimal sarcoma?
- Aorta
- Heart
- Pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary vein
- Systemic vein
Board review style answer #2
C. Pulmonary artery. Answer C is correct because the pulmonary artery is involved in ~47% of cases. Answer A is incorrect because the aorta is involved in ~19.5% of cases. Answer E is incorrect because systemic veins are involved in ~1.9% of cases. Answer B is incorrect because the heart is involved in ~28% of cases. Answer D is incorrect because pulmonary veins are involved in ~0.3% of cases.
Comment Here
Reference: Intimal sarcoma
Comment Here
Reference: Intimal sarcoma