Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Xie Y, Saleeb R. ABCC2. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsABCC2.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding cassette subfamily C member 2 (ABCC2) belongs to the C subfamily of the ABC transmembrane protein transporters
- It is located on chromosome 10 (Nat Rev Cancer 2010;10:147)
- ABCC transporters are involved in active drug transportation
- Contributes to chemotherapy resistance in some tumors by what is thought to be drug efflux mechanisms
- Recent publications show that ATP transporters contribute to cancer aggressiveness beyond the drug efflux effect (Cancer Biol Med 2020;17:253)
- Also called multidrug resistant protein 2 (MRP2)
Essential features
- ABCC2 staining patterns could potentially be used as prognostic biomarkers in papillary renal cell carcinomas (PRCC); the brush border staining pattern was shown to predict disease progression on both univariate and multivariate disease free survival analysis (Hum Pathol 2022;120:57, Mod Pathol 2022;35:657)
- ABCC2 has prognostic significance in some tumors, particularly papillary renal cell carcinoma, as well as breast, colon, pancreas, ovary and fallopian tube
- Might have predictive significance as it has been implicated in chemotherapy resistance
Terminology
- Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding cassette subfamily C member 2 (ABCC2)
- Multidrug resistance associated protein 2 (MRP2)
- Canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter 1 (CMOAT1)
- Canalicular multidrug resistance protein (cMRP)
- ABC30
- Dubin-Johnson syndrome (DJS)
Pathophysiology
- ABC transporters have 7 subfamilies
- In mammals, ABC transporters are expressed in liver, intestine, blood brain barrier, placenta and kidney, with 49 ABC genes in the human genome (Hum Genomics 2009;3:281)
- ABCC2 belongs to the C subfamily, also known as multidrug resistance protein family (Nat Rev Cancer 2010;10:147)
- They are involved in active drug transportation
- ABCC2 itself is only expressed in proximal renal tubules, bile canaliculi and placenta (Drug Metab Rev 2010;42:402)
- ABCC2 contributes to chemotherapy resistance through active ATP dependent efflux of drugs (Nat Rev Cancer 2010;10:147)
- Some studies indicate that ABC transporters play a role in tumor biology beyond the efflux properties (Nat Rev Cancer 2010;10:147, Cancer Biol Med 2020;17:253)
- Transporters are ATP dependent
- Cells enriched in ABC transporters are reported to be larger than average and hold numerous mitochondria to compensate for the high energy demand of the transporter
- This could contribute to the oncocytic nature of some of the reported ABCC2 high tumors (Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2005;5:457)
- Renal drug transporters, including ABCC2, are upregulated downstream to the NRF2-ARE pathway, which is enriched in high grade papillary renal cell carcinoma (old type 2) (N Engl J Med 2016;374:135, Toxicol In Vitro 2015;29:884)
Clinical features
- Germline mutations in ABCC2 are associated with autosomal recessive Dubin-Johnson syndrome
- It is characterized by impaired secretion of conjugated bilirubin by hepatocytes
- Grossly, the liver is black in appearance
- Microscopically, there is accumulation of dark, PASD positive, coarsely granular pigment in the centrilobular zone
- Electron microscopy shows the pigment accumulating in lysosomes
- These patients are usually asymptomatic, with incidental detection of hyperbilirubinemia (StatPearls: Dubin Johnson Syndrome [Accessed 25 July 2023])
Interpretation
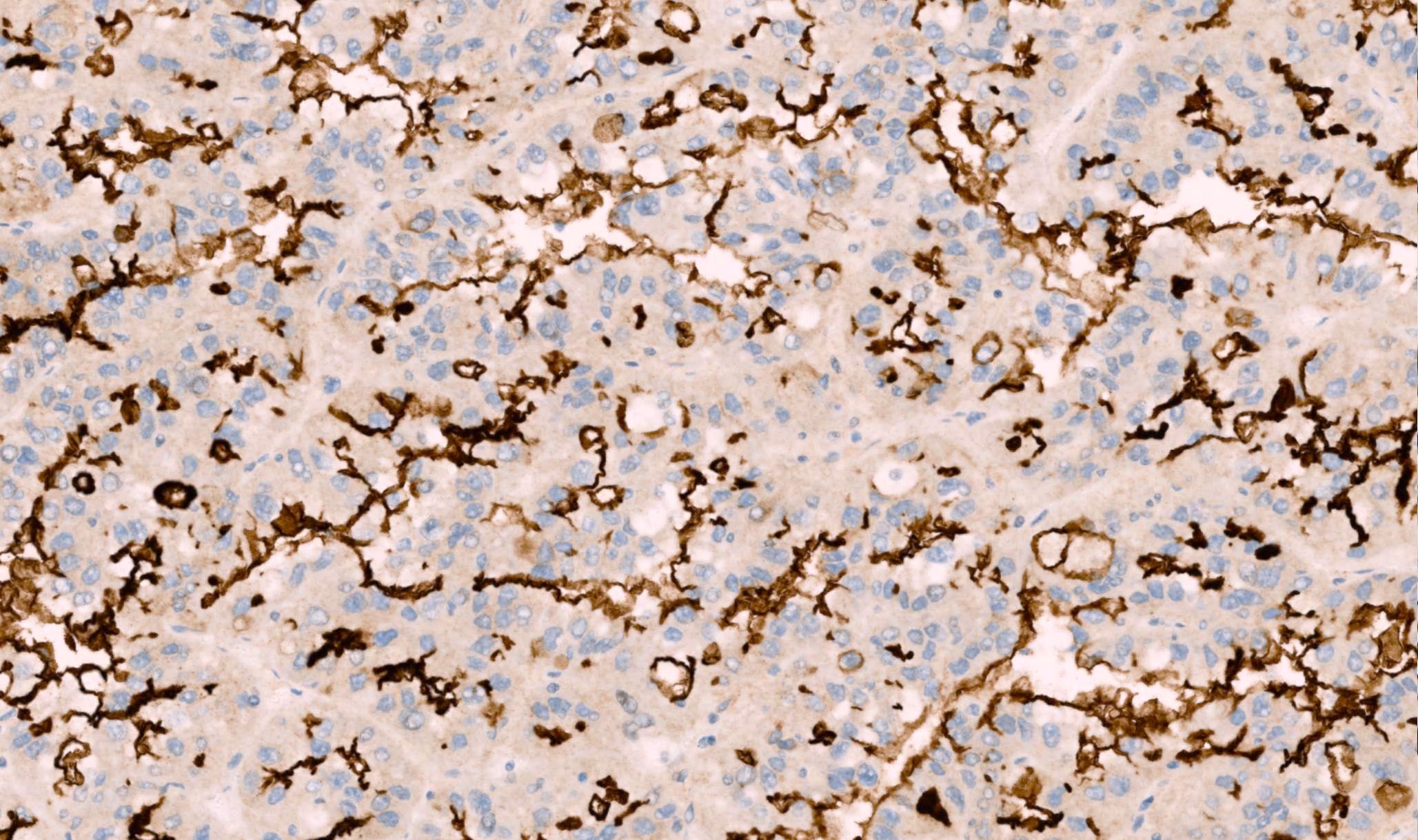
- Normally expressed in the proximal renal tubules and bile canaliculi; it is expressed predominantly as a brush border pattern in proximal renal tubules, accompanied often with some weak / blush granular cytoplasmic staining
- Cytoplasmic and brush border expression using ABCC2 knock out validated monoclonal antibody in papillary renal carcinoma (Hum Pathol 2022;120:57)
- Quantity of brush border staining is shown to be significant in predicting survival (USCAP 2023 Abstracts: Genitourinary Pathology (Including Renal Tumors) [Accessed 25 July 2023])
- Additional nuclear staining reported in breast, ovary and fallopian tube (Pathol Oncol Res 2012;18:331, Clin Cancer Res 2006;12:7149, Arch Gynecol Obstet 2013;287:563)
Uses by pathologists
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma: pattern of ABCC2 expression provides prognostic stratification
- Latest evidence shows that only brush border expression predicts disease progression in papillary renal cell carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1618, Hum Pathol 2022;120:57, USCAP 2023 Abstracts: Genitourinary Pathology (Including Renal Tumors) [Accessed 25 July 2023])
- There is some evidence that ABCC2 expression might have predictive value in papillary renal cell carcinoma (Mol Oncol 2018;12:1673)
- Dubin-Johnson syndrome related cholestasis: loss of MRP2 / ABCC2 in canalicular membranes of hepatocytes
Prognostic factors
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma can be prognostically stratified using monoclonal knock out validated ABCC2 IHC (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1618, Eur Urol Focus 2018;4:740, Hum Pathol 2022;120:57, USCAP 2023 Abstracts: Genitourinary Pathology (Including Renal Tumors) [Accessed 25 July 2023])
- Negative and cytoplasmic staining showing favorable survival outcomes
- Brush border expression associated with poor prognosis
- Prognostic and predictive marker for other tumors
- ABCC2 immunohistochemistry is reported to have prognostic value and potential predictive value (associated with chemotherapy resistance) in colon carcinoma, pancreatic carcinoma, ovarian carcinoma, fallopian tube carcinoma and breast carcinoma (Gynecol Oncol 2006;100:239, Clin Cancer Res 2000;6:2401, Clin Cancer Res 2006;12:7149, Pathol Oncol Res 2012;18:331, Arch Gynecol Obstet 2013;287:563, Sci Rep 2019;9:19782)
- Possible predictive value in metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma (Mol Oncol 2018;12:1673)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1618, Hum Pathol 2022;120:57, USCAP 2023 Abstracts: Genitourinary Pathology (Including Renal Tumors) [Accessed 25 July 2023])
- Negative: shows complete absence of ABCC2 staining
- Cytoplasmic: weak (blush) granular cytoplasmic staining equal to the background proximal renal tubules
- < 50% brush border: patchy or focal brush border ABCC2 staining in < 50% of the tumor; internal control for brush border expression is the proximal renal tubules
- ≥ 50% brush border: strong or diffuse brush border staining involving ≥ 50% of the tumor
- May help to distinguish some oncocytic / eosinophilic papillary renal cell carcinomas (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1099, USCAP 2023 Abstracts: Genitourinary Pathology (Including Renal Tumors) [Accessed 25 July 2023])
- Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity: weak cytoplasmic staining of ABCC2 and negative for brush border expression, which corresponds to no or minimal RNA ISH transcripts; they harbor GATA3+ nuclear staining
- Eosinophilic papillary renal cell carcinoma: brush border ABCC2 expression, with corresponding high RNA ISH transcript level
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Renal tubules (weak blush cytoplasmic and brush border; monoclonal antibody) (Hum Pathol 2022;120:57)
- Liver bile canaliculi (bile canaliculi expression, brush border expression; monoclonal antibody) (J Tissue Eng Regen Med 2018;12:2287)
- Endocrine pancreas - membranous (Histopathology 2002;41:65)
- Small intestine / colon (Histopathology 2002;41:65)
Positive staining - disease
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma (weak blush cytoplasmic and brush border) (Hum Pathol 2022;120:57)
- Colon adenocarcinoma (cytoplasmic) (Clin Cancer Res 2000;6:2401)
- Pancreatic adenocarcinoma - brush border (Sci Rep 2019;9:19782)
- Ovarian cancer (cytoplasmic and nuclear) (Gynecol Oncol 2006;100:239, Clin Cancer Res 2006;12:7149)
- Breast carcinoma (cytoplasmic and nuclear) (Pathol Oncol Res 2012;18:331)
- Fallopian tube carcinoma (cytoplasmic and nuclear) (Arch Gynecol Obstet 2013;287:563)
Negative staining
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma (low risk group) (Hum Pathol 2022;120:57)
- Glomeruli (Hum Pathol 2022;120:57)
- Brain (J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2004;311:449)
- Lymph nodes (Histopathology 2002;41:65)
- Endocrine pancreas (Histopathology 2002;41:65)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Molecular analysis of papillary renal cell carcinoma showed statistically significant very high ABCC2 gene expression by RNA sequencing platform in papillary renal cell carcinoma formerly classified as type 2
- Data was based on The Cancer Genome Atlas papillary cohort (Eur Urol Focus 2018;4:740)
- ABCC2 RNA transcripts can be quantitatively assessed by ISH (USCAP 2023 Abstracts: Genitourinary Pathology (Including Renal Tumors) [Accessed 25 July 2023])
- Negative: complete absence of RNA signals
- Cytoplasmic blush: focal cytoplasmic RNA ISH signals
- Brush border < 50%: scattered punctate RNA ISH signals
- Brush border ≥ 50%: dense, numerous RNA ISH signals
- Studies on colon cancer, breast carcinoma, fallopian tube carcinoma and ovarian carcinoma showed correlation between ABCC2 gene expression by polymerase chain reaction and clinical outcomes, as well as chemotherapy resistance (Gynecol Oncol 2006;100:239, Clin Cancer Res 2000;6:2401, Clin Cancer Res 2006;12:7149, Pathol Oncol Res 2012;18:331, Arch Gynecol Obstet 2013;287:563)
Sample pathology report
- Kidney, mass, nephrectomy:
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma (see comment)
- Comment: ABCC2 brush border staining pattern > 50% shown by immunohistochemistry.
Board review style question #1
A 56 year old man has an incidentally discovered renal mass, 4 cm in size. He was treated with partial nephrectomy. Microscopic examination shows a papillary renal cell carcinoma (PRCC). An immunopanel including ABCC2 IHC stain is ordered. Which pattern of staining may predict a poor clinical outcome?
- Brush border staining in ≥ 50% of the PRCC cells
- Complete absence of ABCC2 staining in the tumor with preserved staining in renal tubules
- Concurrent ABCC2 and GATA3 expression in PRCC cells
- Weak patchy cytoplasmic ABCC2 staining in the PRCC cells
Board review style answer #1
A. Brush border staining in ≥ 50% of the PRCC cells. Brush border ABCC2 staining in the tumor is shown to be a poor prognostic feature in papillary renal cell carcinoma ≤ 4 cm in size. Brush border pattern also correlates with higher ABCC2 RNA transcript by ISH. Answers B and D are incorrect because completely negative or cytoplasmic expression shows a relatively better prognosis. Answer C is incorrect because GATA3 positive papillary renal cell carcinoma is known as the entity of papillary renal neoplasm of reverse polarity which is quite indolent.
Comment Here
Reference: ABCC2
Comment Here
Reference: ABCC2