Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Electron microscopy images | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Kösemehmetoğlu K, Pernick N. D2-40 (Podoplanin). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsD240.html. Accessed April 18th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Podoplanin is a 40 kDa, transmembrane, oncofetal, O linked sialoglycoprotein (mucin type) found on lymphatic endothelium, mesothelium and fetal testis (also other cells as indicated below)
- D2-40 is a monoclonal antibody that reacts to podoplanin
- Podoplanin expression is encoded by the PDPN gene (1p36.21) and regulated by the PROX1 gene
Essential features
- D2-40 is a monoclonal antibody that reacts to podoplanin showing membranous staining
- Mostly used to show lymphatics (e.g. lymphovascular invasion) and lymphatic differentiation in vascular tumors
- Also useful as a part of IHC panel in mesothelioma versus adenocarcinoma and seminoma versus nonseminoma differentiation
Terminology
- Podoplanin is also known as Aggrus, OTS8, gp36, M2A and T1A2
Pathophysiology
- Increases endothelial cell adhesion, migration and tube formation
- Platelet aggregation (Aggrus)
- Barrier function in high endothelial venules
- Maintenance of physical elasticity of lymph nodes
- Reference: OMIM: Podoplanin; PDPN [Accessed 28 October 2021]
Interpretation
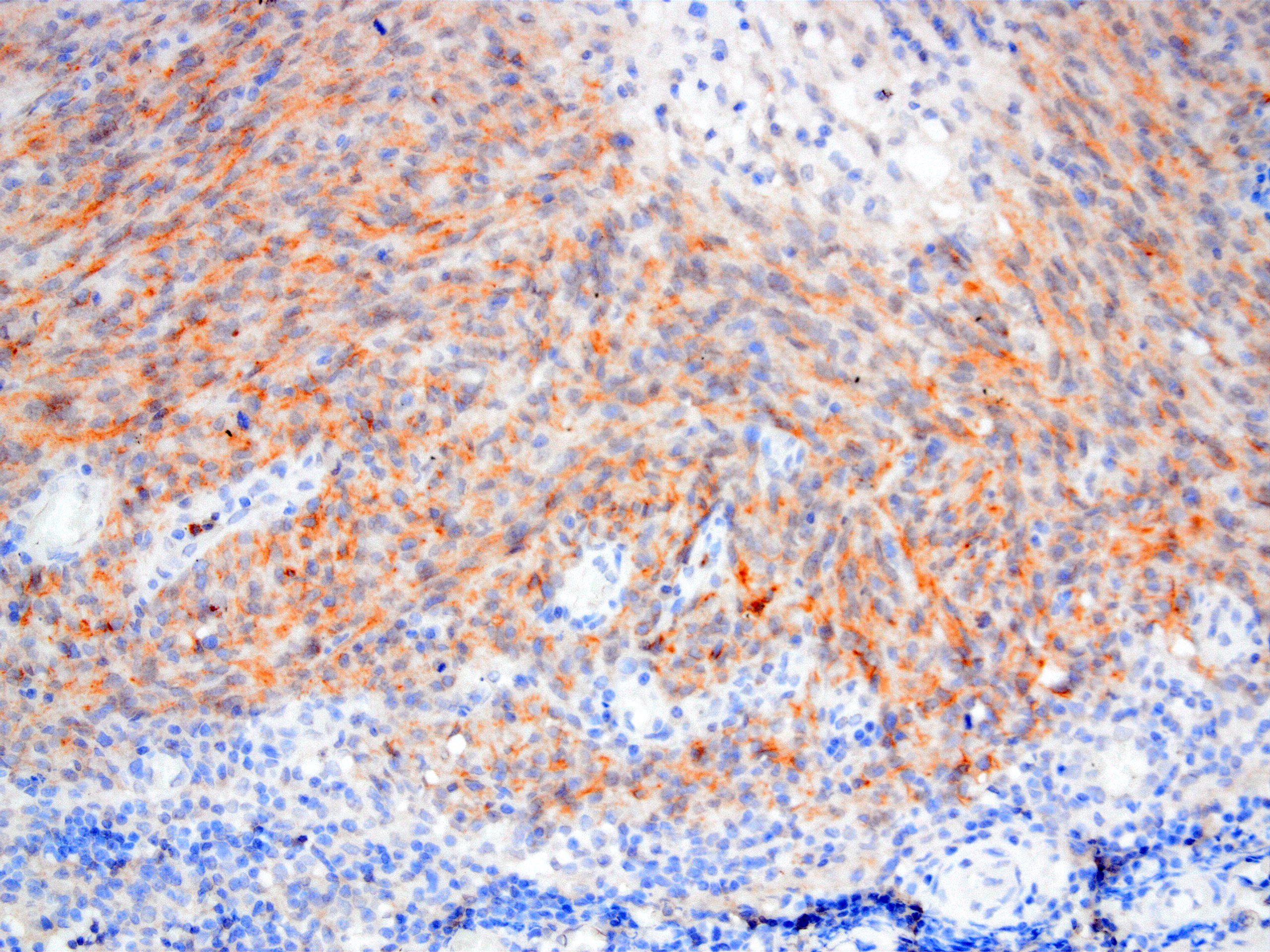
- Membranous staining (Adv Anat Pathol 2006;13:83)
- Dot-like (e.g. ependymoma) (Clin Neuropathol 2009;28:373)
Uses by pathologists
- Limited use because of lack of specificity; most efficient in IHC when used in an IHC panel
- To determine presence of lymphatics in various conditions (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1511)
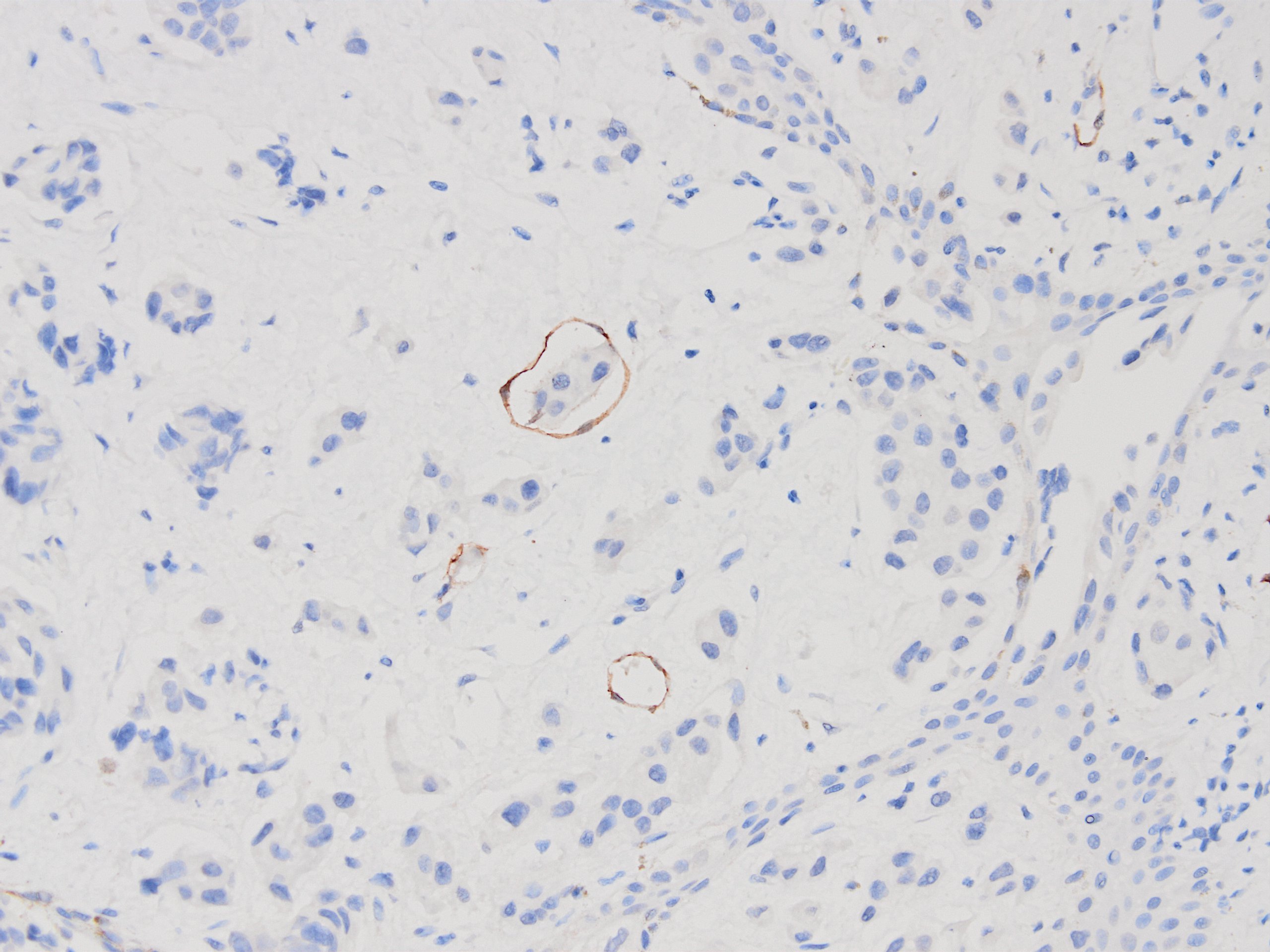
- Confirmation of lymphovascular invasion (Ann Diagn Pathol 2009;13:168, Mod Pathol 2007;20:183, Mod Pathol 2009;22:216, Int J Colorectal Dis 2009;24:1069, J Cutan Pathol 2009;36:1157, Arch Dermatol 2008;144:462, Hum Pathol 2008;39:901, Am J Surg Pathol 1989;13:177)
- Dermatopathology, bone and soft tissue pathology:
- Unlike other vascular markers (CD34, CD31, ERG, FLI1), D2-40 expression is limited to lymphatic differentiation
- To identify lymphatic differentiation in evaluation of vascular tumors
- Also expressed in a subset of angiosarcomas and Kaposi sarcomas, reflecting lymphatic differentiation in some of these tumors (Histopathology 2005;46:396, Mod Pathol 2002;15:434)
- Dermatofibroma (+) versus dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) (-) (Mod Pathol 2010;23:434)
- Primary skin adnexal tumors (+) versus metastatic adenocarcinoma (-) (Am J Dermatopathol 2018;40:389, J Cutan Pathol 2010;37:403)
- Chondrosarcoma (+) versus chordoma (-) (Acta Neuropathol 2007;113:87)
- Uropathology:
- Seminoma (+) versus nonseminoma (-)
- Note that some embryonal carcinomas may also express D2-40 up to 30% (Virchows Arch 2006;449:200, Mod Pathol 2007;20:320)
- In situ germ cell neoplasm (+)
- Adrenocortical neoplasms (+) versus renal cell carcinoma (-) (J Clin Pathol 2008;61:293)
- Utility in distinguishing intraductal spread of urothelial carcinoma from prostatic stromal invasion (Anticancer Res 2008;28:2997)
- Thoracic pathology:
- Mesothelioma (+), even in effusions, versus adenocarcinoma (-) (Diagn Cytopathol 2007;35:342, Cancer 2007;109:933)
- Note the presence of expression in significant proportion of ovarian, lung and breast carcinomas (30 - 50%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:878)
- Hemangioblastoma (+) versus clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis
Prognostic factors
- Controversial results of prognostic significance in detecting lymphovascular invasion with D2-40 compared to H&E in breast and other cancers (Mod Pathol 2009;22:216, Mod Pathol 2007;20:183, Hum Pathol 2018;77:98, Cancer Med 2016;5:3121, Anticancer Res 2008;28:2997, Cancer Lett 2007;246:167)
- D2-40 expression in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is associated with metastasis and poor prognosis (J Histotechnol 2020;43:147, J Cutan Pathol 2017;44:144, J Am Acad Dermatol 2012;67:1310)
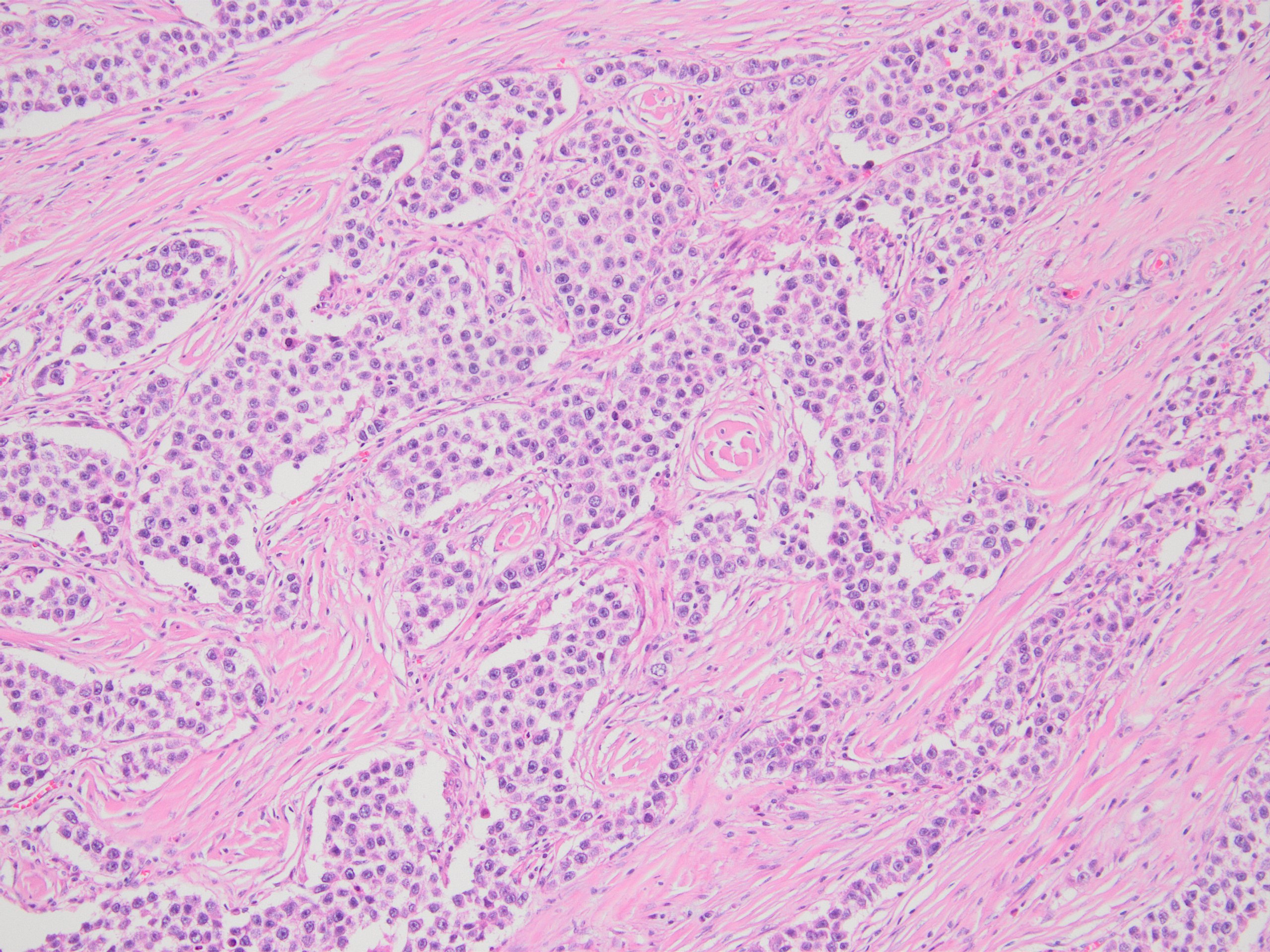
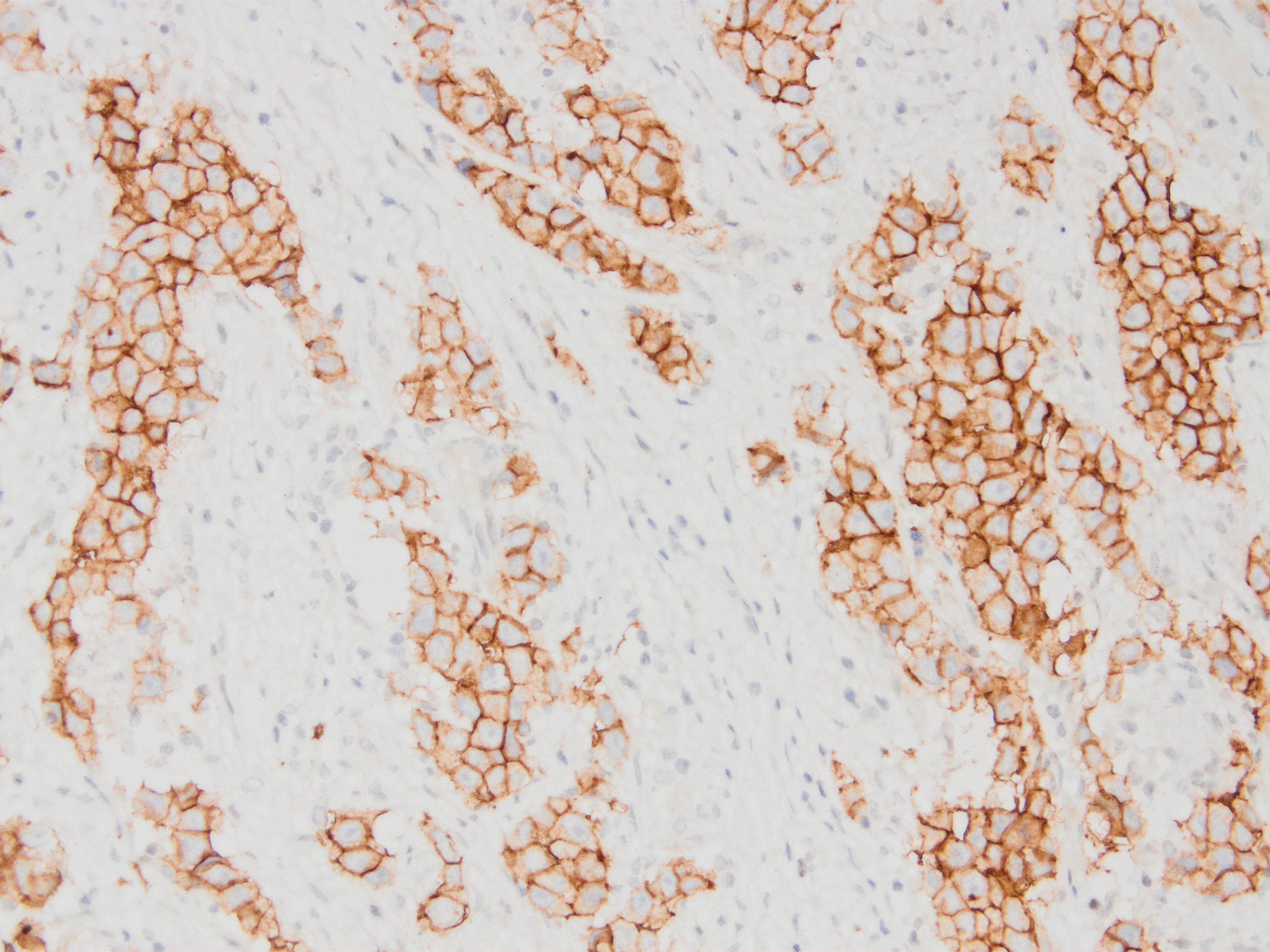
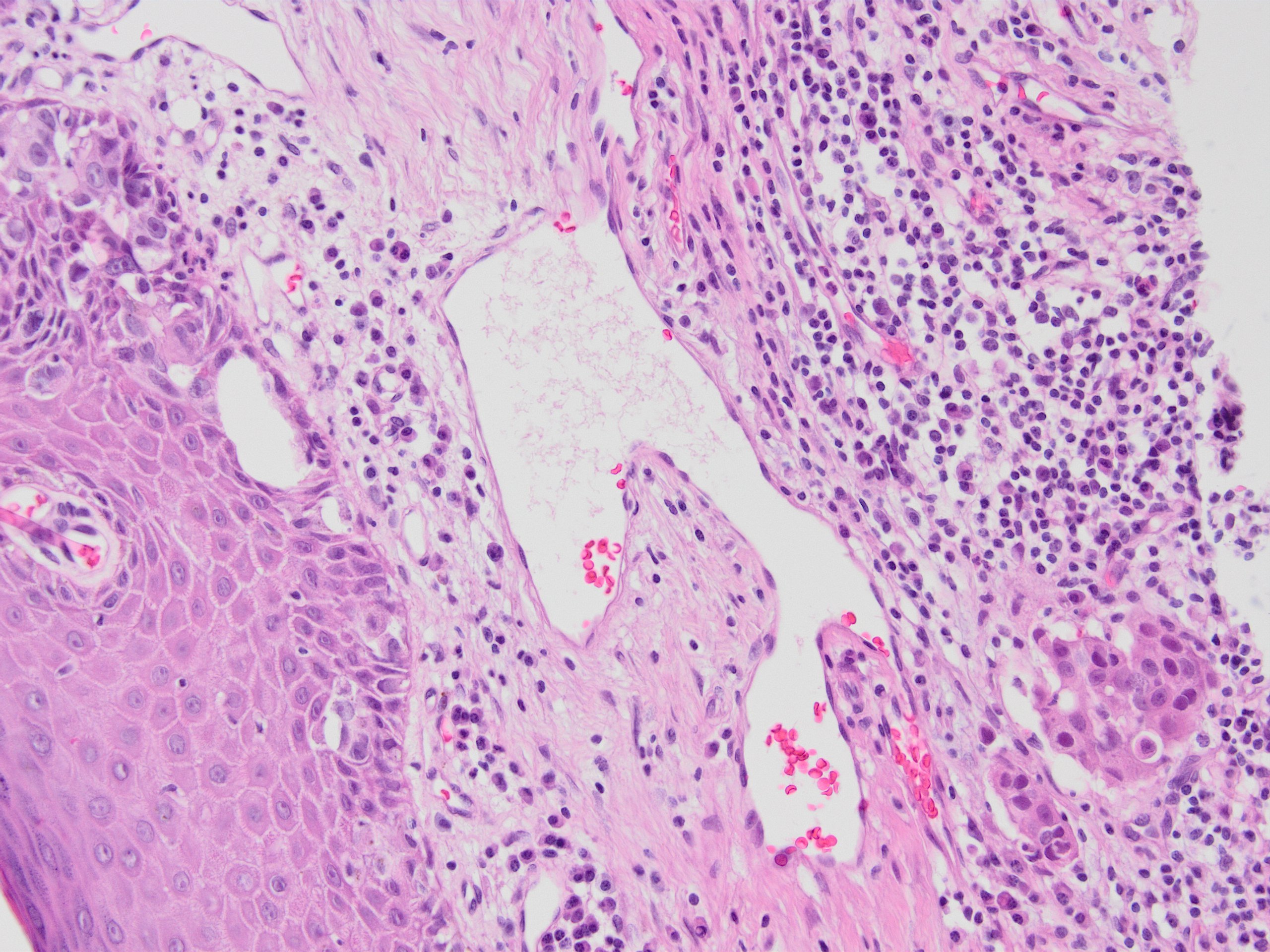
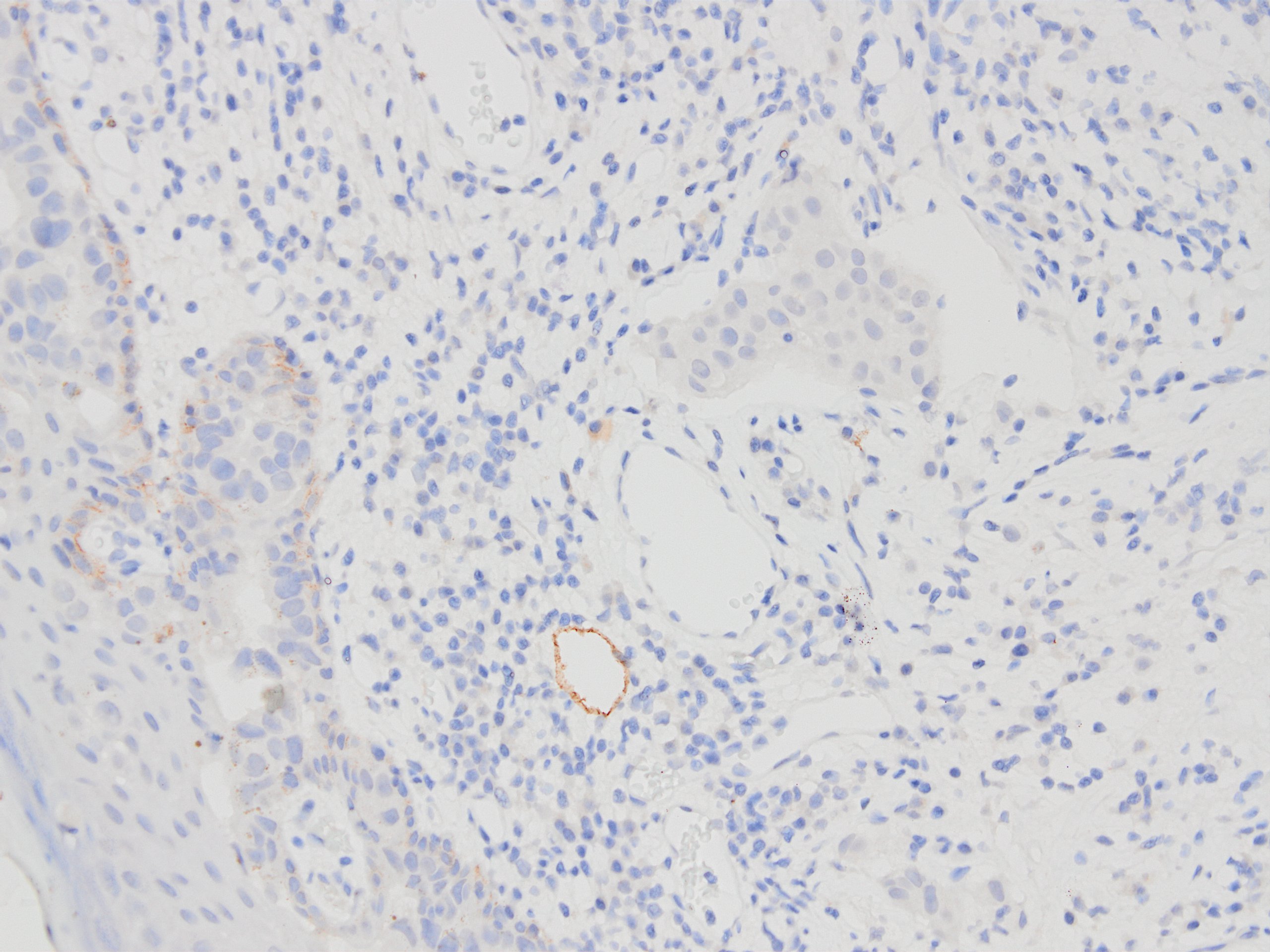
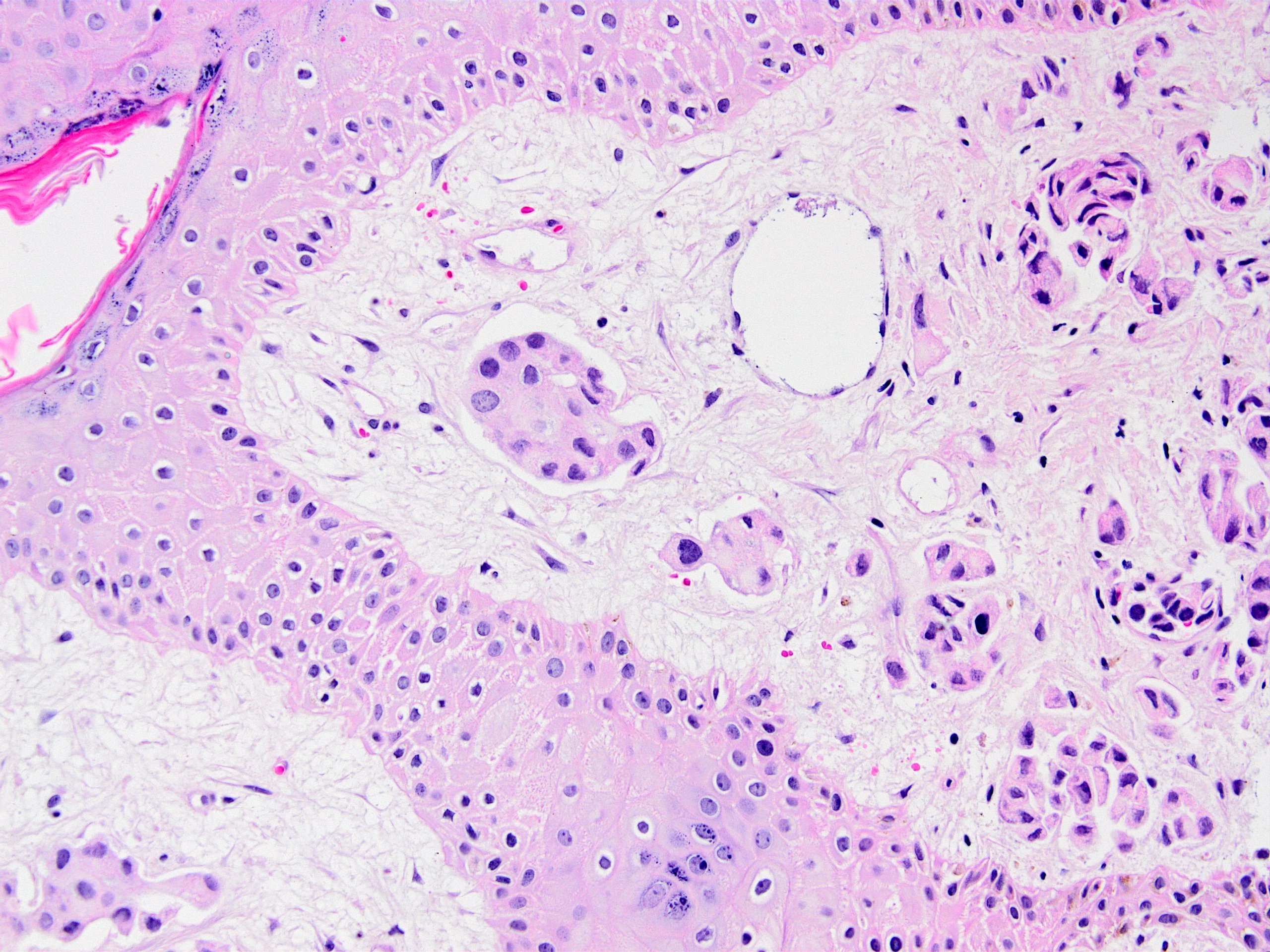
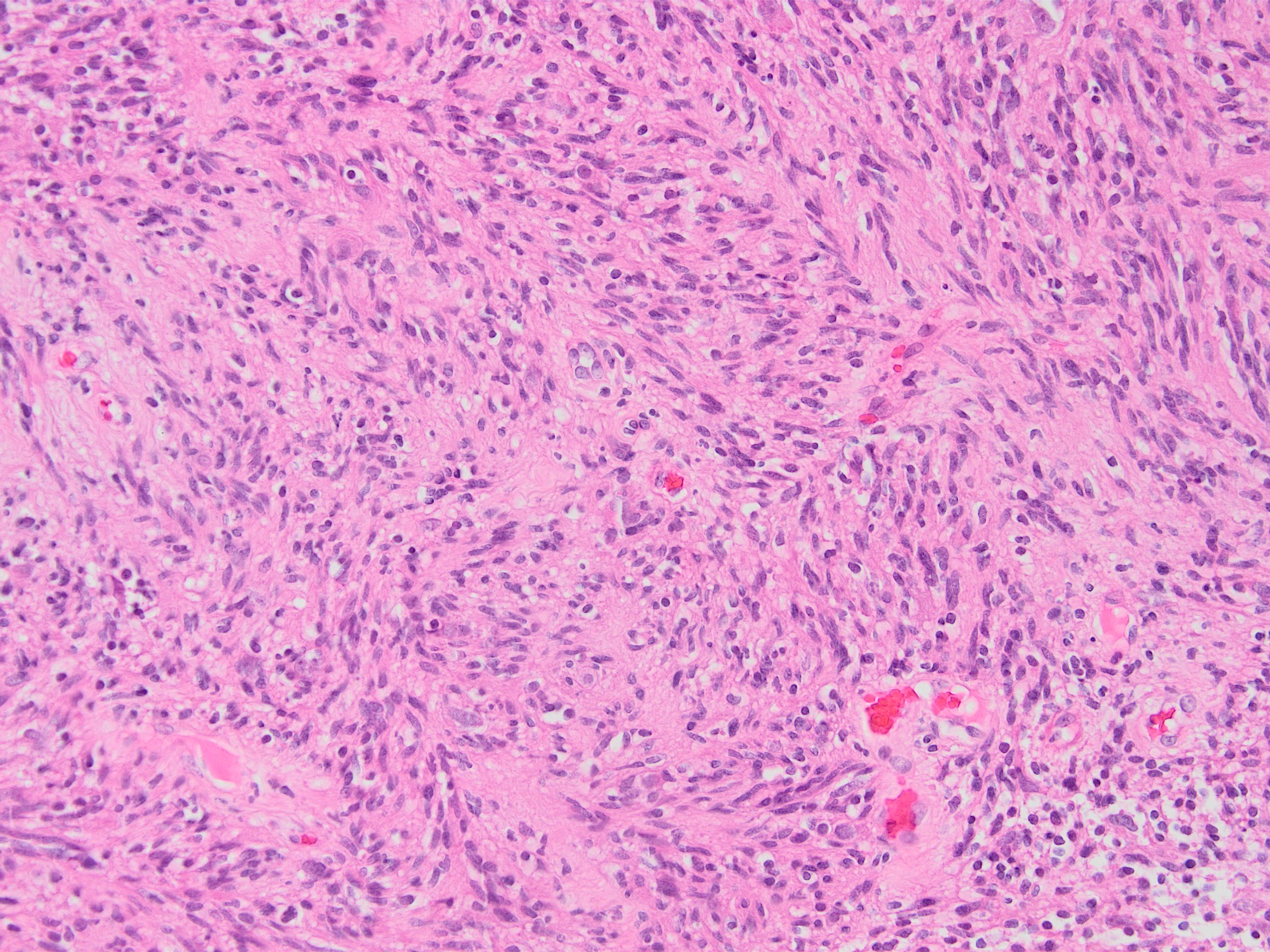
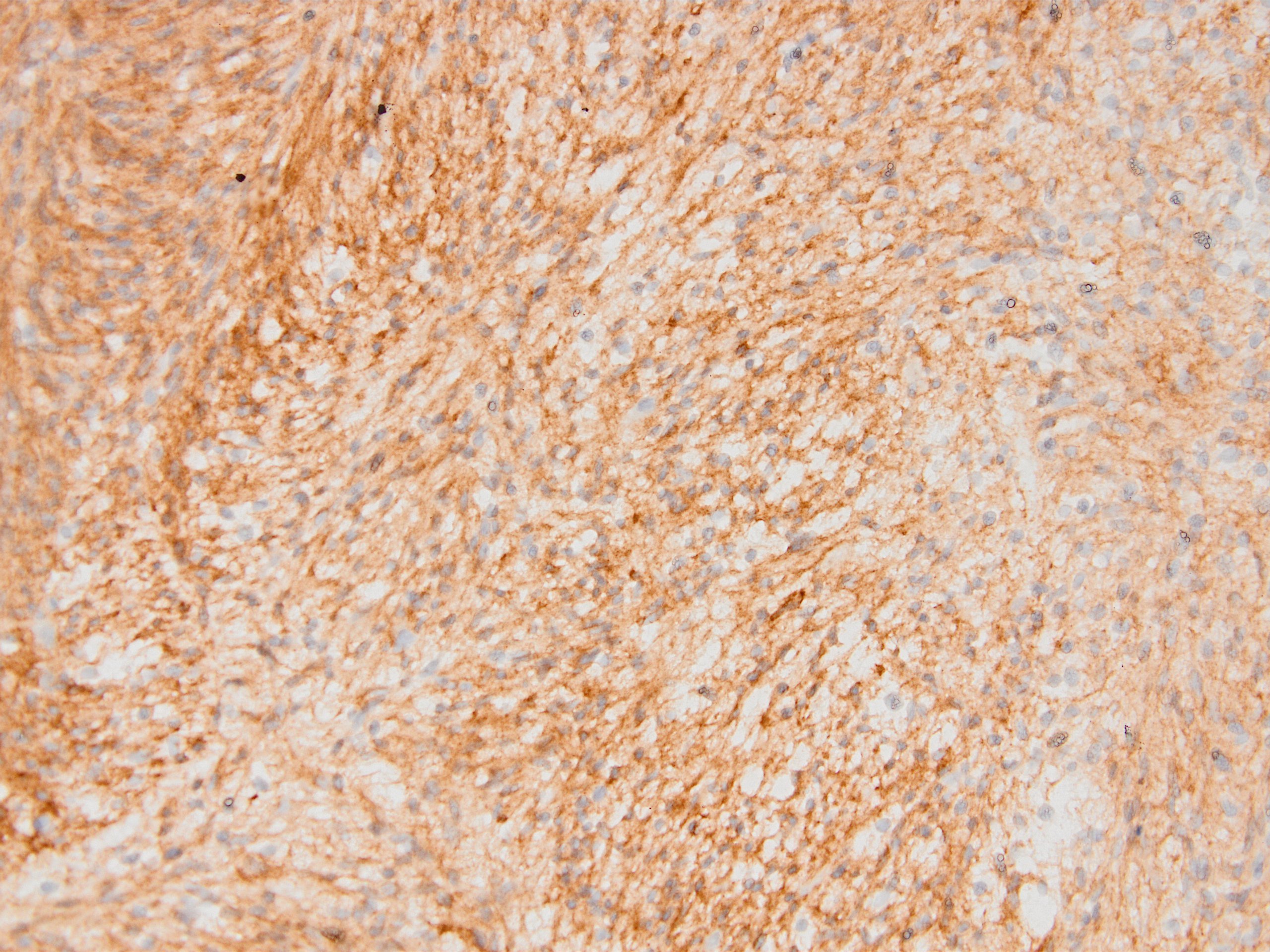
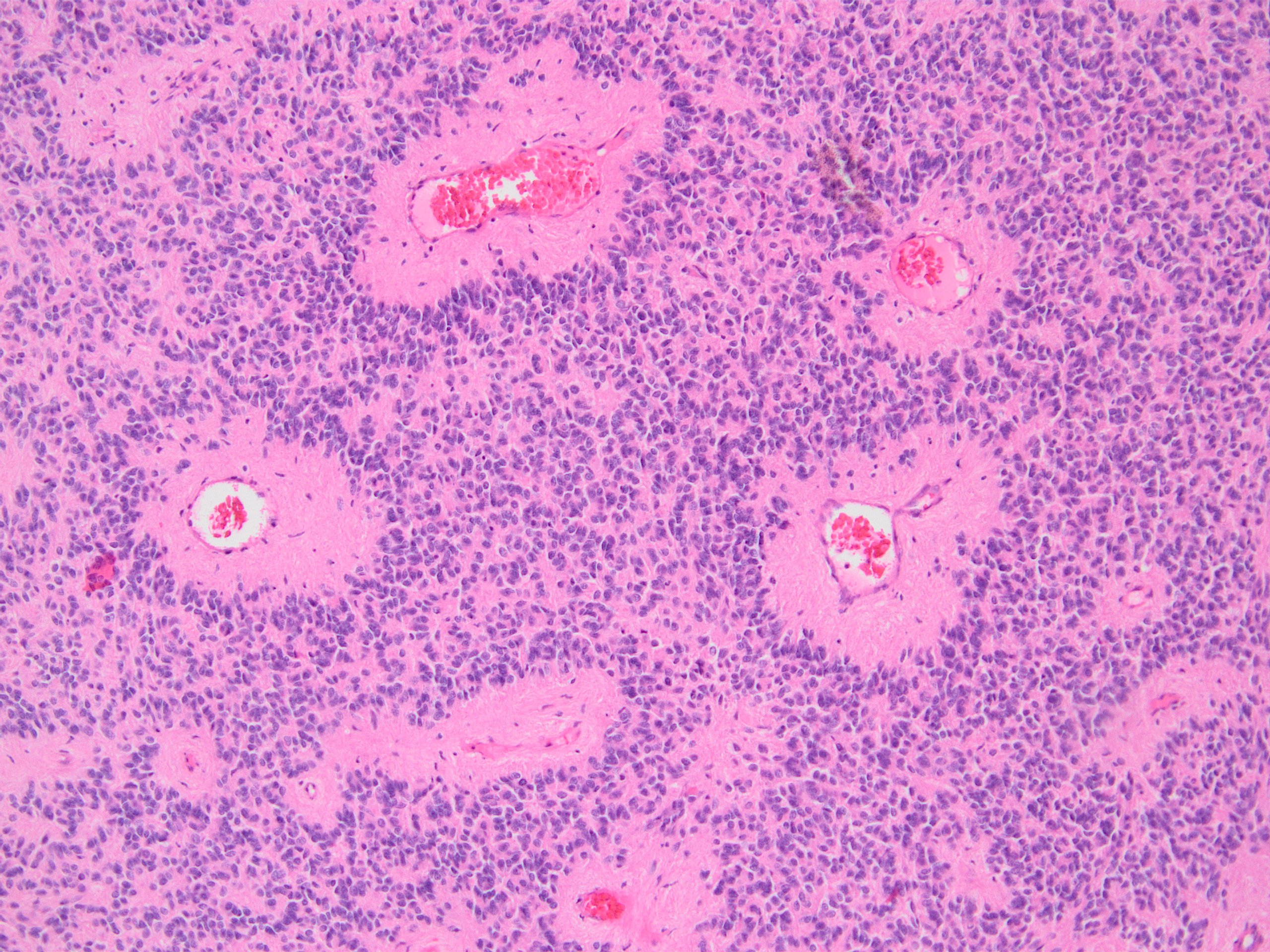
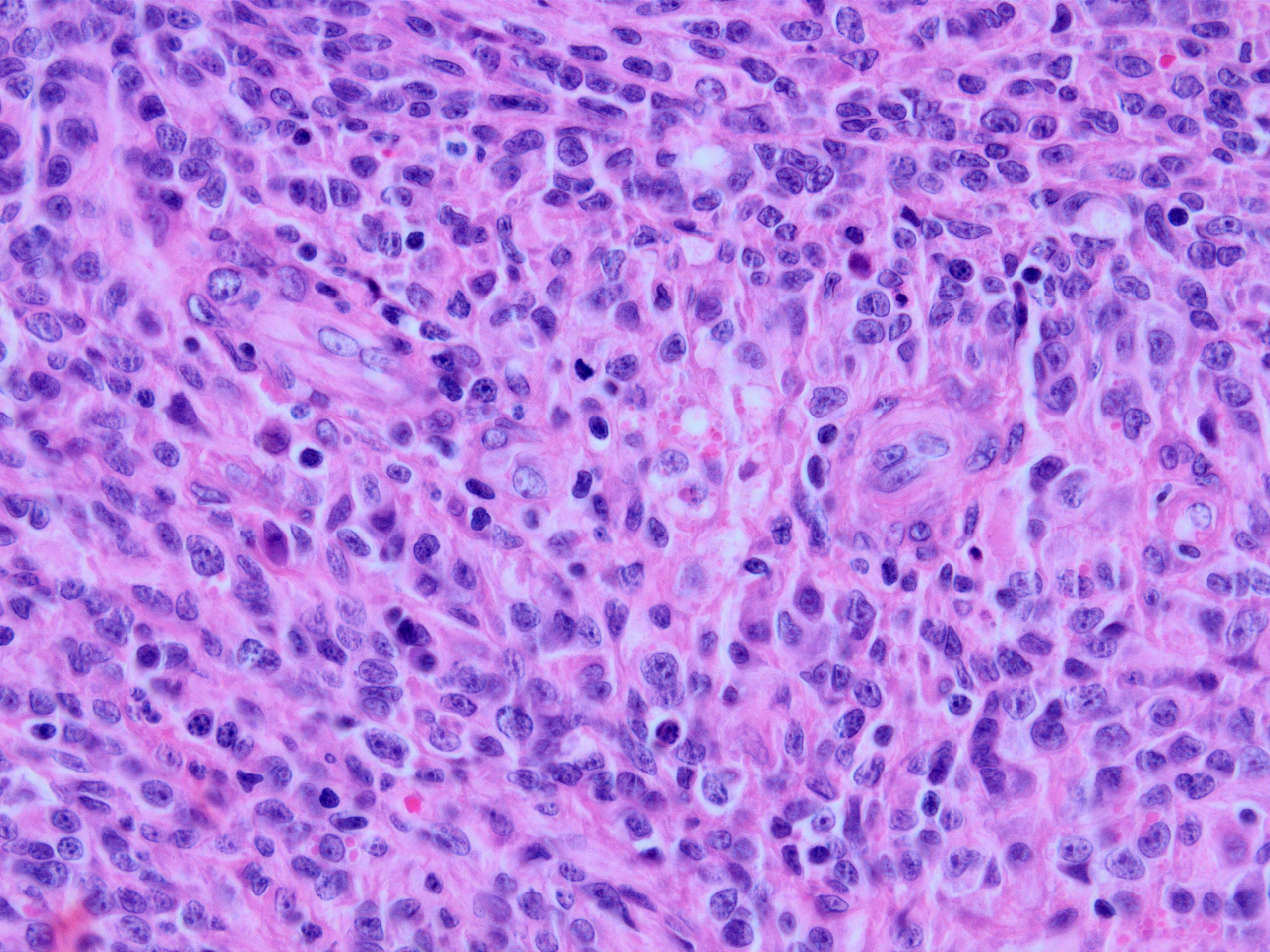
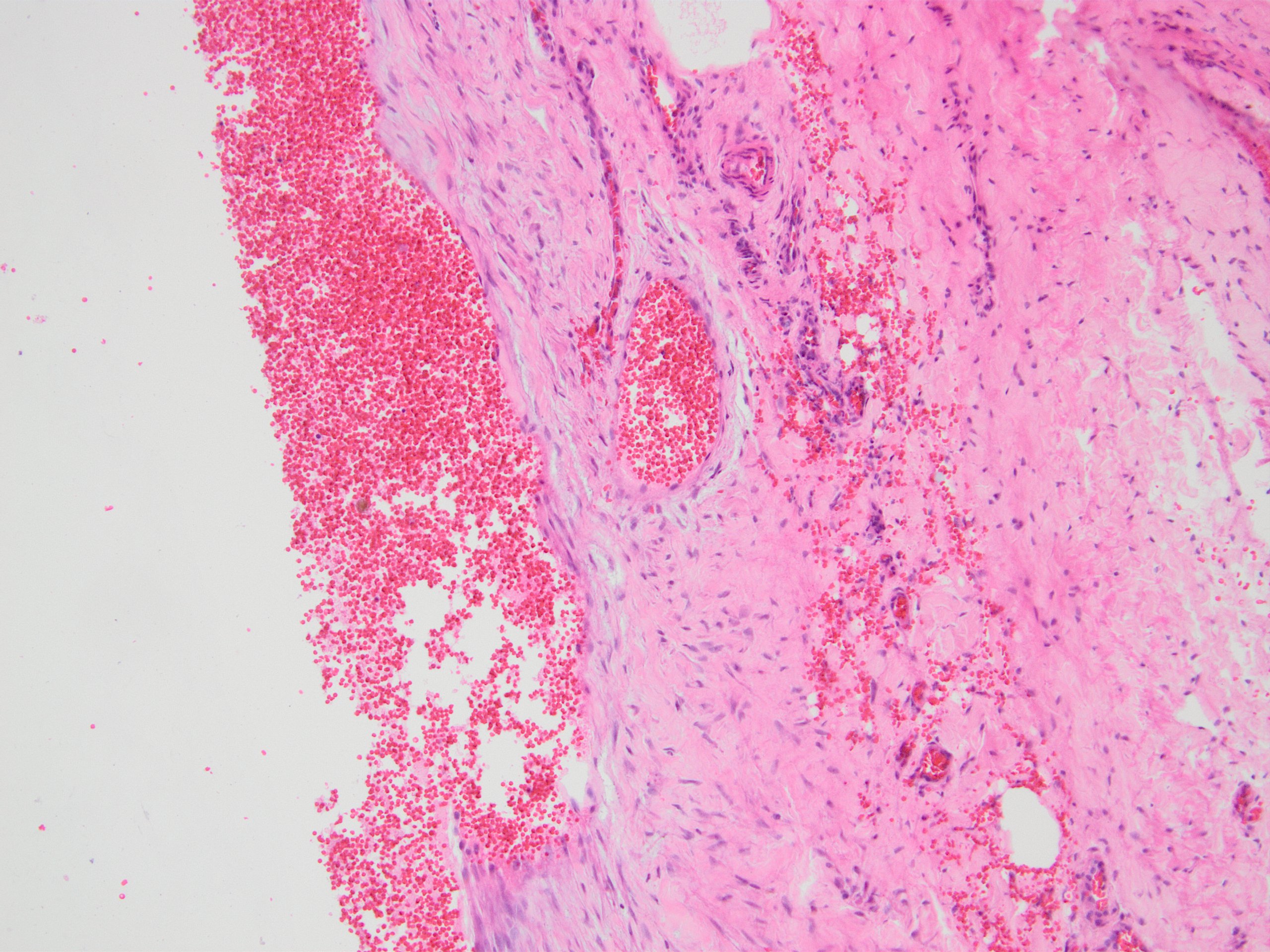
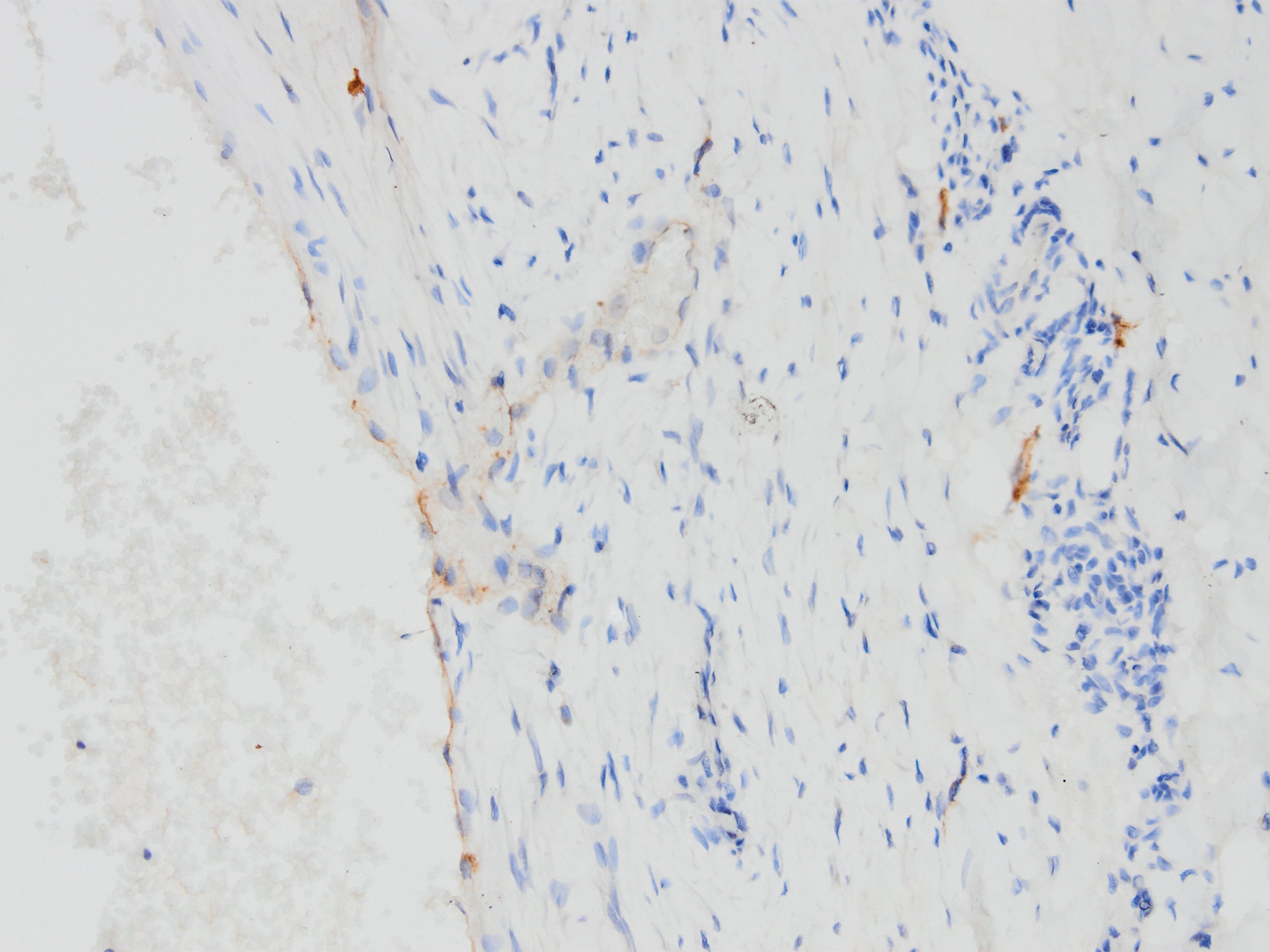
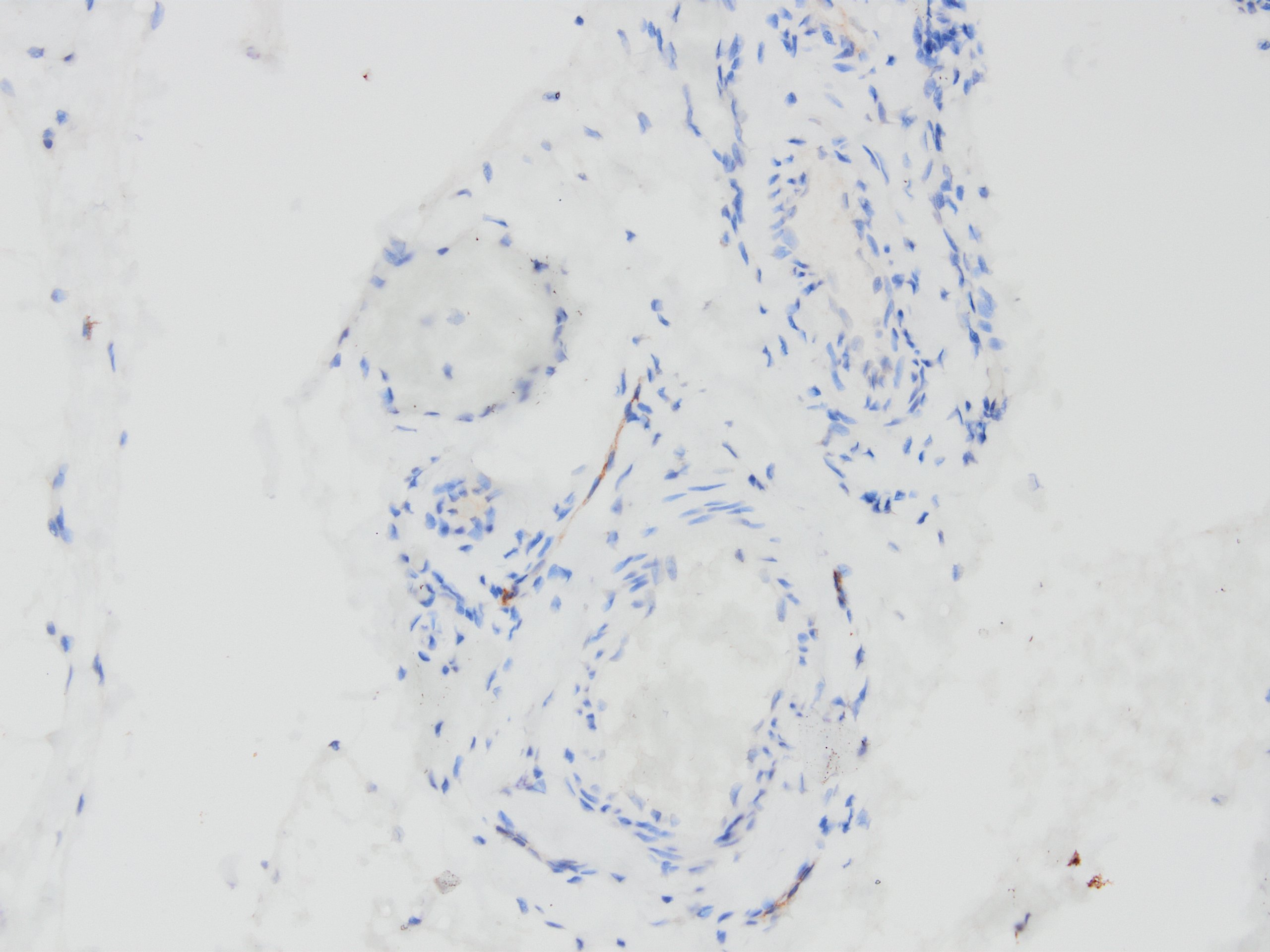
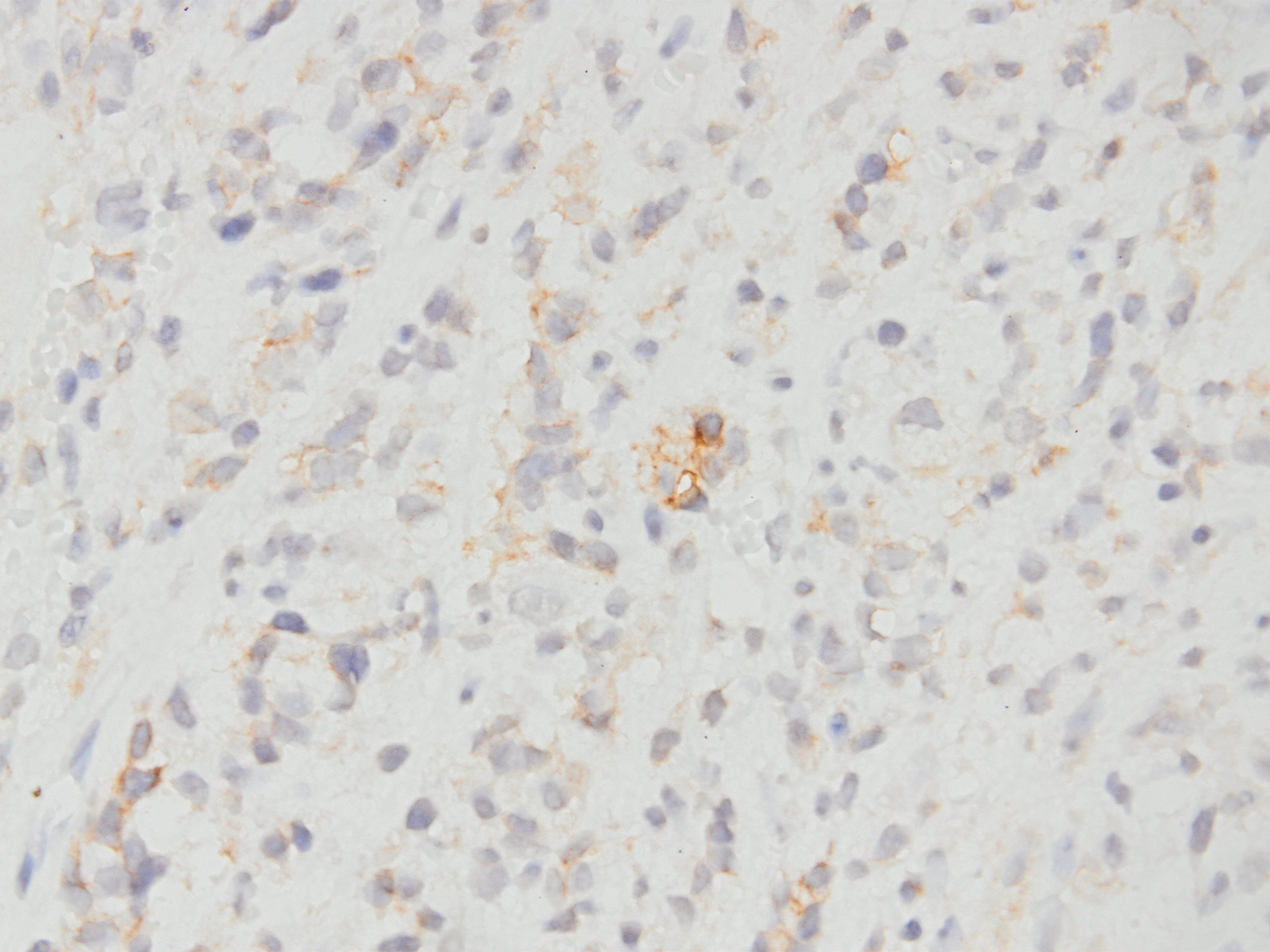
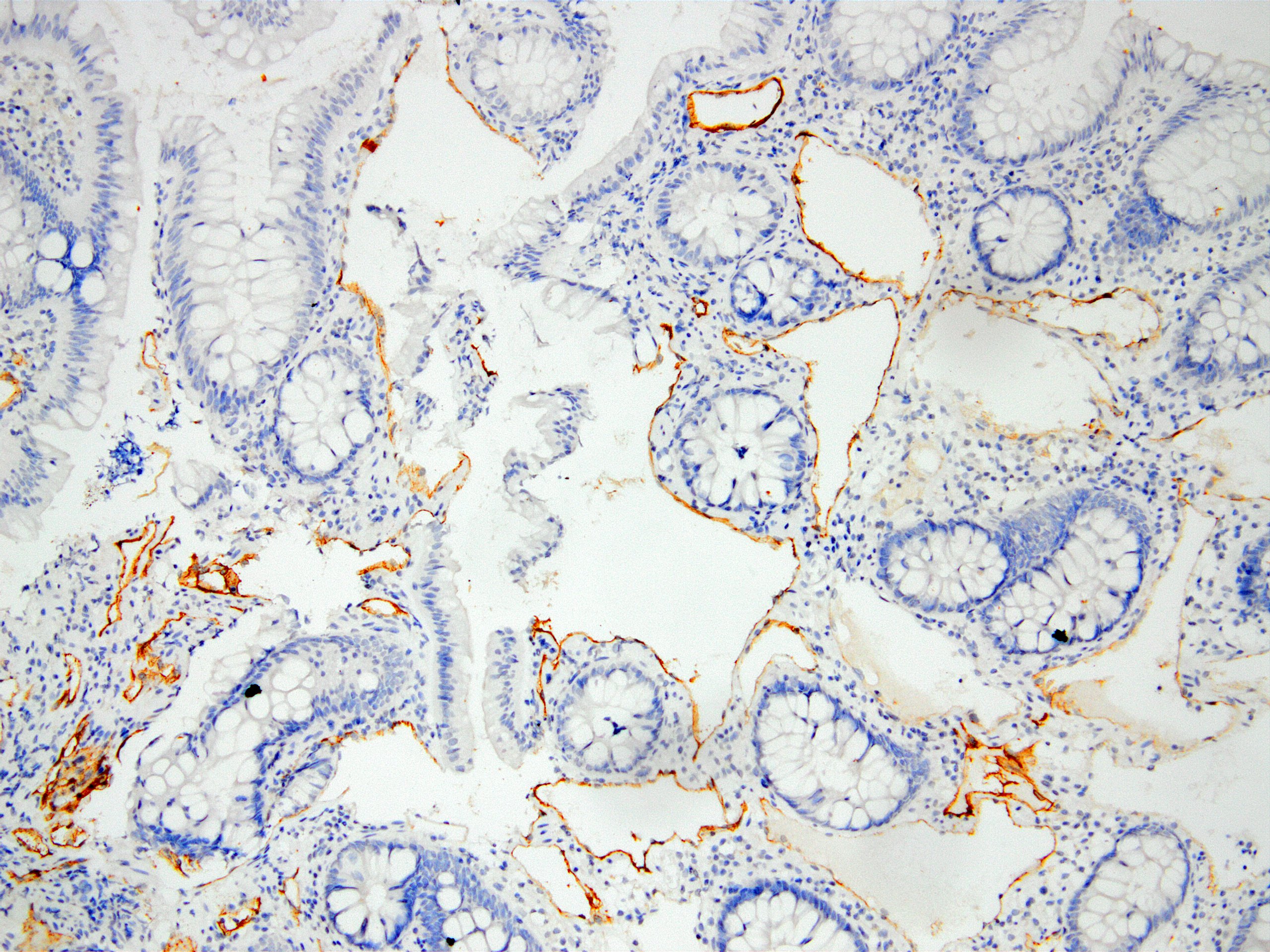
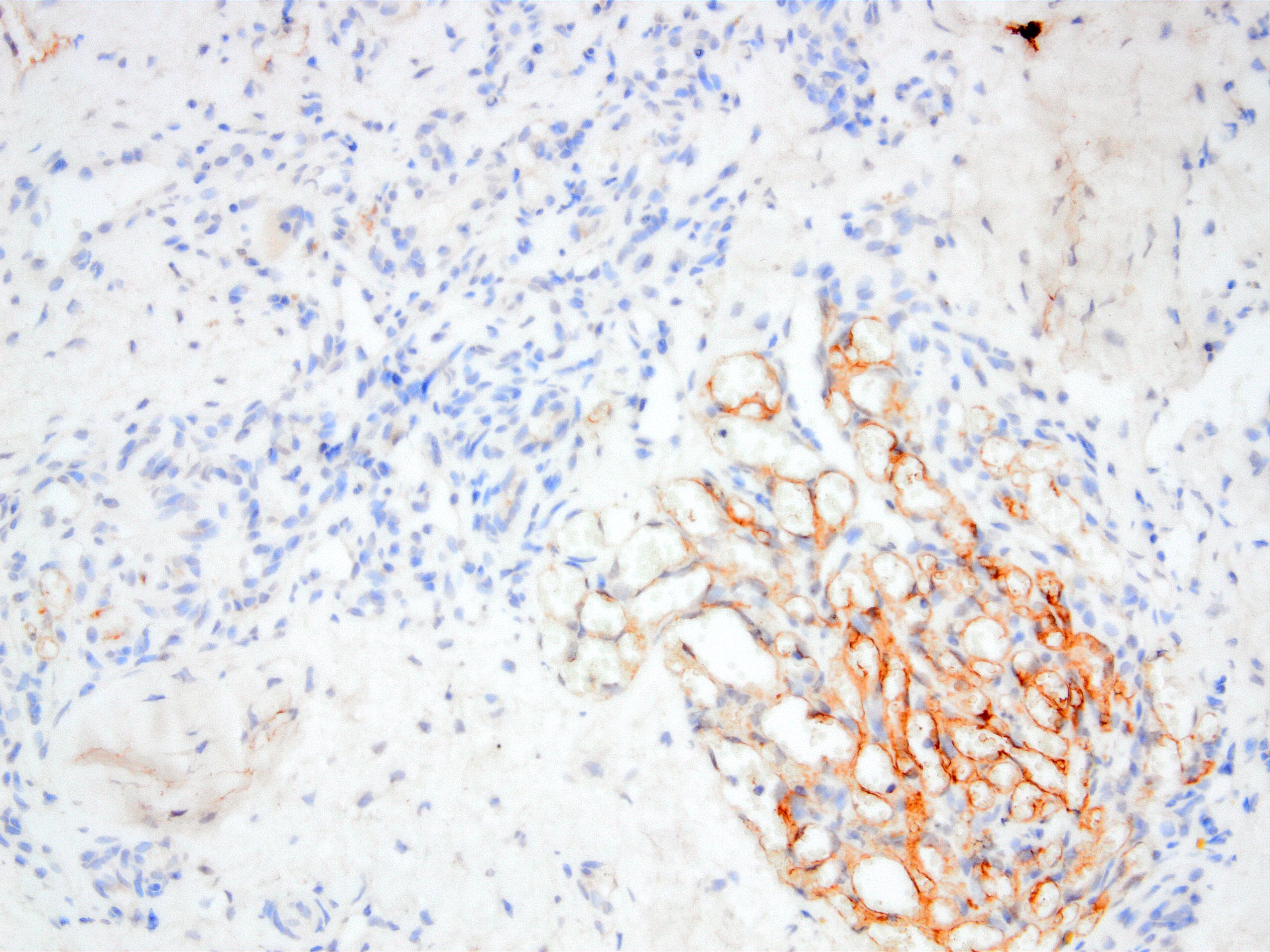
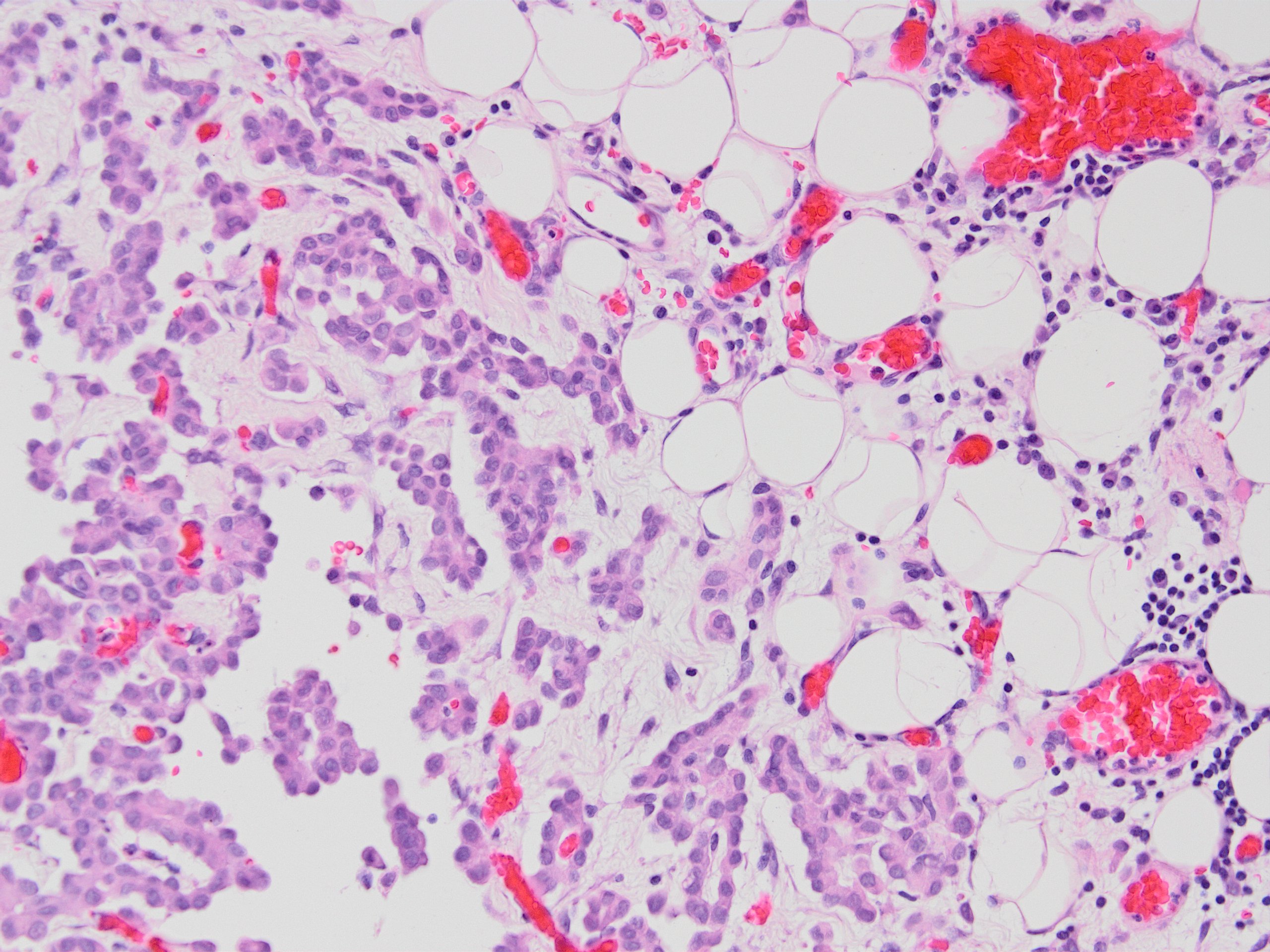
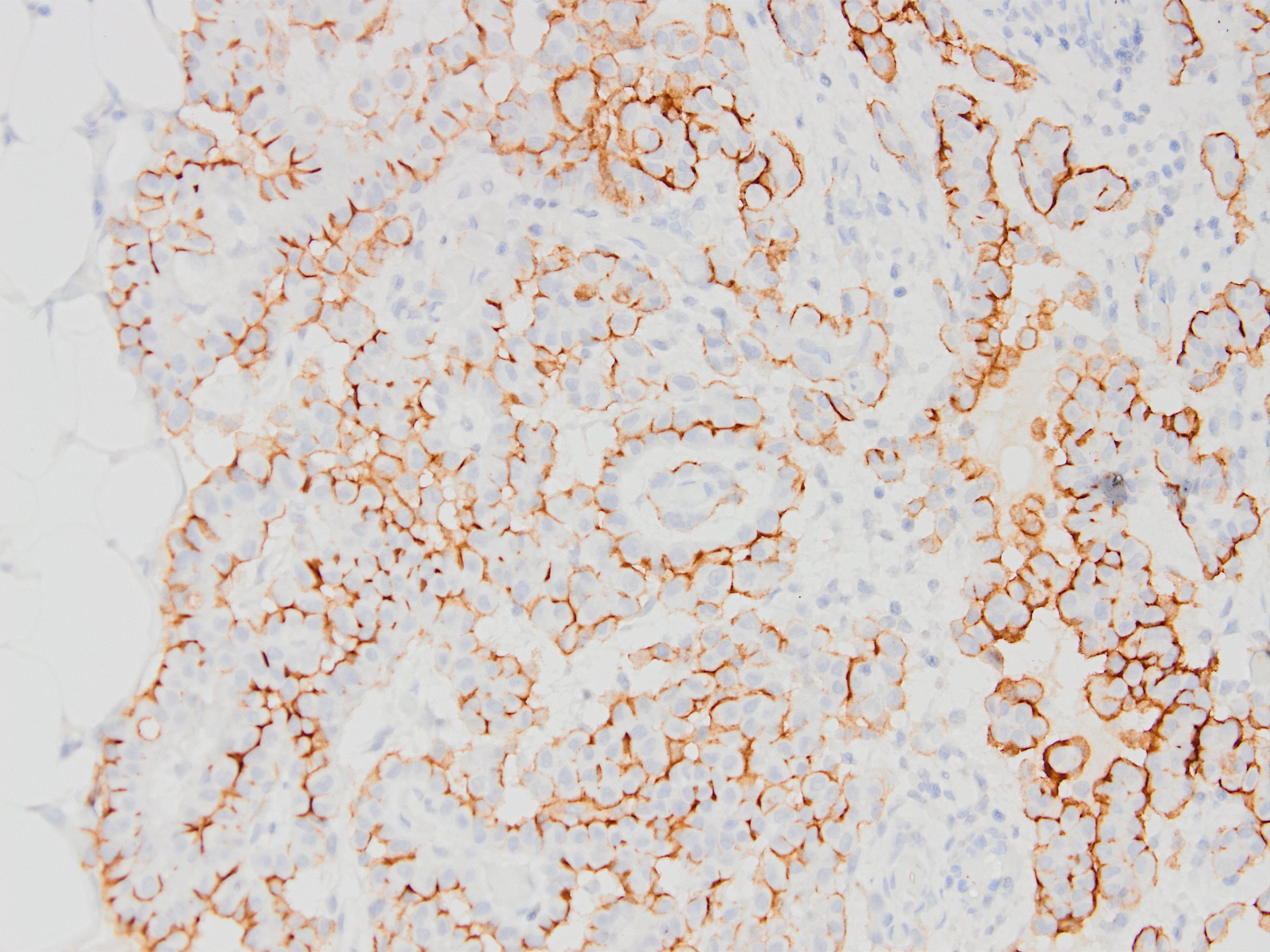
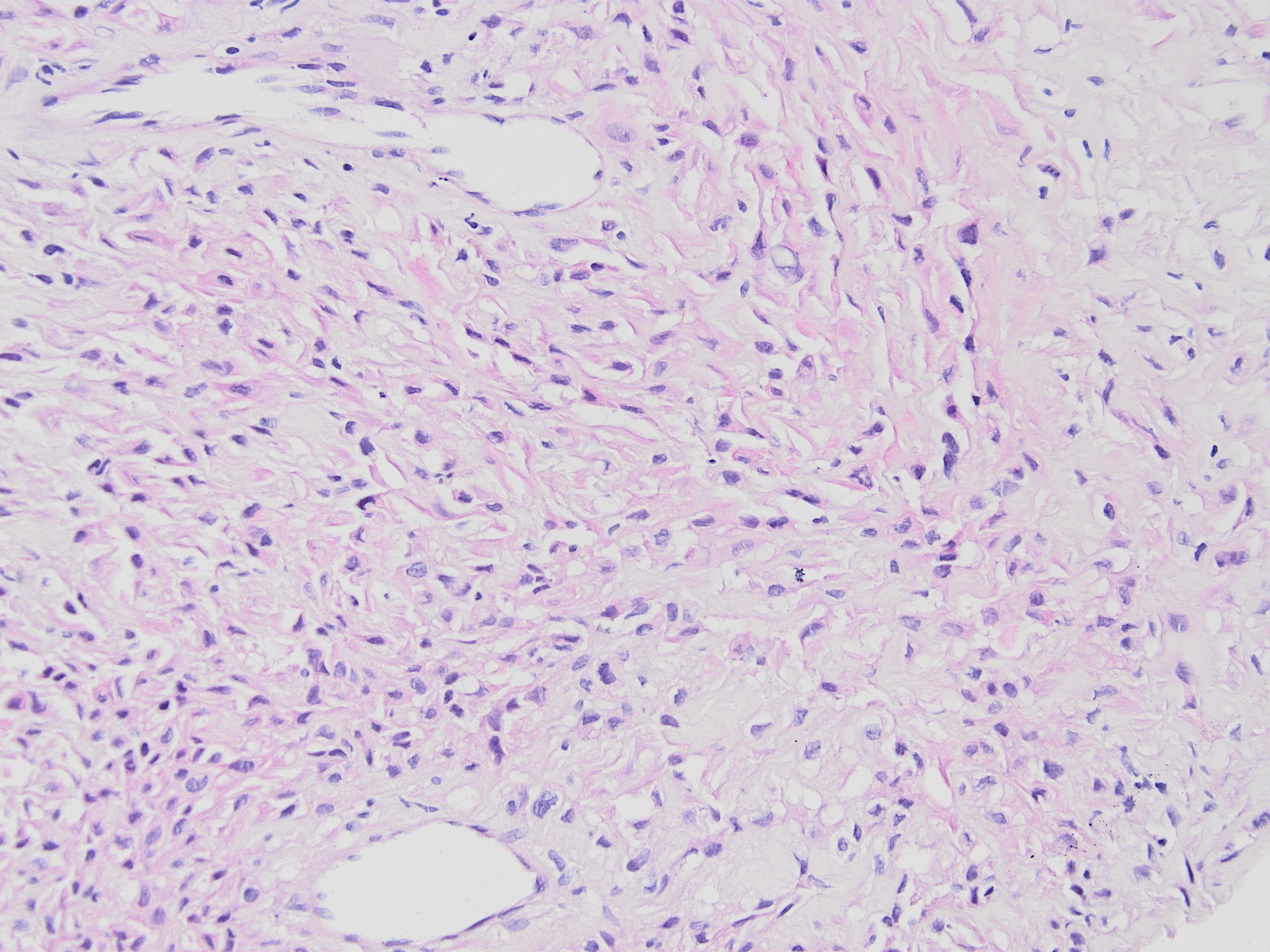
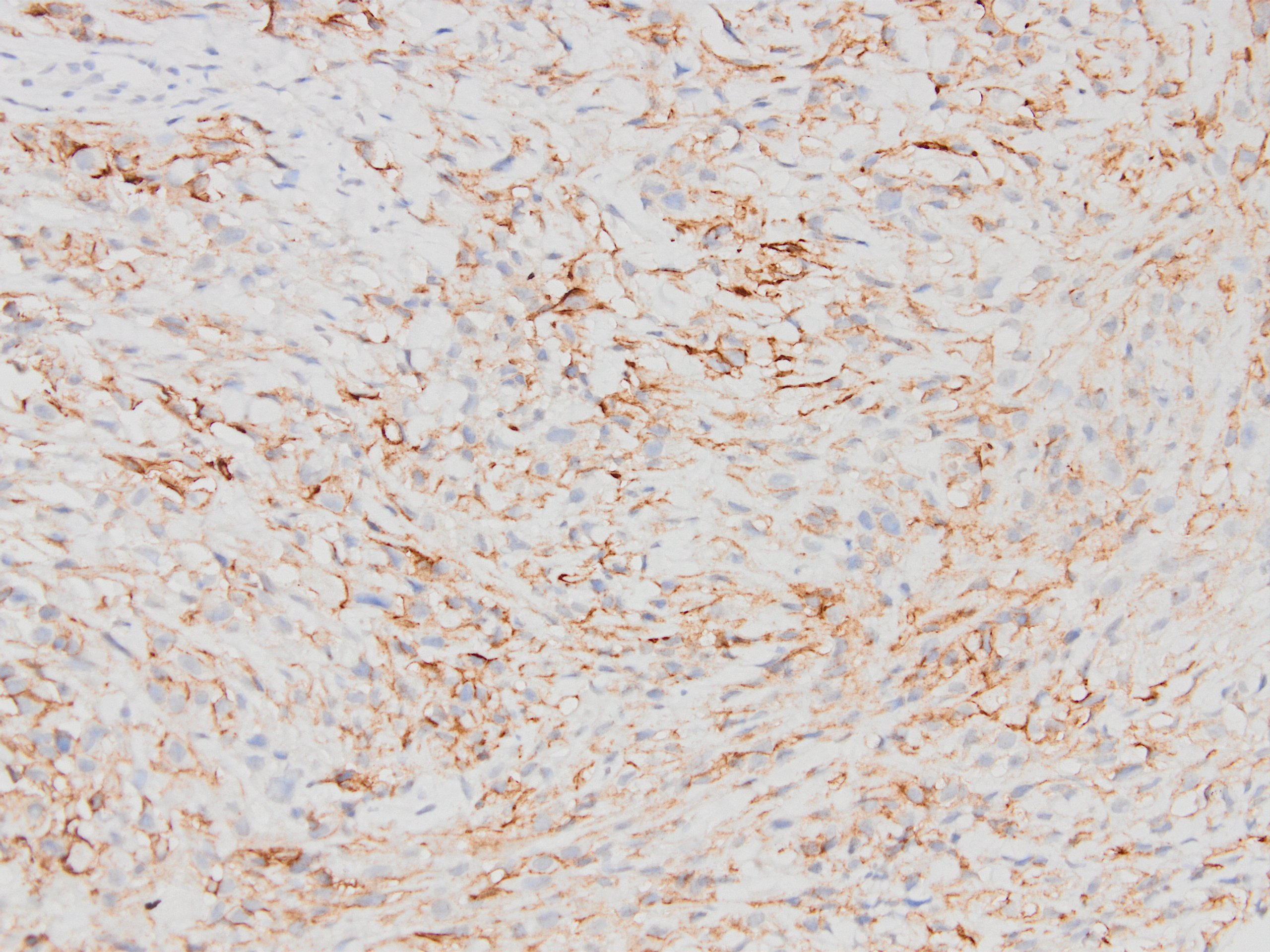
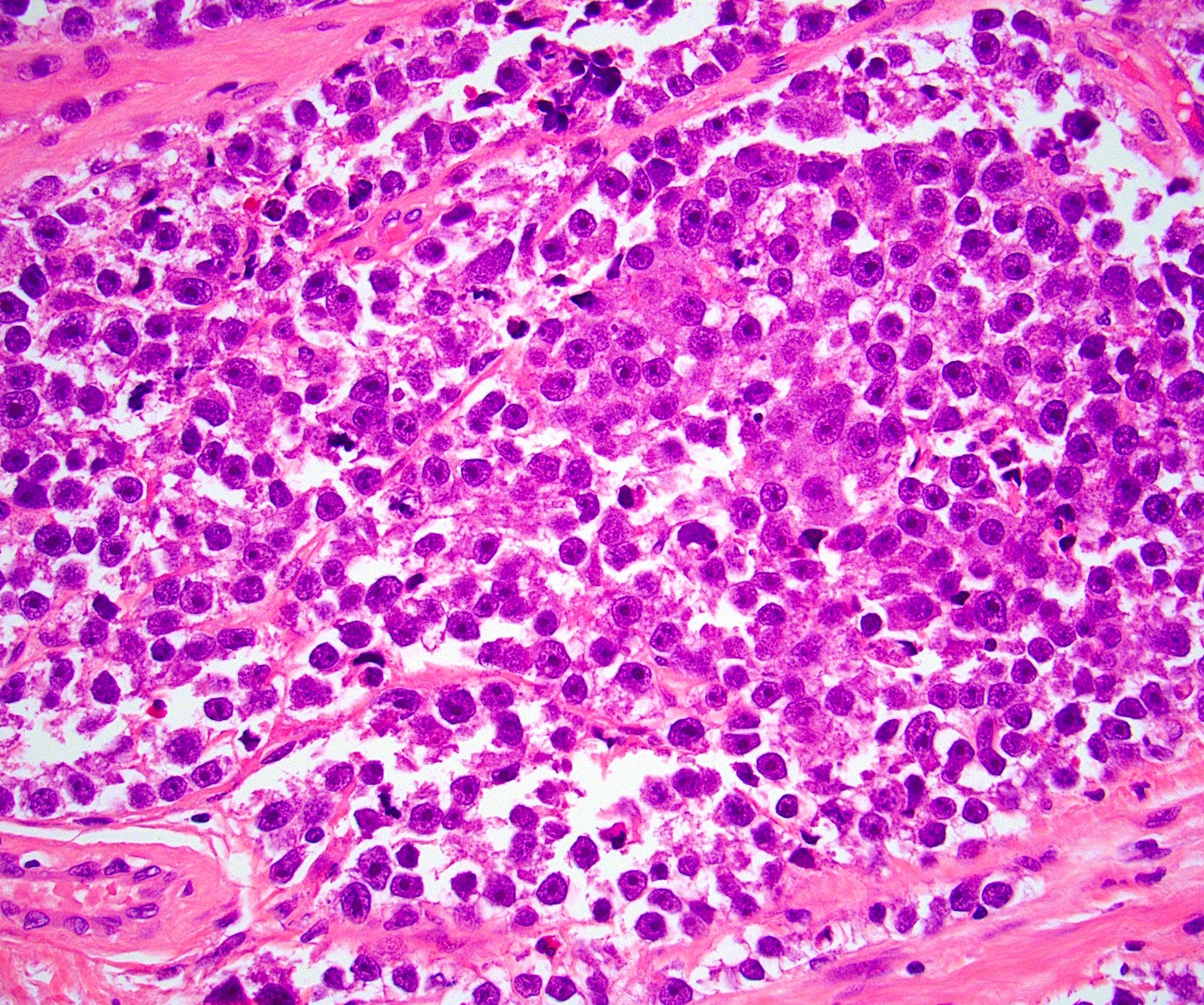
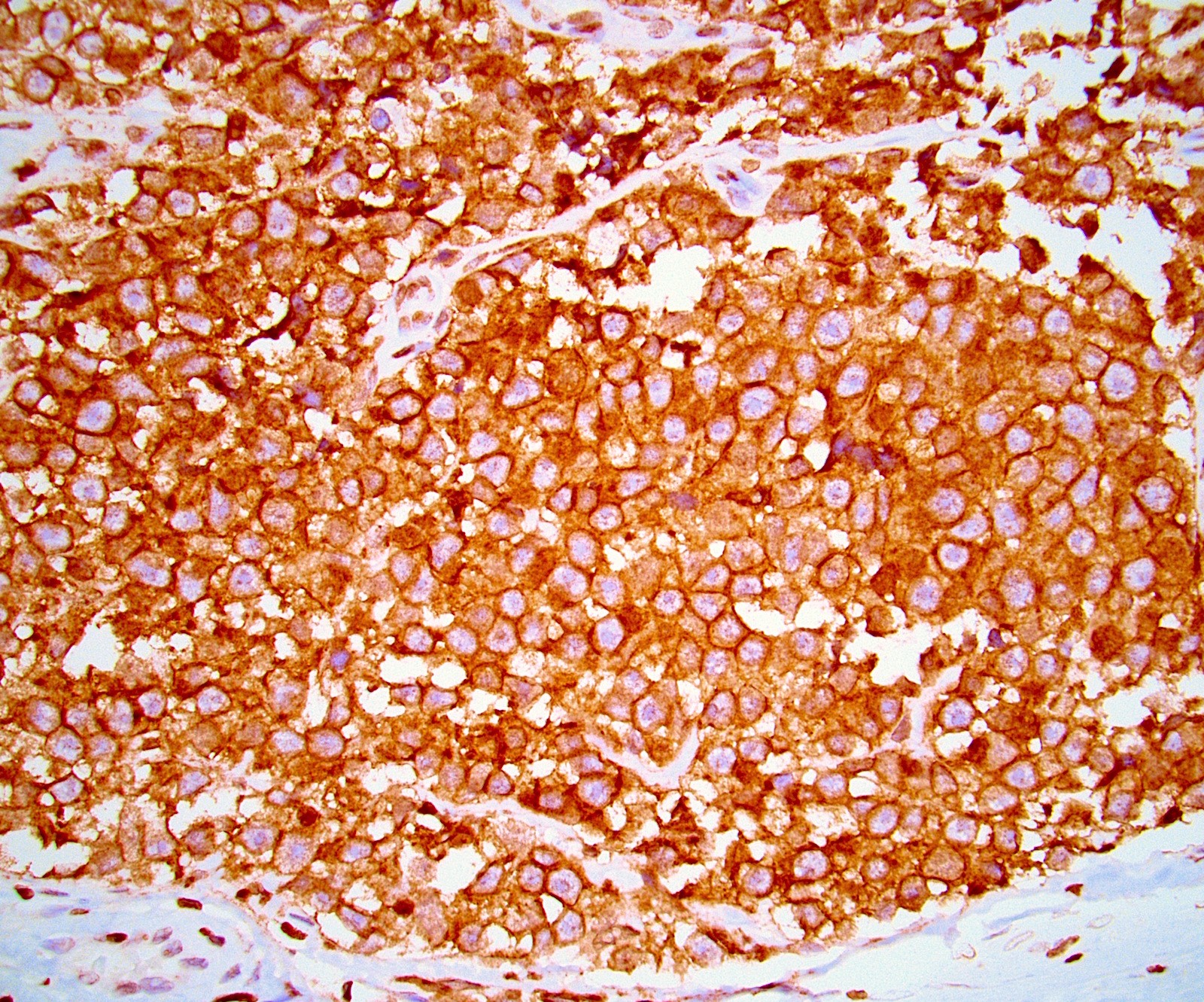
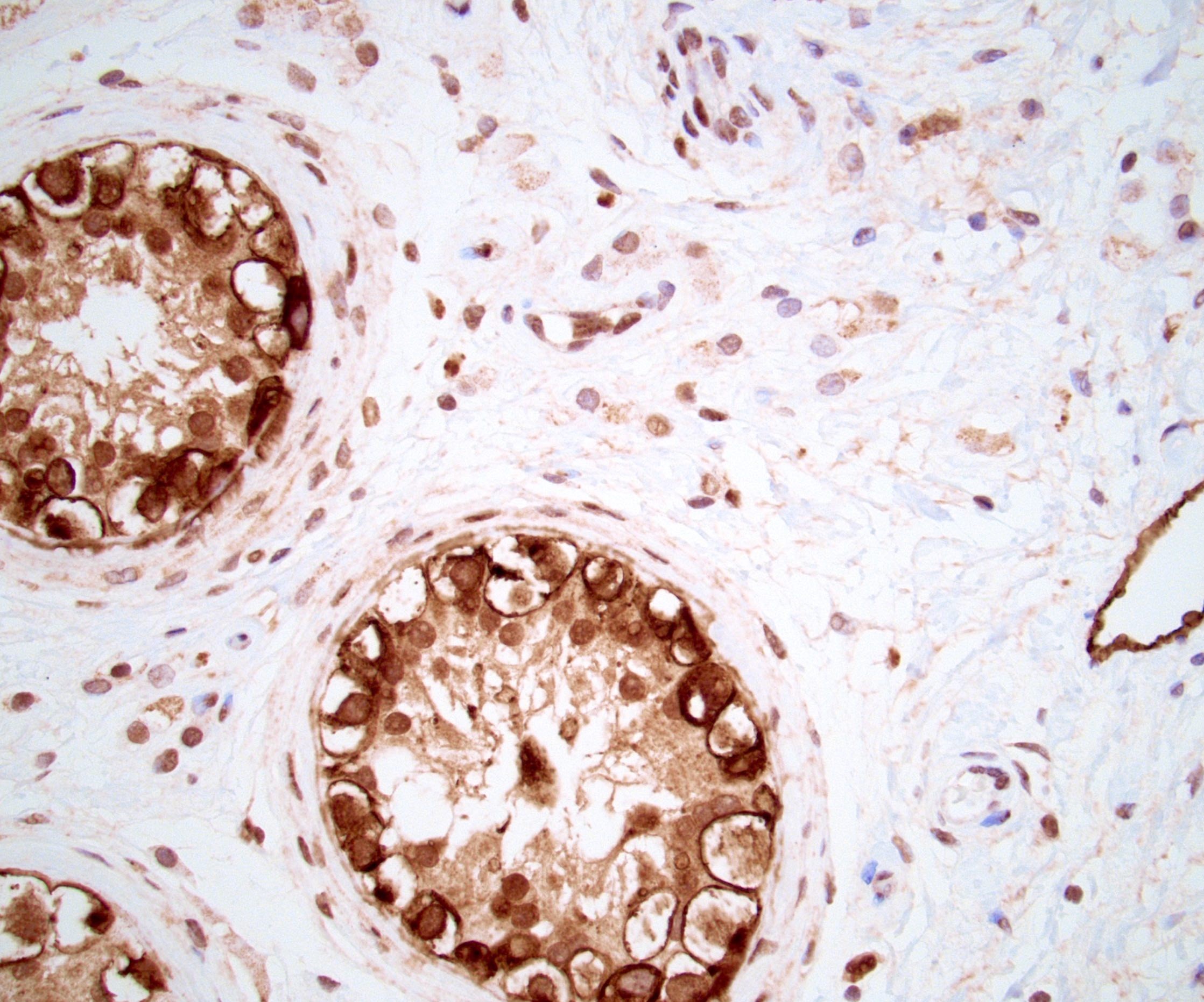
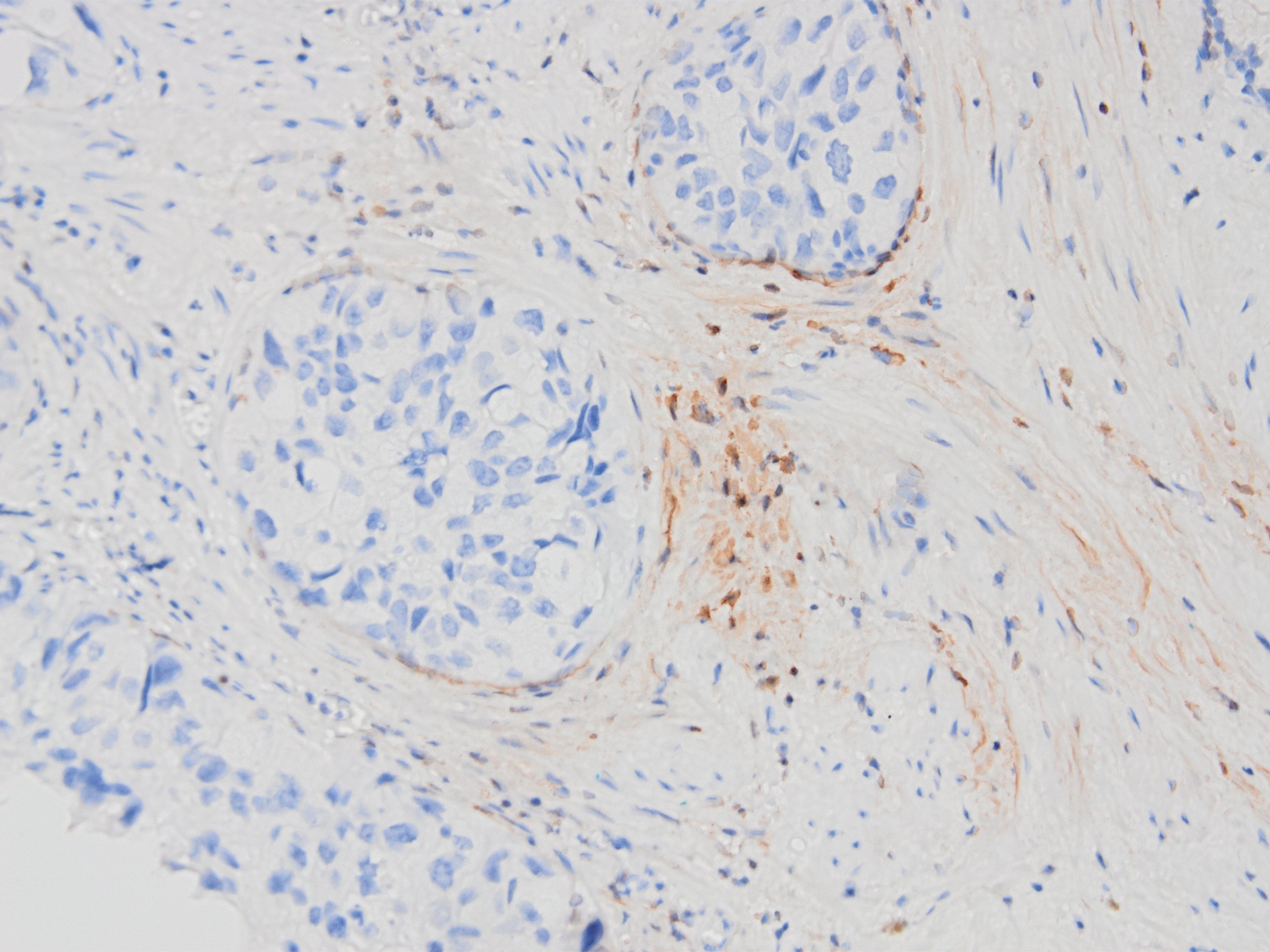
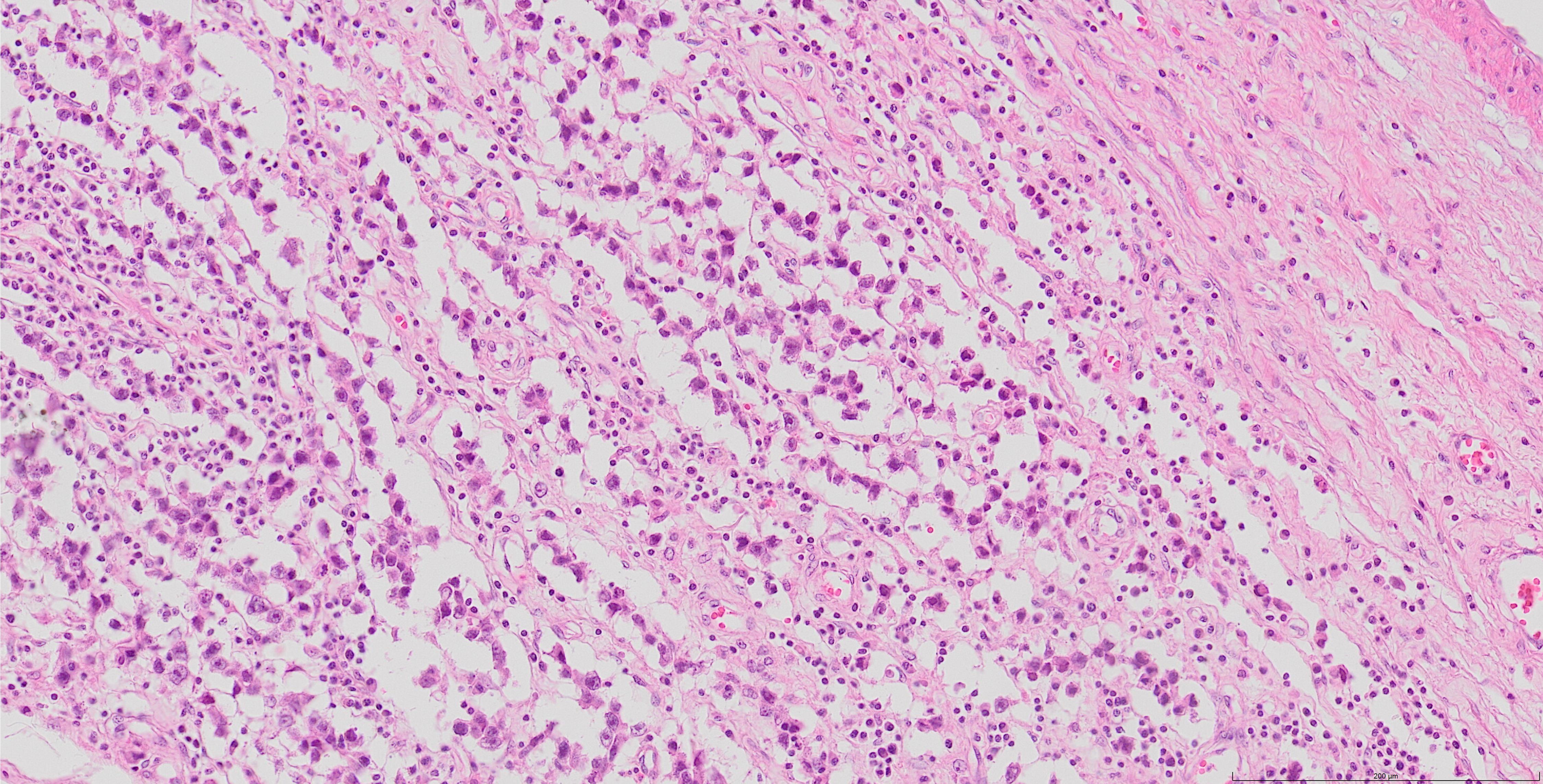
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Kemal Kemal Kösemehmetoğlu, M.D. and Debra Zynger, M.D.
Virtual slides
Positive staining - normal
- Lymphatic endothelium (Am J Pathol 1999;154:385)
- Adrenal cortical cells, normal and neoplastic (J Clin Pathol 2008;61:293)
- Breast myoepithelium, patchy, in normal and neoplastic breast (Hum Pathol 2008;39:175)
- Follicular dendritic cells (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2009;17:102)
- Granulosa cells (Am J Pathol 2005;166:913)
- Mesothelium, normal and reactive (Mod Pathol 2005;18:105)
- Prostatic basal cells (Anticancer Res 2008;28:2997)
- Odontogenic epithelial cells (J Oral Pathol Med 2017;46:618)
- Skin, basal cells of hair follicle outer root sheath (J Cutan Pathol 2008;35:926)
- Developing testis (Virchows Arch 2006;449:200)
- Developing brain (Mod Pathol 2006;19:974)
- Basal cells of squamous mucosal epithelium (tonsil, esophagus)
Positive staining - disease
- Soft tissue tumors
- Vascular tumors / lesions
- Angiosarcoma (40 - 80%) (Am J Pathol 1999;154:385, Histopathology 2005;46:396, Mod Pathol 2002;15:434)
- Kaposi sarcoma (100%) (Am J Pathol 1999;154:385, Histopathology 2005;46:396, Mod Pathol 2002;15:434)
- Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma (95 - 100%) (J Cutan Pathol 2006;33:492, Mod Pathol 2005;18:1454)
- Atypical vascular proliferations of breast postradiation (Cancer 2007;109:1584)
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of liver (80%) (Mod Pathol 2008;21:125)
- Lymphatic malformations (Histopathology 2005;46:396)
- Dermatofibroma, including cellular variant (Mod Pathol 2010;23:434)
- Sinonasal hemangiopericytoma (Virchows Arch 2006;448:459)
- Solitary fibrous tumor (some, Pathol Int 2007;57:618 but see Virchows Arch 2006;448:459)
- Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma (80 - 90%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:1)
- Vascular tumors / lesions
- CNS tumors
- Myoxid / chondromyxoid lesions of CNS:
- Chondroid and chordoid tumors: skeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma (100%), enchondroma (96%), low grade chondrosarcoma (95%), chordoid meningioma (80%) and chordoid glioma (75%) but not chordoma or extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma (Mod Pathol 2006;19:746, Acta Neuropathol 2007;113:87)
- Hemangioblastoma (Acta Neuropathol 2005;109:497)
- Schwannoma, most of epithelioid malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs), occasional neurofibromas or MPNSTs (Am J Clin Pathol 2008;129:886)
- Ependymoma but also widely expressed in other CNS tumors, such as meningioma, glioblastoma, choroid plexus tumors, pilocytic astrocytoma (Clin Neuropathol 2009;28:373, Virchows Arch 2006;448:493)
- Myoxid / chondromyxoid lesions of CNS:
- Follicular dendritic cell tumor (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2008;1:276)
- Malignant mesothelioma, including sarcomatoid subtype (Mod Pathol 2006;19:34, Mod Pathol 2005;18:105, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:123)
- Germ cell tumors
- Gonadal / extragonadal seminoma (dysgerminoma) (Am J Clin Pathol 2007;128:767, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2009;28:347)
- Some (30%) embryonal carcinomas of testis (Mod Pathol 2007;20:320)
- Epithelial neoplasia / carcinomas
- Serous carcinoma of gynecologic tract (ovarian 23%, endometrial 43%) (Mod Pathol 2008;21:1147)
- In effusion cytology, ovarian (58%), lung (33%), breast (30%), adenocarcinomas of unknown origin (42%), usually focal staining in contrast to mesothelioma (Mod Pathol 2005;18:105)
- Squamous cell carcinoma (80%) (Am J Pathol 2005;166:913)
- Lung, pleomorphic carcinomas (33%) (Pathol Int 2008;58:771)
- Skin, adnexal carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:304)
- Adrenocortical carcinomas (J Clin Pathol 2008;61:293)
- Ameloblastic tumors (most) (J Oral Pathol Med 2017;46:618)
- Renal angiomyolipoma, lymphatics are prominent; not in liver angiomyolipoma (Mod Pathol 2006;19:669, Hum Pathol 2009;40:374, Mod Pathol 2008;21:125)
- Crohn's disease due to increased lymphatics (Virchows Arch 2008;452:57)
Negative staining
- Capillary endothelium
- Glomus tumor (Histopathology 2005;46:396)
- Retiform hemangioendothelioma, usually (Am J Dermatopathol 2008;30:31)
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) (Mod Pathol 2010;23:434)
- Chordoma (Acta Neuropathol 2007;113:87)
- Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (Acta Neuropathol 2005;109:497)
Sample pathology report
- Right breast, core biopsy:
- Infiltrative ductal carcinoma, grade II (see comment)
- Comment: The presence of lymphovascular invasion was supported by D2-40, which highlighted lymphatic endothelium of vessels with tumor emboli.
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
In which of the following differential diagnoses is D2-40 useful?
- Adrenocortical carcinoma versus adrenocortical adenoma
- Kaposi sarcoma versus angiosarcoma
- Mesothelioma versus squamous cell carcinoma
- Prostatic stromal invasion versus intraductal spread of urothelial carcinoma
- Seminoma versus in situ germ cell neoplasm
Board review style answer #2
D. Prostatic stromal invasion versus intraductal spread of urothelial carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: D2-40 (Podoplanin)
Comment Here
Reference: D2-40 (Podoplanin)