Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Siegele B. DUX4. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsDUX4.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Double homeobox 4 transcription factor, encoded by retrogene material within D4Z4 polymorphic macrosatellite repeat sequence
- Involved in normal development in fetal skeletal muscle
- Expression in differentiated tissues is normally suppressed through epigenetic mechanisms
Essential features
- Nuclear marker with limited expression in normal tissues (fetal skeletal muscle, mature testis)
- Variable expression in skeletal muscle of patients with facioscapulohumeral dystrophy 1 (FSHD1)
- Diffuse, strong expression in CIC-DUX4 fusion tumors with both t(4;19) and t(10;19) translocations
Clinical features
- Decreased epigenetic repression of the D4Z4 macrosatellite array and resulting expression of DUX4 is hypothesized to be primarily responsible for facioscapulohumeral dystrophy 1 (FSHD1) pathophysiology
- Translocations overexpressing the DUX4 double homeodomain cause B cell leukemia (Cell Rep 2018;25:2955)
Interpretation
- Nuclear stain
Uses by pathologists
- Differentiate CIC-DUX4 fusion tumors from many other small round blue cell tumors in pediatric, adolescent and young adult population (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:423)
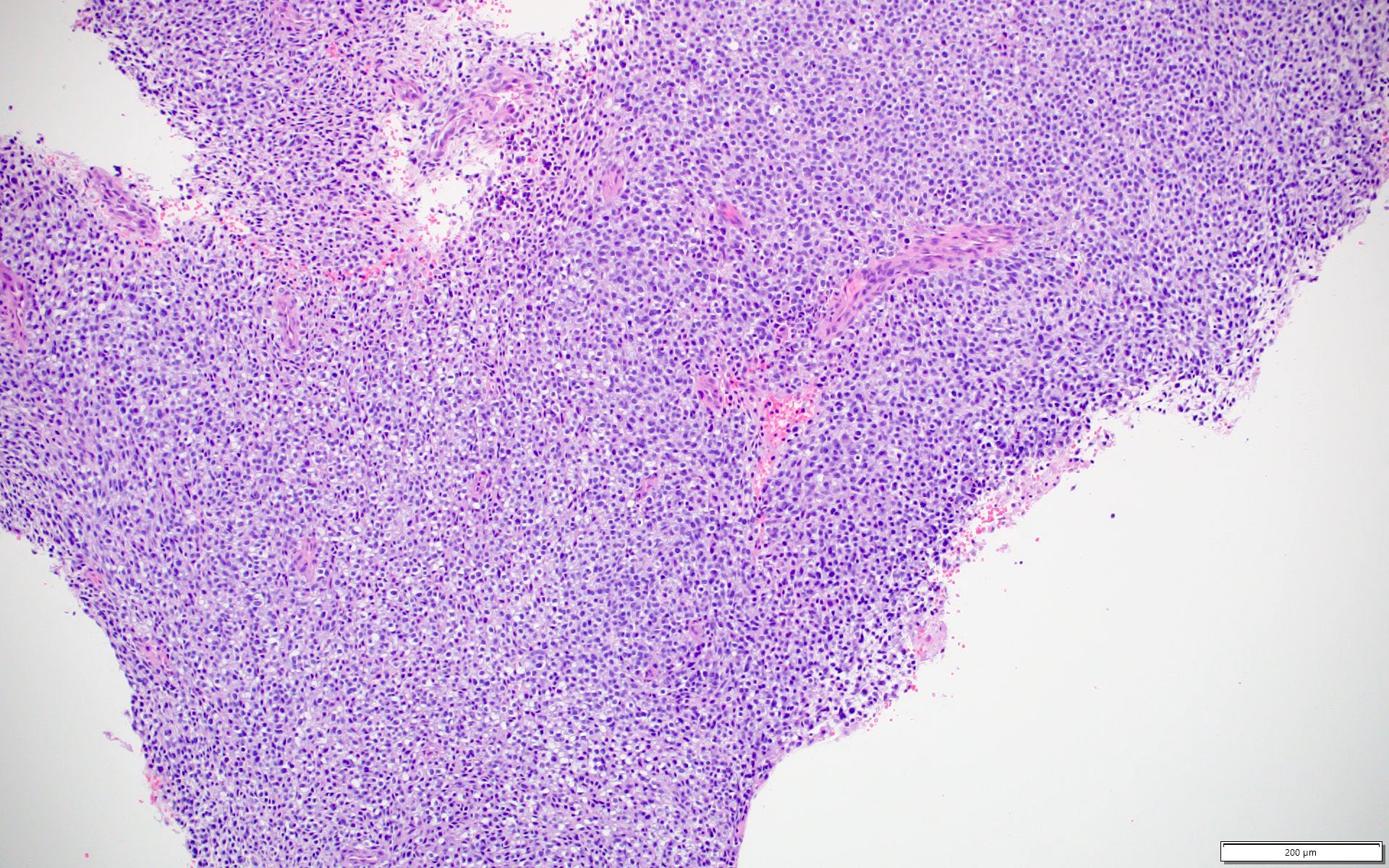
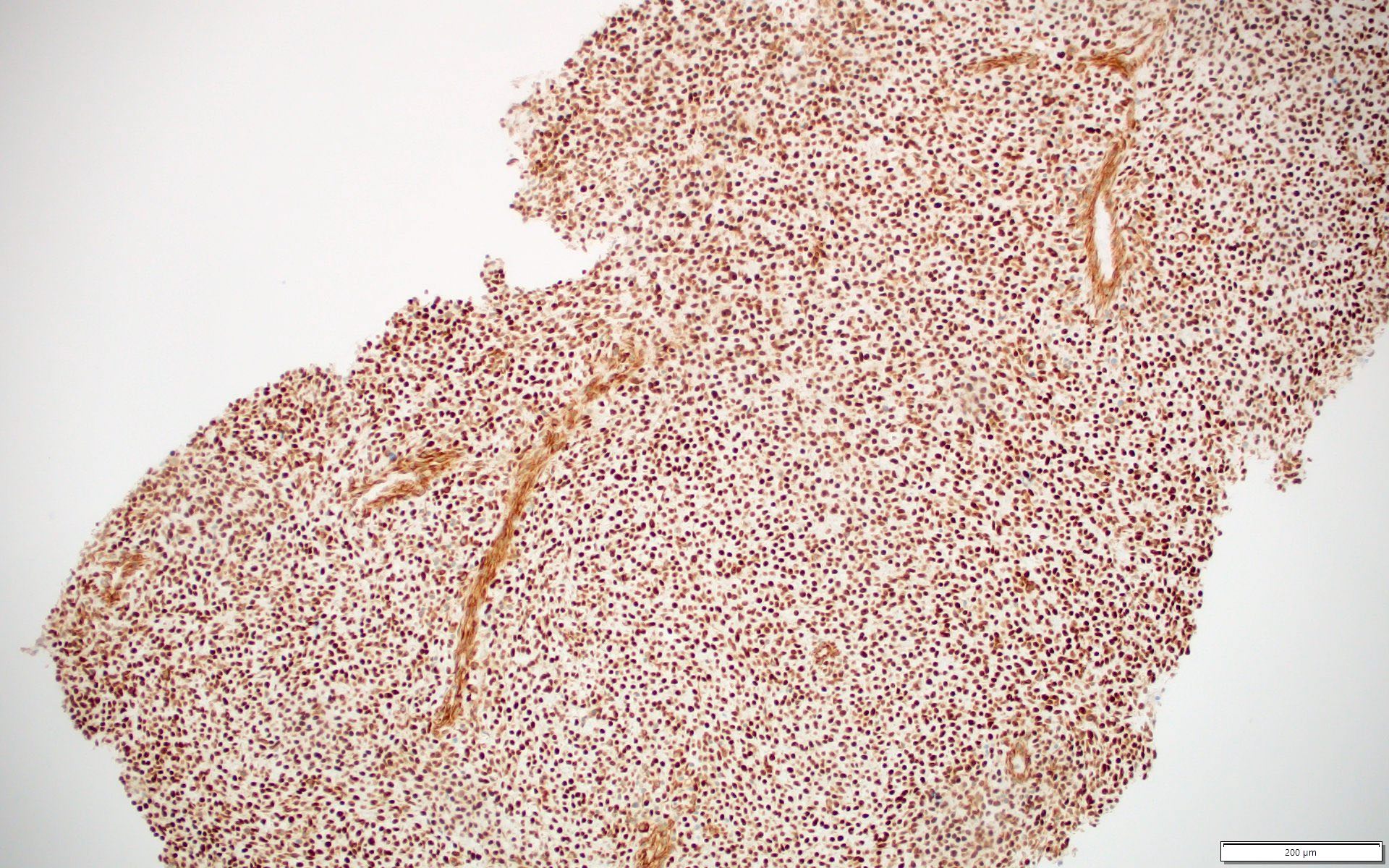
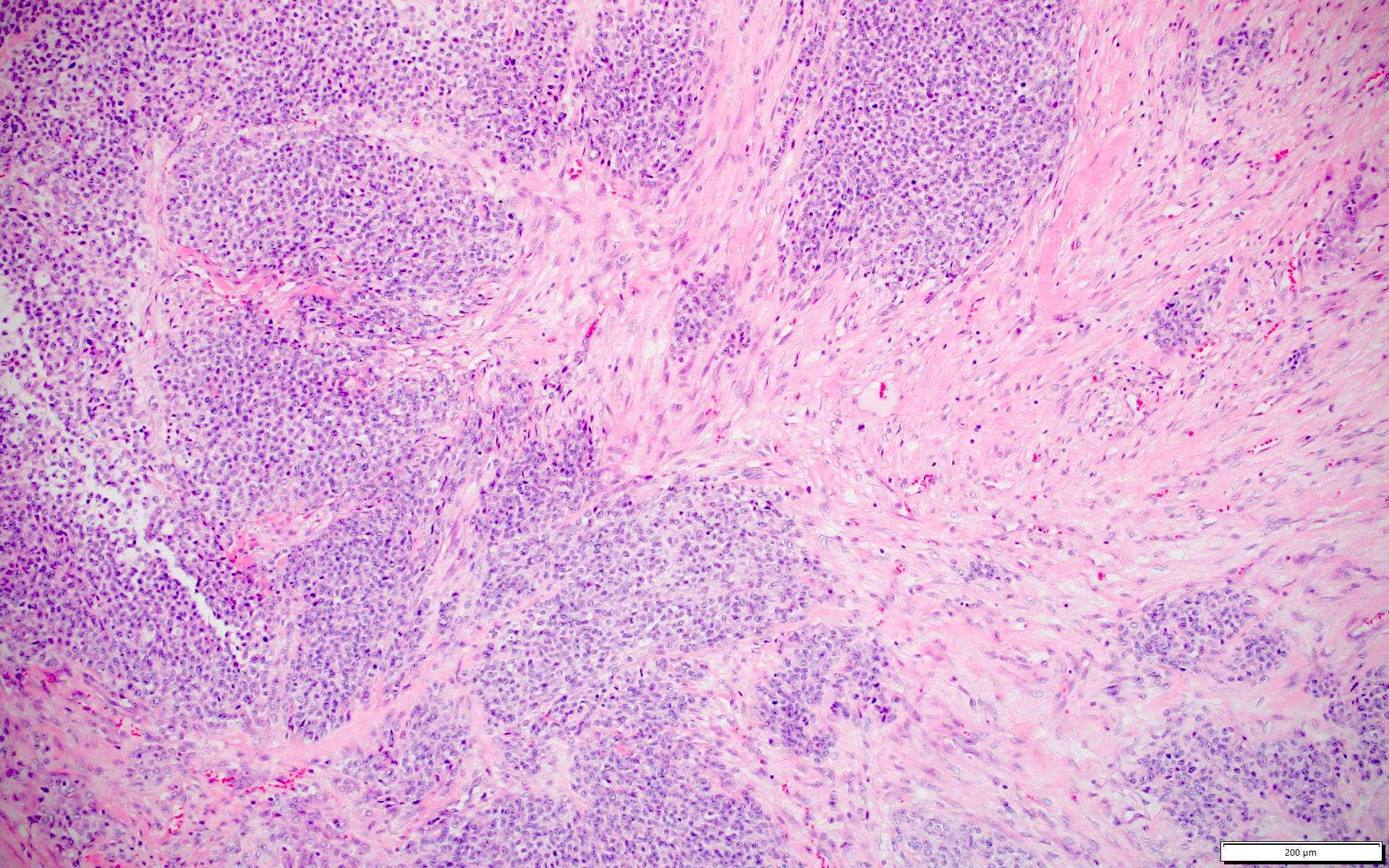
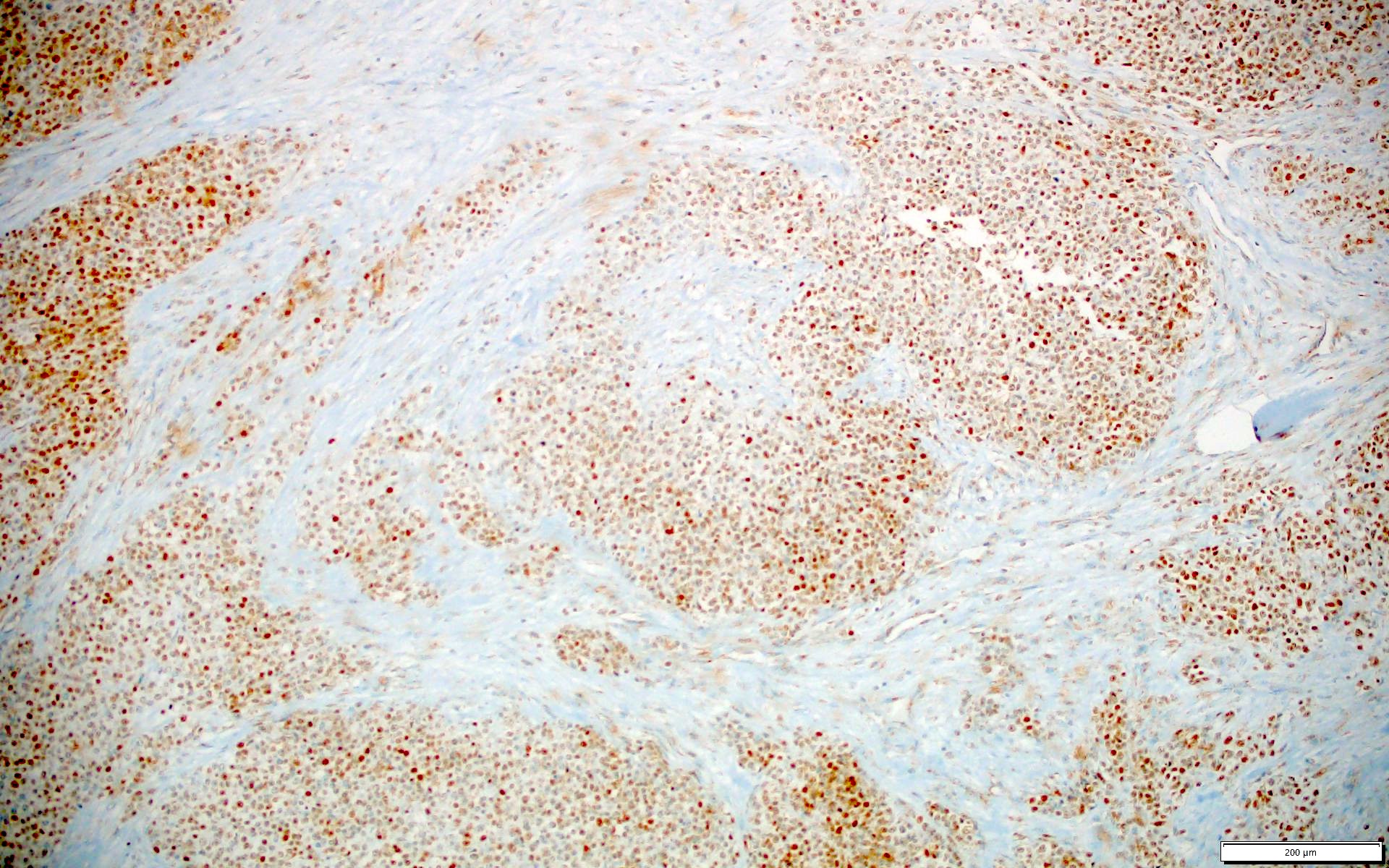
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
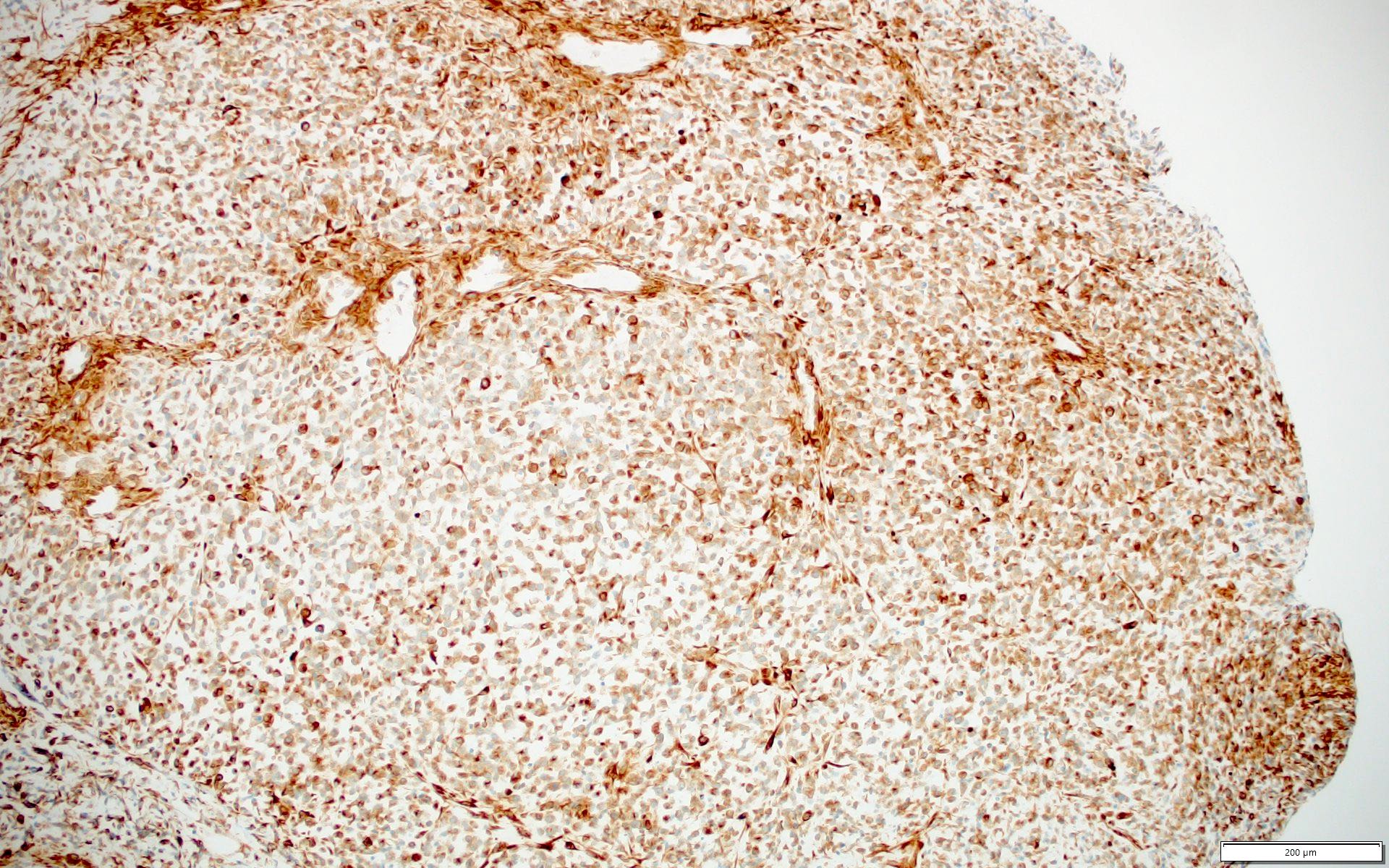
- Mature testis (PLoS One 2016;11:e0160022)
- Fetal skeletal muscle (Nat Genet 2017;49:941)
Positive staining - disease
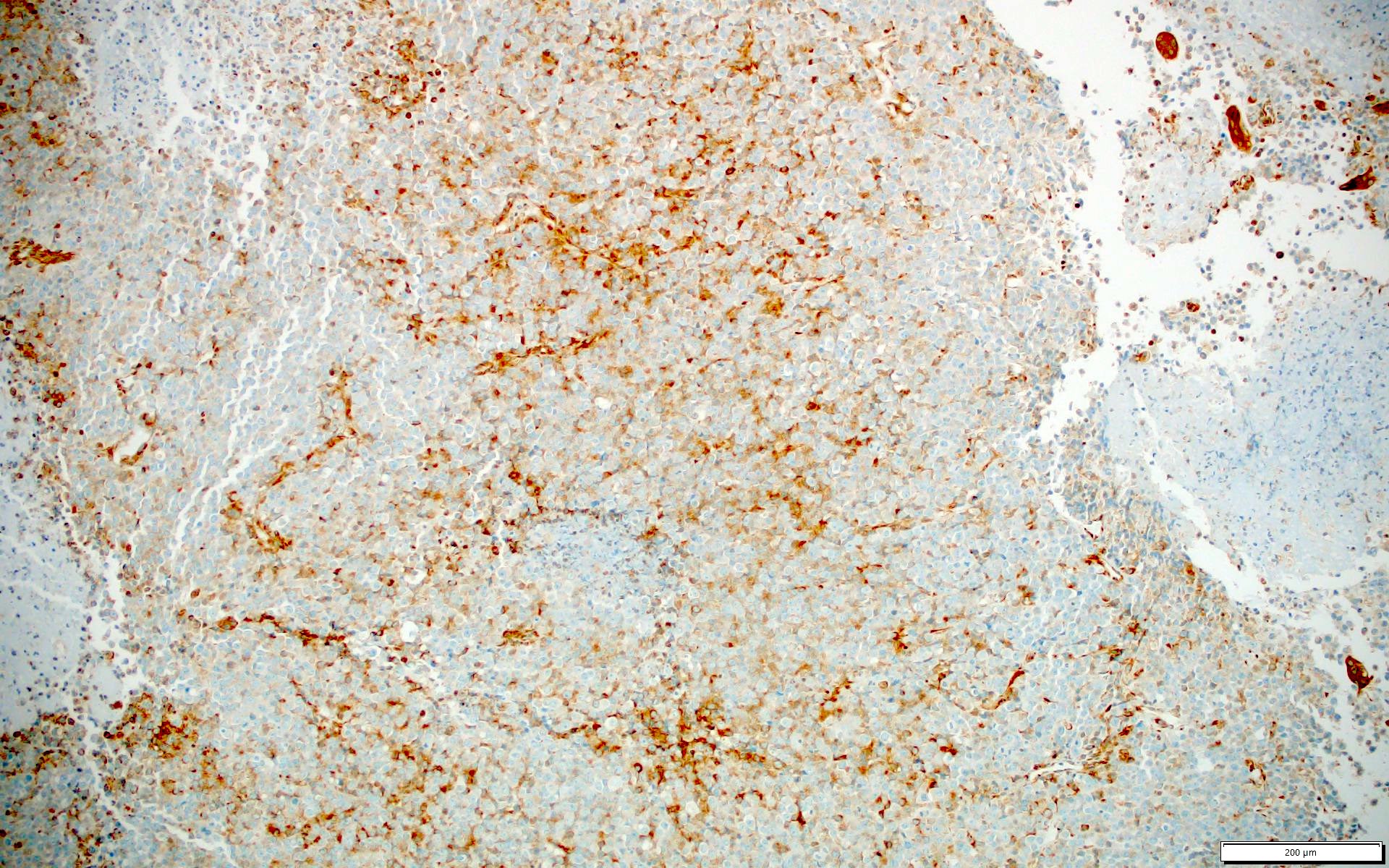
- CIC-DUX4 fusion tumors (nuclear, 100%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:423, Hum Pathol 2019;86:57)
Negative staining
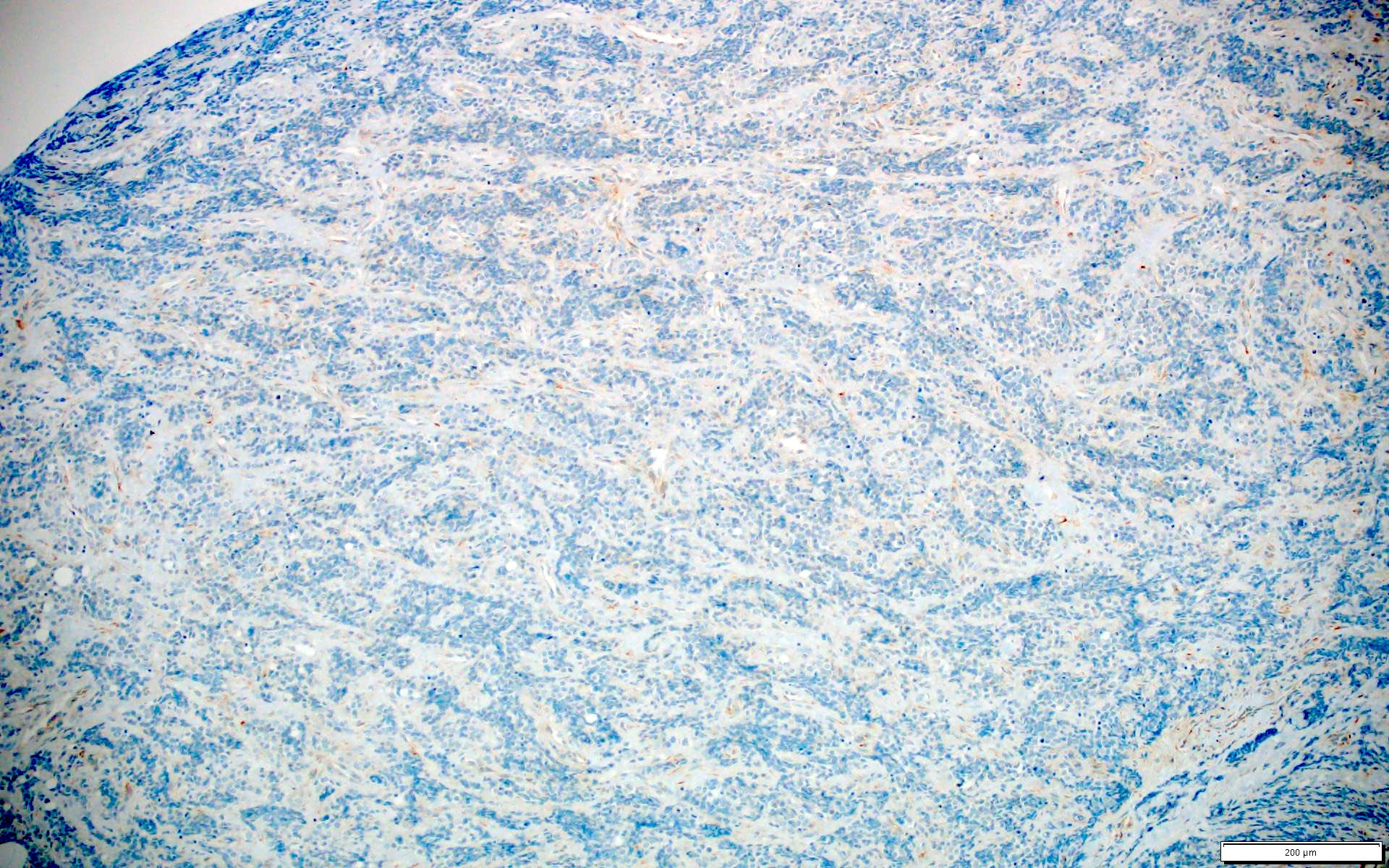
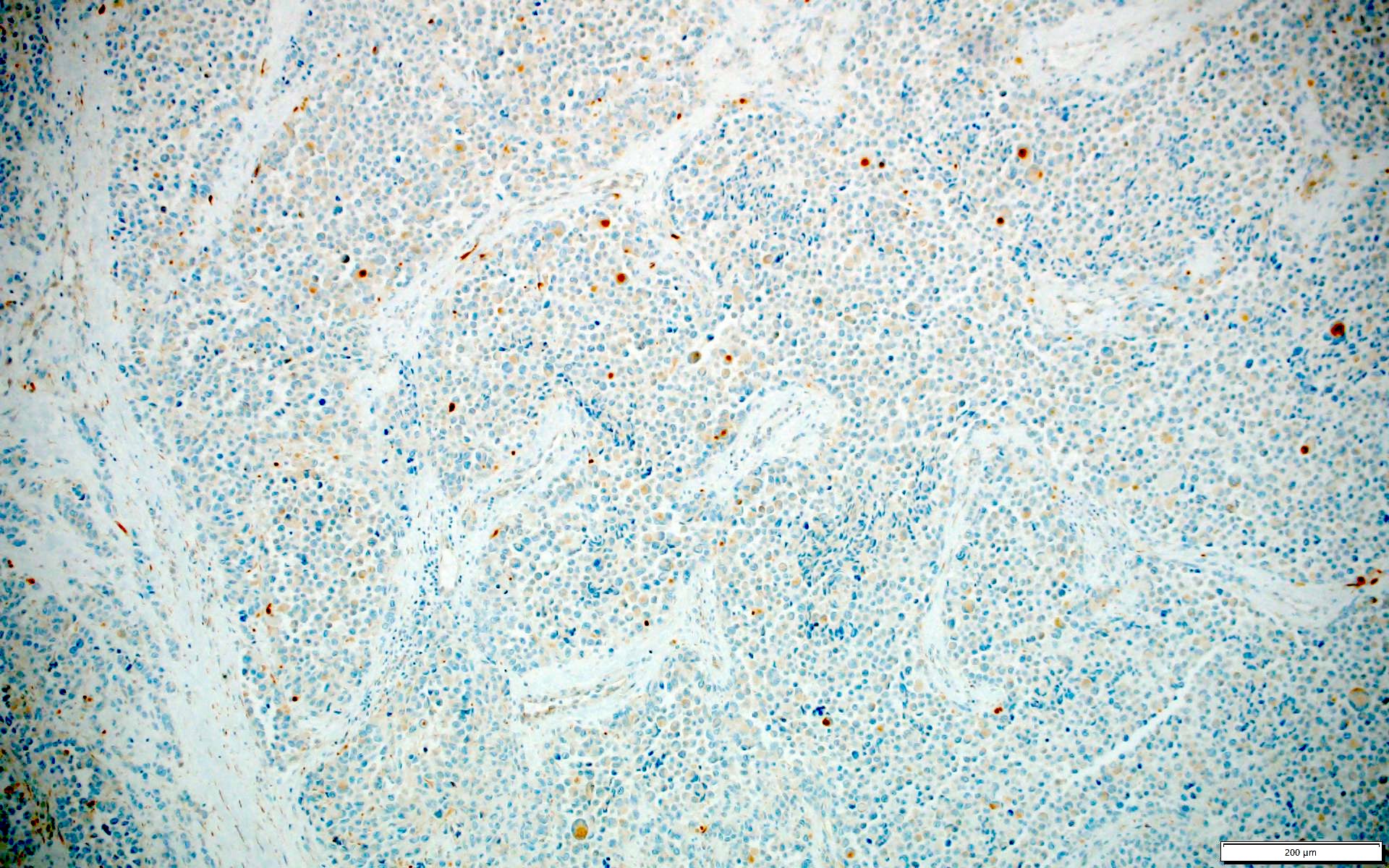
- Ewing sarcoma (0%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:423)
- Sarcoma with BCOR genetic alterations (0%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:423)
- Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (0%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:423)
- Embryonal rhabdomyosarcomas (0%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:423)
- Synovial sarcomas (0%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:423)
- Desmoplastic small round cell tumors (0%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:423)
- Malignant rhabdoid tumors (0%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:423)
- Neuroblastoma (0%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:423)
- Clear cell sarcoma (0%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:423)
Sample pathology report
- Soft tissue, flank, excision:
- Round cell tumor with CIC rearrangement and DUX4 expression by immunohistochemistry (see comment)
- Comment: This case was sent for fluorescence in situ hybridization for rearrangement of the CIC gene, which was detected. This finding, in combination with strong, diffuse nuclear expression of the DUX4 protein by immunohistochemistry, is consistent with a CIC-DUX4 fusion tumor.
Board review style question #1
A CIC-DUX4 fusion tumor and DUX4 IHC images are shown. Which immunohistochemical profile is commonly seen in CIC-DUX4 fusion tumor?
- DUX4+ (cytoplasmic), CD99+ (diffuse), AE1 / AE3-, desmin-, WT1-
- DUX4+ (cytoplasmic), CD99+ (patchy), AE1 / AE3-, desmin+ (patchy), WT1-
- DUX4+ (cytoplasmic), CD99+ (patchy), AE1 / AE3+ (patchy), desmin-, WT1-
- DUX4+ (nuclear), CD99+ (diffuse), AE1 / AE3+ (patchy), desmin-, WT1+
- DUX4+ (nuclear), CD99+ (patchy), AE1 / AE3-, desmin-, WT1+
Board review style answer #1