Table of Contents
Definition / general | Uses by pathologists | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative stainingCite this page: Pernick N. HMB45. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsHMB45.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Human Melanoma Black, discovered in 1986 (Am J Pathol 1986;123:195)
- Monoclonal antibody originally identified from melanoma abstract, recognizes melanosomal glycoprotein gp100 (Pmel17)
- Membrane protein required to form melanosomal fibrils, facilitates maturation of stage I pre-melanosomes to stage II
- Identifies oncofetal glycoconjugate associated with immature melanosomes and probably related to the tyrosinase enzymatic system (J Histochem Cytochem 1992;40:207)
Uses by pathologists
- Common marker to confirm melanoma (invasive melanomas with paradoxical maturation show at least focal deep HMB45 reactivity, in contrast to nevi, which are negative in deep dermis)
- Evaluating sentinel lymph nodes for melanoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:1039)
- Diagnosis (or ruling out diagnosis) of perivascular epithelioid cell tumors (angiomyolipoma, lymphangioleiomyomatoisis, PEComa, clear cell "sugar" tumor)
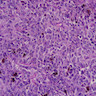
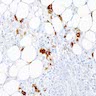
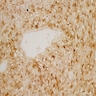
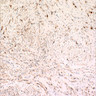
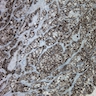
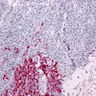
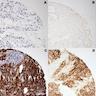
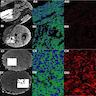
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
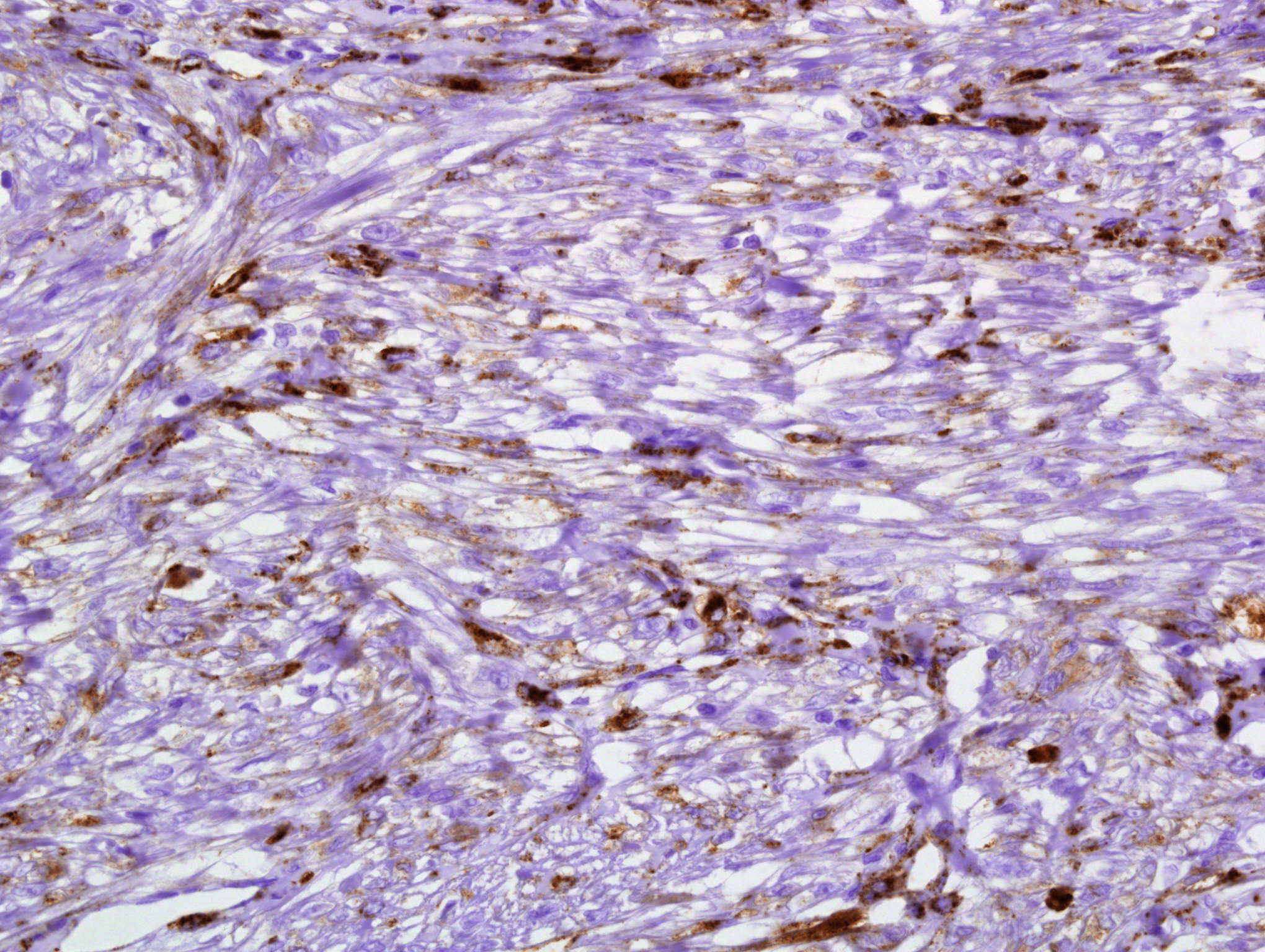
- Lymph nodes: scattered mononuclear cells
- Skin: junctional melanocytes, activated melanocytes
Positive staining - disease
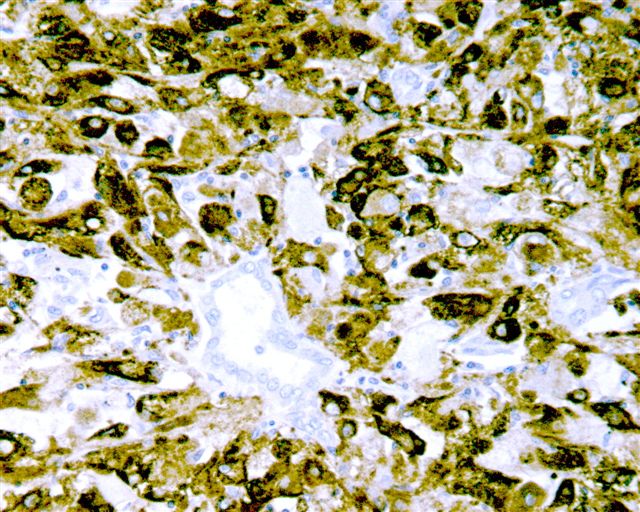
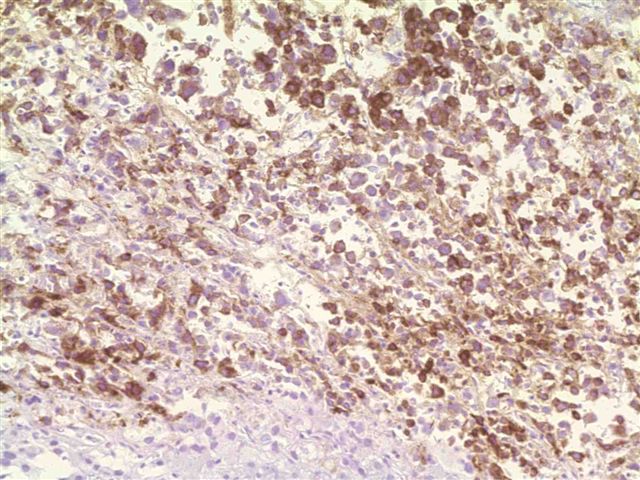
- Skin and other sites: melanoma (85-90%, see exceptions under Negative staining)
- Also blue nevus, Spitz nevus (Spitz nevi may be HMB45- at other sites)
- Nevus cells may be HMB45+ in intraepidermal and superficial dermal component
- Nevus cells may also have weak nuclear staining that is overwhelmed by hematoxylin and usually not seen (Mod Pathol 2008;21:1121)
- Angiomyolipoma (various sites, usually negative in nasal cavity)
- Clear cell sarcoma of soft tissue (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:452)
- Clear cell "sugar" tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:670)
- Epithelioid sarcoma (occasional)
- Kidney: t(6;11)(p21;q12) renal cell carcinoma (Hum Pathol 2012;43:726)
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (also stains nonproliferative cells)
- Melanocytosis
- PEComa (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1558)
- Pheochromocytoma (30%, Arch Pathol Lab Med 1992;116:151)
- Pigmented neural tumors (some), including some nerve sheath tumors, some neurofibromas (Hum Pathol 2005;36:871), pigmented neuroectodermal tumor of infancy
- Tuberous sclerosis complex components
Negative staining
- Adult / resting melanocytes
- Some melanomas: desmoplastic, oral mucosal, spindle cell (but 50% of HMB45 negative melanoma cells have premelanosomes on EM)
- Atypical fibroxanthoma
- Epithelioid malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors
- Leiomyosarcoma, liposarcoma
- Paget disease of breast, scrotum, vulva
- Pigmented dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, pigmented epithelioid melanocytoma
- Uterine tumors resembling ovarian sex cord tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1749)