Cite this page: Pernick N. Acid fast / Auramine-rhodamine. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsacidfast.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Acid fast refers to microorganisms whose cell wall has a high lipid content of mycolic acids and long chain fatty acids, which traditionally is considered to cause them to bind and retain the complex basic dye carbol-fuchsin even after strong decolorization with acid-alcohol (thus "acid-fast") (Wikipedia)
- Hänscheid et. al. believe auramine O actually binds to nucleic acids, not to the cell wall (see Lancet Infect Dis 2007;7:236, J Microbiol Methods 2008;74:119)
- Partially acid fast organisms exhibit both acid fast and non-acid fast bacilli and filaments in a single strain
- Standardization recommended for interpretation (Hum Pathol 2012;43:1845)
- Sputum smears may misidentify acid-fast bacilli as Mycobacterium tuberculosis in HIV+ patients (J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2013;63:168)
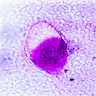
- Acid fast organisms include Mycobacteria, oocysts of Cryptosporidium parvum, Cyclospora, Isospora; also hooklets of cysticerci
- Partially acid fast organisms include Actinomyces: Dietzia (Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2006;56:1667), Gordonia (Emerg Infect Dis 2000;6:382), Nocardiae (Surg Infect (Larchmt) 2012;13:163), Rhodococcus (South Med J 1991;84:1217), Tsukamurella (J Med Case Rep 2008;2:207); also rarely Mycobacterium peregrinum (J Clin Microbiol 2005;43:2015)
- Note: nucleic acid based tests can rapidly detect and speciate mycobacteria (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2008;132:1333, Thorax 2008;63:317)
Methods
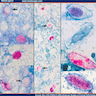
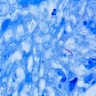
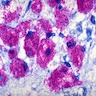
- Ziehl-Neelsen (classic): common method; bacteria stain bright red due to retention of carbol-fuchsin dye; background is methylene blue counterstain; procedure involves heat (#1, #2)
- Ziehl-Neelsen (modified bleach): may be more sensitive than classic stain (Acta Cytol 2008;52:325,J Cytol 2012;29:165)
- Ziehl-Neelsen (modified for stool specimens): does not require heating (Centers for Disease Control)
- Kinyoun: common method; uses more concentrated fuchsin dye and lipid solvent, but no heat; bacteria stain bright red against green background (#1, #2)
- Fite: to detect M. leprae (leprosy) and Rhodococcus (Diagn Cytopathol 2001;24:244); combines peanut / vegetable oil with xylene to minimize exposure of bacteria cell wall to organic solvents and protect precarious acid-fastness of organism (#1, #2)
- Ellis and Zabrowarny: protocol excludes phenol; procedure (J Clin Pathol 1993;46:559)
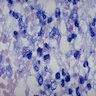
- Auramine-rhodamine: mixture of Auramine O and Rhodamine B dyes, auramine binds to mycolic acid in cell wall; detection requires a fluorescence microscope (mercury vapor lamp or LED), but is most sensitive stain for mycobacteria (Hum Pathol 1984;15:1085, PLoS One 2011;6:e22495); saves time in searching for microorganisms (Clin Infect Dis 2008;47:203); procedure
- Water filters are recommended to reduce false positives due to non-TB mycobacteria (Appl Environ Microbiol 2007;73:6296)
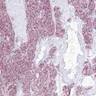
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
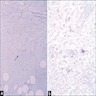
Cryptosporidium:
Videos
Acid fast stain