Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - disease | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Mehta V, Lilley CM, Picken MM. Adenovirus. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsadenovirus.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Antiadenovirus is a cocktail of mouse monoclonal antibodies derived from cell culture supernatant
- Though there are numerous genera within the Adenoviridae family, the antigen targeted (group specific hexon antigen) in commercially available antiadenovirus cocktails has been selected to detect all known, clinically important adenovirus serotypes
Essential features
- Antiadenovirus is a cocktail of mouse monoclonal antibodies with nuclear and cytoplasmic staining pattern developed to detect all known serotypes of adenovirus
- False positives are extremely uncommon
- Most false negatives (cases with positive viral cytopathic effect and negative IHC) result from exhaustion of the diagnostic tissue
Pathophysiology
- Double stranded, nonenveloped DNA viruses with a single, nonsegmented linear genome capped by covalently bound terminal proteins at either end of the genome
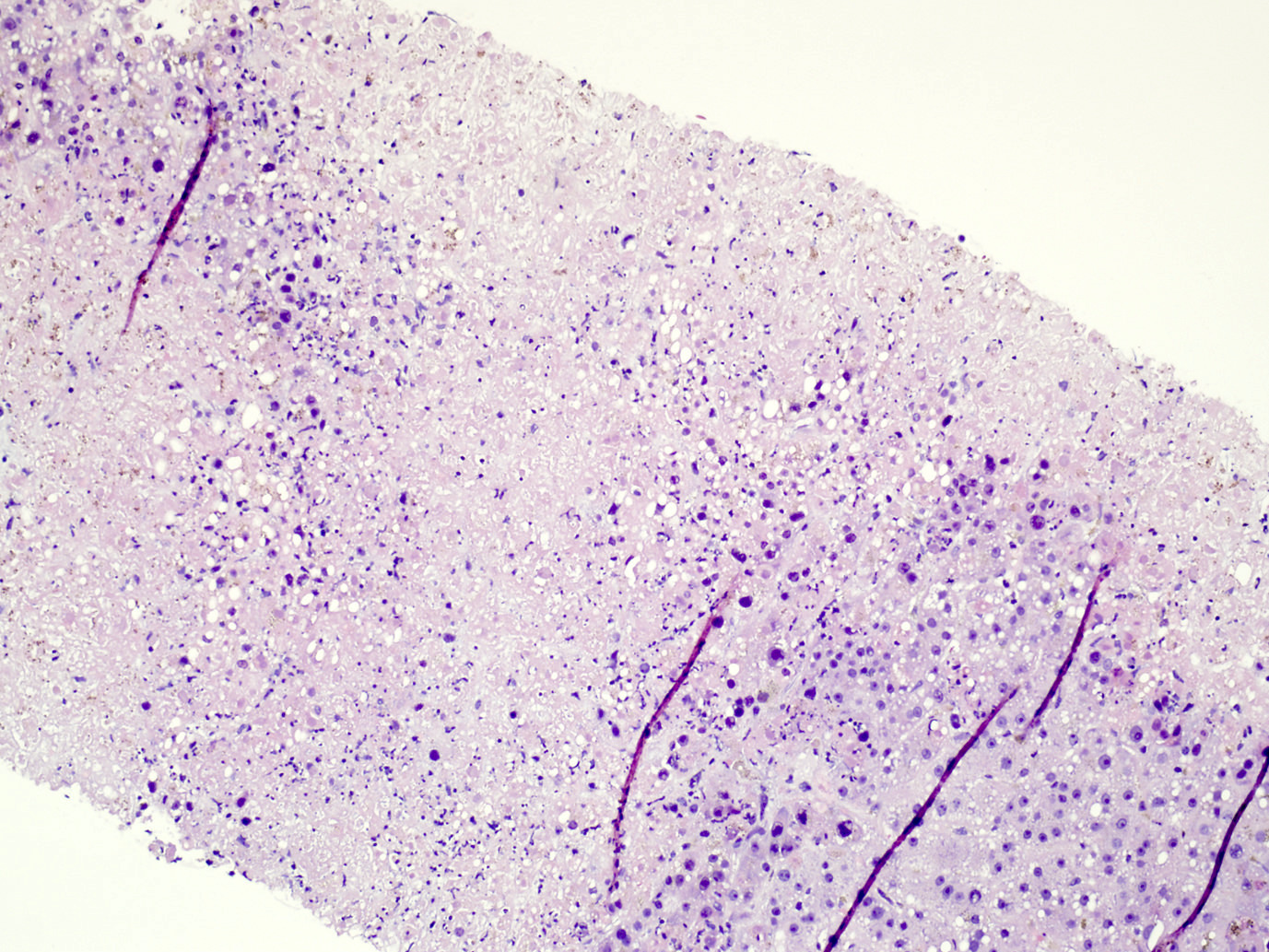
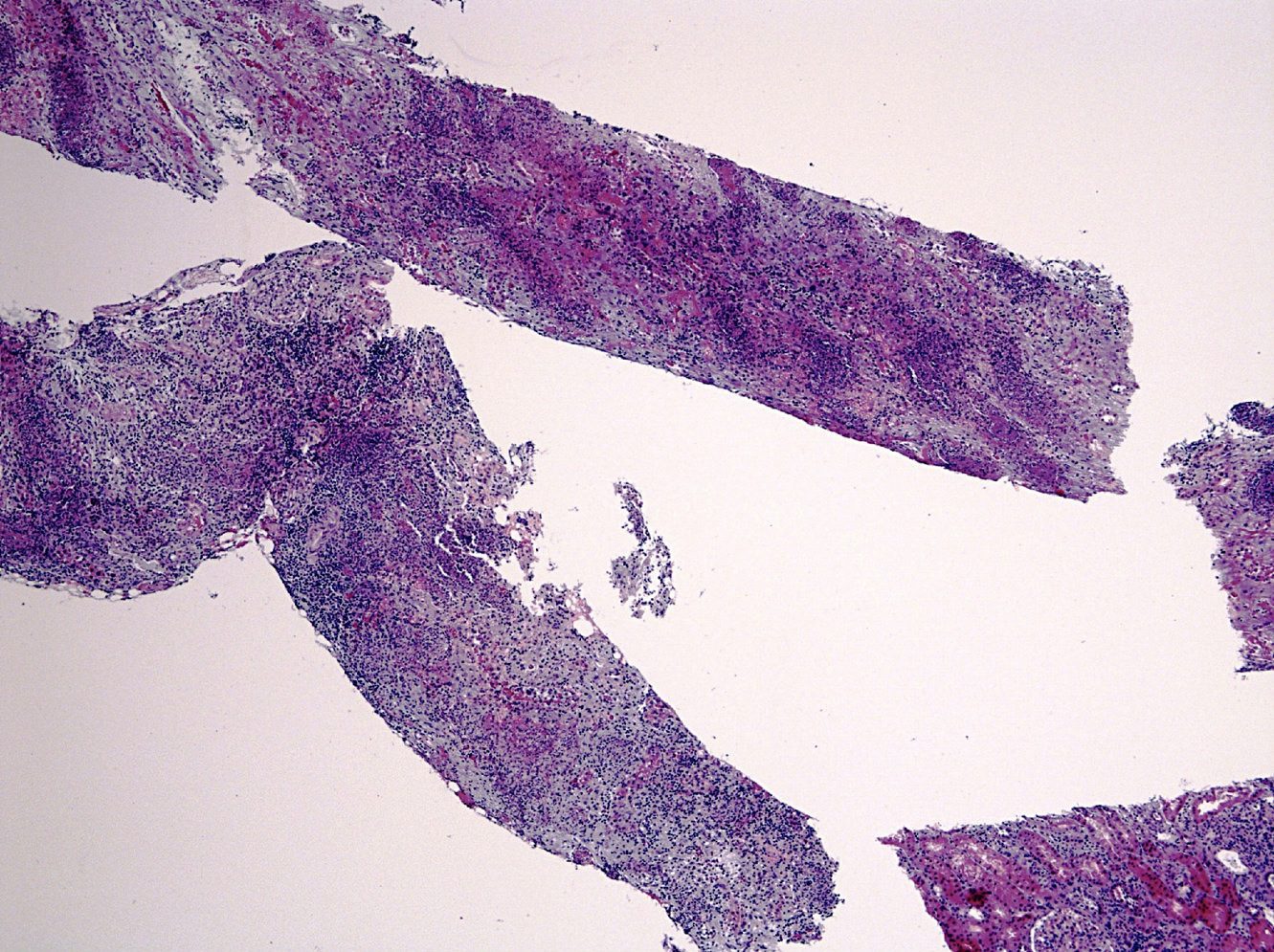
- Adenovirus produces nuclear inclusions without cytomegaly
- Virus binds to coxsackie adenovirus receptor, CD46 (complement regulatory protein), desmoglein 2 or sialic acid (primary receptor used depends on the viral serogroup), followed by viral internalization (Rev Med Virol 2009;19:165, Nat Med 2011;17:96)
- Viral replication cycle takes ~32 - 36 hours and up to 10,000 virions can be produced; new virions remain in the cell until it degenerates and lyses (Tille: Bailey & Scott's Diagnostic Microbiology, 13th Edition, 2013)
Clinical features
- Adenoviruses are spread via aerosols, in fecal matter or through close contact
- Adenovirus infection is especially common in military barracks and college dormitories
- Children under 14 and immunocompromised patients (including transplant recipients) are especially vulnerable
- Though certain viral subclasses exhibit seasonality, adenovirus infections occur all year round
- Reference: Trends Mol Med 2023;29:4
Interpretation
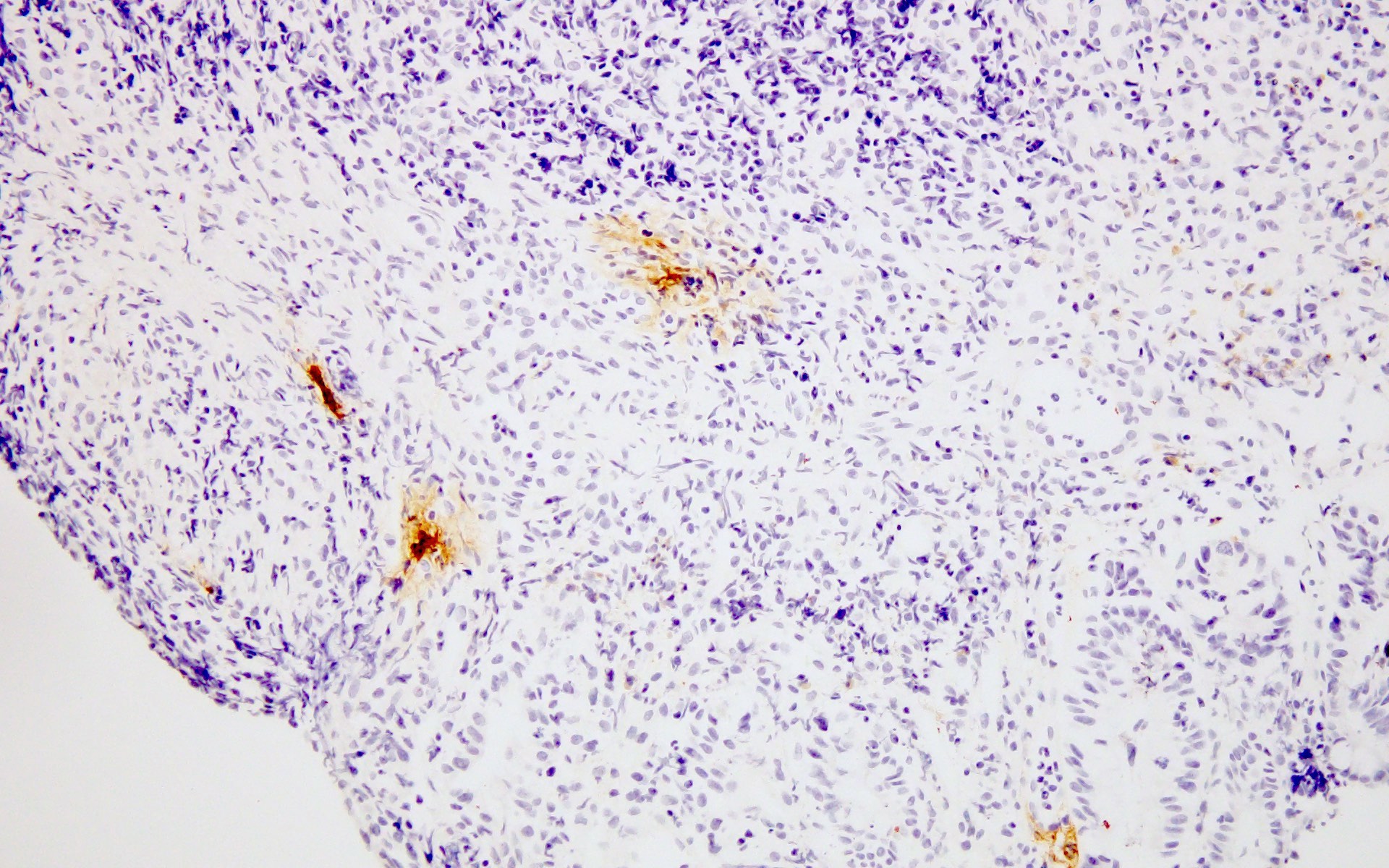
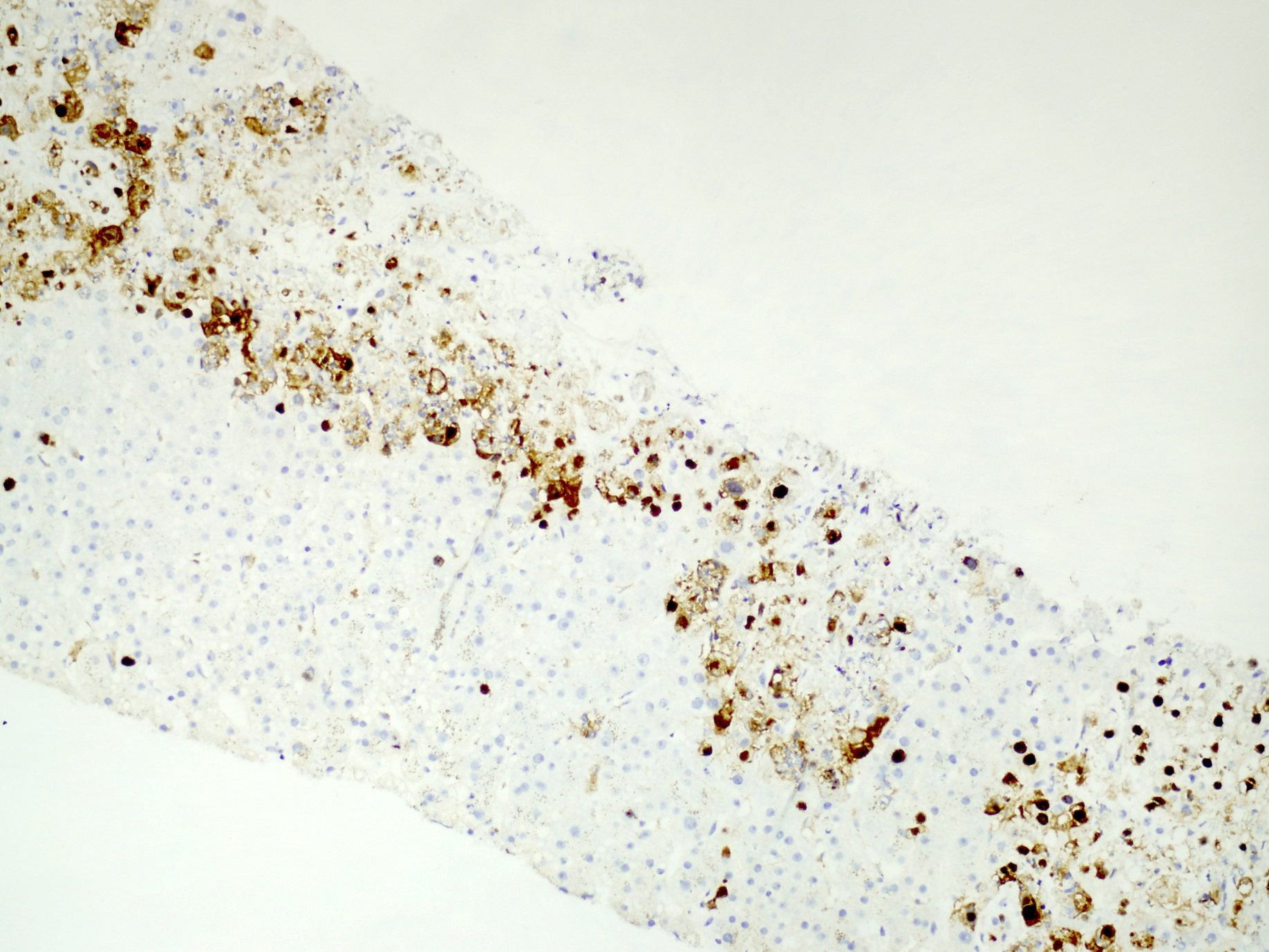
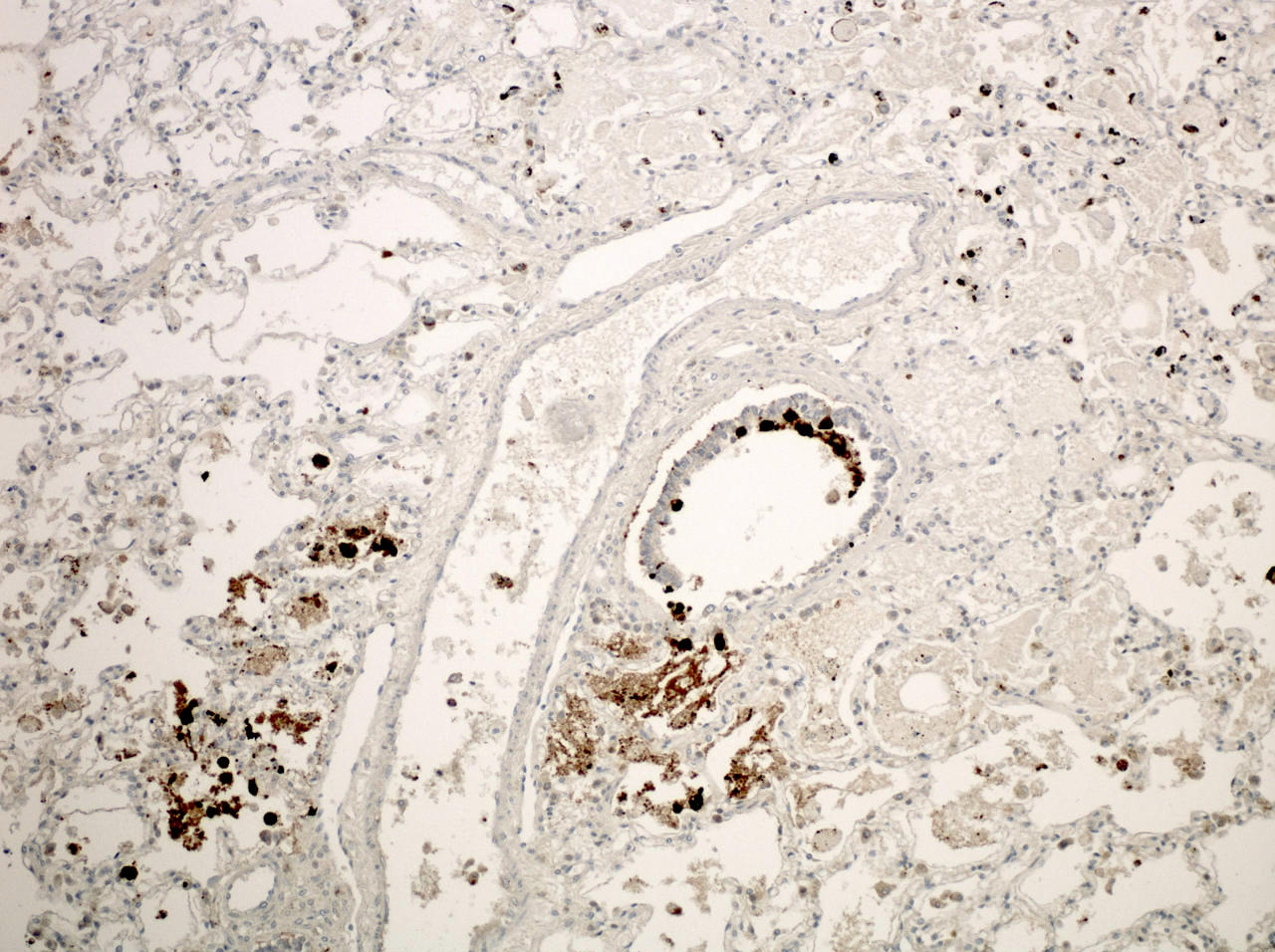
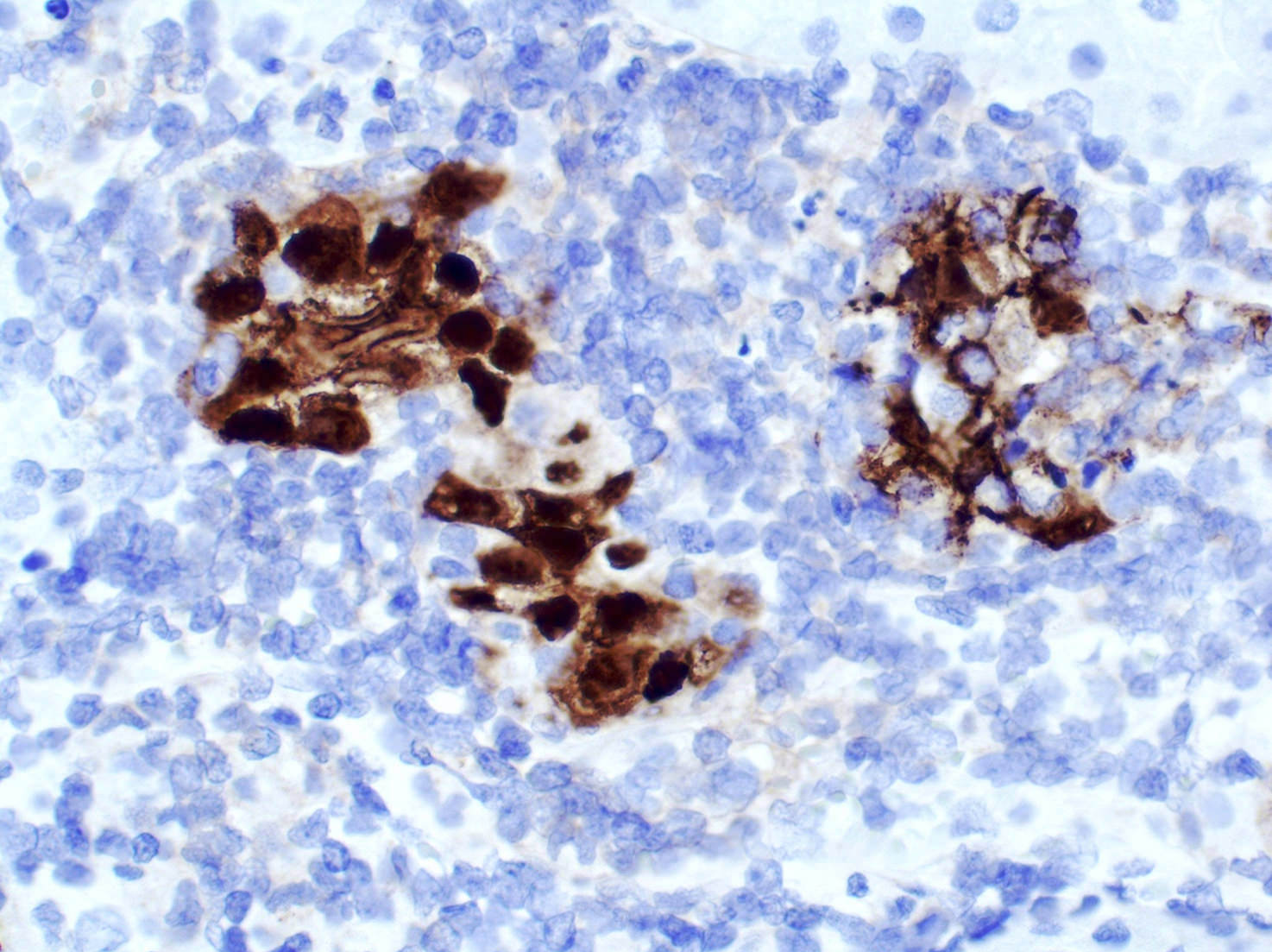
- Nuclear and cytoplasmic
- False positives are extremely uncommon
- Most false negatives (cases with positive viral cytopathic effect and negative IHC) result from exhaustion of the diagnostic tissue (Am J Clin Pathol 2017;147:96)
- Other limitations of this and other IHC tests are fixation time of tissues, dilution factor of antibody, retrieval method utilized and incubation time; optimal performance should be established through positive and negative controls
Uses by pathologists
- Various commercially available antibodies used for immunohistochemistry may not provide complete coverage against all 51 serotypes of adenovirus; diagnosis needs to be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction or electron microscopy
- Allograft infection in solid organ transplant recipients (Virchows Arch 2015;467:603)
- Adenovirus interstitial nephritis in renal allograft recipients (Kidney Int 2023;103;378, Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2012;7:1884)
- Adenoviral enteropathy in small bowel transplantation recipients (Clin Transplant 2016;30:1433, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2008;132:703)
- Adenovirus hepatitis in the adult allograft liver (Transplantation 1997;64:1483)
- Detection of adenovirus in hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients (Leuk Lymphoma 2004;45:873)
- Similar antibodies used to detect adenoviruses on tissue section are commercially available for laboratory use in enzyme immunoassays
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - disease
- Adenovirus infection in pediatric solid organ and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (Curr Infect Dis Rep 2012;14:658)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Gene amplification or DNA in situ hybridization can be used for identification
Sample pathology report
- Kidney, needle core biopsy:
- Adenovirus nephritis (see comment)
- Comment: Renal parenchyma with necrotizing tubulointerstitial nephritis is consistent with adenovirus nephritis. Immunohistochemical stain for adenovirus shows nuclear and cytoplasmic expression in affected cells.
- Liver, needle core biopsy:
- Adenovirus hepatitis (see comment)
- Comment: Liver parenchyma with necrotizing hepatitis is consistent with adenovirus hepatitis. Immunohistochemical stain for adenovirus shows nuclear and cytoplasmic expression in affected cells.
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
D. Nuclear and cytoplasmic. Of the choices listed, nuclear and cytoplasmic staining is seen in IHC for adenovirus. However, a virus specific diagnosis cannot be made based on the pattern of stain alone, as other stains can show nuclear and cytoplasmic staining. For example, diffuse and strong nuclear or nuclear and cytoplasmic staining involving the basal and parabasal layers of squamous epithelium is seen in p16 testing for HPV (block-like staining). Thus, the diagnosis is based on the antibody specificity while the pattern of stain is helpful. Moreover, the type of infected cell can be helpful in the differential diagnosis (e.g., CMV typically infects endothelium while adenovirus infects epithelial cells, as illustrated in this topic). Cytoplasmic stain is typically seen in IHC for several keratins or other intracytoplasmic proteins; stain for CK20 in Merkel cell carcinoma is an exception. Dot-like stain is typically seen for CK20 in Merkel cell carcinoma. Nuclear stain is positive in IHC for polyoma virus.
Comment Here
Reference: Adenovirus
Comment Here
Reference: Adenovirus