Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Vargas AC. ALK. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsalk.html. Accessed September 25th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene is at 2p23; protein is called ALK1, CD246
- Membrane spanning tyrosine kinase receptor, member of insulin receptor family
- First discovered in anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) with t (2;5) being the first ALK fusion identified to NPM (nucleophosmin protein)
- References: OMIM: 105590 [Accessed 25 June 2021], Science 1994;263:1281, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002;34:354
Essential features
- ALK overexpression occurs as a result of diverse alterations, including translocation, mutation and amplification / polysomy, among others
- Tumors harboring ALK translocations are potentially sensitive to ALK inhibitors
- Pathologists should be aware of the frequency of ALK overexpression and translocations according to tumor type to maximize ALK screening in the appropriate clinical setting
- Understanding the limitations of testing methodologies is important to avoid pitfalls in interpretation
- ALK expression in itself is a defining feature of specific entities, which when present, enables tumor classification and subtyping in routine pathology practice.
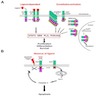
Pathophysiology
- Activation of ALK receptor requires ligand binding, which triggers homodimerization and transphosphorylation of its tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) domain
- ALK is an orphan receptor with no known ligand; heparin is one of the known activating ligands, which promotes ALK signaling through heparin sulfation, leading to ALK dimerization (Science Signaling 2015;8:ra6)
- Downstream signaling pathways triggered by ALK include STAT3, ERK1 / ERK2, PLC and PI3K / AKT, which upon activation lead to cell proliferation and survival
- In the inactive state, the ALK receptor promotes apoptosis via caspase 3 activation, leading to kinase inactivation
- In ALK chromosomal rearrangements, the 3' portion of ALK, which contains the TKI domain, fuses with the 5' of a partner gene that provides the N-terminus with the dimerization domain
- Fusion chimeric oncoproteins result in constitutive autophosphorylation of the ALK kinase, leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation and survival
- References: Oncol Lett 2019;17:2020, Cancers (Basel) 2019;11:275
Clinical features
- Large group of unrelated malignant and benign tumors express ALK; its expression is not a marker of malignant phenotype
- Prognostic significance of ALK expression depends on tumor type, the underlying molecular mechanism of ALK expression and sensitivity to ALK inhibitors
- ALK rearrangement predicts response to ALK inhibitors
- Testing for ALK rearrangements is recommended in all patients with lung adenocarcinomas to guide therapy
- ALK inhibitors are offered to any ALK rearranged tumor in the advanced or metastatic setting
- Therapeutic inhibition of ALK fusion oncoproteins is achieved through small molecule TKI, with crizotinib being the first ALK TKI approved by the FDA
- ALK driven resistance occurs due to secondary mutations in the kinase domain or gene amplification
- Second (i.e. ceritinib and alectinib) and third (i.e. lorlatinib) generation TKI are used to overcome resistance, including emerging new targets of the ALK signaling pathway (i.e. STAT3, PI3K or ERK / MEK)
- References: Cancers (Basel) 2019;11:275, Oncol Lett 2019;17:2020
Interpretation
- Detection of ALK gene alterations by current technology
- Immunohistochemistry
- Strong granular cytoplasmic expression for ALK with or without membranous or nuclear expression is predictive of ALK rearrangement and response to ALK TKI
- Positive IHC correlates with tumor response to ALK inhibitors even in ALK FISH negative cases (J Clin Pathol 2021 [Epub ahead of print], Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018;142:321)
- Absence of ALK protein expression indicates that a tumor is unlikely to harbor ALK rearrangement or to respond to ALK inhibitors
- Different clones available: D5F3, 5A4, 1A4 and ALK1 (J Clin Pathol 2021 [Epub ahead of print], Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018;142:321)
- 5A4 and D5F3 are equivalent alternatives to ALK FISH testing; in particular, the Ventana ALK D5F3 CDx Assay is an FDA approved companion diagnostic assay to determine eligibility for ALK inhibitors (J Clin Pathol 2021 [Epub ahead of print], Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018;142:321)
- Clone ALK1 is currently mostly limited to ALCL and not recommended for screening rearrangements in solid tumors due to poor sensitivity (67 - 100%) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018;142:321)
- Pattern of ALK staining varies, depending on the gene fusion partner:
- Nuclear and cytoplasmic expression: NPM1-ALK and RANBP2-ALK fusions and the ALKATI isoform (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:25, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:135, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:786)
- Membranous and cytoplasmic expression: TPM3-ALK fusions (Semin Diagn Pathol 2020;37:57)
- Diffuse cytoplasmic expression: identified with the following fusion partners: EML4, ATIC, TFG, TPM4, MYH9, ALO17, TRAF1, PABPC1, EEF1G; CLTC-ALK fusion shows cytoplasmic granular / dotted pattern (Semin Diagn Pathol 2020;37:57, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:25)
- Pitfalls in ALK IHC:
- Faint cytoplasmic labelling for ALK should be designated as equivocal, as this can occur in the absence of specific targeted alterations
- False positive stain in neuroendocrine cells
- Nonspecific background staining in mucin
- False negative stain in cells with signet ring cell morphology due to nuclear displacement by mucin (J Clin Pathol 2021 [Epub ahead of print])
- Immunohistochemistry
- Reference: Tsao: IASLC Atlas of ALK and ROS1 Testing in Lung Cancer, 2nd Edition, 2016
Uses by pathologists
- ALK immunohistochemistry (IHC) is used as a predictive biomarker of an underlying ALK translocation (or other gene alteration), to identify patients who can potentially benefit from ALK inhibitors
- Presence of ALK positivity by IHC in the context of specific histological features allows tumor classification in routine pathology practice
- References: J Clin Pathol 2021 Apr 19 [Epub ahead of print], Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018;142:321
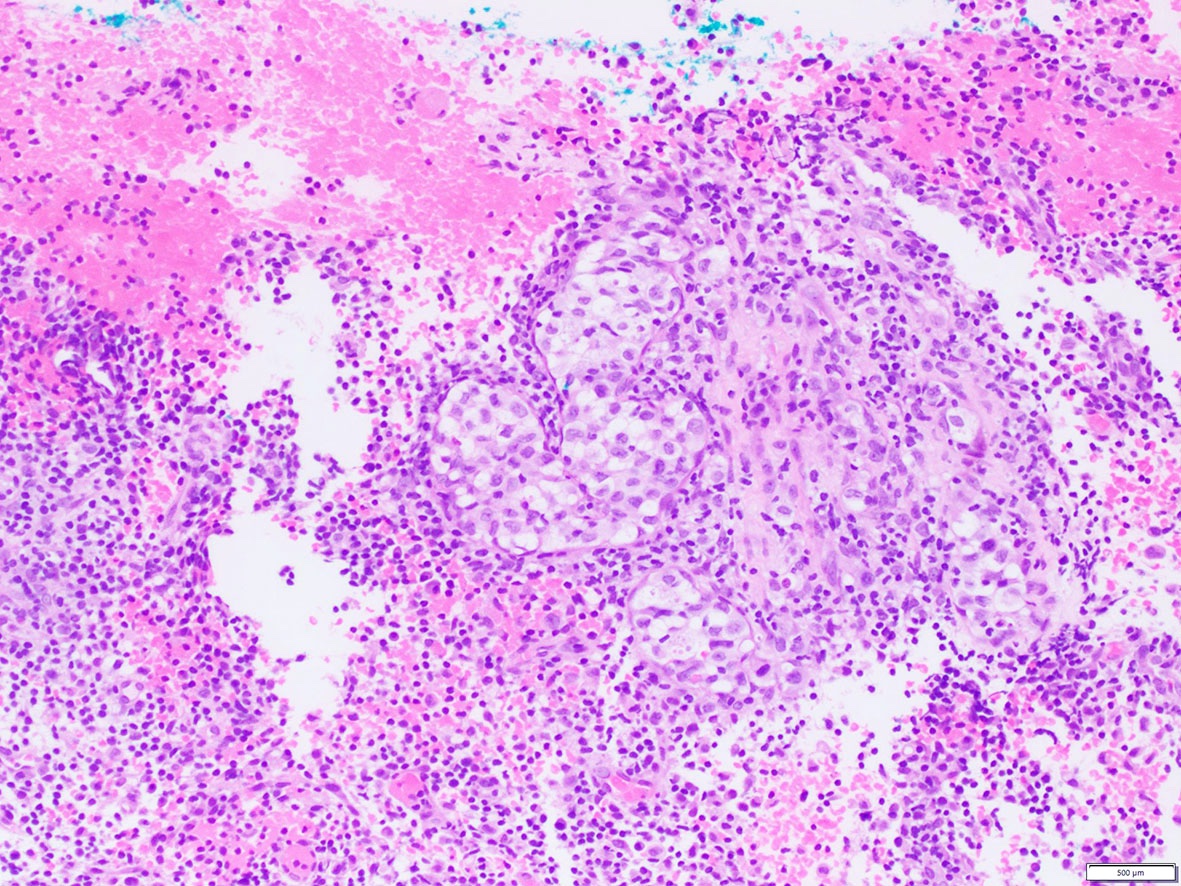
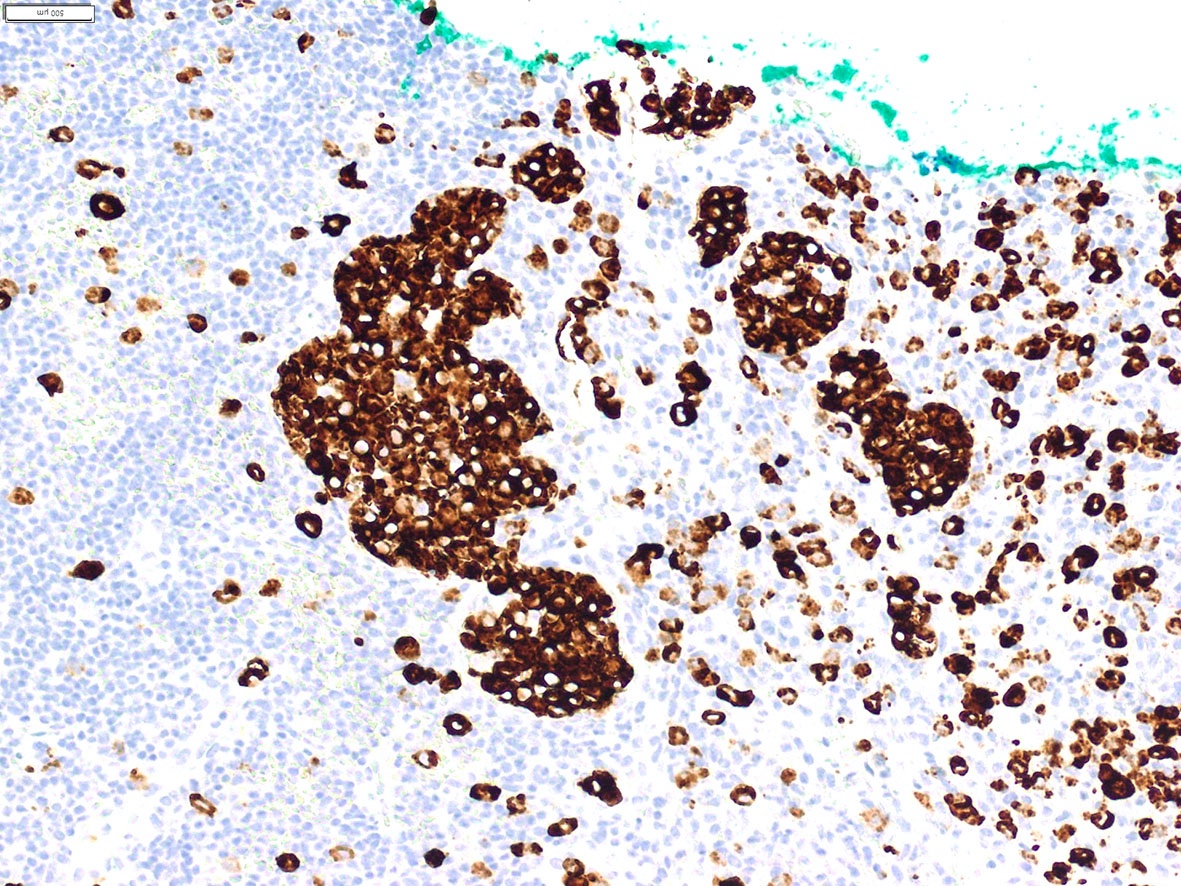
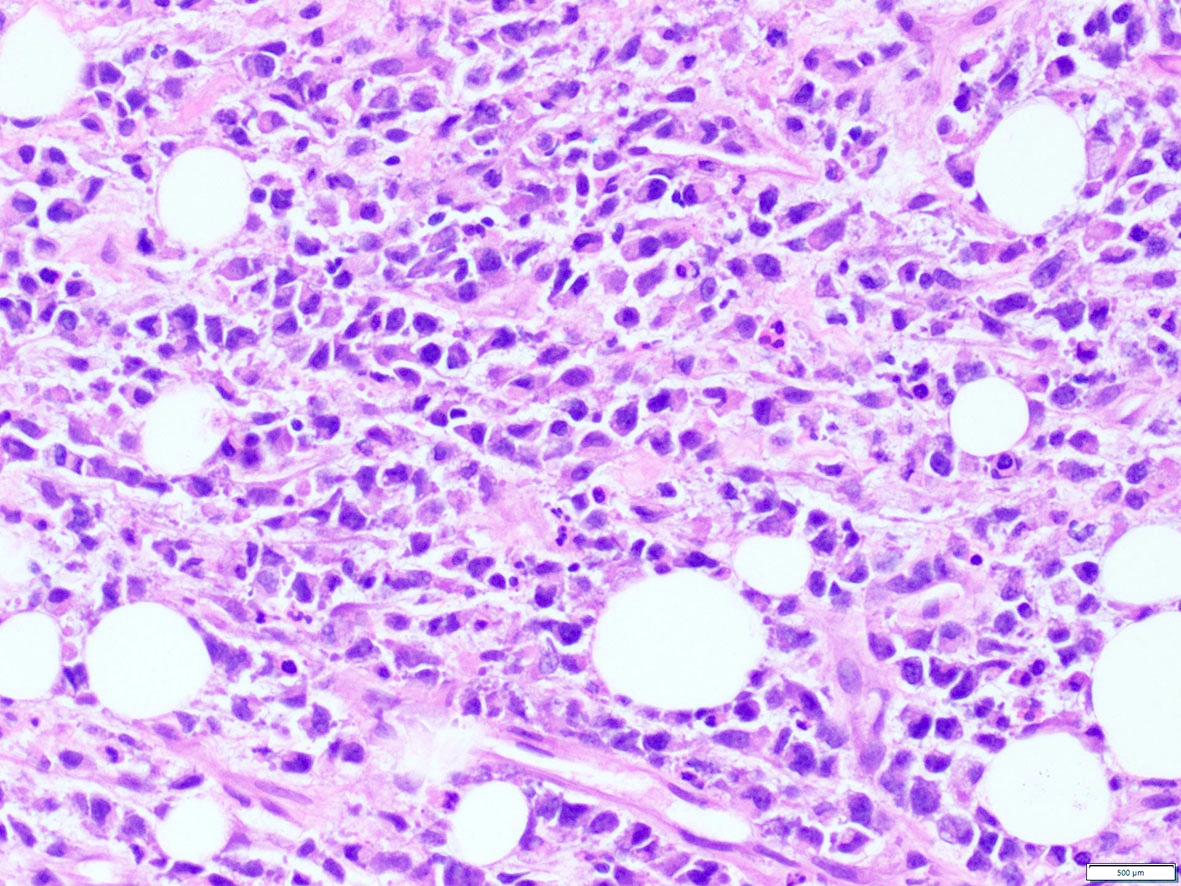
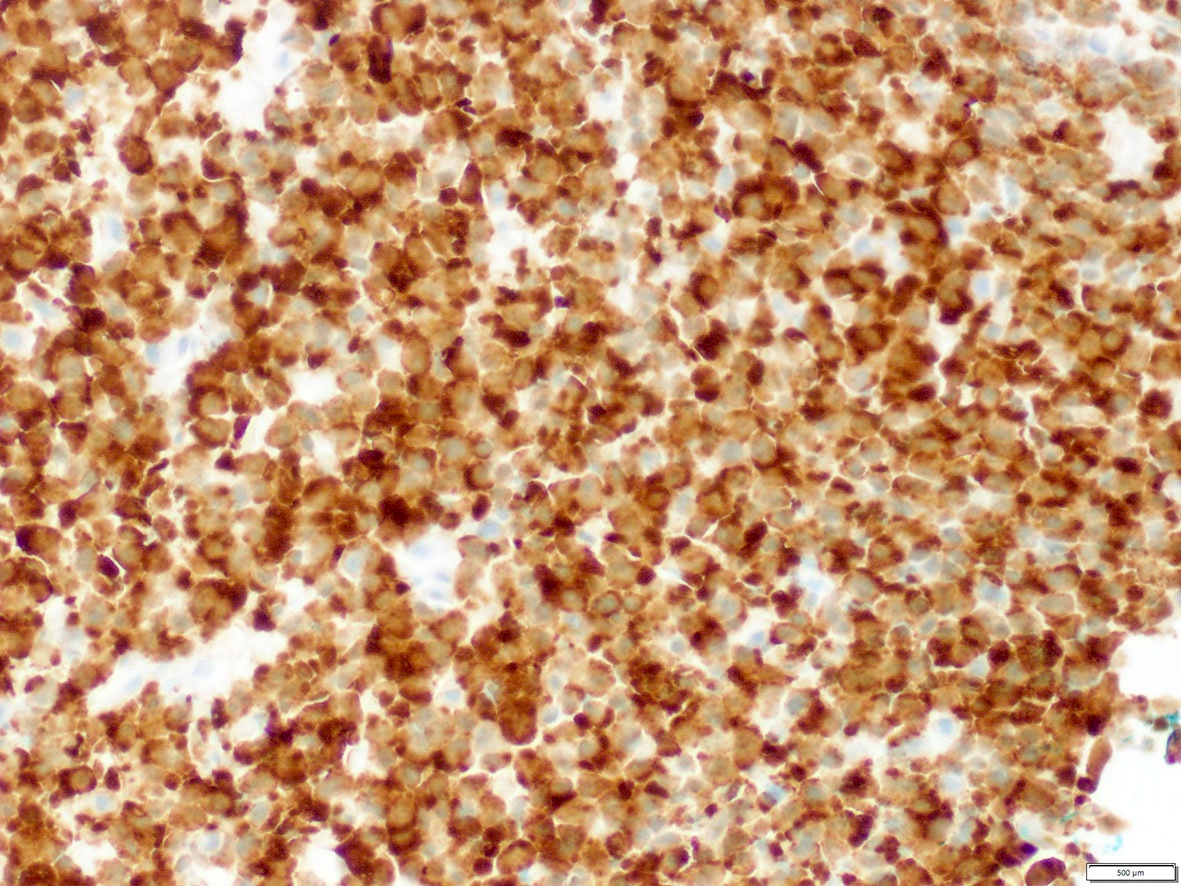
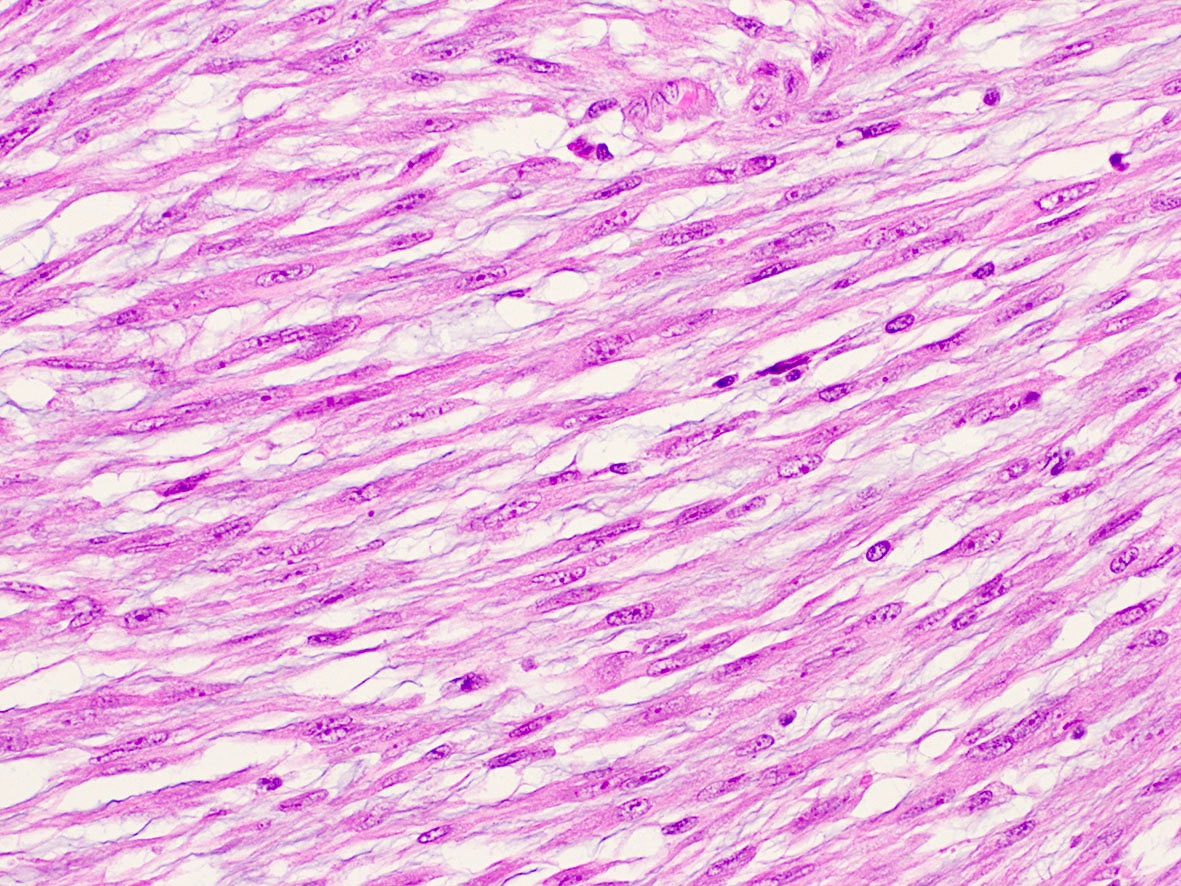
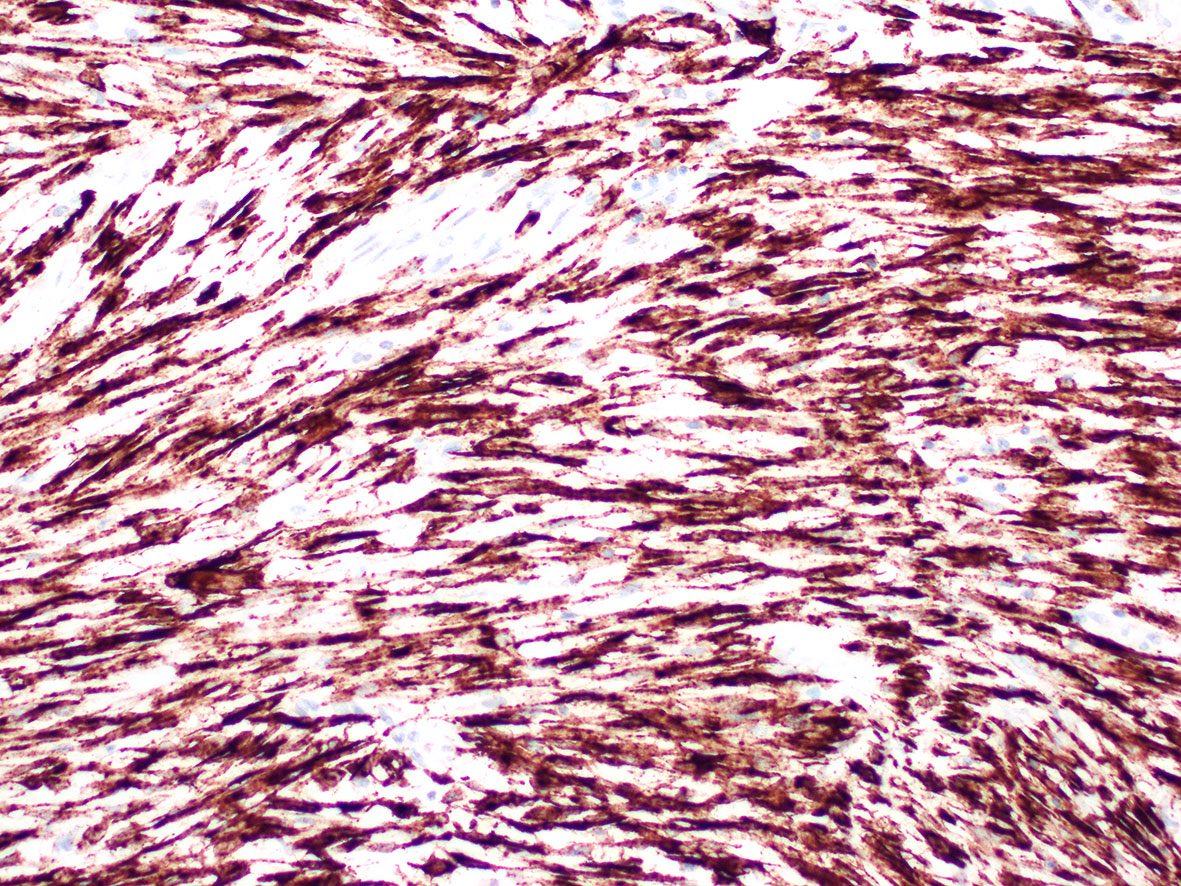
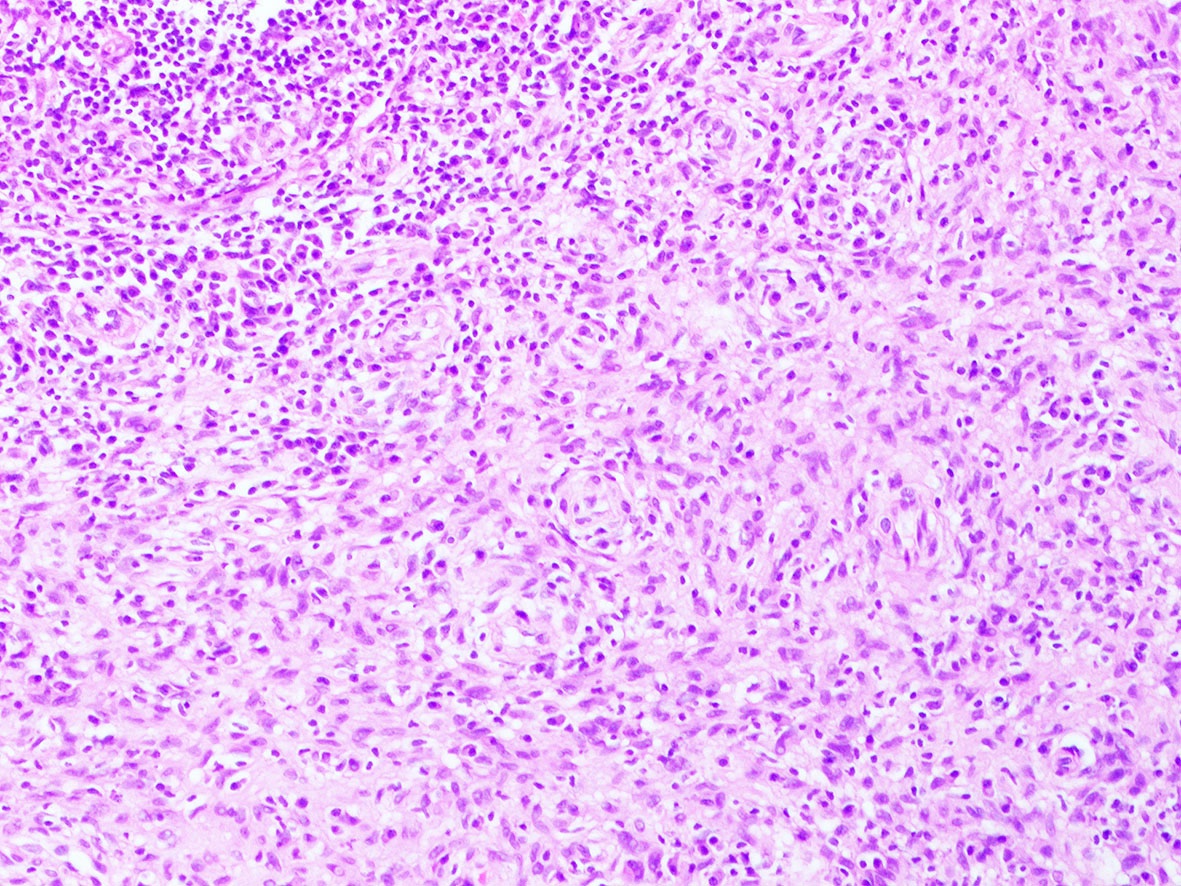
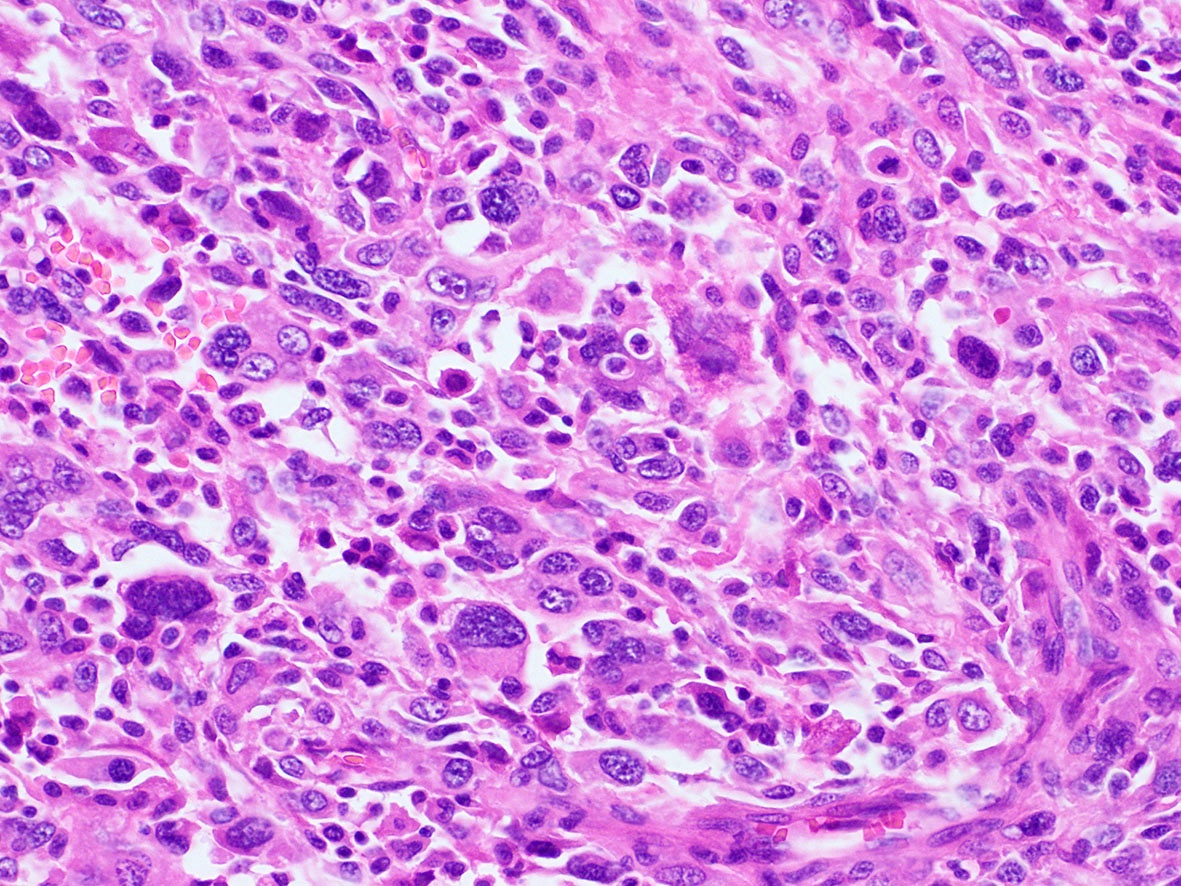
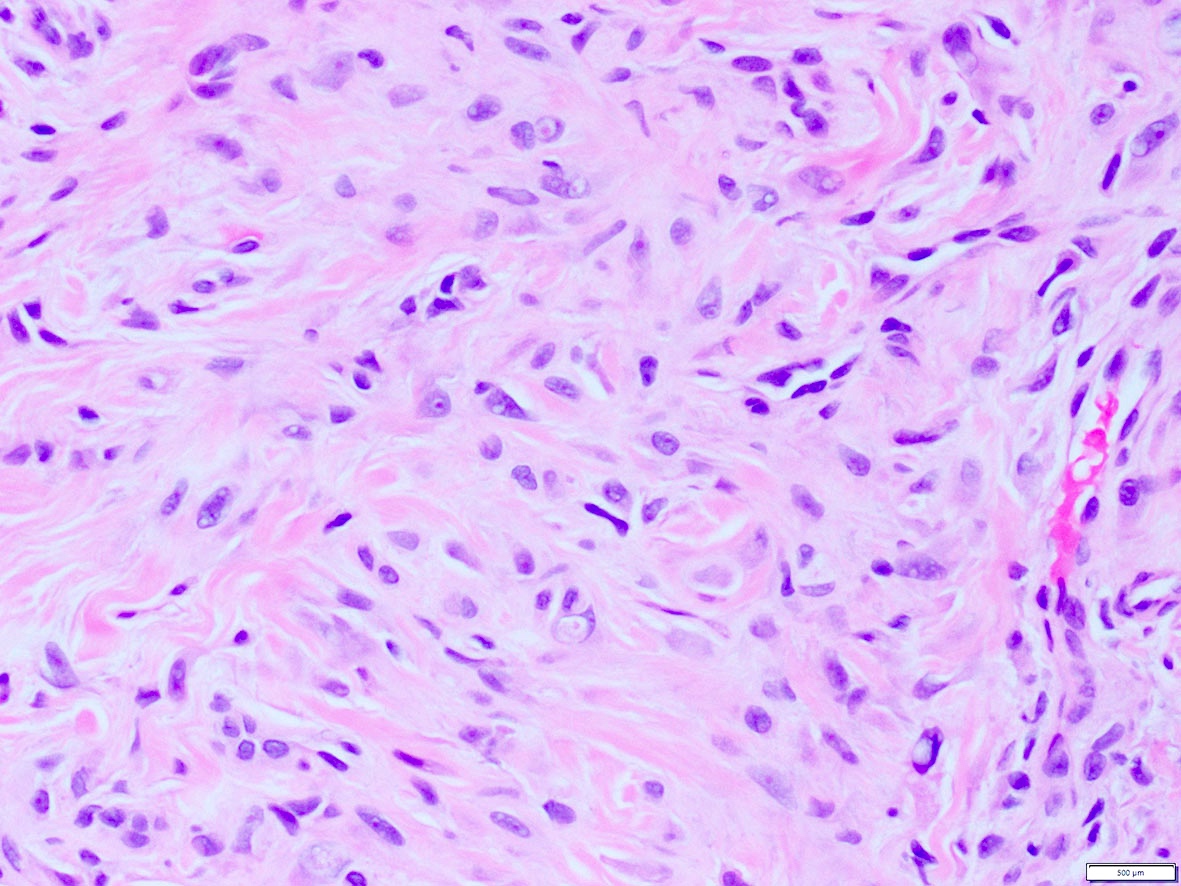
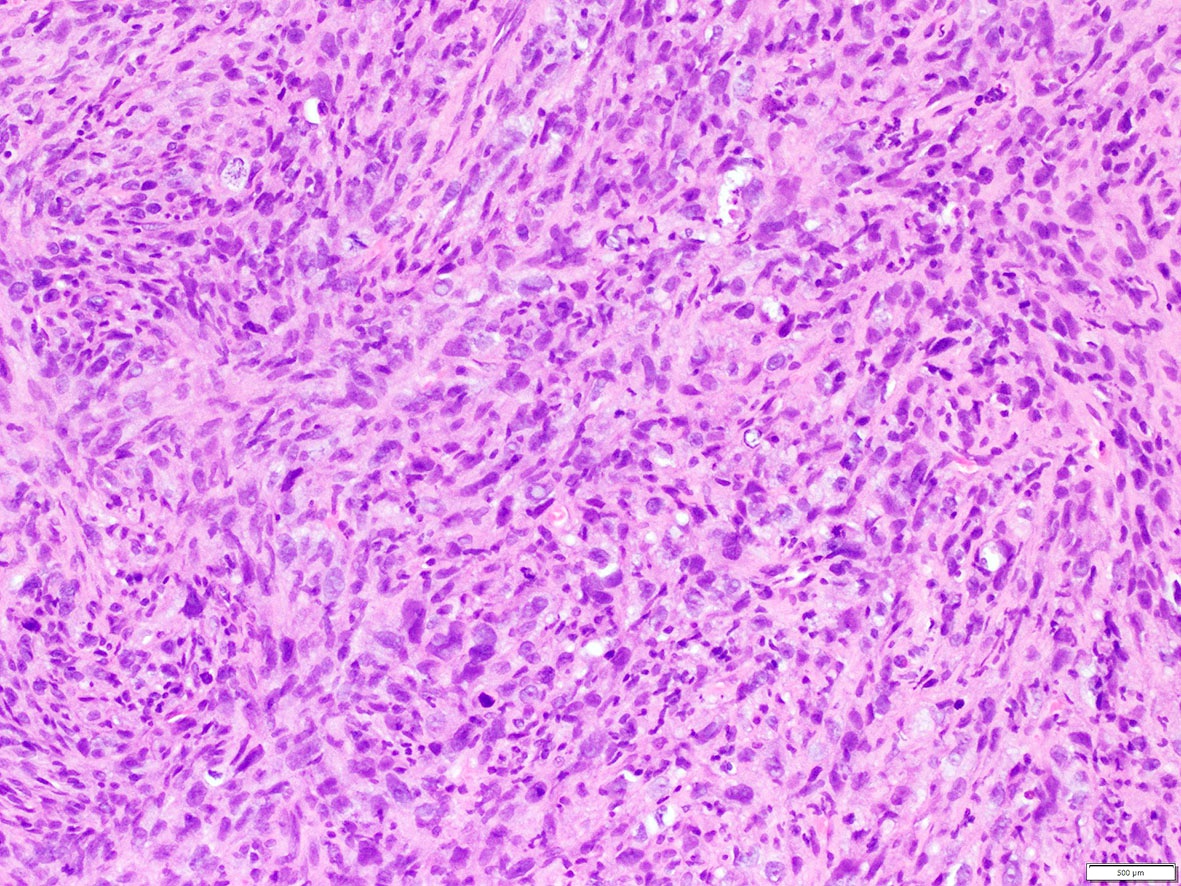
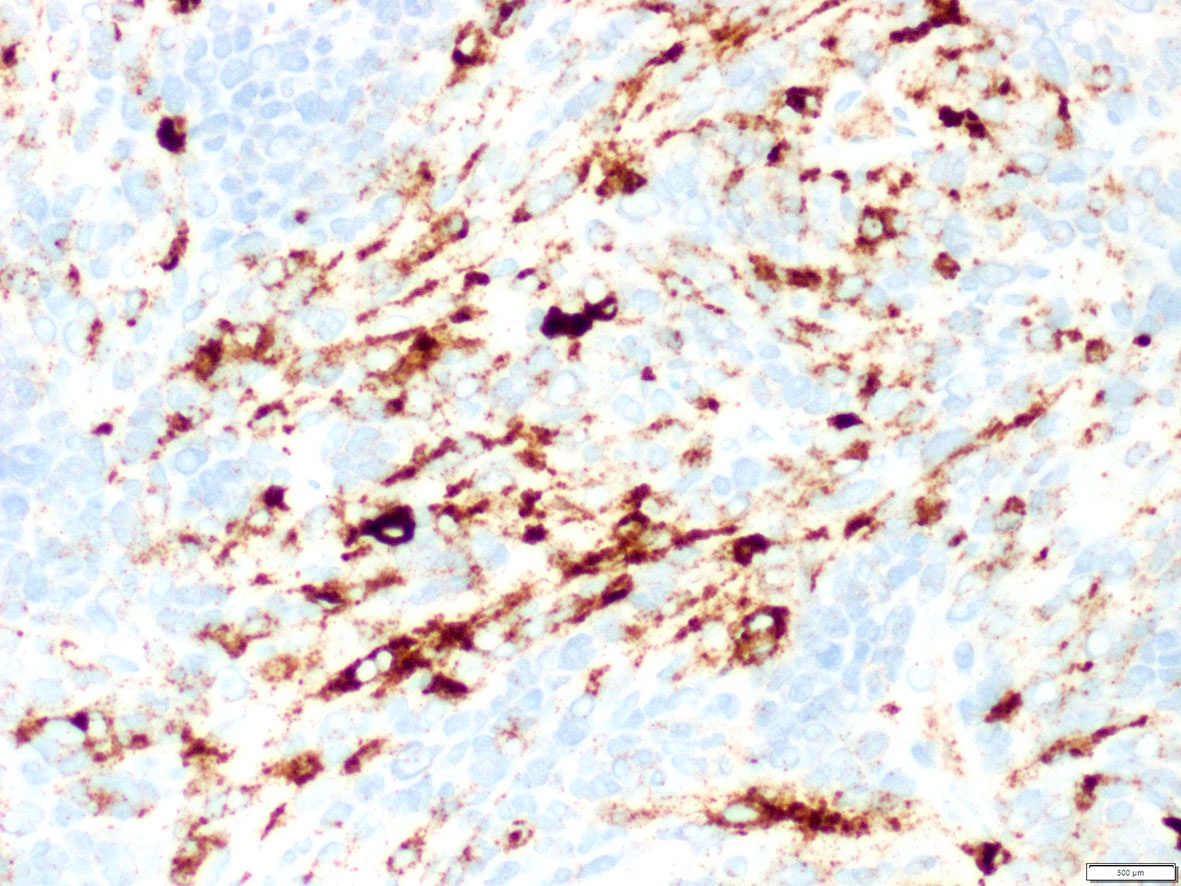
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by A. Cristina Vargas, M.B.B.S., Ph.D., Patricia Guzman, M.D., Fiona Bonar, M.B.B.Ch., Alison Cheah, M.B.B.S. and Martin Jones, M.B.B.S.
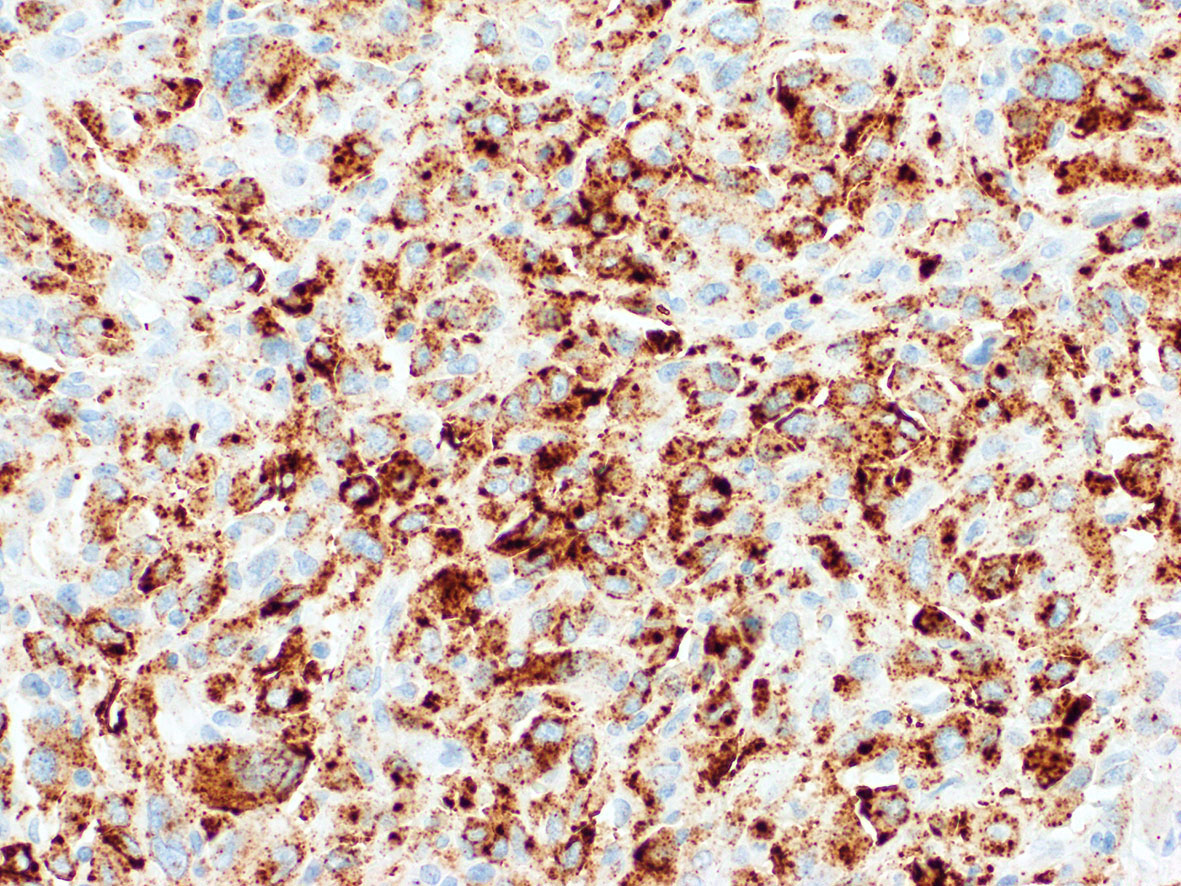
Positive staining - normal
- ALK expression in normal tissue is limited to restricted zones of the brain, peripheral nervous system and testis
Positive staining - disease
- ALK overexpression as a result of gene translocations / fusions:
- ALK+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) (Science 1994;263:1281, Semin Diagn Pathol 2020;37:57)
- Approximately 4% of lung adenocarcinomas, which show an association with mucinous cribriform and solid signet ring cell patterns and usually lack significant pleomorphism (J Clin Pathol 2021 [Epub ahead of print], Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1226)
- 50% of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors (IMT) (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:957)
- Including the aggressive variant, epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:135)
- Thyroid carcinomas, predominantly papillary (in particular the follicular variant), poorly differentiated and anaplastic (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:652, Endocr Relat Cancer 2019;26:803)
- 10% of Spitz tumors, including nevi, atypical Spitz tumors and Spitzoid melanomas (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:581)
- ALK+ large B cell lymphoma, a variant of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:25)
- Distinct subgroup of renal cell carcinomas, usually in the pediatric population (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2016;55:442)
- Rare salivary gland carcinomas, including myoepithelial carcinoma, secretory carcinoma, intraductal carcinoma and salivary duct carcinoma (Virchows Arch 2021;478:933, Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:962)
- ALK+ histiocytosis, which can present as localized disease or systemic involvement at a wide age range (Mod Pathol 2019;32:598)
- Including presentation as breast masses (Am J Surg Pathol 2021;45:347)
- Rare cases (0.1%) of colorectal carcinomas, usually DNA mismatch repair deficient and pancreatic adenocarcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1224, J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2017;15:555)
- Subset (3%) of peritoneal mesotheliomas, including pediatric cases but not in the pleural counterpart (JAMA Oncol 2018;4:235, Am J Surg Pathol 2021;45:653)
- Unrelated cutaneous neoplasms:
- Epithelioid fibrous histiocytoma (> 80%) (Mod Pathol 2015;28:904)
- Non neural granular cell tumor (NNGCT) (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1133)
- Primary ALK+ cutaneous ALCL (2%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:776)
- Other soft tissue tumors:
- 2.4% of leiomyosarcoma (Mol Cancer Res 2019;17:676)
- And a group of mesenchymal spindle cell neoplasms with a specific phenotype (S100+ / SOX10- / CD34+) (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2021;60:282, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2018;57:611)
Table: ALK gene fusion partners according to tumor entity
| Tumor type | Most common ALK gene fusion partners | References |
| Lung adenocarcinoma | EML4 (80%), NPM1, CLTC, TPM3, RANBP2, STRN, ATIC, KIF5B, TPM4, TFG, HIP1, SQSTM1, A2M, KLC1, TPR | J Clin Pathol 2021 [Epub ahead of print], Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1226, Oncol Lett 2019;17:2020 |
| Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) | NPM1 (80%), TPM3, ATIC, TFG, CLTC, MSN, TPM4, MYH9, ALO17, TRAF1, EEF1G, PAPBC1, SQSTM1 | Science 1994;263:1281, Semin Diagn Pathol 2020;37:57, Oncol Lett 2019;17:2020 |
| ALK+ primary cutaneous ALCL | NPM1, TRAF1, ATIC, TPM3 | Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:776 |
| Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) | TPM3, TPM4, RANBP2, TFG, CARS, ATIC LMNA, PRKAR1A, CLTC, FN1, SEC31A, EML4, DCTN1, PPFIBP1, FN1 | Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:957, Oncol Lett 2019;17:2020 |
| Epithelioid IMT | RANBP2 | Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:135 |
| Spitz tumors | DCTN1, TPM3, NPM1, TPR | Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:581 |
| Thyroid carcinoma | STRN, EML4, TFG, GTF2IRD1, CCDC149, ITSN2, CTSB, PPP1R21, DCTN1 | Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:652, Endocr Relat Cancer 2019;26:803, Oncol Lett 2019;17:2020 |
| Renal cell carcinomas | TPM3, EML4 , STRN, VCL | Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2016;55:442, Oncol Lett 2019;17:2020 |
| Peritoneal mesothelioma | STRN, ATG16L1, TPM1 | JAMA Oncol 2018;4:235, Am J Surg Pathol 2021;45:653 |
| ALK+ histiocytosis | TPM3, KIF5B | Mod Pathol 2019;32:598, Am J Surg Pathol 2021;45:347 |
| Salivary gland carcinomas | MSN (myoepithelial), CTNNA1 (secretory), STRN, MYO18A (intraductal), HNRNPH3, EML4 (salivary duct) | Virchows Arch 2021;478:933, Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:962 |
| Colorectal adenocarcinoma | EML4, TPM4, CAD, SPTBN1, SLMAP, DIAPH2, LOC101929227, DIAPH2, STRN | Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1224, Oncol Lett 2019;17:2020 |
| Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | EML4, STRN | J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2017;15:555 |
| Leiomyosarcoma | STK32B, IGFBP5, ACTG2, TNS1, KANK2 | Mol Cancer Res 2019;17:676 |
| Mesenchymal spindle cell tumors (S100+ / SOX10- / CD34+) | EML4, PPP1CB, CLIP1 | Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2021;60:282, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2018;57:611 |
| Non neural granular cell tumor (NNGCT) | DCTN1, SQSTM1 | Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1133 |
| Epithelioid fibrous histiocytoma | VCL, SQSTM1 | Mod Pathol 2015;28:904 |
| ALK+ large B cell lymphoma | CLTC, NPM1, SEC31A, SQSTM1, RANBP2, IGL | Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:25 |
- ALK overexpression as a result of mutations or other gene alterations
- Medulloblastomas can harbor ALK somatic or germline mutations (e.g. p.M1199L, c.3605delG), amplification or increased mRNA expression (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:781)
- Subset of acral melanoma harbors the so called ALKATI isoform, arising from an alternative transcription initiation (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:786)
- ALK overexpression not associated with gene fusions or well characterized gene alterations
- Rhabdomyosarcomas (RMS) of embryonal and alveolar types including the recently described group FET-TFCP2 rearranged (RMS) (Mod Pathol 2020;33:404)
- Proportion of breast cancers with overexpression due to gene amplification (Breast Cancer Res 2015;17:127)
- Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:93)
- Merkel cell carcinoma (Cancers (Basel) 2017;9:123)
- Small subset of salivary gland carcinomas (Virchows Arch 2021;478:933)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH)
- FISH using break apart (BA) probes is the most widely available technology for detection of ALK gene rearrangements in routine clinical practice
- Currently, the Vysis ALK Break Apart FISH Probe Kit (Abbott Molecular, Des Plaines, Illinois, USA) is the only approved companion diagnostic tool for crizotinib based treatment eligibility
- FISH BA positive result is established using a threshold of 15% tumor cells showing either signals separated by at least 2 probe diameters or 3’ isolated red signals (due to deletion of the 5' probe)
- Isolated 3’ red signal pattern and other atypical signal patterns (5’ green signals or red doublet) can result in false positive and negative results when compared with detection by next generation sequencing
- Polysomy including increased copy number or amplification detected by FISH does not predict response to therapy with targeted ALK inhibitors
- Issues associated with discordant IHC and FISH or false negative FISH: complex deletions / rearrangements, cryptic insertions, alterations of ALK promoter and gene amplification
- Next generation sequencing and mutation testing
- There is a good degree of concordance among FISH, next generation sequencing and IHC but discordant cases occur due to rare fusions or complex rearrangements only detected by next generation sequencing
- RNA sequencing or other next generation sequencing based technology is recommended to elucidate cases with atypical / isolated signal FISH patterns
- Routine somatic testing to identify secondary ALK mutations arising in the setting of acquired resistance to ALK inhibitors is currently not recommended in the routine setting
- ALK germline mutation testing should be targeted in specific clinical settings
- References: Clin Lung Cancer 2019;20:e421, Lung Cancer 2019;131:62, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018;142:321, J Clin Pathol 2021 [Epub ahead of print], Tsao: IASLC Atlas of ALK and ROS1 Testing in Lung Cancer, 2nd Edition, 2016
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- ALK should be reported following the guidelines established for lung adenocarcinoma (e.g. template for biomarker testing established by the College of American Pathologists: Lungbiomarker v1.3.0.2). An example report following this template includes the following:
- ALK rearrangement by molecular methods
- Rearrangement identified
- EML4-ALK
- Rearrangement identified
- Polysomy:
- Absent
- ALK by immunohistochemistry
- Positive: cytoplasmic and nuclear expression (Clone D5F3)
- ALK rearrangement testing method(s)
- In situ hybridization (fluorescence [FISH])
- Immunohistochemistry
- Ventana ALK (D5F3) immunohistochemistry (IHC) assay
- ALK rearrangement by molecular methods
- Full template of report (College of American Pathologists: Lungbiomarker v1.3.0.2) available in CAP: Cancer Protocol Templates [Accessed 30 June 2021]
Practice question #1
What is the expected diagnosis for a uterine spindle cell tumor with this histological appearance? The tumor displayed focal smooth muscle expression, strong ALK overexpression on IHC and an ALK translocation was confirmed by FISH.
- Endometrial stromal sarcoma
- Epitheliod myofibroblastic sarcoma
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor
- Leiomyoma
- Spindle cell tumor (S100+ / SOX10- / CD34+) with ALK translocations
Practice answer #1
Practice question #2
What are the most common tumors harboring ALK translocations?
- Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, Spitz tumors, thyroid carcinomas and renal cell carcinomas
- Colorectal adenocarcinoma, inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors, anaplastic large cell lymphoma and Merkel cell carcinoma
- Lung adenocarcinoma, breast cancer, inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors, rhabdomyosarcoma and Spitz tumors
- Lung adenocarcinoma, inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors, anaplastic large cell lymphoma and Spitz tumors
- Melanoma, lung adenocarcinoma, inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors and diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Practice answer #2
D. Lung adenocarcinoma, inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors, anaplastic large cell lymphoma and Spitz tumors
Comment Here
Reference: ALK
Comment Here
Reference: ALK