Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1Cite this page: Ellis A, Zhang L. TdT. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainstdt.html. Accessed October 4th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Member of the X family of DNA polymerases
- Encoded by DNTT on 10q24.1 (GeneCards: DNTT Gene [Accessed 24 May 2022])
Essential features
- Nuclear marker expressed in most precursor lymphoid neoplasms
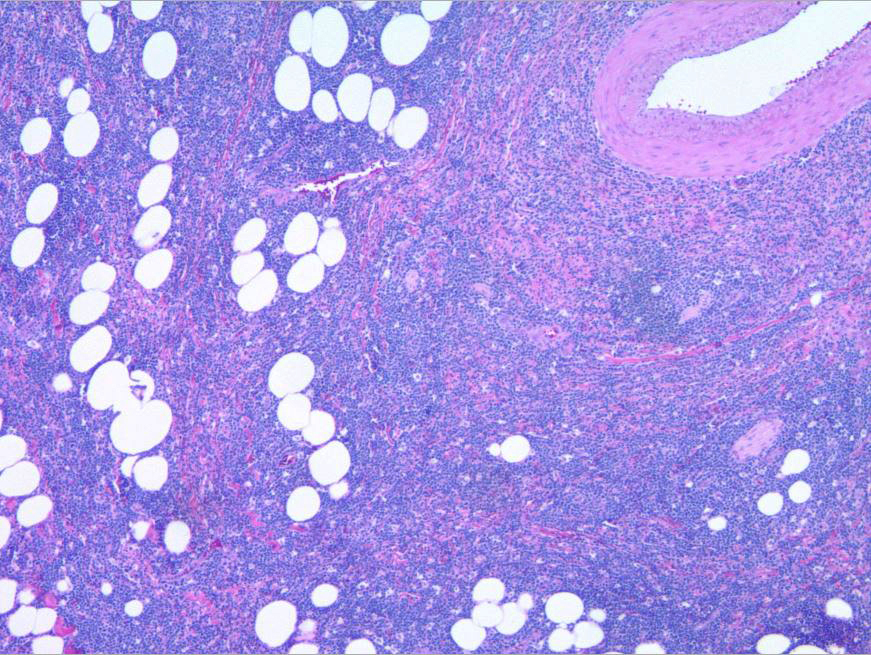
- Expressed in the variable number of nonneoplastic immature T lymphocytes (thymocytes) in thymoma; however, some cases lack clusters of thymocytes
- Expressed in many cases of Merkel cell carcinoma and blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm, which may be a diagnostic pitfall
- Expressed in approximately 10% of acute myeloid leukemia (that is, not lineage defining)
- Not expressed in mature B cell neoplasms that may have blastoid morphology, such as mantle cell lymphoma or high grade B cell lymphoma
- Not expressed in Ewing sarcoma
Terminology
- DNA nucleotidylexotransferase (DNTT)
- Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)
Pathophysiology
- Catalyzes addition of deoxynucleotides to the 3'-OH end of DNA primers
- Adds nontemplated nucleotides at the junctions of V(D)J gene segments (Chembiochem 2019;20:860)
- Contributes to immunoglobulin and T cell receptor diversity
Interpretation
- Nuclear stain
Uses by pathologists
- Differentiating precursor lymphoid neoplasms, which may not express CD45, from other small blue cell tumors
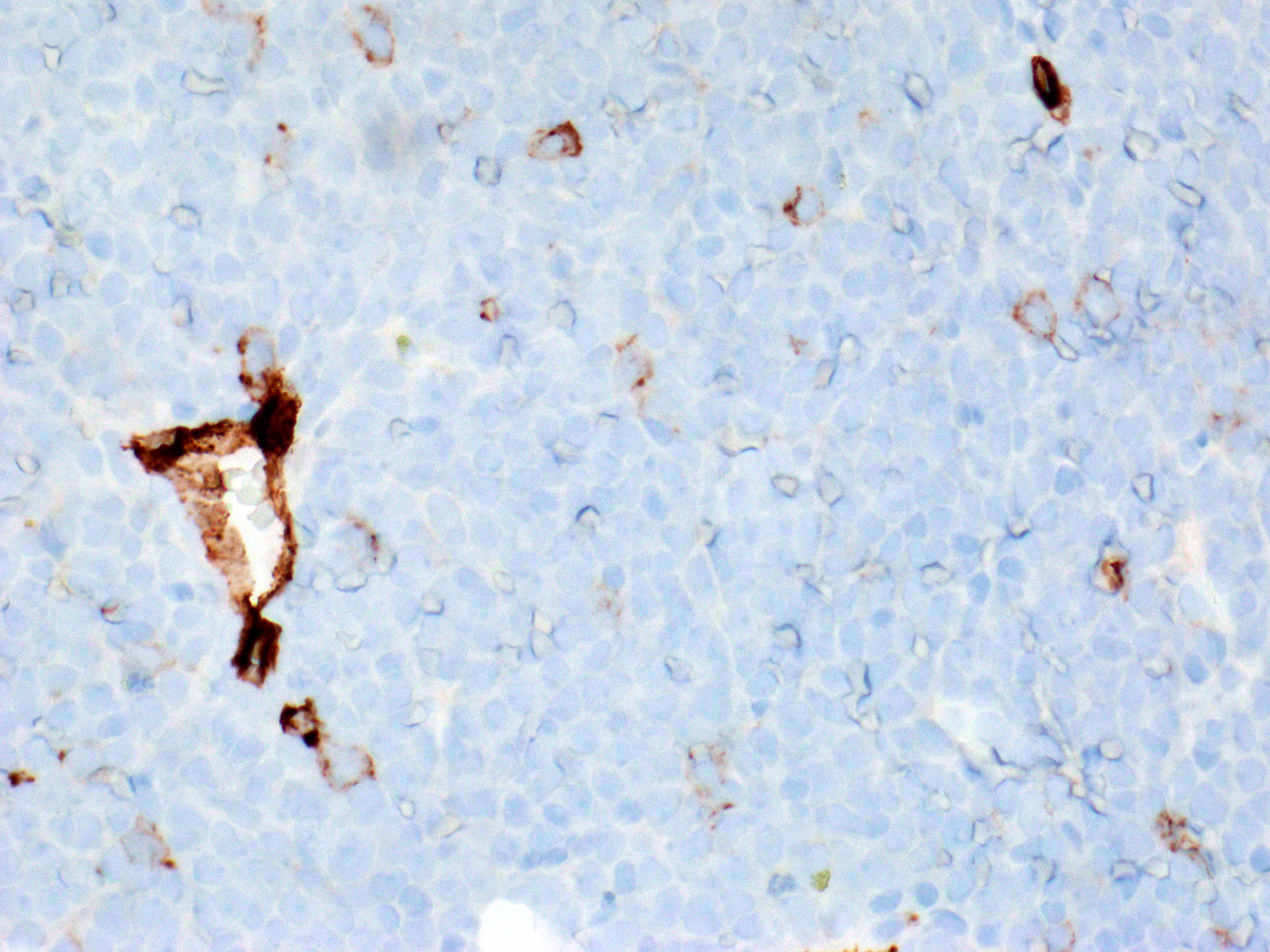
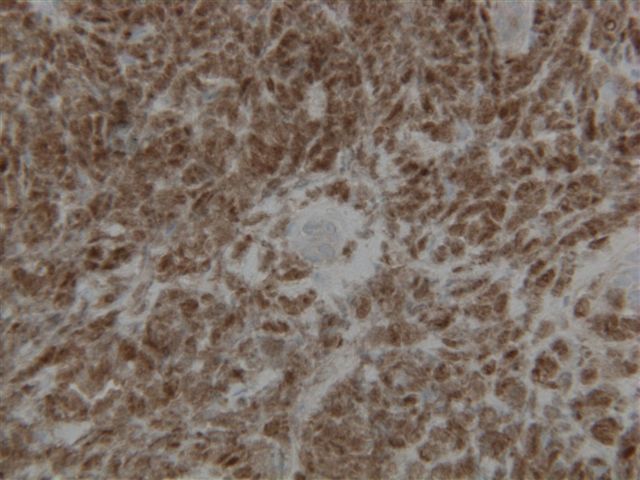
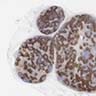
- Identifying clusters of thymocytes in thymoma, which are typically absent in thymic carcinoma
Prognostic factors
- B lymphoblastic leukemia / lymphoma that does not express TdT may be associated with KMT2A rearrangements and lower 5 year event free survival (Mod Pathol 2021;34:2050)
- TdT expression in acute myeloid leukemia with an intermediate risk karyotype may be associated with increased risk of relapse (Int J Hematol 2020;112:17)
- TdT expression in Merkel cell carcinoma may be associated with improved overall survival (Am J Clin Pathol 2020;154:38)
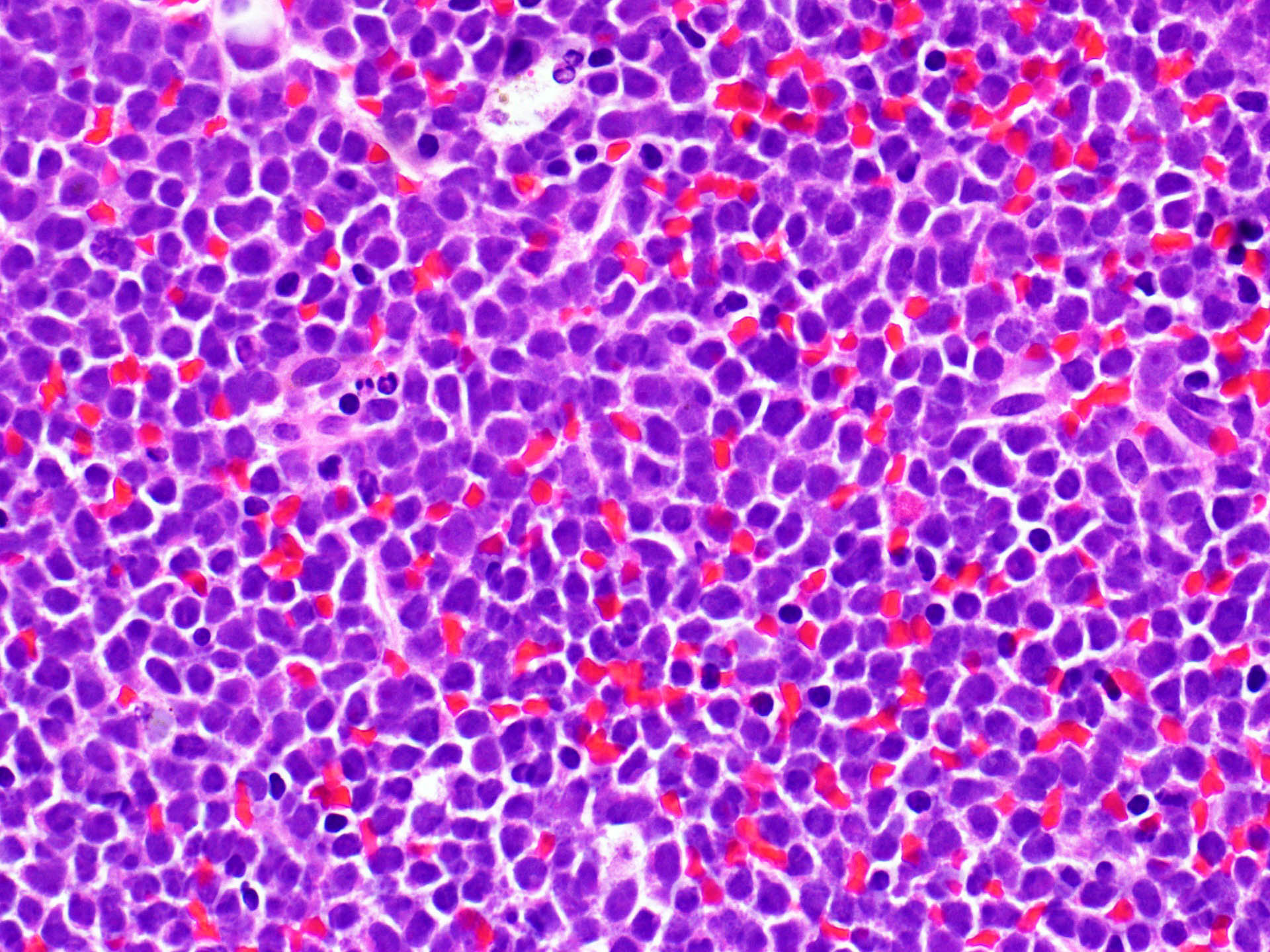
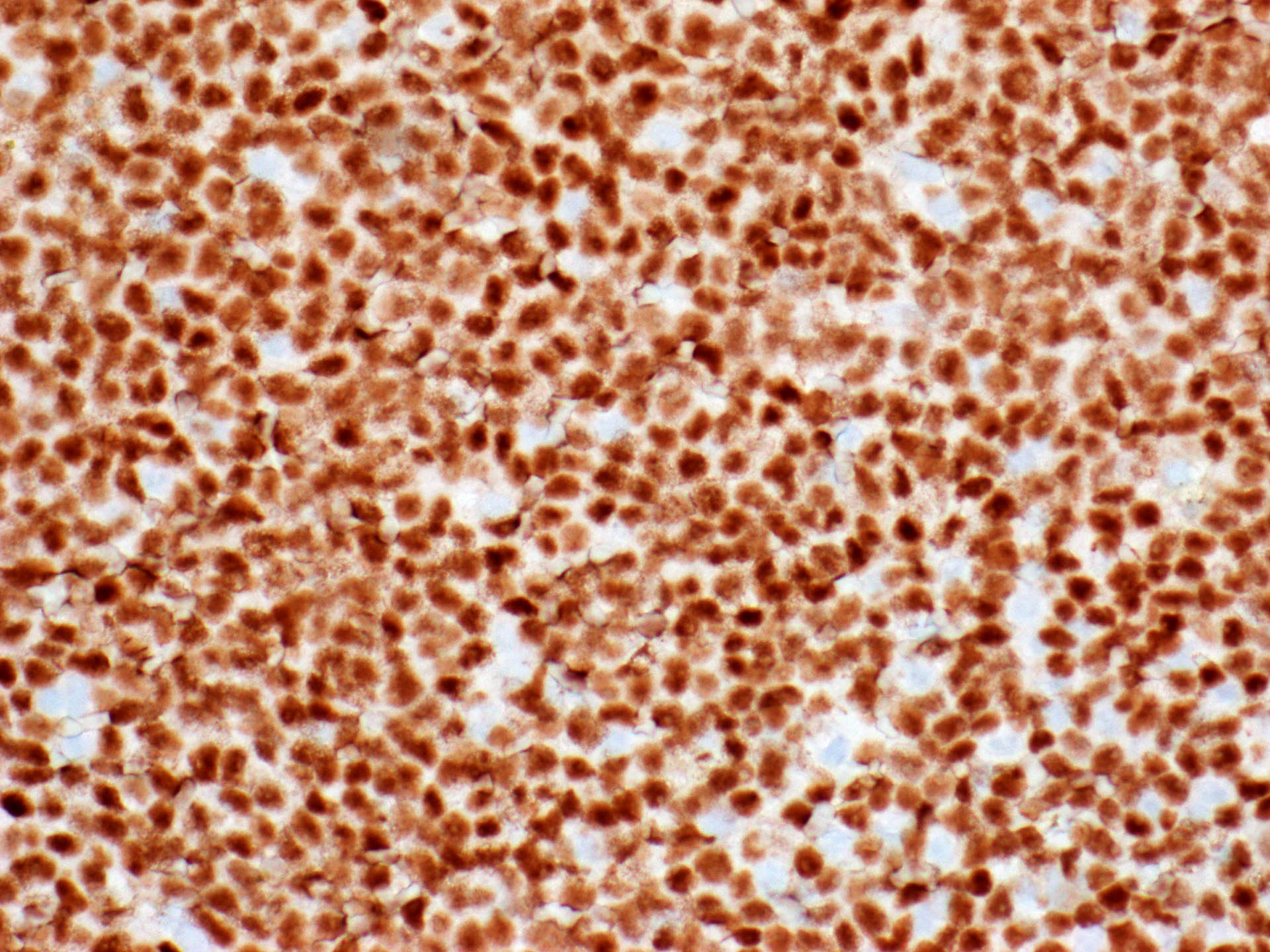
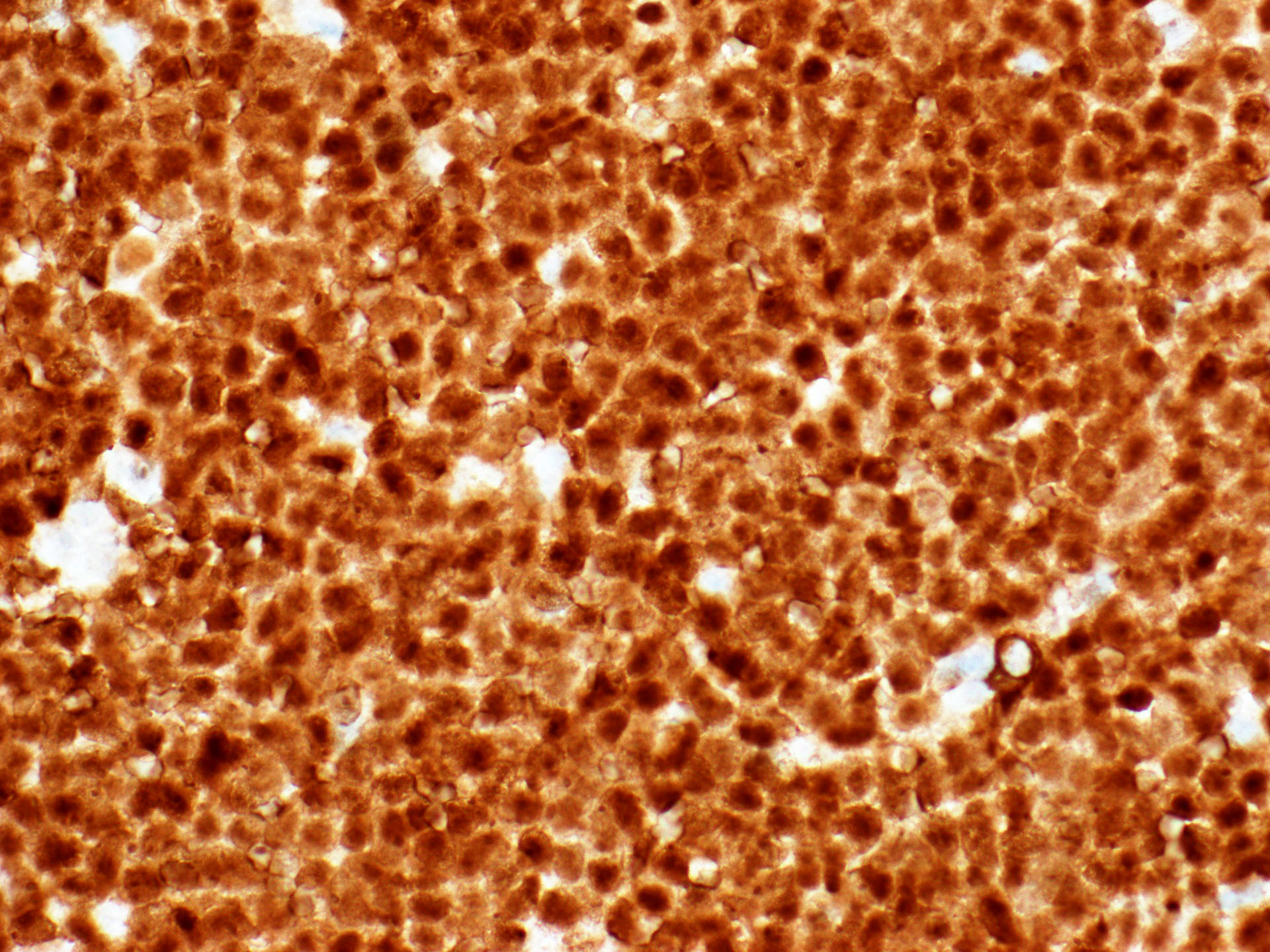
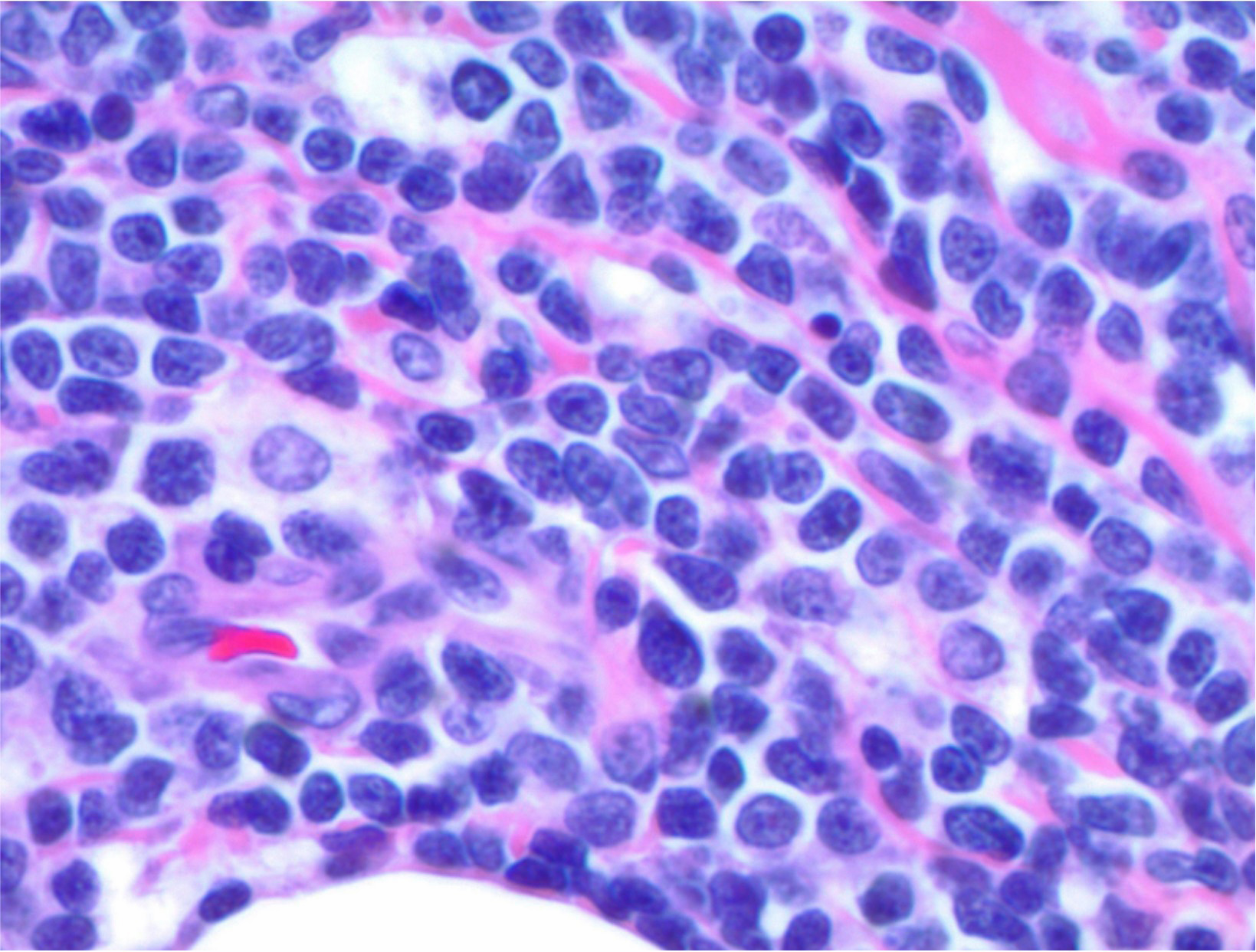
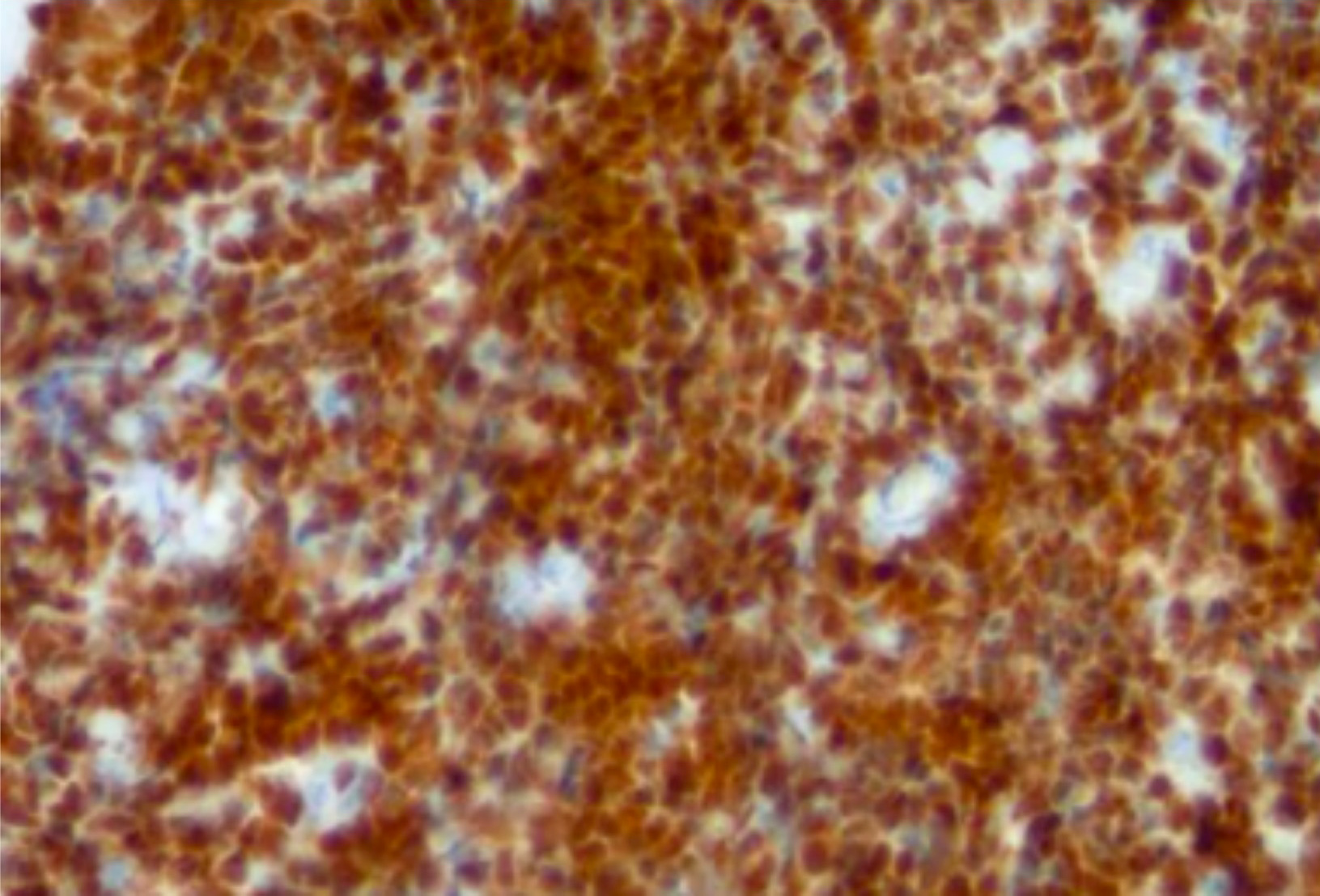
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Early (stage 1) hematogones (Am J Clin Pathol 2008;129:700)
- Progenitor T cells and cortical thymocytes (J Immunol 1983;131:195)
- Myoepithelial cells of the breast, salivary gland and sweat glands (Int J Surg Pathol 2020;28:711)
Positive staining - disease
- B lymphoblastic leukemia / lymphoma (Am J Clin Pathol 1996;106:462, Am J Clin Pathol 2001;115:11)
- T lymphoblastic leukemia / lymphoma (Am J Clin Pathol 1996;106:462)
- Thymoma (34/44, 77%) (Cancers (Basel) 2022;14:2299)
- Indolent T lymphoblastic proliferations (Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2020;98:282)
- Mixed phenotype acute leukemia (4/5, 80%) (Am J Clin Pathol 1996;106:462)
- Merkel cell carcinoma (28/40, 70%) (Am J Clin Pathol 2011;135:831)
- Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (5/12, 42%; 22/37, 59%) (Mod Pathol 2014;27:1137, Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:75)
- Germ cell neoplasia in situ (Int J Gen Med 2021;14:119)
- Seminoma (Int J Gen Med 2021;14:119)
- Dysgerminoma (Int J Gen Med 2021;14:119)
- Extragonadal germinoma (Int J Gen Med 2021;14:119)
- Embryonal carcinoma (Int J Gen Med 2021;14:119)
Negative staining
- Acute myeloid leukemia (6/46, 13% positive) (Am J Clin Pathol 1996;106:462)
- Ewing sarcoma (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;115:11)
- Mature B cell malignancies (Acta Haematol 1986;75:12)
- Mantle cell lymphoma (Cancer Biol Med 2015;12:46)
- Burkitt lymphoma (Am J Clin Pathol 2007;128:558)
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (Am J Clin Pathol 2007;128:558)
- Small cell carcinoma (7/30, 7% positive) (Am J Clin Pathol 2011;135:831)
- Thymic carcinoma (1/37, 3% positive) (Cancers (Basel) 2022;14:2299)
- Synovial sarcoma (Pol J Pathol 2009;60:151)
- Yolk sac tumor (Int J Gen Med 2021;14:119)
- Teratoma (Int J Gen Med 2021;14:119)
- Sex cord stromal tumor (Int J Gen Med 2021;14:119)
- Mycosis fungoides (Dermatopathology (Basel) 2019;6:182)
Sample pathology report
- Mediastinal mass, needle core biopsy:
- T lymphoblastic leukemia / lymphoma (see comment)
- Comment: The needle core biopsy demonstrates sheets of intermediate size lymphoid cells with somewhat irregular nuclear contours, finely stippled chromatin and scant cytoplasm. Scattered tingible body macrophages are present. The neoplastic cells are positive for CD3 (cytoplasmic), CD5, CD7, CD4, CD8, CD10 and TdT and negative for CD30 and ALK1. Ki67 is 95%.
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 19 year old man presents with respiratory distress. Computed tomography (CT) of his chest identifies a mass in the anterior mediastinum. Core biopsy of the mass consists of sheets of intermediate size cells with finely stippled chromatin and scant cytoplasm. The cells are negative for CD45 and positive for CD99 and TdT. Cytokeratin AE1 / AE3 is negative. Scattered tingible body macrophages are present. Which of the following is true regarding the lesional cells?
- TdT expression indicates they are derived from precursor lymphoid cells
- TdT expression precludes a diagnosis of thymic hyperplasia
- TdT expression supports a diagnosis of Ewing sarcoma
- TdT expression supports a diagnosis of neuroblastoma
Practice answer #1
A. TdT expression indicates they are derived from precursor lymphoid cells
Comment Here
Reference: TdT
Comment Here
Reference: TdT