Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Gilani SI, Jimenez RE. Teratoma-neuroendocrine tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/testiscarcinoid.html. Accessed April 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Well differentiated neuroendocrine tumor (NET) is a low grade epithelial neoplasm with neuroendocrine differentiation
Essential features
- Primary testicular NETs can be pure (75%) or associated with teratoma (25%)
- Tumors show an insular or trabecular growth pattern with salt and pepper nuclear chromatin pattern
- Most are not associated with isochromosome 12p or germ cell neoplasia in situ (GCNIS)
Terminology
- Also known as pure NET, testicular NET, prepubertal type or postpubertal type or monodermal teratoma
- Terminology not recommended: carcinoid, atypical carcinoid, neuroendocrine carcinoma
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8240/3 - well differentiated neuroendocrine tumor (monodermal teratoma)
- ICD-11: 2F77 & XH8DS0 - neoplasms of uncertain behavior of male genital organs & neuroendocrine tumor, NOS
Epidemiology
- Extremely rare, accounting for < 1% of all testicular neoplasms (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:519)
- More common in ovaries than testes (15:1)
- Mean age at presentation: 46 years (range: 10 - 83 years)
- Most cases are reported in Europe and the U.S. with fewer cases from Asia and Africa
- Metastatic neuroendocrine tumor from other sites (e.g., lung or gastrointestinal tract) to the testis has been reported
Sites
- NET in the genitourinary tract is rare and can occur in the kidney, bladder, prostate, testicle or urethra
Pathophysiology
- Arise in the setting of prepubertal teratoma (testicular NET, prepubertal type)
- 75% occur as pure NET, with the remaining 25% occurring with other teratomatous components (dermoid and epidermoid cysts) (Cancer 1978;42:2696, Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:519, Cancer 1993;72:1726)
- Most are not associated with GCNIS or isochromosome 12p
- Rare cases of postpubertal type testicular NET have been reported (Clin Cancer Res 2008;14:1393)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Most commonly presents as a testicular mass or swelling, which may or may not be associated with testicular pain
- Bilateral involvement is uncommon and association with cryptorchidism is rare
- 10% of cases occur in association with hydrocele (Cancer 1993;72:1726)
- Clinical carcinoid syndrome (hot flashes, diarrhea and palpitations) has been reported in 7 - 12% of cases (Cancer 1993;72:1726, Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:519)
- Metastases occur via hematogenous spread to lungs, liver, bones, soft tissue, skin, heart as well as contralateral testis; however, lymphatic spread is also seen
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis of testicular NET is made based on histologic examination of the surgical resection specimen
Prognostic factors
- Primary testicular NET associated with testicular teratoma seems to have a better prognosis than pure NET
- Metastatic disease is associated with atypical features, including larger tumor size (> 7 cm), increased mitotic activity and carcinoid syndrome (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:519, Cancer 1993;72:1726)
Case reports
- 23 year old man with asymptomatic scrotal swelling (Arch Ital Urol Androl 2016;88:245)
- 29 year old man with scrotal swelling and pain (Tumori 2019;105:NP20)
- 34 year old man with chronic right scrotal swelling and pain (Am J Case Rep 2015;16:328)
- 44 year old man with primary testicular NET (BMC Urol 2020;20:197)
- 49 year old man with primary testicular NET presenting with carcinoid heart disease (Indian J Urol 2015;31:65)
Treatment
- Orchiectomy
- In a metastatic setting, retroperitoneal dissection and receptor targeted radiotherapy may be used; however, chemotherapy and radiotherapy are reported to provide minimal benefits
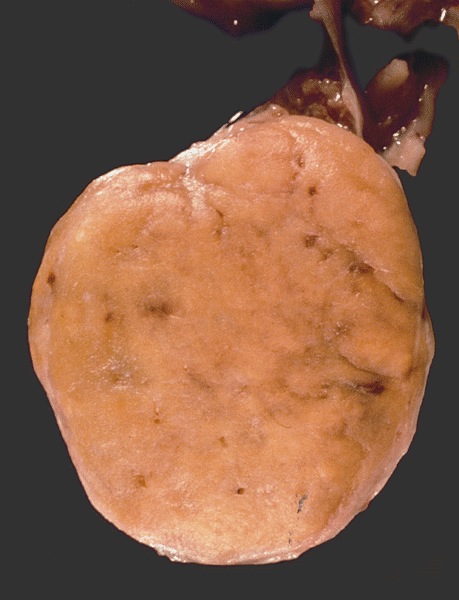
Gross description
- Well circumscribed, solid, yellow-tan to brown and ranging in size from 0.5 cm up to 11 cm (Cancer 1993;72:1726)
- Cystic changes or calcifications can be seen in association with teratomatous component
- Extratesticular growth with involvement of spermatic cord occurs uncommonly
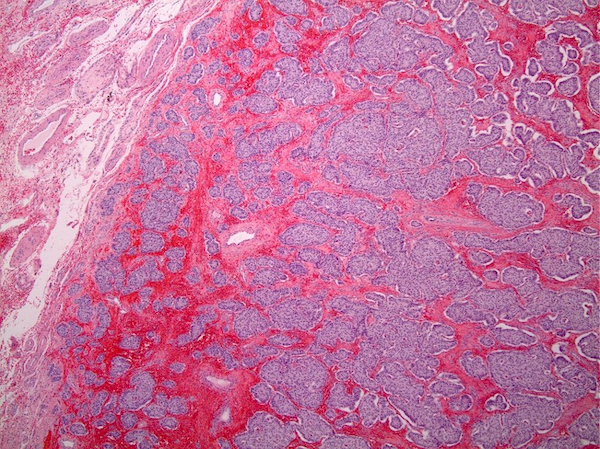
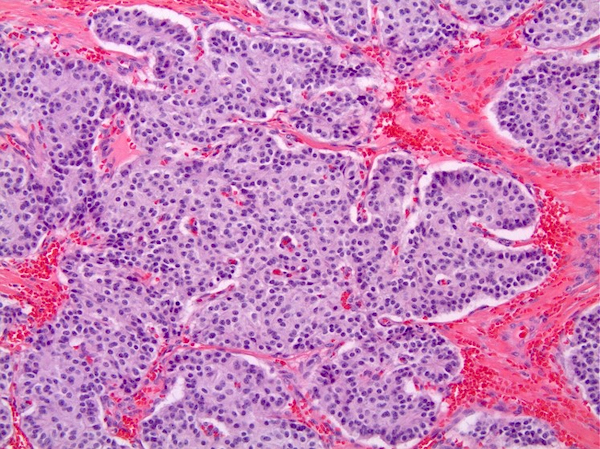
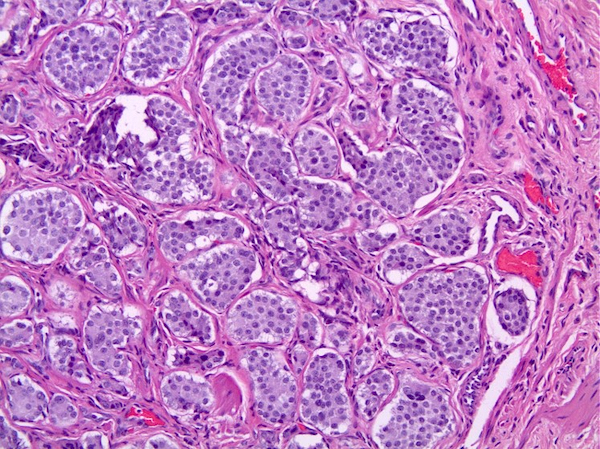
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Growth pattern
- Mostly solid nests, insular or trabecular growth patterns
- Acinar and glandular growth pattern with luminal mucin admixed with other growth patterns may be seen (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:519, Clin Cancer Res 2008;14:1393)
- Stroma
- Delicate fibrous or hyalinized stroma (Tumori 2019;105:NP20)
- Neoplastic cells
- Monomorphic with abundant granular eosinophilic to pale cytoplasm
- Uniform round nuclei with fine or salt and pepper chromatin (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:519)
- Most cases are unassociated with GCNIS (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:519)
- Mitotic figures, necrosis and vascular invasion are infrequently seen (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:519)
- Atypical features include necrosis, nuclear atypia and > 2 mitoses per 10 high power fields (HPF) (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:519, Am J Clin Pathol 2003;120:182)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Isolated or sheets of neoplastic cells with granular cytoplasm, uniform round nuclei and uniformly distributed fine nuclear chromatin
Positive stains
- Cytokeratins, synaptophysin, chromogranin A and CD56 are mostly positive (Cancer 1993;72:1726, Oncol Lett 2015;9:2017)
- Substance P, gastrin, VIP and neurofilaments are less frequently expressed (Am J Clin Pathol 1982;78:860)
Negative stains
- OCT 3/4, CD30, KIT, TTF1, SF1, SOX2, alpha inhibin and CDX2 (Clin Cancer Res 2008;14:1393)
Electron microscopy description
- Pleomorphic to more regular round to oval neurosecretory granules
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- DNA ploidy studies show a near diploid profile (Cancer 1993;72:1726)
- As most cases are not associated with GCNIS, they do not show isochromosome 12p or numerical aberrations in the X chromosome, which are commonly seen in GCNIS derived germ cell tumors
- In rare cases, assessment of isochromosome 12p may be indicated if the postpubertal type is suspected
Videos
Testicular NET
Sample pathology report
- Testis and spermatic cord, left, radical orchiectomy:
- Testicular well differentiated neuroendocrine tumor, prepubertal type (monodermal teratoma) and epidermoid cyst (see comment)
- Comment: No germ cell neoplasia in situ (GCNIS) is identified in the background seminiferous tubules.
Differential diagnosis
- Metastatic neuroendocrine tumor to testis:
- Usually presents with bilateral involvement, multifocality, vascular invasion and extratesticular localization
- Sertoli cell tumor:
- Lacks prominent cytoplasmic granularity and salt and pepper pattern of nuclear chromatin
- Expresses alpha inhibin, calretinin, SF1 and beta catenin (nuclear) and sometimes chromogranin and synaptophysin
- Granulosa cell tumor:
- Neoplastic cells have scant cytoplasm, elongated nuclei with nuclear grooves
- No expression of synaptophysin or chromogranin
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 35 year old man underwent a left radical orchiectomy that demonstrated a 4.0 cm cystic mass (see image). No serological markers (alpha fetoprotein [AFP], beta human chorionic gonadotropin [beta hCG] or lactate dehydrogenase [LDH]) were elevated. Regarding this entity, which of the following statements is true?
- CDX2 is usually positive in testicular neuroendocrine tumor
- Cystic changes can be seen with teratomatous components
- Cytokeratins are usually negative in testicular neuroendocrine tumor
- Glandular growth pattern is not observed
- These tumors are mostly found in association with germ cell neoplasia in situ (GCNIS) / isochromosome 12p
Board review style answer #1
B. Cystic changes can be seen with teratomatous components. Primary testicular neuroendocrine tumor (NET) can occur as pure NET (75%) or in association with testicular teratoma (25%). Cystic changes in these lesions can be seen with teratomatous components. Answer D is incorrect because these tumors mostly exhibit an insular or trabecular growth pattern that can be intermixed with glandular / acinar structures with luminal mucin. Answer E is incorrect because most of these cases are not associated with GCNIS and do not show isochromosome 12p or numerical aberrations in the X chromosome, which are commonly seen in GCNIS derived germ cell tumors. Answers C and A are incorrect because testicular NET expresses cytokeratins and is negative for CDX2.
Comment Here
Reference: Teratoma - neuroendocrine tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Teratoma - neuroendocrine tumor