Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Gupta P, Mehta V. Juvenile granulosa cell tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/testisgranulosajuvenile.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Neoplasm composed of primitive appearing granulosa cells growing in solid and follicular patterns
- Most common neoplasm of the testis during the first 6 months; almost all tumors are seen in first decade of life (J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2020;146:2829)
- No malignant cases reported
Essential features
- Juvenile granulosa cell tumor (JGCT) is a rare neoplasm with a wide morphologic spectrum
- Solid and reticular patterns may pose diagnostic challenges but the lobular appearance and follicular differentiation are characteristic
- Immunostains aid in diagnosis with positive expression of SF1, calretinin, vimentin and inhibin and negative expression of alpha fetoprotein (AFP)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8622/1 - granulosa cell tumor, juvenile
- ICD-11: 2F34 & XH2U25 - benign neoplasm of male genital organs & granulosa cell tumor of the testis, juvenile
Epidemiology
- Rare tumors that account for < 0.5% of all sex cord stromal tumors
- Afflicts patients from 30 weeks gestational age to 10 years old, with 90% occurring in patients ≤ 6 months of age (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1159)
- Association with cryptorchoid testis or dysgenetic gonads (Drash syndrome) (Semin Diagn Pathol 2014;31:323, J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2020;146:2829)
- Chromosomal abnormality linked to the Y chromosome is found in 20% of the cases (Am J Surg Pathol 1994;18:316)
- Can also occur rarely in undescended testes and dysgenetic gonads
Sites
- Almost invariably unilateral
Pathophysiology
- Thought to arise from a specialized gonadal stromal cell of the testicle, which is histologically very similar to JGCT of the ovary
Clinical features
- Most commonly seen as testicular mass (65%) or enlarging testis (25%)
- Testicular masses are asymptomatic and can be present within the abdomen or inguinal region or within the scrotal sac
- Can also present with lack of endocrine features
- Some cases present with the contralateral testis as clinically normal but undescended
Diagnosis
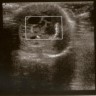
- Imaging: testicular ultrasonography usually reveals a well defined large intratesticular multicystic and solid mass
- Pathological findings after orchiectomy are conclusive
Laboratory
- Serum alpha fetoprotein (AFP) and beta human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) are within normal range and do not aid in diagnosis
Radiology description
- Multiseptated, cystic intratesticular / intra-abdominal mass observed on ultrasonography
Prognostic factors
- Favorable prognosis, with no documented metastasis or relapses
- Lymphovascular invasion has been documented in only 2 cases and involvement of rete testis in 4 cases (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1159)
Case reports
- Newborn boy with enlarged right testis (Autops Case Rep 2014;4:39)
- Newborn boy with left intra-abdominal mass (Urology 2012;79:1152)
- Newborn boy with positive alpha fetoprotein immunohistochemical staining of a juvenile granulosa cell tumor (Urol Case Rep 2017;12:49)
Treatment
- In circumstances where organ preservation is not possible, total orchiectomy is performed
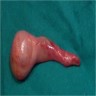
Gross description
- Tumors measure 0.5 - 5 cm (mean: 2 cm; median: 1.5 cm)
- Well circumscribed and yellow-orange or tan-white on cut surface
- Can have a solid (33% cases) or cystic component (67% cases) or both (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1159)
- Watery to mucoid cystic fluid
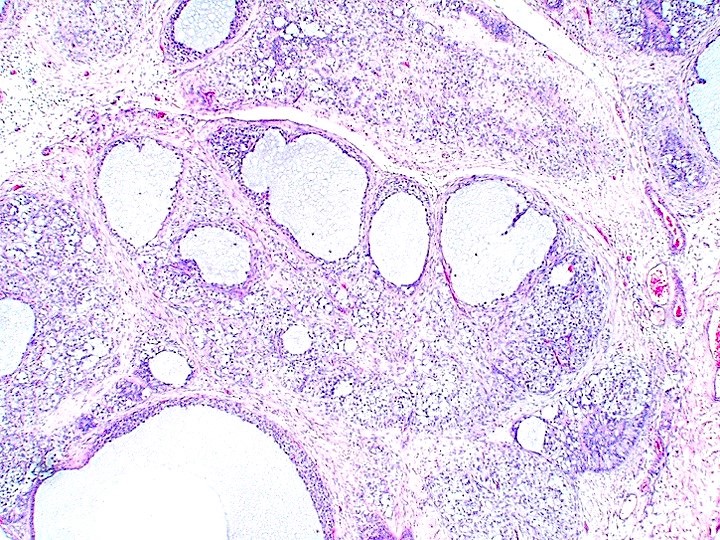
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Solid, nodular or follicular patterns are the most common and sometimes alternate
- Follicles vary from large and round / oval to small and irregular containing basophilic or eosinophilic secretion (mucicarmine+)
- In solid or nodular areas, the cells grow in sheets or irregular clusters
- Cells have moderate to large amounts of pale to eosinophilic cytoplasm, round to oval hyperchromatic nuclei, some of which contain nucleoli
- Mitoses are common, in contrast to adult granulosa cell tumor
- Extensive hyalinization (forming nodules) and prominent myxoid background may be seen
- Call-Exner bodies are uncommon
- Apoptosis, entrapped seminiferous tubules, rete testis involvement and lymphovascular invasion could be seen in rare cases (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1159)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- JGCT stains uniformly positively for FOXL2, SF1 and vimentin
- Majority JGCT also express inhibin, calretinin, WT1 and SOX9 (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1159)
Negative stains
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Association with abnormal karyotypes, including mosaics such as 45, X/47, XXY or 45X/46, X.r(Y) have been seen (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2016;19:471)
Sample pathology report
- Left testis, radical orchiectomy:
- Juvenile granulosa cell tumor (1.5 cm), confined to the testis (see comment)
- Comment: The tumor is small and well circumscribed and shows variable sized follicles lined by bland appearing, oval, round cells arranged in single or multiple layers with outer layers resembling theca cells. Many mitotic figures are identified. No nuclear grooves or Call-Exner bodies identified.
Differential diagnosis
- Yolk sac tumor:
- High elevations of AFP
- Presence of Schiller-Duval bodies
- True follicles are diagnostic of JGCT and are not a feature of yolk sac tumor
- Negative for SF1, FOXL2, inhibin A, calretinin
- Teratoma:
- Numerous ectodermal, mesenchymal and endodermal tissues occur
- Virtually all elements lack cellular atypia
- Cystic dysplasia of the testicle (Front Pediatr 2022;10:898038):
- Rare and benign cause of testicular swelling in pediatric population
- Irregular cystic spaces in the mediastinum of the testis, displacing the testicular parenchyma
- Cysts lined with flattened cuboidal epithelium and separated by fibrous septa
- Frequently associated with genitourinary anomalies, ipsilateral renal agenesia and multicystic dysplasia of the kidney
- Sertoli cell tumor:
- Small size, multifocal, monotonous tubular / cord architecture, associated with androgen insensitivity syndrome and cryptorchidism
- Gonadoblastoma:
- Almost always associated with disorders of sex development
- Round nests and cords composed of germ cells, small sex cord cells and globoid deposits of hyaline basement membrane material
- May also show Charcot-Böttcher crystals
- Unclassified sex cord stromal tumors:
- Mixture of cell types granulosa cell tumor, Leydig cell tumor, thecoma, etc.
- Variable AE1 / AE3 and Ki67 reactivity for germ cell differentiation
- Variable inhibin A, calretinin, CD99 reactivity for sex cord stromal elements
- S100, smooth muscle actin reactivity for spindle cell elements
- Rhabdomyosarcoma:
Board review style question #1
A 5 month old boy presented with a left testicular mass. An ultrasound of the testis showed a variably solid cystic mass with internal septations. An image from the resection specimen is shown above. Which of the following features will point toward the diagnosis of juvenile granulosa cell tumor?
- Presence of intracellular or extracellular eosinophilic hyaline globules, basement membrane material and Schiller-Duval bodies
- Round nests and cords composed of germ cells, small sex cord cells and globoid deposits of hyaline basement membrane material
- Variable morphologic patterns with biphasic epithelioid and spindle cell components
- Variable sized true follicles lined by bland appearing, oval, round cells arranged in single or multiple layers with outer layers resembling theca cells
Board review style answer #1
D. Variable sized true follicles lined by bland appearing, oval, round cells arranged in single or multiple layers with outer layers resembling theca cells. Answer A is incorrect because the features described are found in yolk sac tumors. Answer C is incorrect because variable morphologic patterns with biphasic epithelioid and spindle cell components are found in a subset of sertoli cell tumors, NOS. Answer B is incorrect because the features described are found in gonadoblastoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Juvenile granulosa cell tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Juvenile granulosa cell tumor
Board review style question #2
Which of the following choices represents the immunoprofile of juvenile granulosa cell tumor of testis?
- Desmin+, MyoD1+, myogenin+
- Glypican3+, SALL4+, OCT3/4+
- S100+, SMA+, SF1+
- SF1+, FOXL2+, inhibin+
Board review style answer #2
D. SF1+, FOXL2+, inhibin+. Answer B is incorrect because glypican3+, SALL4+, OCT3/4+ can be seen in immature teratoma. Answer C is incorrect because the features listed are consistent with gonadal stromal tumor, myoid. Answer A is incorrect because the features listed are consistent with rhabdomyosarcoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Juvenile granulosa cell tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Juvenile granulosa cell tumor