Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Gordetsky J. Interdigitating dendritic cell tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/testisinterdig.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Rare tumor of hematopoietic origin arising from interdigitating dendritic cells (IDCs), a type of immune accessory cell found in lymphoid and nonlymphoid organs
- IDCs present antigens to T cells and regulate cellular immune responses (Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2013;88:253)
- Usually arises in lymph nodes (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:1141)
Epidemiology
- IDC tumors have been reported in all age groups (median age 56 years)
Sites
- Can be nodal or extranodal; have been described throughout the body
- Only two reported cases of testicular involvement
Pathophysiology
- Dysregulation of immune system may facilitate malignant transformation of IDCs (Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2013;88:253)
- Recent studies show a clonal relationship between IDC tumors and low grade B cell lymphomas in patients harboring both diseases synchronously or metachronously
- A group of IDC tumors likely develops secondarily after the malignant transformation and trans differentiation of B cells, rather than transformation of IDCs themselves
- IDC tumors have developed following the use of calcineurin inhibitors, tacrolimus and pimecrolimus; these drugs dampen the responses of T cells to which IDCs present antigens
Clinical features
- Painless testicular mass
Laboratory
- Serum tumor markers for testicular germ cell tumors (hCG and alpha fetoprotein) are normal
Radiology description
- Testicular ultrasound is imaging modality of choice for a scrotal mass (Gordetsky: Gordo's Guide to GUPathology: A Resource for Urology and Pathology Residents, 2013)
Prognostic factors
- Worse outcomes seen in younger patients and patients with intraabdominal involvement
- Stage at presentation is most important prognostic factor (Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2013;88:253)
Case reports
- 37 year old man with painless testicular mass (Int J Surg Pathol 2011;19:104)
- 74 year old man with a painless unilateral testicular mass (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:1141)
Treatment
- Surgery with adjuvant chemotherapy
Gross description
- Light tan, solid, may replace entire testis
Microscopic (histologic) description
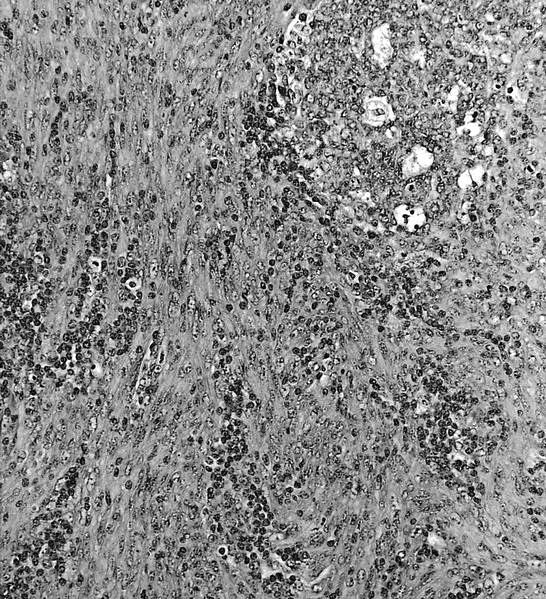
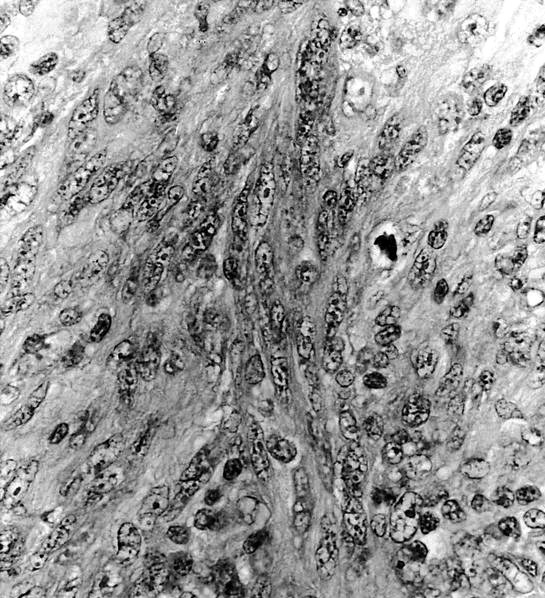
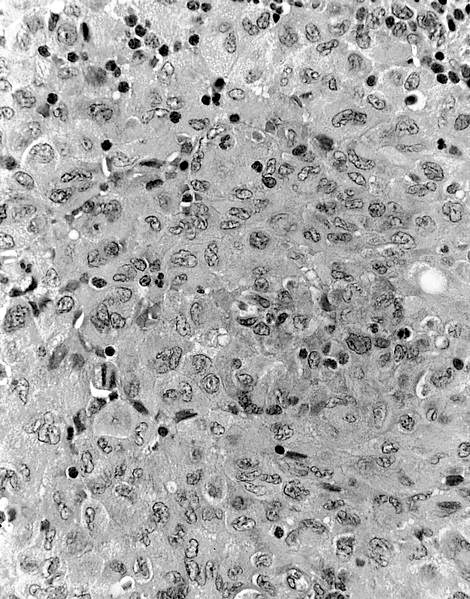
- Whorls and fascicles of spindle cells mixed with small lymphocytes
Microscopic (histologic) images
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Complex interdigitating cytoplasmic dendritic processes, abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum, abundant mitochondria
Differential diagnosis
- Germ cell tumors with a sarcomatous component
- Sex cord stromal tumors
- Infiltration by paratesticular spindle cell neoplasms
- Metastasis