Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Laboratory | Radiology description | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Videos | Additional referencesCite this page: Chi A, Guilmette J. Hyperthyroidism. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/thyroidhyper.html. Accessed September 17th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Increased thyroid hormone synthesis and secretion from the thyroid gland (Lancet 2016;388:906)
- See also Hyperthyroidism-lab diagnosis
Epidemiology
- Approximately 3% of women and 0.5% of men will develop Graves disease during their lifetime (JAMA 2015;314:2544)
Pathophysiology
- Depends upon the underlying cause
- Graves disease (Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2015 Nov 25;(11):CD010576):
- Autoimmune disease caused by the production of auto antibodies against thyroid stimulating hormone receptors
- Stimulation of follicular cells to produce thyroid hormone
Types:
- Primary hyperthyroidism: intrinsic thyroid abnormality
- Low TSH, high free T4, normal TRH stimulation test
- Secondary hyperthyroidism: high TSH, abnormal TRH stimulation test
- Subclinical hyperthyroidism: low TSH (< 0.1 μIU/ml), normal T3 and T4 (Eur J Endocrinol 2005;152:1)
- May be due to exogenous thyroid hormone (Hormones (Athens) 2006;5:119), due to TSH suppressive therapy with L-thyroxine or hormone overreplacement (Eur J Endocrinol 2005;152:1)
- Excessive thyroid hormone may be due to differentiated thyroid cancer (Eur J Endocrinol 2005;152:1)
- Patients have increased risk of coronary heart disease (Int J Cardiol 2008;125:41, Eur J Endocrinol 2005;152:1)
- T3 hyperthyroidism: 1 - 4% of hyperthyroid patients
- Low TSH, high free T3, normal free T4
- Associated with early treatment of hyperthyroidism with antithyroid drugs
- T4 hyperthyroidism: high T4, normal T3
- Due to primary hyperthyroidism causes, also iodine, amiodarone (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:e275), pregnancy (transient gestational hyperthyroidism syndrome, 1 - 3%, Hormones (Athens) 2015;14:59)
Etiology
- Graves disease (85%) or maternal Graves disease, overdose of thyroid hormone, iodide ingestion, hyperfunctioning multinodular goiter or thyroid adenoma, thyroiditis, struma ovarii, choriocarcinoma, hydatidiform mole, pituitary adenoma (Lancet 2016;388:906)
- Radiocontrast iodine based agent (Arch Endocrinol Metab 2016;60:287)
Clinical features
- Early symptoms: anxiety, palpitations, rapid pulse, fatigue, muscle weakness, weight loss, diarrhea, hyperactive reflexes, increased sweating, heat intolerance, warm skin, excessive perspiration, menstrual changes, hand tremor, polydipsia and increased appetite (J Am Geriatr Soc 1996;44:50)
- Late symptoms: cardiac (palpitations, congestive heart failure, cardiomegaly, atrial fibrillation, fatty change), fatty change of skeletal muscle or liver, osteoporosis from bone resorption, generalized lymphadenopathy
- Ocular changes: wide staring gaze and lid lag due to sympathetic overstimulation of levator palpebrae superioris
- Thyrotoxicosis: hypermetabolic clinical syndrome due to elevated serum T3 or T4
- May be due to hyperthyroidism, thyroiditis or excessive ingestion of thyroid hormone ("factitious hyperthyroidism")
- Includes a wide range of symptoms, such as ophtalmopathy, dermatopathy, fever, marked tachycardia, heart failure, tremor, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dehydration, restlessness, extreme agitation, delirium and coma (Endotext - Graves Disease, CMAJ 2003;168:575)
- In severe thyrotoxicosis, death may be secondary to cardiac failure, shock and multiple organ failure (Endotext - Graves Disease)
Laboratory
- Low or suppressed TSH, elevated free thyroxine level (FT4) (CMAJ 2003;168:575)
- 10% of patients have an increased total or free T3 level and normal T4 level with suppressed TSH level, a condition called "T3 toxicosis" (CMAJ 2003;168:575)
- In Graves disease, elevated levels of antitopoisomerase antibodies and antithyroglobulin antibodies are found in 80% and 50% of cases, respectively (Mod Pathol 2000;13:1014)
- See also Hyperthyroidism-lab diagnosis
Radiology description
- Scintigraphy with Tc - 99m pertechnetate shows an enlarged thyroid gland with an increased activity level diffusely through the gland (Radiographics 2003;23:857)
Case reports
- 11 year old boy with undiagnosed hyperthyroidism presenting with fractures and osteoporosis (Pediatrics 2016;137:e20150169)
- 18 year old pregnant woman presenting with aortic aneurysm, tachycardia and hyperthyroidism (Ginecol Obstet Mex 2015;83:627)
- 35 year old man presented with jaundice secondary to Graves disease (BMC Res Notes 2016;9:320)
- 36 year old man with thyroid hemiagenesis presenting with hyperthyroidism symptoms (Hormones (Athens) 2015;14:451)
- 66 year old woman with a history of euthyroid multinodular goiter underwent a head and neck computed tomography scan (Arch Endocrinol Metab 2016;60:287)
Treatment
- Treatment options for Graves disease include antithyroid drugs (such as carbimazole, methimazole, or propylthiouracil / PTU), radioactive iodine therapy and surgery (Lancet 2016;388:906)
- Beta blockers for symptoms, thionamide type drugs to block new hormone synthesis, iodine to block release of T4 / T3, radioactive iodine to destroy thyroid tissue
- Thyroidectomy if other treatments fail or are contraindicated, or when goiter is causing compressive symptoms (Am Fam Physician 2005;72:623)
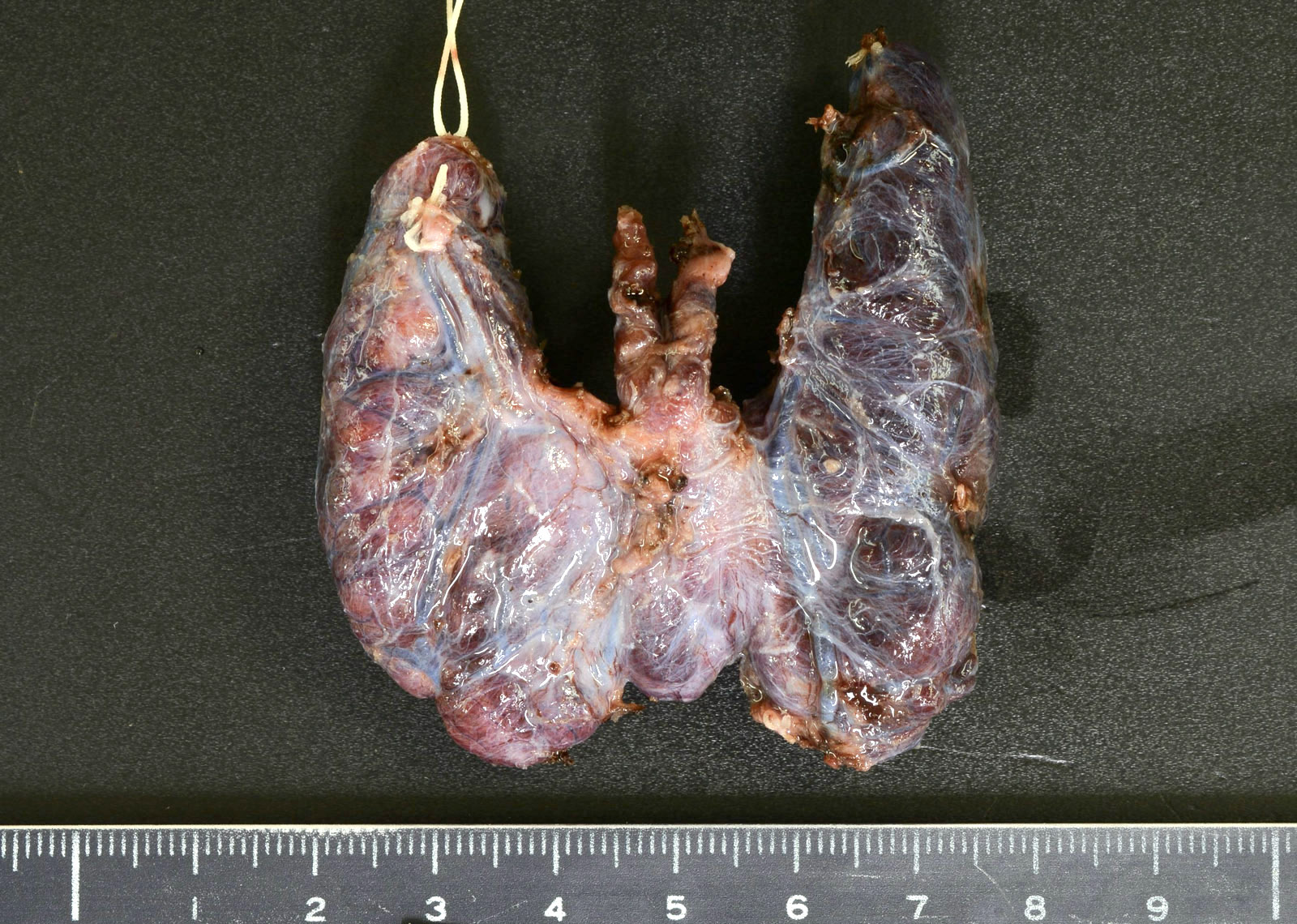
Gross description
- Multinodular goiter (CMAJ 2003;168:575)
- Symmetrically enlarged thyroid gland
Microscopic (histologic) description
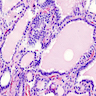
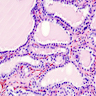
- Papillary hyperplasia and fronds that may lack true fibrovascular cores (Mod Pathol 2000;13:1014), mimicking papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Follicles are hypercellular and lined by tall columnar epithelium
- Treatment may cause follicular cells to become cuboidal rather than columnar
- Limited to absent fibrosis
- Mixed, but predominantly lymphocytic infiltrate, within stroma surrounding follicles
- Small or occluded lumens containing pale or little colloid
- Scalloping of the colloid
- Nuclear features of papillary carcinoma are lacking
Videos
Histopathology Thyroid - Graves Disease