Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Chapel DB, Jennifer B. Epithelioid sarcoma-vulva. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/vulvaepithelioidsarcoma.html. Accessed April 17th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Epithelioid sarcoma of the vulva and deep pelvic soft tissue is a rare malignant neoplasm characterized by SMARCB1 / INI1 deletion
- Most vulvar and pelvic epithelioid sarcomas are of the proximal type and show more aggressive clinical behavior than distal type (classical) epithelioid sarcoma
Essential features
- In vulva and pelvic soft tissues, proximal type epithelioid sarcoma > distal type
- Proximal type epithelioid sarcoma: sheets or nests of epithelioid to rhabdoid cells with nuclear atypia
- Positive immunostains: CK, EMA, CD34 (~ 50%)
- SMARCB1 / INI1 deletion in > 90%, resulting in SMARCB1 / INI1 loss by IHC
- Frequent local recurrence, lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis (especially to lung) and death
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Women, 17 - 80 years (most often in fourth and fifth decades) (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:836, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2010;29:600, Mod Pathol 2001;14:655)
- Rarely diagnosed in pregnancy (Gynecol Oncol 2002;85:218, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2009;17:270)
Sites
- Vulvar epithelioid sarcoma most often involves the labia majora and mons pubis (Cancer 1983;52:1462)
- Superficial inguinal region and deep pelvic soft tissues also affected (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:130, Mod Pathol 2001;14:655)
Pathophysiology
- Histogenesis uncertain
Clinical features
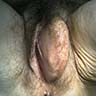
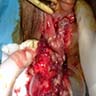
- Typically presents with painless, slow growing vulvar mass (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:130, Mod Pathol 2001;14:655)
- Occasional lesions painful or pruritic (Am J Surg Pathol 1989;13:848, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2010;29:600)
- Present for weeks to years before diagnosis (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:130)
- Rare cases ulcerated (Mod Pathol 2001;14:655)
- Clinically resemble lipoma or Bartholin cyst (Am J Surg Pathol 1989;13:848, Cancer 1983;52:1462)
- Clinical evaluation may underestimate lesion size (Cancer 1983;52:1462)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis typically established on examination of excision specimen
- Occasionally diagnosed on preoperative biopsy (Mod Pathol 2001;14:655, BMJ Case Rep 2015;2015:bcr2014208488)
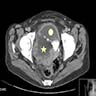
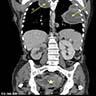
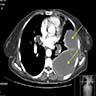
Radiology description
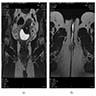
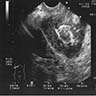
- Ultrasound: may show local tumor infiltration or lymph node metastases (BMJ Case Rep 2015;2015:bcr2014208488)
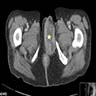
- CT: may show local tumor infiltration or lymph node or distant metastases (BMJ Case Rep 2015;2015:bcr2014208488)
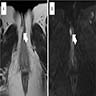
- T2 weighted MRI: signal intensity similar to fat (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8:7526)
- Diffusion weighted MRI: high signal intensity
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Proximal type epithelioid sarcoma (more common in vulva) has poorer prognosis than distal type (classical) epithelioid sarcoma (rare in vulva) (Cancer 1983;52:1462, Mod Pathol 2001;14:655)
- Local recurrence in approximately 67% (Mod Pathol 2001;14:655)
- Metastases (most often to lymph nodes, lung, liver, bone and skin) in approximately 70%, often after one or more local recurrences (Cancer 1983;52:1462, Mod Pathol 2001;14:655, Gynecol Oncol 1980;9:237)
- Approximately 50% die of disease, often within 2 years of diagnosis (Cancer 1983;52:1462, Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:130)
- Large tumor size (> 7.8 cm) and early metastasis (< 28 months after diagnosis) associated with increased mortality (Mod Pathol 2001;14:655)
Case reports
- 32 year old woman with proximal type epithelioid sarcoma of the vulva (Gynecol Oncol Rep 2016;15:31)
- 34 year old woman with proximal type epithelioid sarcoma of the vulva (Case Rep Obstet Gynecol 2015;2015:971217)
- 42 year old woman with proximal type epithelioid sarcoma of the vulva (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8:7526)
- 55 year old woman with proximal type epithelioid sarcoma of the vulva (BMJ Case Rep 2015;2015:bcr2014208488)
Treatment
- Early wide en bloc excision or radical vulvectomy with node dissection; local excision is inadequate (Gynecol Oncol 1980;9:237, Obstet Gynecol 1976;48:14S, Obstet Gynecol 1972;40:839)
- Long term followup for late recurrence (Mod Pathol 2001;14:655)
- Chemotherapy and radiation administered at clinical discretion; robust trials lacking (Gynecol Oncol 1980;9:237, Gynecol Oncol 2007;107:130, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2009;17:270)
- EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat FDA approved for epithelioid sarcoma (Drugs 2020;80:513)
Clinical images
Gross description
- Size range, 1 - 8 cm (average, ~ 3 - 5 cm) (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:130, Mod Pathol 2001;14:655, Gynecol Oncol Rep 2016;15:31)
- Poorly circumscribed, multinodular, firm gray to fleshy white mass (Cancer 1983;52:1462)
- Most often based in subcutis or deep pelvic soft tissues; occasionally dermal (Cancer 1983;52:1462, Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:130, Mod Pathol 2001;14:655)
- Gross necrosis may be present (Cancer 1983;52:1462)
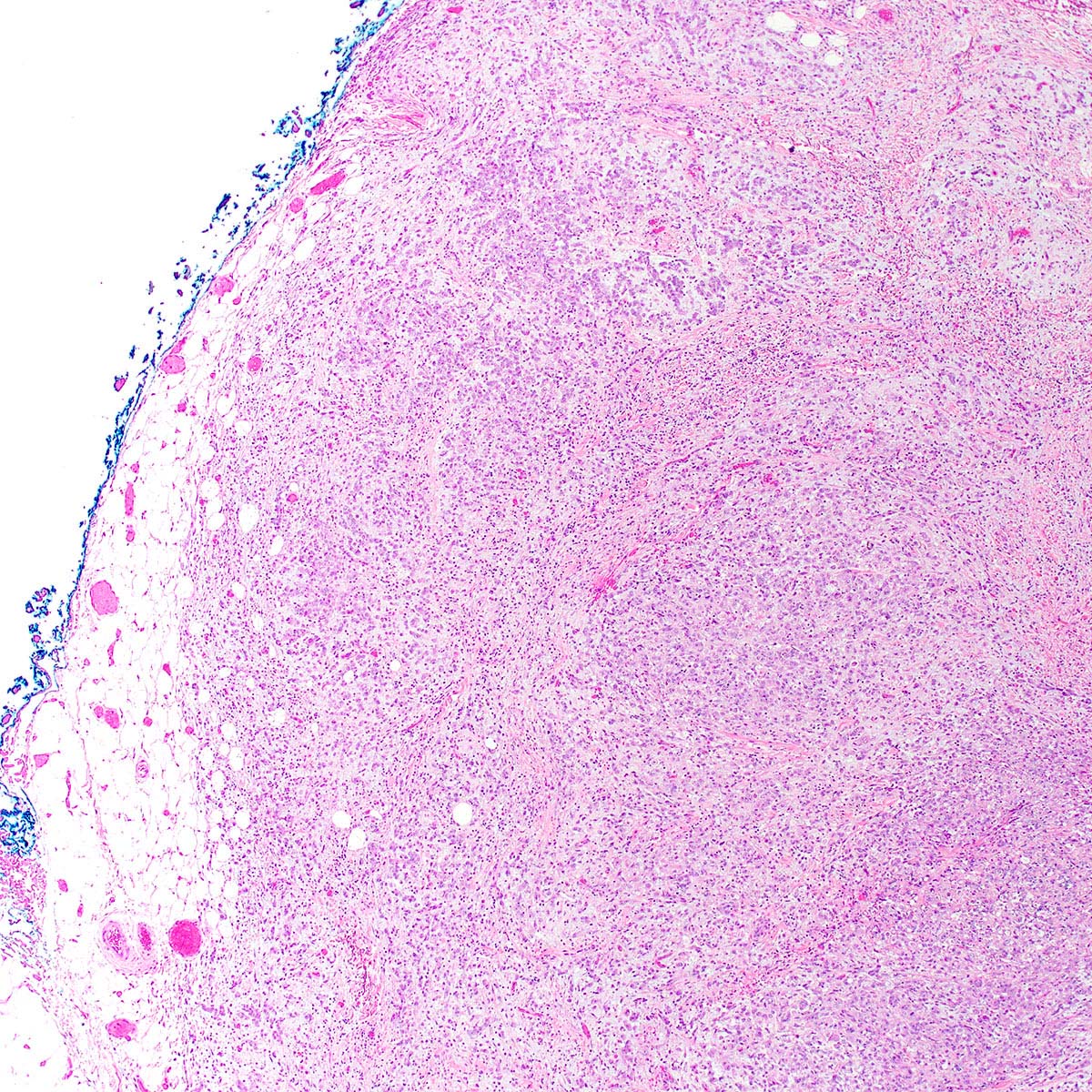
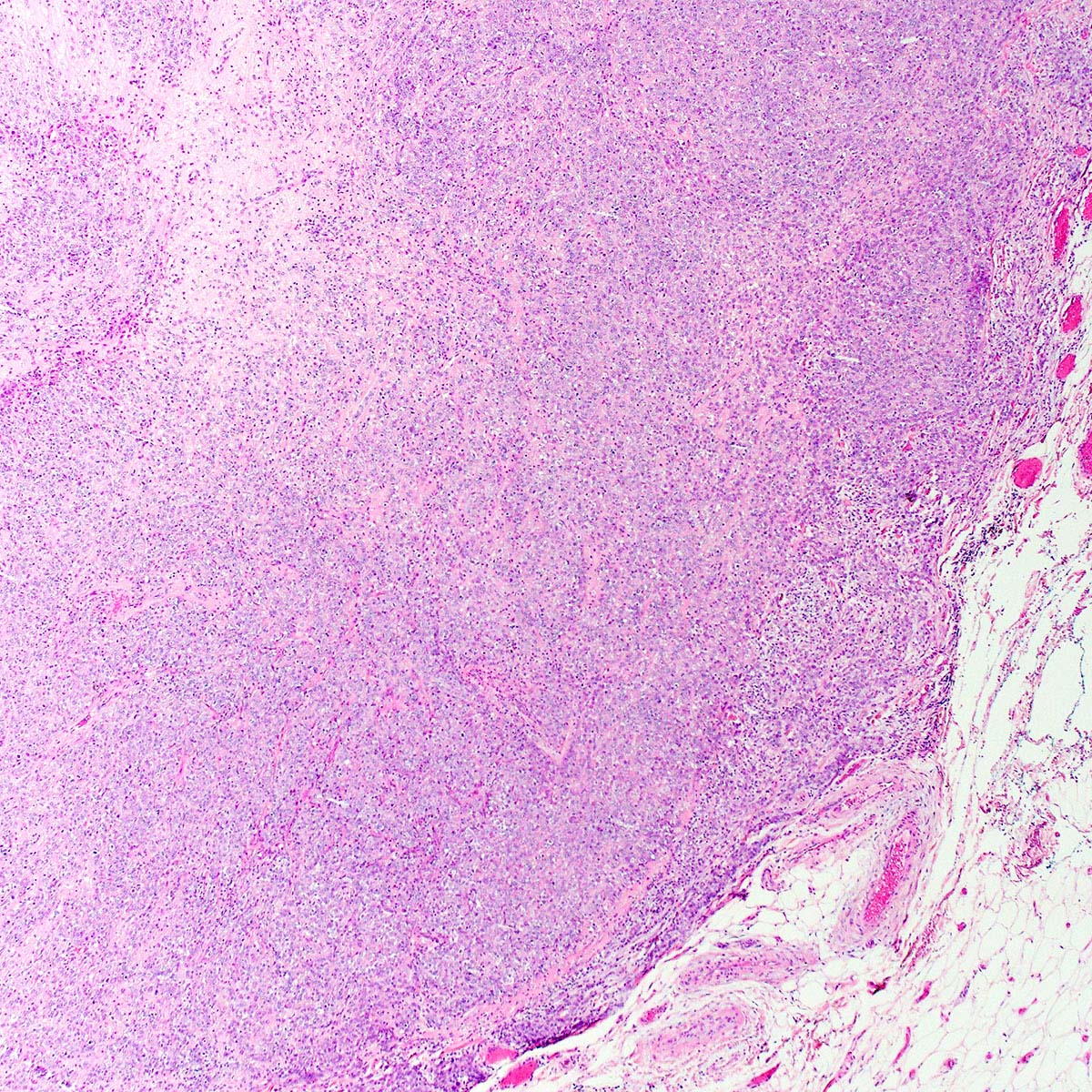
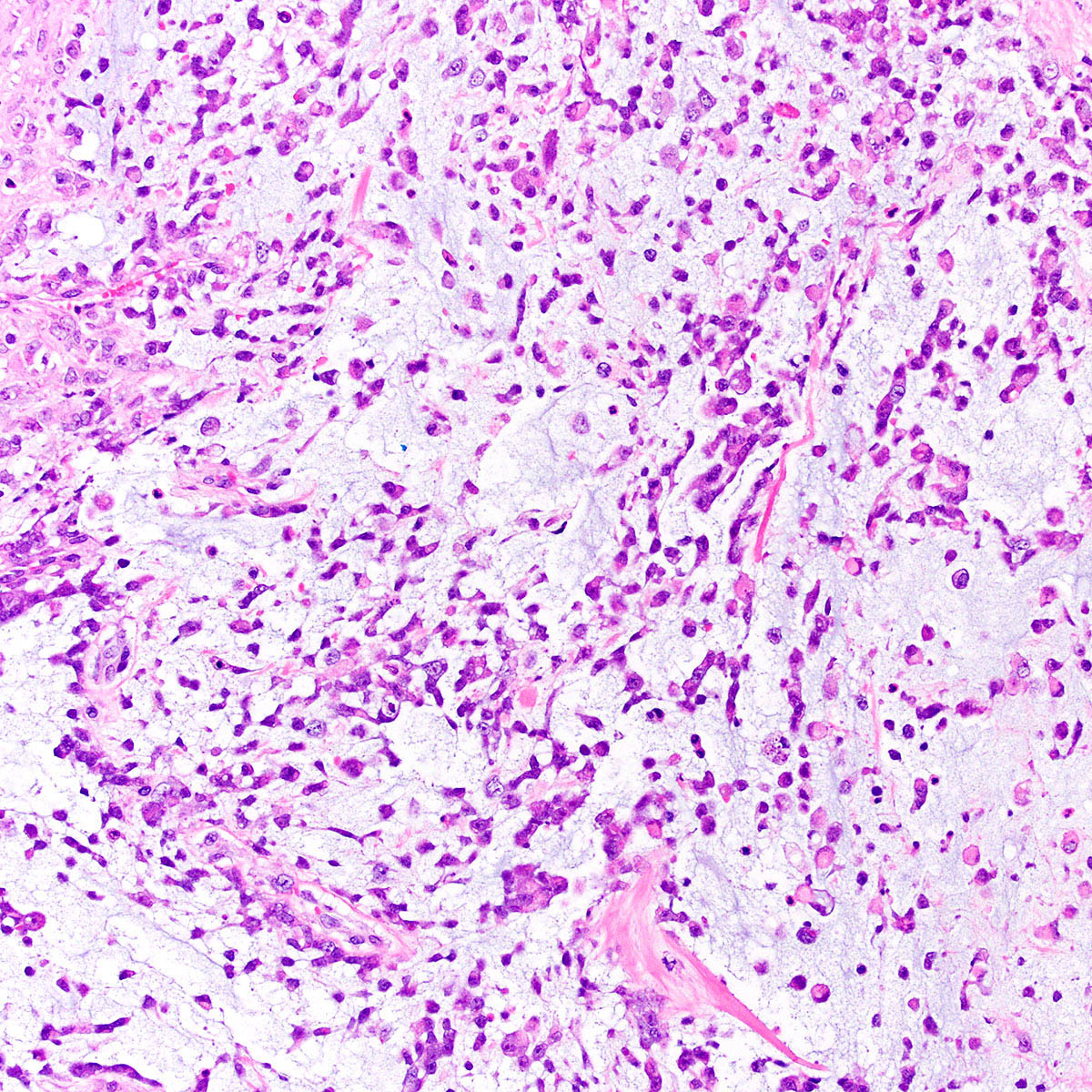
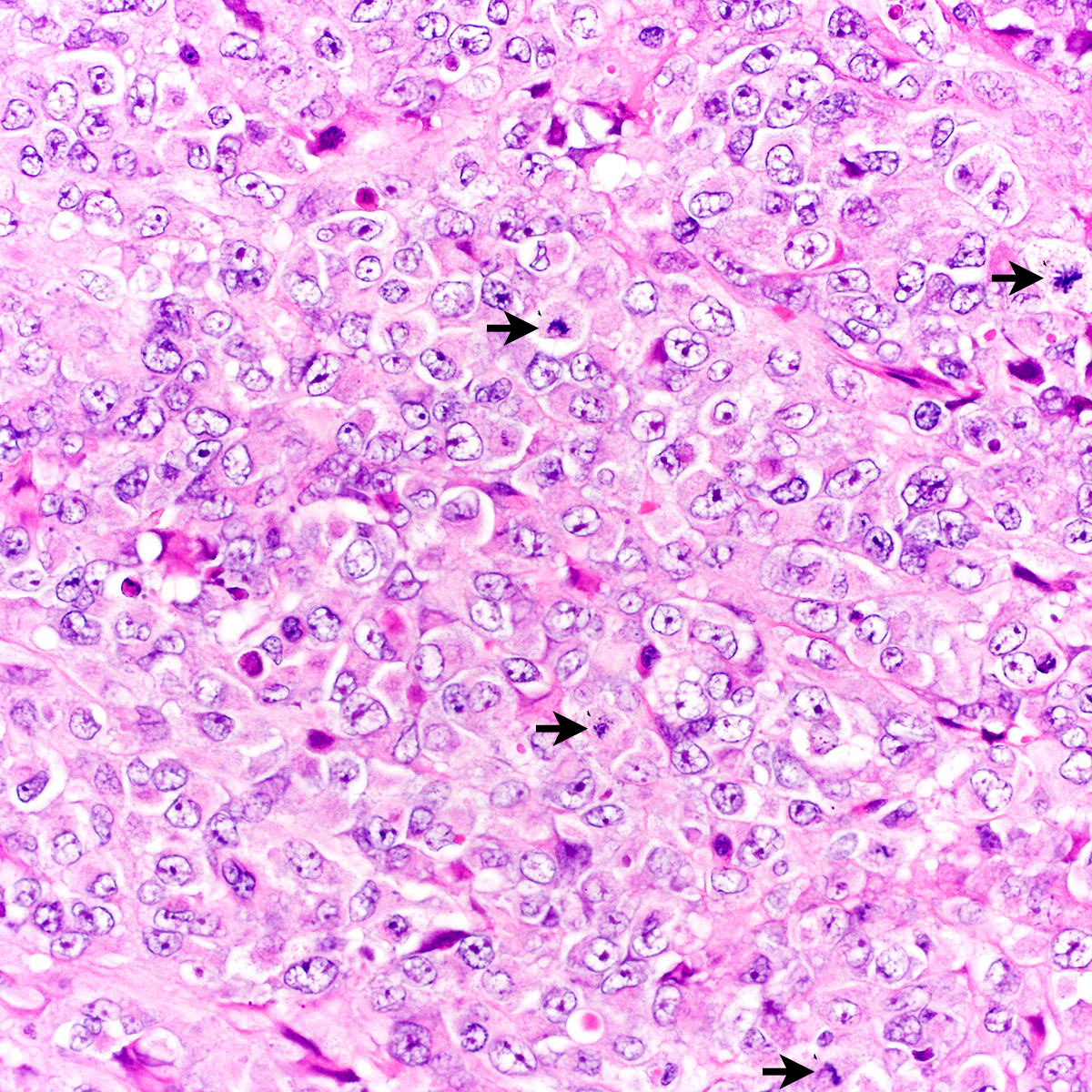
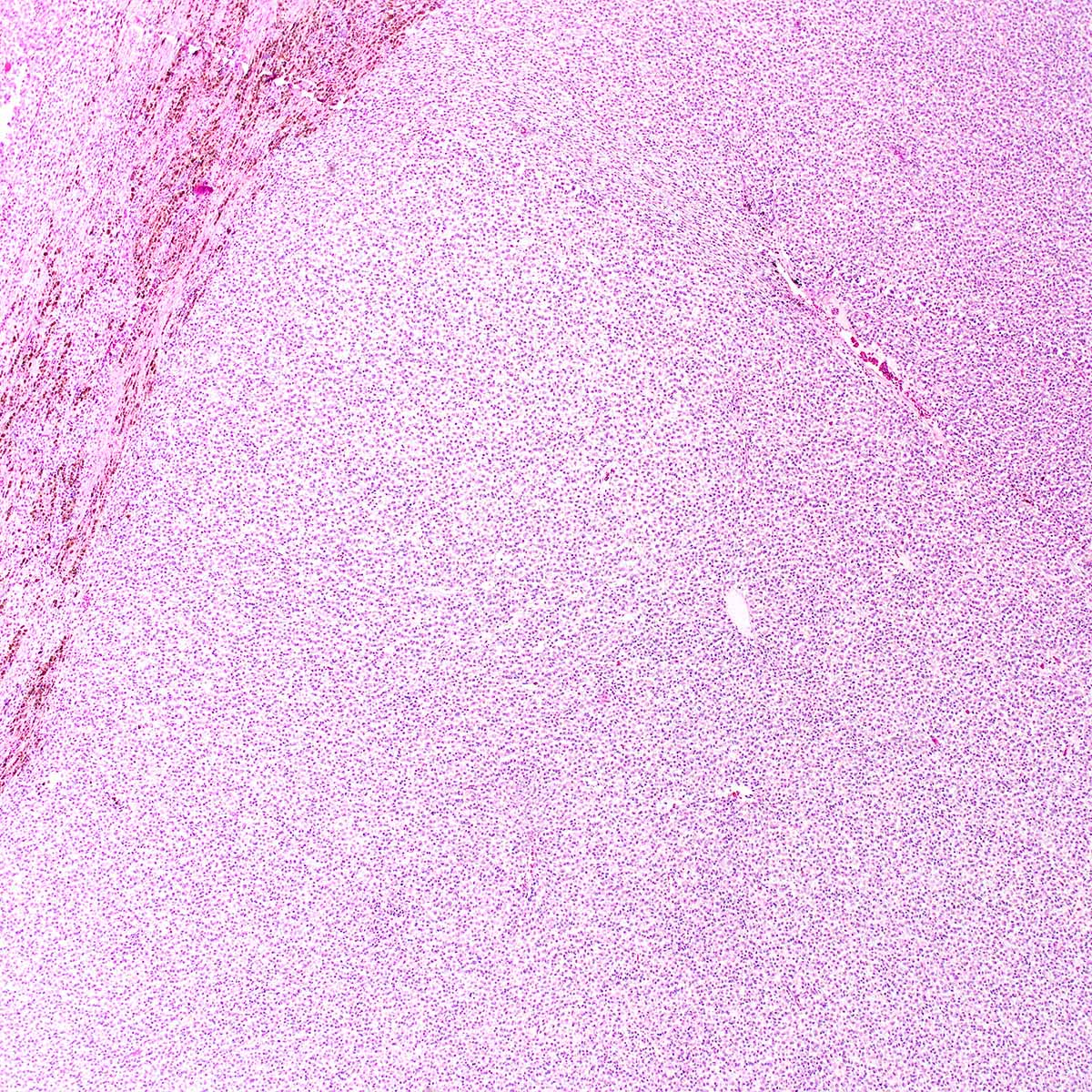
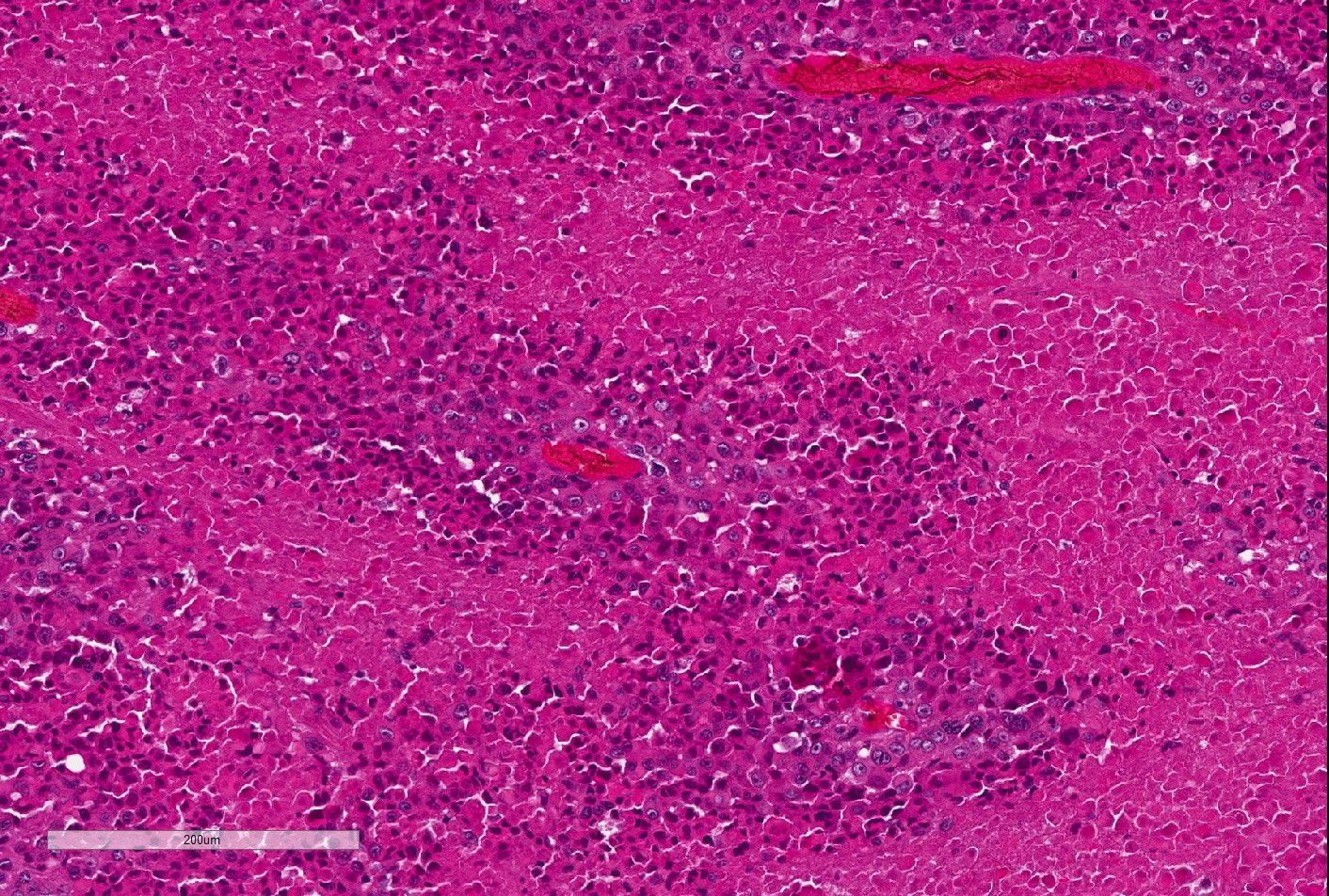
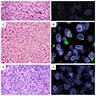
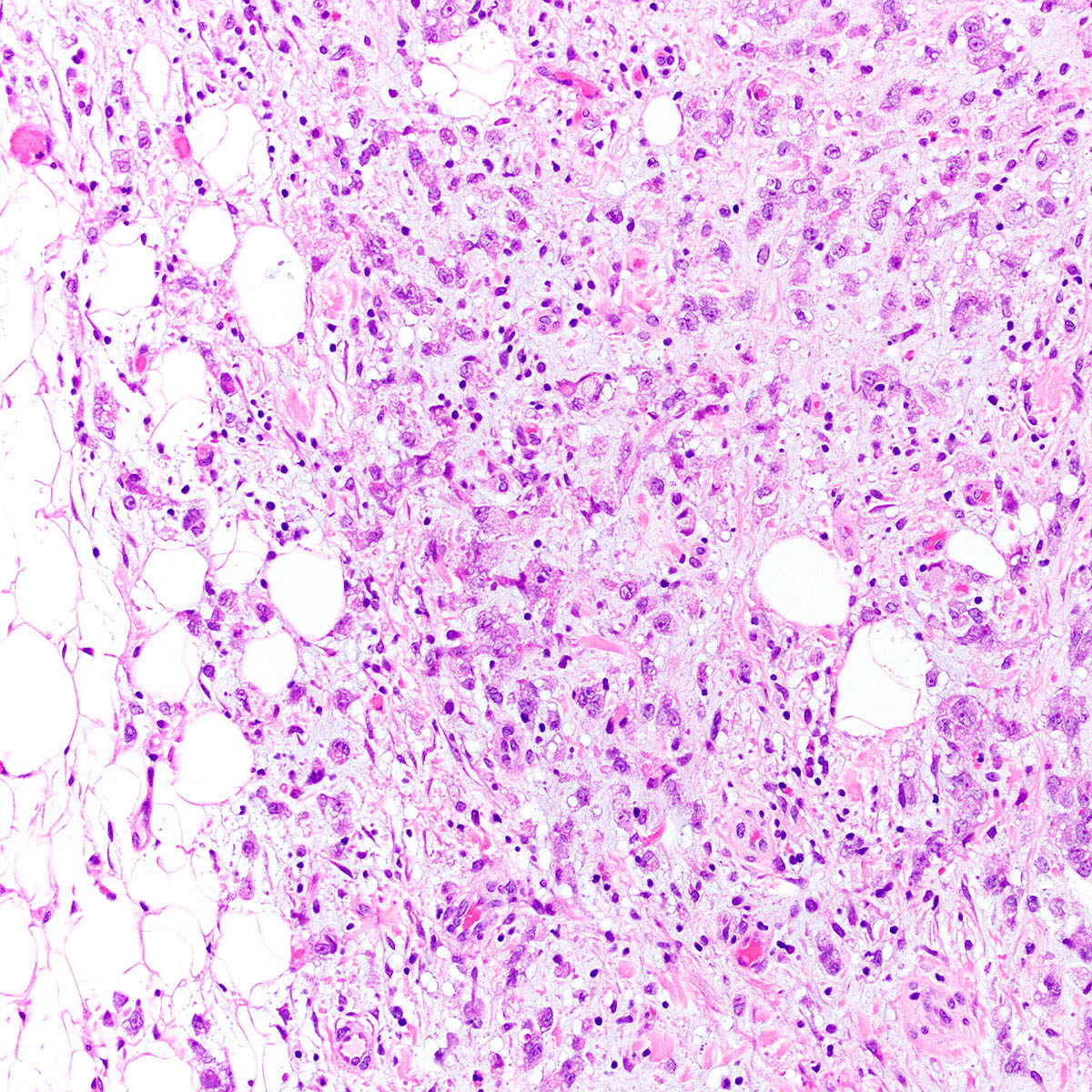
Microscopic (histologic) description
- In vulva: proximal type > distal type
- Proximal type epithelioid sarcoma (Cancer 1983;52:1462, Am J Surg Pathol 1989;13:848, Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:130, Mod Pathol 2001;14:655, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:836):
- Extensively infiltrates surrounding tissues
- Multinodular or diffuse growth pattern in collagenous or myxoid stroma
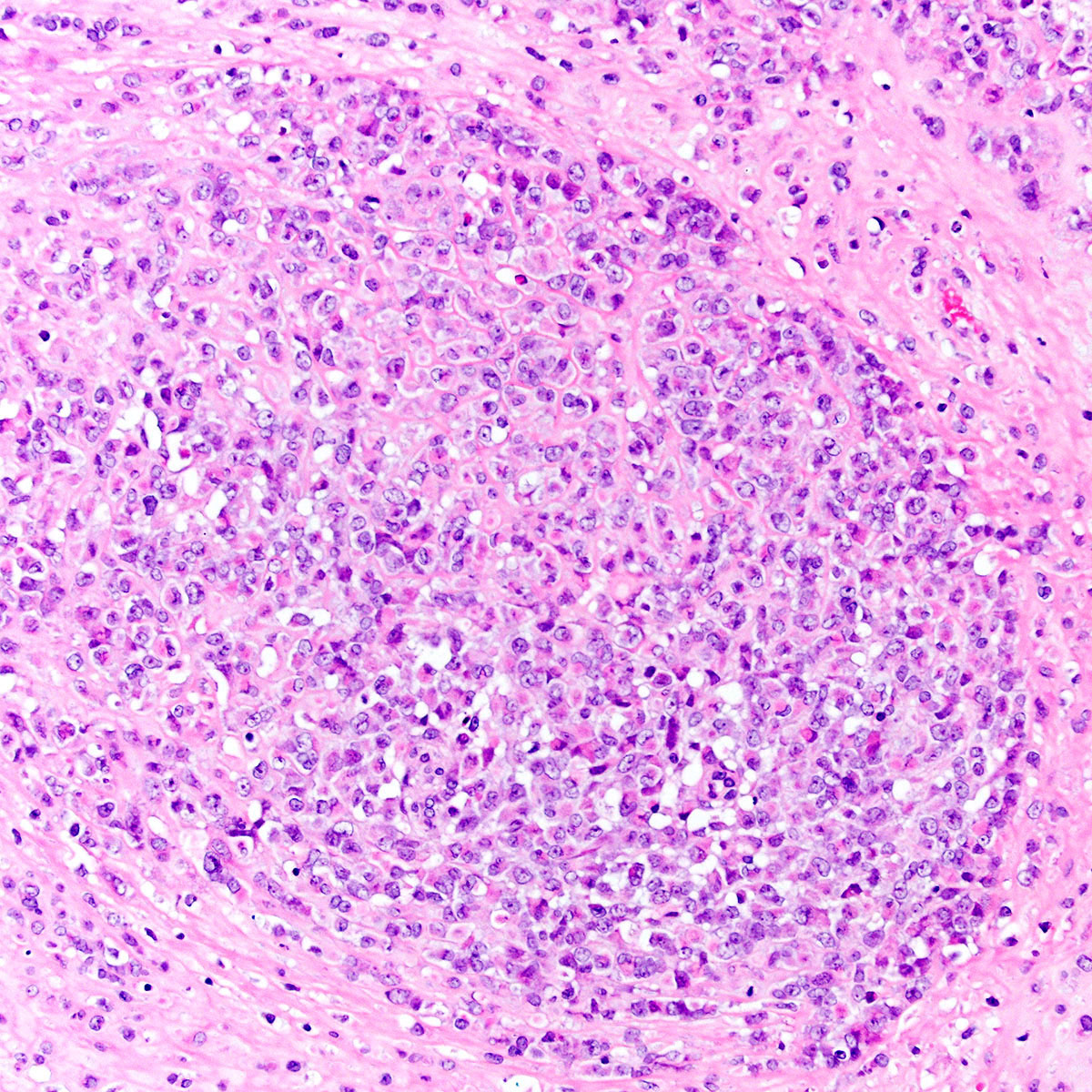
- Atypical polygonal epithelioid cells
- Minor spindle cell population may be present peripherally or admixed
- Coarse vesicular chromatin and 1 - 2 prominent nucleoli
- Abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm with distinct borders
- Cytoplasm may contain an inclusion displacing nucleus peripherally (rhabdoid morphology)
- Subset show exclusively rhabdoid morphology
- Mitoses highly variable (2 - 57 mitoses per 10 high power fields) (Cancer 1983;52:1462)
- Atypical mitoses, necrosis, hemorrhage and lymphovascular invasion common
- Distal type epithelioid sarcoma of the vulva (Am J Surg Pathol 1989;13:848, Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:130):
- Pseudo granulomatous growth pattern: scattered small tumor nodules with central necrosis in a collagenous stroma with prominent lymphocytic inflammation
- Monomorphic eosinophilic epithelioid or histiocytoid cells
- Bland nuclei with inconspicuous nucleoli
- Rhabdoid morphology not common
- 8 mitoses per 10 high power fields in 1 vulvar case (Am J Surg Pathol 1989;13:848)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Virtual slides
Cytology description
- Cellular smear or touch prep with dispersed large epithelioid cells (Cytopathology 2018;29:471, Am J Surg Pathol 1989;13:848)
- Rhabdoid morphology may be seen
- Mitoses brisk
- Perivascular arrangements may be seen (Cancer Cytopathol 2018;126:934)
Positive stains
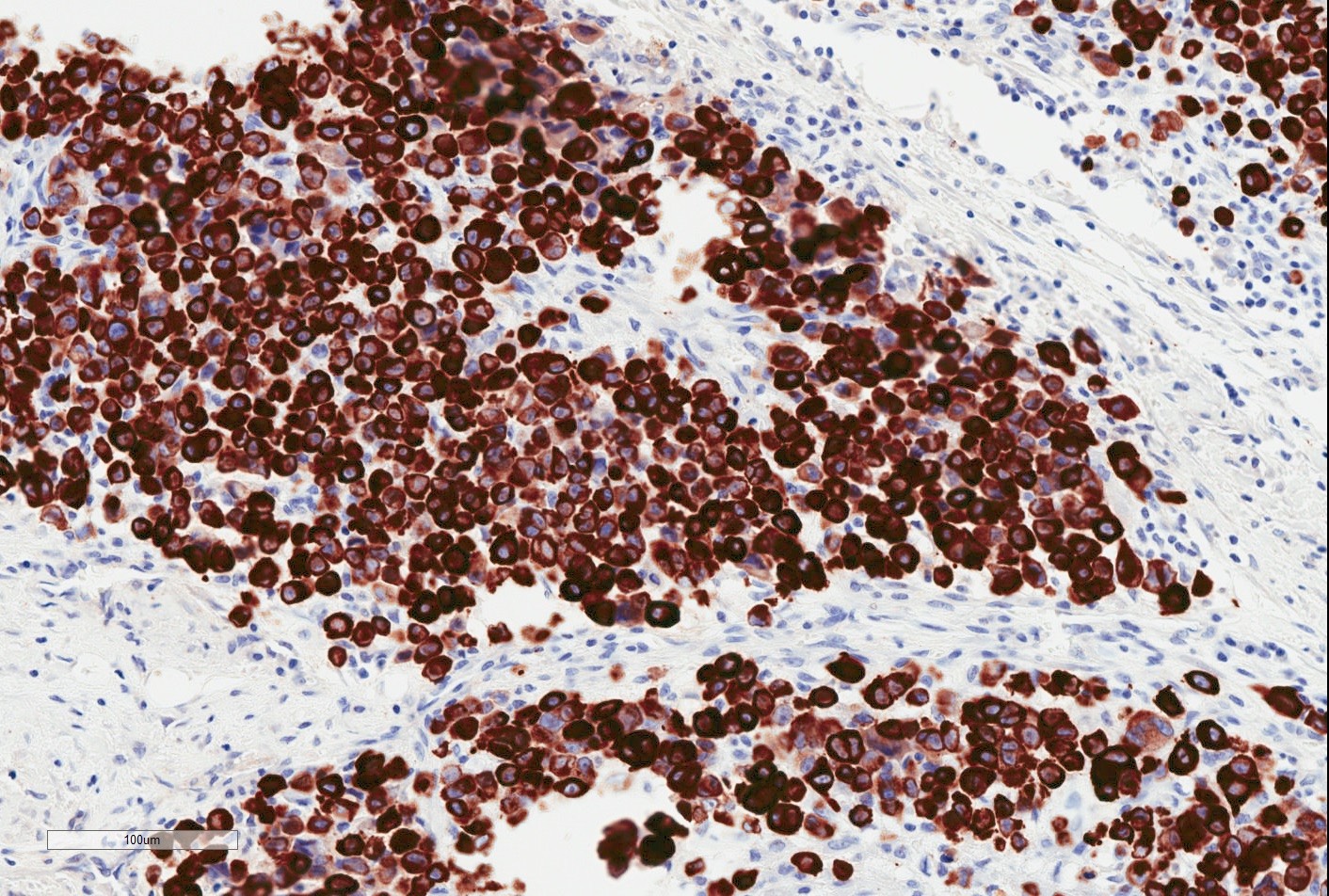
- Cytokeratin (AE1 / AE3, CAM5.2; virtually 100%) (Am J Surg Pathol 1989;13:848, Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:130, Mod Pathol 2001;14:655, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:836)
- EMA (~ 90%)
- CD34 (~ 50%)
- ERG, N terminus (~70%) (Mod Pathol 2014;27:496)
- FLI1 (Mod Pathol 2014;27:496)
Negative stains
- SMARCB1 / INI1 (loss of expression in ~ 95%) (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2010;29:600, Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:542, Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:312, Mod Pathol 2013;26:385)
- S100 (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:130)
- CD31 (Mod Pathol 2014;27:496)
- ER, PR (Gynecol Oncol 2002;85:218)
- ERG, C terminus (Mod Pathol 2014;27:496)
Electron microscopy description
- Mononuclear cells
- Conspicuous intermediate filaments, sometimes as perinuclear whorls (Cancer 1983;52:1462, Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:130, Am J Surg Pathol 1989;13:848)
- Epithelial type cell - cell adhesions (tonofilaments or desmosomes) (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:130)
- Well developed rough endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes and lysosomes
- Few mitochondria (Gynecol Oncol 1980;9:237)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Homozygous deletions of SMARCB1 / INI1 in 80 - 90% of proximal type epithelioid sarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:542, Cancer Res 2005;65:4012, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014;53:475, Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:312, Mod Pathol 2013;26:385)
- SMARCB1 / INI1 deletion correlates strongly with SMARCB1 / INI1 loss by IHC (Eur J Cancer 2011;47:287)
- SMARCA4, SMARCC2 or SMARCC1 alterations in rare cases (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:312)
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Videos
Proximal type epithelioid sarcoma of the groin
Sample pathology report
- Vulva, mass, wide local excision:
- Epithelioid sarcoma, proximal type (6.0 cm) (see comment)
- Margins are negative for tumor
- Comment: Microscopic examination reveals an infiltrative tumor composed of atypical epithelioid cells, some of which show prominent rhabdoid cytoplasmic inclusions. By immunohistochemistry, tumor cells are positive for cytokeratin AE1 / AE3, EMA and CD34 and show loss of SMARCB1 / INI1 expression. S100, CD31, ER and PR are negative. The findings are most consistent with proximal type epithelioid sarcoma. These are aggressive tumors with a high rate of local recurrence, lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis. Clinical and radiographic correlation are advised.
Differential diagnosis
- Squamous cell carcinoma:
- Keratinization or intercellular bridging frequently present
- Associated with usual or differentiated type vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia
- p63 / p40 positive
- HPV in situ hybridization positive in HPV associated tumors
- Mutant pattern p53 immunostaining in a subset of HPV independent tumors
- SMARCB1 / INI1 positive (retained)
- CD34 negative
- Myoepithelial carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:836):
- Less common than epithelioid sarcoma in vulva
- More varied cytology and more prominent spindle cells
- Reticulated architecture in myxoid stroma
- S100 or SMA positive
- SMARCB1 / INI1 IHC negative (lost) in ~ 50% (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:542)
- May harbor EWSR rearrangements (not yet detected in vulvar tumors)
- Extrarenal malignant rhabdoid tumor:
- In adults, most often represents carcinoma, sarcoma or melanoma with rhabdoid morphology (composite rhabdoid tumor)
- Debated whether malignant rhabdoid tumor is an entity distinct from proximal type epithelioid sarcoma (Cancer Res 2005;65:4012, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2010;29:600, Hum Pathol 2015;46:225, Hum Pathol 2009;40:349)
- Malignant melanoma:
- S100, SOX10, HMB45, MelanA positive
- SMARCB1 / INI1 positive (retained)
- Cytokeratin and EMA negative
- Epithelioid angiosarcoma:
- True vascular spaces lined by multiple layers of tumor cells
- Vacuolated tumor cells may contain red blood cells
- CD31 and ERG positive
- Cytokeratin may be positive but EMA is negative
- Epithelioid malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor:
- S100 positive
- SMARCB1 / INI1 IHC negative (lost) in ~ 50% (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:542)
- CD34 positive in ~ 50%
- Cytokeratin and EMA negative
- Epithelioid leiomyosarcoma:
- Rhabdomyosarcoma:
- Desmin, myogenin, myoD1 positive
- SMARCB1 / INI1 positive (retained)
- Epithelioid monophasic synovial sarcoma:
- SMARCB1 / INI1 positive (retained)
- Characteristic t(X;18) fusion, with positive fusion specific immunostain (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:922)
- Necrotizing granulomas (in differential diagnosis with distal type epithelioid sarcoma):
- CD68 and PU.1 positive
- SMARCB1 / INI1 positive (retained)
- Cytokeratin and EMA negative
- Infectious organisms, foreign material or autoimmune etiology may be present
Additional references
- Vulvar soft tissue tumor review (Semin Diagn Pathol 2020 Sep 6 [Epub ahead of print]), additional review of distal type (classical) epithelioid sarcoma (Adv Anat Pathol 2006;13:114), prognostic factors in epithelioid sarcoma (Eur J Surg Oncol 2020;46:1320, Ann Surg Oncol 2015;22:2624)
Board review style question #1
A 44 year old woman presented with a 3 cm painless vulvar mass. Her gynecologist diagnosed a Bartholin cyst and performed a conservative local excision. A representative photomicrograph of the lesion is shown. On immunohistochemical studies, tumor cells were positive for CK AE1 / AE3 and showed loss of INI1 staining. Which of the following is true about this tumor?
- CD34 is expressed in ~ 50%
- Exposure to ultraviolet radiation is the most common risk factor
- Fewer than 10% of patients experience local recurrence
- Hormone receptors (ER, PR) are usually positive
- Lymph node metastases are exceptionally rare
Board review style answer #1
A. CD34 is expressed in ~ 50%. This is a vulvar epithelioid sarcoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Epithelioid sarcoma-vulva
Comment Here
Reference: Epithelioid sarcoma-vulva
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2