Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Kuo E, Gonzalez RS. Sessile serrated adenoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colontumorsessileserrated.html. Accessed May 12th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Serrated neoplastic precursor lesion of colorectal cancer (Am J Gastroenterol 2012;107:1315)
- Defined as having 2 or 3 contiguous crypts demonstrating features of sessile serrated adenoma, as discussed below (per Bosman: WHO Classification of Tumours of the Digestive System, 4th Edition, 2010)
- Criteria for serrated polyposis syndrome include 1 of the following:
- At least 5 serrated polyps proximal to the sigmoid colon with at least 2 greater than 1 cm in size
- Any serrated polyp proximal to the sigmoid colon in a patient with a first degree relative with serrated polyposis syndrome
- More than 20 serrated polyps of any size in the colon
Essential features
- Neoplastic, premalignant lesion of the colorectum
- If present, patient should undergo increased colonoscopy surveillance
- May develop traditional cytologic dysplasia and progress to colorectal carcinoma with microsatellite instability
Terminology
- Current official WHO designation is sessile serrated lesion; former WHO designation was sessile serrated adenoma / polyp
- Examples that develop adenomatous epithelium are termed sessile serrated adenoma with cytologic dysplasia (Gastrointest Endosc 2014;80:307)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: K63.5 - Colon polyp
Epidemiology
- Account for approximately 3 - 9% of all colorectal polyps and 10 - 25% of all serrated polyps (World J Gastroenterol 2014;20:2634)
- Prevalence of sessile serrated adenoma increases slightly with age (Am J Gastroenterol 2012;107:1315)
- More common in women and smokers (Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2017;10:270)
Sites
- More often found in the proximal colon (World J Gastroenterol 2010;16:3402)
Etiology
- Associated with a high fat and meat diet, smoking, alcohol and a high BMI (Gastroenterology 2017;152:92)
Clinical features
- Incidental findings on colonoscopy and have no clinical features unless they progress to malignancy
Diagnosis
- Histopathology is the gold standard for diagnosing sessile serrated adenomas (World J Gastroenterol 2016;22:7754)
- Narrow band imaging can be used during endoscopy to detect sessile serrated adenomas (World J Gastroenterol 2015;21:2896, Lancet Oncol 2009;10:1171)
Radiology description
- Screening CT colonography may identify large (~10 mm) sessile serrated adenomas (Radiology 2016;280:455)
Prognostic factors
- Approximately 15% of patients with sessile serrated adenomas will develop adenomatous polyps with high grade dysplasia or colorectal carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:927)
- > 10 mm in size have a higher risk of developing colorectal carcinoma (Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2017;10:270)
Treatment
- Polypectomy or endoscopic mucosal resection (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7:1275)
- Recommendations are to completely remove all serrated lesions proximal to the sigmoid colon and all serrated lesions > 5 mm in the rectosigmoid colon (Am J Gastroenterol 2012;107:1315)
- Lesions > 1 cm in size or with high grade dysplasia should be managed clinically like a high risk adenoma (Gastroenterology 2012;143:844)
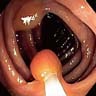
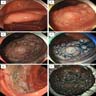
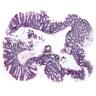
Gross description
- Sessile or flat in appearance (World J Gastroenterol 2010;16:3402)
- Usually red in color, with an adherent mucous cap (World J Gastroenterol 2015;21:2896, Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2017;10:270)
Gross images
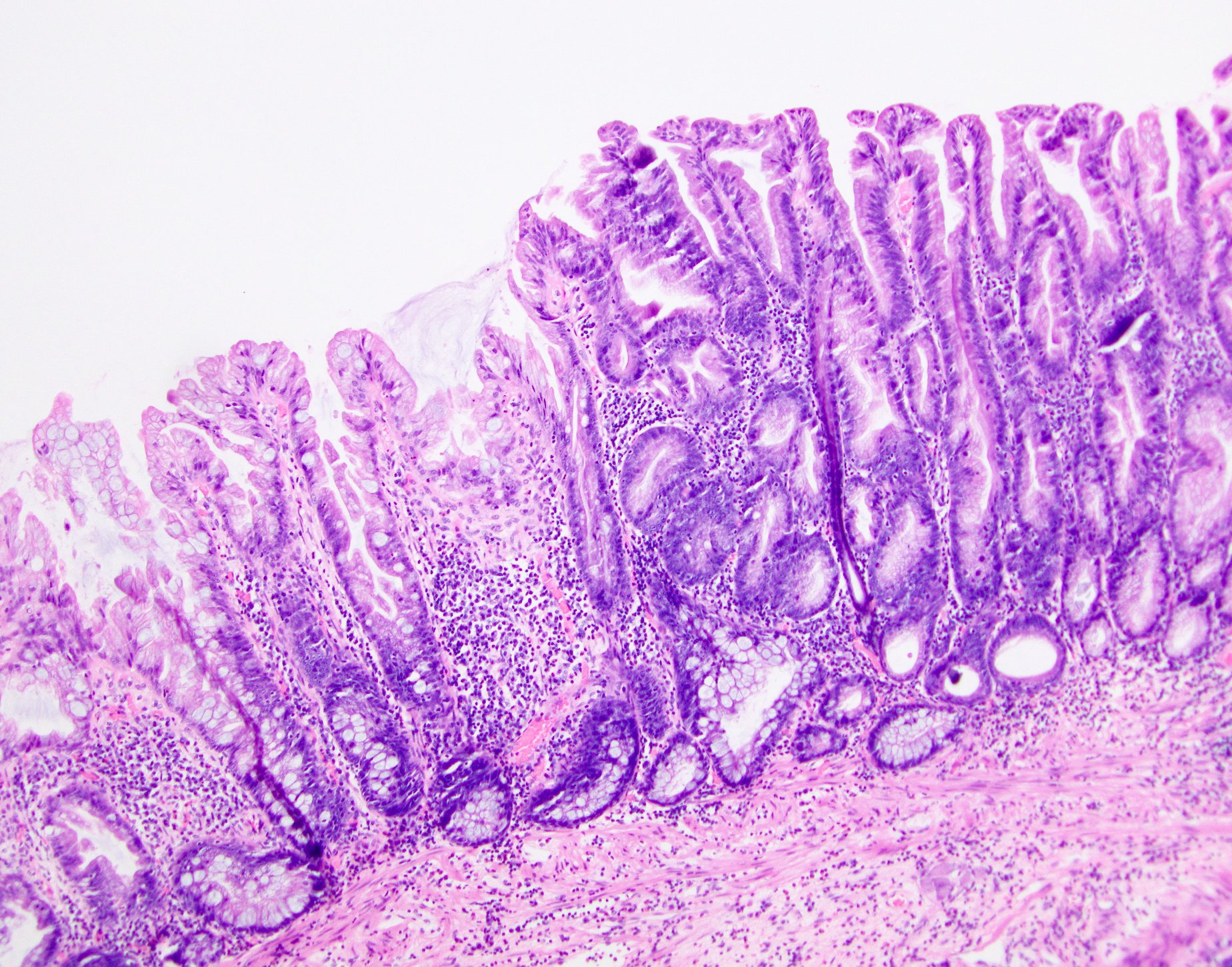
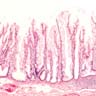
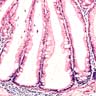
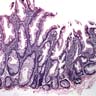
Microscopic (histologic) description
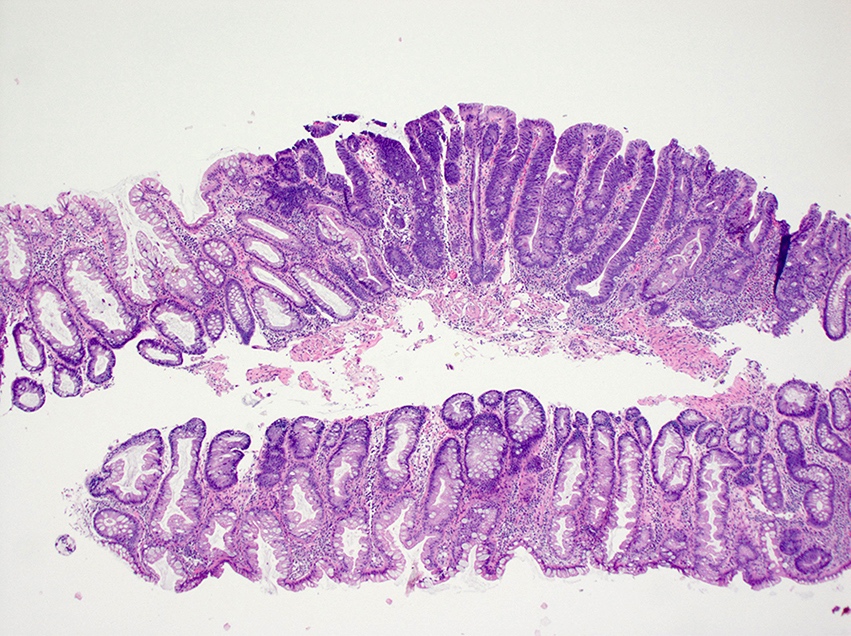
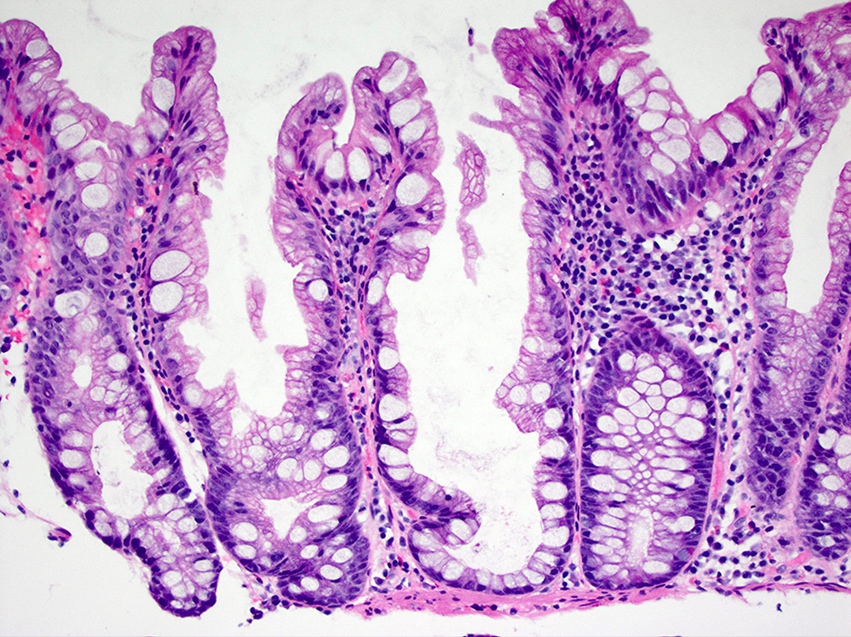
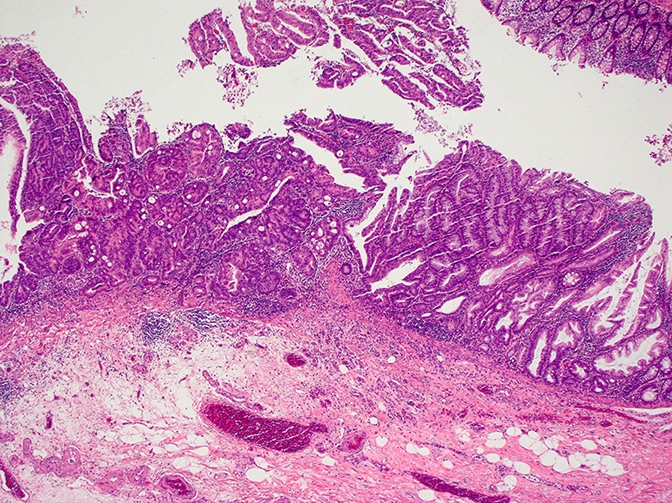
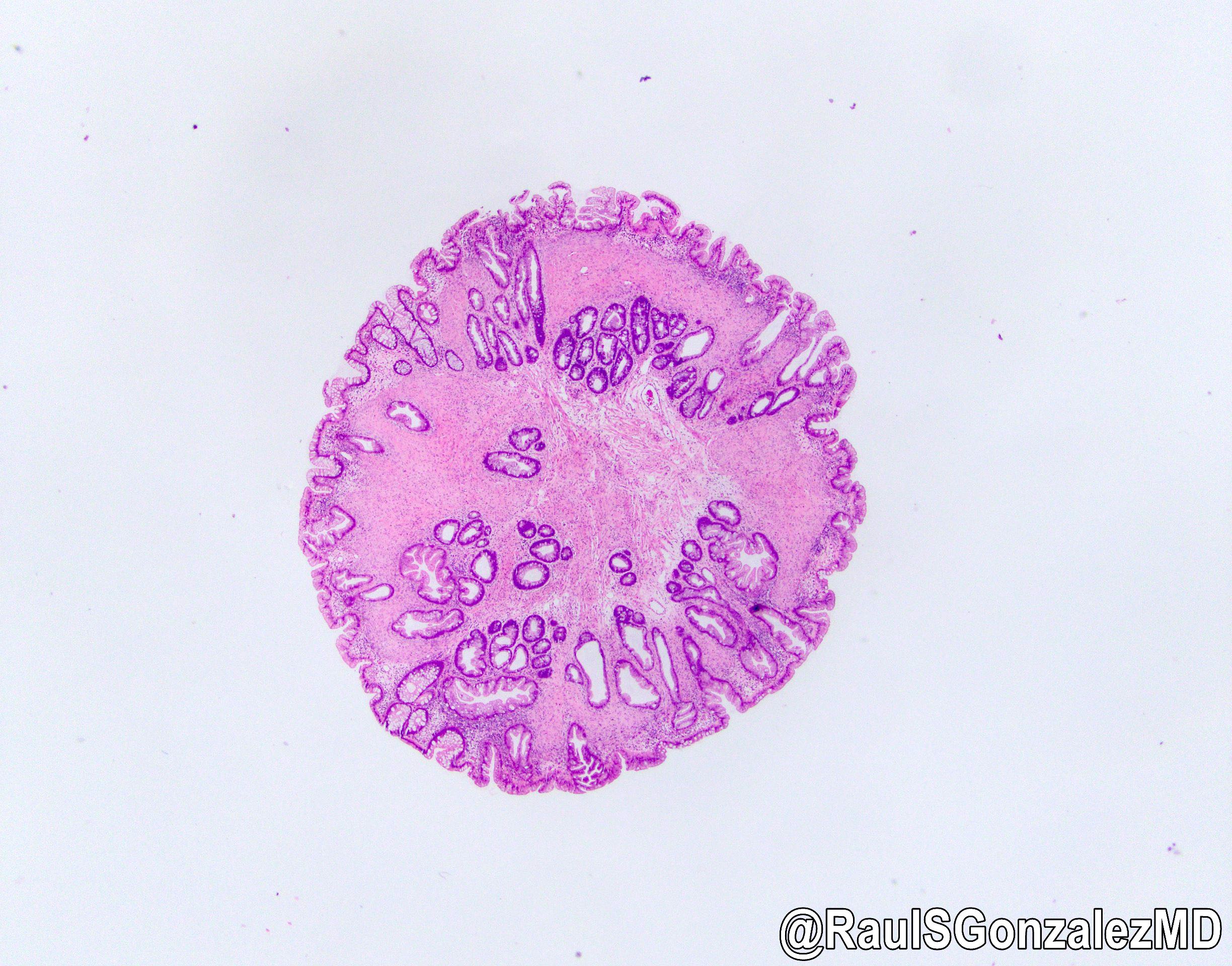
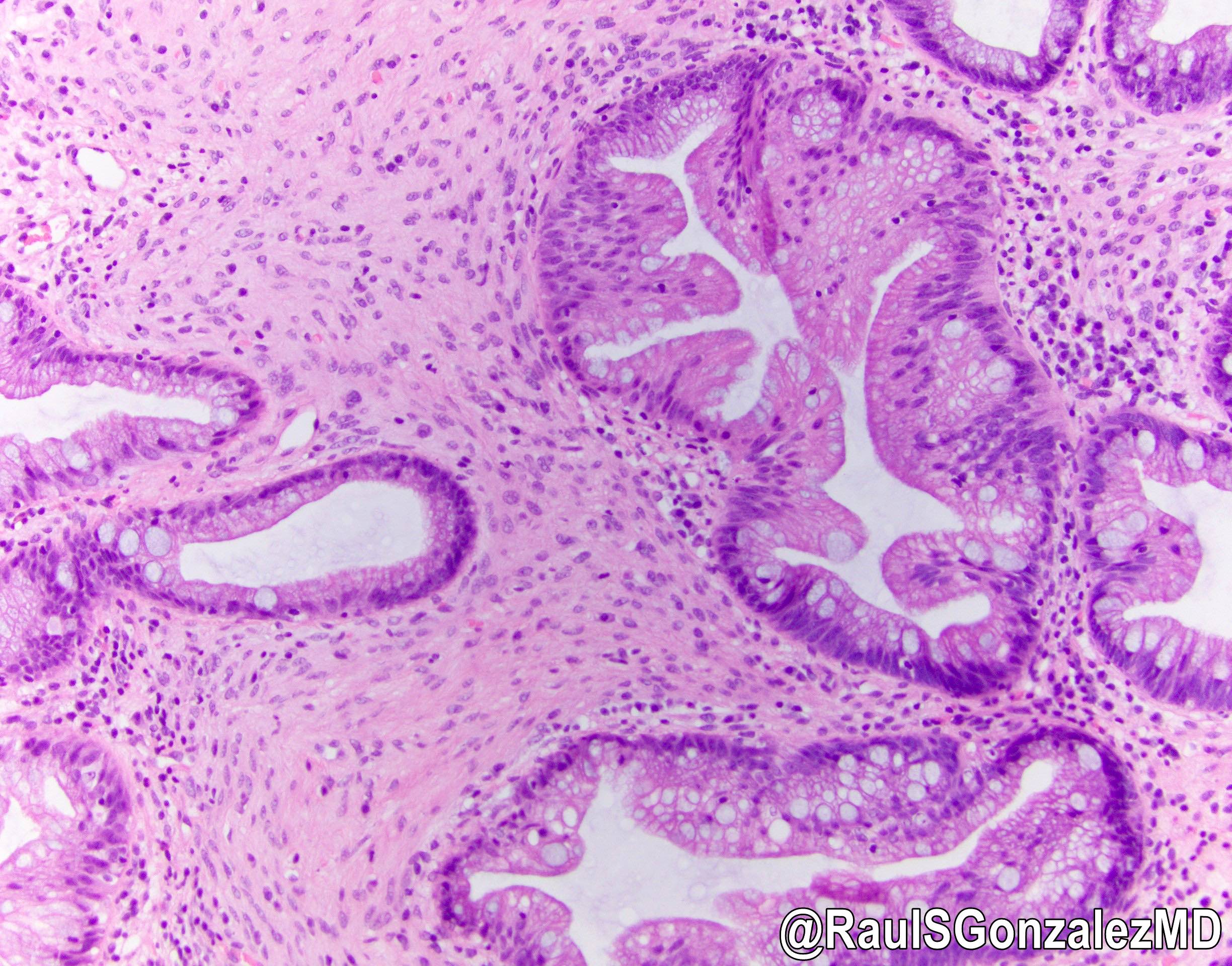
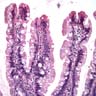
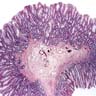
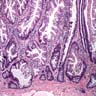
- Sawtooth serrations of the epithelium with abundant mucin, similar to hyperplastic polyps
- Basal crypt dilation with mucous retention
- Bases of the crypts are more serrated compared to the surface and have mature goblet cells and mucinous cells (Am J Gastroenterol 2012;107:1315)
- Lateral spread of the crypt bases (commonly described as boot shaped or anchor shaped crypts)
- May contain fibroblastic / perineuriomatous stroma (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1373)
- Conventional ("adenomatous") dysplasia may also be present, with retention of MLH1 staining; no need to grade per WHO
- Nonconventional forms of dysplasia have also been described, including minimal deviation type (mild architectural and histologic changes, difficult to see on H&E but shows loss of MLH1), serrated type (tightly packed glands with rounded dysplastic nuclei and eosinophilic cytoplasm; MLH1 retained) and not otherwise specified (most common pattern; atypical changes not fitting into any other pattern; often MLH1 loss) (Mod Pathol 2017;30:1728, Mod Pathol 2019;32:1390)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Monika Vyas, M.D. and Christopher Hartley, M.D.
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
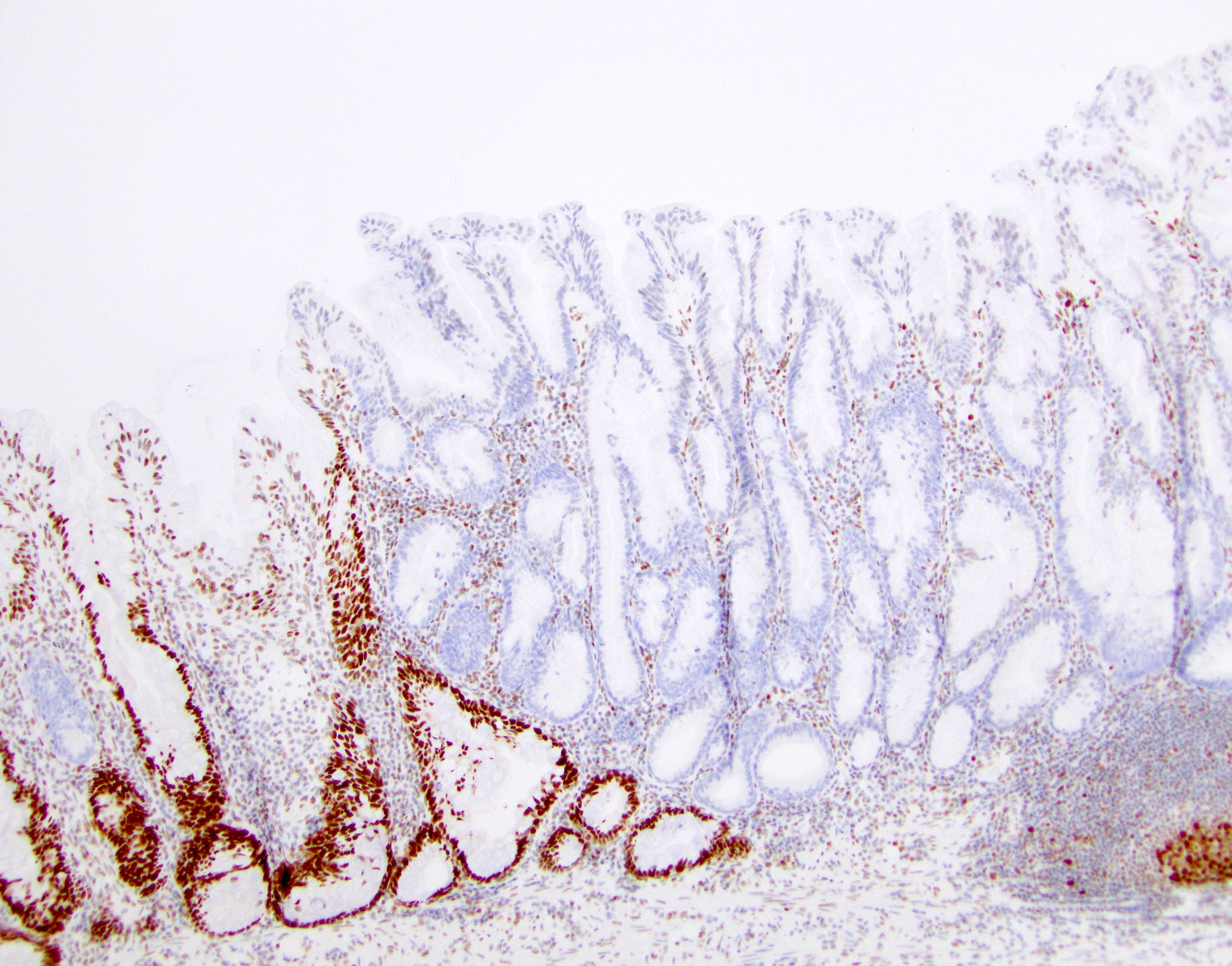
- Agrin positivity in muscularis mucosae may distinguish from hyperplastic polyps (Clin Cancer Res 2020 15;26:1277)
Negative stains
- Loss of HES1 nuclear staining can be used to differentiate sessile serrated adenomas from hyperplastic polyps (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:113)
- Loss of MLH1 and PMS2 can be seen in areas of cytologic dysplasia (Am J Clin Pathol 2006;126:564)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- BRAF (V600E) mutation and CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP), leading to microsatellite instability through promoter hypermethylation of MLH1 (World J Gastroenterol 2016;22:7754, Am J Gastroenterol 2012;107:1315)
- Negative for KRAS mutation
Sample pathology report
- Ascending colon, polyp, endoscopic mucosal resection:
- Sessile serrated lesion
- Lateral margins of resection unremarkable.
Differential diagnosis
- Hyperplastic polyp:
- Crypts in hyperplastic polyps are less distorted and will not be laterally dilated at the base
- Serrations are more pronounced at the epithelial surface than the base (World J Gastroenterol 2016;22:7754, Am J Gastroenterol 2012;107:1315)
- Traditional serrated adenoma (TSA):
- TSAs have a tubulovillous architecture with pseudostratified epithelium
- Cells have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm with thin, hyperchromatic, pencillate nuclei at the base (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:1290)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
What mutations can be seen in sessile serrated adenoma?
- Beta catenin and KRAS
- BRAF and beta catenin
- BRAF and CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP)
- KRAS and CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP)
Board review style answer #1
C. BRAF and CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP).
KRAS and beta catenin mutations are not associated with sessile serrated adenomas and are instead seen in traditional serrated adenomas and tubular adenomas.
Comment here
Reference: Sessile serrated adenoma
Comment here
Reference: Sessile serrated adenoma