Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Skala SL. Paratubal cysts. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/fallopiantubesparatubalcyst.html. Accessed May 10th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Fluid filled cyst with ciliated lining adjacent to fallopian tube
Essential features
- Ciliated cyst adjacent to fallopian tube
- Typically asymptomatic
- Almost always benign, with rare reports of borderline tumor
Terminology
- Paraovarian cyst
- Hydatid cyst
- Not recommended: hydatid of Morgagni
ICD coding
- ICD-10: N83.8 - other noninflammatory disorders of ovary, fallopian tube and broad ligament
Epidemiology
- Common benign incidental finding (~7 - 10% of women) (J Pediatr Surg 2011;46:2161)
- All age groups, most commonly third to fifth decade
Sites
- Paratubal (between fallopian tube and ovary)
Pathophysiology
- Unknown
Etiology
- Believed to originate from mesothelium or be remnant of Müllerian duct or Wolffian duct
Clinical features
- Most cysts are small and asymptomatic (< 1 to 8 cm; rarely, 20+ cm)
- Size of paratubal cysts may correlate with obesity (J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2017;30:571)
- May be found during surgery or incidentally on radiological study performed for another reason
- Larger lesions may become symptomatic, causing pressure or pain (J Pediatr Surg 2011;46:2161)
- May lead to torsion of adnexa, resulting in acute pain (J Pediatr Surg 2011;46:2161)
Diagnosis
- Typically noted incidentally on intraoperative or gross examination
Radiology description
- While not often diagnosed on imaging, paratubal cysts are unilocular and anechoic or hypoechoic on ultrasound (J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000;85:1021)
Prognostic factors
- Paratubal cysts are benign
- Rarely gives rise to serous borderline tumor or even more rarely malignancy (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2017;25:e21)
Case reports
- 15 year old girl with giant paratubal serous cystadenoma (J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2020;33:438)
- 17 year old girl with paratubal borderline tumor (J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2016;29:74)
- 34 year old nulligravid woman with paratubal cyst and bilateral hydrosalpinges diagnosed during evaluation of infertility (Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 2014;53:239)
Treatment
- Surgical excision of the paratubal cyst represents definitive treatment for symptomatic patients (J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000;85:1021)
- Benign follow up is expected; treatment is not required for asymptomatic patients
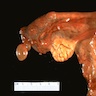
Gross description
- Simple fluid filled cyst(s) near fallopian tube
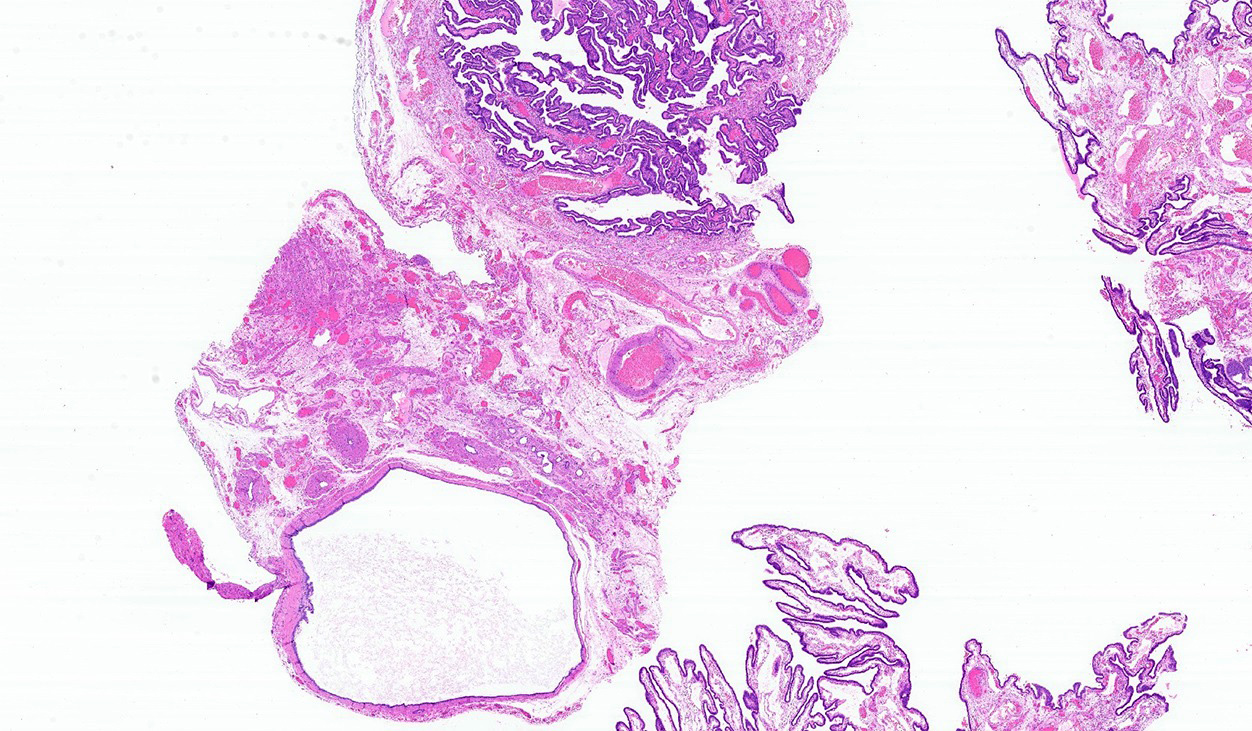
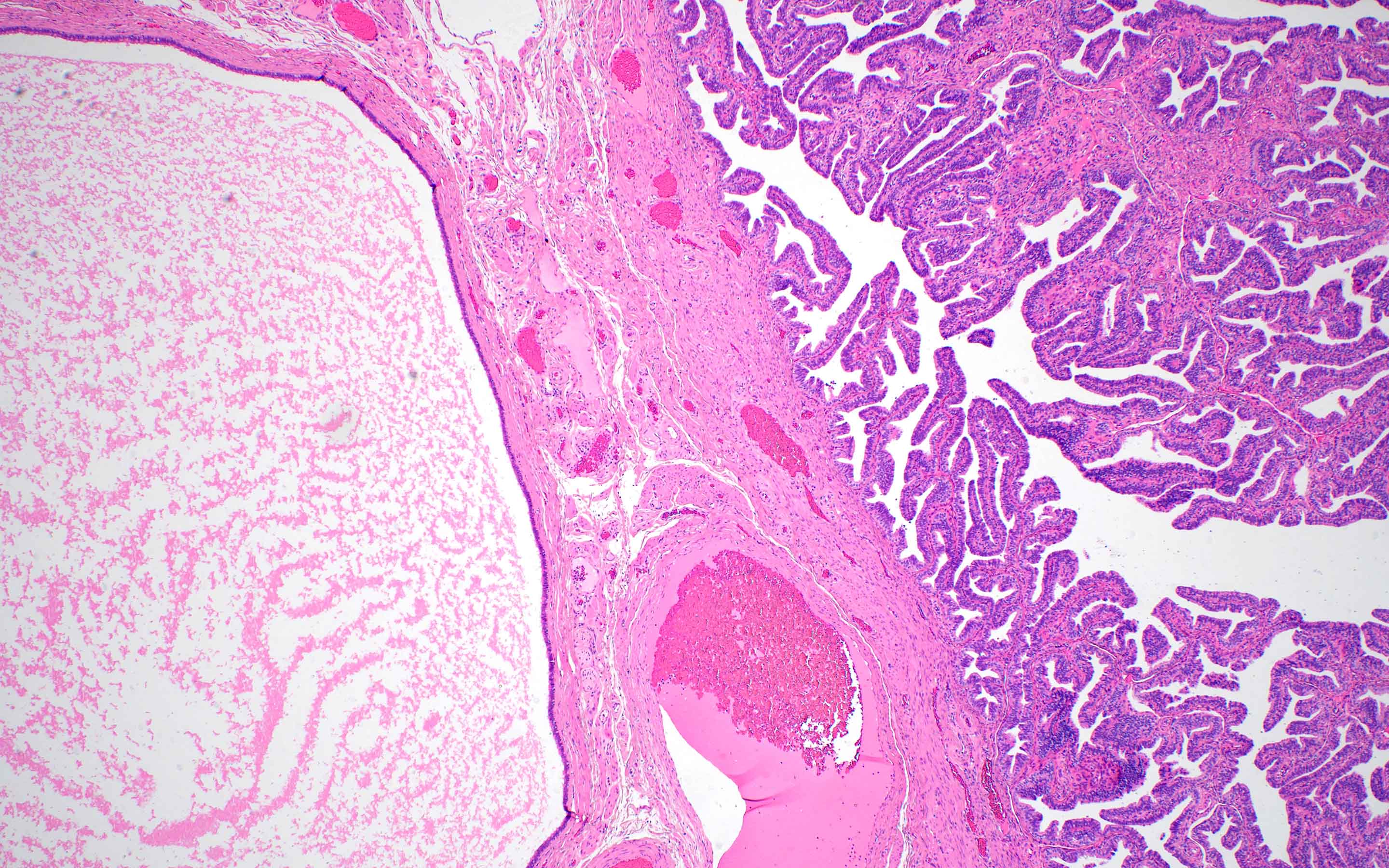
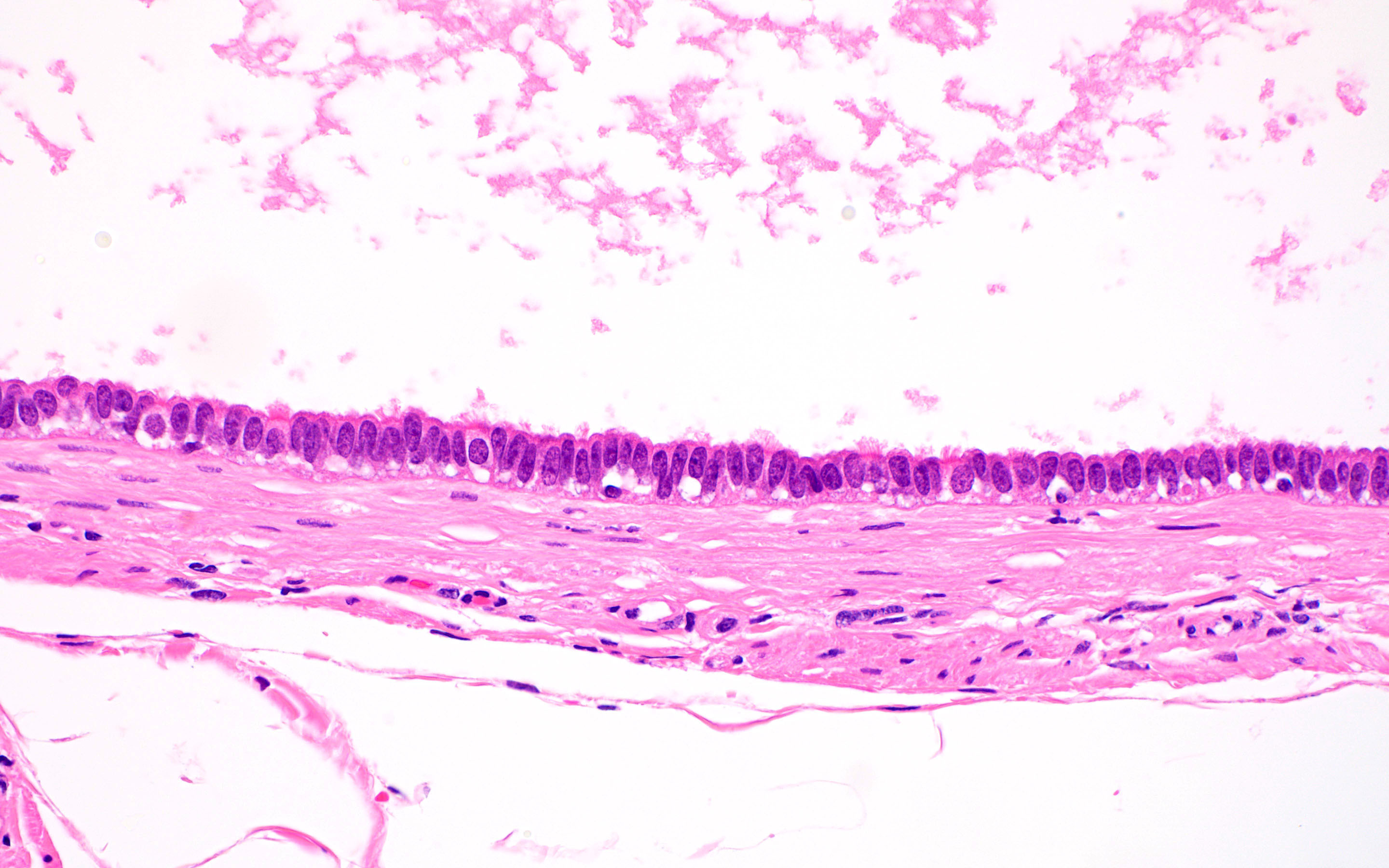
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Simple fluid filled cyst lined by ciliated tubal type epithelium
- Focal papillary projections may be seen
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Fallopian tubes, bilateral salpingectomy:
- Benign fallopian tubes with paratubal cysts
Differential diagnosis
- Endometriotic cyst:
- Associated with endometrial type stroma with or without hemosiderin laden macrophages
- Serous cystadenoma:
- Histologically identical to paratubal cyst but > 1 cm in size
- Hydrosalpinx:
- Dilation of the fallopian tube lumen with attenuation of the tubal epithelium with or without diminished plicae
- Distinction based largely on location of the cystic space within rather than near the fallopian tube
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is true about paratubal cysts?
- Large paratubal cysts may cause torsion
- Large paratubal cysts often progress to borderline tumors
- Paratubal cysts are frequently diagnosed on MRI
- Paratubal cysts are an unusual finding
Board review style answer #2