Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Chundriger Q, Rahim S, Ahmad Z. Cyclin D1. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainscyclind1.html. Accessed April 26th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Member of cyclin family of cell cycle regulators; 11q13.3 locus
Essential features
- Cell cycle regulator that controls transition from G1 to S phase in normal tissues
- Mutation leads to increased cell proliferation via disruption of downstream pathways, resulting in tumorigenesis
- Expression by immunohistochemistry is valuable in diagnosis of some tumors as well as predicting prognosis in a number of tumors
Terminology
- BCL1 (B cell lymphoma 1)
- CCND1
- PRAD1 (parathyroid adenomatosis 1)
Pathophysiology
- Cyclin D1 is activated in the G1 phase of the cell cycle; it activates CDK4, followed by activation of cyclin / CDK (cyclin dependent kinase) complexes leading to progression of the cell cycle to S phase (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2020;117:17177)
- Also regulates transcription in different cell models (J Clin Invest 2018;128:4132)
- Tumorigenesis: it binds to either CDK4 or CDK6, resulting in phosphorylation of pRB, E2F release and subsequent promotion of the G1 / S phase transition (Nat Rev Cancer 2007;7:750)
Clinical features
- Degradation of cyclin D1 in neural stem cells has been found to contribute to neurogenic cortical defects in Down syndrome (EBioMedicine 2015;2:120)
- Positive cyclin D1 is associated with increased risk of loss of MSH2 expression in colorectal cancers (Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2020;21:343)
- Cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism is associated with increased risk of multiple myeloma (Genet Mol Res 2015;14:5856)
Interpretation
- Nuclear staining
Uses by pathologists
- Diagnosis of mantle cell lymphoma: up to 98% positive (Am J Hematol 2018;93:E134)
- Differentiating clear cell sarcoma of kidney (positive for cyclin D1) from blastema rich Wilms tumor (blastemal component is negative for cyclin D1) (Diagn Pathol 2019;14:13)
- Differentiating adenocarcinoma from small cell carcinoma of prostate (shows cyclin D1 loss) (Clin Cancer Res 2015;21:5619)
- Parathyroid tumors (Am J Pathol 2001;158:1355)
- Plasma cell neoplasms with t(11;14), increased copies of chromosome 11 or CCND1 gene amplifcation (Hematol J 2000;1:181 Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2014;14:215)
- Dim expression in hairy cell leukemia (Mod Pathol 2000;13:1308, ASH: Hairy cell leukemia involving bone marrow, Cyclin D1 positive [Accessed 22 June 2021]
- Dim expression within chronic lymphocytic leukemia / small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL / SLL) proliferation centers (Am J Clin Pathol 2012;138:132
Prognostic factors
- Plasma cell neoplasm: overexpression may be associated with longer event free survival in certain treatment settings (Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2019;19:397)
- Breast cancer: overexpression is associated with tamoxifen resistance but good overall survival (Breast Cancer Res 2012;14:R57, Nat Commun 2020;11:5513, Indian J Surg Oncol 2019;10:167)
- Colorectal cancer: expression is associated with adverse prognosis (Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2019;20:2471, BMC Gastroenterol 2004;4:22)
- Prostatic adenocarcinoma: expression is suggestive of tumor aggressiveness (Braz J Med Biol Res 2014;47:515)
- Oral squamous cell carcinoma: expression is associated with poor survival (Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2011;12:2199)
- Gastric cancer: expression is associated with poor tumor differentiation and survival (Oncol Lett 2017;14:4517)
- Esophageal cancer: expression is associated with poor survival (Onco Targets Ther 2018;11:5171)
Case reports
- 53 and 71 year old men with splenic marginal zone lymphoma with prolymphocytic transformation (Case Rep Hematol 2018;2018:5761953)
- 65 year old man with composite in situ mantle cell neoplasia and follicular lymphoma (Case Rep Hematol 2014;2014:145129)
- 72 year old man with primary cutaneous presentation of blastoid mantle cell lymphoma (Am J Dermatopathol 2009;31:398)
- 78 year old man with plasma cell myeloma with lymphoplasmacytic morphology and cyclin D1 expression (Blood 2016;127:1619)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Staining is predominantly nuclear
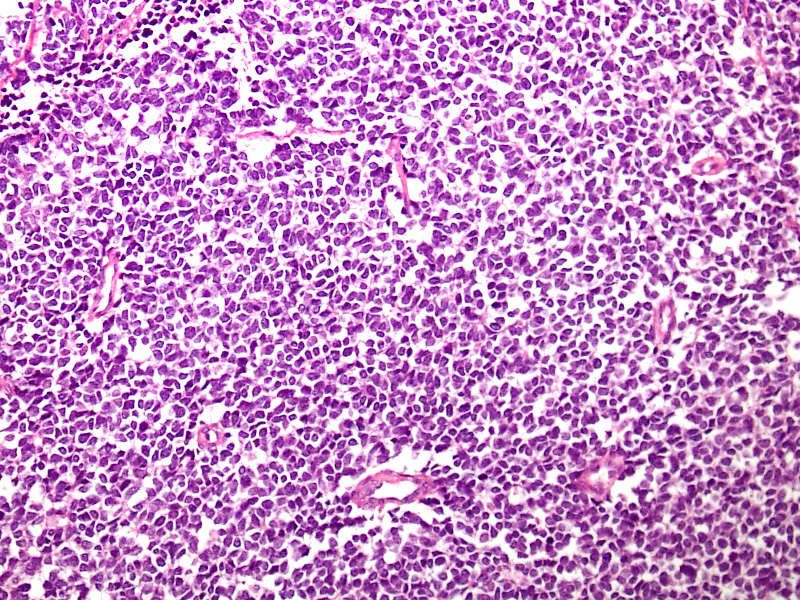
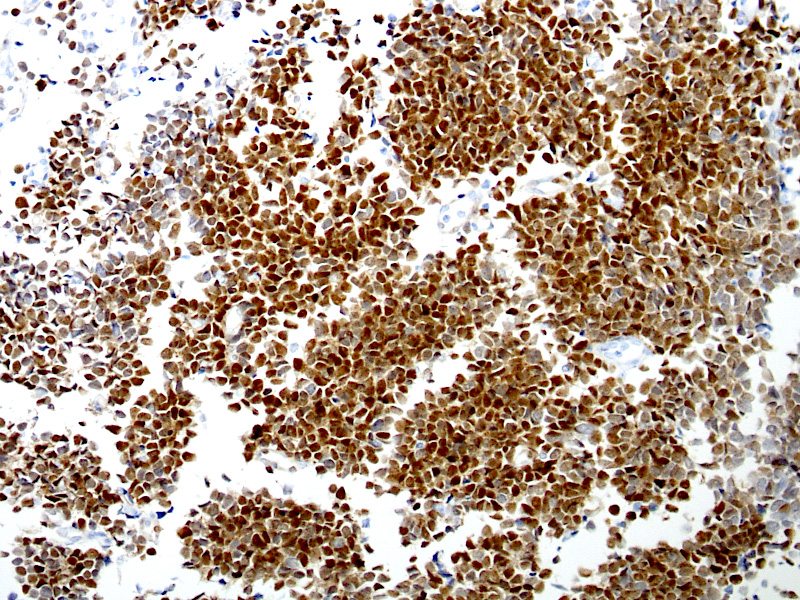
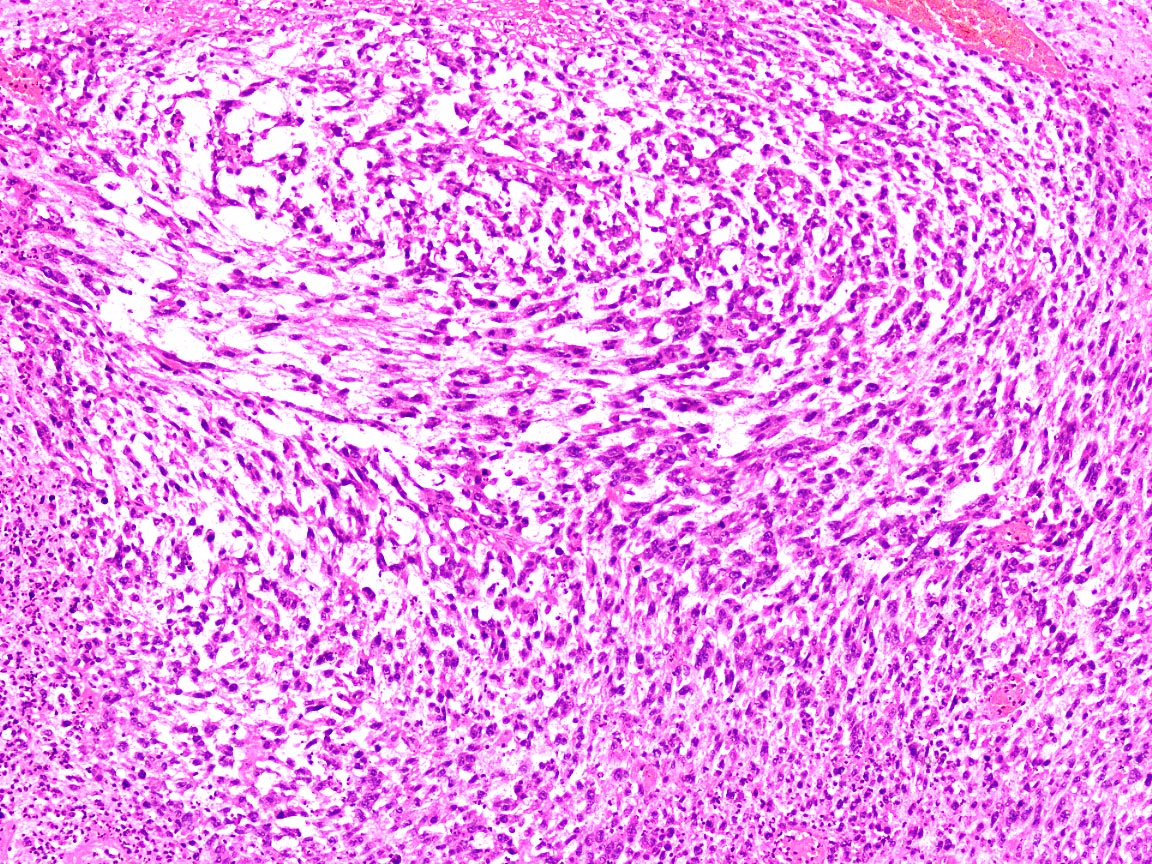
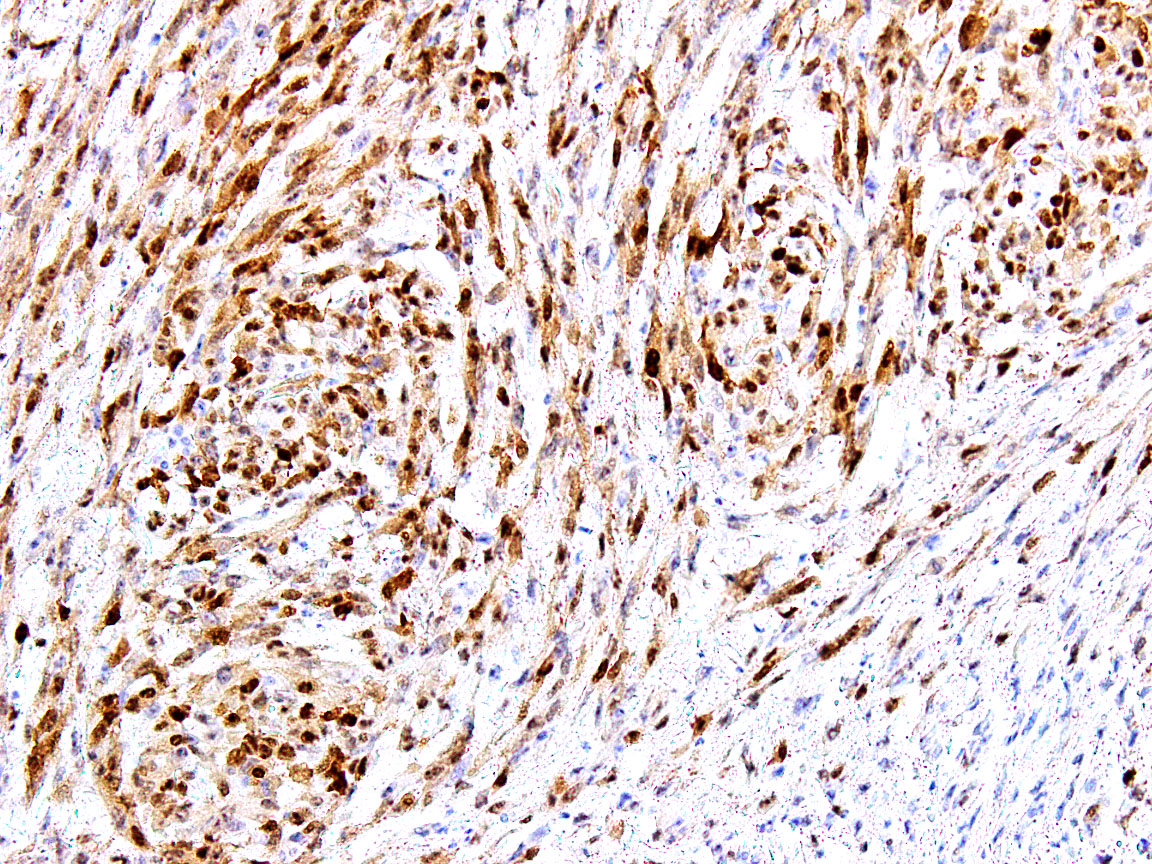
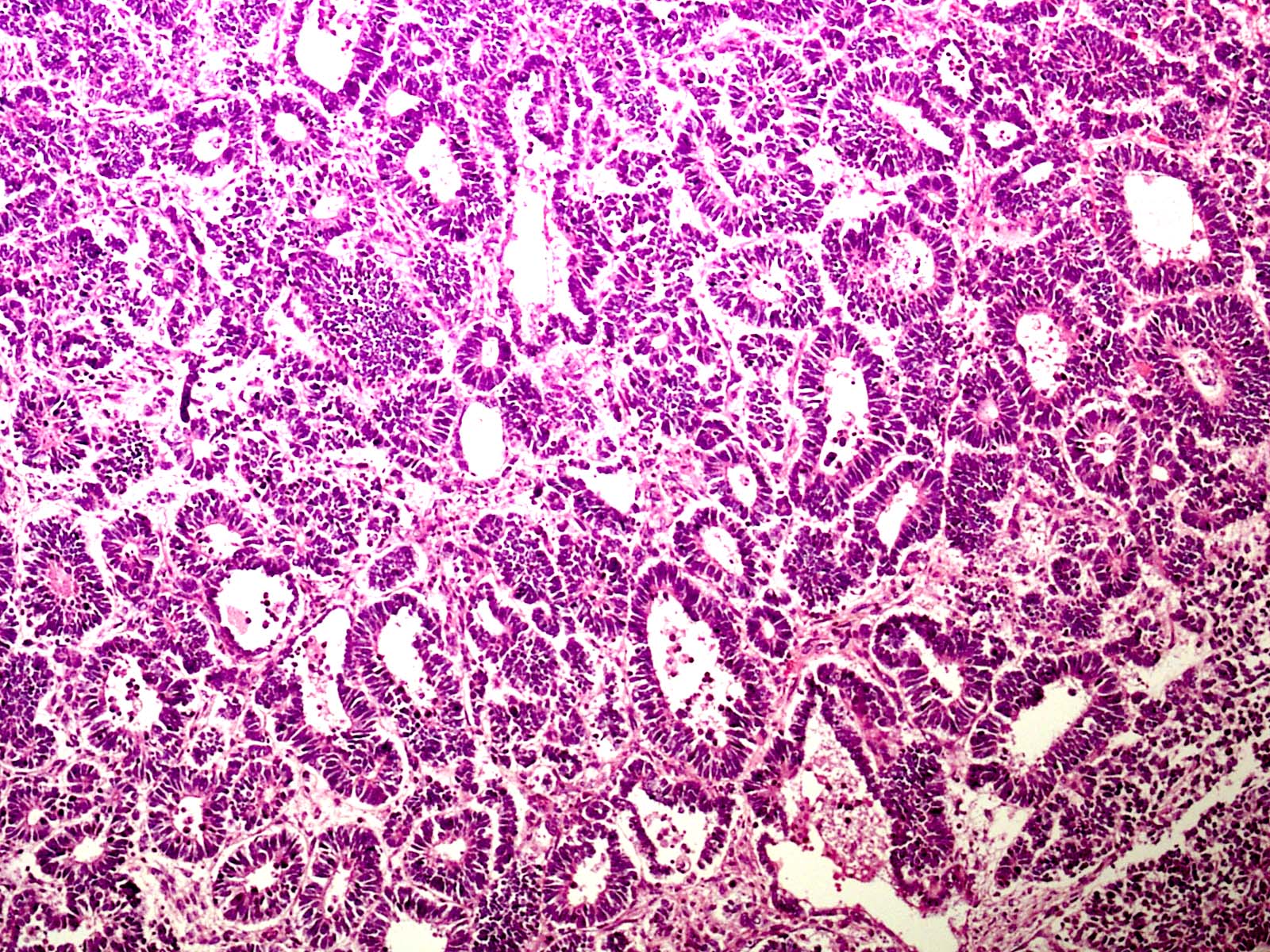
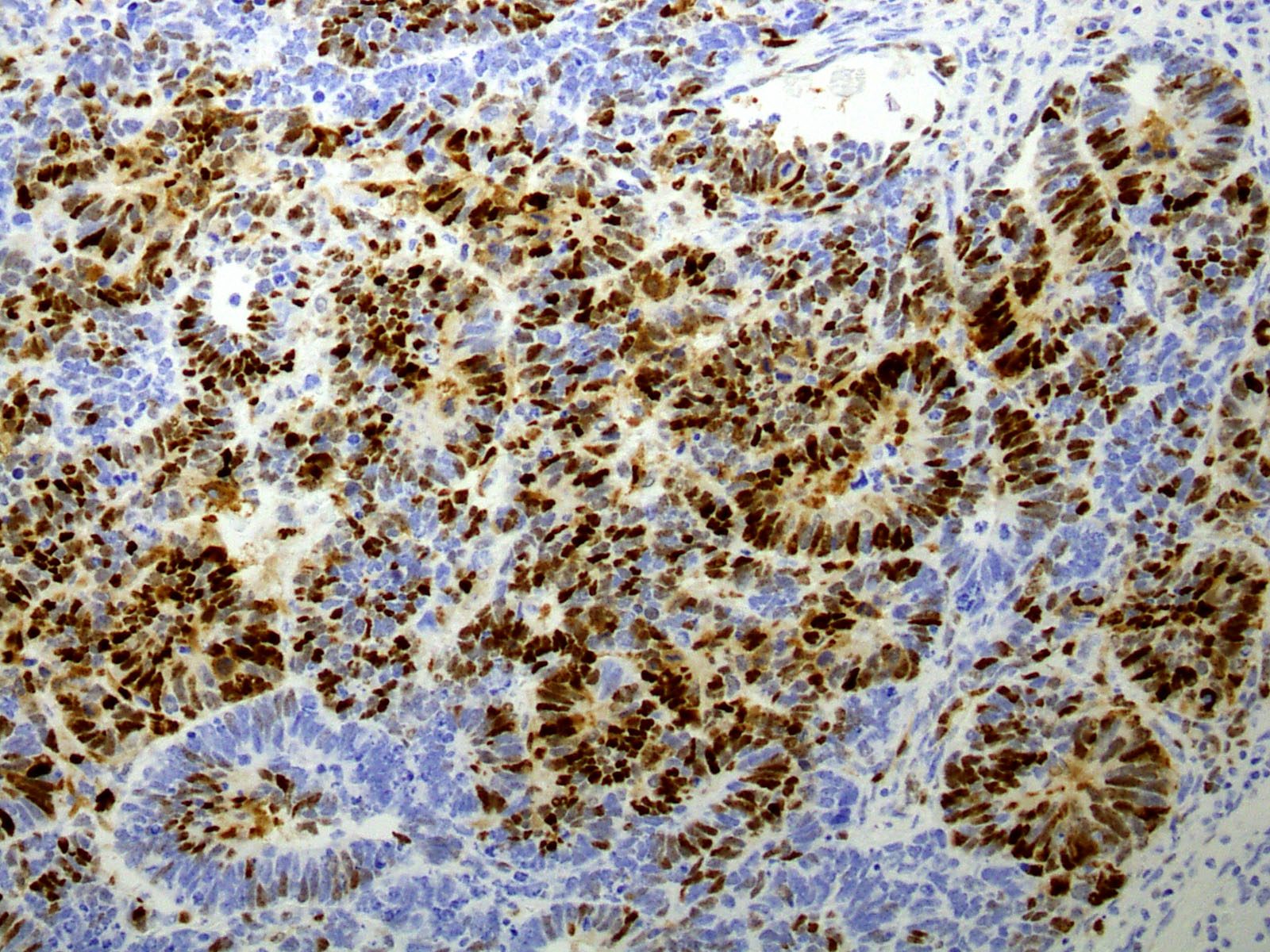
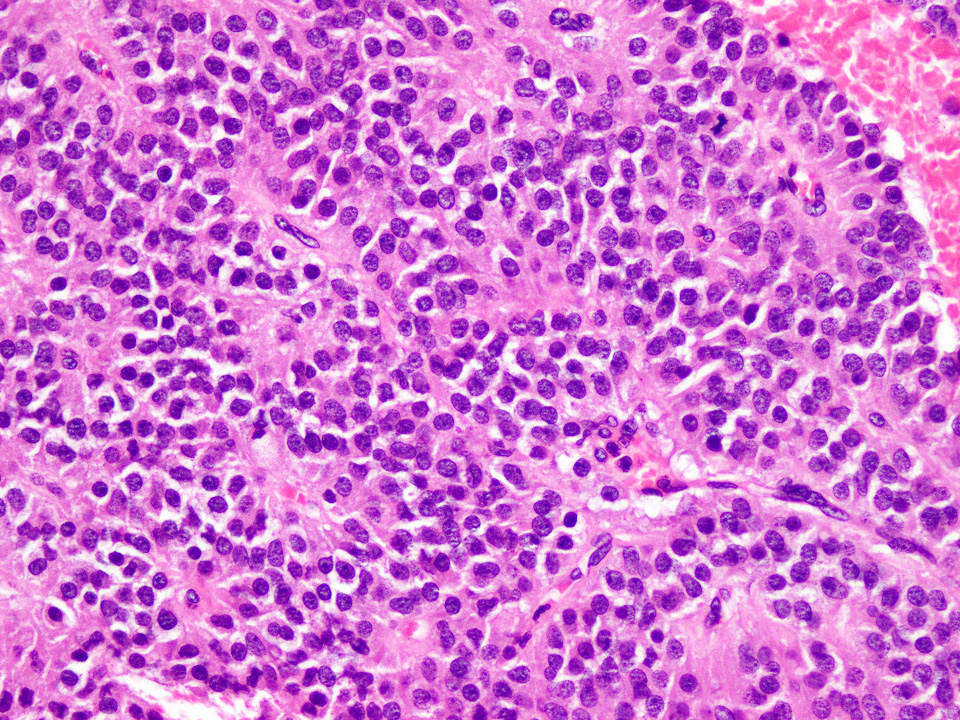
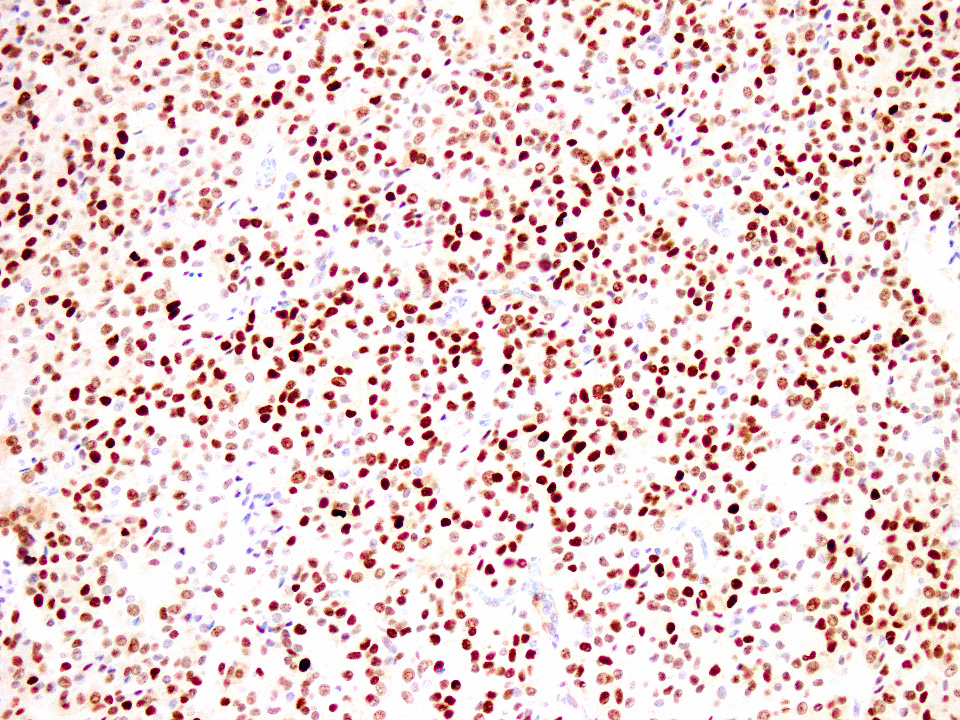
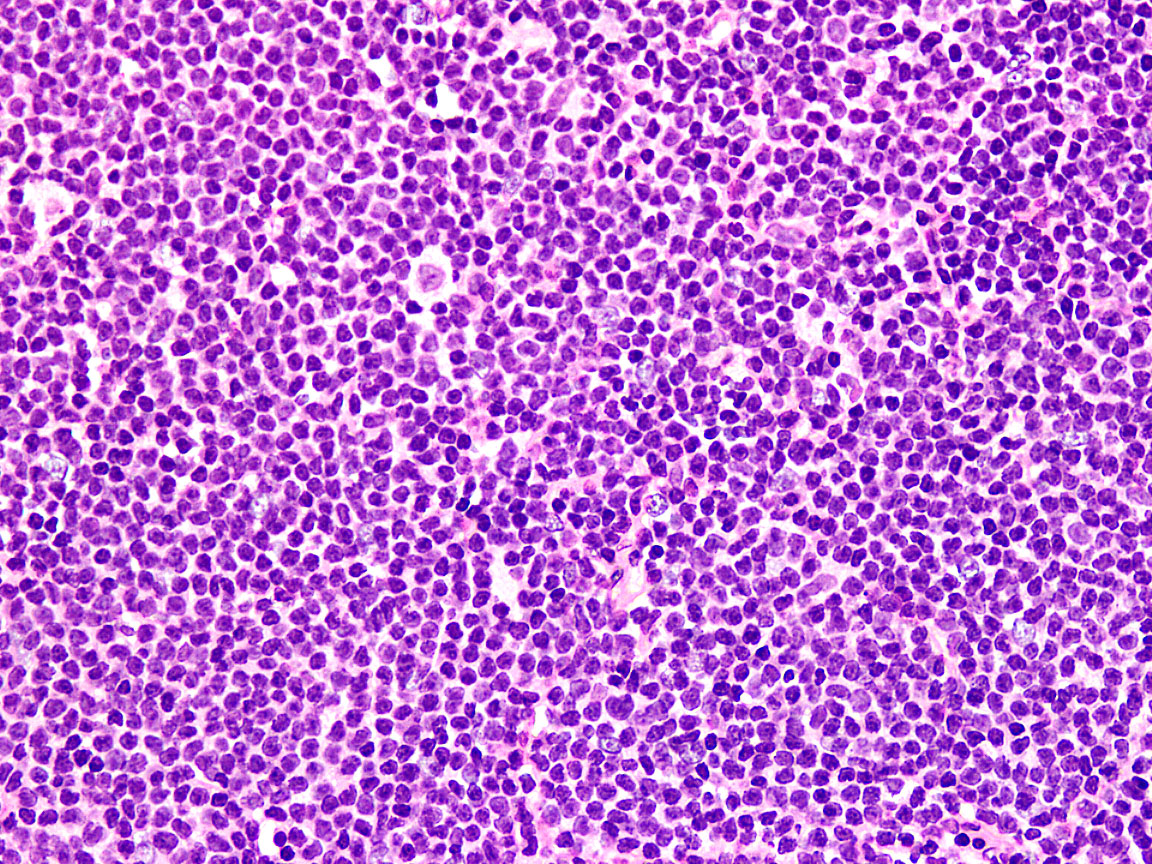
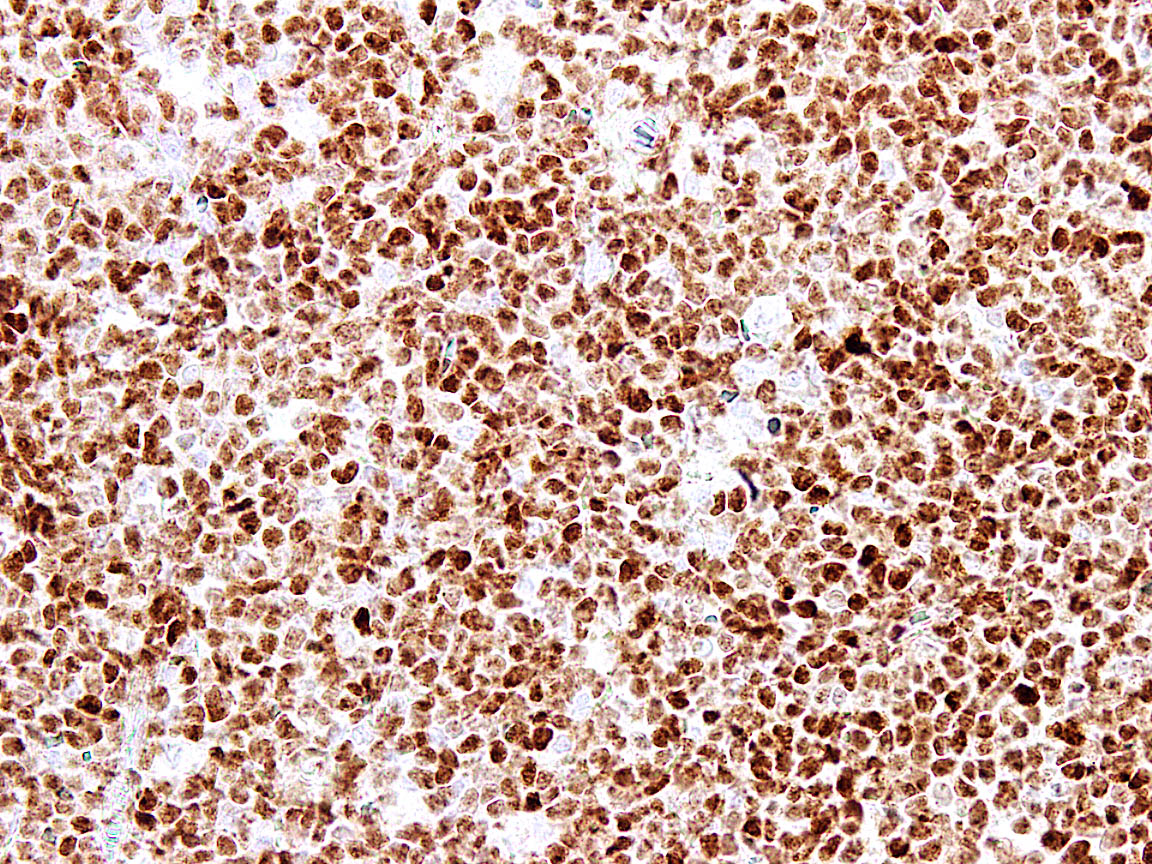
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Basal and suprabasal layers of epidermis: nuclear staining (Mol Med Rep 2018;17:735)
- Luminal cells of prostate glands: cytoplasmic staining (Biomed Res Int 2020;2020:1692658)
- Endocervical epithelium: nuclear staining (Mod Pathol 2010;23:611)
Positive staining - disease
- Parathyroid carcinoma (Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2018;61:22)
- Parathyroid adenoma (Am J Pathol 2001;158:1355)
- Clear cell sarcoma of kidney (Diagn Pathol 2019;14:13)
- Adenocarcinoma of prostate (Clin Cancer Res 2015;21:5619)
- Endometrial stromal sarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1562)
- Multiple myeloma (Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol 2013;34:283, Am J Clin Pathol 2006;125:615)
- Vulval carcinoma (Hum Pathol 2012;43:1386)
- Central giant cell granuloma of jaw (J Dent (Shiraz) 2018;19:253)
- Astrocytic tumors: 60% (Mod Pathol 2016;29:1306)
- Hairy cell leukemia (variable intensity) (Pathol Oncol Res 2015;21:203)
- Hepatoblastoma with poorly differentiated histology (Clin Cancer Res 2001;7:901)
- Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of pancreas (Diagn Pathol 2020;15:139, Cell Oncol 2010;32:331)
- Ewing sarcoma (Clin Cancer Res 2004;10:1344, Oncotarget 2015;6:30178)
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1390)
- Rosai-Dorfman disease, strong staining (Br J Haematol 2019;186:837)
- CLL / SLL dim expression in proliferation centers (Am J Clin Pathol 2012;138:132)
- Subset of ALK positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma (26%) (Mod Pathol 2016;29:1306)
- Mantle cell lymphoma (Am J Clin Pathol 2009;132:699)
Negative staining
- Follicular lymphoma (J Cytol 2018;35:163)
- Marginal zone lymphoma (Case Rep Ophthalmol Med 2016;2016:2798304, Pan Afr Med J 2017;26:111)
- Small lymphocytic lymphoma / chronic lymphocytic leukemia (except proliferation centers)
- Wilms tumor (epithelial component) (Diagn Pathol 2019;14:13)
Sample pathology report
- Cervical lymph node, excision biopsy:
- Mantle cell lymphoma (see comment)
- Comment: The tumor expresses CD5 and cyclin D1 in addition to other B cell markers, with a low proliferative index and negative CD23, consistent with a diagnosis of mantle cell lymphoma. Further molecular testing and clinical workup is recommended.
Additional references
Board review style question #1
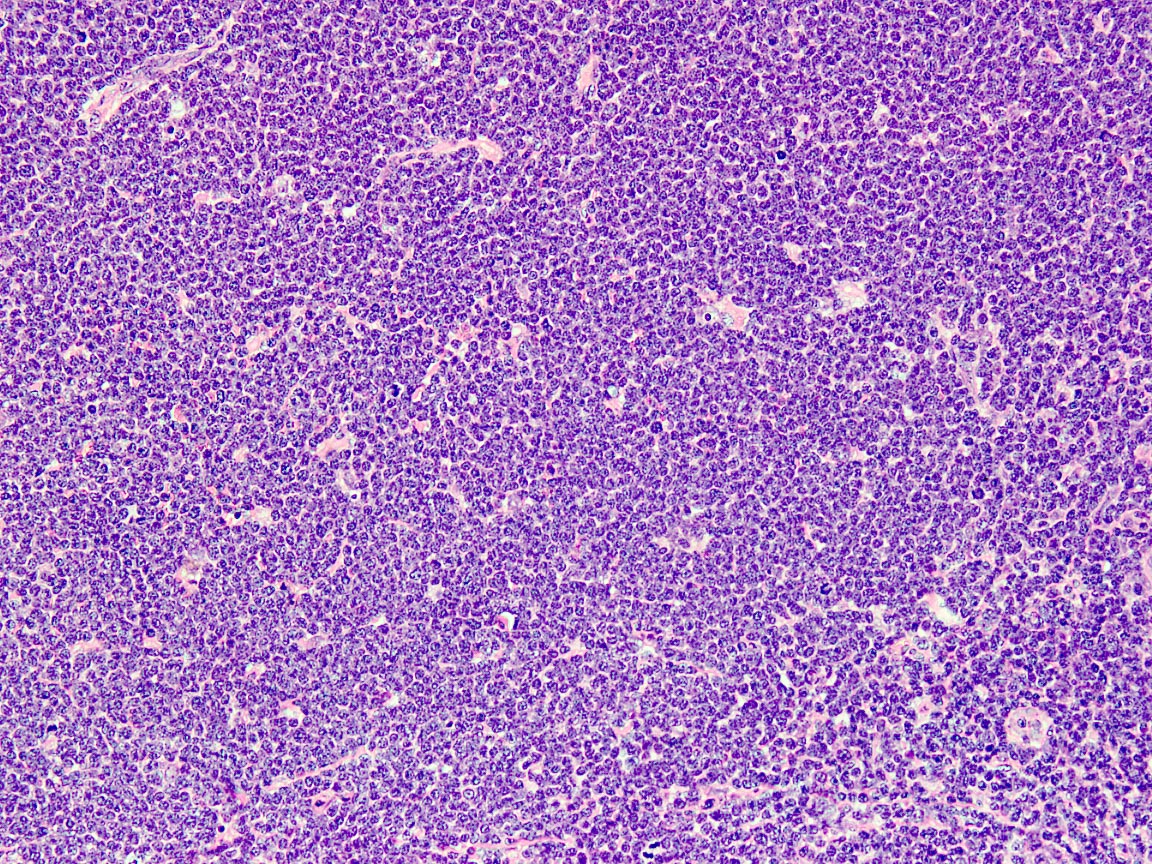
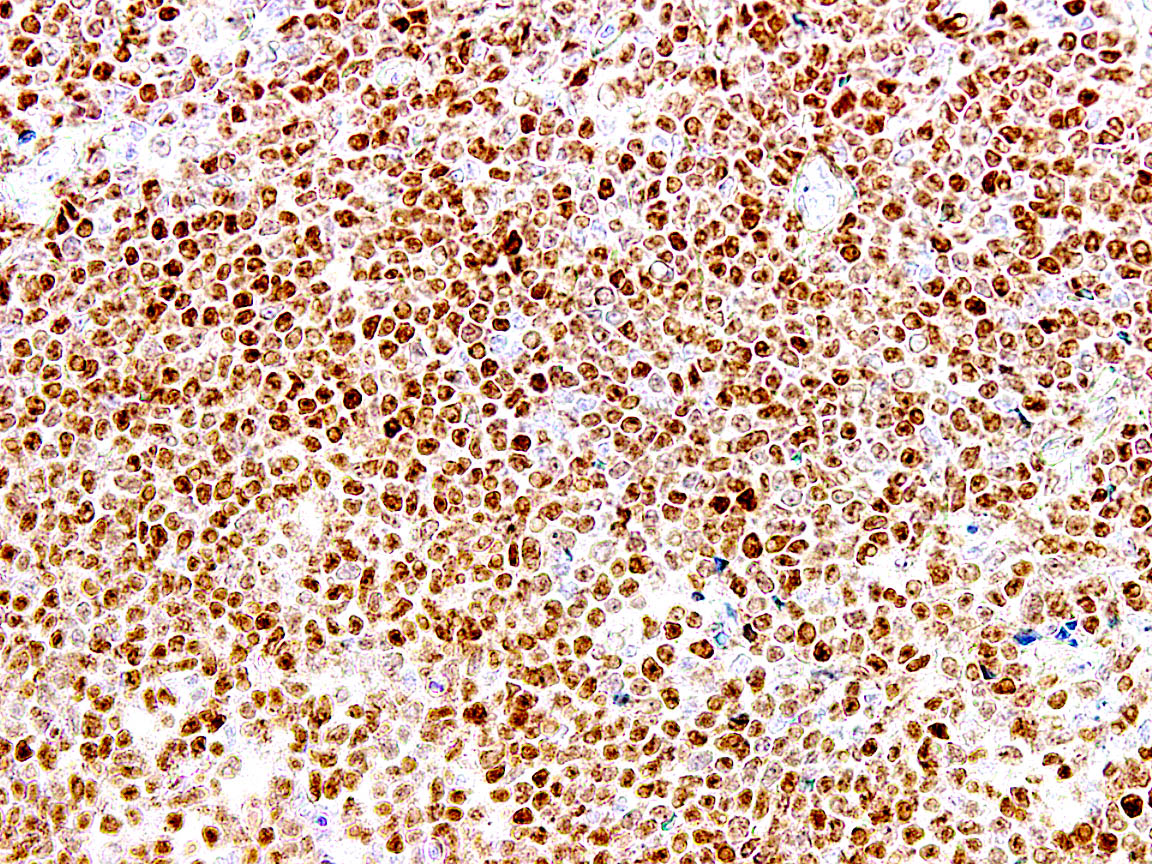
A 54 year old man presents with low grade fever, malaise and enlarged cervical and supraclavicular lymph nodes. The biopsy from one of the cervical nodes shows effaced architecture and sheet-like growth of small sized lymphocytes with irregular nuclear contours (Figure A). Immunohistochemical analysis shows positivity for pan B cell markers, CD5 and cyclin D1 (Figure B). The diagnosis in this case is
- Follicular lymphoma
- Hairy cell leukemia
- Mantle cell lymphoma
- Marginal zone lymphoma
- Small lymphocytic lymphoma
Board review style answer #1
C. Mantle cell lymphoma. Follicular lymphoma (answer A) is negative for CD5 and shows positivity for CD10. Hairy cell leukemia (answer B) may show positivity for cyclin D1 but is negative for CD5 and shows positivity for annexin A and other stains. Marginal zone lymphoma (answer D) is negative for both CD5 and cyclin D1. Small lymphocytic lymphoma (answer E) is the main differential diagnosis for CD5 positive B cell lymphomas and may show dim cyclin D1 positivity in proliferation centers.
Comment Here
Reference: Cyclin D1
Comment Here
Reference: Cyclin D1