Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Marques-Piubelli ML, Miranda RN. CD30. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cdmarkerscd30.html. Accessed October 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- CD30 is a transmembrane, type I, glycoprotein receptor from the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) superfamily (Blood Cancer J 2017;7:e603, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022 Apr 26 [Epub ahead of print], J Mol Recognit 2003;16:28, Oncologist 2022 Aug 10 [Epub ahead of print], Blood 1995;85:1, Histopathology 2022;81:55, Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2014;12:1)
Essential features
- CD30 is a transmembrane, type I, glycoprotein receptor from the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) superfamily (Blood Cancer J 2017;7:e603, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022 Apr 26 [Epub ahead of print], J Mol Recognit 2003;16:28, Oncologist 2022 Aug 10 [Epub ahead of print], Blood 1995;85:1, Histopathology 2022;81:55, Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2014;12:1)
- BerH2 (J Mol Recognit 2003;16:28, Blood Cancer J 2017;7:e603, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:378, Blood 2014;124:2983)
- Most commonly used clone to fabricate the antibody and has good correlation with mRNA levels of CD30
- Composed of 2 linear epitopes with identical sequence
- Targetable biomarker (Oncologist 2022 Aug 10 [Epub ahead of print])
- High expression by neoplastic cells
- Low expression by normal cells
- Extracellular localization
Terminology
- Ki1 (J Mol Recognit 2003;16:28, Blood 1995;85:1)
- Discontinuous epitope of 2 regions
- Close to N terminus region
- Close to membrane spanning region
- Discontinuous epitope of 2 regions
- Ki2 (J Mol Recognit 2003;16:28)
- Single chain Fv linear fragment
- BerH2 (J Mol Recognit 2003;16:28, Blood Cancer J 2017;7:e603, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:378, Blood 2014;124:2983)
- Most commonly used clone and has good correlation with mRNA levels
- Composed by 2 linear epitopes with identical sequence
- TNFRSF8
Pathophysiology
- CD30 gene is located at 1p36
- Close to TNFR2 and OX40
- Molecular weight of the protein: 120 kD
- Mature form of CD30 protein is processed from a precursor weighing 84 kD and during transit in the Golgi complex gains weight through glycosylation
- 3 domains:
- Extracellular (361 amino acids)
- Flower-like configuration
- 2 subdomains: D1 and D2
- Similar sequence when compared to TNFR molecules: 6 cysteine rich stretches of amino acids
- Implications in antibody binding
- Soluble form of CD30 (sCD30) is an 85 - 88 kD protein detected in inflammatory scenario and it is a product of the extracellular domain
- Transmembrane (28 amino acids)
- Intracellular (188 amino acids)
- Contains several serine / threonine residues, which can be phosphorylated
- Docking sites for protein binding and signaling transduction
- Contains several serine / threonine residues, which can be phosphorylated
- Extracellular (361 amino acids)
- Expression and function are related to the composition and functionality of the immune microenvironment (Blood Cancer J 2017;7:e603, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022 Apr 26 [Epub ahead of print], J Mol Recognit 2003;16:28, Oncologist 2022 Aug 10 [Epub ahead of print], Blood 1995;85:1, Histopathology 2022;81:55, Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2014;12:1)
- First monoclonal antibody was derived from Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines and identified in 1982 (Blood Cancer J 2017;7:e603)
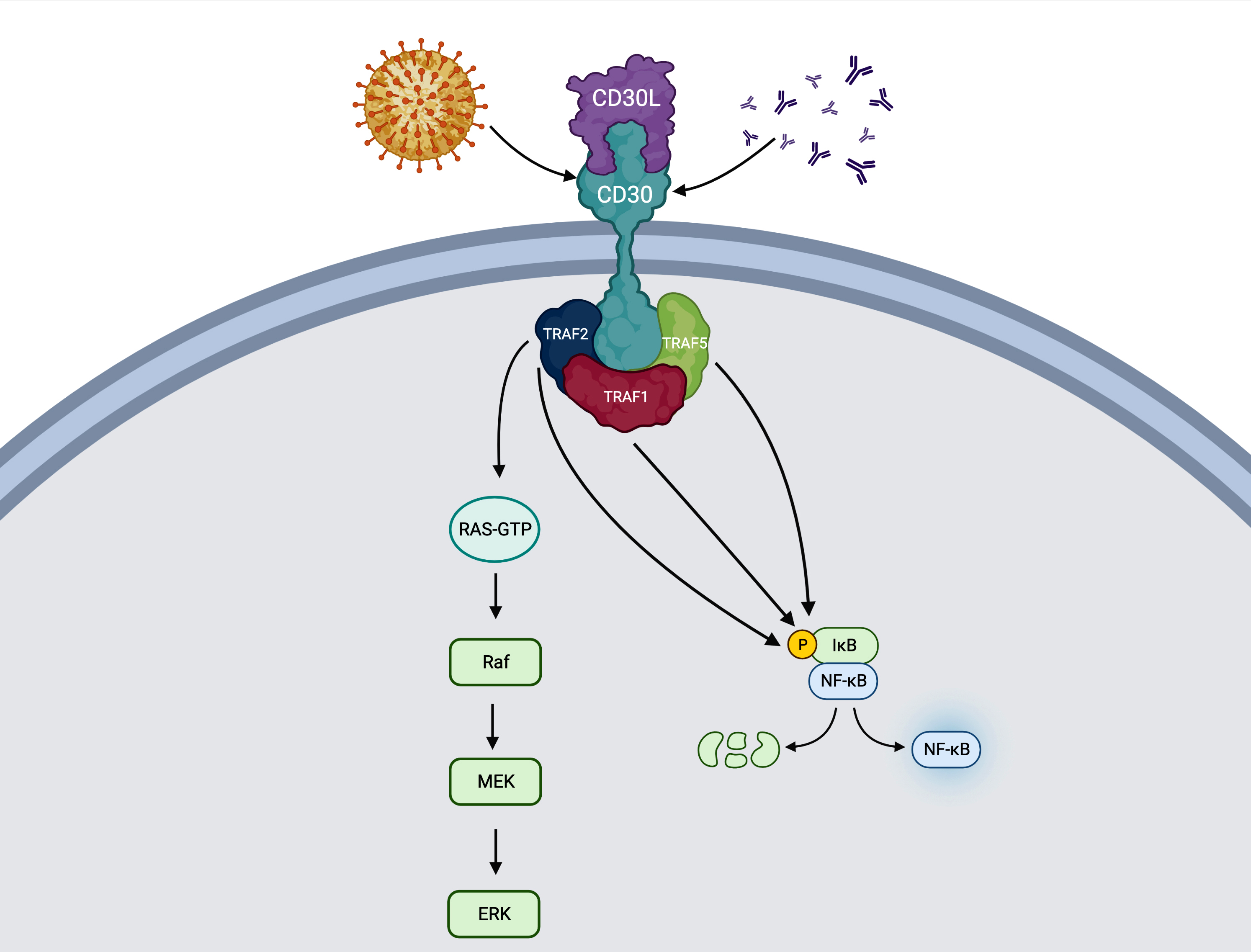
- Ligand is CD30L (or TNFSF8 or CD153) (Blood Cancer J 2017;7:e603, J Mol Recognit 2003;16:28)
- Type II glycoprotein
- Extracellular C terminal domain is similar to TNFα, TNFβ, FasL, CD40L and CD70
- Can be detected in activated lymphocytes, histiocytes and granulocytes
- Stimulation of CD30 transmembrane protein leads to receptor trimerization and transduction of the signal to TNFR associated factor (TRAF) proteins (TRAF1, TRAF2 and TRAF5) (Blood Cancer J 2017;7:e603, Histopathology 2022;81:55)
- Signaling complex may activate both MAPK / ERK1 / ERK2 and NFκB pathways
- Direct or indirect (via JunB) activation of antiapoptosis, prosurvival or activation effects
- Signaling complex may activate both MAPK / ERK1 / ERK2 and NFκB pathways
- Viral infection may induce activation of CD30 in both B and T cells (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022 Apr 26 [Epub ahead of print], Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2014;12:1)
- Cells that carry Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and human T cell leukemia / lymphoma virus type I (HTLV1)
- Elevated expression in autoimmune diseases (Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2014;12:1)
- Rheumatoid arthritis, primary progressive multiple sclerosis, localized scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematous, atopic dermatitis, asthma and allergic rhinitis
- Role in the development of graft versus host disease (GVHD) (Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2014;12:1)
- Inhibition is linked to decreased incidence of GVHD
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Targetable biomarker (Oncologist 2022 Aug 10 [Epub ahead of print])
- High expression by neoplastic cells
- Low expression by normal cells
- Extracellular localization
- CD30 antibody drug conjugate (ADC): brentuximab vedotin (BV) (Blood Cancer J 2017;7:e603, Oncologist 2022 Aug 10 [Epub ahead of print])
- Composed of an IgG1 monoclonal antibody SGN 30 in combination with mono methyl auristatin E (MMAE) and a cathepsin linker
- ADC binds to the CD30 positive cell
- Receptor endocytosis and MMAE release
- Leads to inhibition of tubulin formation and cell apoptosis
- Receptor endocytosis and MMAE release
- Indications of BV
- Classic Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL) after autologous stem cell transplant or failure of at least 2 major multiagent chemotherapies
- Systemic or primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma or CD30 positive mycosis fungoides after failure of at least 1 multiagent chemotherapy
- Frontline treatment of peripheral T cell lymphomas that express CD30, in combination with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin and prednisone
- There is no correlation between CD30 expression levels by immunohistochemistry and response to therapy
- CD30 specific chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR T) cells (Blood Cancer J 2017;7:e603, J Clin Oncol 2020;38:3794, Sci Rep 2022;12:10488, Front Immunol 2022;13:858021)
- 3 generations of anti-CD30 CAR T cells
- Phase I / II studies in relapsed / refractory CHL
- Association with anti-PD1 regimen can improve the efficacy of CD30 CAR T therapy
Interpretation
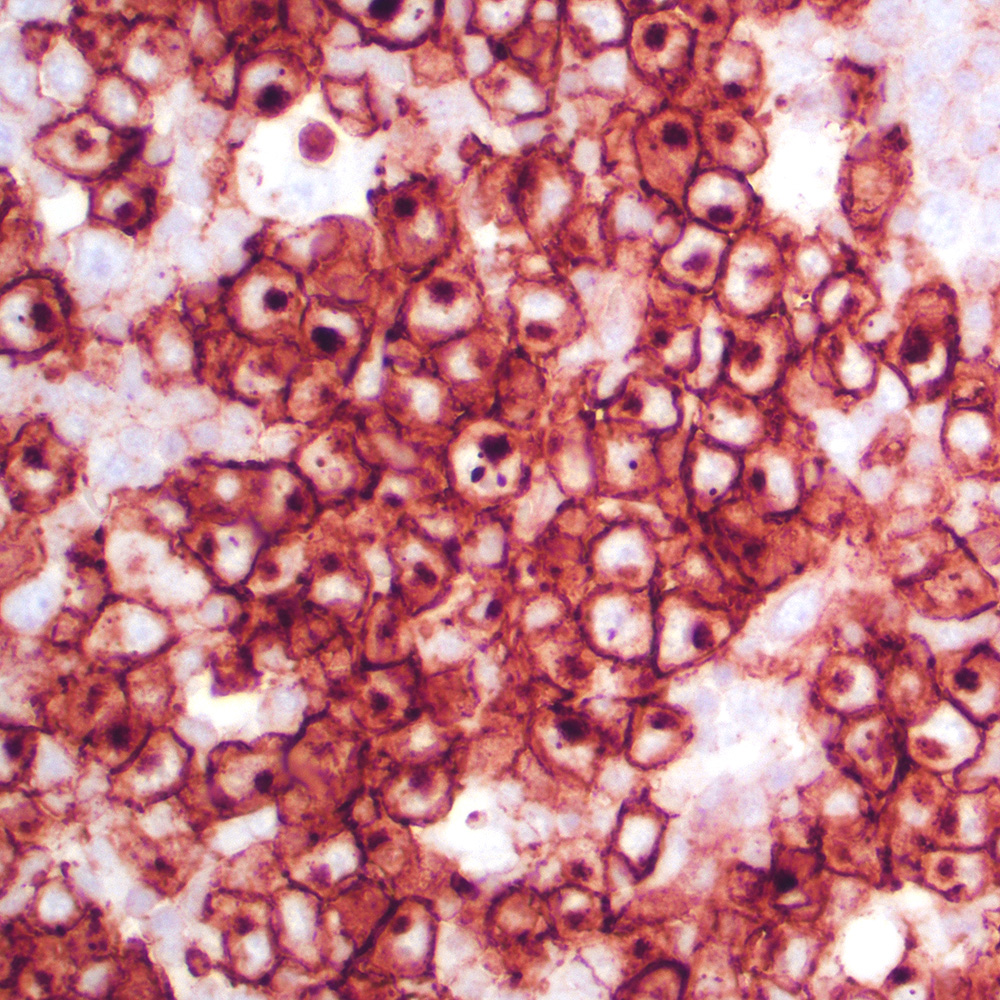
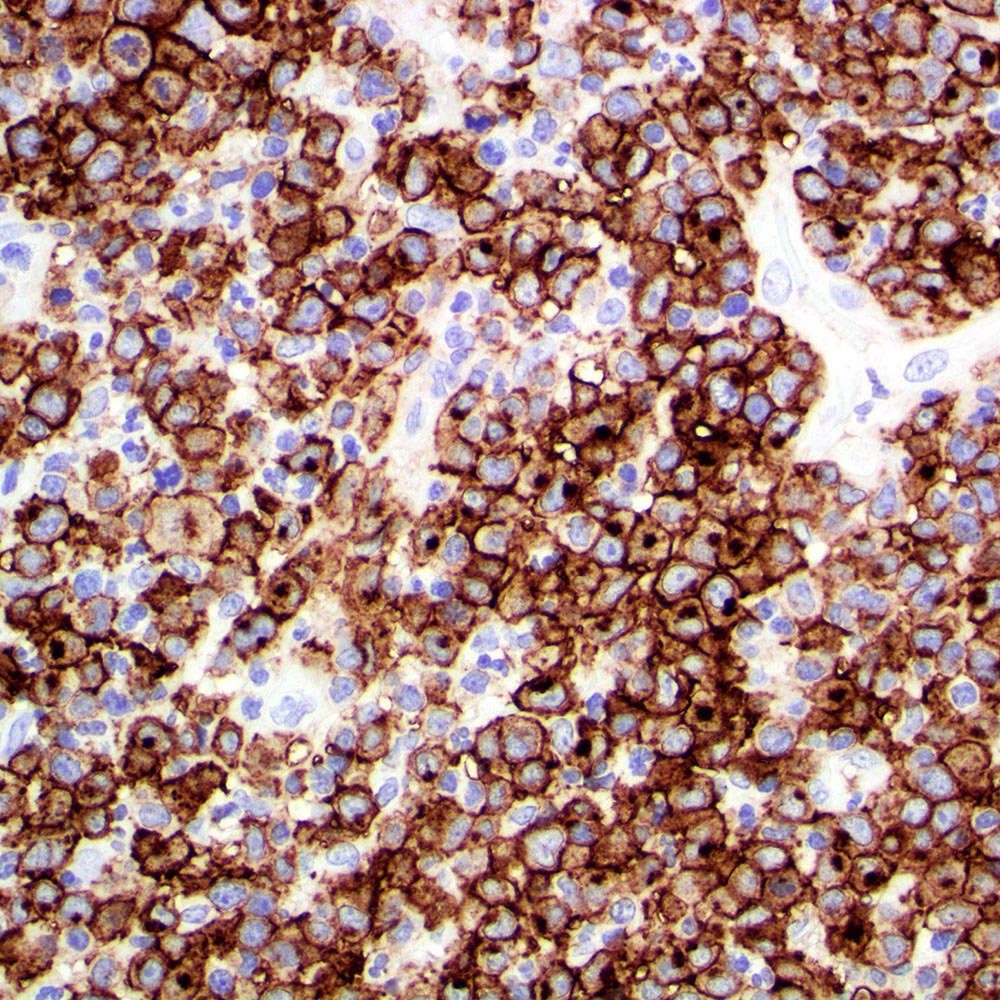
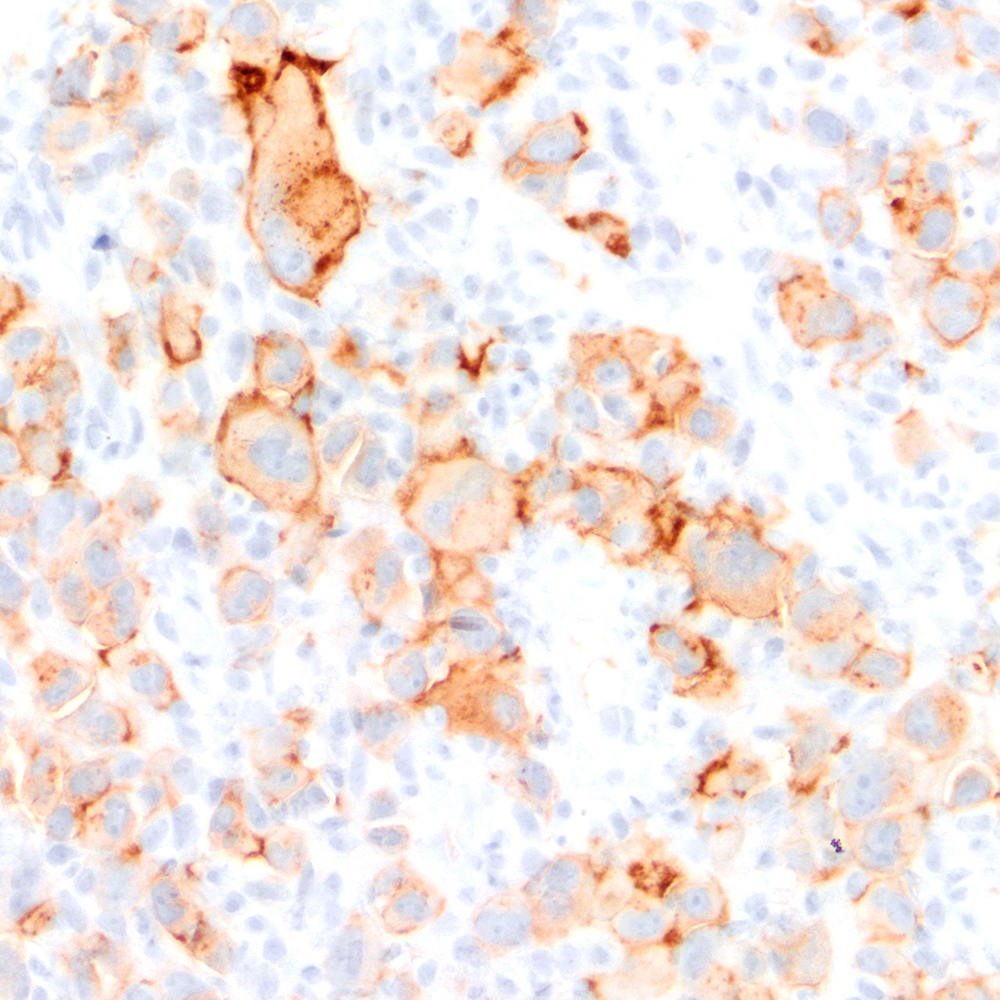
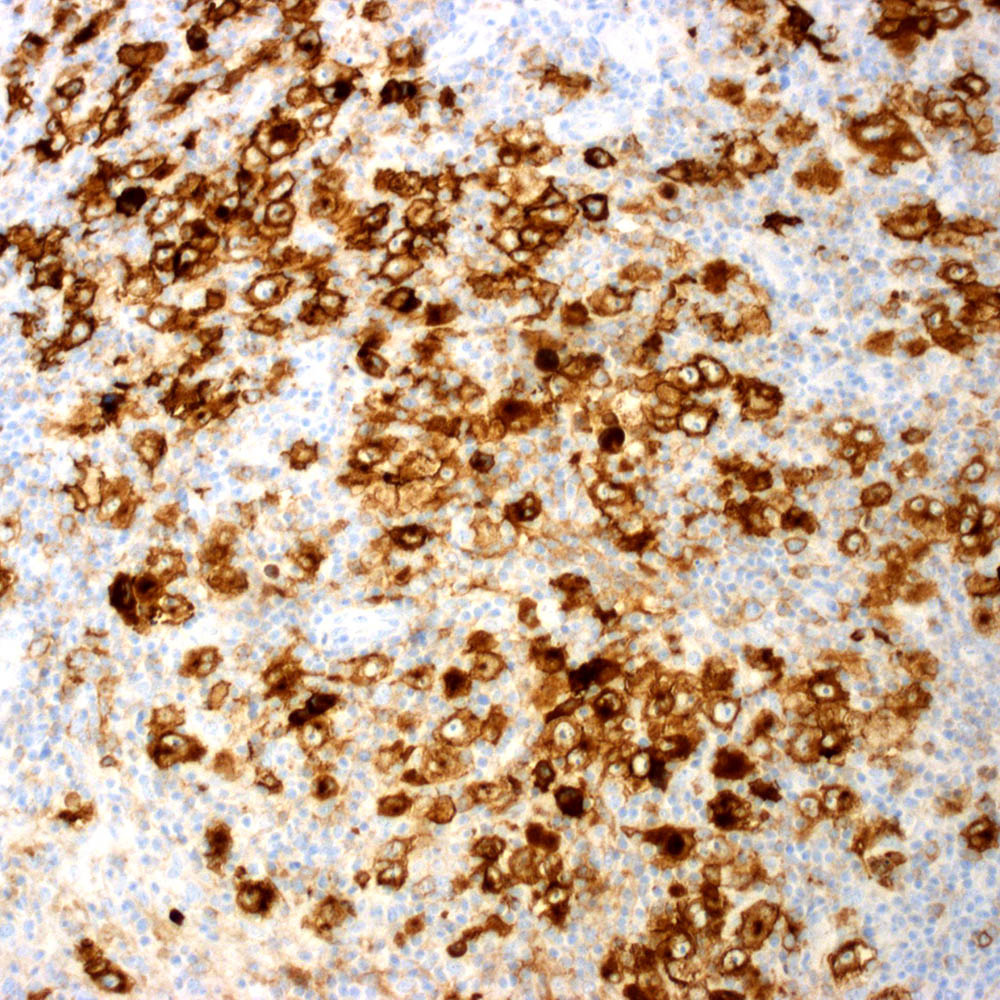
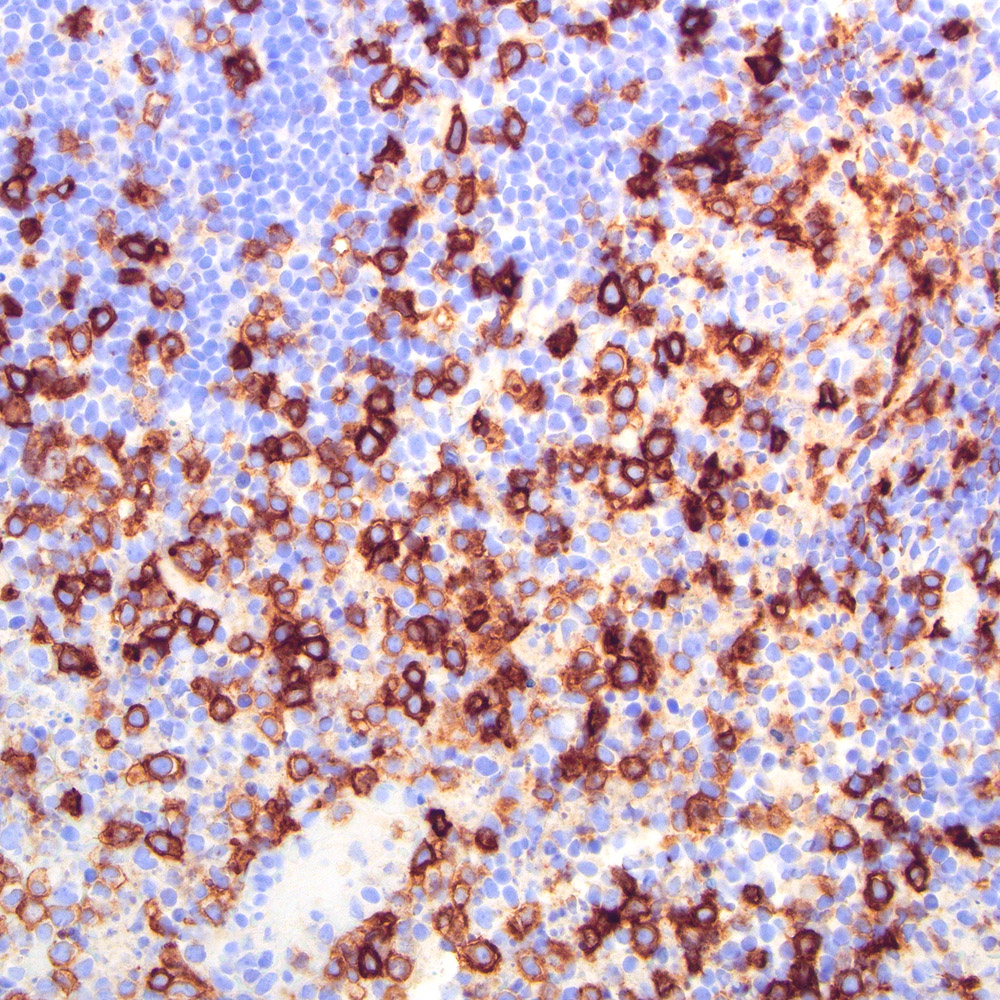
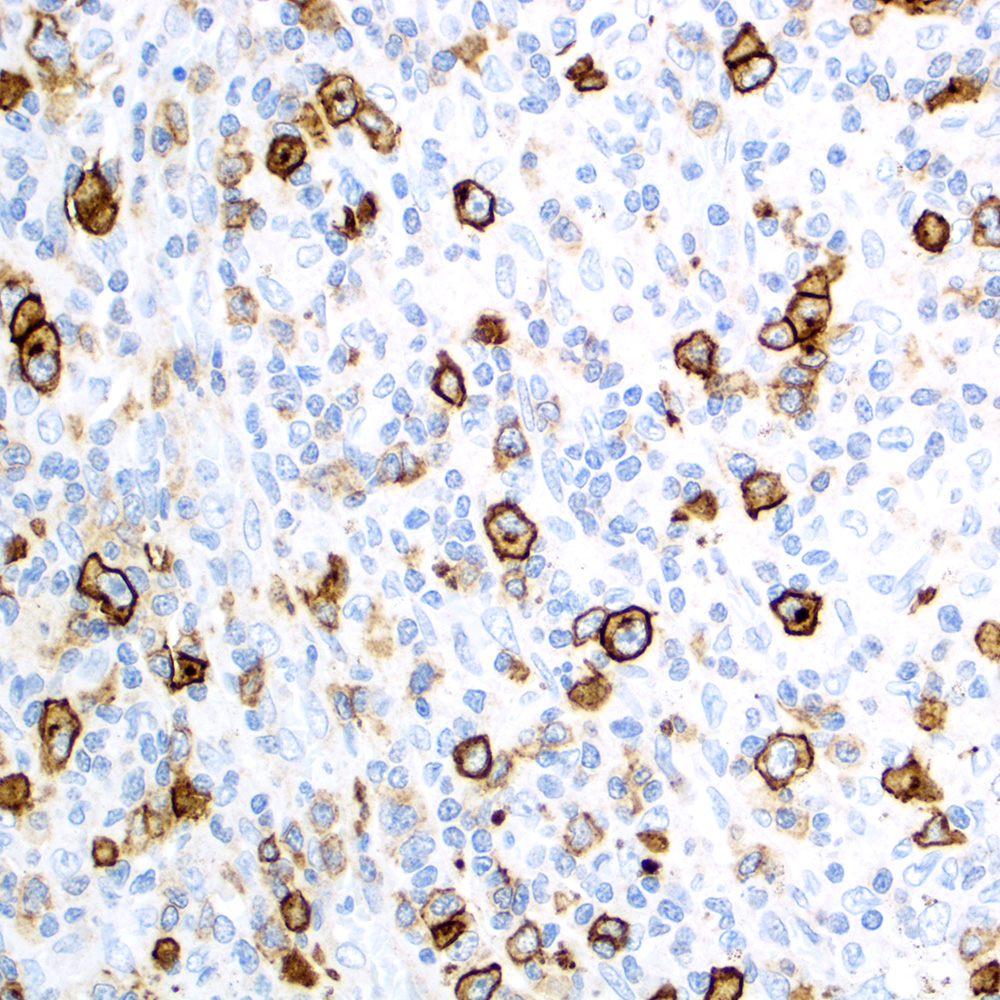
- Typically expressed in cytoplasmic / membrane compartments (Histopathology 2022;81:55)
- May have weak, moderate or strong intensity
- Golgi pattern can also be found isolated or in association with cytoplasmic / membrane staining
- Rare
- Nuclear staining is not acceptable
- May have a membrane enhancement in reactive mesothelial cells
Uses by pathologists
- Differential diagnosis and assessment of lymphomas in which the neoplastic cells universally express CD30 (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022 Apr 26 [Epub ahead of print], Oncologist 2022 Aug 10 [Epub ahead of print], Am J Clin Pathol 2022;158:173)
- Classic Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL)
- Anaplastic large cell lymphoma and subtypes
- Usually negative for IRF8, helping in the differential diagnosis with CHL
- Lymphomatoid papulosis
- Any degree of CD30 expression should be reported (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022 Apr 26 [Epub ahead of print])
- BerH2 is the most used (J Mol Recognit 2003;16:28)
- Recommendations for testing (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022 Apr 26 [Epub ahead of print])
- All cases of T cell lymphomas
- Relapsed / refractory setting of diffuse large B cell lymphoma or primary mediastinal B cell lymphoma
- Clinical trial requests
- IHC testing is the preferred methodology (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022 Apr 26 [Epub ahead of print])
- Recommendations for assay best performance
- Preanalytical phase
- Tissue should be fixed in 10% neutral pH, phosphate buffered formalin for 8 - 72 hours
- Analytical phase
- Follow protocols and control tissues from NordiQC
- Postanalytical phase
- Estimation of positive neoplastic cells: 0%, 1 - 10% and after in 10% increments (or ranges)
- Record descriptively the nonneoplastic cells in the background and if possible, estimate the percentage
- Excisional biopsy is the preferred tissue for testing; better than needle biopsies or fine needle aspirates
- Preanalytical phase
- Sensitivity of flow cytometry varies with the type of tumor and demands technical skill
- Recommendations for assay best performance
Prognostic factors
- Expression of CD30 is associated with outcomes in lymphomas in which there is a heterogeneous expression
- Decreased hazard of death in transformed mycosis fungoides (Am J Clin Pathol 2021;156:350)
- Poor overall and progression free survival in extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma cases with expression of CD30 in 50% or more of the neoplastic cells (Oncol Lett 2017;13:1211, BMC Cancer 2014;14:890)
- Expression of CD30 is correlated with presence of B symptoms and elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase
- Better outcomes in cases of diffuse large B cell lymphoma treated with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone (R-CHOP) (Hum Pathol 2017;60:160)
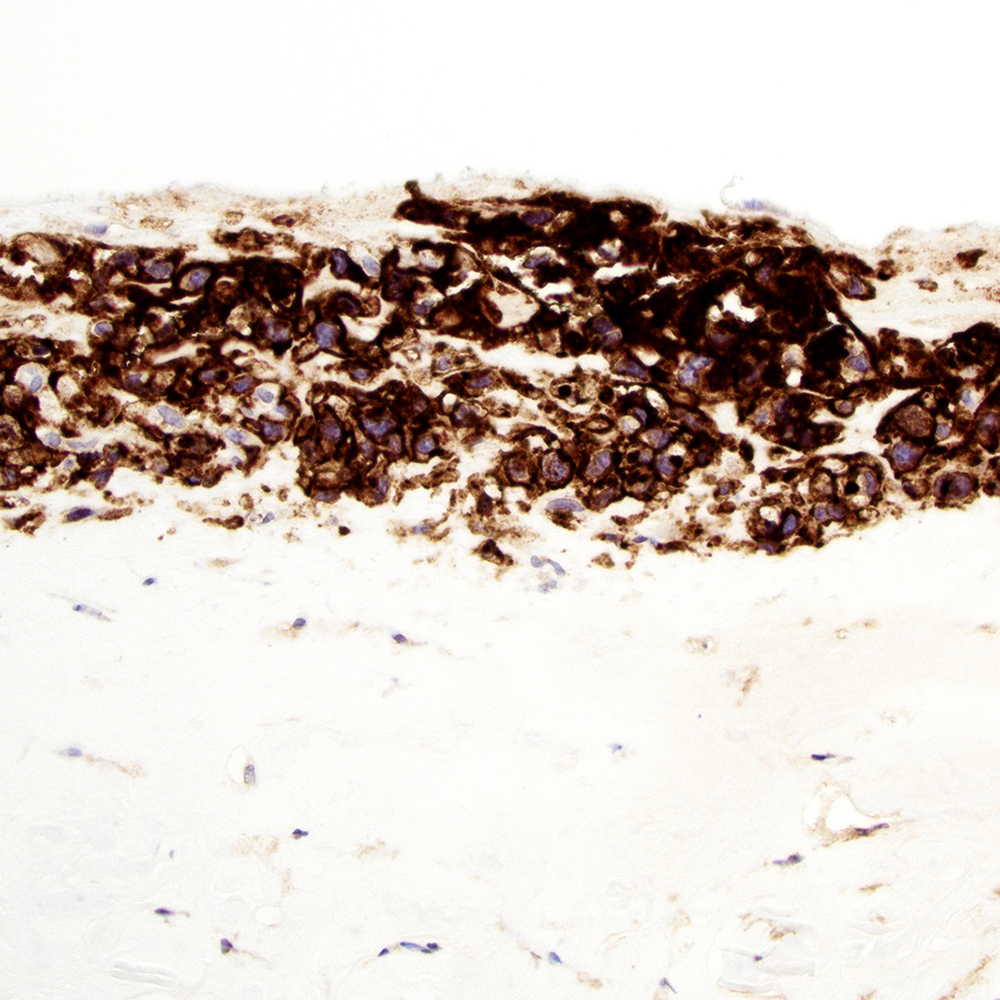
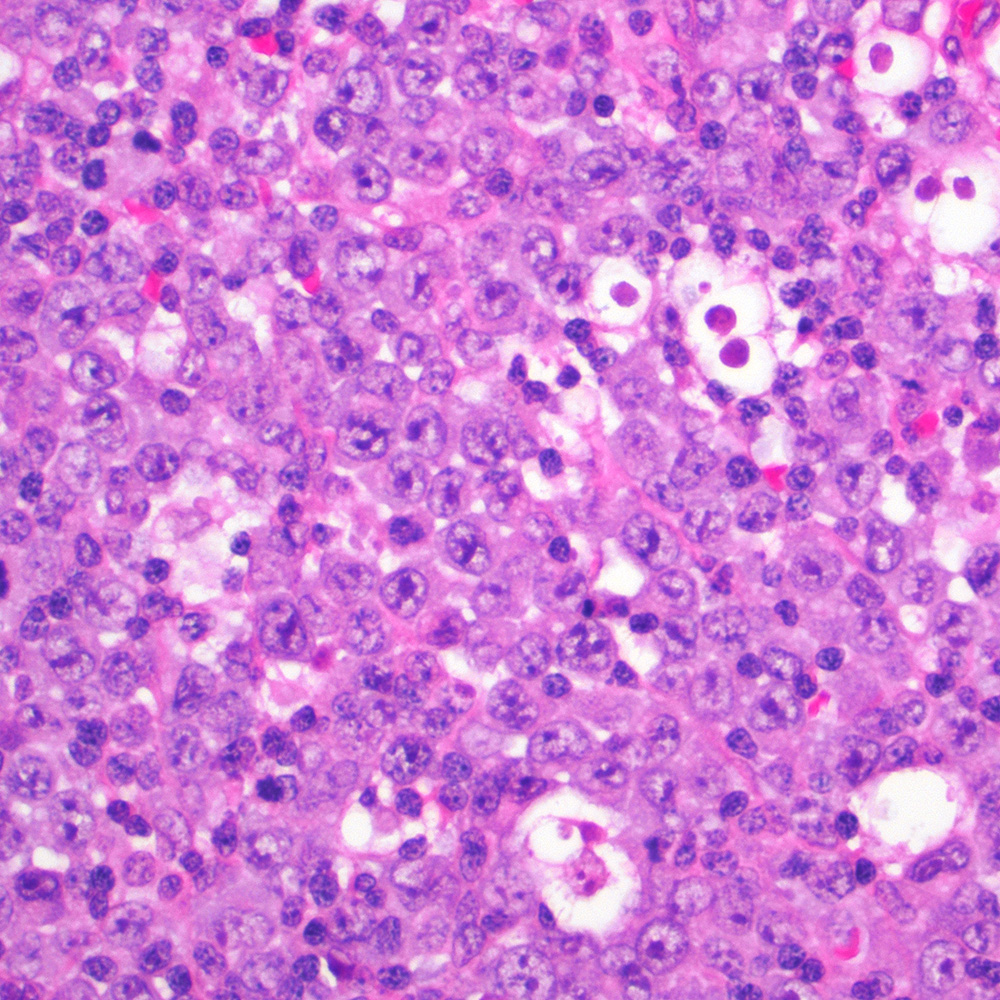
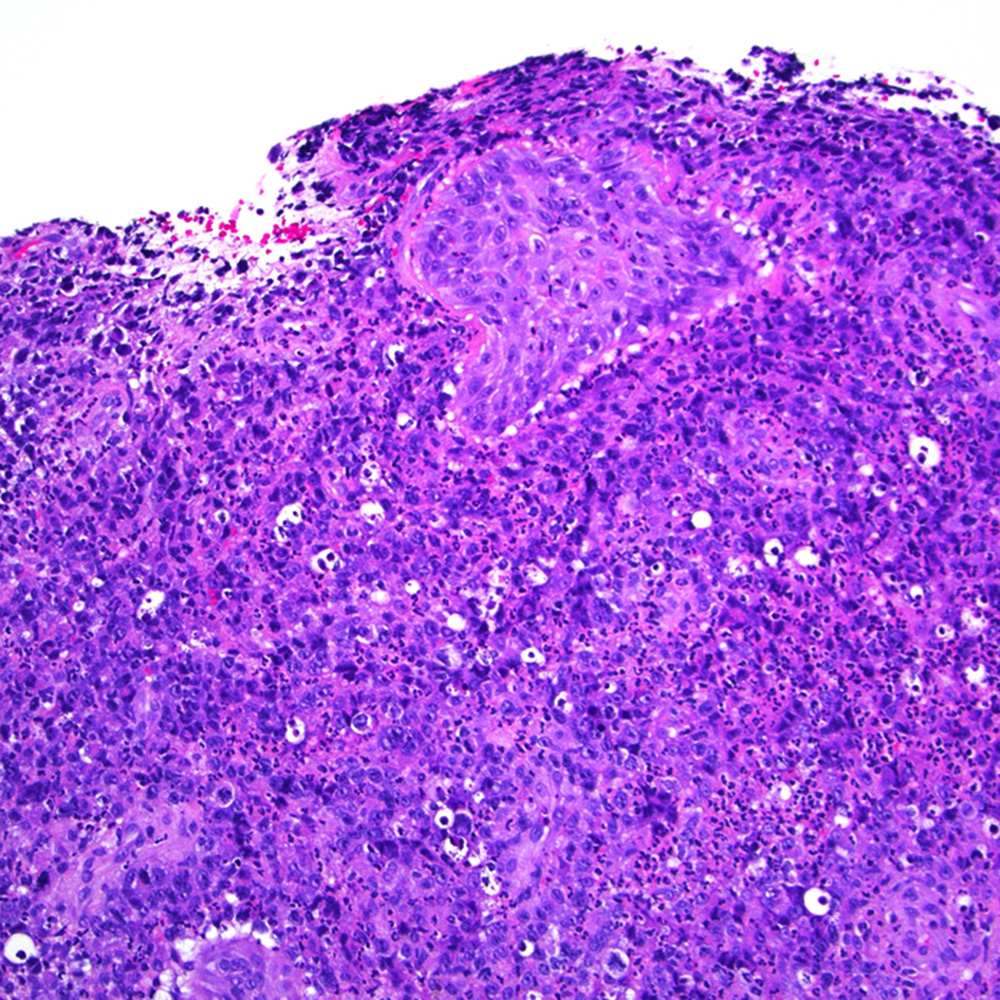
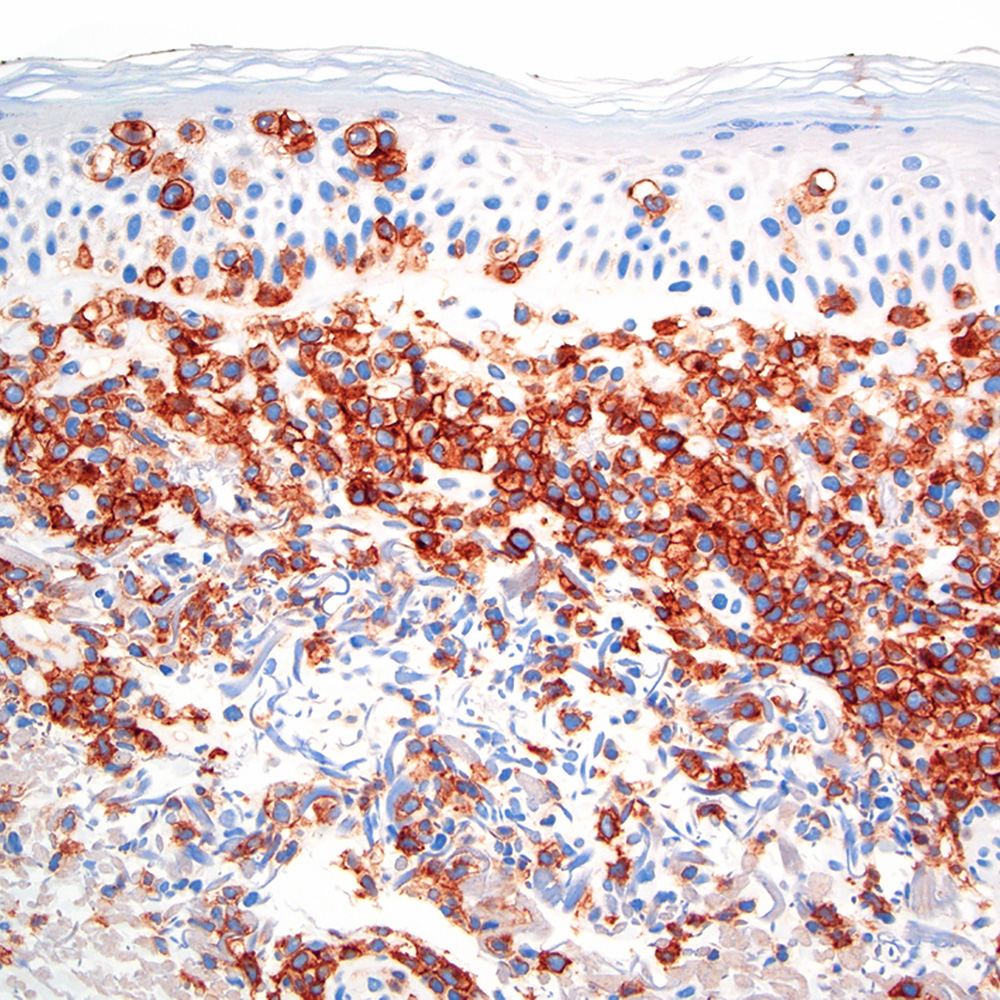
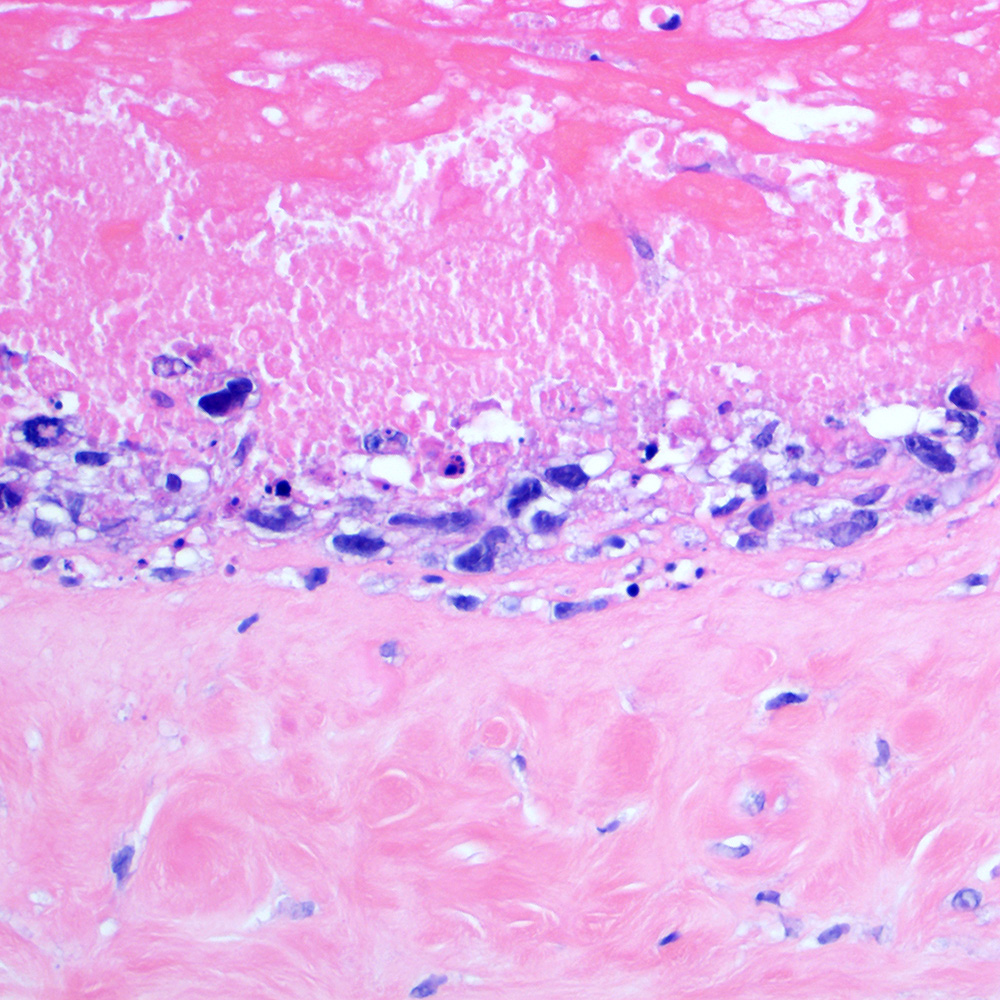
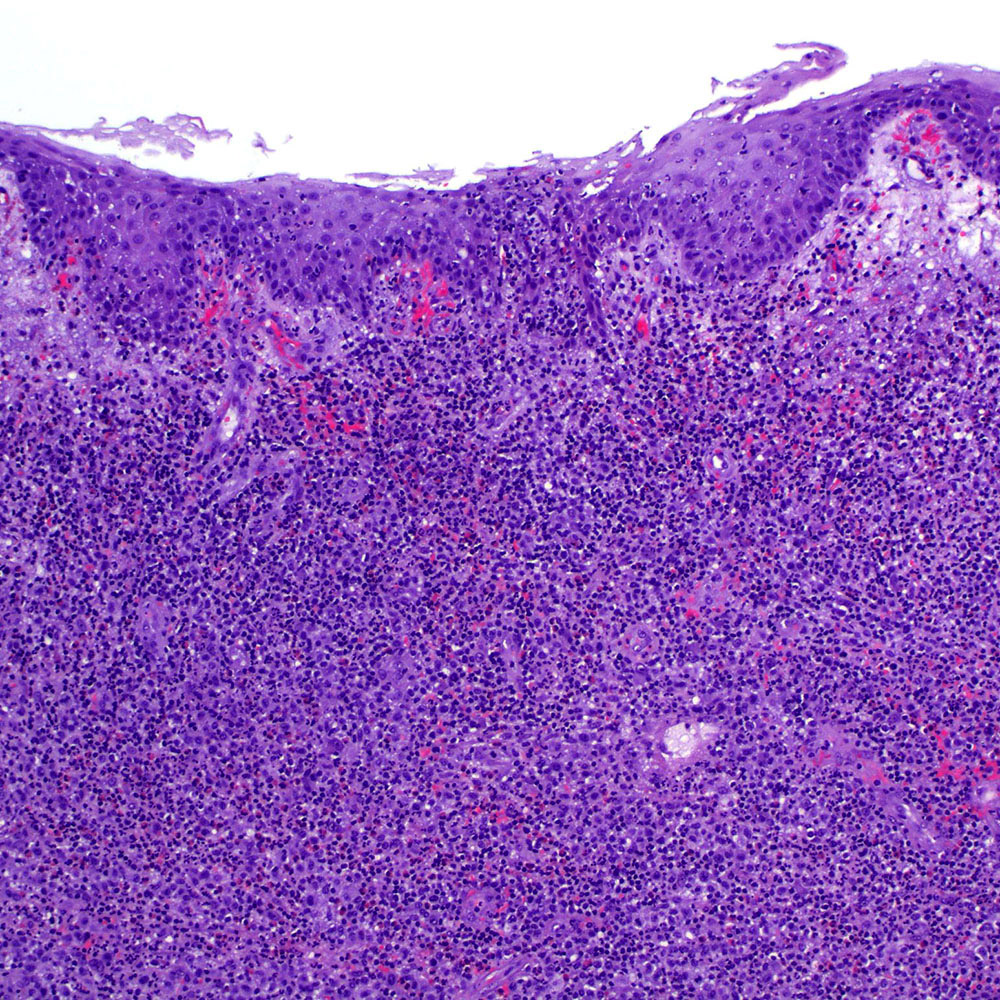
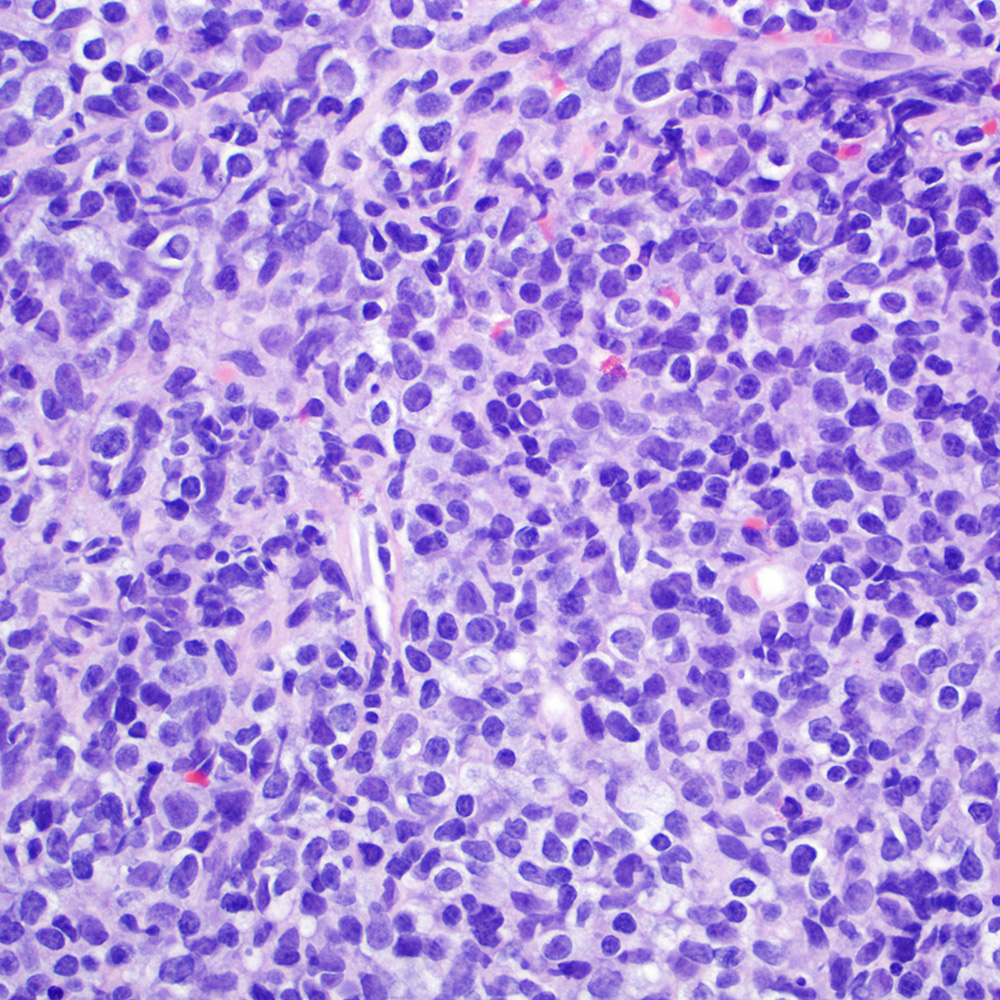
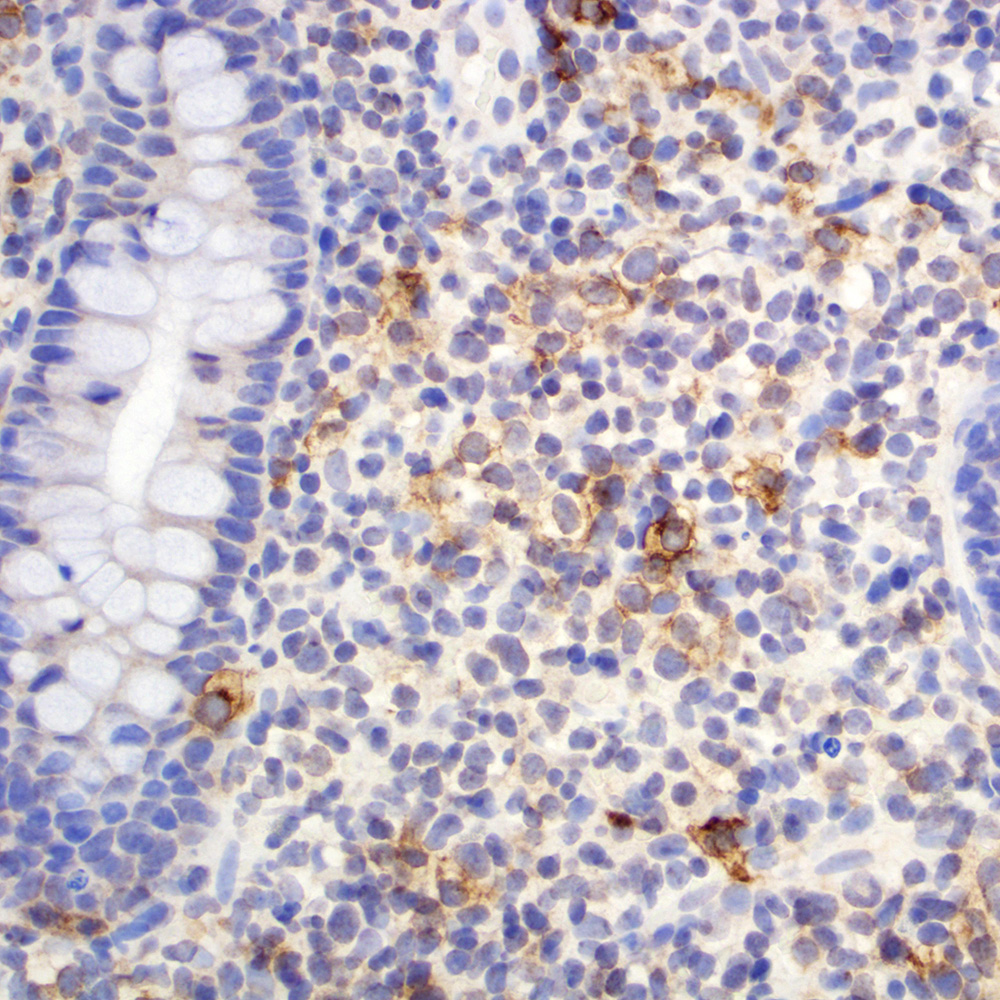
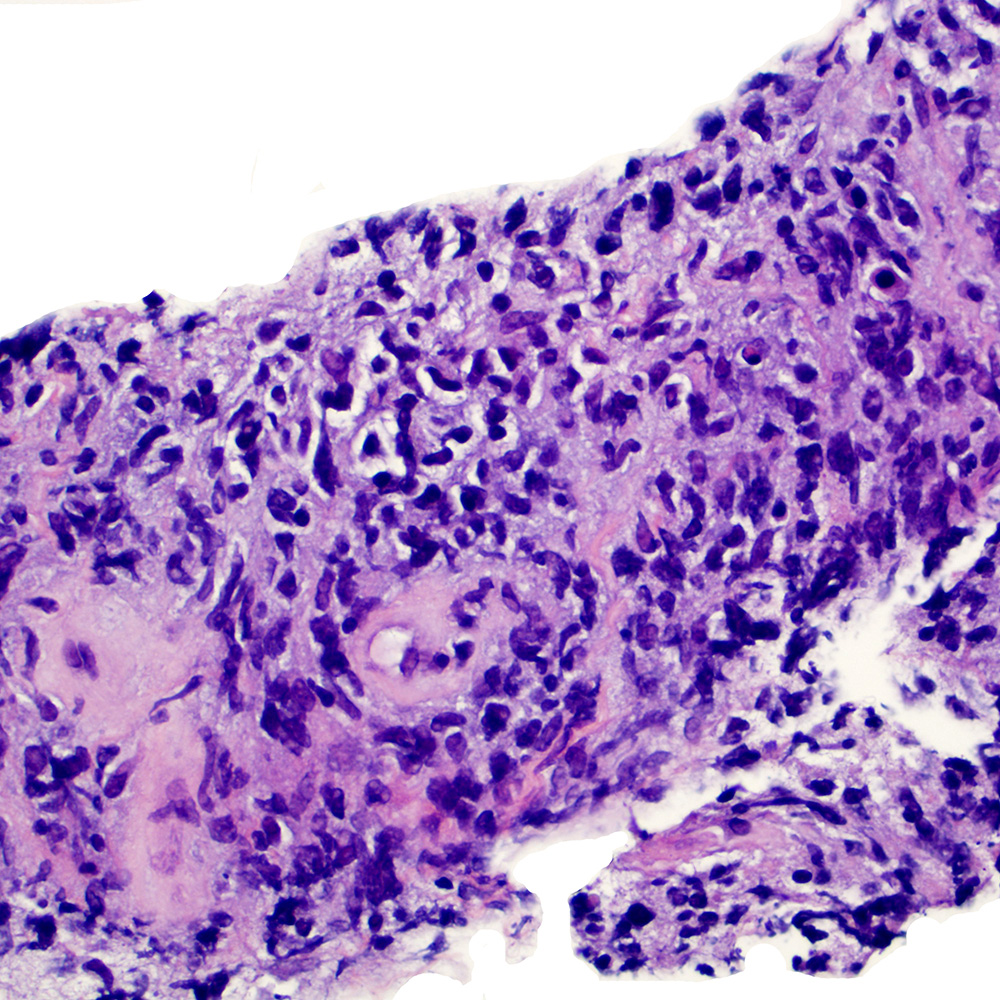
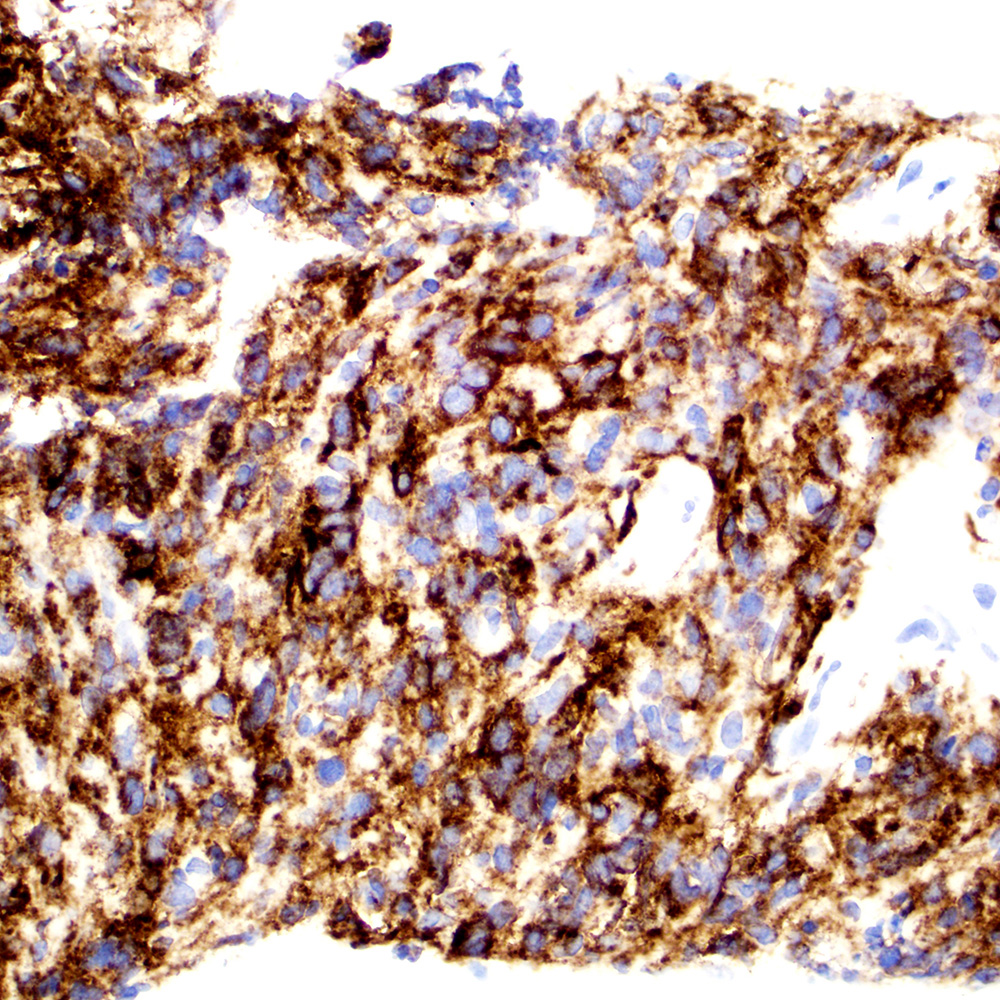
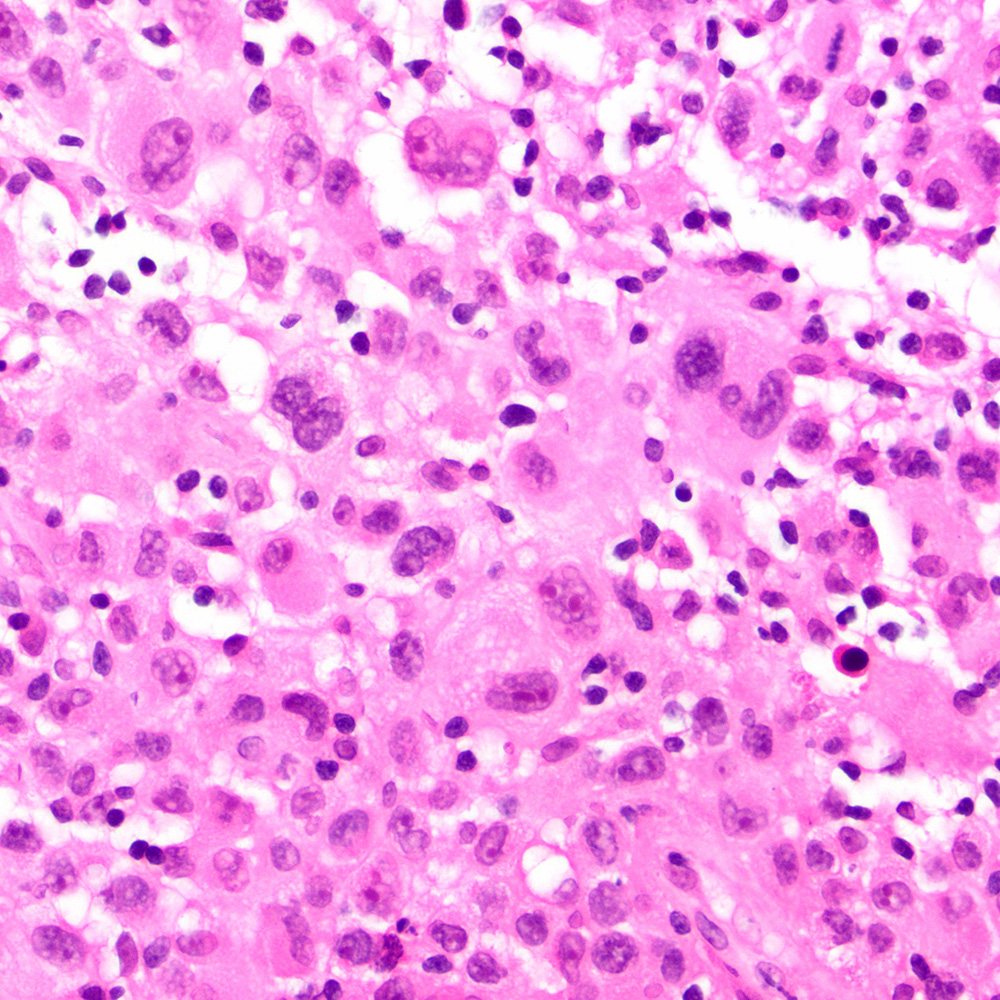
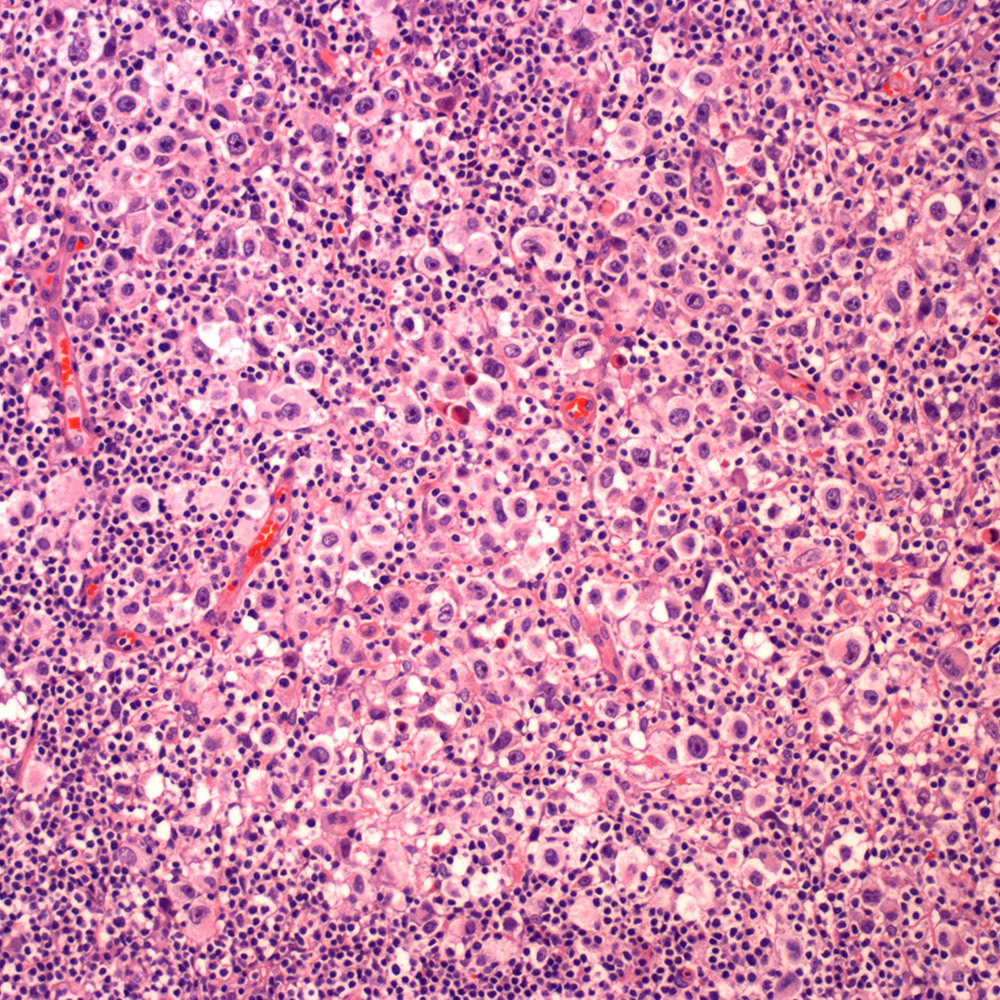
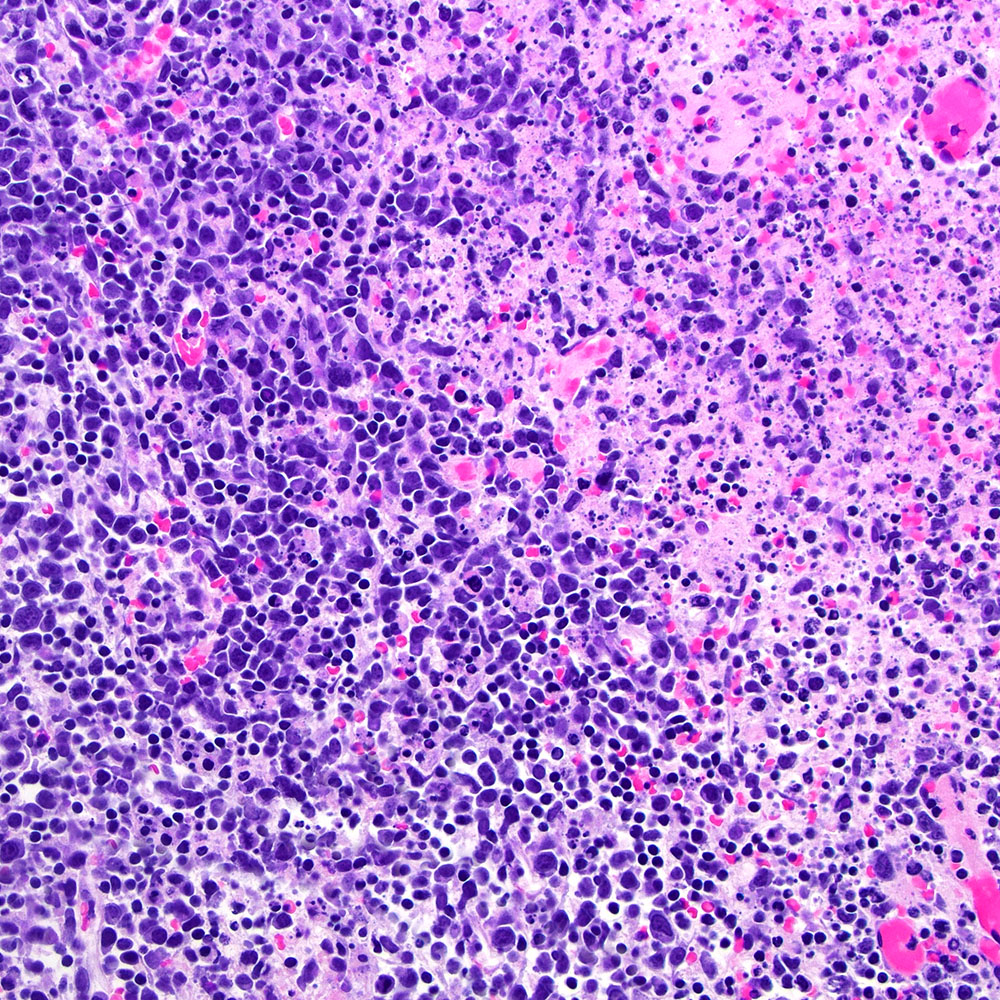
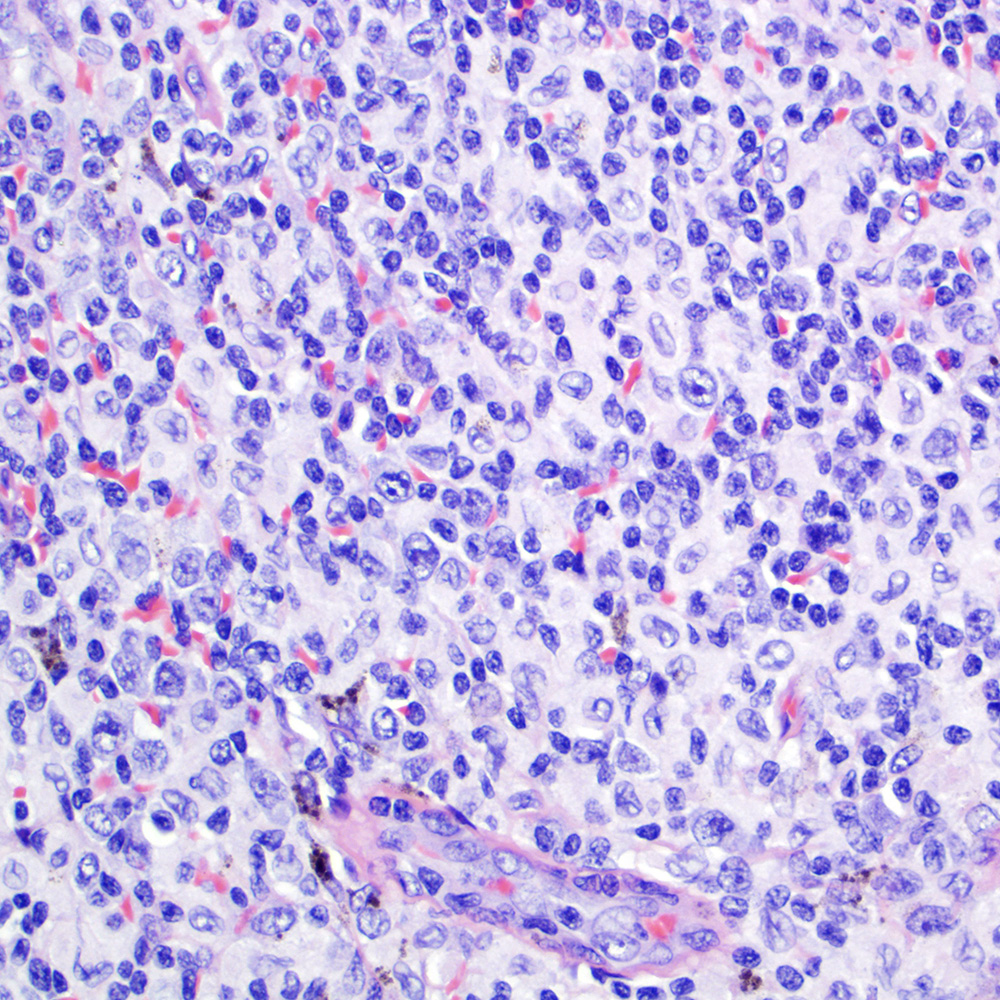
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Roberto N. Miranda, M.D.
Positive staining - normal
- Transient activated B, T and NK lymphocytes (Blood Cancer J 2017;7:e603, Oncologist 2022 Aug 10 [Epub ahead of print], J Pathol 2000;190:613)
- < 1% of circulating cells
- Range of expression intensities from weak to strong
- Stimulated B immunoblasts at the edge of the germinal center
- Subpopulations of CD4+ / CD45RO+ and CD8+ cells in lymph node and thymic medulla
- Faint reactivity in scattered lipoblasts, myoepithelial cells and decidual cells (J Pathol 2000;190:613)
- Heterogeneous positivity in activated mesothelium (J Pathol 2000;190:613)
- Early human fetal development tissues (Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2014;12:1)
- 8 - 10 weeks: expression by all 3 germ layers
- 10 - 12 weeks: skin and hematolymphoid tissues
- After 12 weeks: hematolymphoid tissues
Positive staining - disease
- Classic Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL) (Blood Cancer J 2017;7:e603, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;158:173)
- Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) and subtypes: defined as > 75% of the cells (Blood Cancer J 2017;7:e603, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;158:173)
- ALK+ ALCL
- ALK- ALCL
- Primary cutaneous ALCL
- Breast implant associated ALCL
- Lymphomatoid papulosis (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2020;34:59)
- Primary effusion lymphoma and variants (Onco Targets Ther 2018;11:3747)
- Primary mediastinal large B cell lymphoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022 Apr 26 [Epub ahead of print])
- EBV+ diffuse large B cell lymphoma (Blood Adv 2021;5:3227)
- Mediastinal gray zone lymphoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022 Apr 26 [Epub ahead of print])
- EBV+ large B cell lymphoma associated with breast implants (Mod Pathol 2021;34:2154)
- EBV+ mucocutaneous ulcer (Am J Clin Pathol 2017;147:129)
- EBV+ T and NK cell lymphoid proliferations and lymphomas of the childhood (Blood 2013;122:3101)
- Variable positivity in hydroa vacciniforme lymphoproliferative disorder and severe mosquito bite allergy
- Extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma but it can be detected in up to 47% of cases (Oncol Lett 2017;13:1211, BMC Cancer 2014;14:890, Chin J Cancer 2017;36:43)
- Mycosis fungoides (Blood Cancer J 2017;7:e603, Oncologist 2022 Aug 10 [Epub ahead of print], Histopathology 2022;81:55)
- Can be detected in up to 90% of the patients but usually has scattered positivity in the neoplastic cells; more consistent CD30 reactivity in cases of large cell transformation
- Usually located in the dermal neoplastic cells
- Variability within individual patients and individual lesions
- Primary cutaneous gamma delta T cell lymphoma; can be positive in up to 60% of cases (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022 Apr 26 [Epub ahead of print], Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:431)
- Enteropathy associated T cell lymphoma (Blood 2014;124:2983, Gastroenterology 2007;132:1902)
- Frequent positivity but scattered: < 50% of the neoplastic cells
- Usually associated with anaplastic morphology
- Advanced systemic mastocytosis (Blood Cancer J 2017;7:e603)
- Hodgkin-like histiocytosis (Histopathology 2022;81:371)
- Embryonal carcinoma (Blood Cancer J 2017;7:e603, J Pathol 2000;190:613)
- Infectious mononucleosis (Blood 1995;85:1)
Negative staining
- Acute myeloid leukemia / myeloid sarcoma; reactivity weak in 30% of AML cases and negative in acute monocytic leukemias (Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2013;13:307)
- Multiple myeloma (Leuk Lymphoma 2021;62:2845)
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma; CD30 expressed in 10 - 15% of cases (Hum Pathol 2017;60:160, Mod Pathol 2015;28:1202)
- Follicular lymphoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022 Apr 26 [Epub ahead of print])
- Lymphomatoid granulomatosis (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:141)
- Plasmablastic lymphoma; expressed in 20 - 30% of cases (Blood 2015;125:2323)
- ALK+ large B cell lymphoma; 14% of cases were positive (Leuk Lymphoma 2021;62:2845)
- Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma; when positive, reactivity is faint (Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2017;2017:324)
- Sézary syndrome (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022 Apr 26 [Epub ahead of print])
- Hepatosplenic T cell lymphoma (Blood 2014;124:2983)
- Adult T cell leukemia / lymphoma (Blood 2014;124:2983)
- Indolent T cell lymphoma of the gastrointestinal tract (Haematologica 2020;105:1895)
- Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:378)
- Majority of cases show scattered positive cells
- Can be positive in both B and T cell compartments
- Peripheral T cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:378)
- Heterogeneous and scattered positivity
- Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy (Mod Pathol 2020;33:1104)
- Scattered immunoblasts in the background may be positive
- Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2018;26:274)
- Positivity in scattered immunoblasts
- Progressive transformation of germinal centers (Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2002;65:195)
- Syphilis (Am J Dermatopathol 2022 Jul 19 [Epub ahead of print])
- Rare cases reporting strong and diffuse positivity in the lymphocytic infiltrate
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (Leuk Lymphoma 2021;62:2845)
- Malignant melanoma (Blood 1995;85:1)
- Seminoma (J Pathol 2000;190:613)
- Malignant mesothelioma (J Pathol 2000;190:613)
- Yolk sac tumor (J Pathol 2000;190:613)
- Choriocarcinoma (J Pathol 2000;190:613)
- Spermatocytic tumor (J Pathol 2000;190:613)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Chromosomal aberrations of the short arm of chromosome 1 are described in CHL, which could be related to the CD30 expression in this entity (Blood 1995;85:1)
Sample pathology report
- Right breast capsule, complete capsulectomy:
- Fibrous breast capsule with mild chronic inflammation
- No morphologic or immunophenotypic support for lymphoma
- Histologic sections of the right breast capsule show a fibrinous breast capsule with scattered small and mature lymphocytes. Synovium-like lining formation and silicone particles are occasionally seen. There are rare foci of breast glandular epithelium on the outer surface of the specimen.
- Immunohistochemical stains are performed and the cells are negative for CD30, while CD3 and CD20 highlight small and mature T and B lymphocytes, respectively.
- Left breast capsule, complete capsulectomy:
- Breast implant associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (see comment)
- Tumor is confined to the inner surface of the peri-implant capsule (pathologic stage T1) and margins are negative
- Comment: According to clinical notes, the patient is a 52 year old woman with a history of bilateral breast implant placement 9 years ago due to aesthetic reasons. She noticed swelling of the left breast 10 months ago and it was initially attributed to capsular contracture and spontaneously resolved; however, 1 month ago, the swelling recurred with an ipsilateral accompanying effusion, which was aspirated. The cytologic and immunophenotypic examination showed neoplastic cells consistent with anaplastic large cell lymphoma and a bilateral complete capsulectomy was recommended.
- Histologic sections of the left breast capsule show a thick and fibrinous breast capsule with rare, large and atypical lymphocytes with hyperchromatic and irregular surface in the luminal side of the capsule. Associated with the atypical lymphocytes, there is a dense lymphocytic infiltrate composed predominantly of small and mature lymphocytes.
- Scrapings from the left breast implant surface show a high number of atypical cells with same cytological features of the capsule. Karyorrhectic debris is also present within the implant scrapings.
- Touch preparation slides performed on the left breast capsule show rare large cells with irregular, multilobated nuclei and moderate cytoplasm.
- Immunohistochemical stains are performed. The neoplastic cells are positive for CD2, CD5, CD8 and CD30 and are negative for CD3, CD4, CD7, CD10, CD56, TCR alpha beta and TCR gamma delta. Epstein-Barr virus encoding region (EBER) in situ hybridization is negative.
- In summary, the clinicopathological features are diagnostic of breast implant associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma.
Additional references
Practice question #1
Which of the following is true about CD30 expression?
- CD30 belongs to tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily
- High CD30 expression is required in lymphoma cells to predict better response to anti-CD30 therapy (brentuximab vedotin)
- It is a protein with exclusive extracellular domain
- Naïve normal B and T cells can express CD30
- There is an inconsistent correlation between the immunohistochemical expression of CD30 and mRNA levels
Practice answer #1
A. CD30 belongs to tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. CD30 is a transmembrane glycoprotein, which belongs to tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. CD30, also known as BerH2, Ki1 or TNFRSF8, is a transmembrane glycoprotein receptor that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) and was first identified in Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines but also expressed in normal activated B and T cells. This protein has an extracellular transmembrane and intracellular domains and the similarity of CD30 and other proteins of TNFR family is restricted only to the extracellular domain. Immunohistochemical expression of CD30 has a high concordance with mRNA levels. Interestingly, patients with any number of positive CD30+ cells in lymphoma cases can benefit from therapy with brentuximab vedotin, not only those cases that show all tumor cells positive for CD30.
Comment Here
Reference: CD30
Comment Here
Reference: CD30
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2
A. Classic Hodgkin lymphoma and anaplastic large cell lymphoma are typically positive for CD30, while nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma, follicular lymphoma and hepatosplenic T cell lymphoma are negative for CD30. Testicular embryonal but not choriocarcinoma is usually positive for CD30.
Comment Here
Reference: CD30
Comment Here
Reference: CD30