Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Uses by pathologists | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Additional referencesCite this page: Pernick N. CD43. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cdmarkerscd43.html. Accessed October 5th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Pan T cell marker important in T cell and neutrophil adhesion to endothelium
Terminology
- Also called leukosialin, sialophorin
Pathophysiology
- Serves as a ligand for E-selectin on T cells and may regulate T cell trafficking (Blood 2006;107:1421, J Immunol 2005;175:8042)
- Has both antiadhesive and proadhesive roles in neutrophil rolling (J Immunol 2008;181:3628)
Clinical features
- Has defective expression in T cells of males with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (MIM 301000)
Uses by pathologists
- Pan T cell marker
- Diagnosis of myeloid (granulocytic) sarcoma (J Clin Pathol 2005;58:211)
- Classify subtypes of T cell lymphomas and low grade B cell lymphomas
- Differentiate pulmonary MALT lymphoma (CD20+ CD43+) from lymphoid hyperplasia (CD43 negative, Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:76)
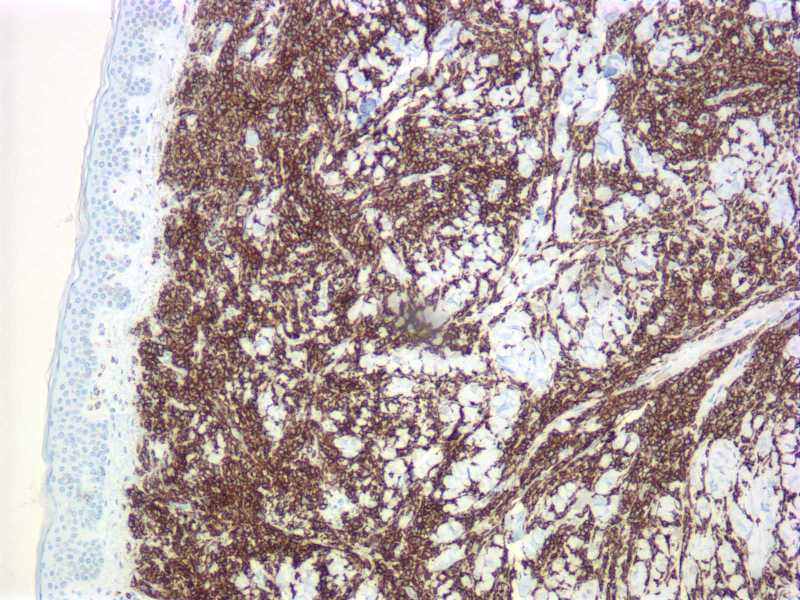
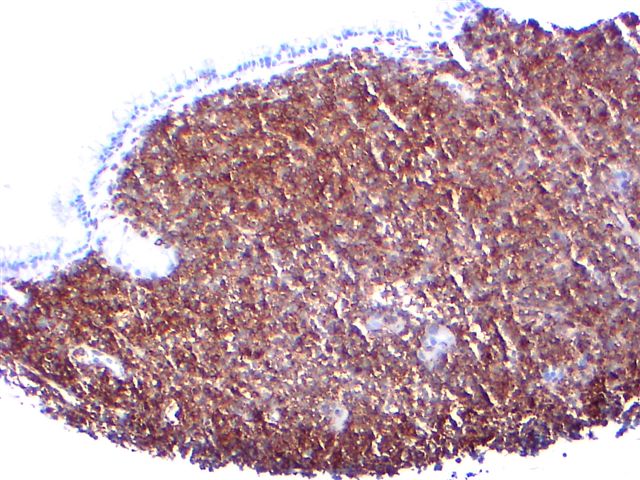
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Most T cells, activated B cells, B cells in terminal ileum (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2005;13:138), plasma cells (Scand J Immunol 1991;33:211)
- Basophils, erythrocytes, granulocytes, hematogones (Br J Haematol 2005;128:820), macrophages (some), megakaryocytes, monocytes, NK cells, platelets (weak)
- Brain, Langerhans cells, thymocytes
Positive staining - disease
- T/NK cell lymphomas - anaplastic large cell (variable), CD4+/CD56+ hematodermic neoplasm / blastic NK (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1274), hepatosplenic gamma-delta T cell, NK/T cell-nasal type (96%, Hum Pathol 2004;35:86), peripheral T cell, subcutaneous panniculitis-like
- B cell lymphomas - ALL (most), Burkitt’s (almost all), Burkitt’s-like (almost all, Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1652), lymphoblastic (variable), mantle cell (100%, Am J Clin Path 2003;119:218), marginal zone (variable, most common in salivary gland, stomach, and upper aerodigestive tract, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:1673), nodal marginal zone (variable, Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:762), plasmablastic, SLL/CLL (Am J Clin Path 1999;112:319)
- Other: AML (including leukemia cutis, Am J Clin Pathol 2009;132:101), granulocytic sarcoma, hemangioma, Langerhans cell histiocytosis, mast cell disease (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:703), plasmacytoma; early colonic adenoma (Oncol Rep 2004;11:327)
Negative staining
- Colonic epithelium, follicular lymphoma, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, lymphoepithelioma-like thymic carcinoma, primary effusion lymphoma, splenic marginal zone lymphoma
Additional references