Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1Cite this page: Bruehl F, Schürch CM. CD99. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cdmarkerscd99.html. Accessed September 10th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Transmembrane protein with various functions and limited diagnostic utility
- In the differential diagnosis of small round blue cell tumors
Essential features
- Exists in 2 isoforms and has variable oncogenic and tumor suppressor functions
- Positivity for CD99 is not specific but its absence rules out Ewing sarcoma in the workup of a small blue round cell tumor
- Dot-like staining pattern has been reported in several disease entities but has so far not been proven to be diagnostically useful
Terminology
- Also called MIC2, T cell surface glycoprotein E2, p30 / 32 protein (Hum Mol Genet 1993;2:417)
Pathophysiology
- Gene is located in the pseudoautosomal region of chromosome X (Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 1988;322:145)
- 2 distinct protein variants exist due to splice variants (J Immunol 1997;159:2250):
- CD99 type I (or CD99wt)
- CD99 type II, truncated form (CD99short)
- Functions:
- Regulation of leukocytes (FEBS Lett 2003;554:478)
- Apoptosis of T cells induced by caspase independent pathway (FEBS Lett 2003;554:478)
- Migration of leukocytes (J Exp Med 2015;212:1021)
- General cellular mechanisms
- Transmembrane protein transport (J Immunol 2001;166:787)
- May play a role in actin cytoskeleton arrangement (FEBS Lett 2003;540:217)
- Differentiation of primitive neuroectodermal cells (Exp Mol Med 2003;35:438)
- Thought to possess oncojanus (i.e., dual oncogenic and tumor suppressor type) functions depending on tumor type and tissue of origin, see diagram (Genes (Basel) 2018;9:159)
- Oncogene function: in Ewing / PNET, CD99 may promote growth and migration of tumor cells (Oncogene 2006;25:2795)
- Tumor suppressor gene: in osteosarcoma, CD99 may act as a tumor suppressor gene (Mol Biol Cell 2006;17:1910)
- Regulation of leukocytes (FEBS Lett 2003;554:478)
Clinical features
- Part of Xg blood group system (Nat Genet 1994;8:285)
- Targeting CD99 in neoplastic cells is showing promise in preclinical in vitro studies (J Cell Commun Signal 2018;12:55, Cell Death Dis 2012;3:e425)
Interpretation
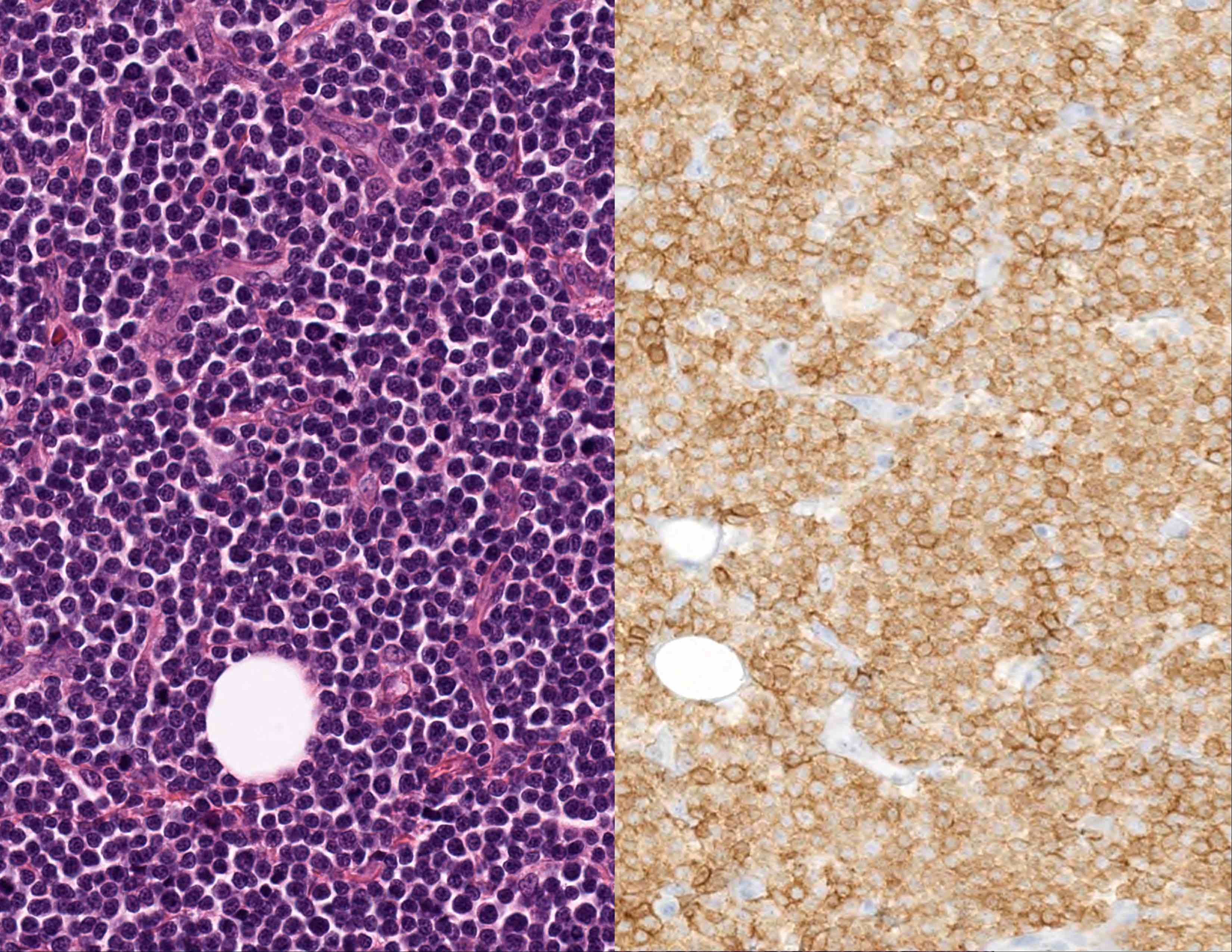
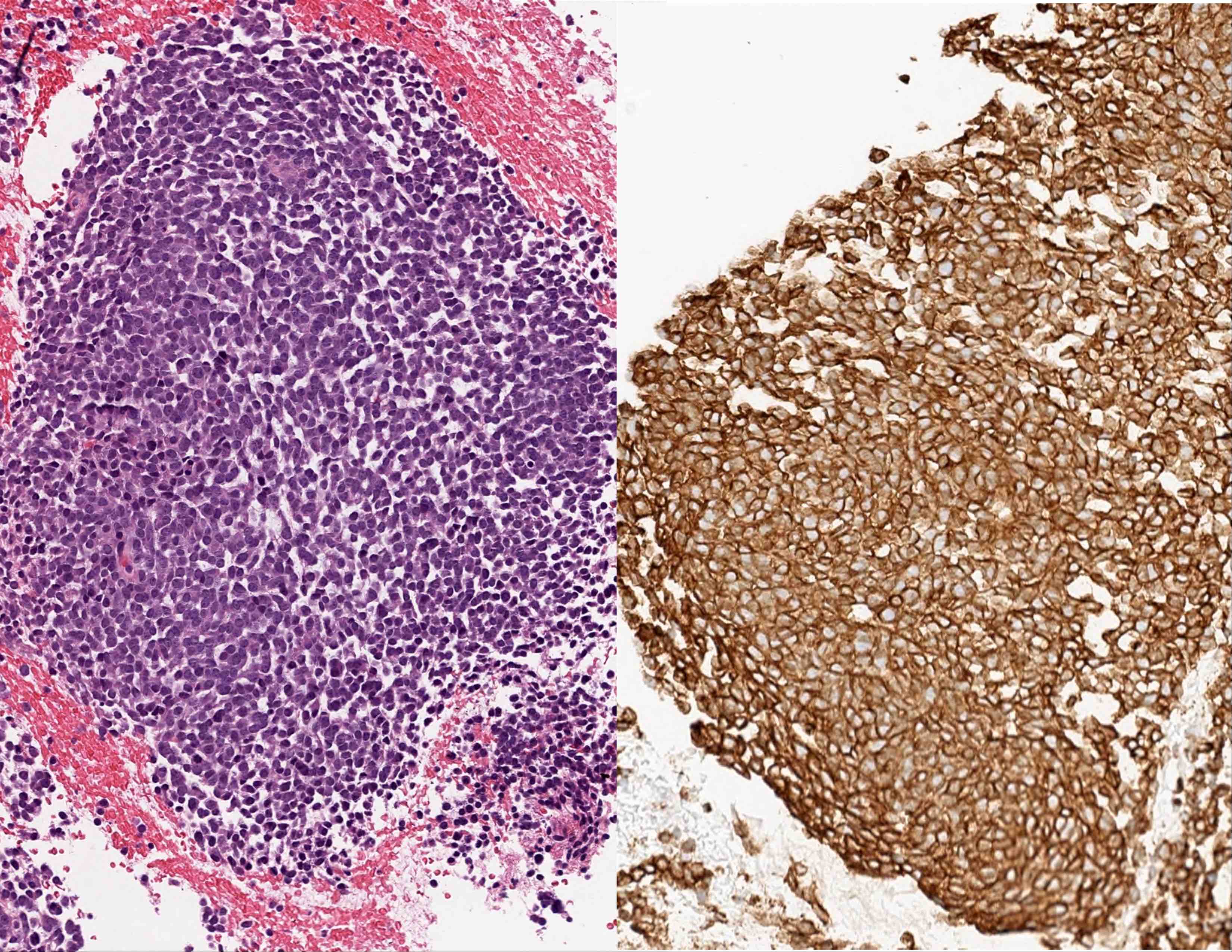
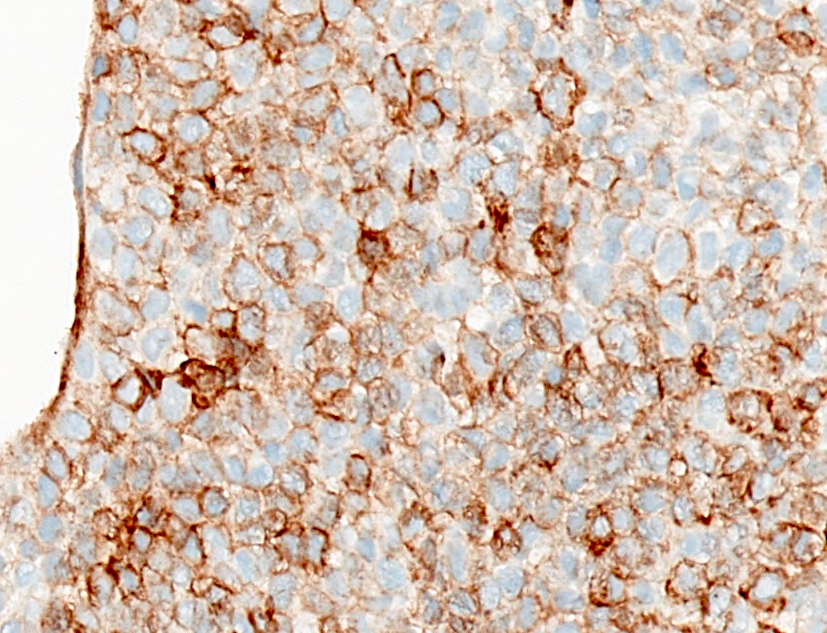
- Only strong, diffuse and membranous staining is considered positive for Ewing sarcoma and acute lymphoblastic leukemia / lymphoma (Am J Clin Pathol 2009;131:574, Mod Pathol 2006;19:659)
Uses by pathologists
- Rule out Ewing sarcoma / PNET (always shows strong membranous CD99 positivity) if the differential diagnosis is desmoplastic small round cell tumor, Ewing-like sarcoma, neuroblastoma, nephroblastoma (Wilms tumor), small cell carcinoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, olfactory neuroblastoma or small cell osteosarcoma (none show strong membranous CD99 positivity)
- If CD99 is negative, Ewing sarcoma / PNET is unlikely
- If CD99 is positive, Ewing sarcoma / PNET needs to be confirmed with additional immunohistochemical and adjunctive molecular testing as many other malignant neoplasms, including lymphoblastic leukemias / lymphomas as well as round and spindle cell sarcomas, are usually CD99 positive (Cancer 1991;67:1886)
- Detect minimal residual disease by flow cytometry in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (CD99 positive) (Leukemia 2004;18:703, Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2018;94:82)
- May help grade and subtype ependymoma (Medscape J Med 2008;10:41)
- CD99 (or other immature T cell markers such as TdT and Cd1a) is particularly useful in evaluating mediastinal and other biopsy samples of possible thymic epithelial neoplasms and in the subtyping of these tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:936, Diagn Pathol 2007;2:13)
Prognostic factors
- Loss of CD99 expression in gastric adenocarcinoma is associated with poor overall survival (Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:2584)
- High CD99 expression in lung non-small cell carcinoma is associated with improved survival (Int J Cancer 2012;131:2264)
- High CD99 expression in B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and large B cell lymphoma is associated with poor survival in (Br J Haematol 2019;184:418, Acta Haematol 2011;125:167)
- High CD99 expression in acute myeloid leukemia and multiple myeloma is associated with improved survival (Haematologica 2020;105:999, Korean J Pathol 2014;48:209)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Cytoplasmic paranuclear and dot-like staining may be seen in solid pseudopapillary tumors, colonic adenomatous lesions and embryonal rhabdomyosarcomas (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:799, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1749, Histopathology 2013;62:814)
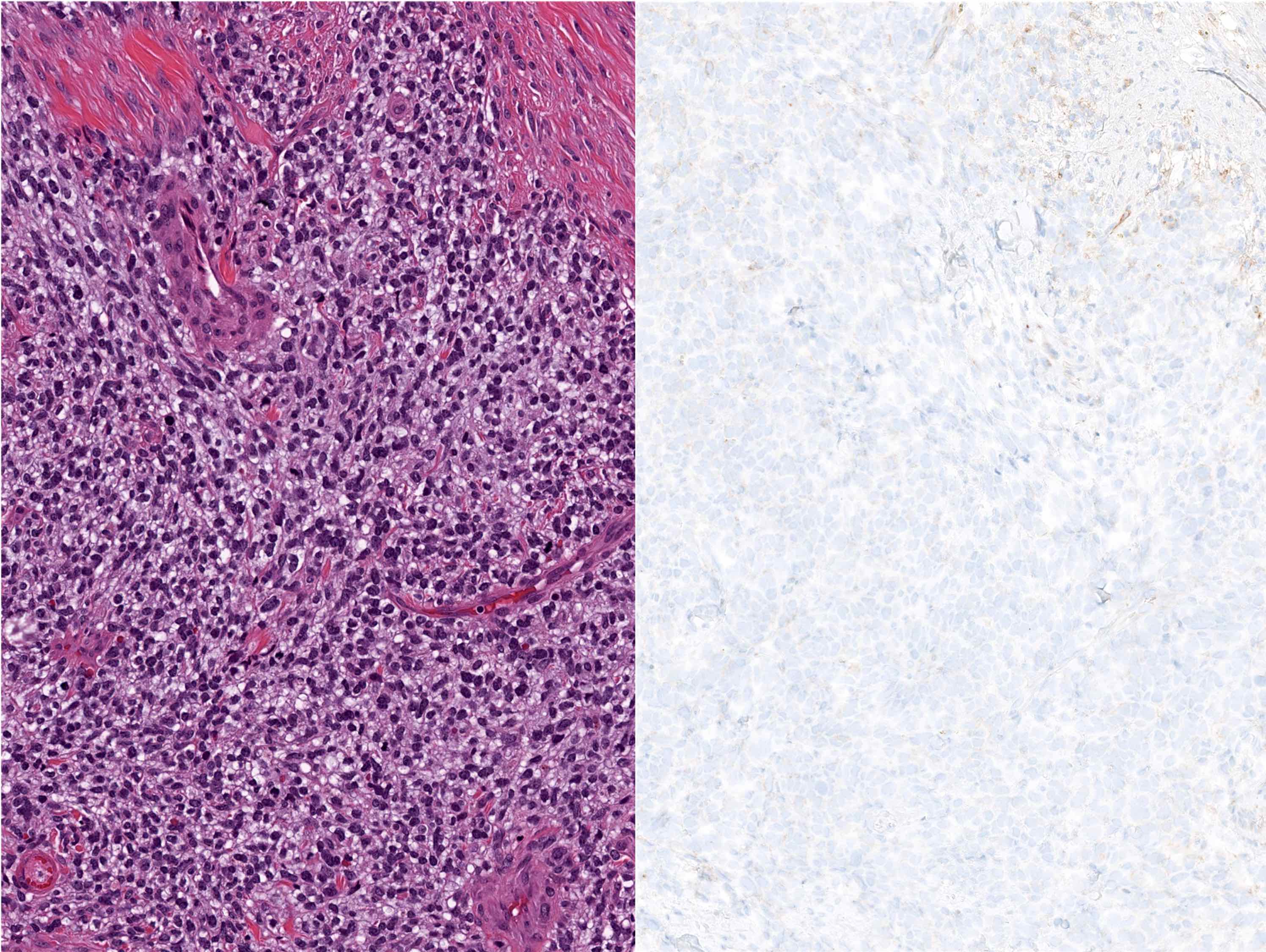
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Endothelial cells, ependymal cells, hepatocytes, gastric foveolar epithelium, ovarian granulosa cells, pancreatic islet cells, testicular Sertoli cells, immature thymic T cells and activated B lymphocytes (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:1115, Blood 1994;83:415, J Korean Med Sci 1999;14:600)
Positive staining - disease
- Ewing sarcoma (ES) / PNET (Biochimie 1976;58:855, Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1025)
- Including of kidney, pancreas, skin, vulva / vagina (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:320, Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:1040, Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:310, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2000;19:103)
- Round cell sarcomas with EWSR1 non-ETS fusions (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2020;59:525)
- EWSR1-NFATC2 translocation associated sarcoma (100%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1112)
- Synovial sarcoma (90 - 100%, all types) (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:1434)
- Leukemia / lymphoma:
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Leukemia 2004;18:703)
- FLT3-ITD positive acute myeloid leukemia (Haematologica 2020;105:999)
- Although the catalog of diagnostic entities that have been reported to label positively with CD99 seems ever expanding and difficult to enumerate, CD99 has been referred to as staining "99 different things"; for an incomplete list of tumors reported to have positive staining, sorted alphabetically, proceed reading below:
- Adamantinoma of ulna (Clin Orthop Relat Res 2003:256)
- Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (Am J Clin Pathol 2009;131:574)
- Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma (Clin Orthop Relat Res 2003:256)
- Atypical fibroxanthoma (Am J Clin Pathol 2002;117:126)
- BCOR rearranged sarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:604)
- Breast metaplastic carcinoma (Histopathology 2001;39:578)
- Calcifying aponeurotic fibroma (Hum Pathol 1998;29:1504)
- Cervicovaginal myofibroblastoma (Pathology 2005;37:144)
- Dermatofibroma (Am J Dermatopathol 2014;36:392, J Cutan Pathol 2003;30:631)
- Ectopic hamartomatous thymoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:e378)
- Ependymoma (Medscape J Med 2008;10:41, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2001;9:125)
- Extrarenal malignant rhabdoid tumor (Ann Diagn Pathol 1998;2:351)
- Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma (J Clin Pathol 2008;61:873)
- Gastric carcinoma, intestinal type (J Korean Med Sci 2002;17:483)
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2002;126:1189)
- Giant cell angiofibroma (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:971)
- Goblet cell adenocarcinoma (78%) (Int J Surg Pathol 2007;15:252)
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2003;46:625)
- Melanoma (J Cutan Pathol 2006;33:663)
- Merkel cell carcinoma of skin (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2000;8:37)
- Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma (Hum Pathol 1996;27:1273)
- Neuroendocrine tumors (Virchows Arch 2000;437:270)
- Neurothekeoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1103)
- Nuchal fibromas (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:970)
- Ovarian sex cord stromal tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:143)
- Pancreatic endocrine neoplasms (Histopathology 2004;45:384)
- Perineurioma, sclerosing type (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:1433)
- Pleomorphic hyalinizing angiectatic tumor (Pathol Int 2002;52:664)
- Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm (J Cytol 2013;30:151, Diagn Pathol;15:139)
- Solitary fibrous tumor (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8:13166, Mod Pathol 1999;12:463, Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:900, Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:1424, Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:1501)
- Superficial acral fibromyxoma (Hum Pathol 2001;32:704)
- Testicular sex cord stromal tumors (Hum Pathol 2000;31:1055)
- Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (J Cutan Pathol 2006;33 Suppl 2:24)
- Uterine translation associated sarcomas (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2019;38:528)
- Uterine tumors resembling ovarian sex cord tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1749, Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:403)
Negative staining
- Acute myeloid leukemia (Mod Pathol 2000;13:452, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:153)
- CIC rearranged sarcoma (cytoplasmic but not the typical membranous staining pattern can be observed in some cases) (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014;53:622, Mod Pathol 2015;28:57)
- Desmoplastic small round cell tumor (DSRCT) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:728)
- Epithelioid sarcoma (Mod Pathol 2001;14:655)
- Esthesioneuroblastoma / olfactory neuroblastoma (Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:391, Hum Pathol 1995;26:639)
- Extraskeletal myxoid chrondrosarcoma (43%) (Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 2016;45:25)
- Hodgkin lymphoma (Blood 2000;95:294)
- Leiomyosarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:403)
- Mesothelioma (Histopathology 1998;33:508)
- Myelodysplastic syndrome (Mod Pathol 2000;13:452)
- Myeloma (Korean J Pathol 2014;48:209)
- Neuroblastoma
- Adults (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:918)
- Children (Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:327)
- NUT midline carcinoma (Head Neck Pathol 2011;5:31)
- Ovarian epithelial tumors (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000;124:563)
- Retinoblastoma (Ann Diagn Pathol 2001;5:148)
- Rhabdomyosarcoma (Oral Oncol 2002;38:450, Histopathology 2013;62:814)
- Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:156)
- Small cell carcinoma (Am J Clin Pathol 1994;102:692)
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin (J Cutan Pathol 2010;37:744)
- Stomach adenocarcinoma (J Korean Med Sci 2002;17:483)
- Thymic carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:936)
- Wilms tumor / nephroblastoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:320)
Additional references
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
C. Rule out the diagnosis of Ewing sarcoma. CD99 cannot be used to confirm the diagnosis of Ewing sarcoma, as other entities in the differential diagnosis may express CD99. Confirmation of Ewing sarcoma requires demonstration of EWSR1 gene rearrangement.
Comment Here
Reference: CD99
Comment Here
Reference: CD99