Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Peripheral smear description | Peripheral smear images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Mais DD. Hemoglobin C disease. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/hematologyhemoglobinCdisease.html. Accessed April 26th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Homozygosity for C (βC) allele of hemoglobin beta chain (HBB) gene
Essential features
- Mild chronic hemolysis
- Characteristic blood smear morphology
- Relative protection against severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria
- Diagnosed by electrophoresis or high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
Terminology
- HbC disease, HbCC
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D58.2 - other hemoglobinopathies
Epidemiology
- Found worldwide
- Most prevalent in West African countries such as Ghana and Ivory Coast (BMC Res Notes 2018;11:215)
- Prevalence of hemoglobin C gene in Black Americans approximately 2% (Hemoglobin 2013;37:16)
Sites
- Bone marrow, spleen
Pathophysiology
- HbC has lysine (AAG) substituted for glutamate (GAG) at position 6 of the beta chain
- Has poor solubility, leading to precipitation in red blood cells
- Activation of potassium / chloride channels leads to cellular dehydration
- Slightly shortened red blood cell survival (hemolytic anemia)
Etiology
- Inherited genetic mutation
Clinical features
- Mild chronic hemolysis, usually well compensated and asymptomatic
- Some patients have mild anemia, splenomegaly or gallstones (Hemoglobin 2013;37:16)
- Protects against severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria (Sci Rep 2017;7:14267)
- Note that heterozygous C train (HbAC) is clinically asymptomatic, manifesting only as target cells in the peripheral blood smear but does confer some protection against severe P. falciparum malaria
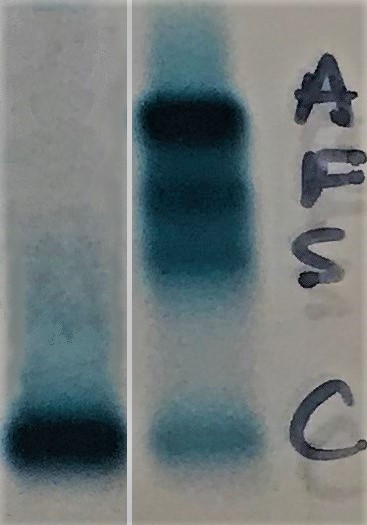
Diagnosis
- Hemoglobin electrophoresis or HPLC shows about 95% HbC with no HbA and less than 5% HbA2 and HbF
- Molecular genetic testing important in some cases; beta gene sequencing currently best method
Laboratory
- Normal to mildly decreased hemoglobin (Hemoglobin 2013;37:16)
- Normal to slightly increased reticulocytes (Hemoglobin 2013;37:16)
- Normal to slightly increased bilirubin and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
- Decreased mean corpuscular volume (microcytosis), on average about 55 fL
- Normal to increased mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)
- Normal to slightly increased red cell distribution width (RDW)
- Relative reduction in glycated HbA1C (Clin Chim Acta 2012;413:819)
Prognostic factors
- Overall prognosis good; no known reduction in overall life expectancy
Case reports
- 21 month old girl with anemia (Am J Hematol 2019;94:144)
- 23 year old woman with sickle cell disease (Transfusion 2012;52:466)
- 56 year old man with gallstones (Am J Hematol 2015;90:174)
Treatment
- No treatment required
- Genetic counseling may be indicated to address risk of compound heterozygosity in offspring
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Bone marrow is hypercellular with relative erythroid hyperplasia
- Irregular nuclear contours and other dyspoietic changes may be seen
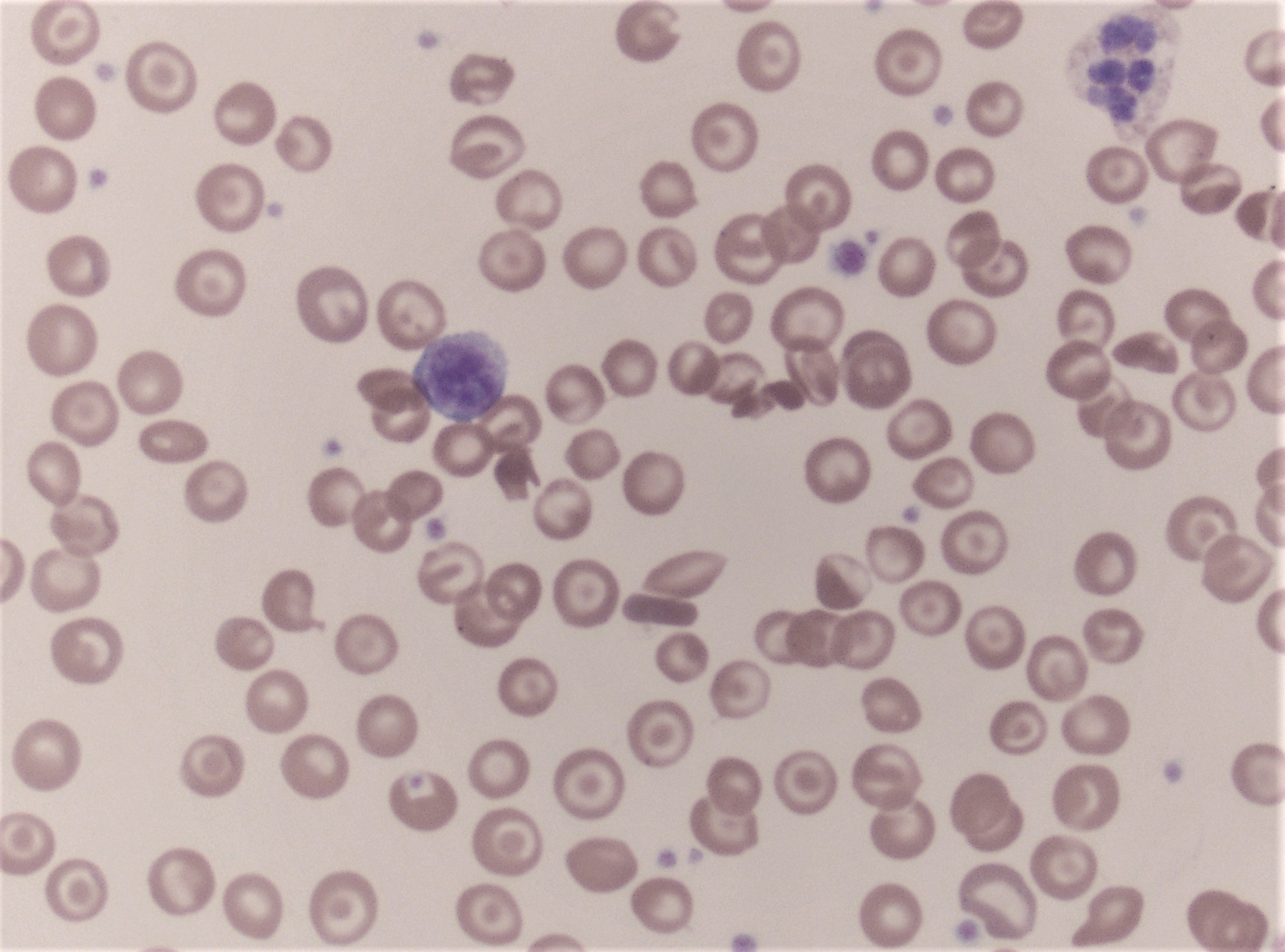
Peripheral smear description
- Microcytosis
- Numerous target cells
- Irregularly contracted cells
- Occasional rhomboid crystals, more numerous postsplenectomy
Peripheral smear images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Beta globin (HBB) gene located at 11p15.5
- Point mutation in sixth codon, GAG > AAG
- Lysine encoded instead of glutamate at sixth amino acid (β6 glu→lys)
- Same amino acid position affected in HbS (β6 glu→val)
Sample pathology report
- Hemoglobin electrophoresis:
- Consistent with hemoglobin C disease (see comment)
- Comment: Blood smear demonstrates microcytic red cells, frequent target cells, boat cells and occasional blunt ended hemoglobin crystals. Electrophoresis shows 96.7% HbC.
Differential diagnosis
- On cellulose acetate electrophoresis at alkaline pH, migrates with:
- HbE
- HbO Arab
- HbC Harlem
- HbA2
- Distinguished on citrate agar
- On HPLC, migrates very close to:
- HbA2
- Hb Lepore
- Distinguished by electrophoresis
- Rarely, transient acquired HbC after exchange transfusion (Ann Clin Lab Sci 2015;45:627)
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is true regarding HbC disease?
- Affected patients are more prone to severe malaria
- Affected patients are usually transfusion dependent
- Affected patients may have falsely low glycated HbA1c
- HbC comigrates with HbE and HbO Arab on citrate agar
- It is clinically more severe than sickle cell disease
Board review style answer #1
C. Affected patients may have falsely low glycated HbA1c
Comment Here
Reference: Hemoglobin C disease
Comment Here
Reference: Hemoglobin C disease
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2