Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Epidemiology | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Immunohistochemistry & special stains | Additional referencesCite this page: Andeen NK, Tretiakova M. Donor evaluation . PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneydonorevaluation.html. Accessed September 10th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Performed to determine suitability of allograft prior to transplantation
- Findings to report: specimen type (wedge or core biopsy), # glomeruli, # and % of globally sclerosed glomeruli, # arteries, interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy, interstitial inflammation, arterial intimal fibrosis, arteriolar hyalinosis, other findings (such as FSGS or suspicious lesions) (Am J Transplant 2017;17:140)
- Biopsy should be of renal cortex, 10 mm long × 5 mm wide × 5 mm deep, and contain at least 25 glomeruli
- Donor glomerulosclerosis, chronic vascular and interstitial damage are prognostic for graft outcome (Kidney Int 2005;67:1595)
Essential features
- Demand for donor kidneys far exceeds supply
- Frozen section may be performed to determine suitability of allograft prior to transplantation
- Findings to report: specimen type (wedge or core biopsy), # glomeruli, # and % of globally sclerosed glomeruli, tubular atrophy, interstitial fibrosis, interstitial inflammation, # arteries, arterial intimal fibrosis, arteriolar hyalinosis, other findings (such as FSGS, periglomerular fibrosis, etc) (Am J Transplant 2017;17:140)
Epidemiology
- Demand for donor kidneys far exceeds supply
- Discard rate of recovered kidneys is > 40%
Prognostic factors
- Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN) recommends preimplantation biopsy for all kidneys with a Kidney Donor Profile Index (KDPI) > 85%
- KDPI is derived from 10 donor factors: age, height, weight, ethnicity, serum creatinine, history of diabetes, hypertension, hepatitis C virus, cause of death, and donor after circulatory death status
- KDPI ability to predict graft failure is 0.6; further assessment and pathologic findings may help improve on this (Am J Transplant 2017;17:140)
- Preimplantation biopsy findings correlate with flow and resistance to machine perfusion (Transplant Proc 2012;44:2197)
- Expanded Criteria Donor: These are at increased risk of graft failure (relative HR 1.7 compared with Standard Criteria Donor; Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2009;4:1827)
- At time of death, donors age > 60 OR
- Aged 50 - 59 with any 2 of the following:
- Cause of death is cerebral vascular accident
- Pre existing hypertension
- Terminal serum creatinine > 1.5 mg / dL
Case reports
- 4 cases of living donor renal transplant with incidental renal cell carcinoma from donor allograft (Transplant International 2015;28:1126)
- Donor monoclonal gammopathy and lymphoproliferative disorders in solid organ transplant recipients (Am J Transplant 2016;16:2676)
- Donor kidneys with miliary papillary renal cell neoplasia: the role of the pathologist in determining suitability for transplantation (Ann Transplant 2014;19:362)
Treatment
- A decision to implant or discard may be based on the frozen section analysis
Gross description
- Wedge or needle biopsy
Microscopic (histologic) description
-
Recommended microscopic findings to report: (adapted from Am J Transplant 2017;17:140)
- Periglomerular sclerosis and FSGS should be recorded under other glomerular findings
- Artery: vessel with internal elastic lamina OR diameter greater than one third the diameter of a typical glomerulus cut in the median plane OR a vessel with 3 or more layers of smooth muscle
- # glomeruli, # and % of global glomerulosclerosis have good reproducibility
- In most cases, tubular atrophy, interstitial fibrosis, and nonspecific interstitial inflammation are seen together
- Interstitial inflammation and tubular atrophy are often easier to see than fibrosis on frozen sections
- Reproducibility is fair for interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy, interstitial inflammation, and arteriosclerosis
- Assessment of interstitial fibrosis and arteriolar hyalinosis is compromised by freeze artifact
| Type of specimen (wedge or core biopsy) | |
| GLOMERULAR FINDINGS | |
| Number of glomeruli | |
| Number of globally sclerosed glomeruli | |
| Percentage of global glomerulosclerosis | |
| Other glomerular findings | |
| TUBULOINTERSTITIAL FINDINGS | |
| Tubular atrophy, interstitial fibrosis, non-specific interstitial inflammation | |
| VASCULAR FINDINGS | |
| Number of arteries | |
| Arterial intimal fibrosis | |
| Arteriolar hyalinosis | |
| OTHER FINDINGS | |
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Nicole K. Andeen, M.D.
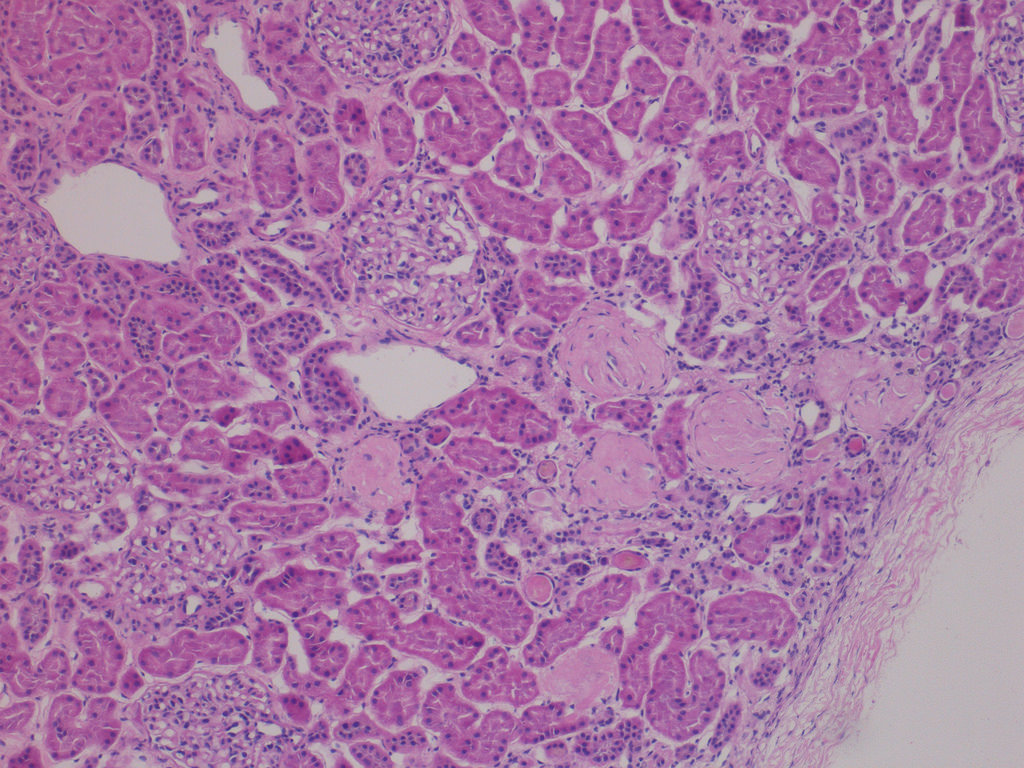
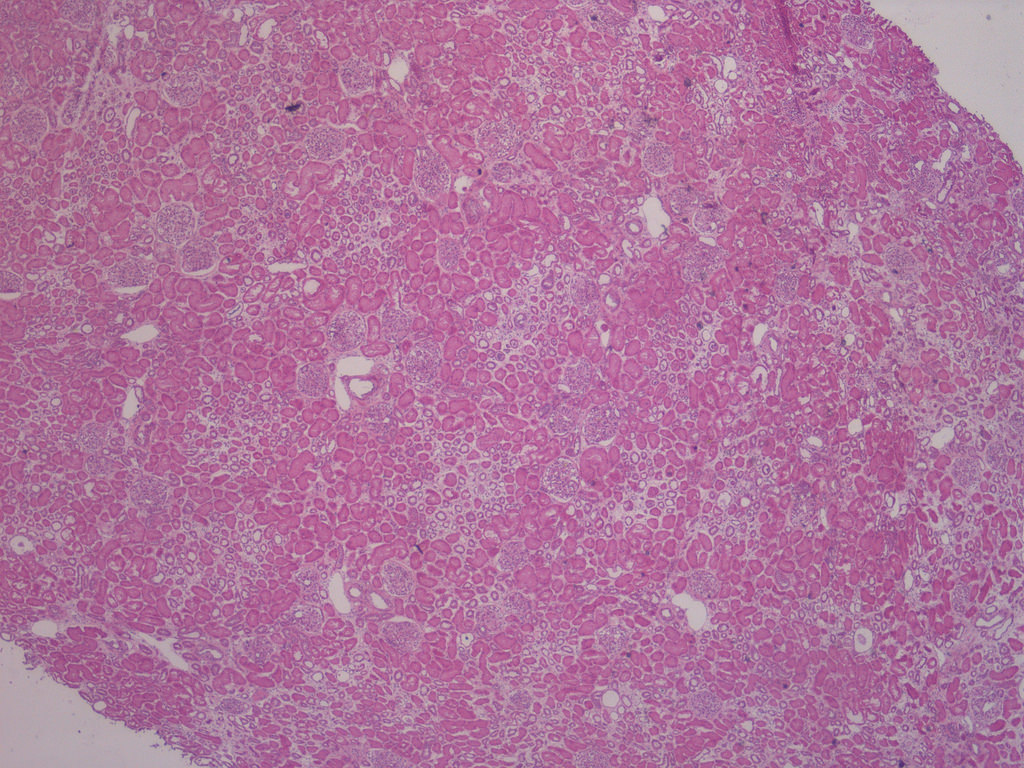
Case 1:
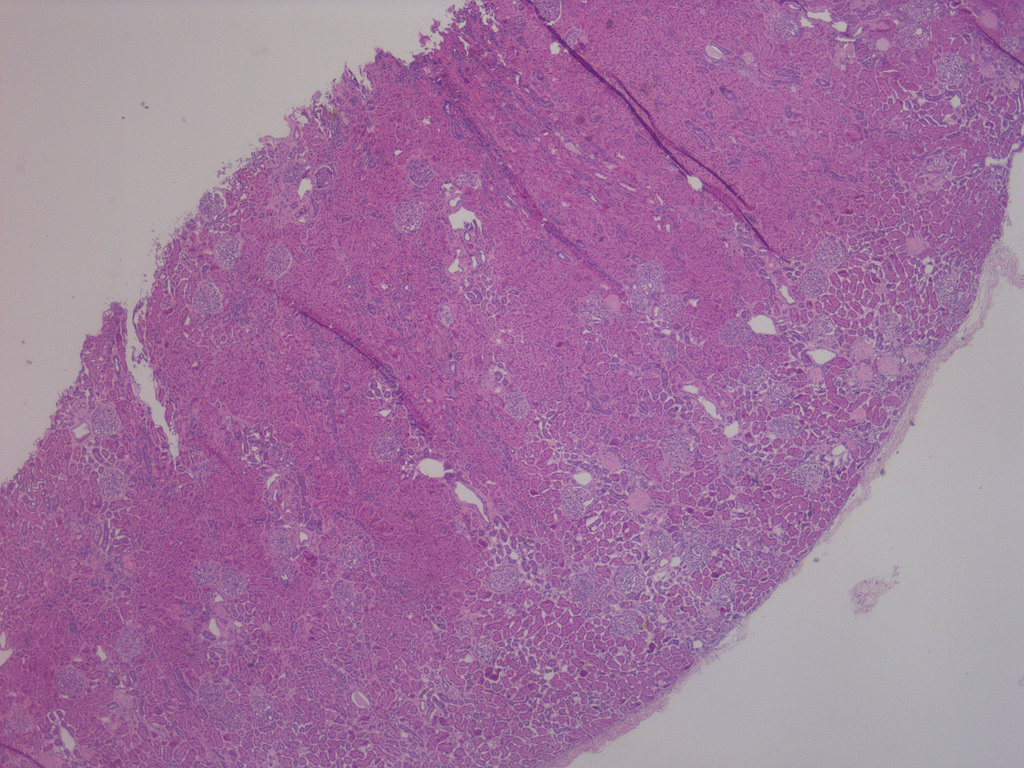
Low power with focal global GS
predominantly in subcapsular
region and patchy tubular atrophy
and IF (H&E perm from FS)
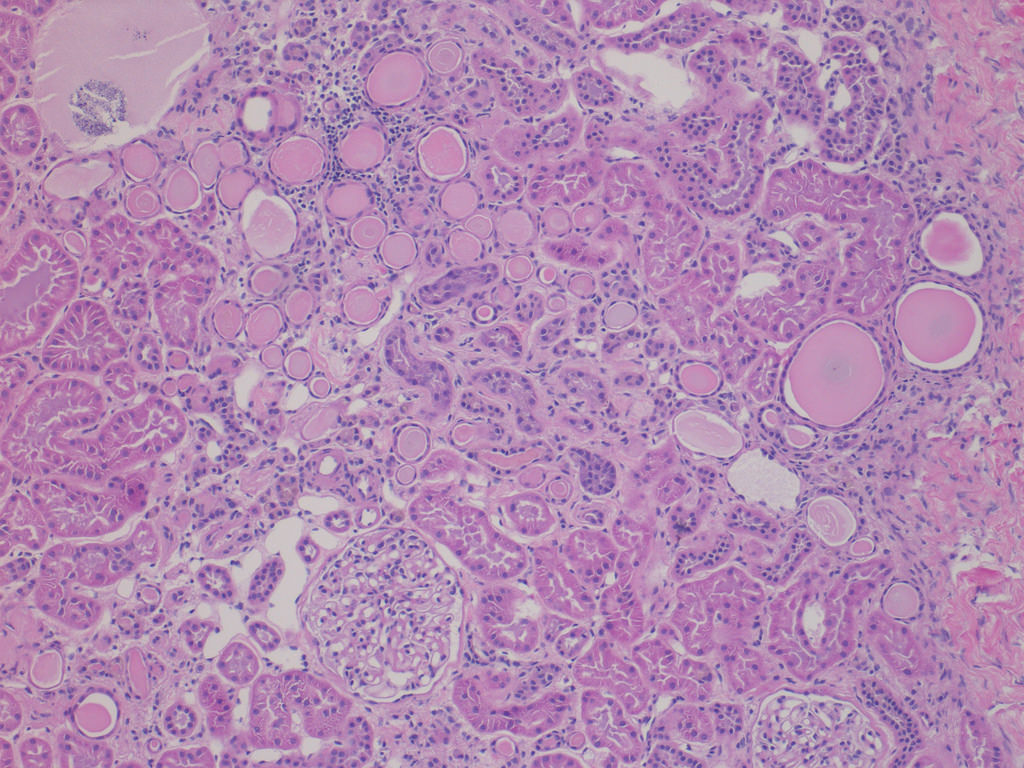
Case 2:
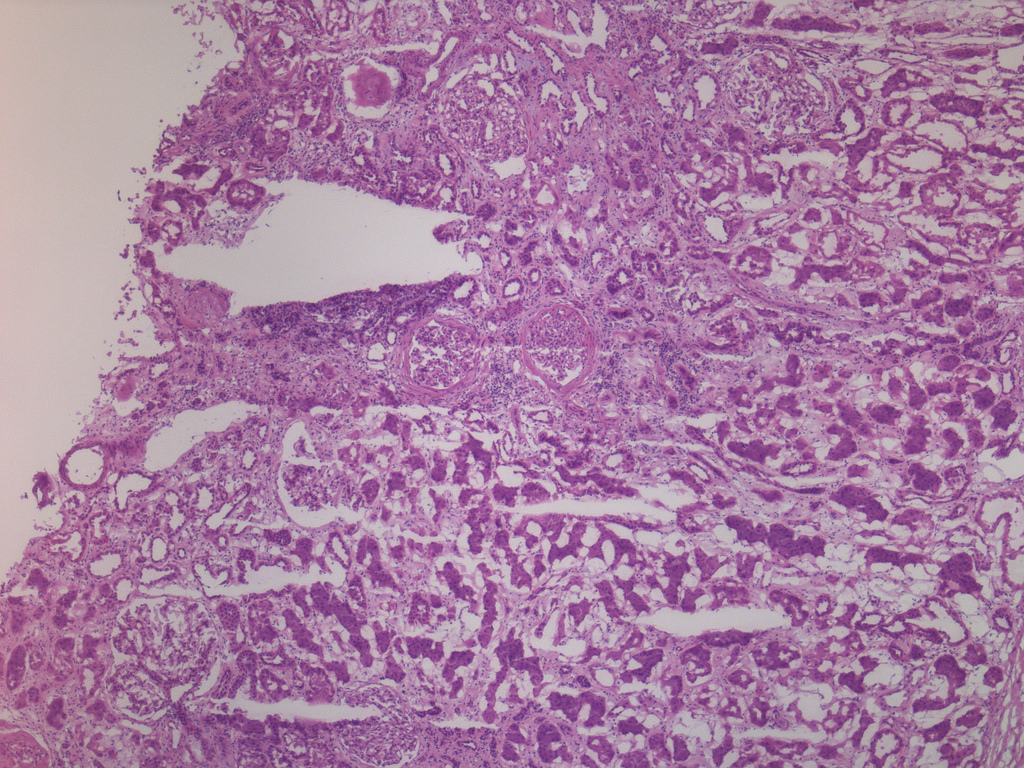
Focal global GS, ischemic glomeruli
with periglomerular fibrosis, adjacent
tubular atrophy, IF and nonspecific
interstitial inflammatory infiltrate (FS)
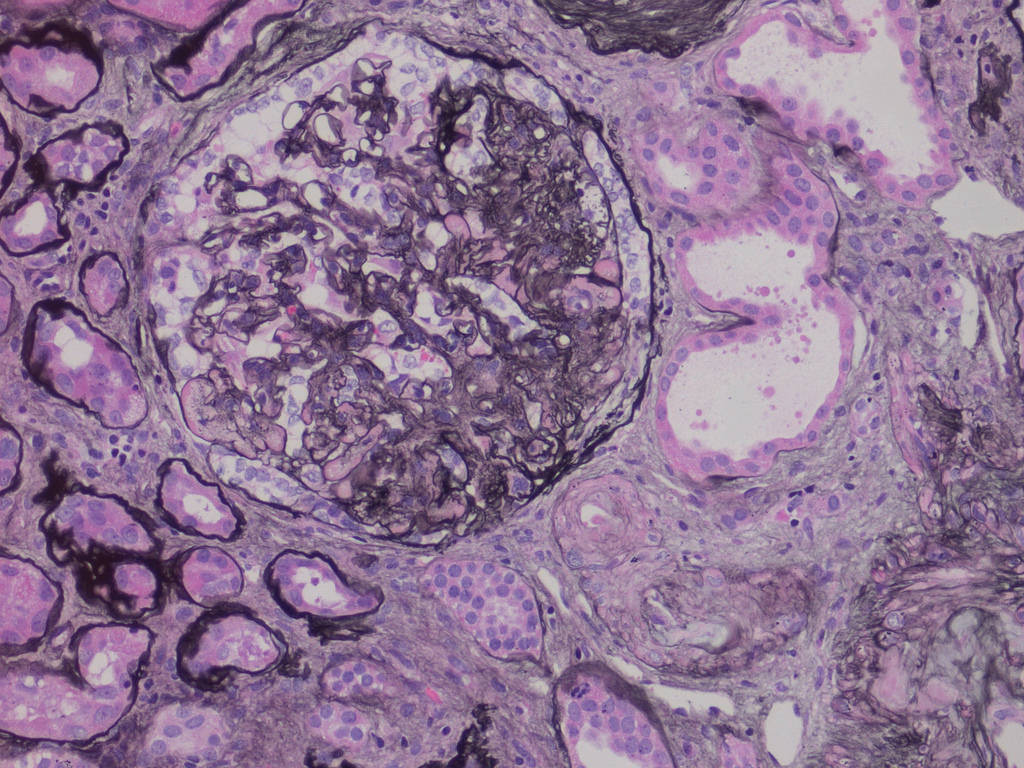
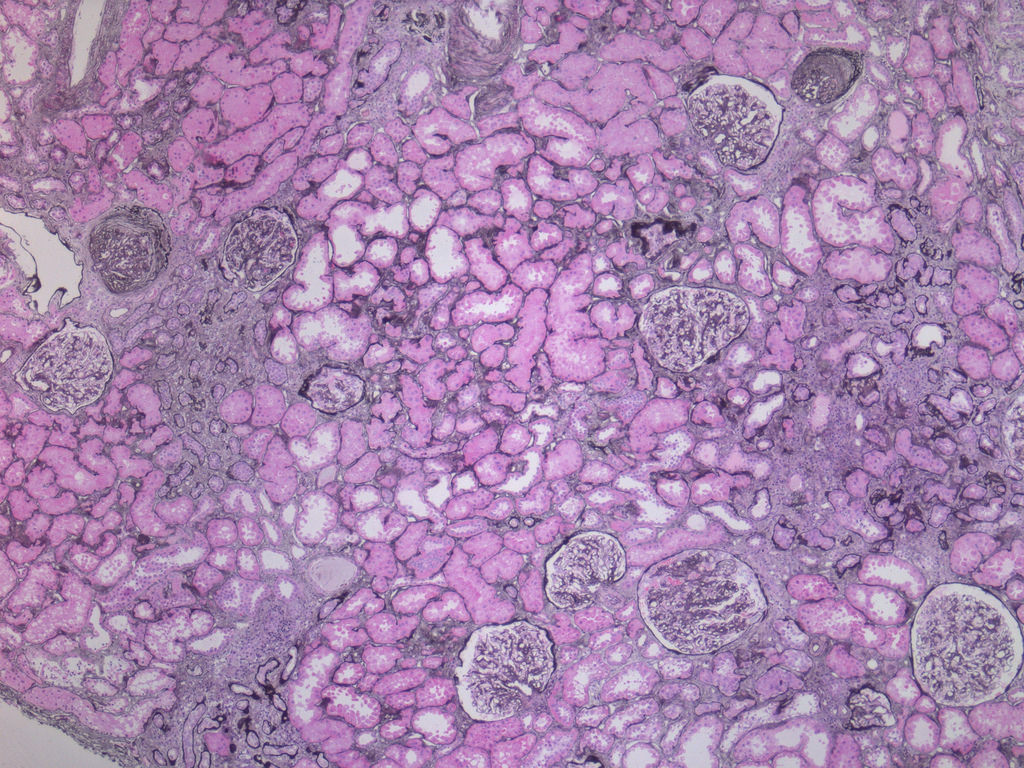
Focal segmental GS, adjacent
arteriolar hyalinosis, tubular atrophy
and IF (perm, Jones silver stain)
Note: FS = frozen section, GS = glomerulosclerosis, IF = interstitial fibrosis, perm = permanent section
Immunohistochemistry & special stains
- On permanent sections, a basement membrane stain (Jones silver, PAS), and thin sections (2 microns) aid in evaluation of potential underlying donor disease (FSGS, diabetes)
Additional references