Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Immunofluorescence description | Positive stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Genetics | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2 | Practice question #3 | Practice answer #3Cite this page: Cazzaniga G, L'Imperio V. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis-general. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneyfsgs.html. Accessed August 24th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Group of podocytopathies with different etiologies presenting with focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) along with nephrotic or subnephrotic proteinuria (Front Med (Lausanne) 2020;7:604961)
- Podocytes are the principal target of the lesions, leading to the characteristic sclerotic pattern involving part (segmental) of some (focal) glomeruli (Nephron 2020;144:413)
Essential features
- FSGS is a glomerular disease characterized by segmental and focal sclerosis of the tuft in the absence of underlying immune complex mediated disease
- Patients generally present with nephrotic or subnephrotic proteinuria
- Primary, genetic and secondary / maladaptive forms are recognized
- Distinction should be made between the nonimmune complex mediated disease (FSGS) and the pattern of injury (segmental and focal sclerosis) due to other underlying glomerular conditions (e.g., immune complexes)
Terminology
- Often abbreviated as focal sclerosis or FSGS (Nephrol Dial Transplant 2015;30:375)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: N04.1 - nephrotic syndrome with focal and segmental glomerular lesions
Epidemiology
- Difficult to establish due to marked geographical and racial differences (Am J Kidney Dis 2016;68:533)
- FSGS is one of the leading cause of end stage renal disease (ESRD), with an increasing incidence rate, likely due to improved recognition and detection of the entity (Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2017;12:502)
- Incidence of FSGS is ~7 per 1 million, with a prevalence of 4% (Am J Kidney Dis 2004;44:815)
- Typically, idiopathic FSGS is seen in patients aged 18 - 45; however, no age group is exempt (StatPearls: Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis [Accessed 25 April 2023])
- Incidence of FSGS is 3 - 7 times higher in young African American men than in European Americans (Kidney Int 2009;75:736)
Sites
- Kidney - glomerular disease
Pathophysiology
- FSGS is considered a podocytopathy, which is characterized by damage directed against the podocyte causing foot process effacement of different extension (J Pathol Transl Med 2016;50:405)
- Different mechanisms have been advocated for its development, starting from inherited alterations to structural podocyte genes, to circulating factors (e.g., cytokines) and mechanical stressful conditions (e.g., hypertension and obesity) (Biomed Res Int 2016;2016:1630365)
- In genetic forms, mutation to genes encoding for proteins with structural and signaling function either of the podocyte or glomerular basement membranes (GBM) causes disruption of the glomerular filtration barrier (Clin Kidney J 2018;11:179)
- Autoimmunity is linked to the observation of several antibodies in the serum of patients with minimal change disease (MCD) / primary FSGS, such as antinephrin, antiannexin A2 and anti-UCHL1 antibodies, suggesting a link / progression between MCD and FSGS (Front Immunol 2022;13:985925)
- Maladaptive forms of secondary FSGS ensue from a reduction in the number of functioning nephrons or from a normal nephron population subjected to abnormal stress (J Am Soc Nephrol 2017;28:2825)
- Other forms of secondary FSGS include virus associated FSGS and drug induced FSGS, which typically improve on resolution of the infection or cessation of the drug (Expert Opin Drug Saf 2006;5:95, Clin Kidney J 2013;6:1)
- These mechanisms lead to progressive podocyte loss and podocytopenia, increased nonselective filtration flow through bare areas of GBM, eventual collapse and occlusion of capillary loops on bare areas of GBM, disruption of glomerular tuft and adhesion to Bowman capsule (Biomed Res Int 2016;2016:1630365)
Etiology
- Recently proposed clinicopathological classification divided FSGS based on etiology into 3 categories
- Primary FSGS
- Secondary FSGS
- Genetic FSGS
- In primary FSGS, circulating permeability factors such as soluble urokinase receptor (suPAR), cardiotrophin-like cytokine 1 and angiopoietin-like 4 (Angptl4) have been proposed as the initiating factors of podocyte injury in primary FSGS (Nat Rev Nephrol 2016;12:768)
- Recent description of autoantibodies (e.g., antinephrin) in patients with nephrotic syndrome, especially in MCD forms, suggested an autoimmune etiology for these forms, adding evidences to the link of MCD and primary FSGS (J Am Soc Nephrol 2022;33:238)
- In secondary FSGS, different etiologies are recognized that either cause an excessive stress to the glomerular filtration barrier (maladaptive) or cause podocyte damage
- Maladaptive forms can be due to systemic hypertension, obesity, increased lean body mass, renal vaso-occlusive disease, cyanotic congenital heart disease, sickle cell anemia, reduced number of functioning nephrons (e.g., unilateral renal agenesis, renal dysplasia, oligomeganephronia, glycogen storage disease, low birth weight) (Biomed Res Int 2016;2016:1630365, J Am Soc Nephrol 2018;29:759)
- Infection associated forms have been described in association with HIV (established), CMV (probably), parvovirus B19 (possibly), EBV (possibly), HCV (possibly), hemophagocytic syndrome (possibly), COVID-19 (established) (Biomed Res Int 2016;2016:7351964)
- Drug induced forms are secondary to pamidronate, direct acting antiviral therapy (ledipasvir, sofosbuvir), mTOR inhibitors, calcineurin inhibitors, anthracyclines, heroin (adulterants), lithium, interferon, anabolic steroids (Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2015;10:1291)
- In genetic FSGS, > 50 genes have been described as potential sites of mutation responsible for monogenic forms of FSGS
- > 90% of childhood and adolescence onset cases have mutations involving a limited number of genes: NPHS1, NPHS2, WT1, LAMB2, PLCE1, COL4A5 and SCARB2 (Clin Kidney J 2018;11:179)
- Genetic predisposing factor for the development of FSGS, especially in African American ethnicity, is recognized in APOL1 polymorphisms, for which the trigger of environmental factors (e.g., viral infection) most frequently leads to collapsing forms (J Am Soc Nephrol 2011;22:2129)
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Proteinuria is the most common presenting feature of FSGS (Biomed Res Int 2016;2016:4632768)
- In patients with primary FSGS, full nephrotic syndrome is very common and the degree of renal insufficiency depends on the chronic changes of the renal parenchyma (Biomed Res Int 2016;2016:4632768)
- Tip variant FSGS typically presents with sudden onset nephrotic syndrome with anasarca and weight gain (Am J Kidney Dis 2020;75:955)
- In secondary FSGS, patients tend to have subnephrotic range proteinuria at presentation (although nephrotic range proteinuria will develop in the majority over time) in the absence of edema, hypoproteinemia or hypoalbuminemia (Biomed Res Int 2016;2016:4632768)
Diagnosis
- Extensive history collection and large panel of laboratory test (including autoimmune and viral serology, serum and urine protein electrophoresis and immunofixation) should be done to exclude other causes of proteinuria (Nephron 2020;144:413)
- Presentation (sudden onset of nephrotic syndrome or more subtle gradual changes) and associated medical conditions (infections, obesity, hypertension, etc.) help to make a distinction between primary and secondary FSGS (Nephron 2020;144:413)
- Biopsy is necessary to establish the diagnosis of FSGS and determine the subtype of FSGS (Nephron 2020;144:413)
- There is consensus on performing genetic tests in steroid resistant FSGS in patients with positive family history or extrarenal physical signs suggestive of a genetic disorder (Fabry disease, nail patella syndrome or Alport syndrome) (Nephron 2020;144:413)
- New markers such as suPAR have been proposed to diagnose and predict FSGS recurrence after transplantation and monitor treatment response in patients with primary FSGS (Biomed Res Int 2016;2016:4632768)
Laboratory
- Full nephrotic syndrome: proteinuria (> 3.5 g per 1.73 m² body surface area per day or > 40 mg per square meter body surface area per hour in children), hypoalbuminemia (< 2.5 g/dL), hyperlipidemia and edema (Kidney Int 2021;100:S1)
Radiology description
- Imaging studies are generally not helpful in assessing persons with nephrotic syndrome (Am Fam Physician 2009;80:1129)
Prognostic factors
- ~30 - 60% of patients will inexorably progress to end stage kidney disease (ESKD) over a 5 - 10 year period of observation (Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 2011;18:332)
- It can recur in 20 - 25% of patients who receive a kidney transplant (Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 2011;18:332)
- Tip variant exhibits a better outcome in terms of achieving remission, the collapsing variant is the worst one (BMC Nephrol 2014;15:52)
- Prognosis of collapsing FSGS is much worse in the Black population compared to the White population (StatPearls: Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis [Accessed 25 April 2023])
Case reports
- 23 year old man with rapid recurrence of FSGS after transplantation with graft reused in 78 year old man (Am J Kidney Dis 2021;78:897)
- 25 year old woman with INF2 mutation developing unusual FSGS (Kidney Int Rep 2022;7:2741)
- 46 year old woman with pembrolizumab induced FSGS (Medicine (Baltimore) 2021;100:e27546)
Treatment
- High dose oral glucocorticoids is the first line immunosuppressive treatment for primary FSGS (Kidney Int Rep 2022;7:2081)
- Immunosuppression should not be used in adults with FSGS of undetermined cause (FSGS-UC) or in those with secondary FSGS; renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) blockade may have a role (Kidney Int 2021;100:S1)
- For adults with steroid resistant primary FSGS, cyclosporine or tacrolimus may be given for ≥ 6 months rather than continuing with glucocorticoid monotherapy or not treating (Kidney Int 2021;100:S1)
- Limited role for plasmapheresis (Nephron 2020;144:413)
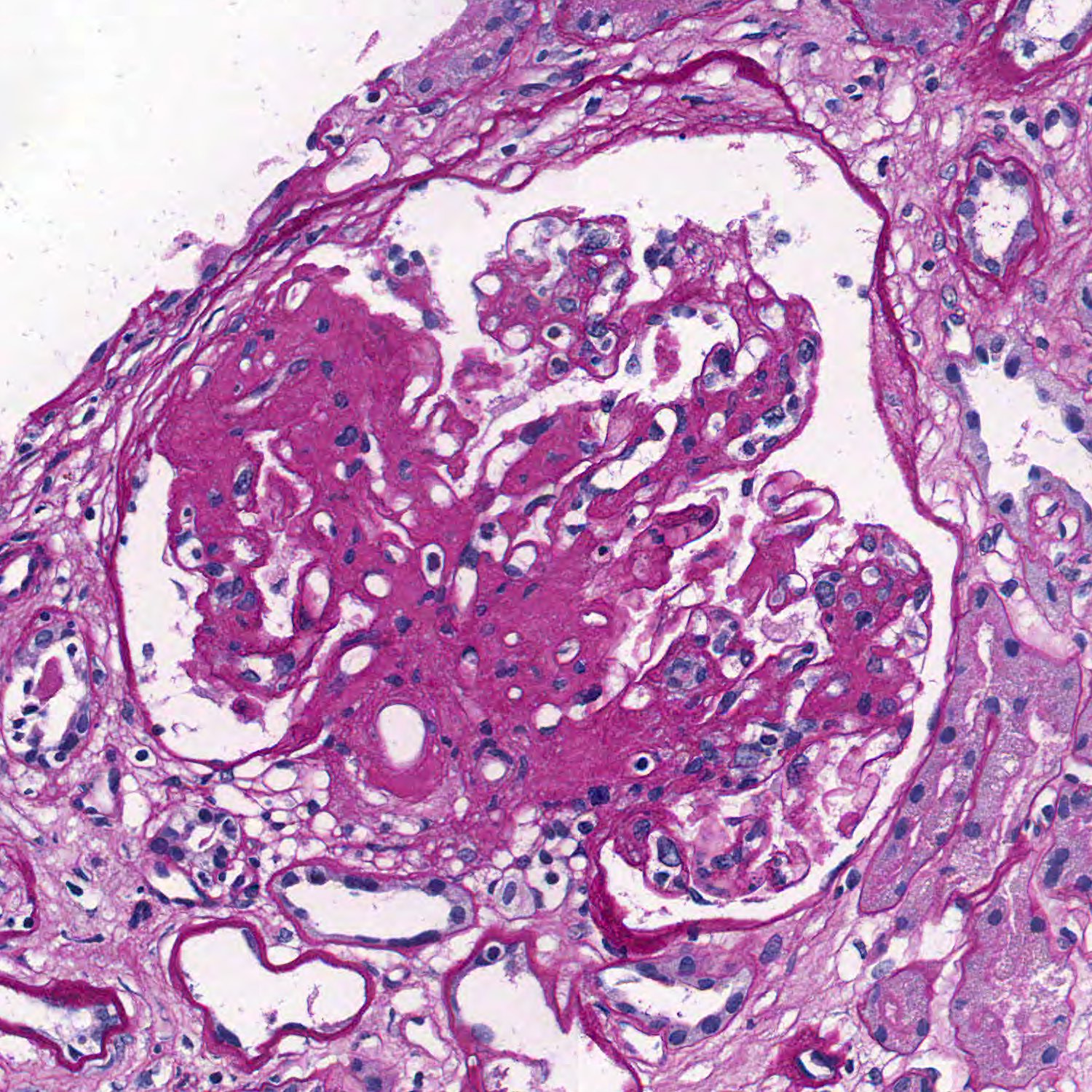
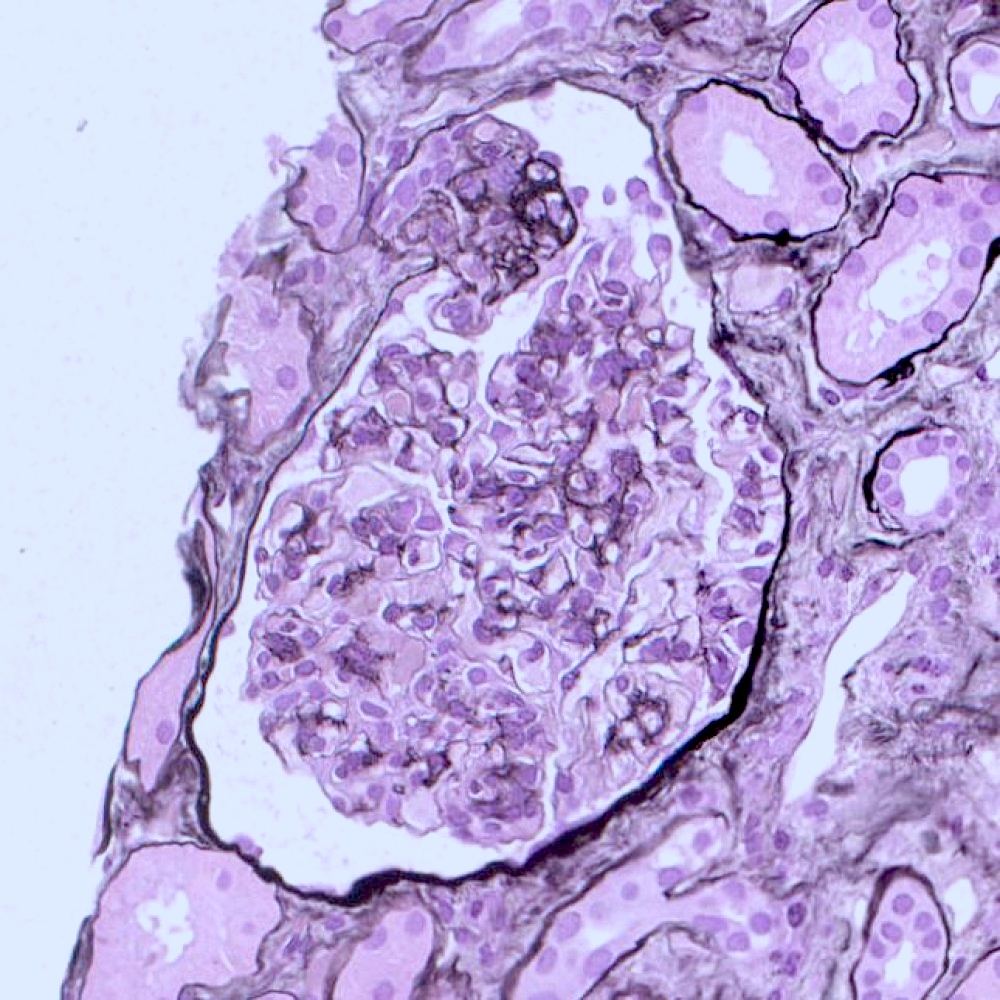
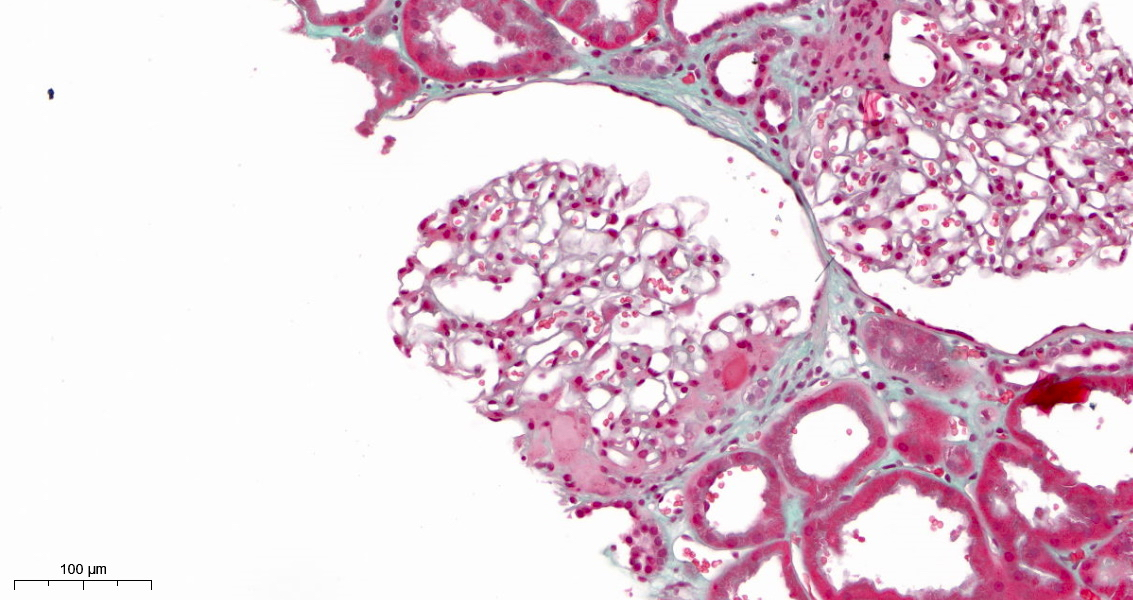
Microscopic (histologic) description
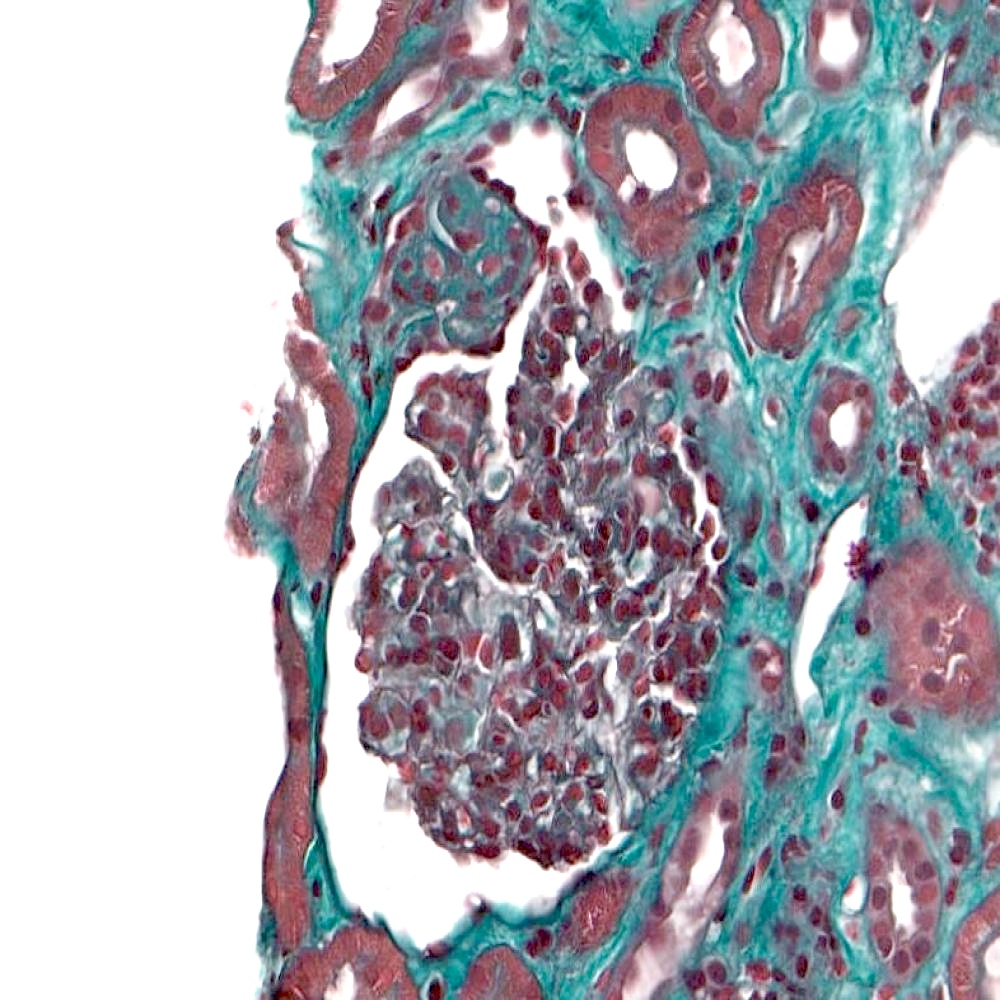
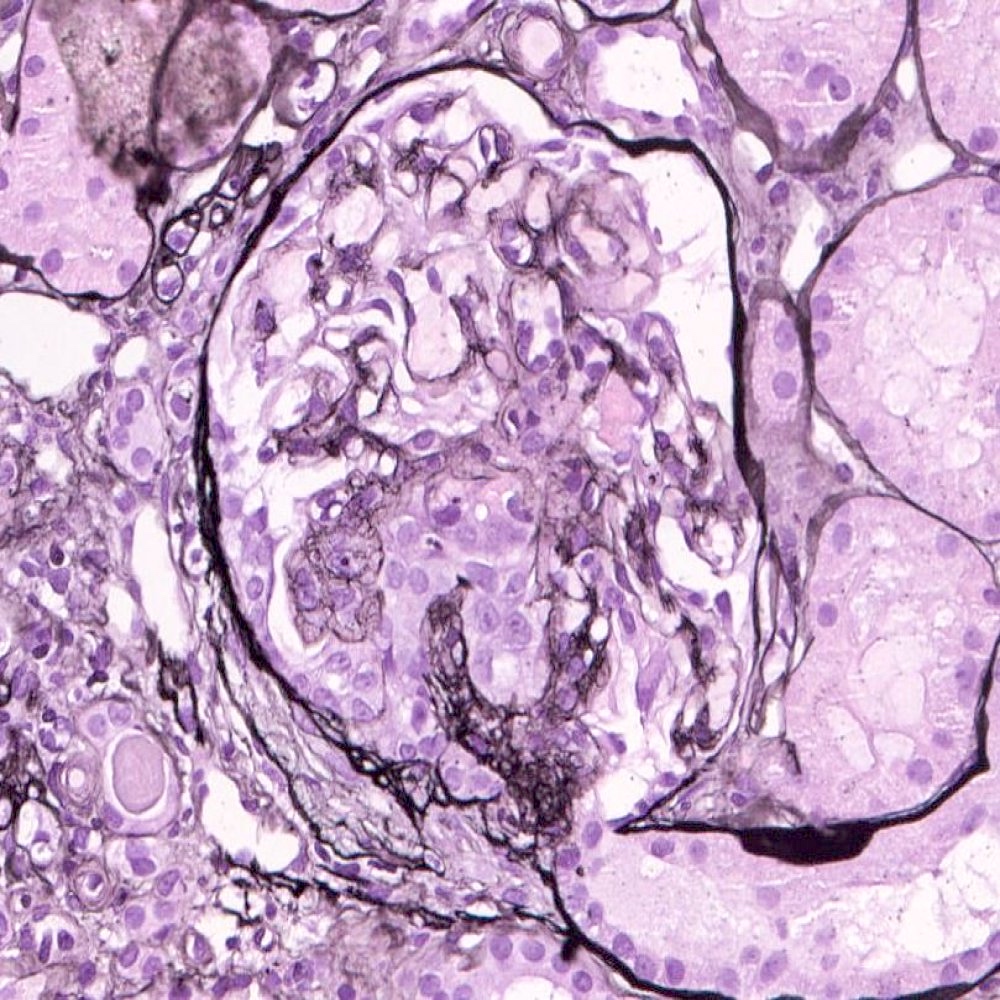
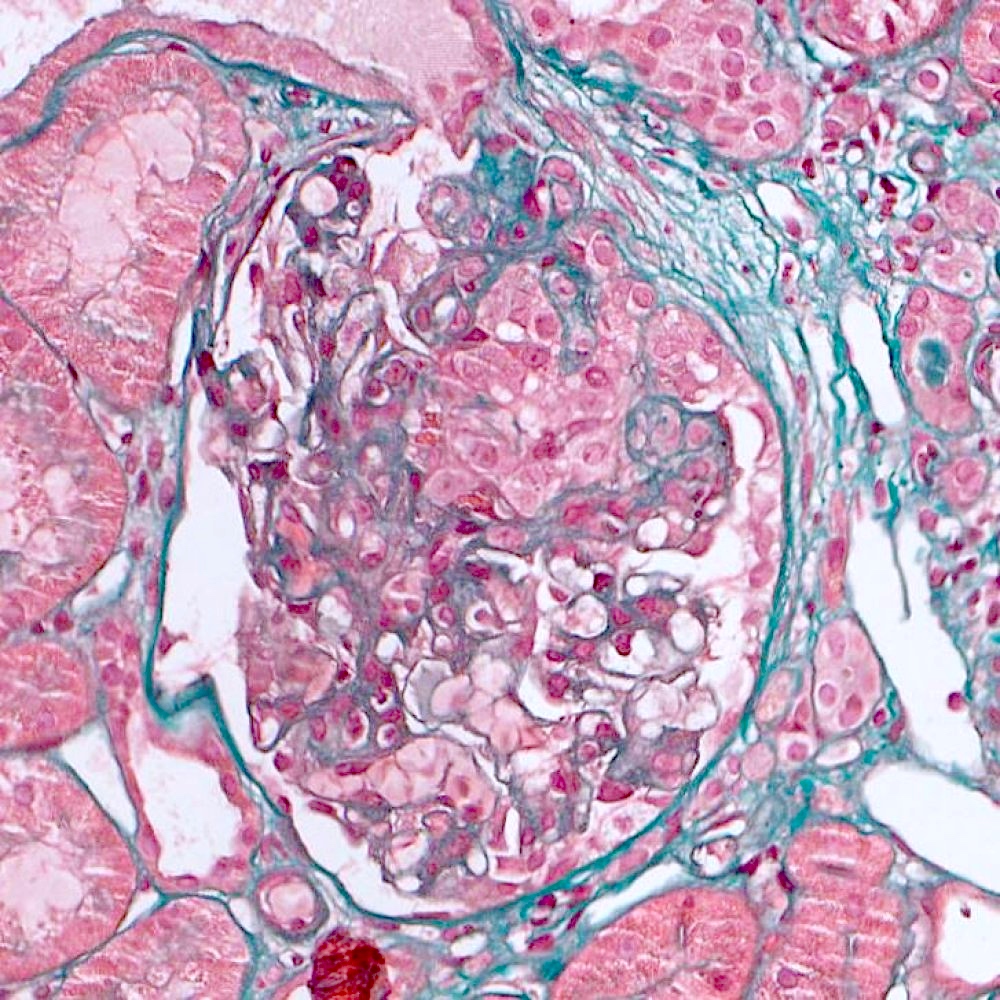
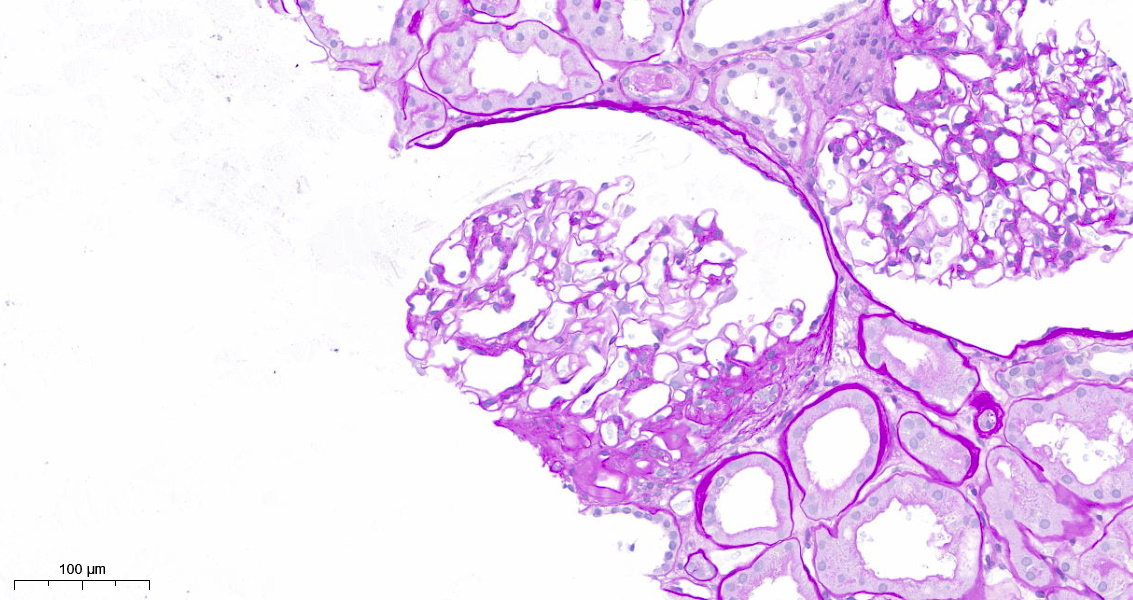
- FSGS is characterized by focal (involving some but not all glomeruli) and segmental (< 100% glomerular tuft involvement with some residual patent glomerular capillaries) sclerosis of glomeruli without underlying immune complex disease (Nephrol Dial Transplant 2020;35:1219)
- Based on differences in the sclerotic lesion, a 5 tiered classification system (Columbia classification) was proposed in 2004 (Am J Kidney Dis 2004;43:368)
- Collapsing variant: at least 1 glomerulus with segmental or global collapse and overlying podocyte hypertrophy and hyperplasia
- Tip variant
- At least 1 segmental lesion involving the tip domain (outer 25% of tuft next to origin of proximal tubule)
- Tubular pole must be identified in the defining lesion
- Lesion must have either an adhesion or confluence of podocytes with parietal or tubular cells at the tubular lumen or neck
- Tip lesion may be cellular or sclerosing
- Cellular variant: at least 1 glomerulus with segmental endocapillary hypercellularity occluding lumina, with or without foam cells and karyorrhexis
- Perihilar variant: at least 1 glomerulus with perihilar hyalinosis, with or without sclerosis in > 50% of glomeruli
- FSGS, not otherwise specified (NOS): at least 1 glomerulus with segmental increase in matrix obliterating the capillary lumina; there may be segmental glomerular capillary wall collapse without overlying podocyte hyperplasia
- Glomerulosclerosis is accompanied by tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis with interstitial lymphocytes, proportional to the degree of scarring in the glomerulus (Am J Kidney Dis 2015;66:e1)
- In collapsing glomerulopathy, tubular lesions are disproportionately severe (Am J Kidney Dis 2015;66:e1)
- Cases of FSGS associated with severe tubulointerstitial lesions were also reported in patients taking cocaine, heroin, calcineurin inhibitors or lithium (Front Med (Lausanne) 2020;7:604961)
- Perihilar variant is generally associated with secondary maladaptive FSGS (Nat Rev Nephrol 2015;11:76)
- Cellular variant might be an early abnormality revealed by light microscopy for recurrent FSGS in a kidney transplant (Am J Kidney Dis 2015;66:e7)
- Etiology and pathogenesis of tip lesions has not yet been defined
- Injury to podocytes by turbulent flow at the tubular pole has been proposed (Am J Kidney Dis 2015;66:e5)
- Collapsing variant is commonly present in HIV associated nephropathy (HIVAN), COVID-19 associated nephropathy (COVAN) and APOL1 FSGS
- Other etiologies include infection, autoimmune disease, malignancy, drugs (bisphosphonates, interferon, anabolic steroids, calcineurin inhibitors and mTOR inhibitors) and posttransplantation (J Nephropathol 2012;1:87)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Immunofluorescence description
- Immunofluorescence typically negative or shows nonspecific IgM and C3 trace staining in sclerotic areas (Am J Kidney Dis 2015;66:e1)
Positive stains
- Jones methenamine silver (JMS), periodic acid-Schiff (PAS): highlight glomerular architecture and sclerosis
- Further stains are not required and often not helpful in differential diagnosis
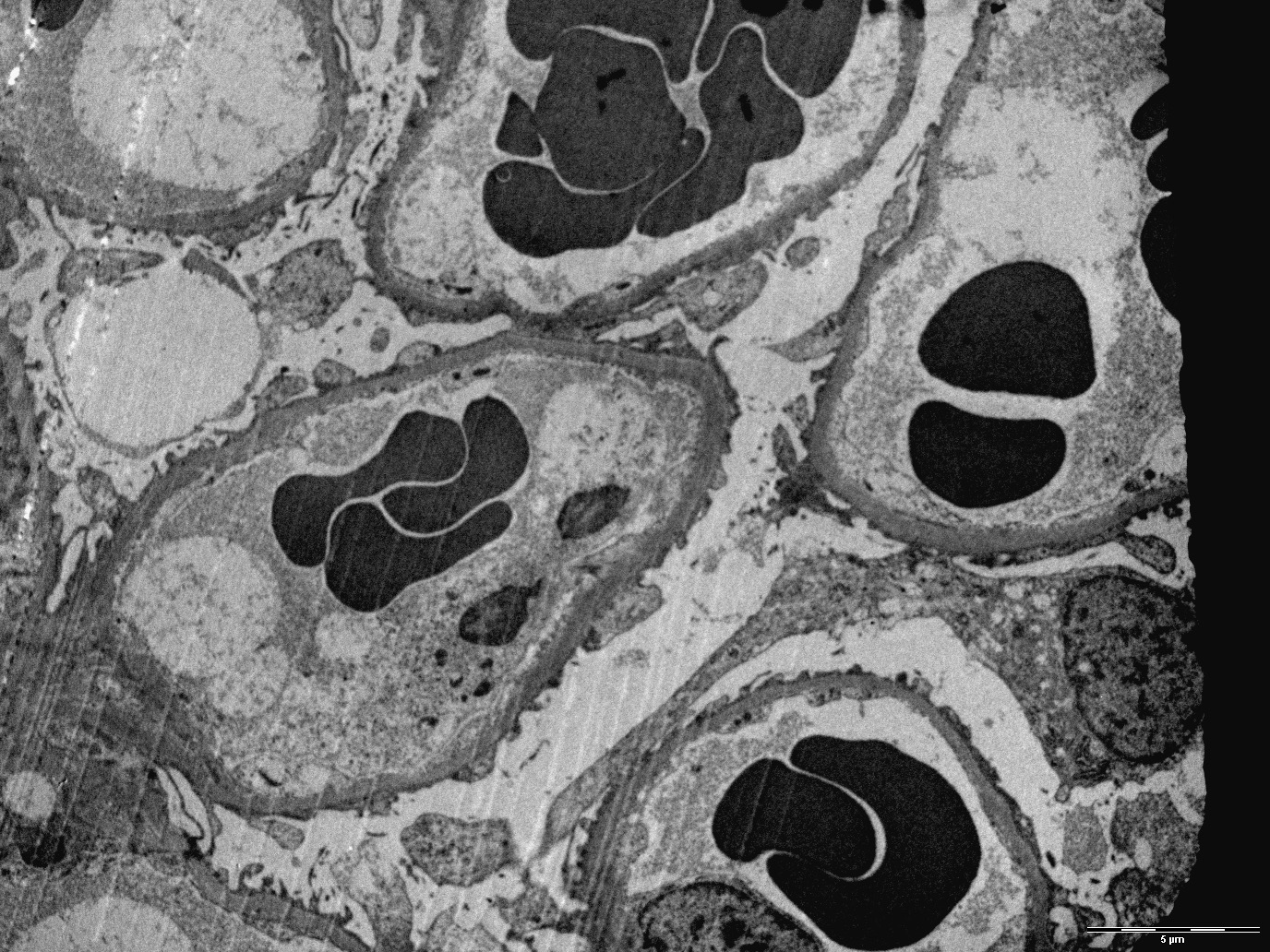
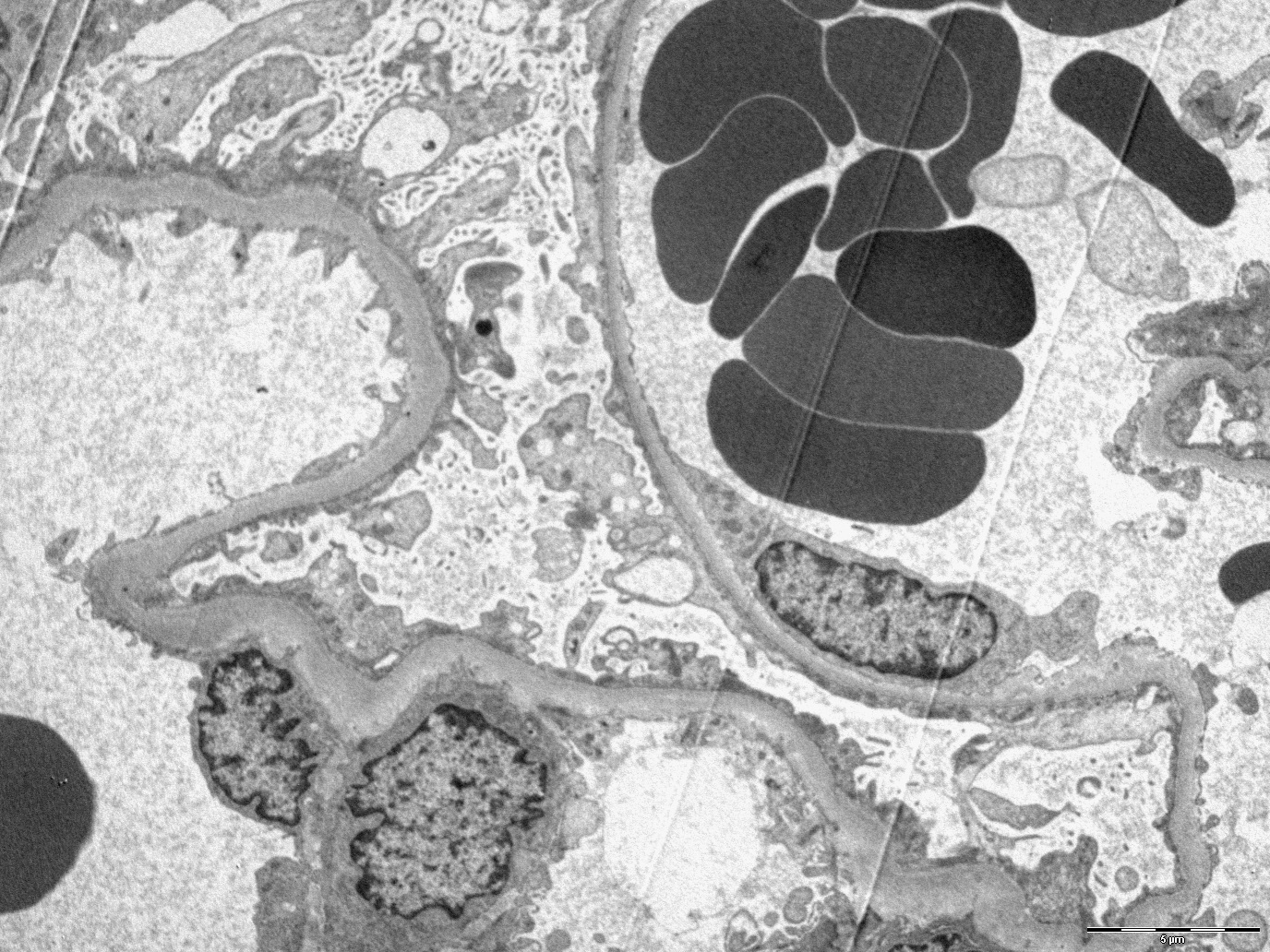
Electron microscopy description
- Due to its focal and segmental nature, diagnosis of FSGS could also be challenging on electron microscopy (Kidney Int 2008;74:1568)
- Podocyte injury including foot process effacement, microvillous transformation, detachment from the underlying GBM and cytoplasmic vacuolization (Kidney Int 2008;74:1568)
- Podocyte effacement in patients with FSGS secondary to maladaptive responses is less extended than in idiopathic FSGS (Kidney Int 2008;74:1568)
- Thick GBM in cases of maladaptive FSGS, thin GBM or lamellated appearance in cases of genetically determined FSGS correlated with Alport syndrome (Kidney Int 2008;74:1568)
- Multiple foci of increased mesangial matrix volume, exceeding the width of 2 mesangial cell nuclei (Kidney Int 2008;74:1568)
- Mild increase in the number of podocytes (Ultrastruct Pathol 2019;43:6)
Electron microscopy images
Genetics
- See Etiology
Sample pathology report
- Left kidney, needle core biopsy:
- Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis, NOS (see comment)
- Comment:
- Microscopic description: Expansion of the mesangial matrix resulting in 2 glomeruli in segmental sclerosis of the tuft with adhesion to Bowman capsule and satellite podocyte hyperplasia. Interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy involving ~10% of the cortex with slight interstitial lymphocytic infiltrate. No significant changes in the vascular structures.
- Immunofluorescence: Trace focal and segmental staining for IgM. Negative IgG, IgA, C3, C1q, kappa and lambda light chains.
- Electron microscopy: Extensive foot process effacement, microvillous transformation of the cytoplasm of podocytes. No electron dense deposits.
Differential diagnosis
- Minimal change disease (MCD):
- No remarkable modifications to the glomerular tuft, no detectable glomerular sclerosis
- Biopsies containing up to 10 glomeruli have a 35% chance of missing a segmental sclerosis involving 10% of the nephrons; this probability decreases to 12% in biopsies with 20 glomeruli (Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2017;12:502)
- Immune complex glomerulonephritis with sclerosis:
- Immunofluorescence shows glomerular deposits with distribution and composition that depends on the specific underlying immune complex glomerulonephritis
Practice question #1
Which of these focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) variants is considered the most favorable in terms of outcome?
- FSGS, cellular variant
- FSGS, collapsing variant
- FSGS, perihilar variant
- FSGS, tip variant
Practice answer #1
D. FSGS, tip variant.
The tip variant of FSGS is considered the most favorable in terms of outcome (BMC Nephrol 2014;15:52). Answer B is incorrect because the collapsing variant has a worse prognosis, especially in the Black population (StatPearls: Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis [Accessed 25 April 2023]). Answers C and D are incorrect because other variants show variable outcomes.
Comment Here
Reference: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis - general
Comment Here
Reference: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis - general
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2
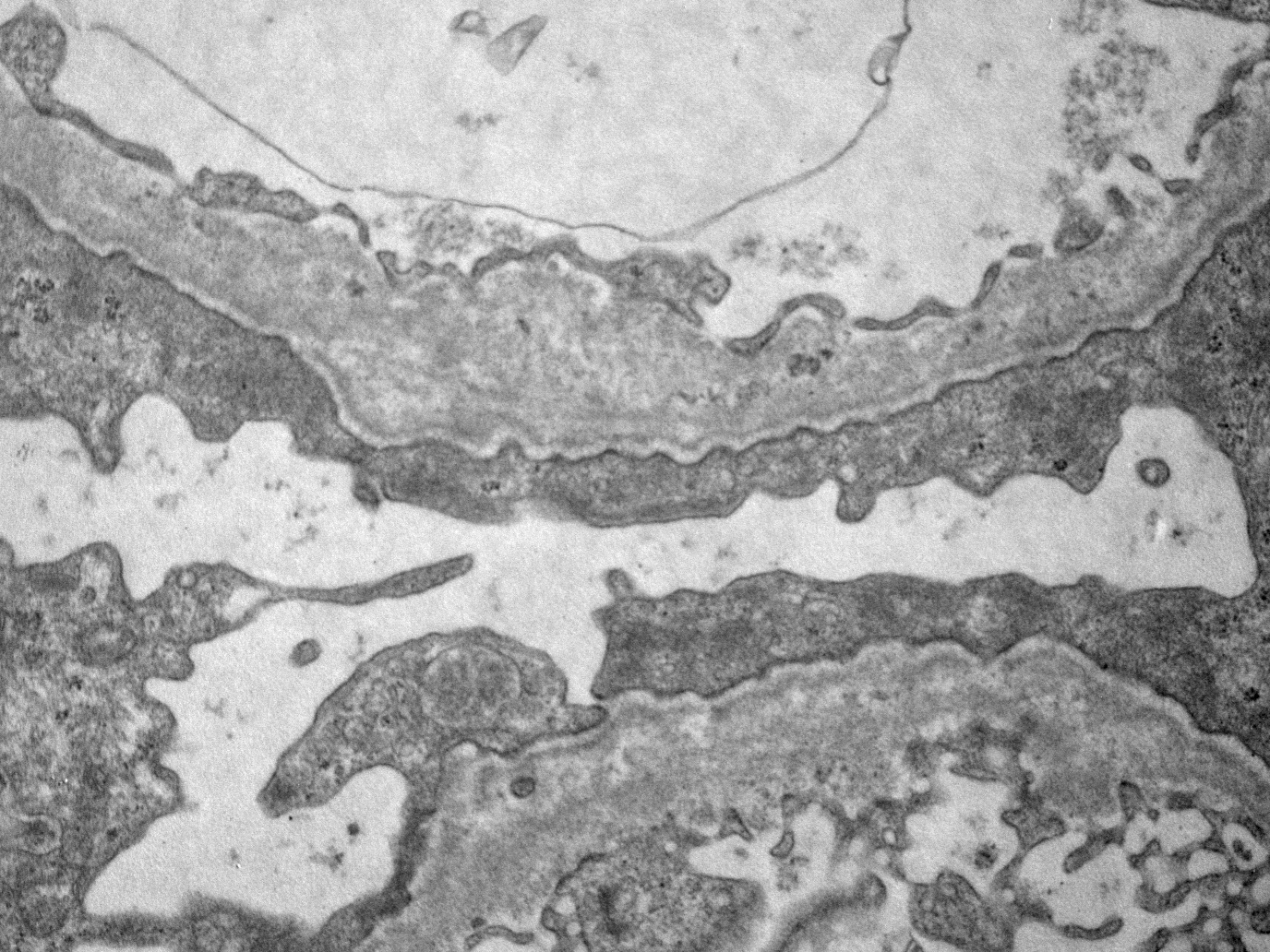
B. Podocyte effacement.
The electron micrograph shows a low power view of a glomerulus with extensive foot process effacement of podocytes along the capillary walls. Answer D is incorrect because subepithelial humps are haystack shaped electron dense deposits typical of infection related glomerulonephritis, not usually present in FSGS. Answer A is incorrect because microtubular structures are generally seen in cryoglobulin related glomerulonephritis within the deposits. Answer C is incorrect because subendothelial immune complex deposits can be seen between endothelial cells and GBM in a variety of immune complex glomerulonephritis (e.g., lupus nephritis).
Comment Here
Reference: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis - general
Comment Here
Reference: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis - general
Practice question #3
Practice answer #3
D. FSGS, tip variant.
FSGS, tip variant is characterized by at least 1 segmental lesion involving the tip domain (outer 25% of tuft next to origin of proximal tubule). Answer A is incorrect because the cellular variant has at least 1 glomerulus with segmental endocapillary hypercellularity occluding lumina, with or without foam cells and karyorrhexis. Answer B is incorrect because the collapsing variant has at least 1 glomerulus with segmental or global collapse and overlying podocyte hypertrophy and hyperplasia. Answer C is incorrect because the perihilar variant has at least 1 glomerulus with perihilar hyalinosis, with or without sclerosis in > 50% of glomeruli.
Comment Here
Reference: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis - general
Comment Here
Reference: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis - general