Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Gross anatomy - mediastinum | Embryology and anatomy - thymus | Physiology - thymus | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Laboratory | Gross description - thymus | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Videos | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Stringham N. Anatomy & thymus histology. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/mediastinumgeneral.html. Accessed May 13th, 2024.
Definition / general
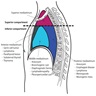
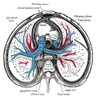
- Mediastinum is the central portion of the thoracic cavity (between the pleural cavities, from sternum to spine and thoracic inlet to diaphragm), which contains the heart, great vessels, esophagus, trachea and thymus as well many other vessels and neural components; it can be divided into 4 regions
- Thymus is a partially lobulated, encapsulated, primary lymphoid organ that plays a central role in the development of cell mediated immunity and T cell differentiation
Essential features
- Mediastinum is the centrally located portion of thorax, which notably contains the heart, aorta, vena cava, esophagus, trachea, thymus, thoracic duct, sympathetic trunk, phrenic and vagus nerves, internal thoracic arteries, azygos and hemiazygos veins
- Mediastinum can be divided into 4 regions: superior, anterior, middle and posterior
- Thymus is a partially lobulated, encapsulated, primary lymphoid organ that plays a central role in the development of cell mediated immunity and T cell differentiation
- Thymus is active before birth and in childhood; after puberty the cortex involutes and is replaced by adipose tissue
Terminology
- Mediastinal cavity
Gross anatomy - mediastinum
- Mediastinum is the anatomical compartment that runs the length of the thoracic cavity (longitudinally from the thoracic inlet to the diaphragm) and comprises the area between the lungs / pleura; it is further divided into 4 compartments
- Superior mediastinum
- Area inferior to the thoracic outlet (~first rib) and superior to the thoracic plane (sternal angle ventrally and the T4 - T5 junction dorsally)
- Contains the aortic arch (including brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid and left subclavian arteries), esophagus, trachea, thymus, phrenic and vagus nerves
- Anterior mediastinum
- Area that is ventral to anterior cardiac border and aortic root and dorsal to the body of the sternum
- Contains the internal thoracic arteries and transversus thoracis muscles
- Middle mediastinum
- Area inferior to the thoracic plane, medial to the pleural sacs and superior to the diaphragm
- Contains the heart, ascending aorta and superior vena cava, pulmonary trunk and veins, trachea and bronchi
- Posterior mediastinum
- Area ventral to the posterior thoracic body wall and dorsal to the posterior surface of the heart (base)
- Contains the descending aorta, esophagus, thoracic duct, sympathetic trunk, azygos and hemiazygos veins
- Superior mediastinum
- References: Thorac Surg Clin 2011;21:251, Ann Ital Chir 2007;78:351, StatPearls: Anatomy, Thorax, Heart and Pericardial Cavity [Accessed 26 February 2024], StatPearls: Anatomy, Thorax, Mediastinum [Accessed 26 February 2024], Mediastinum 2023;7:14
Embryology and anatomy - thymus
- Thymus arises from the endoderm of the third and fourth branchial clefts (Br Med J 1963;2:459)
- At week 6, it develops as 2 separate lobes and at week 8, the lobes migrate to fuse in the anterior superior mediastinum; however, the blood supply, lymphatic drainage and innervation of each lobe remain separate
- At week 10, lobules begin to form as a result of the migration of hematopoietic cells from the liver
- Differentiation into cortex and medulla occurs at 14 - 16 weeks
- Thymus reaches maturity in utero
- Ratio of thymus to body weight is its greatest before birth; however, the thymus reaches its maximum weight just before puberty, before undergoing involution
- Mature thymus
- Located in the anterior superior mediastinum, retrosternally
- Bilobed organ with a cortex and medulla
- It is supplied with blood via the internal thoracic and inferior thyroid arteries
- Has no afferent lymphatic vessels
- Has a blood thymus barrier that prevents the transport of macromolecules from the vasculature into the thymic cortical parenchyma
- Involution of the thymus involves its cellular structure being replaced with adipose tissue; this also is related to a decrease in function
- Thymic remnants may be present in adult prepericardial or retrocarinal fat
- References: StatPearls: Anatomy, Head and Neck - Blood Thymus Barrier [Accessed 26 February 2024], Radiographics 2006;26:335
Physiology - thymus
- Primary organ responsible for the production and maturation of lymphocytes and development of the immune system (Adv Clin Exp Med 2016;25:369)
- It has an important role in development of cell mediated immunity and T cell differentiation
- Positive selection of self antigen recognizing T cells induces apoptosis; surviving T cells do not react with self antigen
- Negative selection of lymphocytes that have high affinity binding with the antigen; these also undergo apoptosis
- Lymphocytes that pass both positive and negative selection can travel outside the thymus, where they are activated by bacteria, viruses or other foreign antigens
- In thymus, 95% of all T cells undergo apoptosis due to their ability to recognize self antigen presented by the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) system
- Clonal selection / activation of only those cells that can recognize antigen; this leads to secretion of antibodies, mitosis of T cells and a resulting increase in T cells that recognize the antigen to a pathogen
- Once the pathogen is eliminated, most of the activated cells undergo apoptosis, with a few surviving as memory cells
- Thymic involution (Geroscience 2021;43:1369, Adv Clin Exp Med 2016;25:369, Z Gerontol Geriatr 2000;33:341)
- Normal age related loss of organized architecture with increased adipose cell deposition, resulting in a replacement of functional cells with fat throughout the organ
- Scarcity of T cell precursors from bone marrow and effects of circulating cytokines and hormones (e.g., hypothesized sex hormone dependent involution) contribute to involution
- Involution is thought to contribute to immunosenescence, which increases susceptibility to neoplasia, infection and autoimmune diseases
- Undernutrition / malnutrition can affect thymic microenvironment and immune function (Front Nutr 2022;9:948488)
- Early programming of thymus, sexual dimorphism, specific T cell progenitors and thymic microenvironment may influence long term immunity and determine progression of involution at older ages (Aging Dis 2012;3:280)
- Thymocytes in people > 60 years old have higher levels of Ki67 and p53 (Bull Exp Biol Med 2011;151:460)
- ABH histoblood group antigens are heterogenically expressed in the epithelial cells and lymphocytes of normal thymus and may become immunoreactive in myasthenia gravis and thymoma (APMIS 2006;114:669)
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Superior mediastinum: lymphoma, thyroid lesions, parathyroid adenoma
- Thymus: thymomas, thymic cyst
- Myasthenia gravis: thymic hyperplasia, thymoma
- Anterior mediastinum: thymic epithelial tumors and cysts, substernal thyroid, germ cell neoplasms, lymphoproliferative lesions, lymphoma, retrosternal thyroid glandular proliferations, parathyroid lesions, aorticopulmonary type paragangliomas, lymphangioma, hemangioma, lipoma (JBR-BTR 2012;95:281)
- Middle mediastinum: aneurysm, pleuropericardial cyst, bronchogenic cyst, diaphragmatic hernia, lymphadenopathy
- Posterior mediastinum: neurogenic masses (schwannoma, neurofibroma, ganglioneuroma, ganglioneuroblastoma, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor, neuroblastoma, paraganglioma), meningocele, lymphoma, esophageal disease, aneurysm
- Superior vena cava syndrome: partial blockage or compression of the superior vena cava; affects superior and middle mediastinum
- Mediastinal fibrosis / sclerosing mediastinitis: benign, progressive proliferation of fibrous tissue within the mediastinum (BJR Case Rep 2016;2:20150274)
Laboratory
- Percutaneous needle biopsy with imaging guidance allows for extrapleural access (Radiographics 2005;25:763)
- Parasternal approach for anterior or middle mediastinal lesions
- Paravertebral approach for subcarinal and posterior mediastinal lesions
- Transsternal approach for anterior or middle lesions that are not accessible by the parasternal approach
- Suprasternal approach for superior mediastinal lesions
- Ultrasound guided transthoracic biopsy has been shown to be a viable approach in countries without ready access to video assisted procedures (Cureus 2021;13:e13914)
- Diagnosis of thymoma is usually via clinical and radiological findings; laboratory blood tests are not indicated
- However, laboratory studies may be helpful in those suspected to have myasthenia gravis or another autoimmune condition or to rule out germ cell tumor
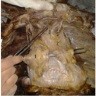
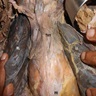
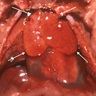
Gross description - thymus
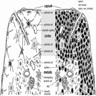
- Thymus is a partially lobulated lymphoid organ with connective tissue capsule, cortex and medulla; its parenchyma is made of T cells and stroma is made of epithelial reticular and other cells (StatPearls: Anatomy, Head and Neck, Thymus [Accessed 26 February 2024])
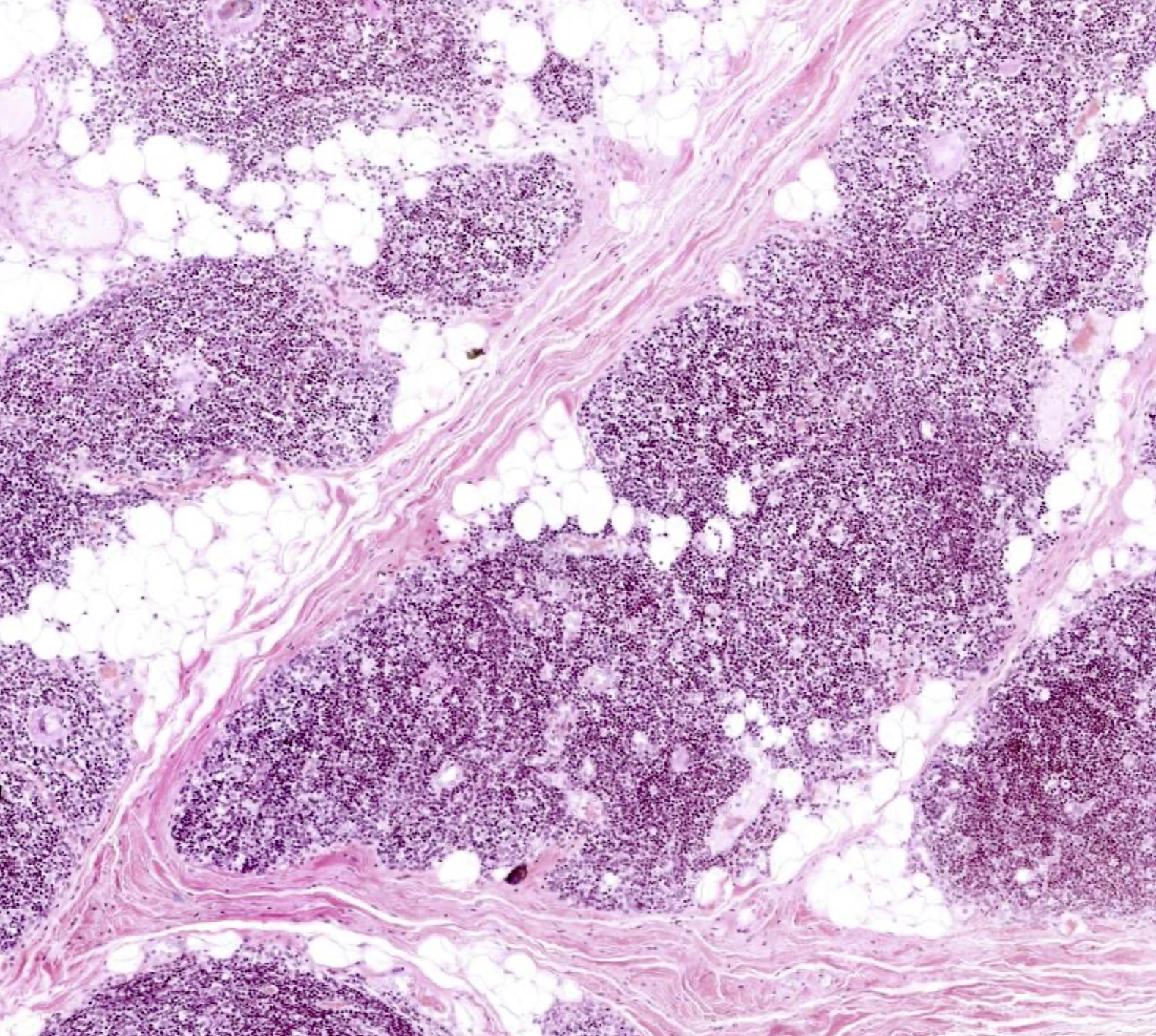
- Cortex: densely packed T cells, basophilic, early T cell development, partially lobulated by connective tissue septa
- Medulla: Hassall corpuscles, T cell later development, continuous appearance and lighter staining on H&E
- Thymus has no nodules (B cells), no hilus (only efferent lymphatics) and no subcapsular sinus
- Mature adult thymic cortex is mostly adipose tissue, where most of the lymphocytes have been replaced by fat; in this case, the most prominent features are Hassall corpuscles
Gross images
Frozen section description
- In one study, intraoperative frozen section of mediastinal neoplasm without preoperative cytological or histological diagnosis resulted in the correct diagnosis of benign lesions 91% of the time (Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 1990;4:584)
- However, in 35.5% of cases, intraoperative classification was not possible and in 27.6% of cases, the diagnosis was wrong, resulting in surgical overtreatment for lymphoma in 3 cases
Microscopic (histologic) description
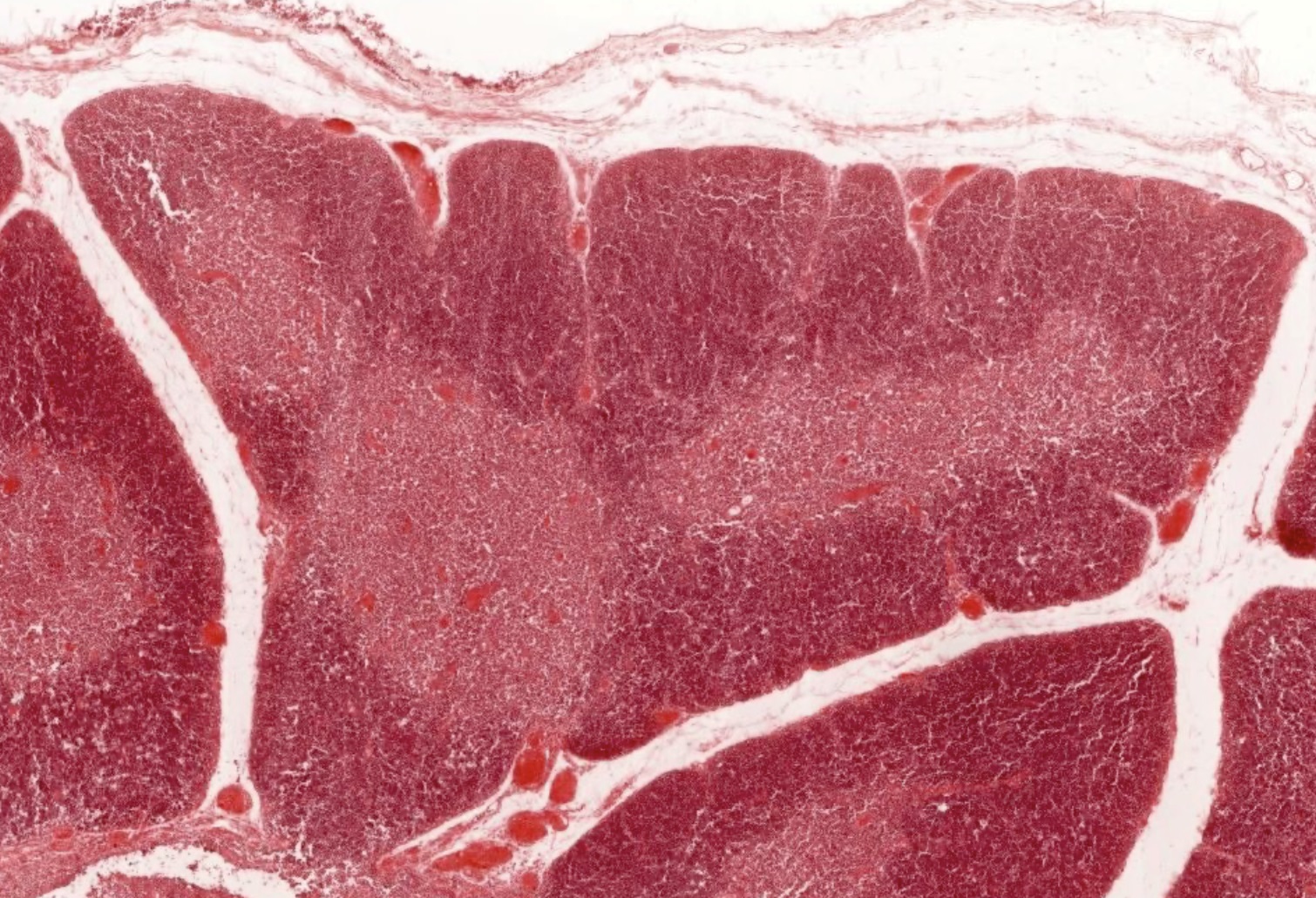
- Thymus has a connective tissue capsule with septa that extend into the organ, forming partial lobules
- Lymphocyte nuclei are numerous in the cortex, giving it a generally darker microscopic appearance (on H&E) and a lighter appearing medulla
- Parenchyma consists of T cells (of varying phenotypes) and B cells within the medulla and perivascular space (which increase with age) (Hum Pathol 2001;32:926)
- Thymus of children ages 3 - 6 seem to be the most active, demonstrating high numbers of total thymocytes and many CD34+ progenitors (J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005;115:834)
- Thymic stroma consists of all of the nonhematopoietic components of the thymus and is arranged into 2 regions, the cortex and medulla
- Stromal components comprise the thymic structure and provide a matrix for thymocyte development
- Keratin positive cells: cortical thymic epithelial cells (cTECs) and medullary TECs (mTECs)
- Keratin negative cells: fibroblasts, nonfibroblastic mesenchymal cells, endothelial cells of the vasculature and connective tissue that forms the capsule and septa
- Other stromal cells: Hassall corpuscles, dendritic cells, macrophages and CD45+ hematopoietic cells
- Mature thymus will show many clusters of adipose cells where the process of involution has replaced the thymic parenchyma with fat (Gerontology 2005;51:14)
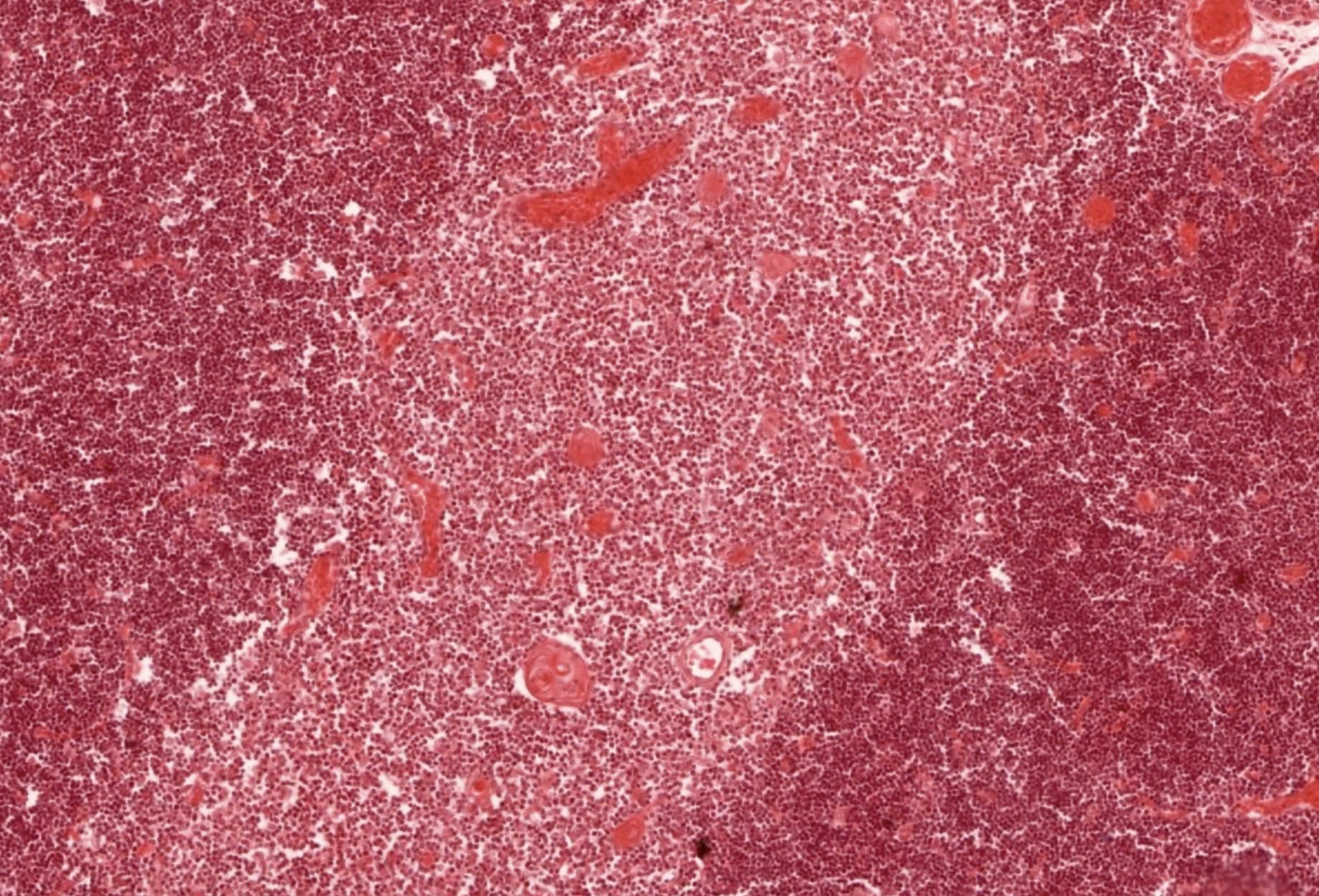
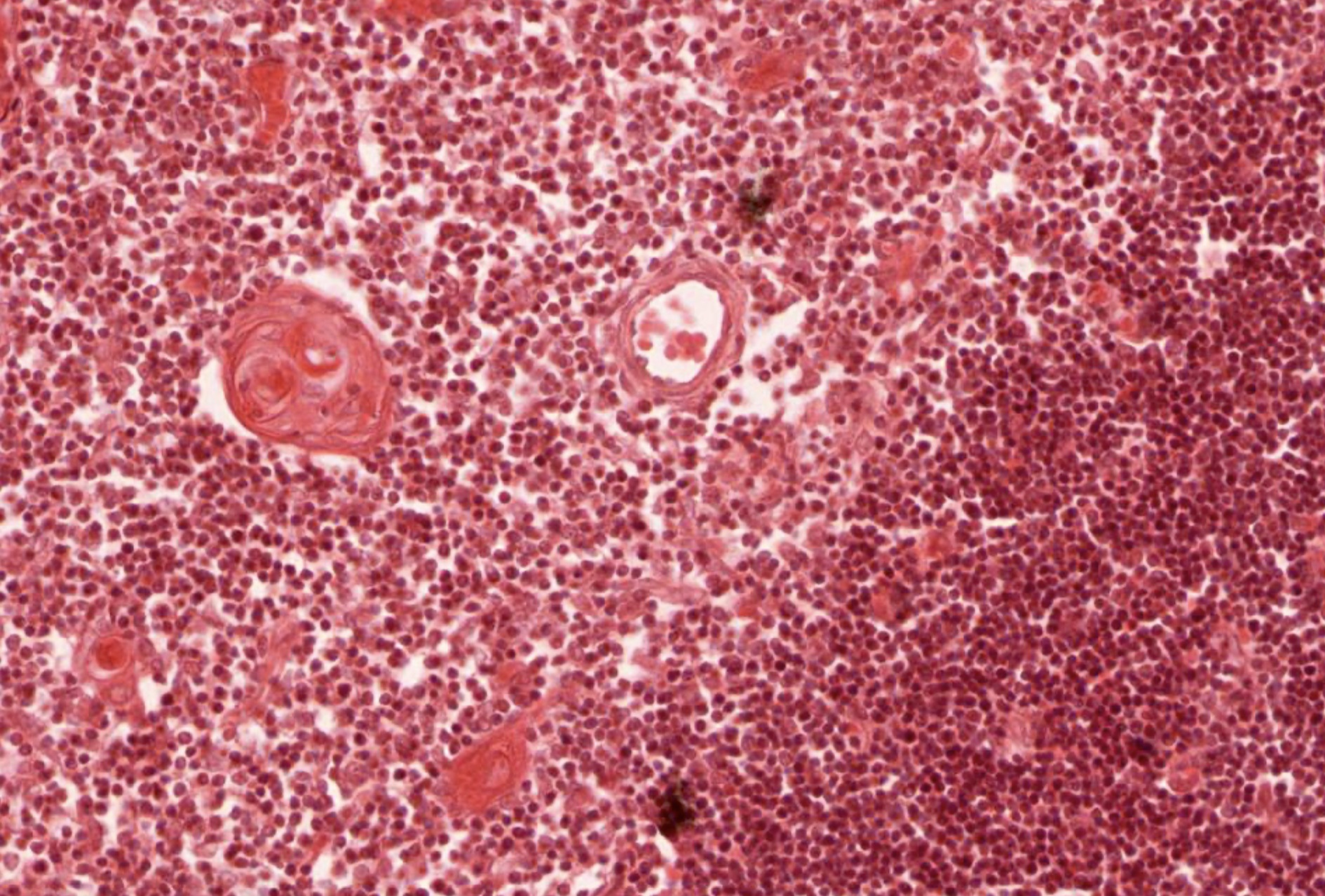
- Hassall corpuscles are unique to the thymus and are involved in thymocyte maturation, clearing of apoptotic cells and lymphopoiesis (Age (Dordr) 2014;36:313)
- Concentrically arranged type VI epithelial reticular cells
- Reside in the medulla, not in cortex
- Well developed in mature thymus
- Blood thymus barrier is composed of several layers of cells; these include vascular endothelial cells, pericytes, squamous TECs connected by desmosomes and occluding junctions, macrophages, cTECs, mTECs and stellate TECs (StatPearls: Anatomy, Head and Neck - Blood Thymus Barrier [Accessed 26 February 2024])
- Reference: Z Gerontol Geriatr 2000;33:341
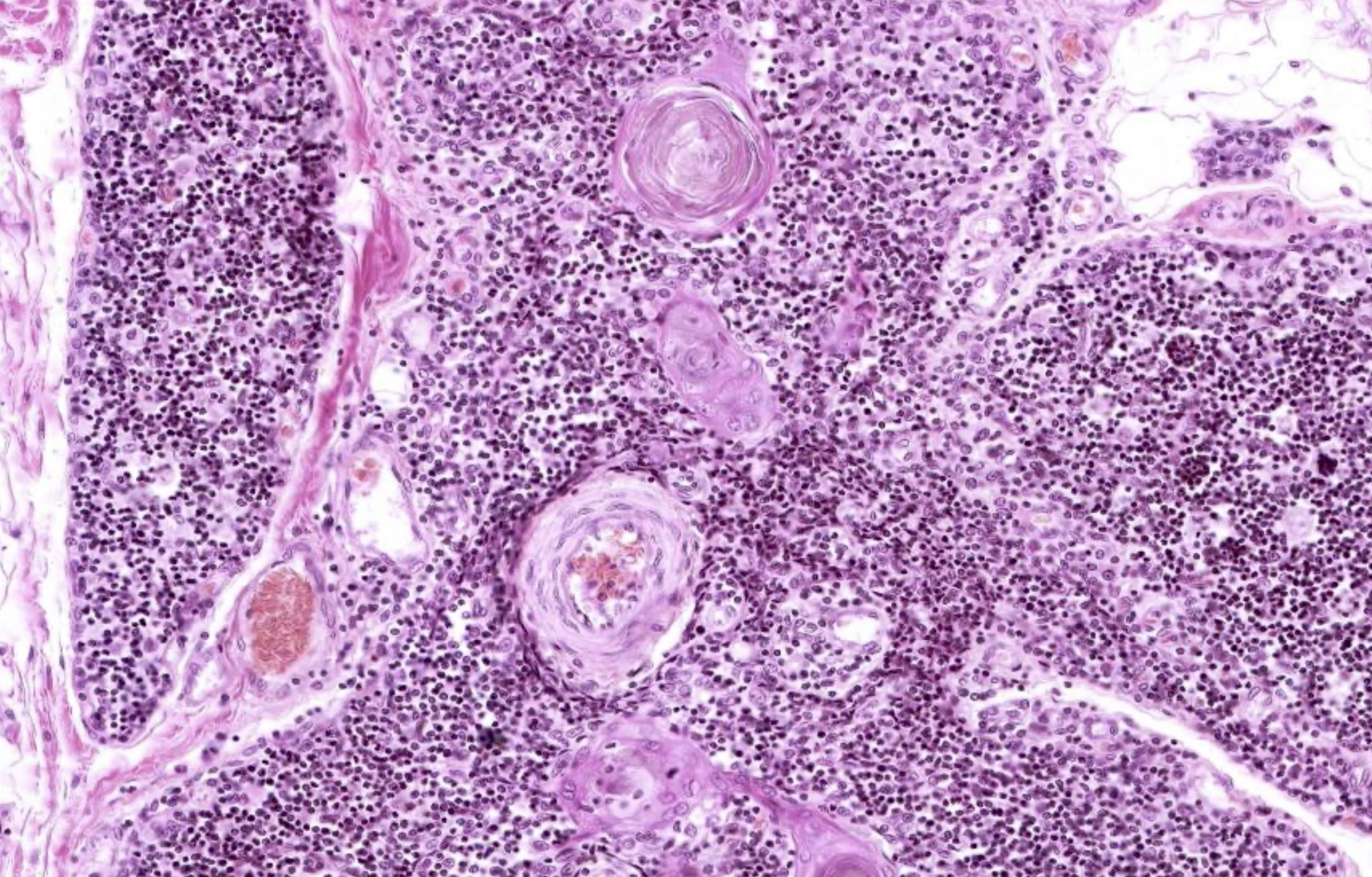
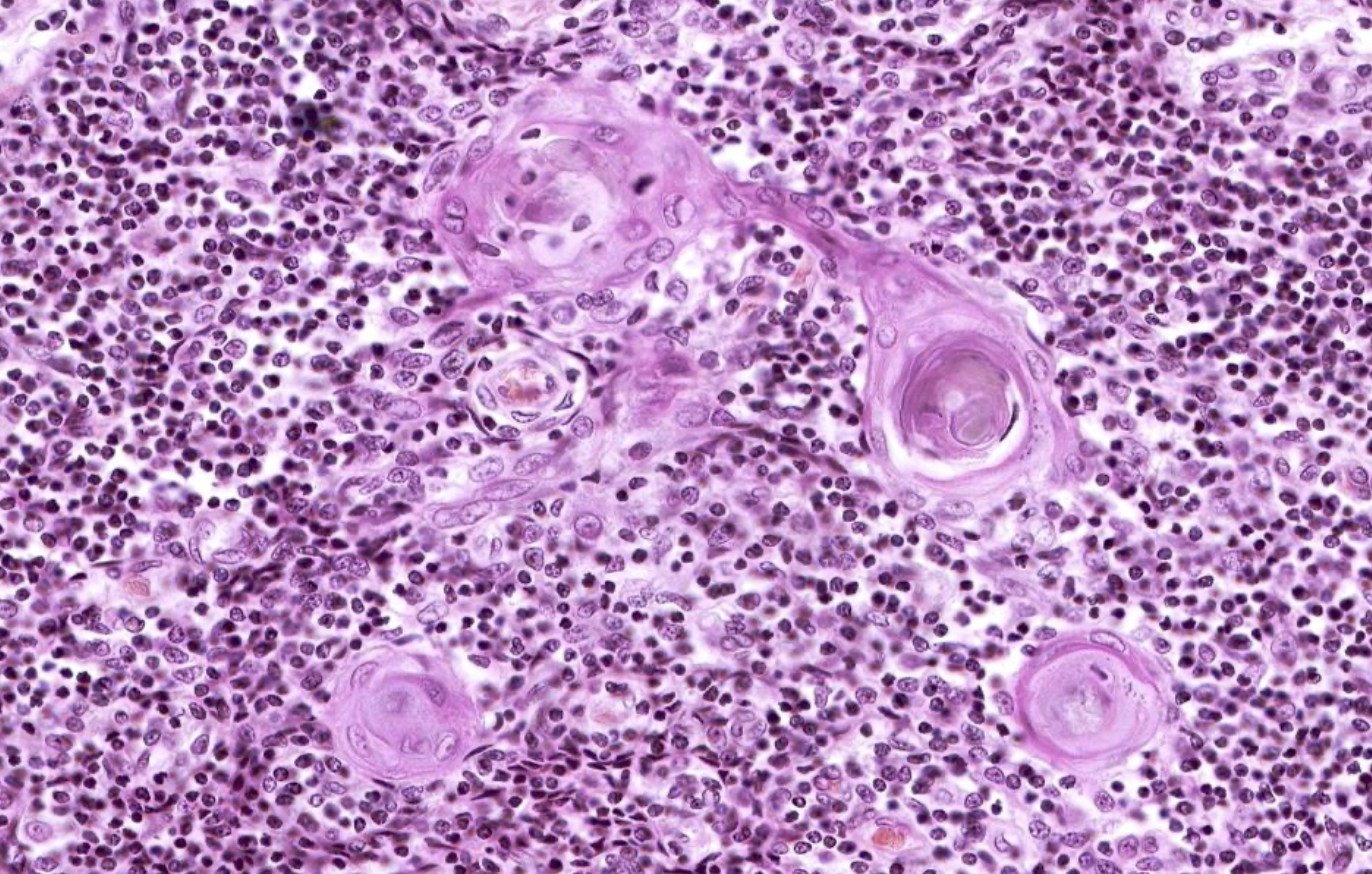
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Nicole Stringham, Ph.D. (source: University of Michigan virtual slide box and Duke University virtual slide collection)
Cytology description
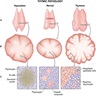
- Hallmark cytology of thymus includes 2 cell types, lymphocytes and epithelial cells (Cancers (Basel) 2022;14:2013)
- Diagnosis of thymic hyperplasia is challenging on cytology due to the difficulty of identifying Hassall corpuscles and because smear cellularity can affect the size and density of epithelial clusters
- Thymic hyperplasia: epithelial cell clusters are more sparse and smaller than those of thymoma and can mimic lymphoid tangles in lymph node aspirates
- Presence of Hassall corpuscles favors hyperplasia over thymoma (although they may be seen in B1 thymoma)
Positive stains
- Epithelial cells: keratin, HLA-DR
- Polyclonal cytokeratins in epithelial cells of Hassall corpuscles
- S100 in Hassall corpuscles; higher rate of positivity in younger thymus (compared to mature)
- Normal involution causes a reduction in CD3, CD20 and S100 positive cells, even in the absence of myasthenia gravis (Rom J Morphol Embryol 2007;48:101)
- Basement membrane proteins (laminin and collagen type IV): useful in the study of thymic structure; discontinuity can highlight characteristic changes of the perivascular space in myasthenia gravis (Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 1987;411:245)
- Cortical thymocytes: antiterminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, OKT6, OKT10 (negative in medullary thymocytes) (Hum Pathol 1984;15:378)
- Medullary epithelium: RFD4 (Am J Pathol 1985;119:462)
- Mast cells (mast cell tryptase positive) are localized exclusively to medulla; this number increases in specimens with thymoma (Int J Exp Pathol 2010;91:17)
- Immature thymus has large numbers of CD34 positive progenitors
Negative stains
- Corpuscles: cytokeratin 7 / 8, vimentin, desmin, CD3, CD68, CD34, neuron specific enolase; also, chromogranin (isolated positive), CD20 (rarely) (Ann Anat 2006;188:345)
- Medullary thymocytes: antiterminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, OKT6, OKT10
Videos
Mediastinum
Histology of the thymus
Board review style question #1
Which anatomical compartment contains the aortic arch, brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid and left subclavian arteries?
- Anterior mediastinum
- Middle mediastinum
- Posterior mediastinum
- Superior mediastinum
Board review style answer #1
D. Superior mediastinum contains aortic arch, brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid and left subclavian arteries as well as the esophagus, trachea, thymus, phrenic and vagus nerves. Answer A is incorrect because anterior mediastinum notably contains the internal thoracic arteries and transversus thoracis muscles. Answer B is incorrect because middle mediastinum contains the heart and ascending aorta but not the arch. Answer C is incorrect because posterior mediastinum contains the descending aorta and other structures that pass from the thorax into the abdomen.
Comment Here
Reference: Mediastinum - Anatomy & thymus histology
Comment Here
Reference: Mediastinum - Anatomy & thymus histology
Board review style question #2
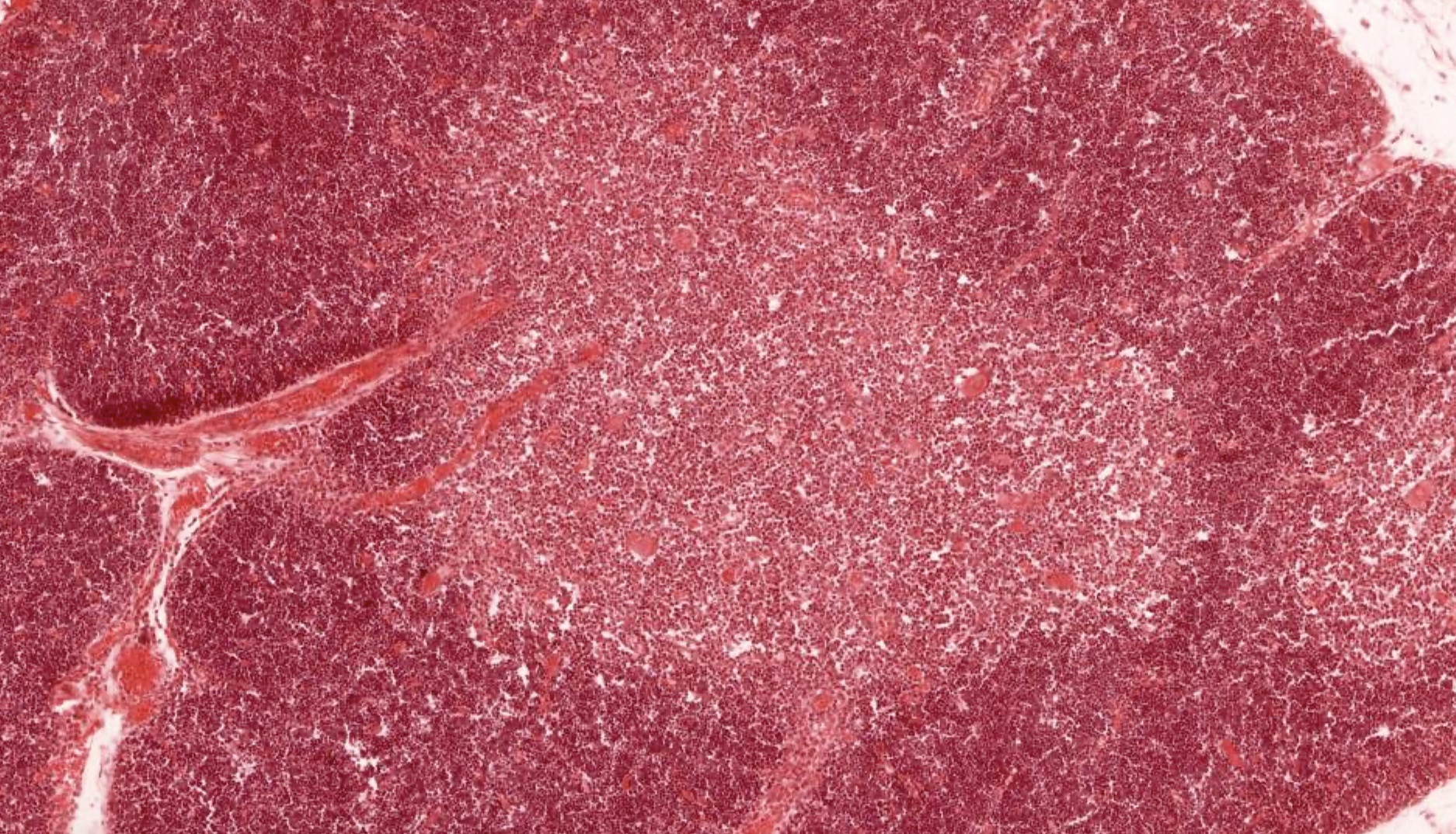
The micro image shown above is in need of evaluation. Features that are present, both in the image and in adjacent areas, include a connective tissue capsule, cortex and medulla, efferent lymphatics (only) and concentrically arranged epithelial reticular cells within the medulla. What is the anatomical origin of this sample?
- Lymph node
- Spleen
- Thymus
- Thyroid
- Tonsil
Board review style answer #2
C. Thymus. The thymus is the only listed option that has numerous lymphocytes (shown in the image) in addition to all of the other listed features. Additionally, the concentrically arranged epithelial reticular cells (i.e., Hassall corpuscles) are unique to the medulla of the thymus. Answer A is incorrect because although lymph nodes have many of these features, including a cortex / medulla arrangement, they do not have Hassall corpuscles. Answer B is incorrect because spleen is histologically arranged as red pulp and white pulp, with nodules throughout the organ, not as a cortex and medulla. Answer E is incorrect because tonsils contain aggregates of lymphocytes but do not have many of the features listed. Answer D is incorrect because thyroid histomorphology would show simple columnar epithelium arranged in spheres around colloid rather than a parenchyma of lymphocytes.
Comment Here
Reference: Mediastinum - Anatomy & thymus histology
Comment Here
Reference: Mediastinum - Anatomy & thymus histology