Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Pathogenesis | Etiology | Clinical features | Case reports | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1Cite this page: Kowalski PJ. Thin cord. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/placentathincord.html. Accessed August 26th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Decrease in the cross sectional diameter of the umbilical cord
- Also called thin cord syndrome
Essential features
- Due to a reduction in the amount and fluid content of supportive Wharton jelly, the number of umbilical vessels present or a combination of both
- Cord diameter < 1.0 cm (normal: 1.25 - 2.5 cm) at term or an umbilical cord cross sectional area (on ultrasound examination) < 10th percentile for gestational age
Terminology
- Thin or lean umbilical cord should be distinguished from segmental thinning of an umbilical vessel, which is due to a paucity of the tunica media layer
Epidemiology
- Present in up to 10% of term infants, in some series
Pathogenesis
- Reduction in Wharton jelly can predispose to compression of the umbilical vessels
Etiology
- Factors that determine the amount and content of Wharton jelly are poorly understood, although Wharton jelly typically increases until 32 weeks gestation and then slightly declines in fluid content thereafter
- Reduction in the number of umbilical vessels is suggested to be due to atrophy of an umbilical artery
Clinical features
- Associated with preeclampsia, intrauterine growth restriction and intrauterine fetal demise
- Associated with fetal distress at the time of delivery (oligohydramnios, low Apgar scores and meconium stained amniotic fluid)
Case reports
- 30 year old pregnant woman with thin cord syndrome (Iran Red Crescent Med J 2014;16:e14122)
- 35 year old pregnant woman at 29 weeks gestation with thin cord syndrome (Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd 2016;76:1186)
Gross description
- Umbilical cord diameter is measurably reduced
- Lower coiling index (reduced number of spirals per unit length) may result in a hypocoiled gross appearance
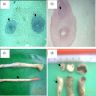
Gross images
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Decrease in Wharton jelly can be appreciated
- Umbilical vein may be diminished in size, while umbilical arteries appear normal in histologic appearance
Practice question #1
Which of the following best describes a thin umbilical cord?
- A cord diameter less than 2 cm at term is characteristic
- A reduction in the size of the tunica media layer
- Associated with preterm labor
- No change in the number of umbilical vessels
- Predisposes the umbilical vessels to compression effects
Practice answer #1
E. Thin cord is due to a decrease in Wharton jelly or a decrease in the number of umbilical vessels, which can predispose the umbilical vessels to compression phenomena.
Comment Here
Reference: Thin umbilical cord
Comment Here
Reference: Thin umbilical cord