Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Saab S. Twins. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/placentatwins.html. Accessed September 16th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Multiple gestations are common and in recent times, more frequently encountered due to advances in assisted reproductive techniques
- Twin pregnancies are higher risk than singletons with monochorionic twins having a significantly higher risk than dichorionic twins, making determination of chorionicity important for the clinical complications inherent to the type of placentation; examples include
- Twin to twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS)
- Fetal growth restriction
- Twin anemia polycythemia sequence (TAPS)
- Twin reversed arterial perfusion (TRAP)
- Conjoined twins
Essential features
- Chorionicity refers to the type of placentation and is not a reflection of zygosity
- Zygosity refers to the type of conception and the degree of similarity of the genetic makeup of the zygotes from which twins develop
Terminology
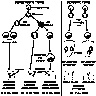
- Chorionicity and zygosity:
- Dichorionic twin placentas can be monozygotic (derived from a single fertilized ovum with identical genotypes) or dizygotic (derived from 2 separate fertilized ova)
- All dizygous twins are dichorionic and placentas can be fused or separate
- Monozygous twins can result in dichorionic or monochorionic placentas
- Monochorionic twin placentas are one placenta shared by twins who may have separate amnions (diamnionic) or a common amnion cavity (monoamnionic); they are predominantly monozygotic, though occasional dizygotic monochorionic twinning has been documented (Eur J Pediatr 2014;173:1249, J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2018;44:576)
- Dichorionic twin placentas can be monozygotic (derived from a single fertilized ovum with identical genotypes) or dizygotic (derived from 2 separate fertilized ova)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: O30.009 - twin pregnancy, unspecified number of placenta and unspecified number of amniotic sacs, unspecified trimester
Epidemiology
- Rate of twin pregnancies in the United States is 32 per 1,000 births (Am J Obstet Gynecol 2015;213:S91)
- Dizygotic twins comprise 70% of twins while monozygotic (identical) twins comprise the remaining 30% (Lancet 2003;362:735)
Pathophysiology
- Mechanism for zygosity in twinning is not completely understood
- Dizygotic (nonidentical) twins result from fertilization of separate ova by different sperm
- Monozygotic (identical) twins arise from a single ovum fertilized by 1 sperm; the resultant zygote can undergo division and the timing of the division translates into the type of placentation:
- Division within the first 3 days after fertilization (morula) usually results in dichorionic placentation (70% of monochorionic placentas)
- Division 3 - 9 days after fertilization (blastocyst) results in monochorionic diamnionic placentation
- Division 8 - 12 days after fertilization results in monochorionic monoamnionic placentation
- Later splitting results in conjoined twins with monochorionic monoamnionic placentation
- Reference: Darwish: Contemporary Gynecologic Practice, 2015
Clinical features
- See Diagnosis
Diagnosis
- Determination of chorionicity is part of fetal surveillance throughout pregnancy
- Gross evaluation of the placenta establishes chorionicity and can identify pathologies of the placenta, especially those unique to twin placentas
- Determination of zygosity by the assumption that all monochorionic twins are monozygotic is unreliable as dizygotic monochorionic twinning has been documented
- Reference: Am J Obstet Gynecol 2015;213:S91
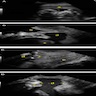
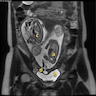
Radiology description
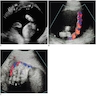
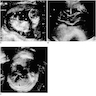
- Traditionally, transabdominal ultrasonographic studies in the second and third trimesters were able to determine chorionicity by demonstrating separate placentation, discordant fetal gender, identification of the twin peak sign (also known as the lambda sign) and thickness of the dividing fetal membrane; these are features of chorionic placentas
- Zygosity could be determined in the setting of discordant fetal genders by ultrasonography
- Chorionicity and amnionicity can be determined in the first trimester transvaginal ultrasound, ideally between 9 and 10 weeks of gestation (Am J Perinatol 2001;18:23)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Twin pregnancies are higher risk than singletons with 4 fold higher perinatal mortality rates with some of the risk attributed to prematurity, fetal growth restriction and chromosomal abnormalities but also to complications directly related to complexities uniquely inherent to the type of chorionicity (Am J Obstet Gynecol 2015;213:S91, Am J Perinatol 2001;18:23)
- Perinatal demise in twin pregnancies accounts for 12.6% of all perinatal mortality (Am J Perinatol 2001;18:23)
- Chorionicity and perinatal mortality: 50% of monoamnionic twins, 26% of diamnionic monochorionic twins and 9% of dichorionic diamnionic twins
Case reports
- 27 year old woman with monochorionic dizygotic, sex discordant twins resulting from spontaneous pregnancy with blood chimerism (J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2009;22:708)
- 28 year old woman who became pregnant with twins with a partial hydatidiform mole and a coexistent live fetus; diagnostic and therapeutic dilemmas (Ginekol Pol 2020;91:589)
- 30 year old woman who became pregnant with monochorionic diamnionic twins discordant for esophageal atresia, duodenal atresia, gastric perforation and hypoplastic left heart structures in 1 twin (J Med Case Rep 2017;11:64)
- 34 year old woman who became pregnant with monochorionic dizygotic twins with sex discordance and confined blood chimerism (Eur J Pediatr 2014;173:1249)
- 39 year old woman with fetal sex discordance in a monochorionic twin pregnancy following intracytoplasmic sperm injection (J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2018;44:576)
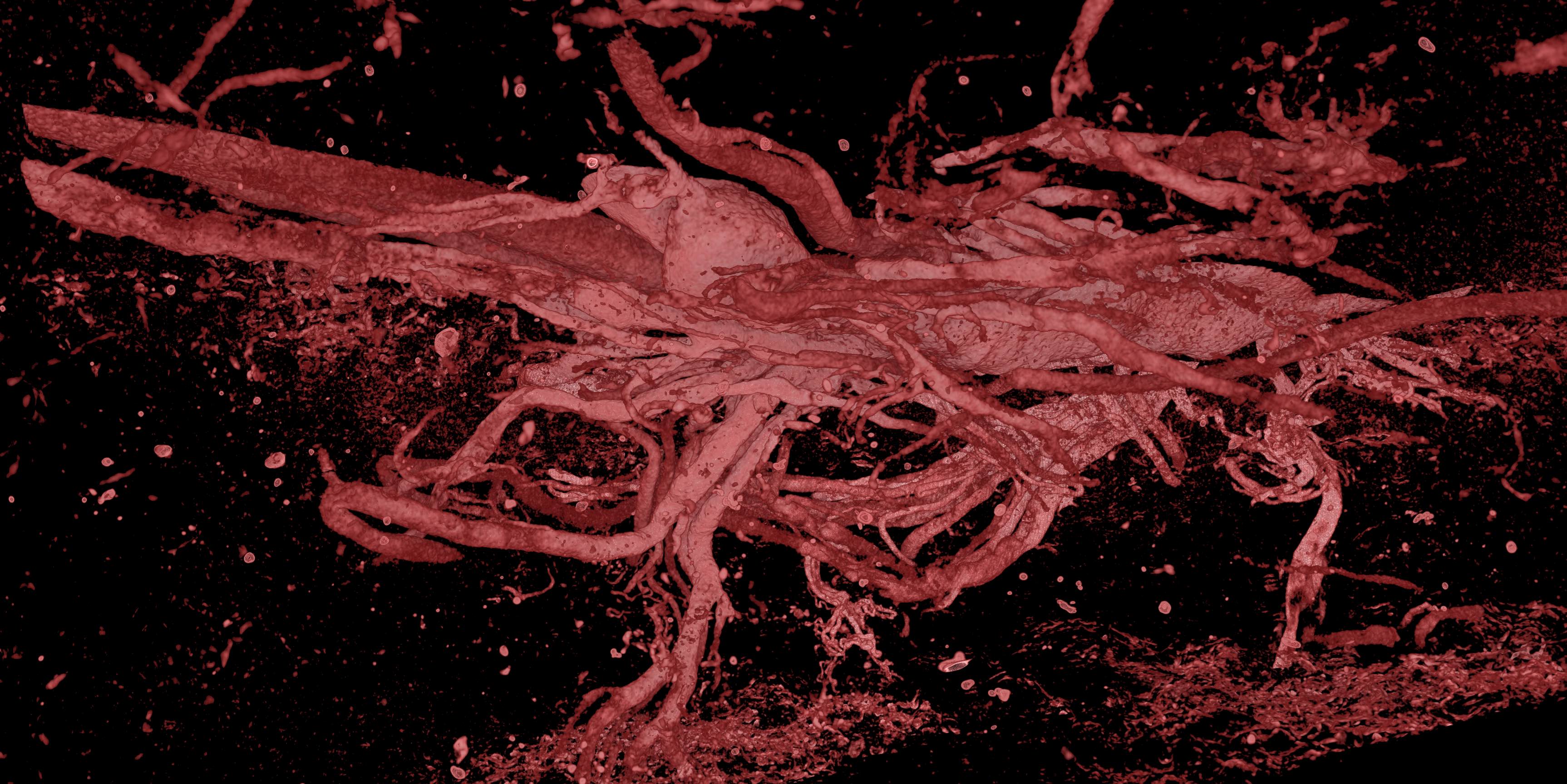
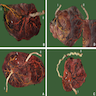
Gross description
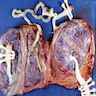
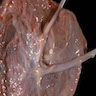
- Dichorionic twins:
- Separate without dividing membrane: 2 separate placentas
- Separate with dividing membrane consisting of 4 layers (2 amnions and 2 chorions)
- Fused with a dividing membrane consisting of 3 or 4 layers (2 layers of amnion and 1 or 2 layers of chorion)
- Monochorionic twins:
- Monochronionic diamnionic: single placental disc with dividing membrane consisting of 2 layers (2 layers of amnion, no chorion)
- Monochorionic monoamnionic: no dividing membrane
- Reference: Darwish: Contemporary Gynecologic Practice, 2015
Gross images
Microscopic (histologic) description
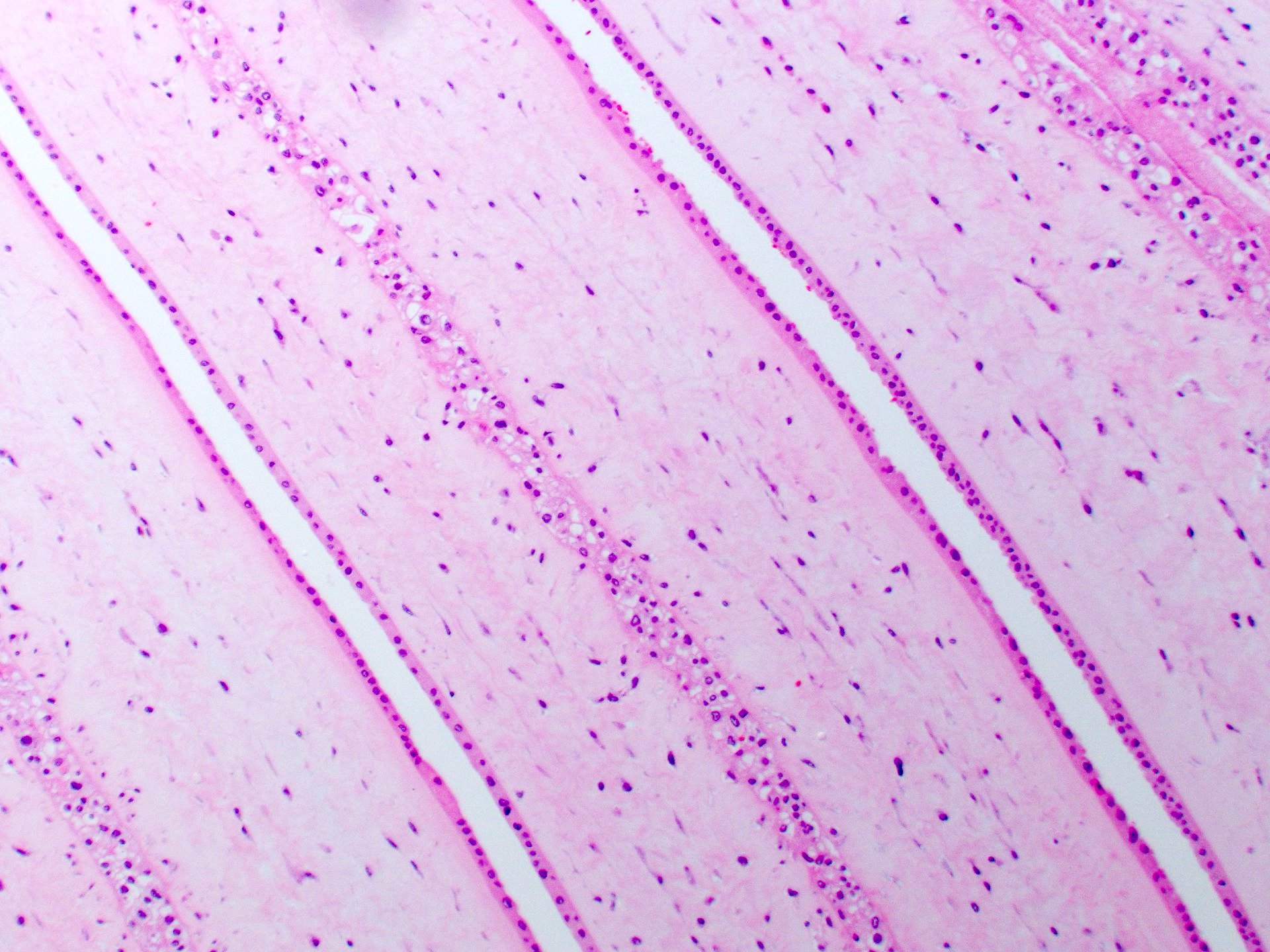
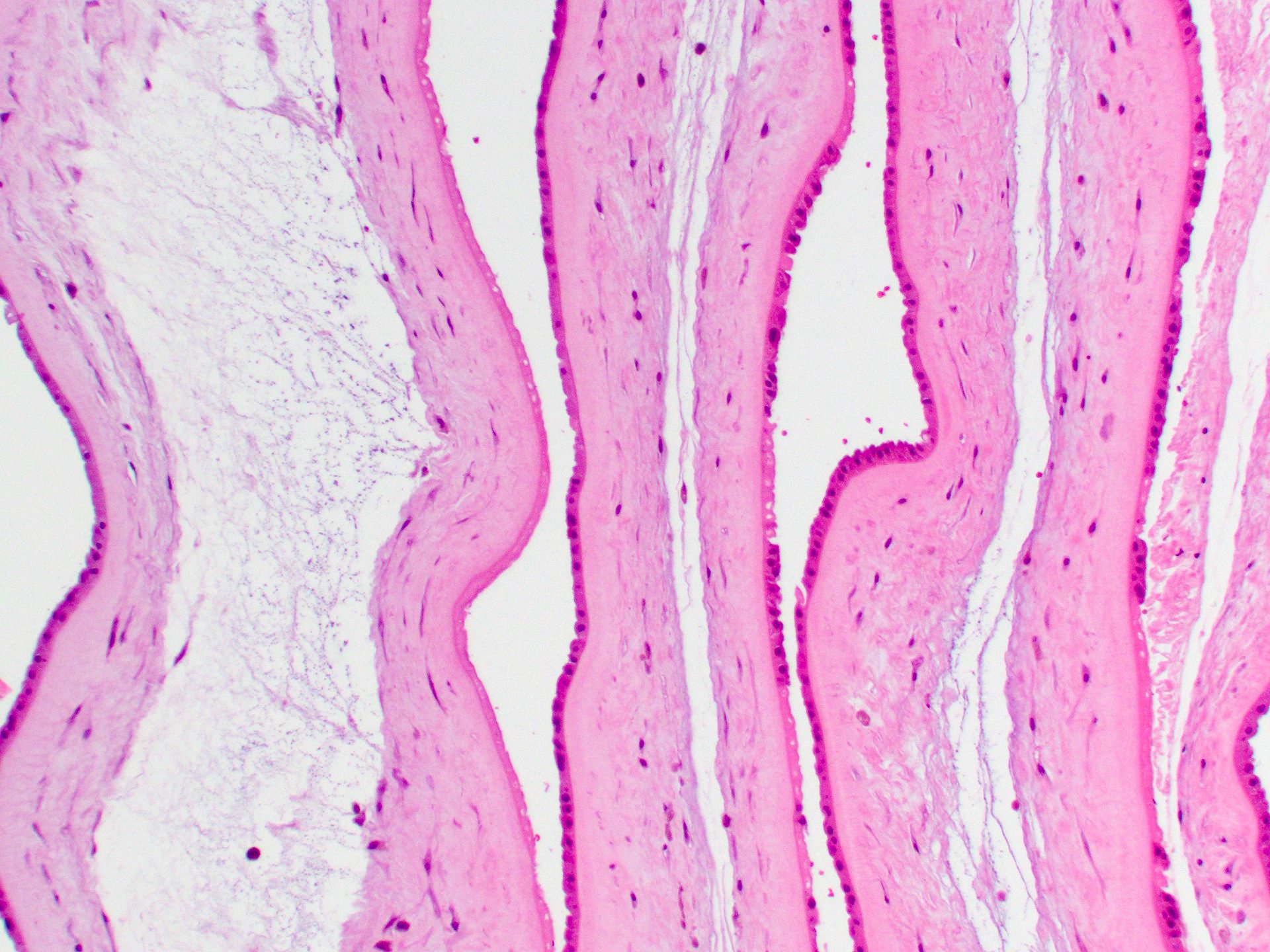
- Dividing membrane in dichorionic placentas shows the separation of amnion layers by chorion layers which may be fused
- Dividing membrane in monochorionic membranes shows juxtaposed amnion layers
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Twin placentas, cesarean section:
- Fused / separate dichorionic diamnionic twin placentas
- Placenta A: mature placenta, 425 g, with no significant histopathologic abnormality
- Placenta B: mature placenta, 420 g, with no significant histopathologic abnormality
- Fused / separate dichorionic diamnionic twin placentas
- Twin placentas, cesarean section:
- Small, slightly immature (mid third trimester) monochorionic diamnionic twin placentas (300 g, less than third percentile for gestational age)
- Placenta A:
- Fetal vascular distribution: 60%
- Single large focus of avascular villi
- Placenta B:
- Fetal vascular distribution: 40%
- Fetal vascular malperfusion (velamentous insertion of hypercoiled umbilical cord with large foci of villous vascular and stromal karyorrhexis)
- Placenta A:
- Small, slightly immature (mid third trimester) monochorionic diamnionic twin placentas (300 g, less than third percentile for gestational age)
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
D. Dichorionic placentas can be either dizygotic or monozygotic (Am J Obstet Gynecol 2015;213:S91)
Comment Here
Reference: Twins
Comment Here
Reference: Twins
Practice question #2
Which of the following is true regarding dividing membranes of twin placentas?
- Dichorionic twins cannot have separate placentas without a dividing membrane
- The dividing membranes of dichorionic diamnionic twin placentas are always comprised of 4 layers
- The dividing membranes of monochorionic diamnionic twin placentas can be comprised of 2 or 3 layers
- The dividing membranes of separate, fused dichorionic diamnionic twin placentas are comprised of 3 or 4 layers
Practice answer #2
D. The dividing membranes of separate, fused dichorionic diamnionic twin placentas are comprised of 3 or 4 layers (Am J Obstet Gynecol 2015;213:S91)
Comment Here
Reference: Twins
Comment Here
Reference: Twins