Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Additional referencesCite this page: Hamodat M. Seborrheic dermatitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skinnontumorseborrheicdermatitis.html. Accessed October 5th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Nummular eczema (silver dollar sized patches) to generalized exfoliative dermatitis (severe atopic dermatitis) to large vesicles on palms and soles (dyshidrosis)
- Not due to any known agents, although associated with irritant contact dermatitis
- One of the most common cutaneous manifestations of AIDS, affecting 20 - 80%
- Also associated with Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, congestive heart failure, obesity, chronic alcoholism, Leiner disease (exfoliative dermatitis of infancy) and zinc deficiency
- May occur as reaction to arsenic, gold, chlorpromazine, methyldopa and cimetidine
Clinical features
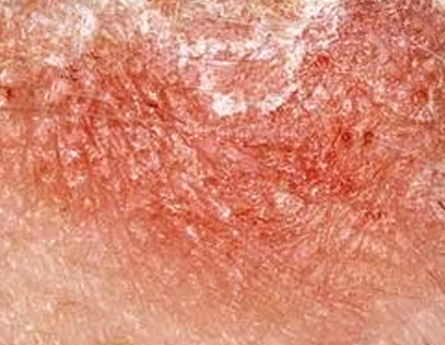
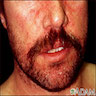
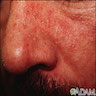
- Erythematous scaling papules and plaques, sometimes with a greasy yellow appearance, with a characteristic distribution on scalp, ears, eyebrows, eyelid margin, and nasolabial area - the so called seborrheic areas
Treatment
- Keratolytic agents, some over the counter
- Anti-inflammatory products, such as topical corticosteroids, have some effect
Clinical images
Microscopic (histologic) description
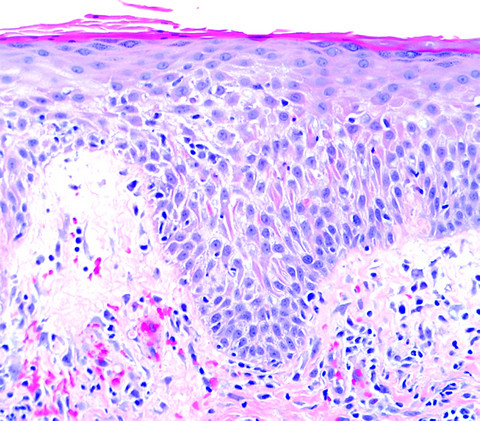
- Acute, subacute or chronic spongiotic dermatitis
- In acute lesions, there is focal, usually mild, spongiosis with overlying scale crust containing a few neutrophils; the crust is often centered on a follicle; papillary dermis is mildly edematous; blood vessels in superficial vascular plexus are dilated and there is mild superficial perivascular infiltrate of lymphocytes, histiocytes and occasional neutrophils; some exocytosis of inflammatory cells but not as prominent as in nummular dermatitis
- In subacute lesions, there is also psoriasiform hyperplasia, initially slight, with mild spongiosis and the other changes already mentioned; numerous yeast-like organisms can usually be found in the surface keratin
- Chronic lesions show more pronounced psoriasiform hyperplasia and only minimal spongiosis; sometimes the differentiation from psoriasis can be difficult but the presence of scale crusts in a folliculocentric distribution favors seborrheic dermatitis
Additional references