Table of Contents
Definition / general | Neurofibromatosis type 1 | NF2 | Diagrams / tables | Mutations | Clinical features | Detection methods | Inhibitor therapy | Mechanisms of resistanceCite this page: Bradish, J., Cheng L. NF1 / NF2. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsnf1nf2.html. Accessed September 18th, 2025.
Definition / general
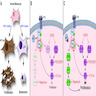
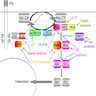
- NF1, neurofibromin 1, is a tumor suppressor gene found on chromosome 17q11.2 which negatively regulates RAS signaling
- NF1 increases the intrinsic GTPase activity of the RAS enzyme which leads to inactivation
- If an NF1 mutation causes subsequent inactivation, it leads to an increase in RAS activity (Cancer Discov 2013;3:260)
- In melanocytes, the NF1 protein regulates differentiation and development (J Cell Sci 2008;121:167)
Neurofibromatosis type 1
- Heterogeneous mutations seen in neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), the most common autosomal dominant inherited disorder in humans (1 per 3000)
- Disorder characterized by benign tumors of peripheral nerves, cafe au lait spots, retinal hamartomas
- Also increased risk of malignancy, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1170)
NF2
- Tumor suppressor protein at 22q11-13.1
- Produces protein called merlin or schannomin
- Deleted in soft tissue perineurioma
- Both copies inactivated in up to 60% of sporadic meningiomas
- Often no protein expression in schwannoma
- May be involved in tumorigenesis of schwannoma and some meningiomas
Mutations
- Many different types of NF1 mutations have been described including frameshift, missense, nonsense, splicing and deletion mutations
- An inactivating mutation of the NF1 gene leads to RAS activation (Monogr Hum Genet 2008;16:63)
Clinical features
- While classically NF1 is associated with an increase in numerous neoplasms, both benign and malignant, NF1 is not associated with an increased risk of melanoma
- There is, however, a well known strong association with pigmentation aberrations (cafe au lait spots, ephelides, etc.) in patients with NF1 germline mutations (Cancer Discov 2013;3:260)
Detection methods
- Comprehensive testing using RNA / cDNA core assay with copy number analysis is the preferred method, as it is more sensitive and specific (Monogr Hum Genet 2008;16:63)
- DNA based sequence analysis is also used
- Other techniques can be used if either a complex or rare mutation is present (total gene mutations, multiple deletions, multiple duplications) (UAB: Neurofibromatosis Type 1 [Accessed 23 April 2021])
Inhibitor therapy
- Currently, there is no approved specific treatment for NF1 mutations
- There are early experiments evaluating antisense morpholino oligomers and imatanib therapy (Hum Mutat 2009;30:454, Am J Med Genet A 2013;161A:viii)
- In vitro studies have demonstrated a response to MEK inhibition in melanocytes containing both RAF and NF1 mutations (Cancer Res 2014;74:2340)
Mechanisms of resistance
- NF1 mutations in BRAF mutated melanocytes has been shown to decrease the response of these melanocytes to RAF inhibitor therapy (PLX4720, the precursor molecule of vemurafenib) (Cancer Discov 2013;3:260, Cancer Res 2014;74:2340)
- One study demonstrated a response to MEK inhibition in melanocytes containing both BRAF and NF1 mutations (Cancer Res 2014;74:2340)