Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Sample pathology report | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1Cite this page: Kösemehmetoğlu K, Johnson G. Actin, alpha smooth muscle type. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsalphasmoothmuscleactin.html. Accessed August 25th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Actin is a 43000 kDa ubiquitous protein found in all cells
- Actins are involved in cell motility (alpha, smooth muscle) and the maintenance of the cytoskeleton (beta and gamma, all cells)
- Antibodies to alpha smooth muscle actin do not detect the other actin isoforms
Essential features
- Involved in cell motility
- Identifies pericytes, myoepithelial cells, smooth muscle cells and myofibroblasts in normal, reactive or neoplastic tissue
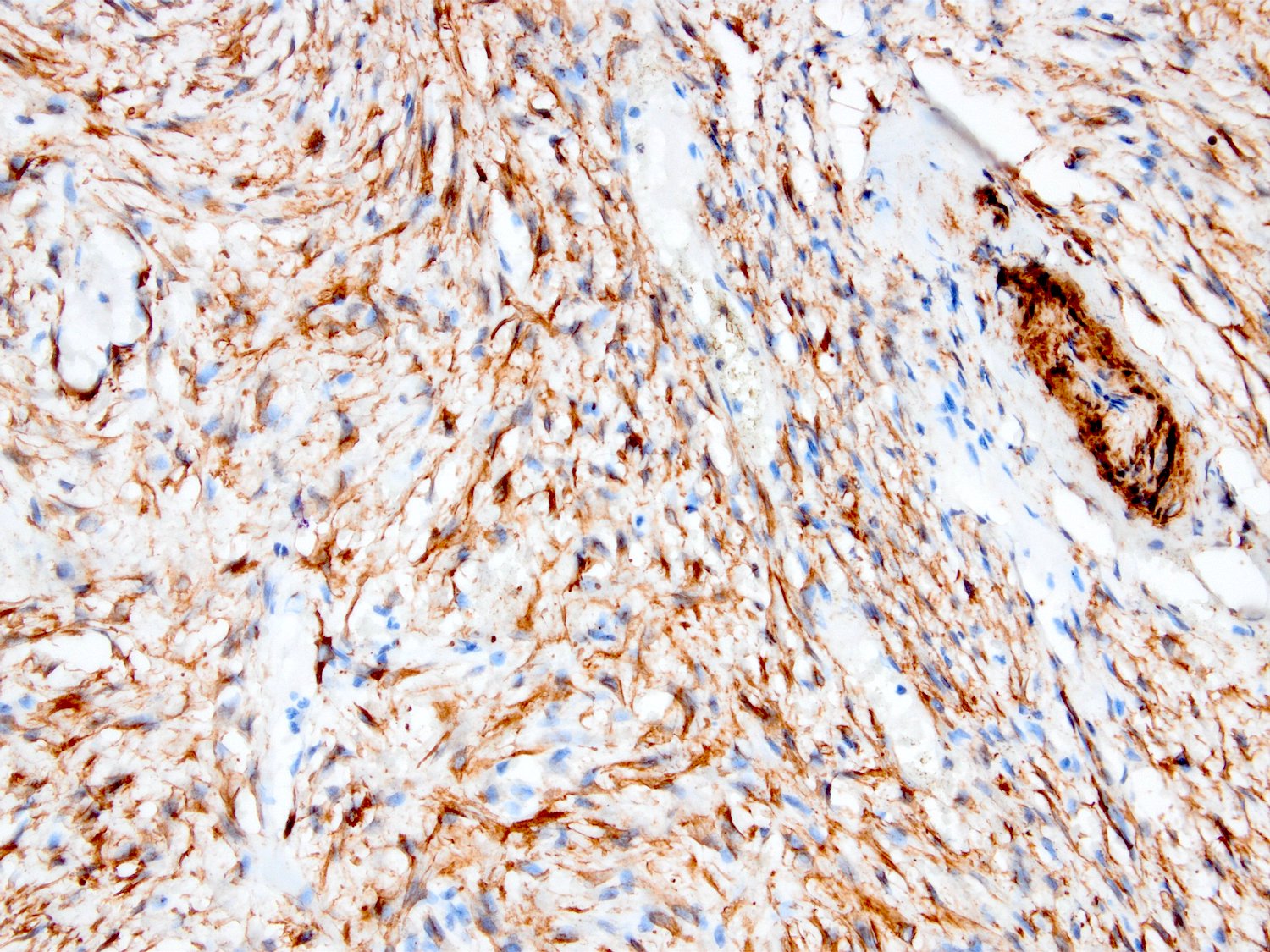
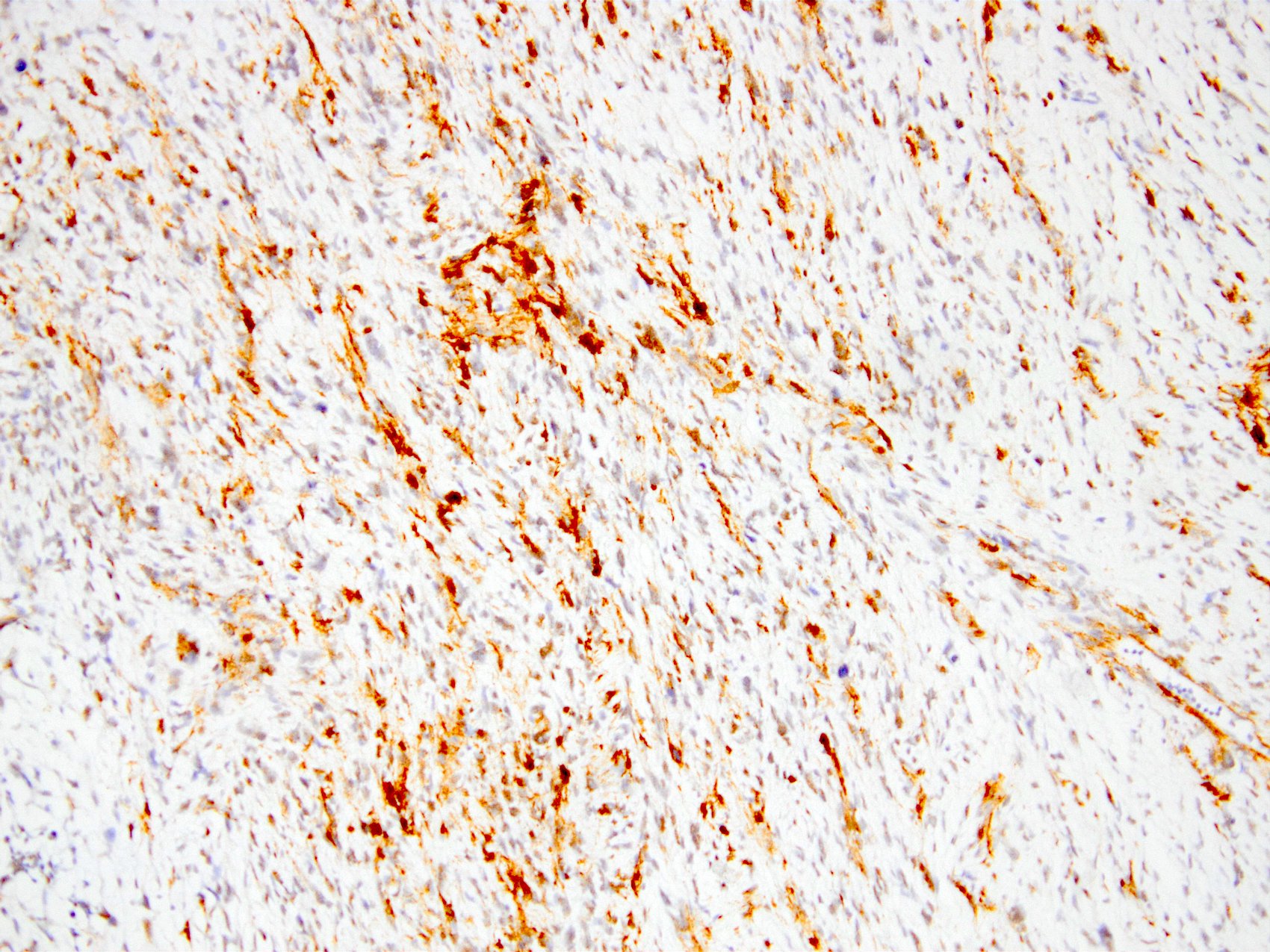
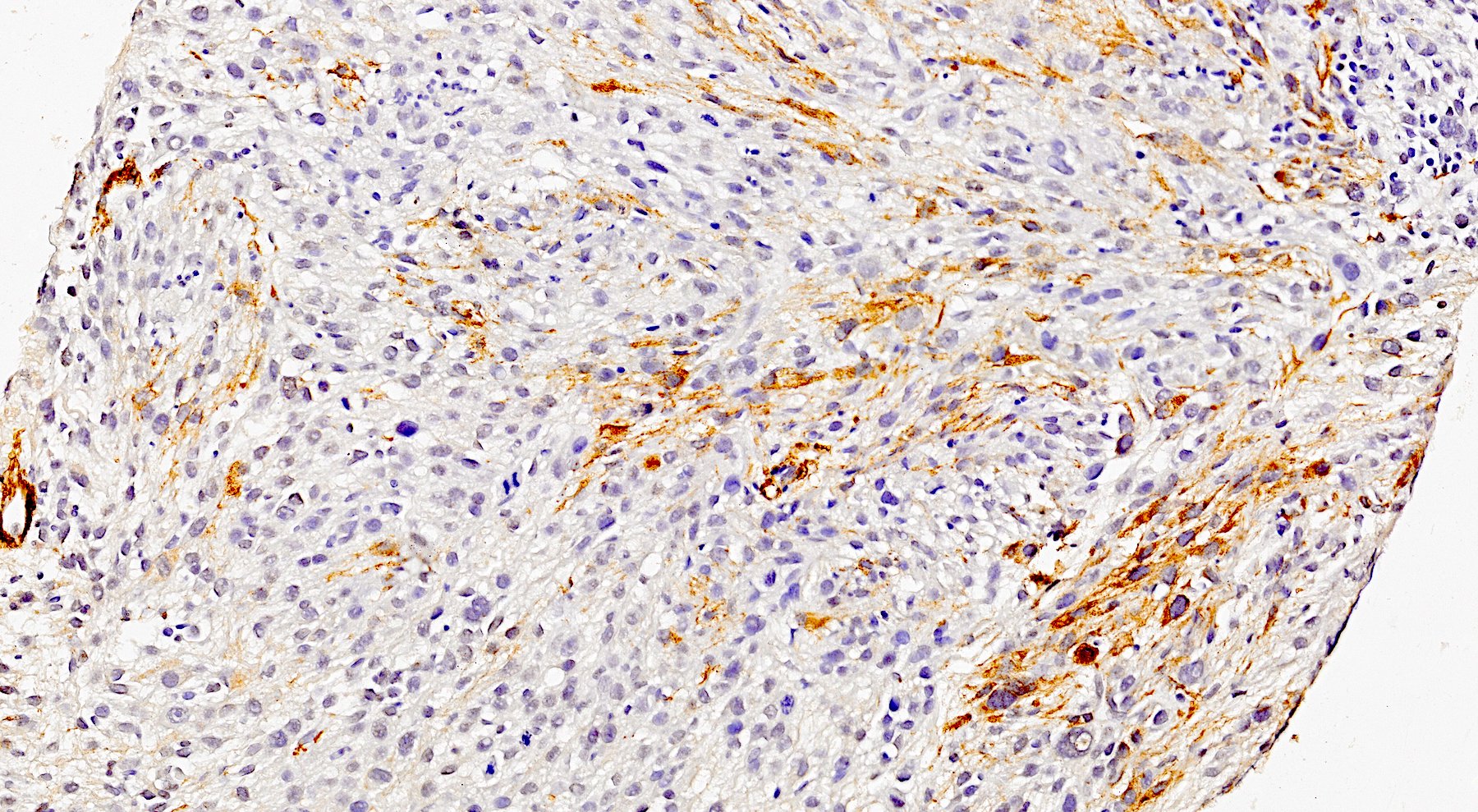
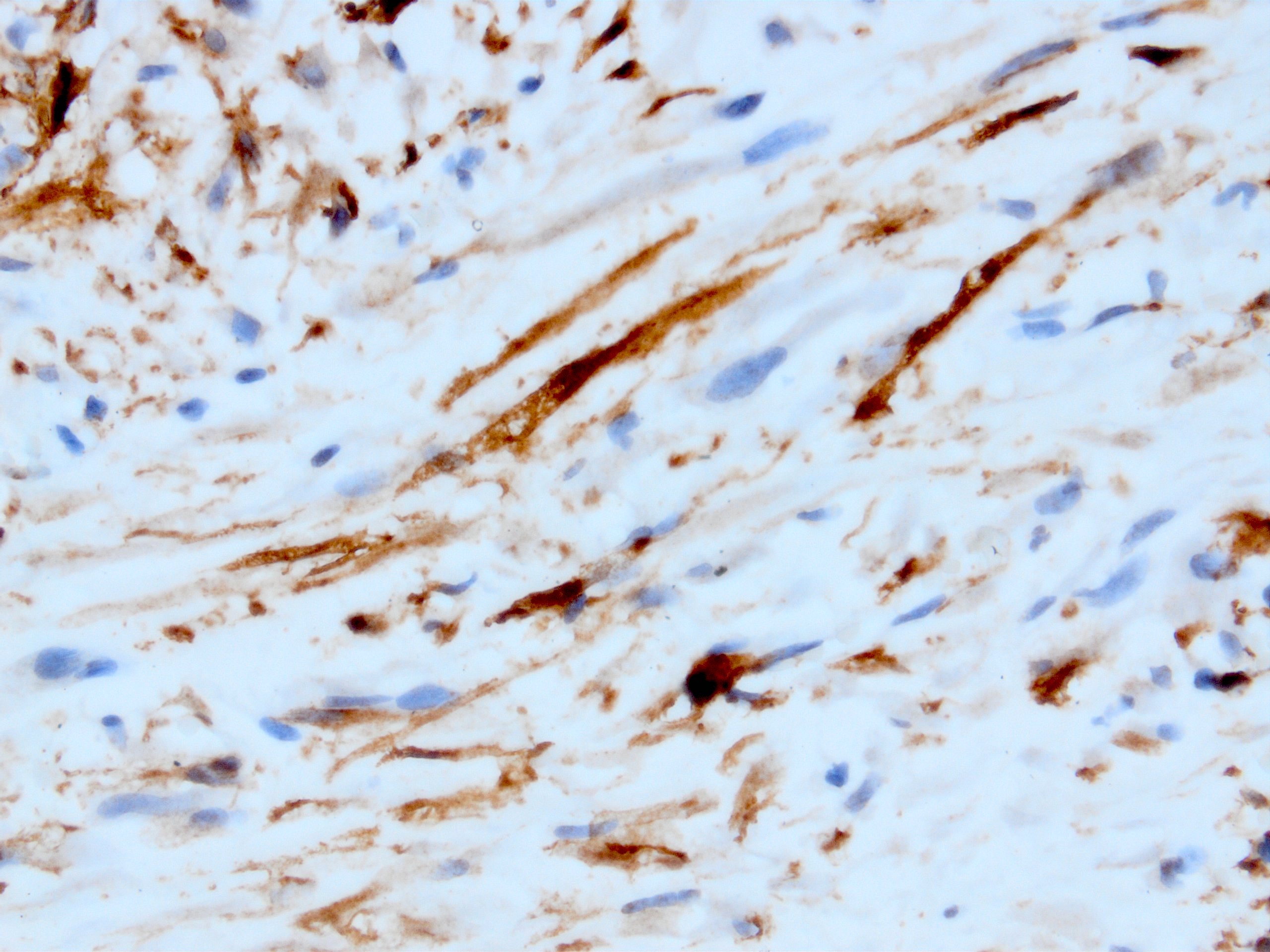
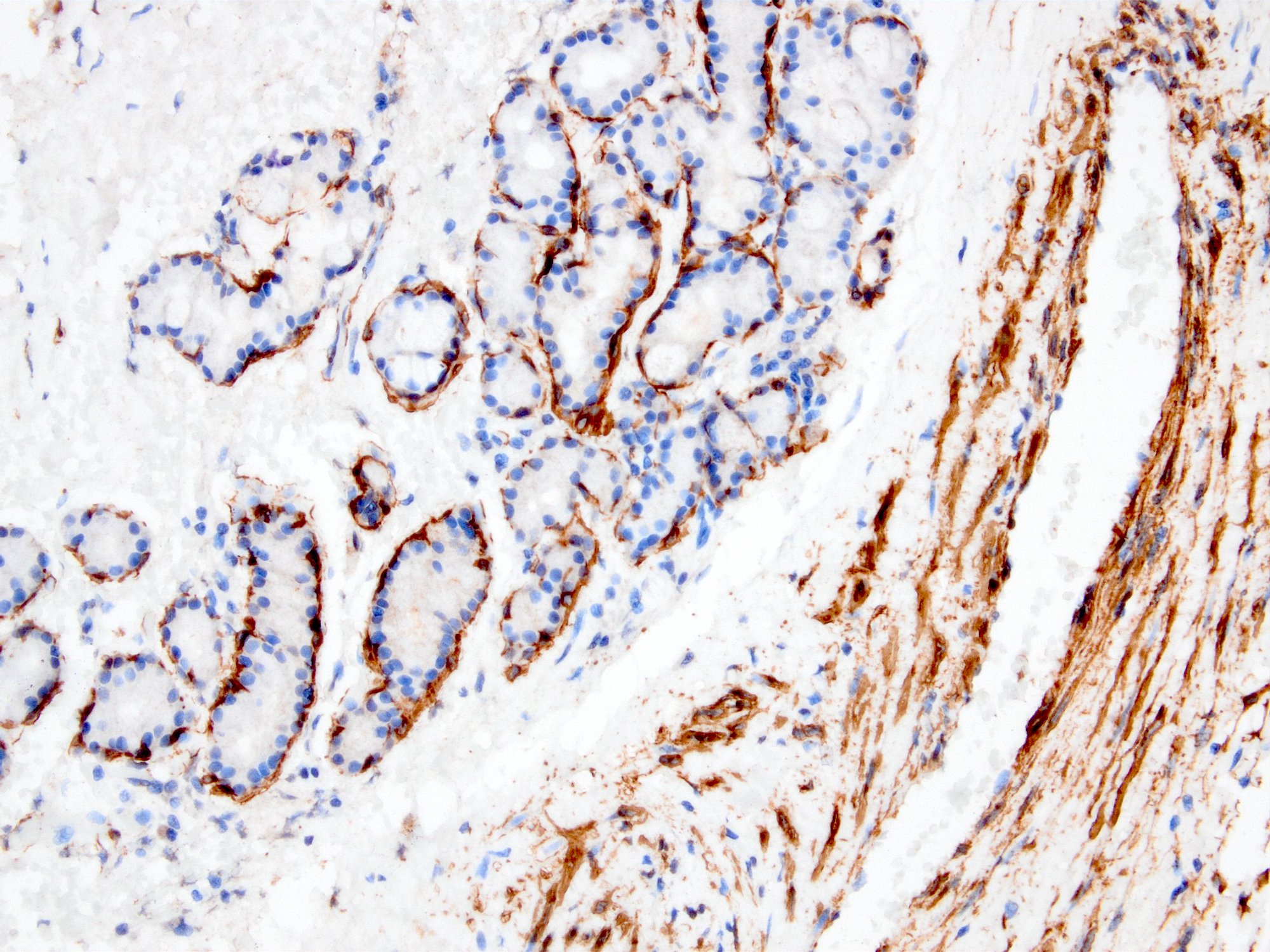
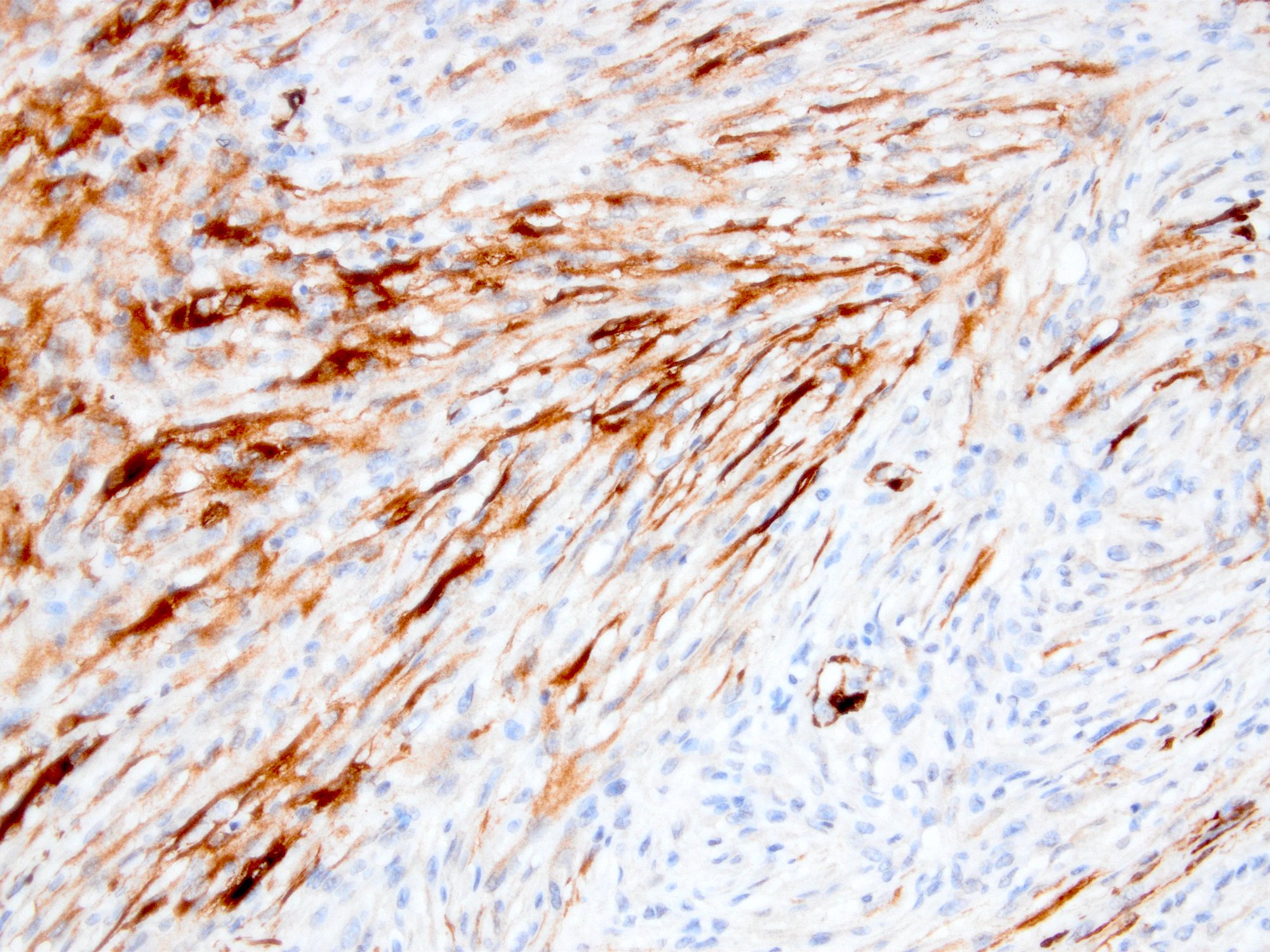
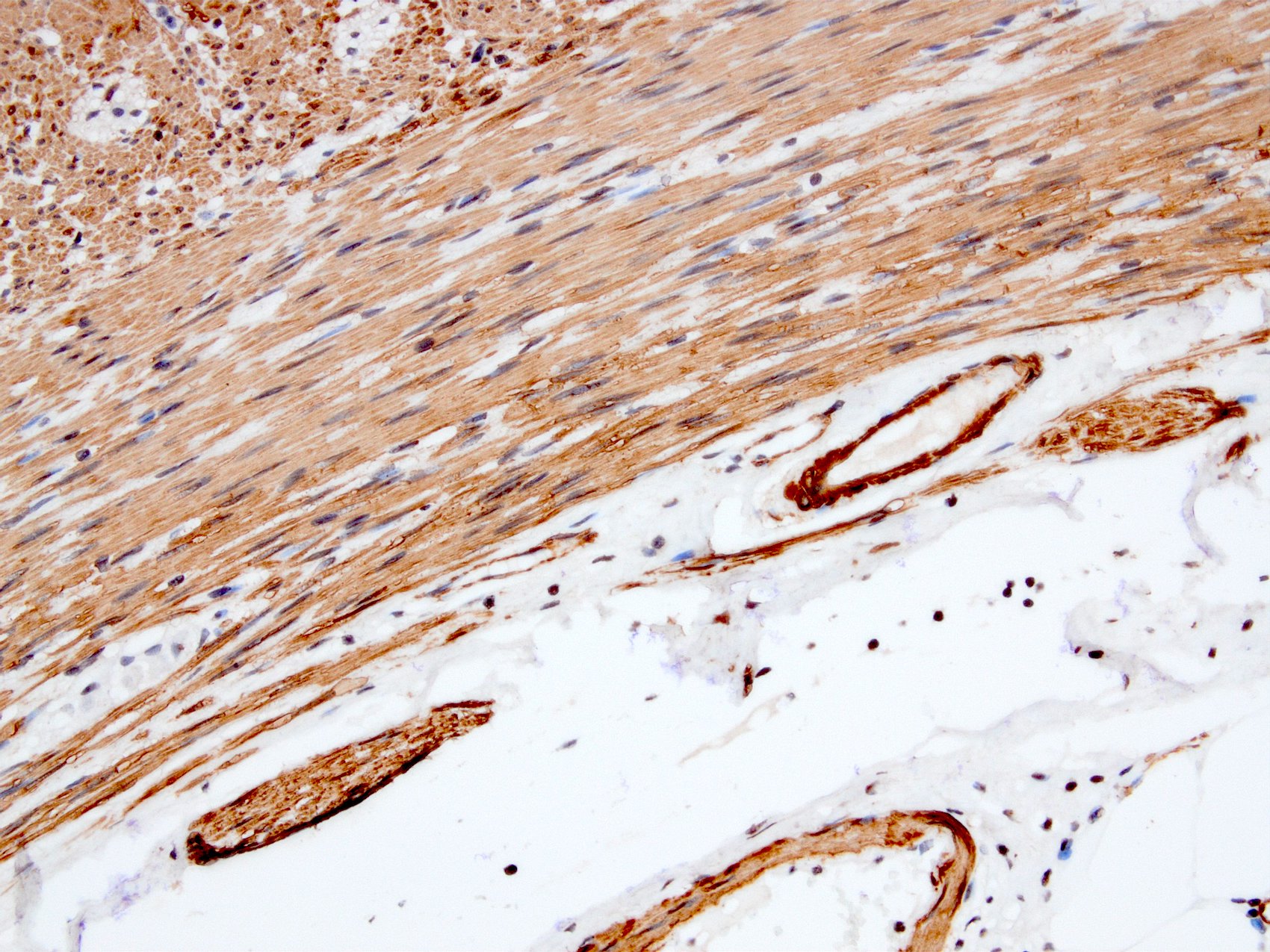
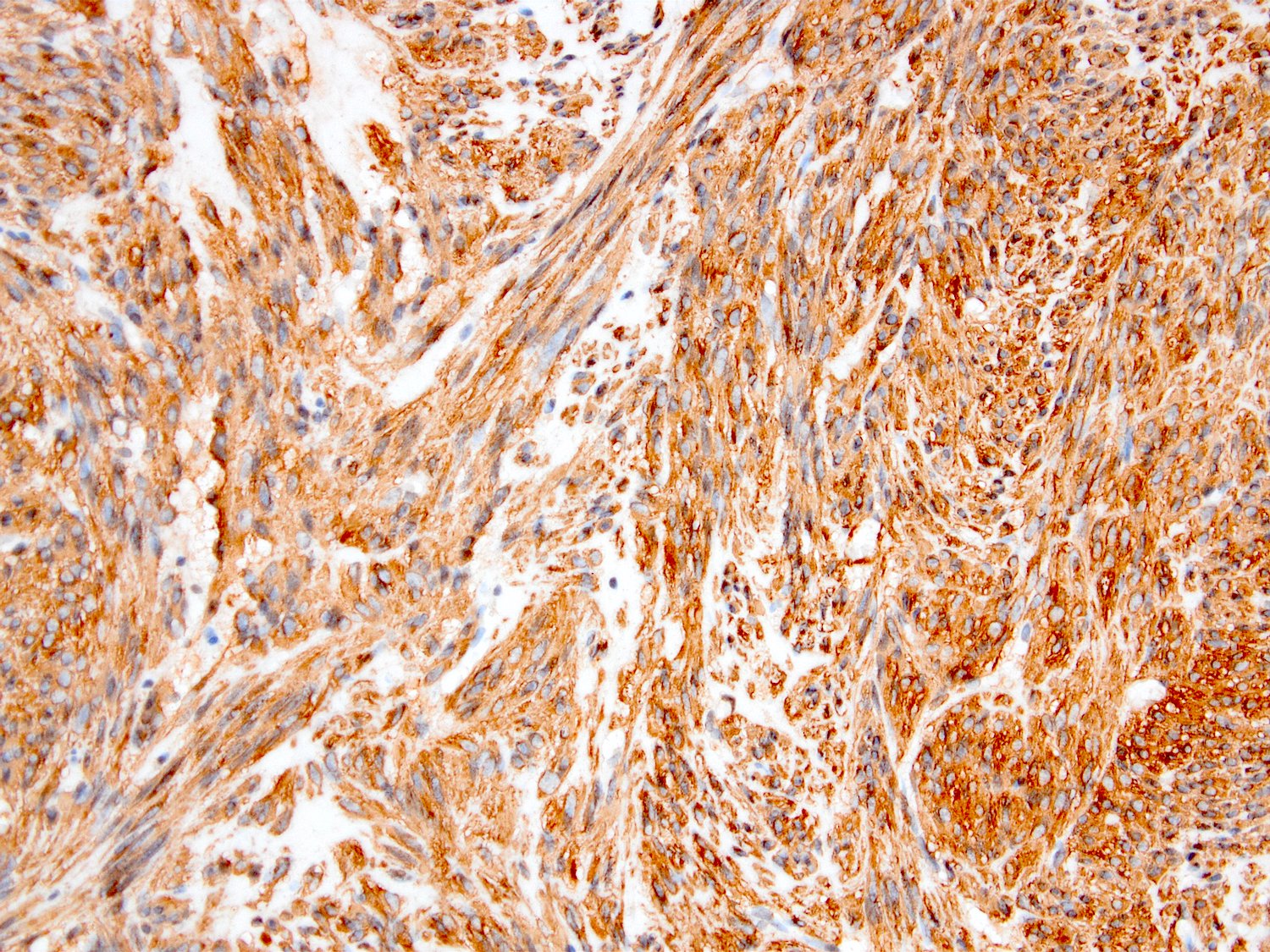
- Myofibroblastic staining (tram track) versus smooth muscle staining (block cytoplasmic)
Terminology
- Also called smooth muscle actin, SMA; clone ASM1 / 1A4 or sm 1
Pathophysiology
- 3 types: alpha, beta and gamma
- Alpha actins are found in muscle tissues and required for contraction, whereas the beta and gamma actins function as components of the cytoskeleton in many cells
- Expression correlates with the activation of myofibroblasts (Mol Cell Biochem 2008;308:201)
- May play a role in epithelial mesenchymal transition of carcinomas (Rom J Morphol Embryol 2014;55:1383)
Clinical features
- Controversial results on deficiency in intestinal pseudoobstruction (J Clin Pathol 2004;57:1168, Pediatr Surg Int 2008;24:1191, Gut 2004;53:1583)
- Immunoexpression may predict aggressive behavior in cutaneous basal cell carcinoma (Hum Pathol 2010;41:1128)
- Potential prognostic factor in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (Clinics (Sao Paulo) 2012;67:1039)
Interpretation
- Membranous or cytoplasmic staining
Uses by pathologists
- Identify smooth muscle cells and myofibroblasts in normal, reactive or neoplastic tissue (Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1999;20:582, Am J Dermatopathol 2006;28:105)
- Identify myoepithelial cells in normal, neoplastic or diseased breast, salivary glands or sweat glands
- May be helpful to rule out invasion
- May be particularly important in cytology specimens
- Reference: Anticancer Res 2003;23:4175
- Identify pericytes to correlate with hematogenous metastasis and prognosis (Oncology 2005;69:159)
- Help distinguish pleuropulmonary desmoid tumors (SMA+) from solitary fibrous tumor (SMA-) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:1503)
- Note: in breast papillary lesions, p63 is more sensitive and specific because smooth muscle actin also stains myofibroblasts / stromal cells (J Clin Pathol 2007;60:315)
Prognostic factors
- Myogenic differentiation (either only SMA or SMA+ desmin) in dedifferentiated liposarcoma significantly decreases 5 year disease free survival (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:799)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Myofibroblastic staining (tram track) versus smooth muscle staining (block cytoplasmic)
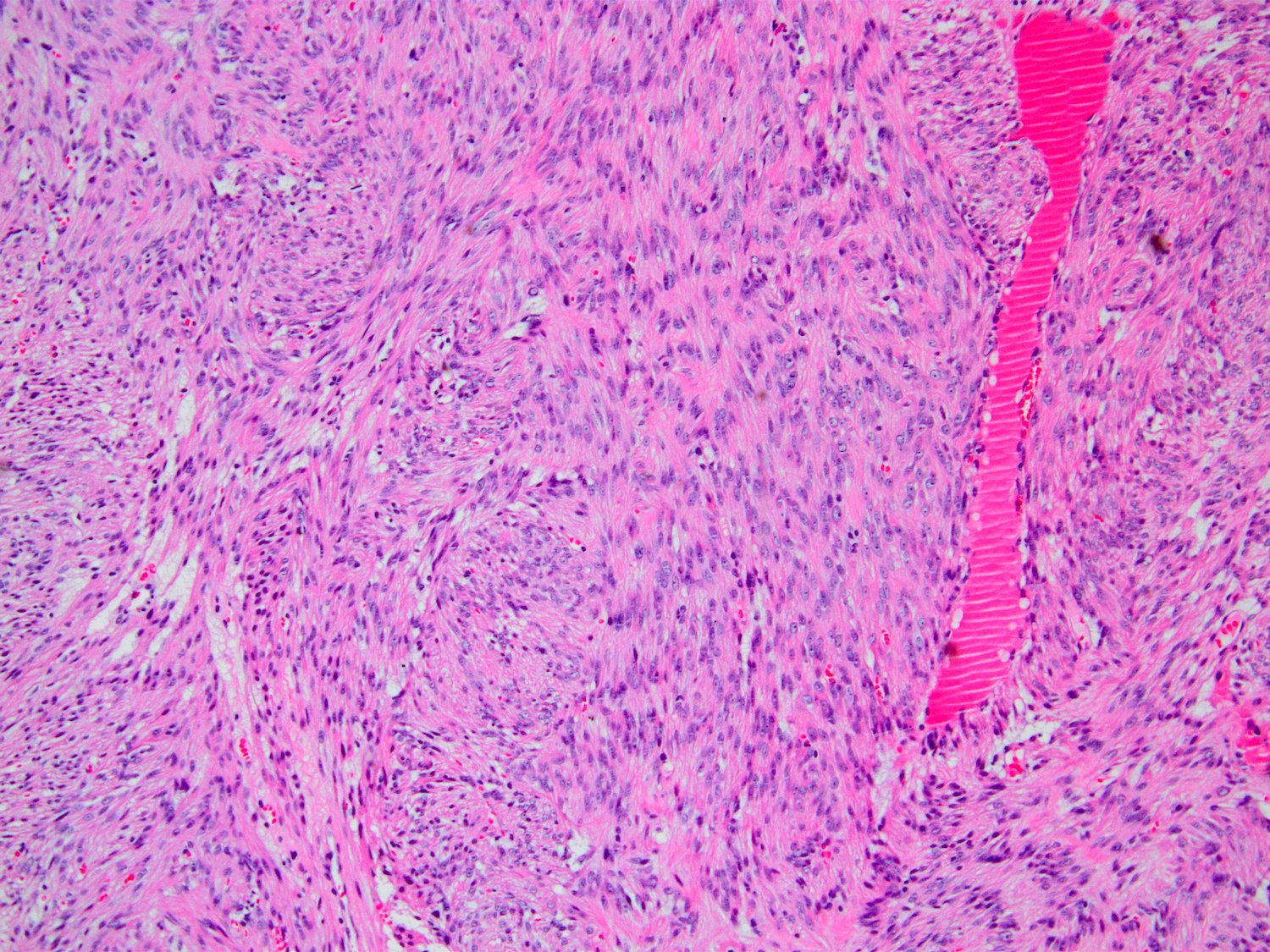
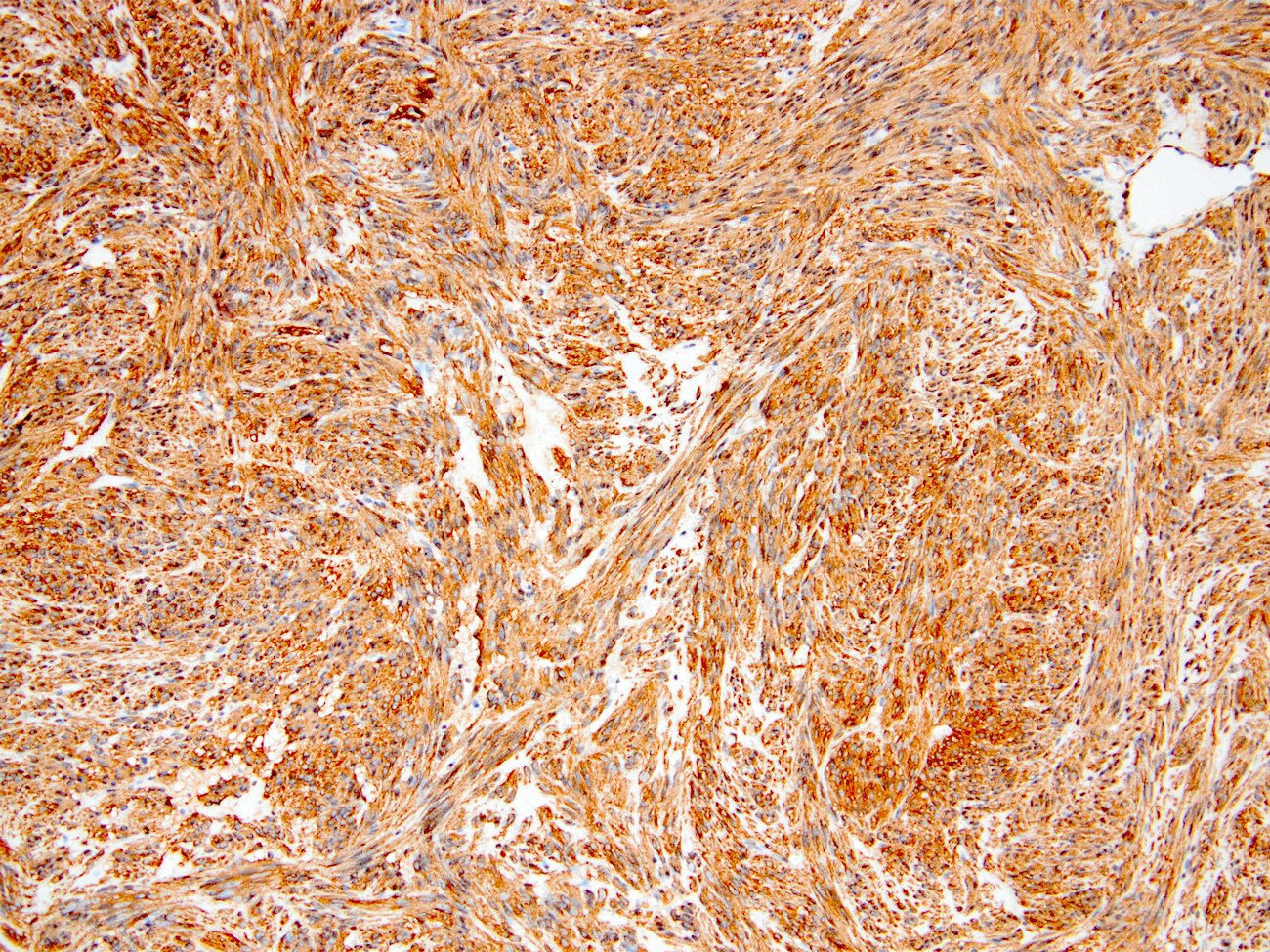
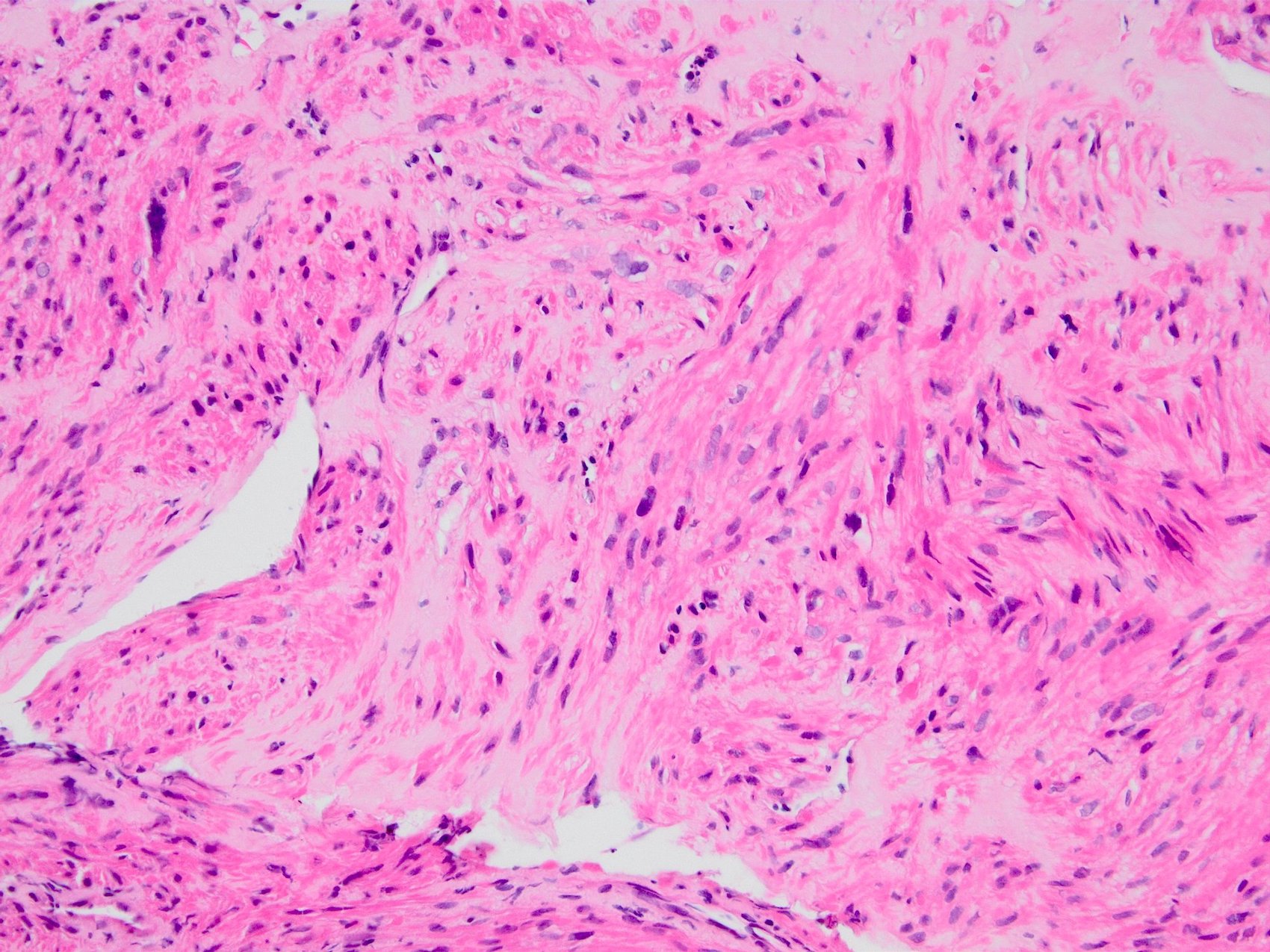
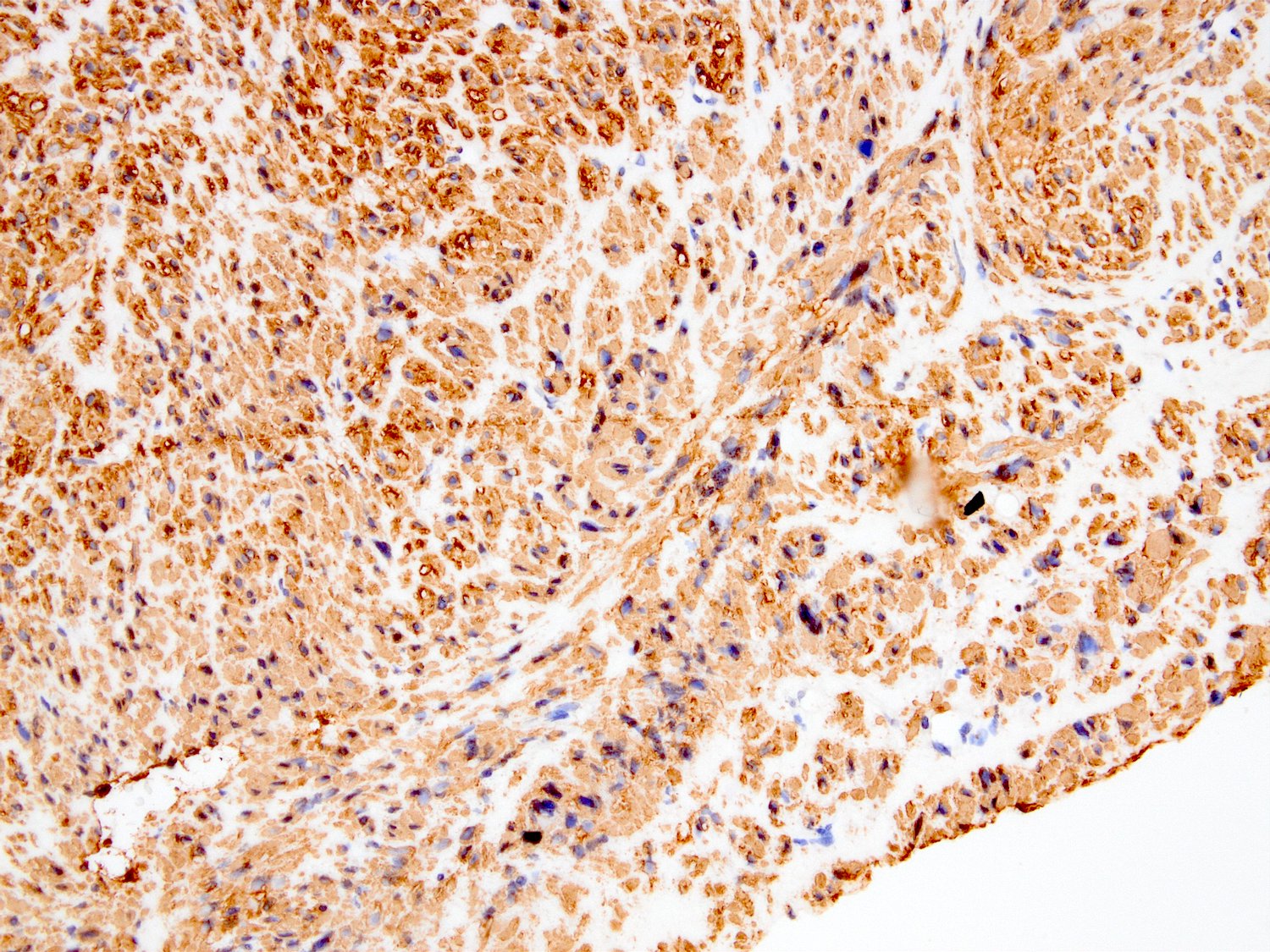
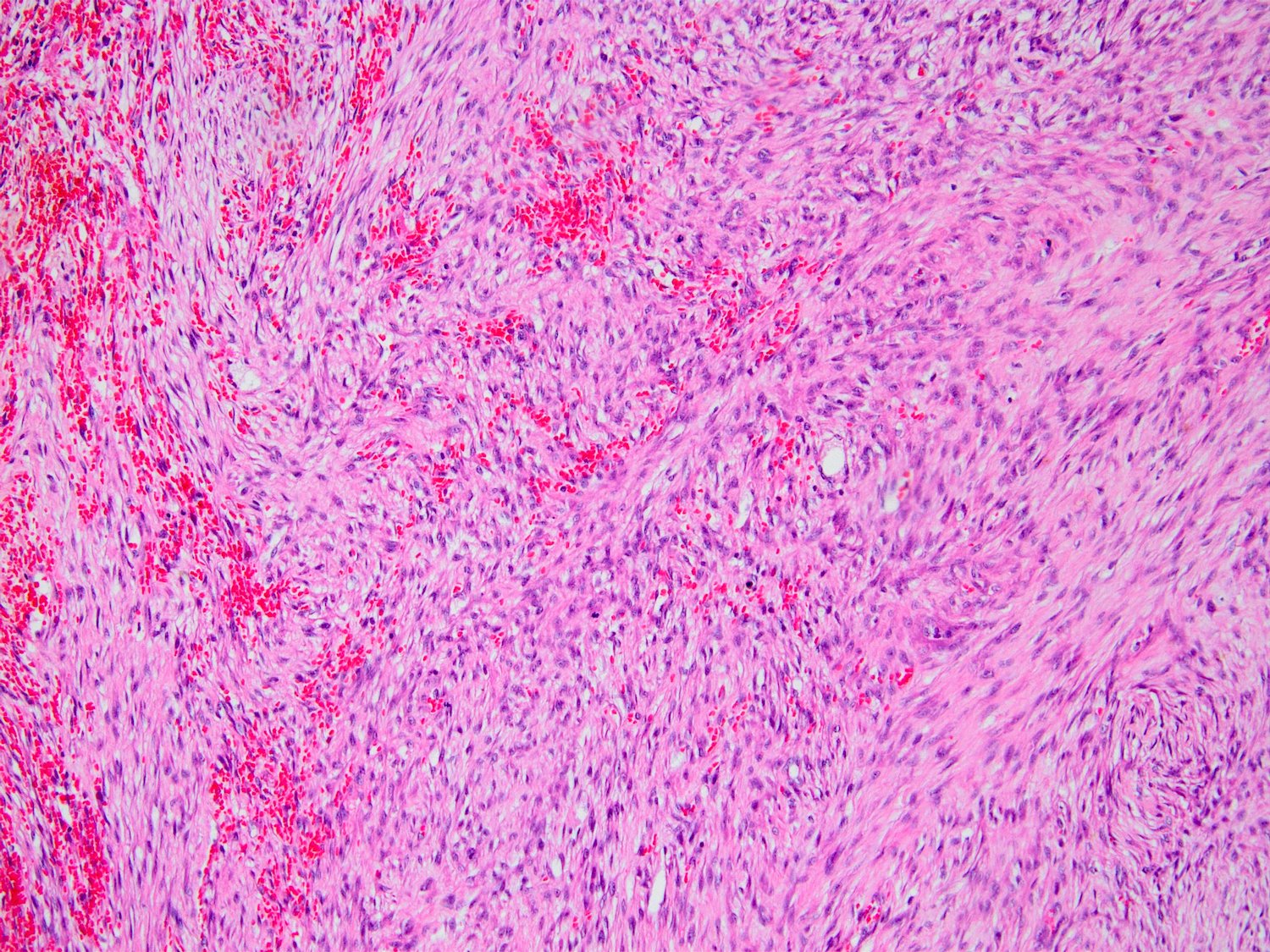
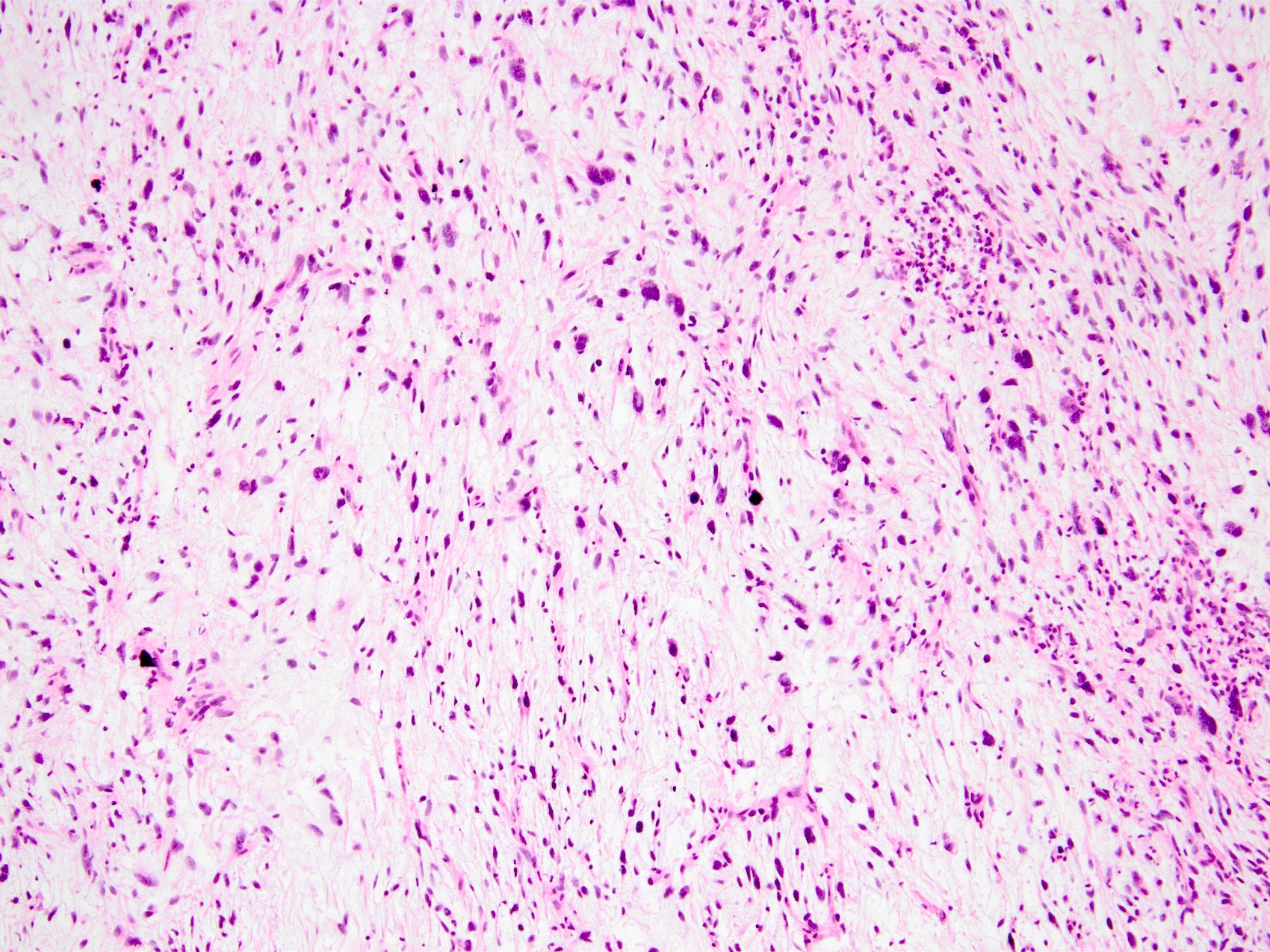
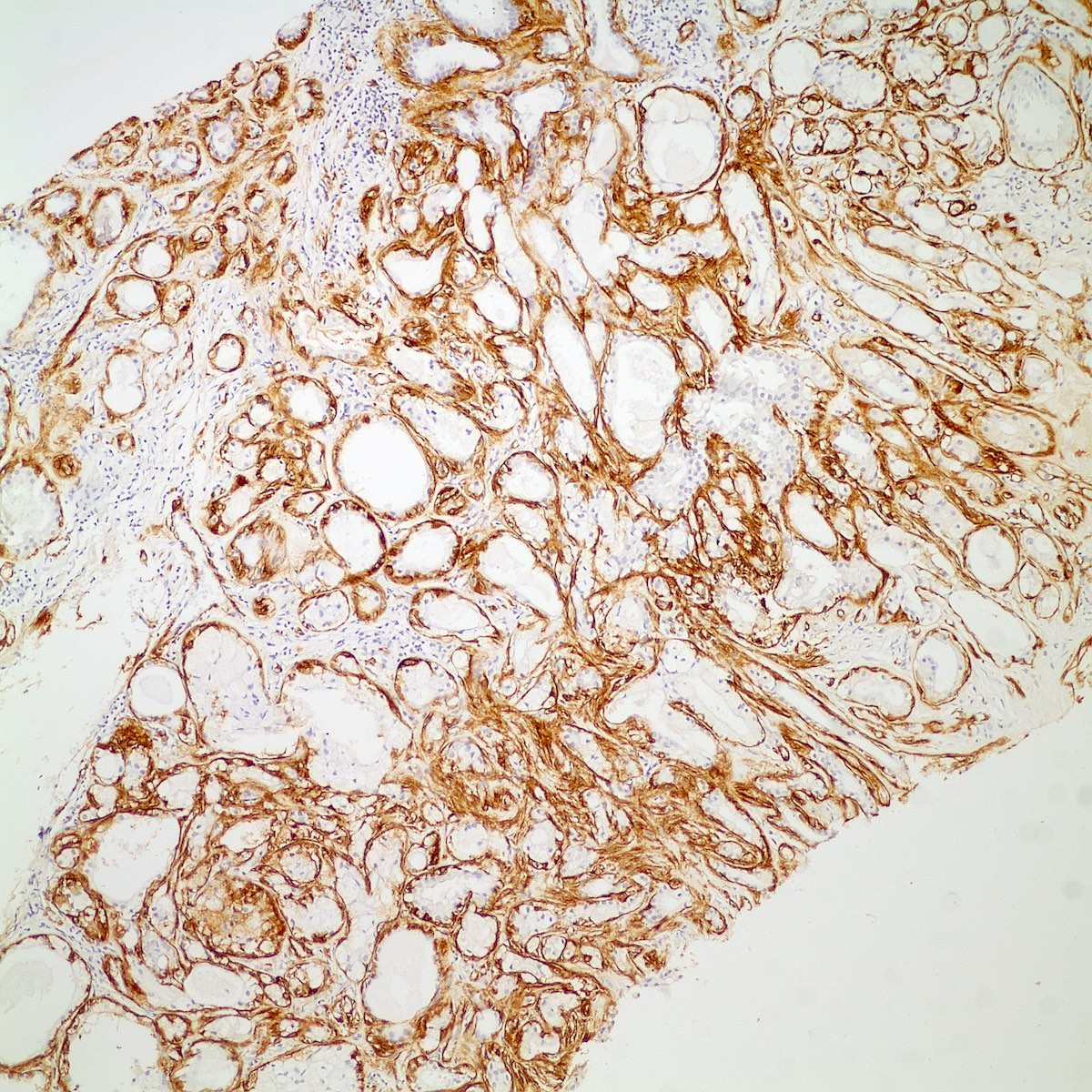
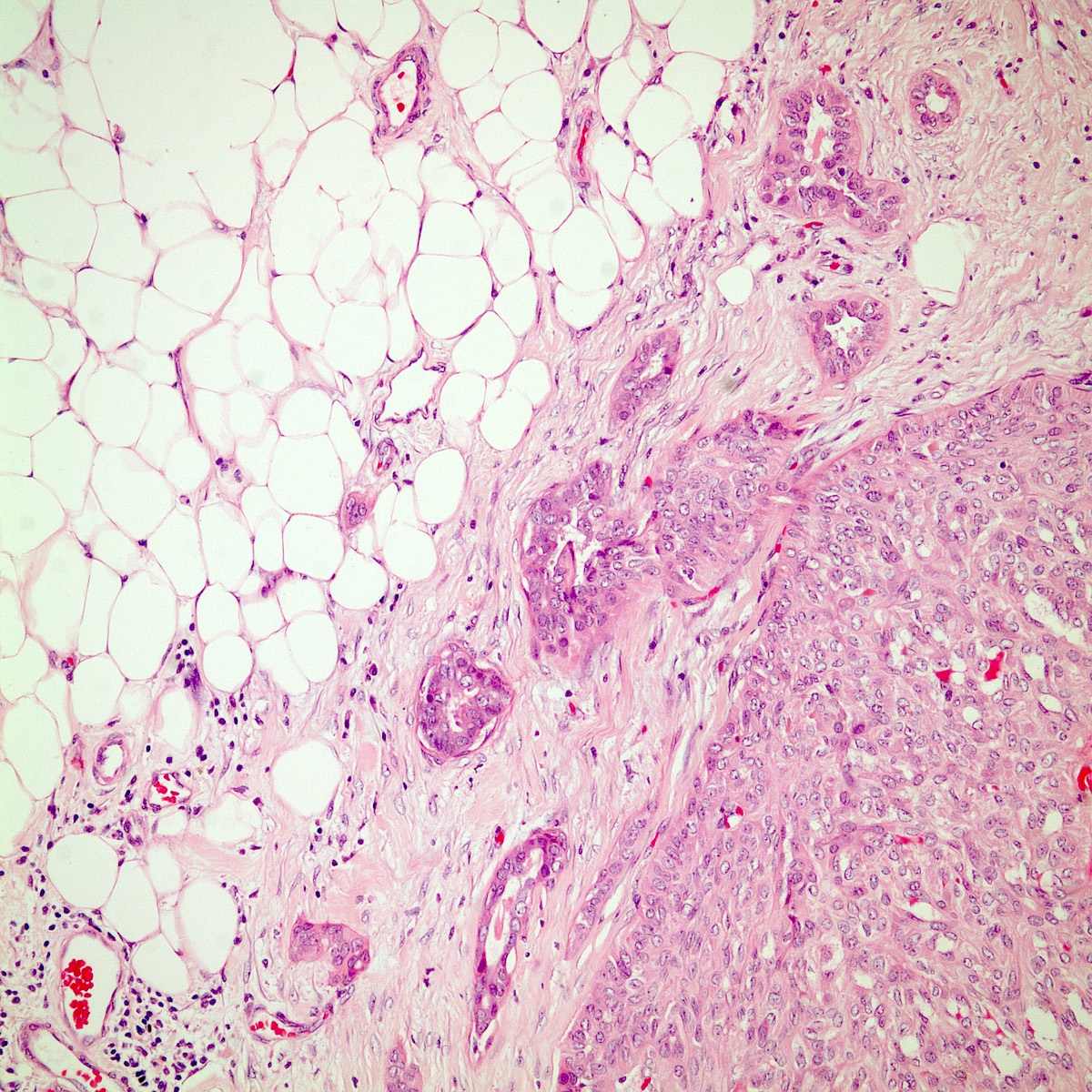
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Kemal Kösemehmetoğlu, M.D.
Virtual slides
Positive staining - normal
- Breast myoepithelial cells (most) (Breast Cancer Res 2003;5:R151, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1993;90:999)
- Chondrocytes, choroidal nonvascular smooth muscle cells (Folia Biol (Praha) 2006;52:167, J Anat 2005;207:381)
- Decidual stromal cells, fibroblastic reticulum cells (Hum Reprod 1999;14:1599, J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 1981;101:149)
- Glomus coccygeum, hepatic stellate cells (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1999;123:905, Virchows Arch 1997;430:195)
- Myofibroblasts (except alveolar and some granulation tissue / scars) (J Histochem Cytochem 1992;40:1955, Lab Invest 1989;60:275, Int J Legal Med 1992;105:99)
- Osteoblasts (J Orthop Res 2002;20:622)
- Pericytes (J Histochem Cytochem 1989;37:315)
- Salivary glands (APMIS 1991;99:405)
- Smooth muscle and vascular smooth muscle (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1981;78:298)
- Sweat glands and tracheobronchial glands (J Histochem Cytochem 1988;36:659)
Positive staining - disease
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1999;123:801)
- Atypical teratoid / rhabdoid tumor (J Neurosurg 1996;85:56, Brain Tumor Pathol 2008;25:79)
- Benign fibrous histiocytoma (in deep form 38%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
- Biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:517)
- Cellular angiofibroma (focal, 41%) (Mod Pathol 2011;24:82)
- Cellular neurothekeoma (at least focal in 57%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:329)
- Collagenous spherulosis (Mod Pathol 2006;19:1351)
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): large airways have increased expression of SMA (Respir Res 2011;12:48)
- Epstein-Barr virus associated smooth muscle tumour (EBV SMT) (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:75)
- Endometrial stromal sarcoma (65%) (Gynecol Oncol 2004;92:71)
- Epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:44)
- Fibromatosis (56%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:1296)
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) (45%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:1296, Am J Pathol 1990;136:771)
- Glomus tumor (Hum Pathol 1999;30:1259, Am J Pathol 1990;136:771)
- Granulosa cell tumors of ovary, both adult and juvenile (variable) (Mod Pathol 1995;8:25)
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 1991;15:1146, Ann Diagn Pathol 2001;5:335, Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:896, Turk J Gastroenterol 2012;23:399)
- Leiomyoma (Am J Dermatopathol 2006;28:105, Am J Pathol 1987;128:91)
- Leiomyosarcoma (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2011;30:236, Anticancer Res 2005;25:1559)
- Liposarcoma, pleomorphic (focal in 40 - 50%), dedifferentiated (50%), well differentiated (in the form of pericytic mimicry) (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:601, Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1257, Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:799, Hum Pathol 2016;54:92)
- Melanoma, desmoplastic / spindle cell (Am J Dermatopathol 1999;21:537, Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:75, Am J Surg Pathol 1996;20:1489)
- Mesothelioma, sarcomatoid (60%) (Histopathology 2003;42:270)
- Myoepithelioma (Hum Pathol 2004;35:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:1183)
- Myofibroma / myopericytoma (Am J Pathol 1987;128:91)
- Myofibroblastic sarcoma (Chin Med J (Engl) 2007;120:363, Int J Oral Sci 2012;4:170, Am J Dermatopathol 2006;28:105)
- Neurothekeoma (40% focal) (Am J Pathol 1987;128:91)
- Nodular fasciitis (Ann Diagn Pathol 2002;6:94, Am J Dermatopathol 2006;28:105)
- PEComas (angiomyolipoma, pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis) (J Egypt Natl Canc Inst 2013;25:125, J Clin Pathol 1993;46:479, Tohoku J Exp Med 2003;199:119)
- Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 1994;18:668, Histopathology 1991;19:503)
- Plexiform fibromyxoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1624)
- Renal mixed epithelial and stromal tumor (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:80, Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao 2008;40:415)
- Rhabdomyoma (focal / rare) (Hum Pathol 1993;24:754, Hum Pathol 1993;24:608)
- Rhabdomyosarcoma embryonal, alveolar and sclerosing / spindle cell (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2005;8:427, Korean J Ophthalmol 2006;20:70, Virchows Arch 2006;449:554)
- Soft tissue perineurioma (21%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:845)
- Synovial sarcoma (25%) Mod Pathol 2007;20:760)
- Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (focal) (J Clin Pathol 2003;56:666, Histopathology 2006;48:453)
Negative staining
- Normal tissue:
- Cardiac muscle (positive during development) (J Cell Sci 2007;120:229)
- Skeletal muscle (J Cell Biol 1985;100:807)
- Basal cells of prostate glands (Am J Surg Pathol 1996;20:1489)
- Disease:
- Angiomyofibroblastoma (rarely focal) (Hum Pathol 1997;28:1046)
- Carcinomas (usually)
- Cellular benign fibrous histiocytoma (Am J Surg Pathol 1994;18:668)
- Clear cell sarcoma (J Clin Pathol 2010;63:416)
- Epithelioid sarcoma proximal type (15 - 33%) (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:130, Mod Pathol 2001;14:655)
- Fibrosarcoma, infantile and adult type (rare / focal; expression does not exclude diagnosis) (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;115:348)
- Hemosiderotic fibrolipomatous tumor (Histopathology 2006;48:453)
- Liposarcoma, myxoid type (rarely focal) (Am J Clin Pathol 1995;103:20)
- Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (LGFMS) (rare / focal) (Lab Invest 2005;85:408)
- Myofibroblastoma (occasionally focally positive) (Pathology 2005;37:144, Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:1022)
- Ossifying fibromyxoid tumor (weak); 6% (J Laryngol Otol 1993;107:75, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1615)
- Thecoma / fibrothecoma (Mod Pathol 1995;8:25)
- Schwannoma, solitary fibrous tumor (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:1503, Diagn Pathol 2021;16:32)
- Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:979)
Sample pathology report
- Right 3rd intercostal space, wide excision:
- Leiomyosarcoma, grade 3 (see comment)
- Comment: Immunohistochemically, neoplastic cells showed diffuse strong cytoplasmic staining for SMA, desmin and h-caldesmon.
- Right thigh, excisional biopsy:
- Nodular fasciitis (see comment)
- Comment: Immunohistochemically, neoplastic cells were positive for SMA in myofibroblastic pattern (tram track staining) and negative for desmin.
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
B. Demonstrates smooth muscle type of SMA staining
Comment Here
Reference: Actin, alpha smooth muscle type
Comment Here
Reference: Actin, alpha smooth muscle type