Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining - disease | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Lérias S, Félix A. HPV (Human papillomavirus). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainshpv.html. Accessed August 14th, 2025.
Definition / general
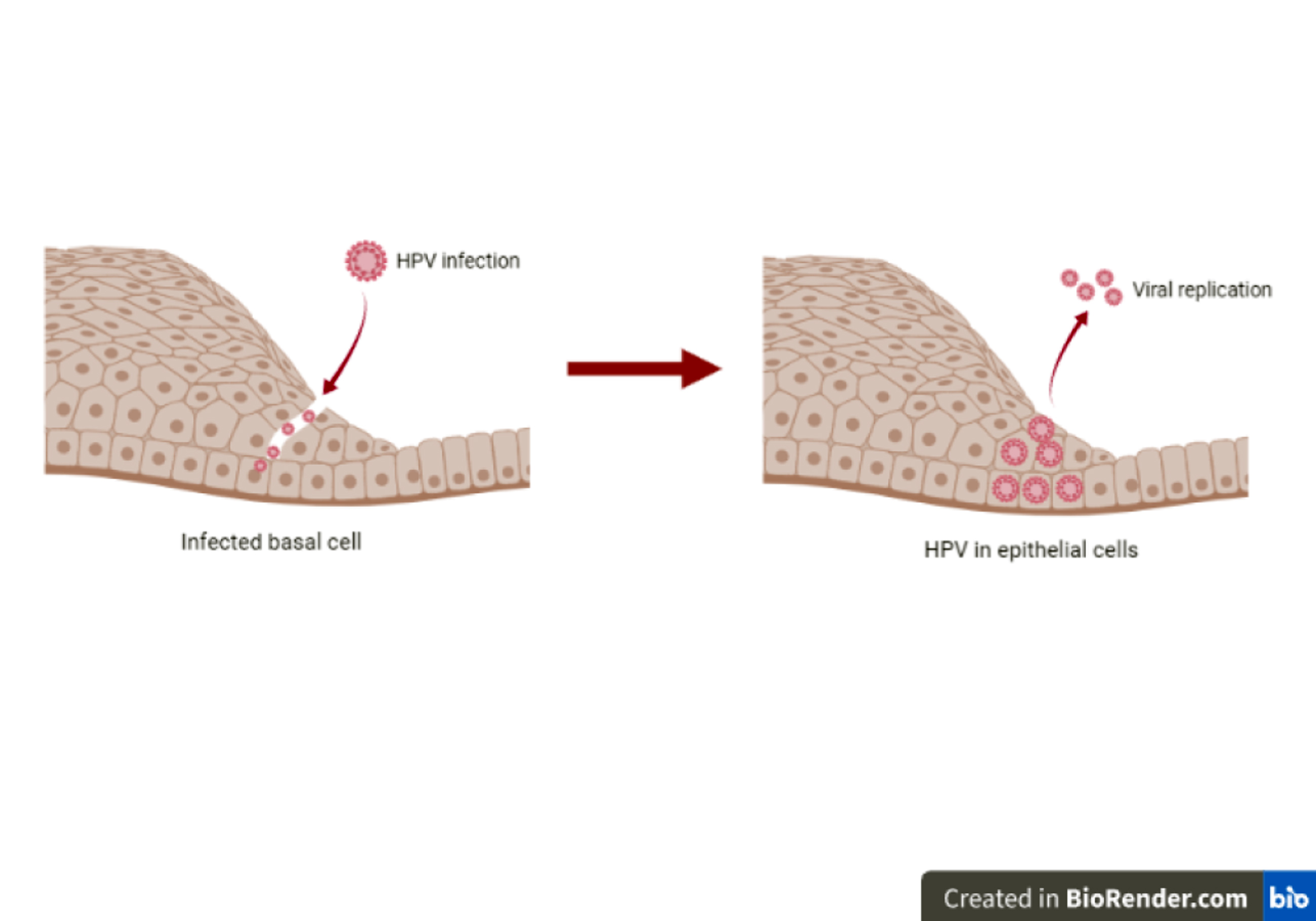
- Human papillomaviruses (HPVs) are a group of small, double stranded DNA viruses that show tropism for squamous epithelium and infect cells in the basal layer of stratified squamous epithelia (Nat Rev Cancer 2010;10:550)
- High risk HPV types are the causative agents of cervical (99%), penile, vaginal, vulvar, anal and oropharynx cancers (Nat Rev Cancer 2010;10:550, Vaccine 2006;24:S3/11)
Essential features
- HPV oncoproteins E5, E6 and E7 are responsible for initiation and progression of HPV associated cancers
- Approximately 40 HPV types are known to infect the anogenital tract
- HPV types are subdivided into high risk, probably high risk and low risk, having the potential to cause cancers and warts around the genital organs
- Current methods available for HPV detection include polymerase chain reaction (PCR) based techniques, DNA in situ hybridization (ISH), RNA ISH and immunohistochemical detection of the p16 (CDKN2A), E4, E6 and E7
Pathophysiology
- Persistent infection with high risk HPV type is necessary but not sufficient for the progression to HPV associated cancer (Nat Rev Cancer 2010;10:550)
- HPV E6 and E7 are the primary transforming viral proteins and E5 enhances proliferation and contributes to cancer progression
- Intense and diffuse expression of p16 reflects functional inactivation of Rb induced by viral oncoprotein E7, which in turn releases E2F, allowing the cell to enter in the S phase of cell cycle (Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 2015;132:135)
- p16 immunohistochemistry represents a surrogate for transcriptionally active high risk HPV, since HPV viral oncoprotein E7 signaling induces strong overexpression of the cellular protein p16INK4a in HPV transformed cells (Nat Rev Cancer 2010;10:550)
- HPV oncoprotein E6 leads to the inactivation of tumor suppressor protein p53, contributing to tumor progression (Nat Rev Cancer 2010;10:550)
Clinical features
- More than 100 HPV types have been differentiated molecularly and at least 40 of them have a tropism for anogenital mucosa (Sci Rep 2018;8:11313)
- HPVs are clinically classified as low risk and high risk, based on the propensity of the HPV associated lesions to undergo malignant progression (Virus Res 2009;143:195)
- Low risk HPVs are associated with benign warts (Virus Res 2009;143:195)
- High risk HPVs are associated with intraepithelial neoplasia and cancers (Virus Res 2009;143:195)
- Only a fraction of women infected with high risk HPVs develop cervical cancer, indicating that additional factors must contribute to malignant progression (Nat Rev Cancer 2010;10:550)
- Certain subtypes of HPVs are the causative agents of cervical (99%), penile, vulvar and anal carcinomas and oropharyngeal carcinomas (Nat Rev Cancer 2010;10:550, Vaccine 2006;24:S3/11)
- High risk HPV is likely to be a causative agent of some low grade bladder carcinomas (Cancer 2011;117:2067)
HPV DNA classification
| Group | HPV types | Comments |
| Alpha HPV types | ||
| 1 | 16 | Most potent HPV type; known to cause cancer at several sites |
| 1 | 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59 | Sufficient evidence for cervical cancer |
| 2A | 68 | Limited evidence in humans and strong mechanistic evidence for cervical cancer |
| 2B | 26, 53, 66, 67, 70, 73, 82 | Limited evidence in humans for cervical cancer |
| 2B | 30, 34, 69, 85, 97 | Classified by phylogenetic analogy to HPV types with sufficient or limited evidence in humans |
| 3 | 6, 11 | -- |
| Beta HPV types | ||
| 2B | 5 and 8 | Limited evidence for skin cancer in patients with epidermodysplasia verruciformis |
| 3 | Other beta and gamma types |
Table: HPV classification according to International Agency for Research on Cancer Monograph Working Group (Lancet Oncol 2009;10:321)
Interpretation
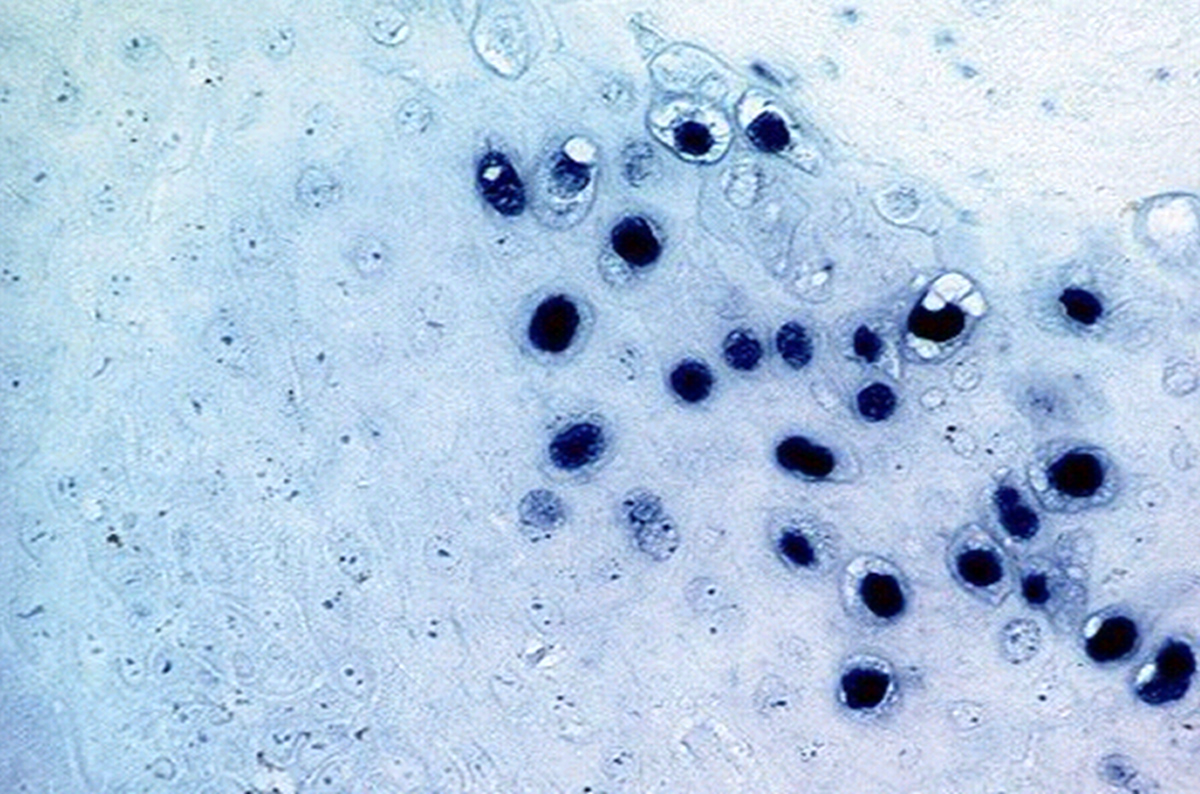
- HPV DNA ISH
- Punctate and dot-like signals within tumor nuclei indicate the presence of integrated HPV, while diffuse nuclear staining is thought to indicate the presence of episomal HPV genomes (Korean J Pathol 2010;44:513)
- RNA ISH
- Dot-like signals of varying sizes in the cytoplasm and nuclei of tumor cells (Hum Pathol 2017;63:184)
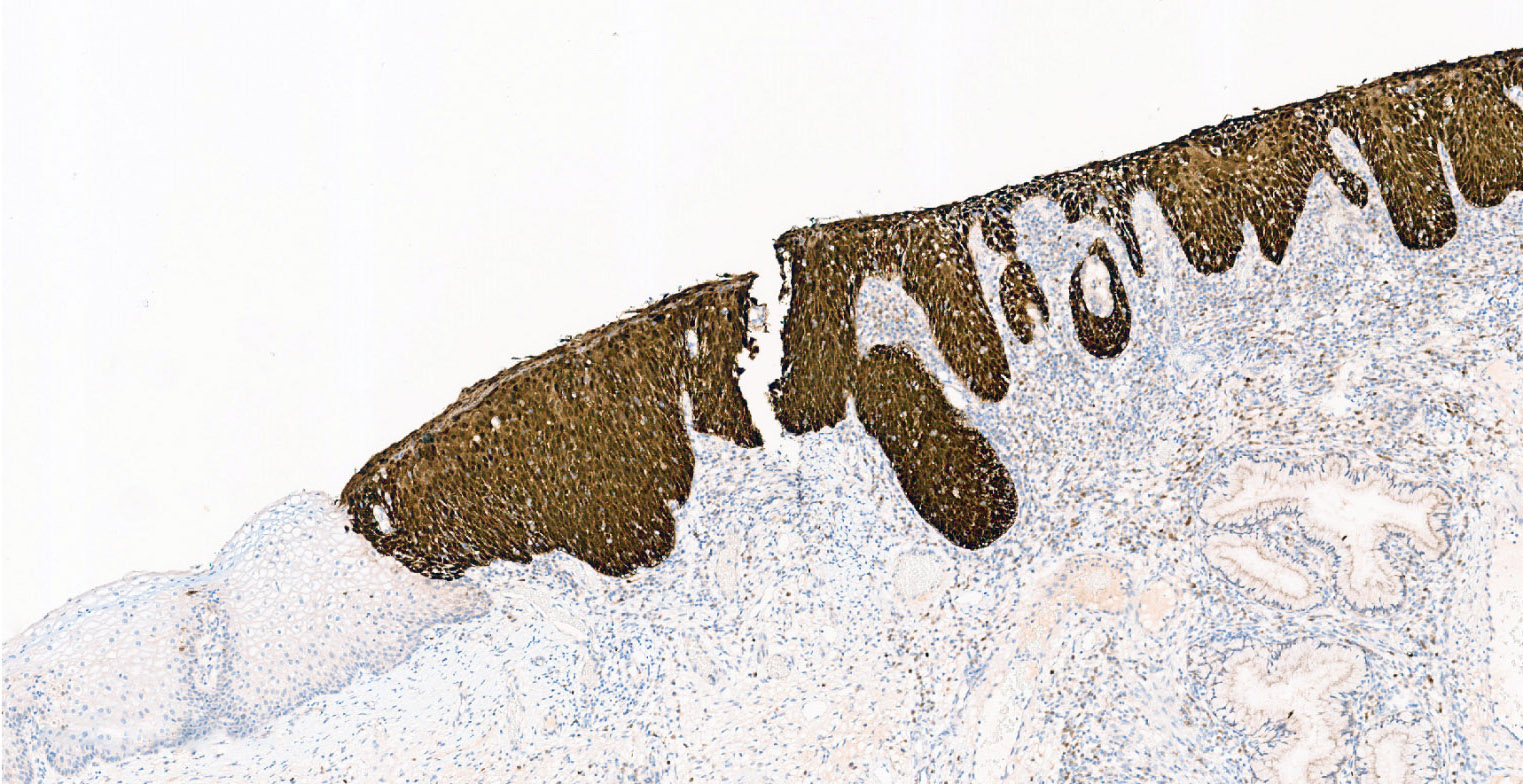
- p16 IHC
- Diffuse and strong nuclear or nuclear and cytoplasmatic staining involving the basal and parabasal layers is considered positive (block-like staining)
- Patchy / weak or cytoplasmatic only staining should be considered negative
- Nuclear and cytoplasmic expression of p16 in ≥ 70% of tumor cells is required for the diagnosis of HPV positive oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018;142:559)
- E6 / E7 IHC
- Cytoplasm staining of the tumor cells with E6 (Abcam, Clone C1P5) or E7 (Chemicon, Clone TGV701Y) oncoproteins is considered positive (Anticancer Res 2016;36:319)
- E4 IHC
- E4 protein is an immunohistochemical biomarker of productive HPV infection and associated with a low short-term progression risk (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1518)
- Cytoplasmic staining of E4 (LBP, clone FH1.1) restricted to the upper quarter of the epithelium, involving the upper half of the epithelium or extensive staining is considered positive (Cancer Med 2020;9:2454)
- E4 protein is absent in cancer, almost always negative in CIN3, while CIN2 and CIN1 can be either E4 positive or negative (Cancer Med 2020;9:2454)
- Expression of p16 above 67% of the epithelium is associated with negative E4, while expression of p16 up to 67% of the epithelium is associated with positive E4 (p < 0.001) (Cancer Med 2020;9:2454)
- Dual marker approach with p16 / E4 may help grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) lesions and improve disease stratification (Mod Pathol 2015;28:977, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1518)
- Serum antibodies to HPV proteins
- Serum antibodies against HPV16 anti-E1 / E4 and anti-E7 proteins are associated with cervical cancer (Int J Cancer 1993;54:624, Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:2769)
- Serum antibodies to the HPV16 oncoproteins E6 and E7 and to the regulatory proteins E1 and E2 are strongly associated with HPV driven oropharyngeal cancer (Int J Cancer 2017;140:2748)
Uses by pathologists
- PCR
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the reverse transcription PCR method to detect E6 / E7 messenger RNA (mRNA) as the gold standard test for HPV detection, which can be used for viral load quantitation, DNA sequencing and mutation analysis (MLO Med Lab Obs 2012;44:14)
- Compared with PCR based methods, DNA / RNA ISH and p16 IHC are more practical tools, with an interpretation fully in the light field (Cancer 2010;116:2166)
- HPV DNA ISH
- Differentiating HPV related oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (ISH+) from HPV independent oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (ISH-) (Cancer 2010;116:2166)
- High specificity (89%) but lower sensitivity (83%)
- Does not provide evidence for transcriptional HPV activity
- HPV E6 / E7 mRNA ISH
- Provides evidence for transcriptional HPV activity (Int J Cancer 2013;132:882)
- 100% concordance with PCR in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas (Int J Cancer 2013;132:882)
- High specificity (93%) and sensitivity (97%) in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas (Br J Cancer 2013;108:1332)
- Highly sensitive method for the detection of anogenital HSIL, cervical squamous cell carcinoma and HPV related oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (sensitivity ≥ 97%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:607)
- Differentiating anogenital low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) (positive in 78% of the cases) from negative / reactive cases (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:607)
- Differentiating LSIL / cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN1) (ISH+) from negative / reactive lesions (ISH-) in cervical samples (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:192)
- Should only be used in cases that are morphologically concerning for LSIL / CIN1 (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:192)
- Differentiating cervical / oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma metastatic to the lung (ISH+) from primary pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma (ISH-)
- Differentiating usual type cervical adenocarcinoma (ISH+) from endometrial carcinoma (ISH-)
- Differentiating usual type cervical adenocarcinoma in situ (ISH+) from microglandular hyperplasia and tuboendometrioid metaplasia (ISH-)
- p16 IHC
- Surrogate marker for HPV driven squamous cell carcinoma, mainly cervical and oropharyngeal, independently of the HPV genotype involved (Hum Pathol 2004;35:689)
- Sensitive but not specific (particularly outside the oropharynx) for the diagnosis of HPV related squamous cell carcinomas (Cancer Clin Oncol 2013;2:51)
- Differentiating high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (p16+) from low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion or a non-HPV associated pathology such as atypical squamous metaplasia (p16-) (J Low Genit Tract Dis 2012;16:205)
- Can be used as an adjunct to morphologic assessment for biopsy specimens interpreted as CIN1 that are at a high risk for missed high grade disease, defined as a prior cytologic interpretation of high grade squamous intraepithelial lesions, ASC-H or ASC-US / HPV16+ (J Low Genit Tract Dis 2012;16:205)
- E6 / E7 IHC
- Oncoproteins expressed in HPV associated cervical and oropharyngeal cancer can be detected by immunohistochemical evaluation (Anticancer Res 2016;36:319)
Prognostic factors
- Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma associated with high risk HPV infection have a significantly better outcome than HPV negative disease (Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2011;79:860)
- HPV negative cervical cancer seems to be associated with a poor prognosis compared with HPV positive but some studies showed no prognostic implication of HPV status (Oncotarget 2017;8:66352, Int J Gynecol Cancer 2007;17:1307, Gynecol Oncol 2018;148:97)
- Negative p16 in patients with HPV DNA positive cervical tumors is associated with a poor overall survival (Mod Pathol 2020;33:128)
- In anatomical locations other than the uterine cervix, HPV associated carcinomas have consistently shown a better prognosis than HPV independent tumors (Gynecol Oncol 2012;125:194, Gynecol Oncol 2013;129:406)
- Negative p16 in high risk HPV DNA positive vulvar squamous cell carcinoma has a significantly worse prognosis (Mod Pathol 2020;33:893)
- Multiple HPV16 infections with 2 high risk genotypes is a major risk of CIN2 / CIN3 (BMC Cancer 2020;20:444)
Positive staining - disease
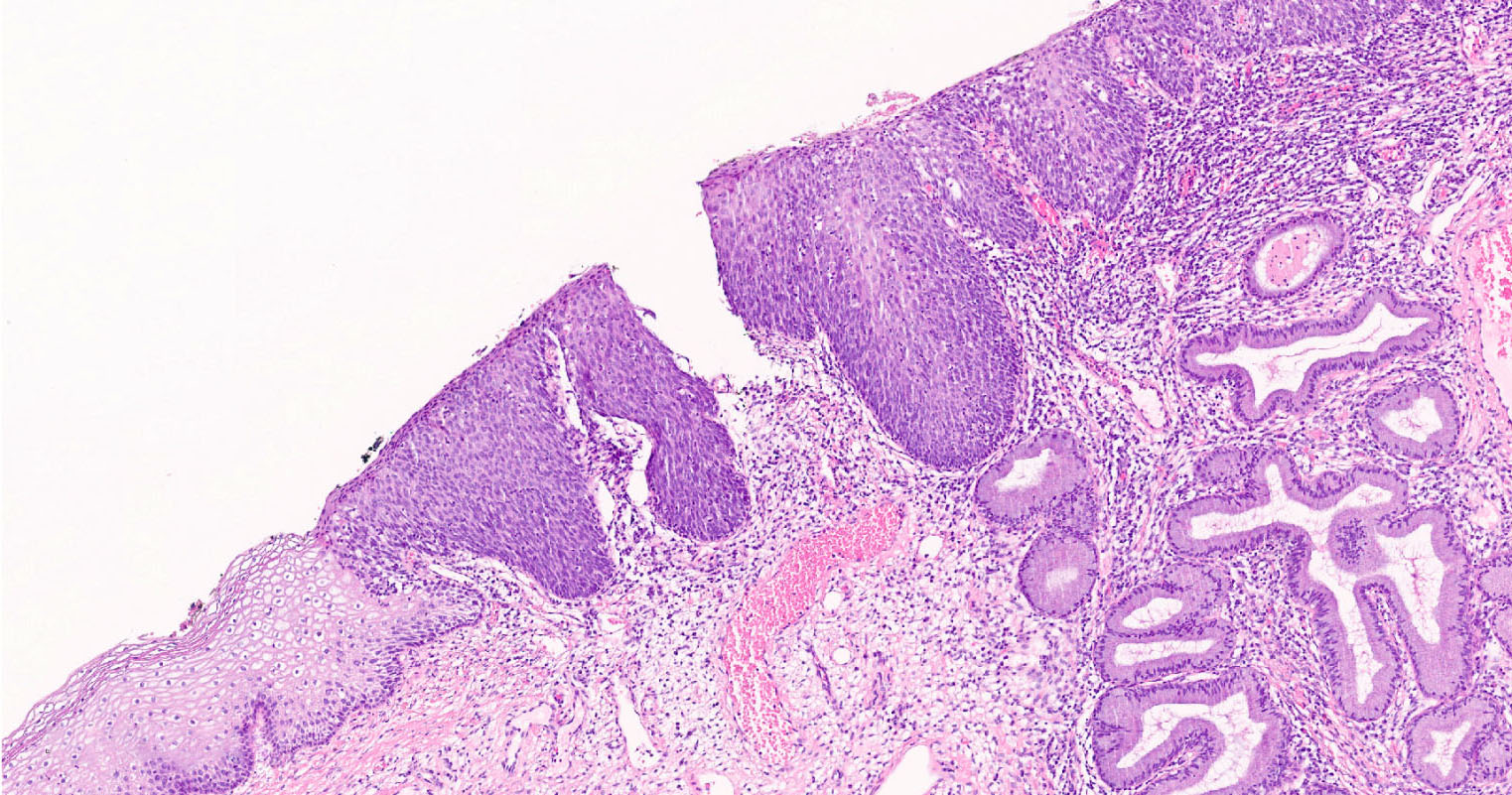
- Squamous intraepithelial lesions (high grade or low grade)
- Lower anogenital tract (cervix, vagina, vulva, perianus, anus, penis, scrotum)
- Oropharynx
- Less commonly, oral cavity and larynx
- Squamous cell carcinoma (Lancet Oncol 2009;10:321)
- Lower anogenital tract
- Oropharynx
- Less commonly, oral cavity and larynx
- Adenocarcinoma
- Uterine cervix (usual type)
Negative staining - disease
- Benign cervical lesions
- Immature squamous metaplasia
- Microglandular hyperplasia
- Tuboendometrial metaplasia
- Adenocarcinoma
- Uterine cervix (clear cell, mesonephric, gastric type)
- Endometrium
- Ovary
- Lung
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Oropharynx
- Oral cavity
- Larynx
- Lung
- Skin
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- PCR
- PCR is a cost effective technique that can be used for viral load quantification, DNA sequencing and mutation analysis (Curr Mol Med 2019;19:237)
- PCR based detection of the HPV DNA can be used in formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) tissues containing a low number of viral DNA copies (Infect Agent Cancer 2020;15:46)
- PCR based detection of the HPV DNA allows individual genotyping of low risk HPV, high risk HPV and probably high risk HPV types, though it cannot distinguish the HPV transcriptionally active infections from those defined as passenger HPV (Infect Agent Cancer 2020;15:46)
- HPV DNA PCR is a highly sensitive technique with a not negligible risk of contamination (Front Oncol 2020;10:1751)
- Quantitative reverse transcription PCR method for the detection of HPV E6 / E7 mRNA reveals that transcriptionally active HPV is present (Int J Cancer 2013;132:882)
- E6 / E7 mRNA reverse transcription PCR detection requires fresh / frozen tissue (Front Oncol 2020;10:1751)
- Quantitative reverse transcription PCR assays correlate highly with slide based HPV RNA in situ hybridization (Int J Cancer 2013;132:882)
- ISH
- Nucleic acid hybridization assays are very effective in detecting the common HPV types (HPVs 6 / 11 or 16) (Curr Mol Med 2019;19:237)
- Great advantage of ISH is that it can be interpreted fully in the light field and ISH probes are commercially available for FFPE tissue (Hum Pathol 2017;63:184)
- DNA ISH has a low sensitivity and requires large amounts of purified DNA (Curr Mol Med 2019;19:237, Mod Pathol 1998;11:971)
- RNA ISH is capable of detecting the HPV E6 / E7 mRNA transcripts in up to 28 HPV types in its transcriptionally active (Infect Agent Cancer 2020;15:46)
- RNA ISH is more sensitive than DNA ISH (100% versus 88%), more specific (87% versus 74%) and the correlation between p16 overexpression and presence of HPV mRNA is high (Hum Pathol 2017;63:184, Oral Oncol 2016;55:11)
- HPV E6 / E7 mRNA ISH shows more than 97% sensitivity for the detection of HPV related (PCR+ and p16+) neoplasia of the cervix, vulva, anus and head and neck (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:607)
- HPV E6 / E7 mRNA ISH positivity is 84% sensitive and 86% specific for an expert adjudicated diagnosis of CIN1 (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:192)
- Multiplex HPV RNA ISH / p16 IHC
- Combined technical approach with potential to improve the identification of HPV associated cancers (Infect Agent Cancer 2020;15:46)
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) testing
- p16 (by immunohistochemistry) for anogenital carcinomas and premalignant lesions
- Negative (cytoplasmic only staining, patchy nonblock type staining or diffuse blush / weak intensity staining)
- Positive (strong and continuous nuclear or nuclear and cytoplasmatic staining involving the basal and parabasal layers - block positive staining)
- Indeterminate
- p16 (by immunohistochemistry) for oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- Negative (< 50% diffuse and strong nuclear and cytoplasmic staining)
- Equivocal (≥ 50% but < 70% diffuse and strong nuclear and cytoplasmic staining)
- Positive (≥ 70% diffuse and strong nuclear and cytoplasmic staining)
- Indeterminate
- HPV DNA (by ISH)
- Negative (no signal)
- Positive (punctate or diffuse)
- Indeterminate
- HPV E6 / E7 mRNA (by ISH)
- Negative (no signal)
- Positive (cytoplasmic or nuclear signals)
- Indeterminate
- HPV DNA - specify HPV genotypes tested (by PCR)
- Undetectable
- High risk HPV detected (specify HPV genotypes)
- Low risk HPV detected (specify HPV genotypes)
- Indeterminate
- HPV E6 / E7 mRNA - specify HPV genotypes tested (by reverse transcription PCR)
- Undetectable
- High risk HPV detected (specify HPV genotypes)
- Low risk HPV detected (specify HPV genotypes)
- Indeterminate
- p16 (by immunohistochemistry) for anogenital carcinomas and premalignant lesions
Practice question #1
Which of the following tumors is more likely to be HPV unrelated?
- Anal squamous cell carcinoma
- Cervix adenocarcinoma
- Colon adenocarcinoma
- Oropharynx squamous cell carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the vulva
Practice answer #1
Practice question #2
Which of the following sentences is true?
- DNA ISH cannot be interpreted by light microscopy
- HPV E4 protein is almost always expressed in high grade squamous intraepithelial lesions / CIN3
- PCR distinguishes the HPV transcriptionally active infections from those defined as passenger HPV
- p16 immunohistochemistry is a surrogate marker for transcriptionally active low risk HPV
- RNA ISH is more sensitive and specific than DNA ISH
Practice answer #2
E. RNA ISH is more sensitive and specific than DNA ISH
Comment Here
Reference: HPV (Human papillomavirus)
Comment Here
Reference: HPV (Human papillomavirus)