Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Sample pathology report | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1Cite this page: Long TH, Moshiri A. Microphthalmia associated transcription factor (MITF). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsmitf.html. Accessed September 8th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Microphthalmia associated transcription factor (MITF), also known as melanocyte inducing transcription factor (GeneCards), is a regulator of gene expression essential for melanocyte survival, development and proliferation; it also has relevance in melanoma biology and nonmelanocyte cellular functions (Genes Dev 2019;33:983)
- MITF labels most melanocytic proliferations but is not specific for them
Essential features
- Transcription factor expressed in melanocytes and a variety of other cell types
- Essential for the survival, development and function of melanocytes
- Nuclear stain, positive in most melanocytic proliferations, with the notable exception of desmoplastic melanoma
- Positive in perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasms
- Nonspecific, with pitfalls including certain soft tissue tumors as well as reactive cells in excision scars
Terminology
- Homolog of mouse microphthalmia
- MI
- Melanocyte inducing transcription factor (renamed by HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee in 2017) (HGNC: Symbol Report for MITF [Accessed 8 April 2021])
- Microphthalmia associated transcription factor (original gene name)
- Class E basic helix - loop - helix protein 32 (BHLHe32)
- Waardenburg syndrome, type 2A (WS2, WS2A)
- CMM8
- COMMAD
Pathophysiology
- Encodes a transcription factor of the basic domain helix - loop - helix leucine zipper (bHLH-LZ) class that binds DNA as dimers
- Located on chromosome 3p14.1
- A member of the MiT subfamily of factors that also includes TFEB, TFE3 and TFEC, with which it can form heterodimers (Genes Dev 1994;8:2770)
- Required for the proper development of several cell lineages, including osteoclasts, melanocytes, retinal pigment epithelial cells, mast cells and natural killer cells (Bone 2004;34:689)
- Hundreds of downstream targets involved in lineage specific functions (i.e. tyrosinase in melanocytes, TRAP in osteoclasts) and a diverse range of additional nonlineage specific functions, including regulation of proliferation, DNA damage repair, metabolism, lysosome biogenesis and autophagy (Genes Dev 2019;33:983)
- Regulates function of pancreatic beta cells and may play a role in glucose homeostasis (Diabetes 2013;62:2834)
Clinical features
- Heterozygous alterations in MITF can cause several genetic syndromes:
- Waardenburg syndrome type 2A
- Tietz albinism - deafness syndrome
- Coloboma, osteopetrosis, microphthalmia, macrocephaly, albinism and deafness
- E318K mutation causes greatly increased risk of malignant melanoma or renal cell carcinoma (OMIM: Microphthalmia Associated Transcription Factor; MITF [Accessed 22 March 2021])
Interpretation
- Nuclear stain
Uses by pathologists
- Marker of melanocytic differentiation or melanin synthesis
- Melanoma margins in Mohs surgery (Dermatol Surg 2016;42:167)
- Diagnosis of perivascular epithelioid cell tumors (PEComas), including angiomyolipoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:65)
Prognostic factors
- Loss of expression in melanomas is associated with decreased survival and increased risk of occult lymph node metastasis (Melanoma Res 2015;25:496)
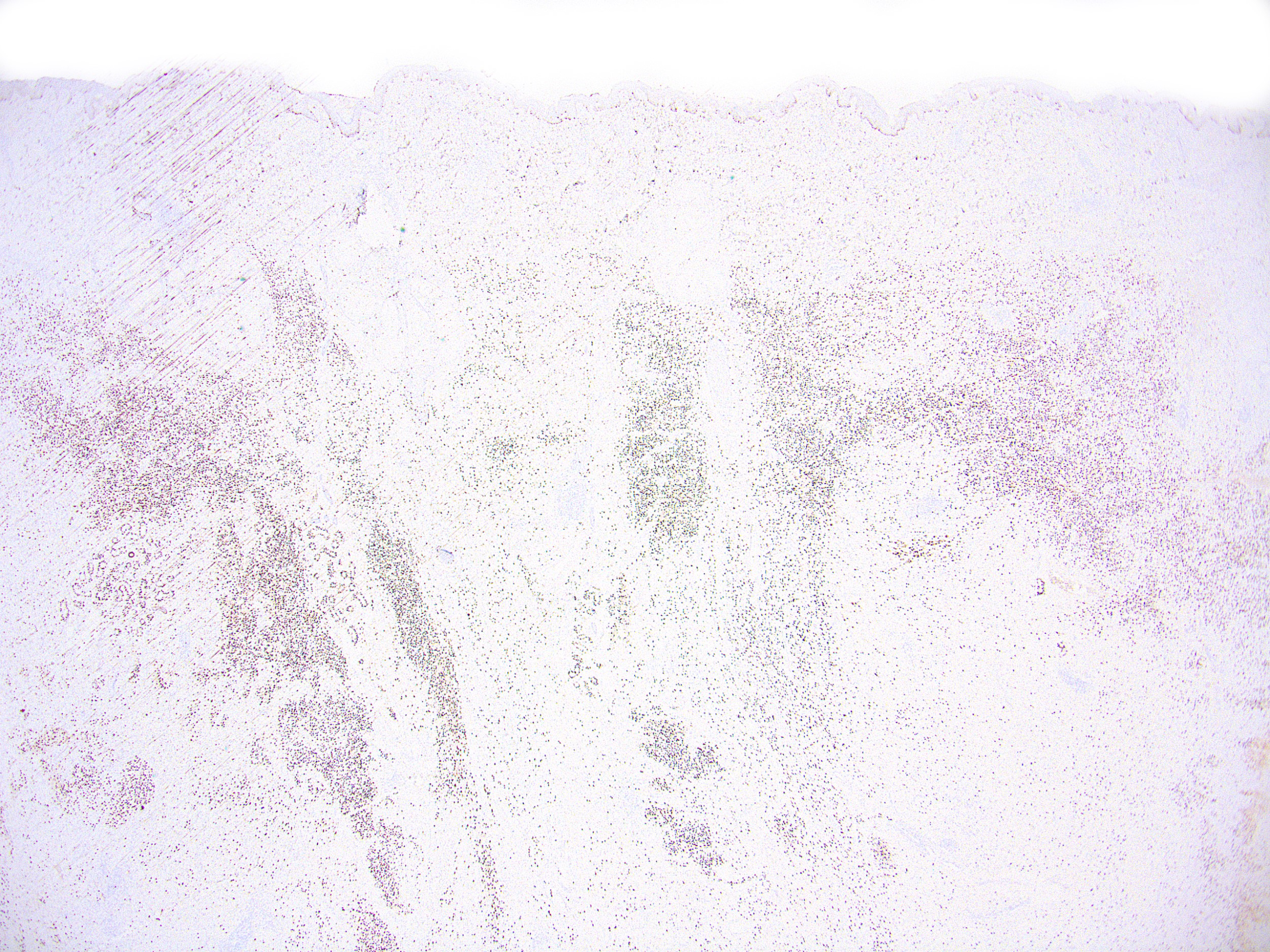
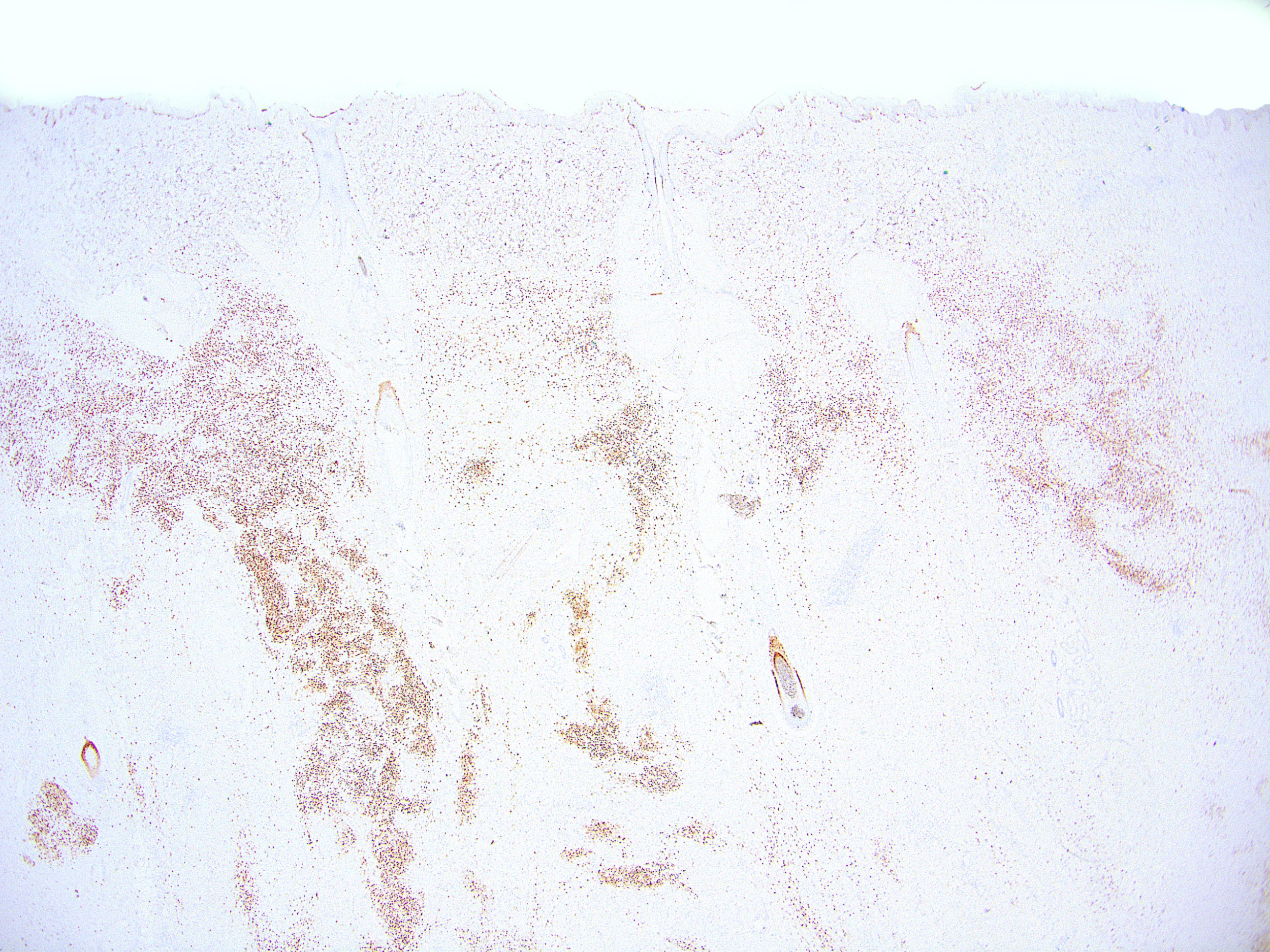
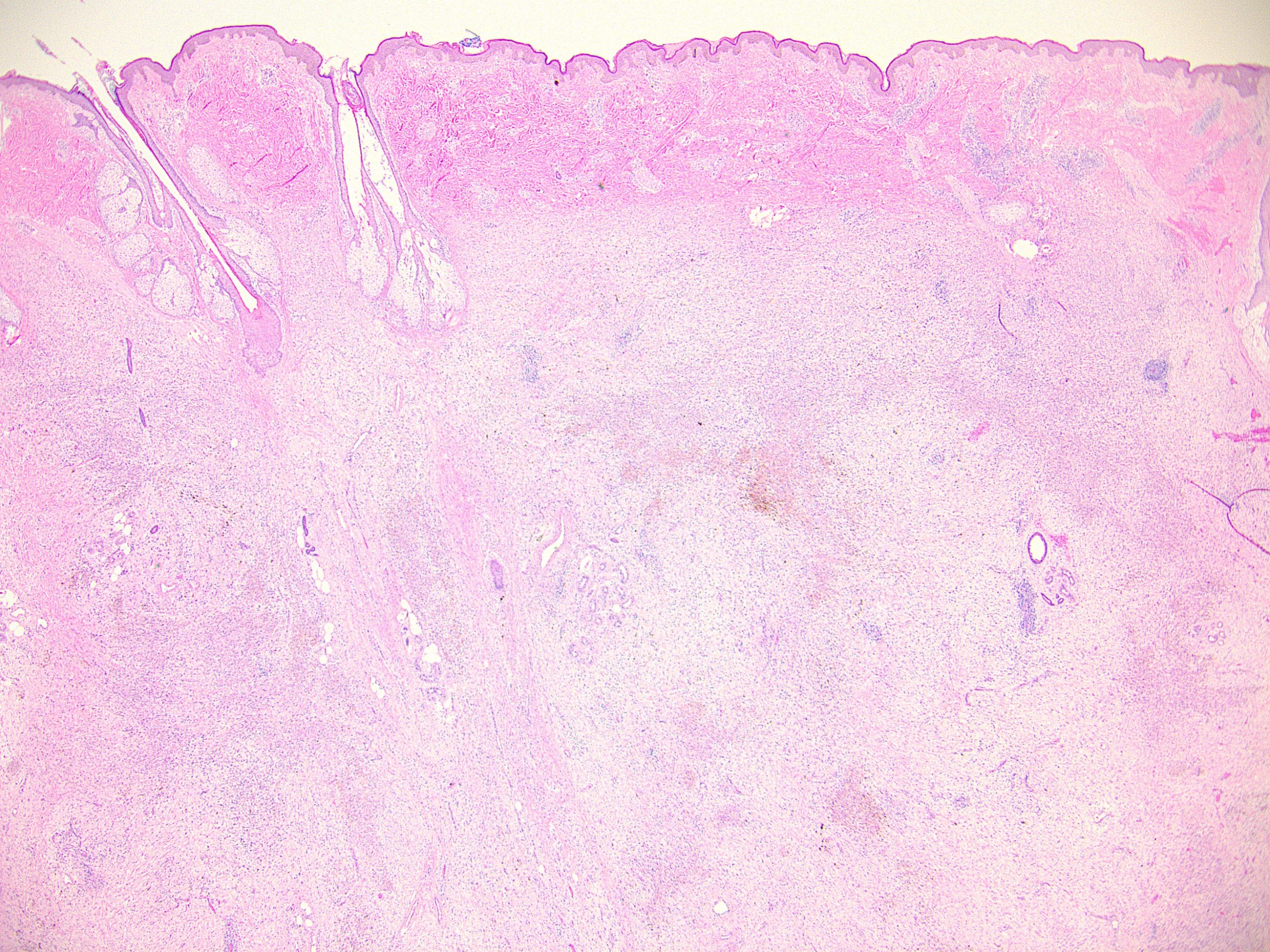
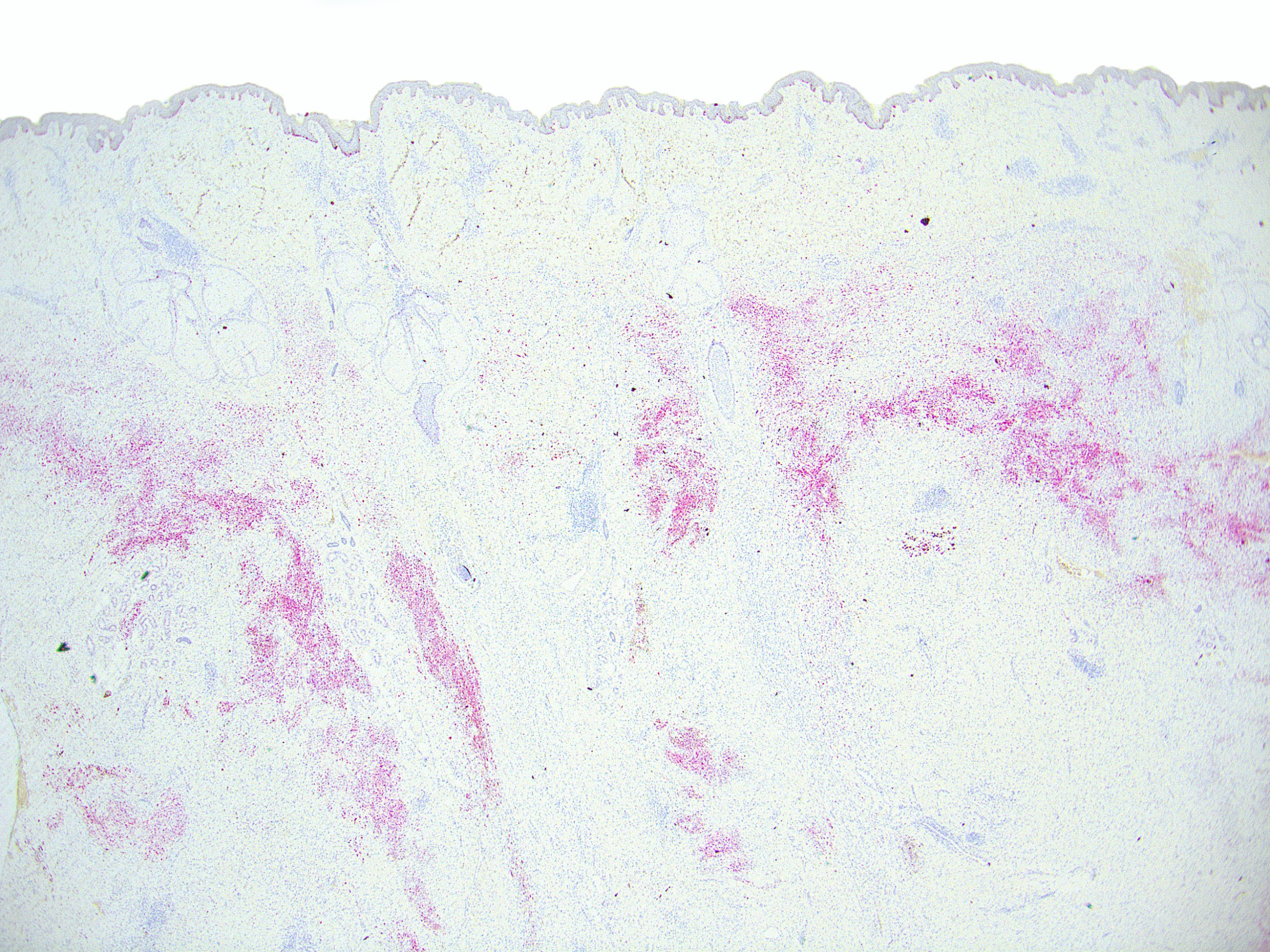
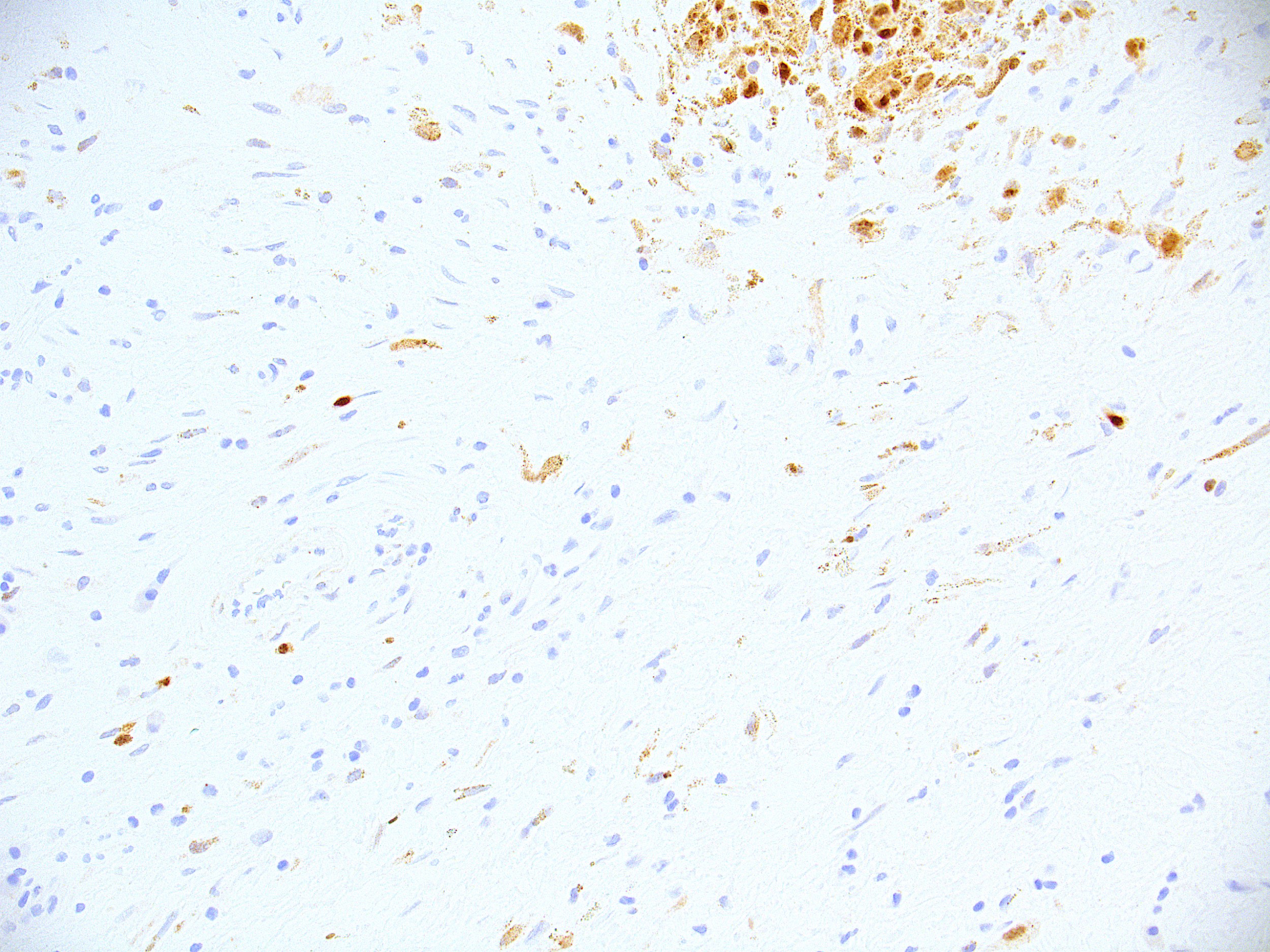
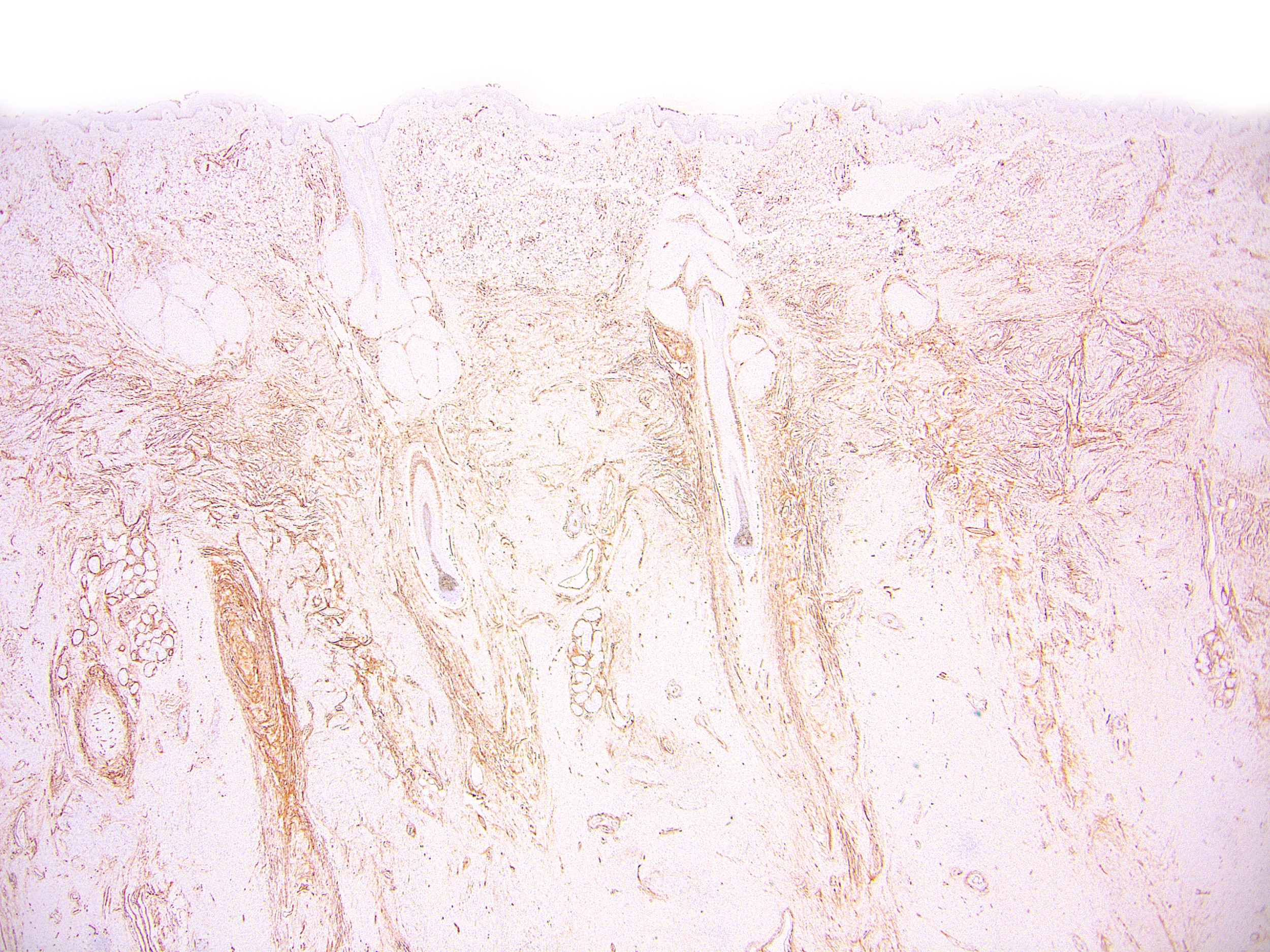
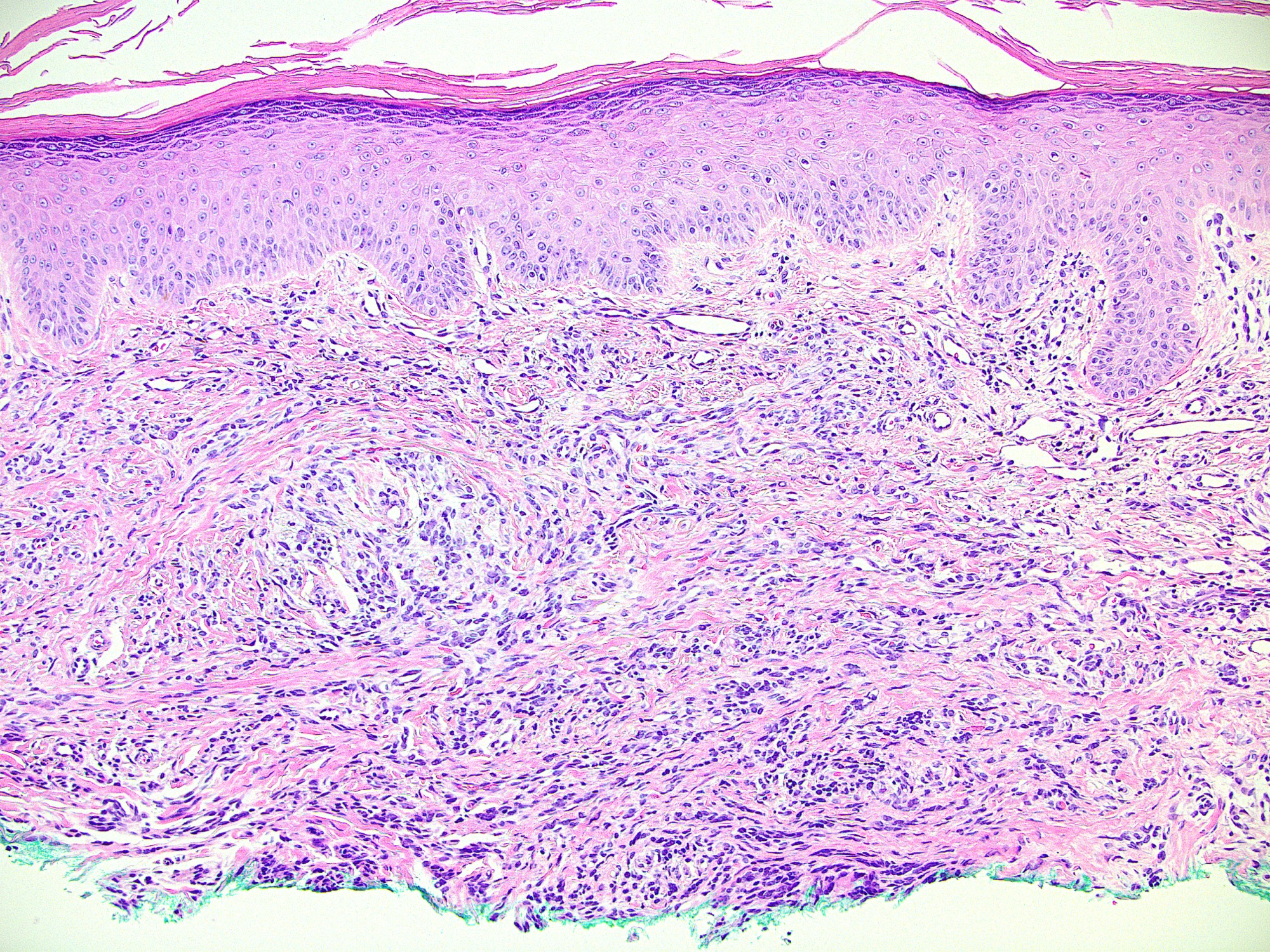
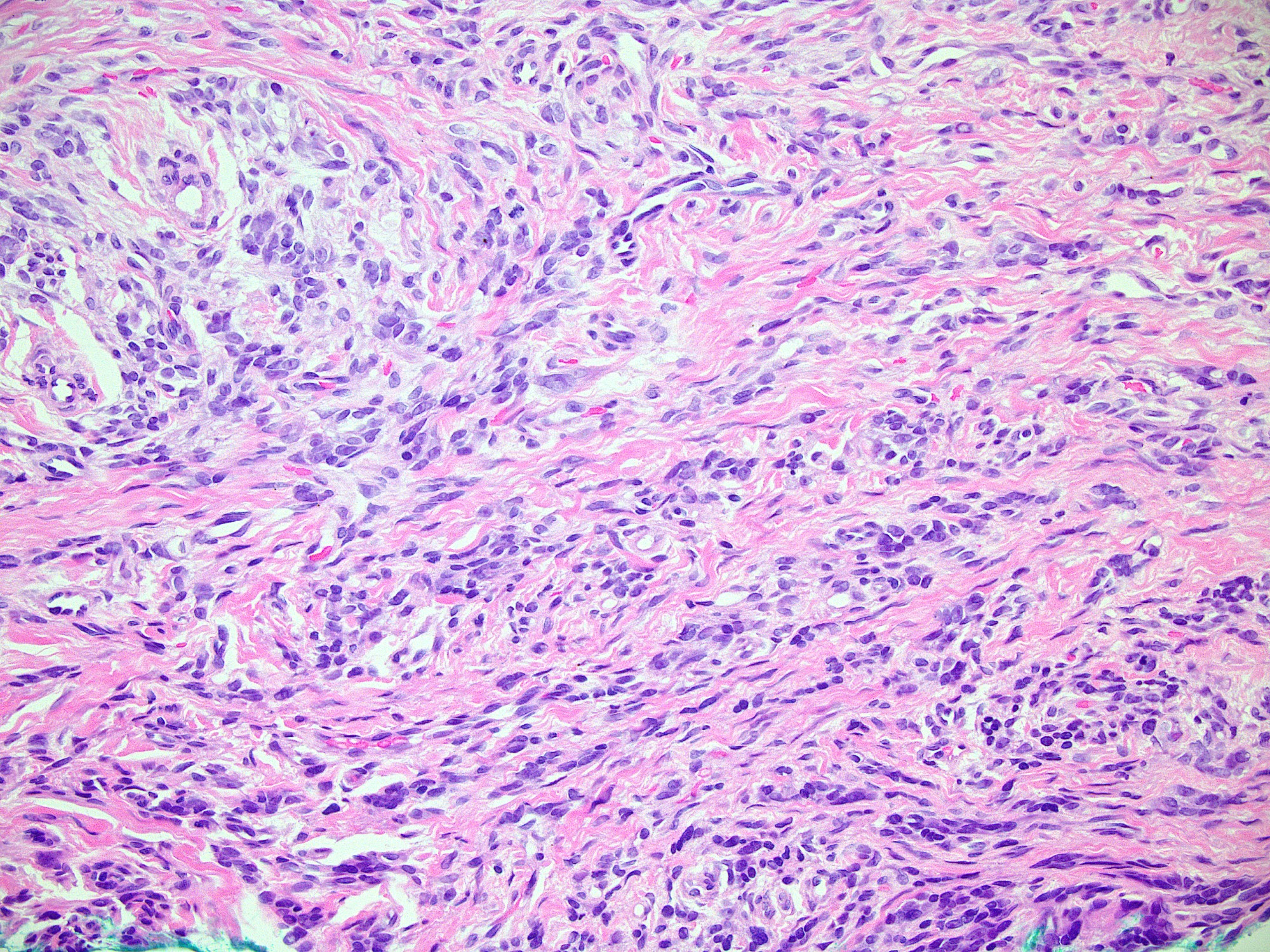
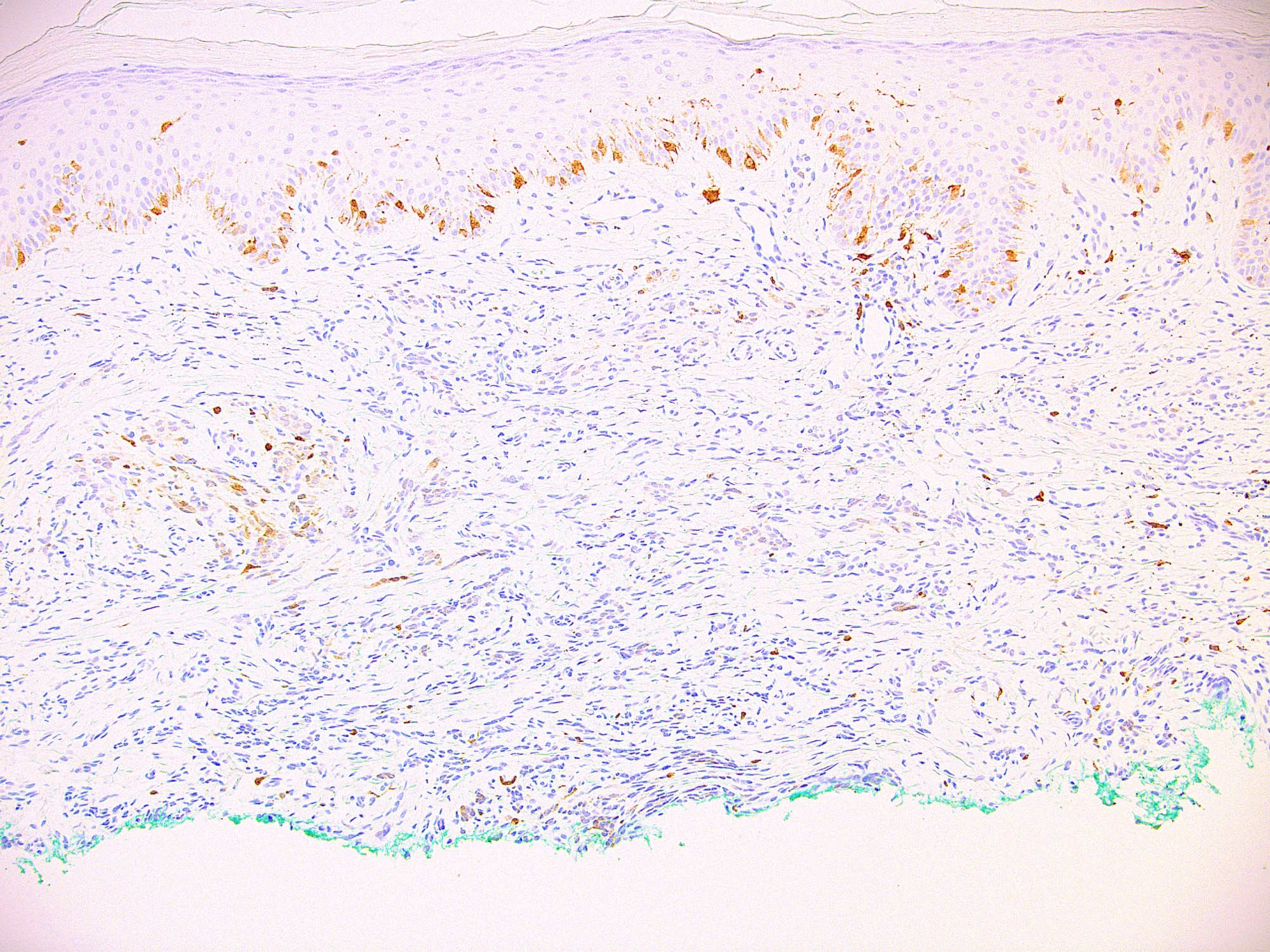
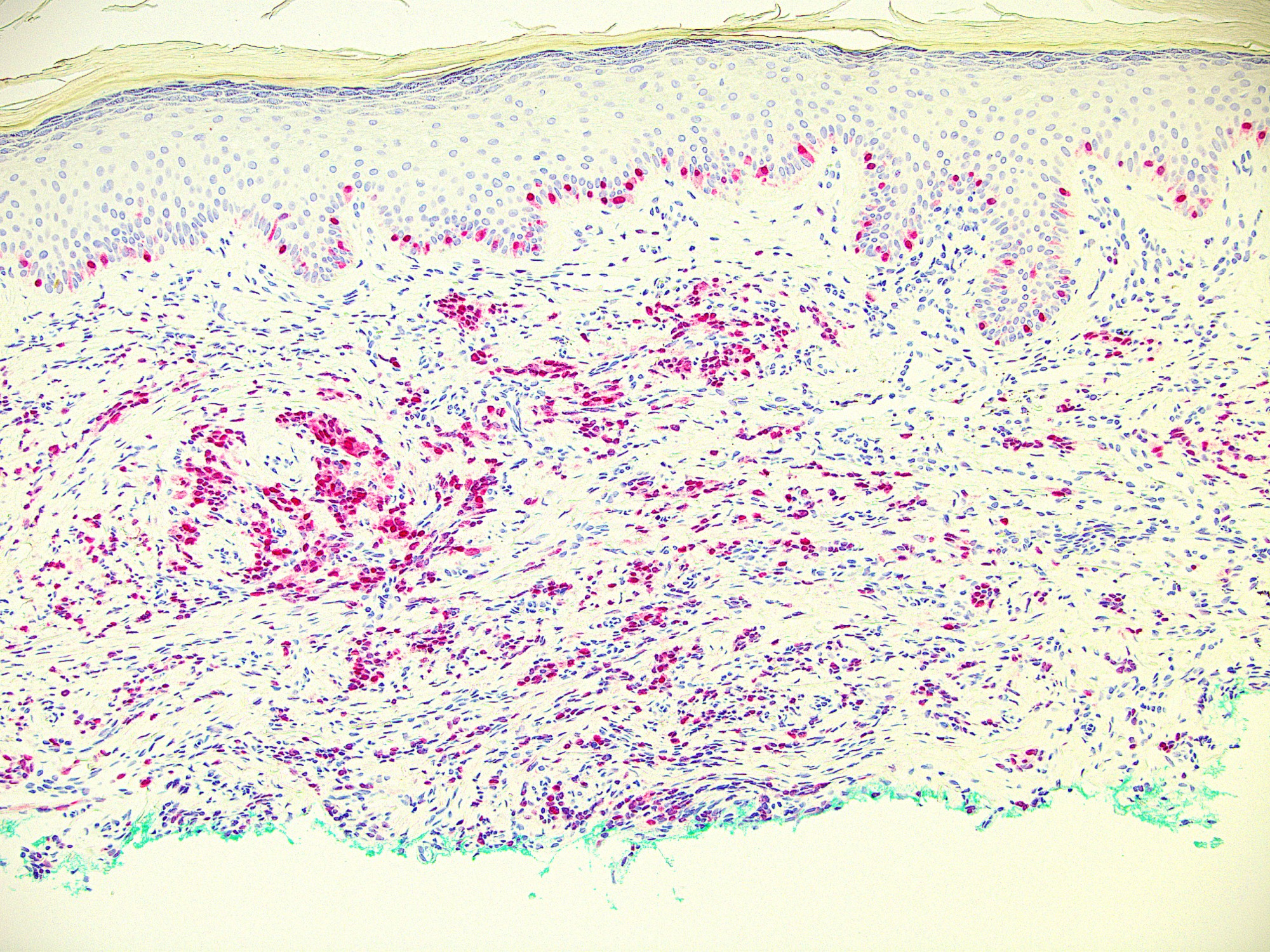
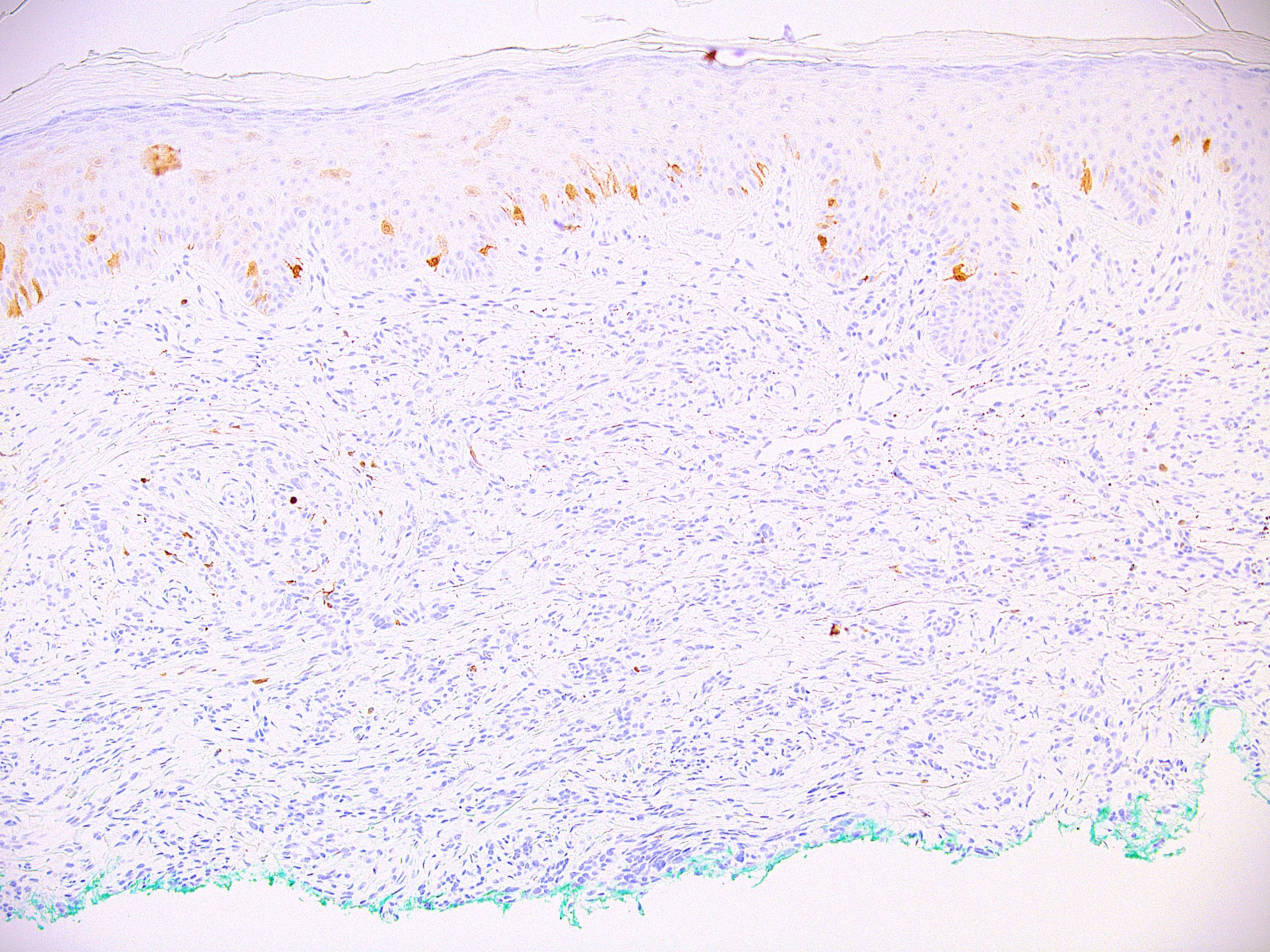
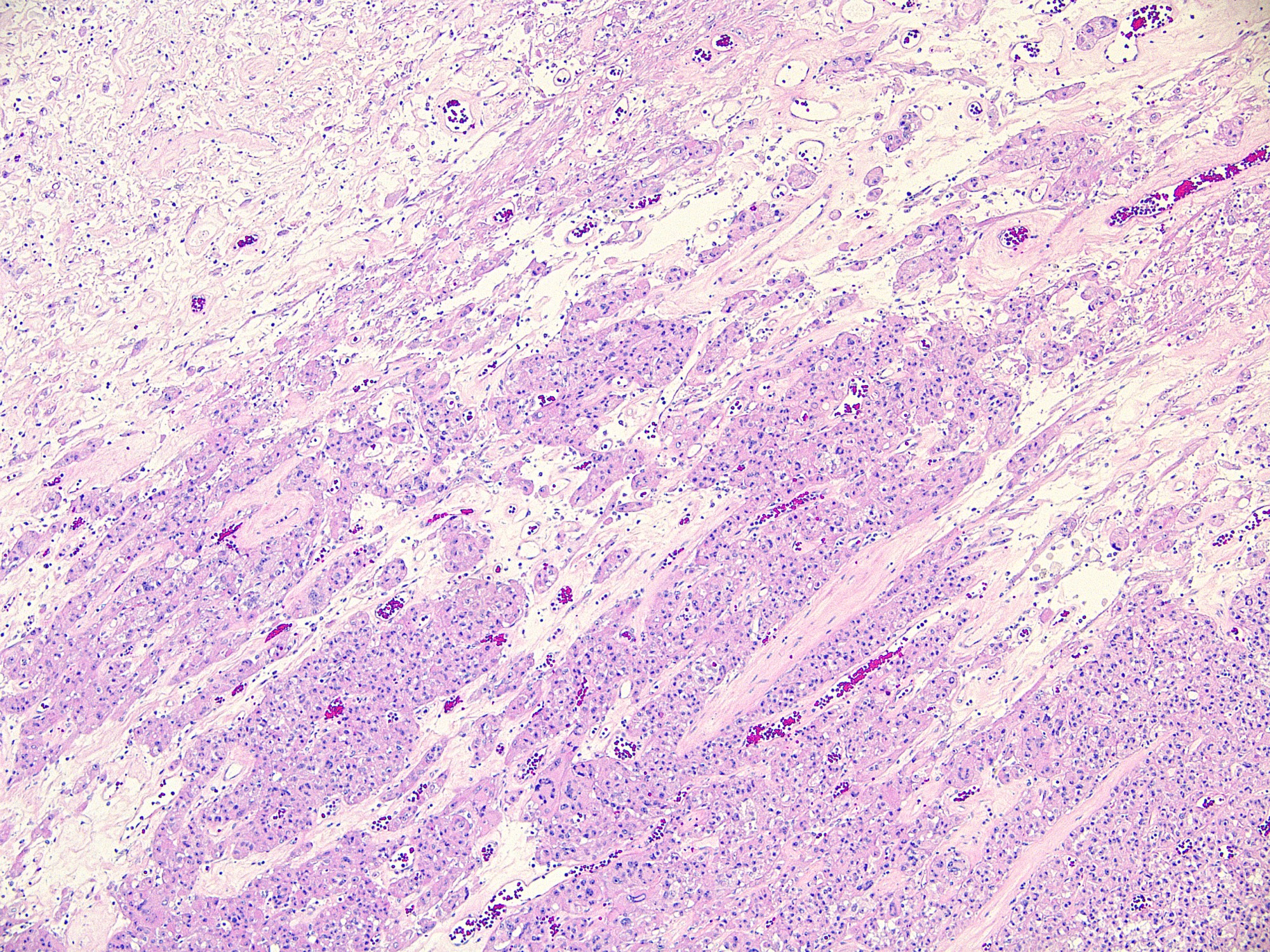
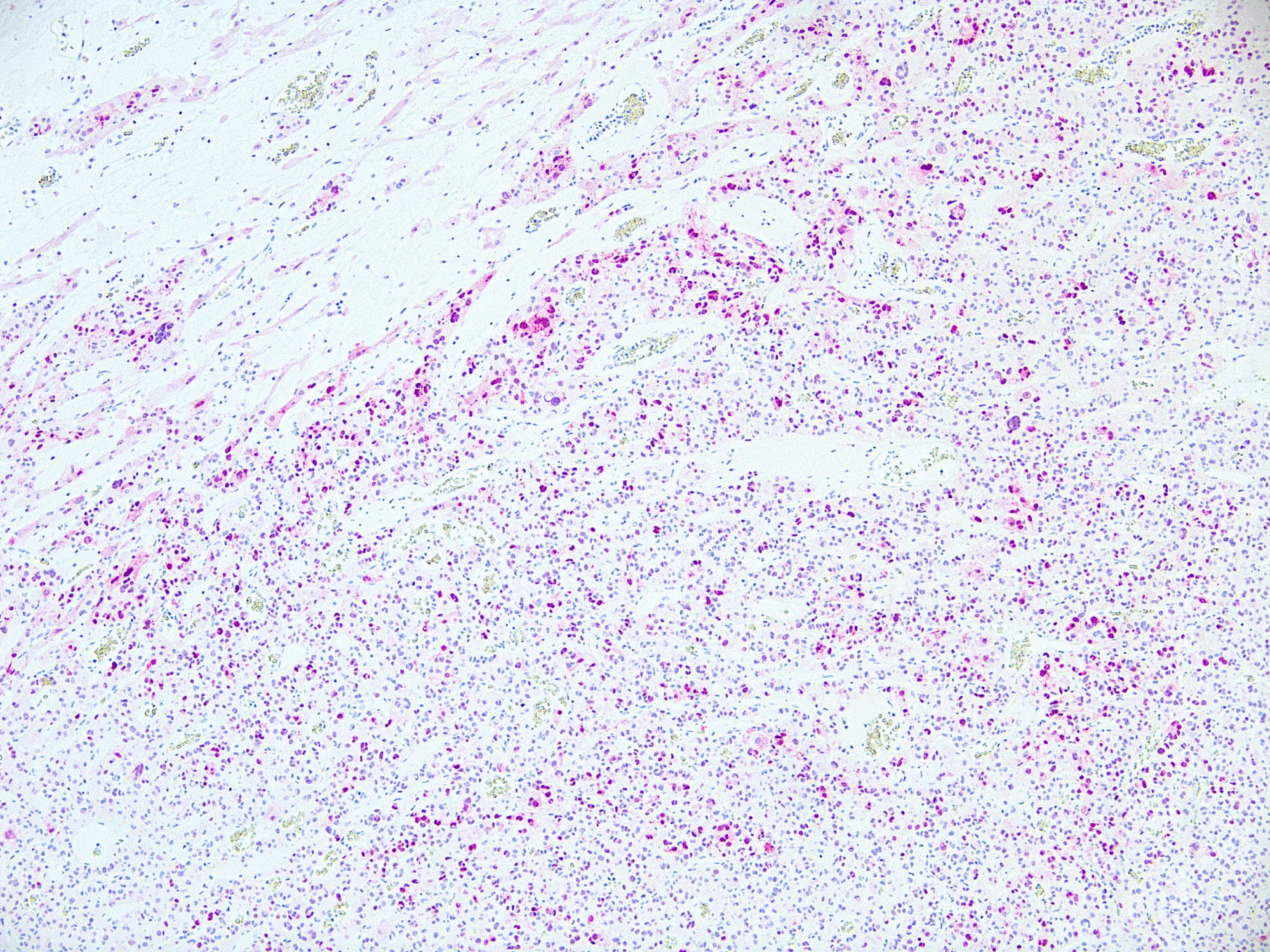
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Ata Moshiri, M.D., M.P.H.
Positive staining - normal
- Melanocytes, retinal pigment epithelial cells, histiocytes (especially multinucleated in disease, see below), osteoclasts, mast cells, heart cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:51)
- Perivascular epithelioid cells (Mod Pathol 2012;25:100)
Positive staining - disease
- Melanocytes in nevi
- Melanocytes in melanomas (desmoplastic growth pattern in melanomas typically negative) (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:205, J Cutan Pathol 2010;37:944)
- Clear cell sarcoma (75%) (Mod Pathol 2001;14:6)
- Angiomyolipoma (75%) and other PEComas (Mod Pathol 2012;25:100, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:493)
- Giant cells or adjacent mononuclear cells of giant cell tumor of bone (89%), tenosynovial giant cell tumor (96%), giant cell reparative granuloma (100%), aneurysmal bone cyst (73%), chondroblastoma (71%), foreign body giant cell reaction (80%) and sarcoidosis (75%) (Mod Pathol 2004;17:1491)
- Variable (68 - 100%) in neurothekeoma / cellular neurothekeoma (J Cutan Pathol 2014;41:640, Am J Dermatopathol 2012;34:157)
- Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (89%) and atypical fibroxanthoma (80%) (Histopathology 2017;70:734)
- Numerous other pitfalls (50 - 100% positive): fibrohistiocytic lesions such as benign histiocytomas, angiofibroma, keloid, fibromatosis, fibroblasts in melanoma re-excision specimens, pigmented basal cell carcinoma and spindle cell carcinoma (Pathol Res Pract 2018;214:821)
Negative staining
- Epidermal dendritic / Langerhans cells, carcinomas (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:205)
- Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor (Am J Dermatopathol 2012;34:157)
- Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (8% positive) (Histopathology 2018;73:969)
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (17% positive) (Pathol Res Pract 2018;214:821)
- Cutaneous myoepitheliomas and mixed tumors (0% in both) (J Cutan Pathol 2014;41:353)
- MiT family translocation renal cell carcinomas (5% positive) (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1295)
Sample pathology report
- Skin, left chest, punch biopsy:
- Mastocytosis (see comment)
- Comment: The dermal mononuclear proliferation stains positively with tryptase, CD117, and MITF, compatible with mast cell lineage.
Practice question #1
Which of the following is the best situation to use the MITF immunohistochemical stain?
- Margin assessment in an excision of a biopsy proven desmoplastic melanoma
- To differentiate melanocytes from epithelioid histiocytes and multinucleated giant cells
- To support a diagnosis of Xp11 translocated renal cell carcinoma with TFE3 gene fusion
- Use in addition to smooth muscle actin and HMB45 to support a diagnosis of angiomyolipoma
- Use as a marker for poorly differentiated melanoma in a pleomorphic spindle cell neoplasm of the skin
Practice answer #1
D. MITF, in combination with HMB45 and SMA would support an angiomyolipoma, which is a type of perivascular endothelial cell tumor (PEComa).
Answer A is incorrect because desmoplastic melanomas are usually negative for MITF. Answer B is incorrect because histiocytes, particularly multinucleated giant cells, can be positive for MITF. Answer C is incorrect because although TFE3 is a transcription factor related to MITF and these tumors are referred to as MiT family translocation renal cell carcinomas, most are negative for MITF by immunohistochemistry. Answer E is incorrect because MITF is nonspecific for the differential diagnosis of melanoma and can be positive in pleomorphic spindle cell lesions of the skin, including undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma, atypical fibroxanthoma and sarcomatoid carcinoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Microphthalmia associated transcription factor (MITF)
Comment Here
Reference: Microphthalmia associated transcription factor (MITF)