Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1Cite this page: Huether S, Jorns JM. Progesterone receptor (PR). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsprog.html. Accessed September 8th, 2025.
Definition / general
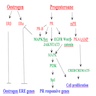
- Progesterone receptor (PR) gene on chromosome 11 encodes PR protein
- Member of hormone receptor family of ligand dependent transcription factors
Essential features
- Hormone receptor with roles in development, physiologic processes and reproduction
- Good prognostic factor in invasive breast carcinoma and indicator of response to hormonal treatment
- Nuclear positivity via immunohistochemical staining
Terminology
- PgR
- PR
Pathophysiology
- 3 isoforms: PRA, PRB, PRC
- PRA and PRB isoforms differ only in that PRB contains an additional 164 amino acid sequence at the N terminal end (Mol Cell Endocrinol 2012;357:18)
- PRA and PRB isoforms are detected nondiscriminately by common PR antibody clones (Ann Diagn Pathol 2018;35:21)
- PR is activated by the binding of progesterone then the complex moves to nucleus where it binds to DNA and activates transcription
- PR gene expression is regulated by ER
- Involved in regulation of genes that affect cellular proliferation and differentiation of nonreproductive tissues (i.e., normal developmental processes)
- Mediates the physiological effects of progesterone in the development of breast cancer
- Loss of expression is associated with abnormal ER signaling pathway
Clinical features
- Reduced immunostaining is associated with adverse histopathological and clinical features in breast carcinoma, endometrioid endometrial carcinoma and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (Anal Cell Pathol (Amst) 2022;2022:6412148)
Interpretation
- Nuclear staining
- Evaluate percentage of tumor cell staining and staining intensity (weak, moderate or strong)
- Cytoplasmic staining or nuclear staining in < 1% of cells is considered negative
- Standardized process for initial test validation is recommended, with ongoing proficiency testing (J Clin Oncol 2010;28:2784)
- Decalcification, alternate fixatives, prolonged cold ischemia time, fixation time out of recommended range are among variables that may negatively impact expression / interpretation (J Clin Oncol 2020;38:1346)
Uses by pathologists
- In breast cancer, used as a favorable prognostic factor and to indicate response to hormonal agents, such as tamoxifen (J Clin Oncol 2020;38:1346)
- Used in combination with ER and HER2 to guide treatment options in invasive breast carcinoma
- Considered optional in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) as it does not provide additional prognostic value in ER positive cases
- Rare (0.6%) cases of DCIS may be ER negative, PR positive so reflexive PR testing may be done with negative ER staining (Am J Surg 2023;225:304)
- For metastatic tumors with unknown primary, diffuse, strong positivity supports breast or gynecological origin
- May be used in combination with ER and other markers to identify breast or gynecological origin in metastatic tumors of unknown origin
Prognostic factors
- Degree of expression is linked to prognosis and therapy response in invasive breast carcinoma (Endocr Relat Cancer 2018 Jul 10 [Epub ahead of print], Clin Cancer Res 2004;10:2751)
- Expression is not linked to prognosis in DCIS, thus testing is now considered optional by CAP / ASCO (J Clin Oncol 2020;38:1346)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Interpretation of percent and intensity (weak, moderate or strong) of nuclear staining in breast cancer (J Clin Oncol 2020;38:1346)
- < 1% is considered negative
- ≥ 1% is considered positive
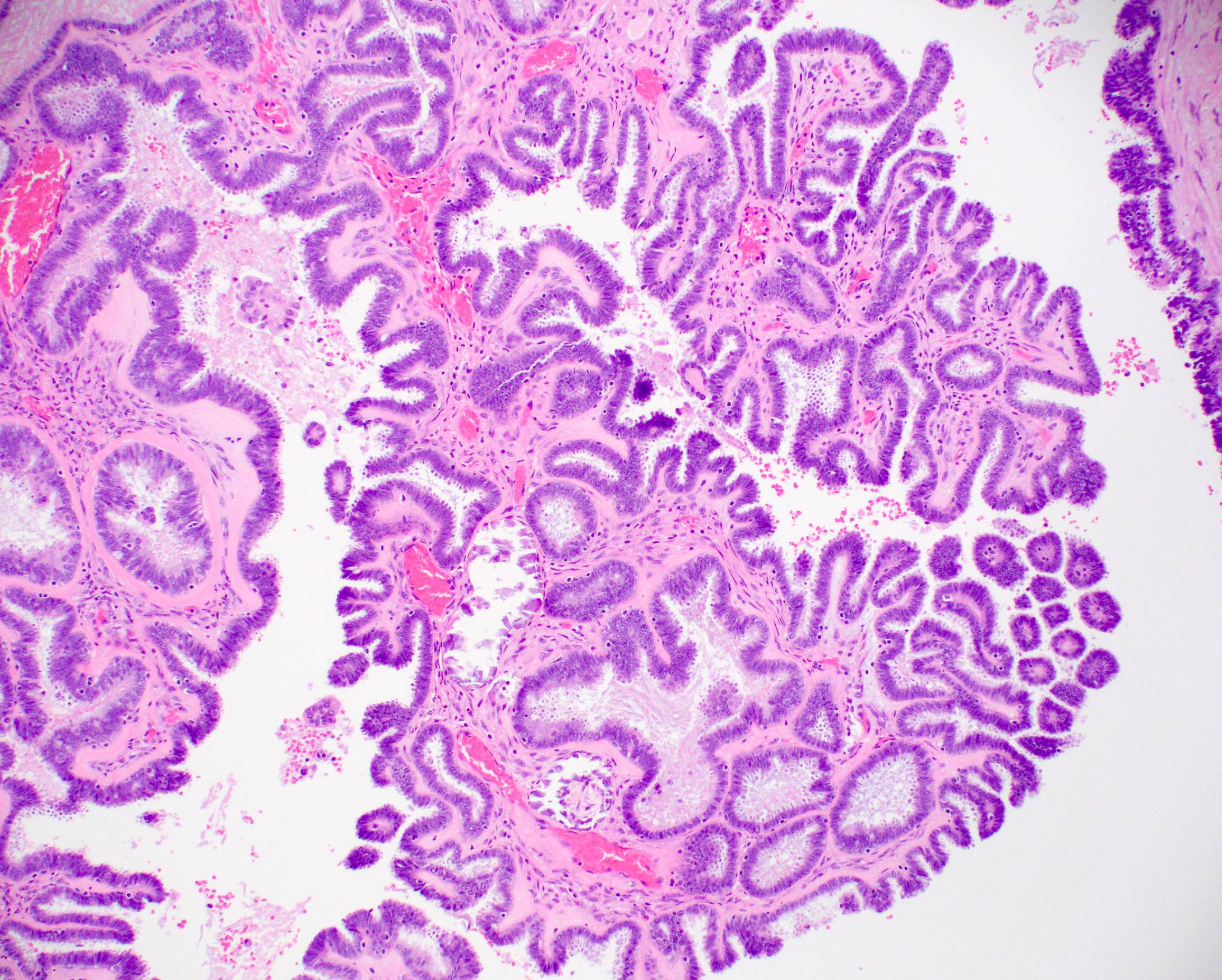
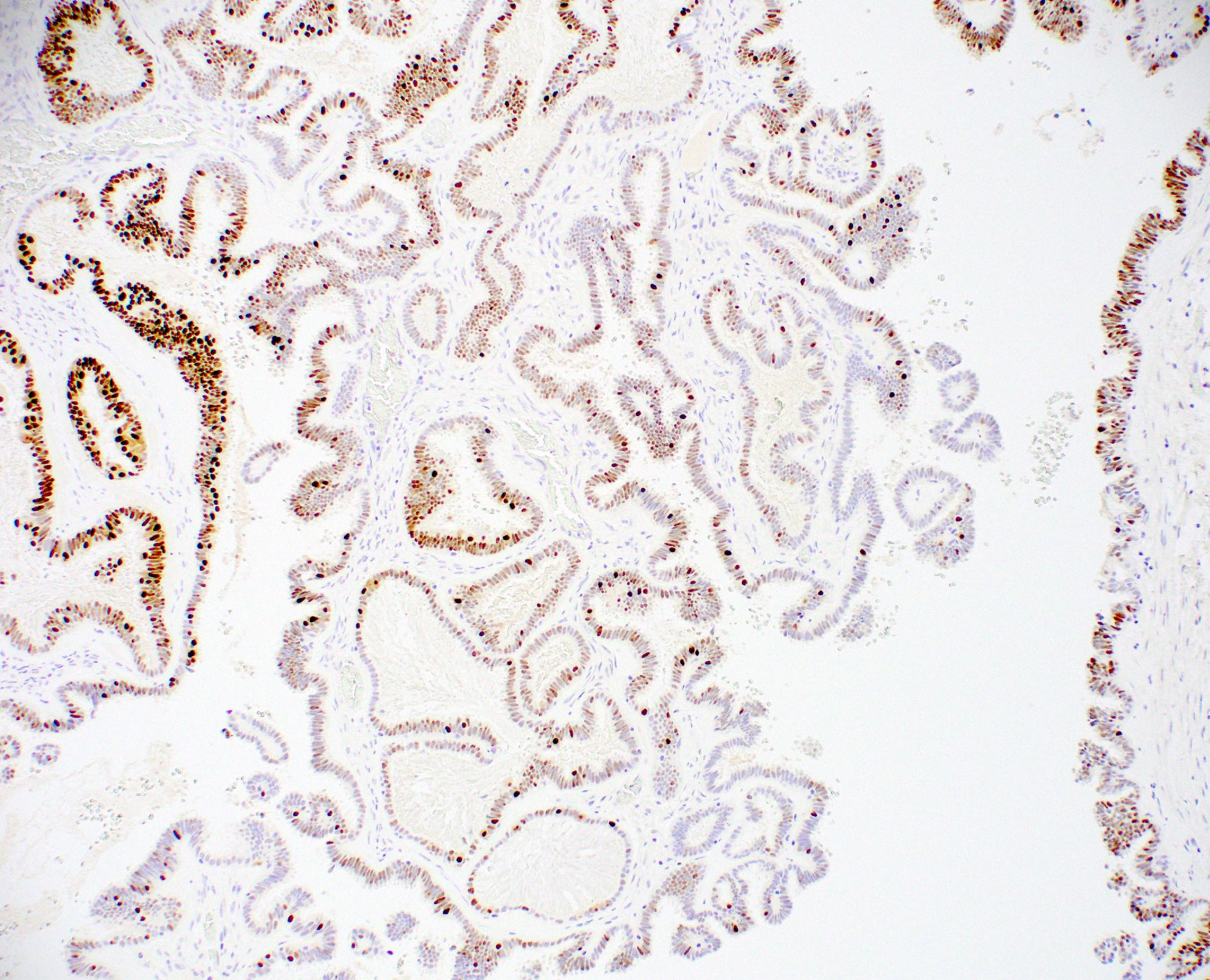
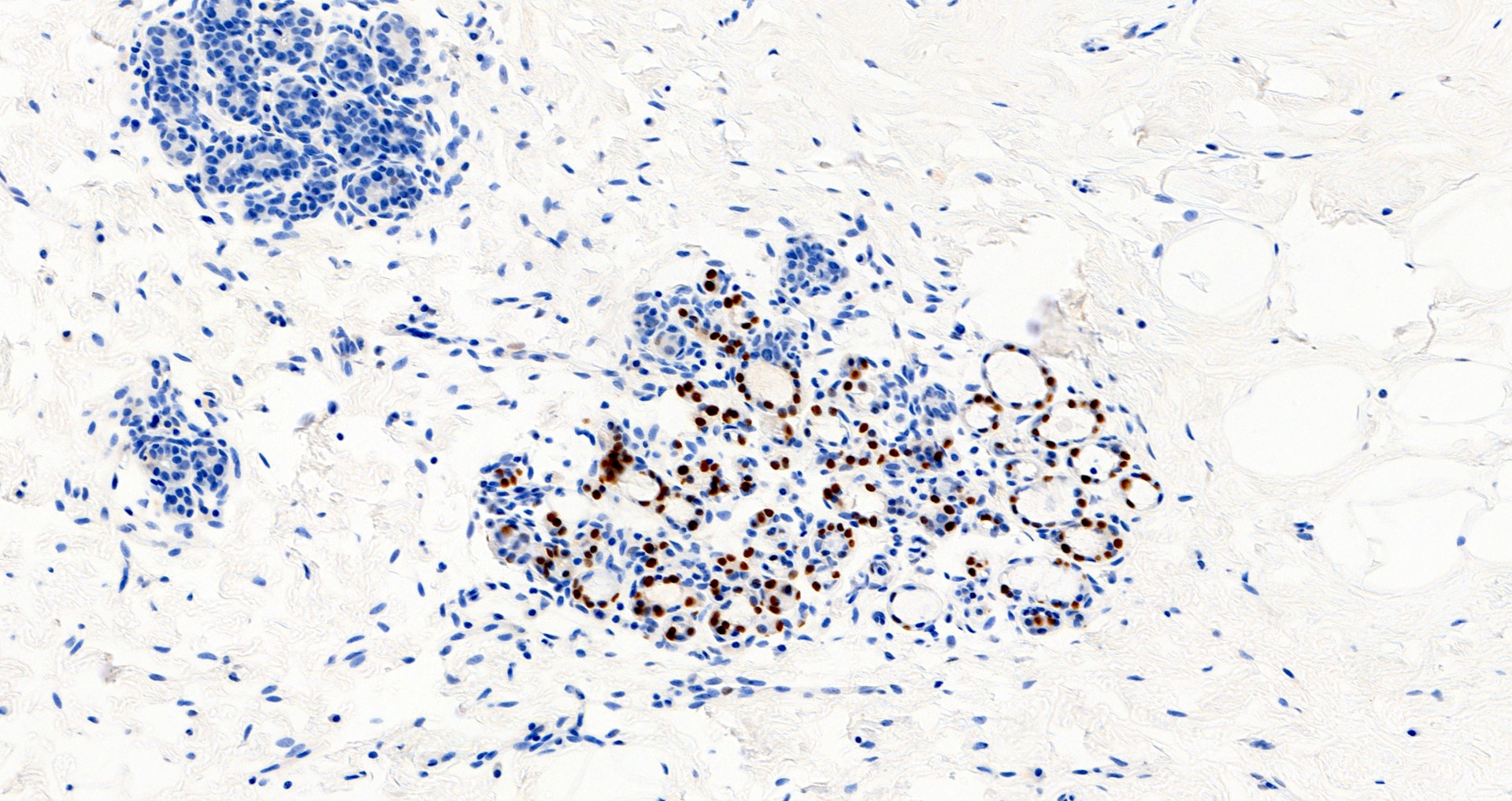
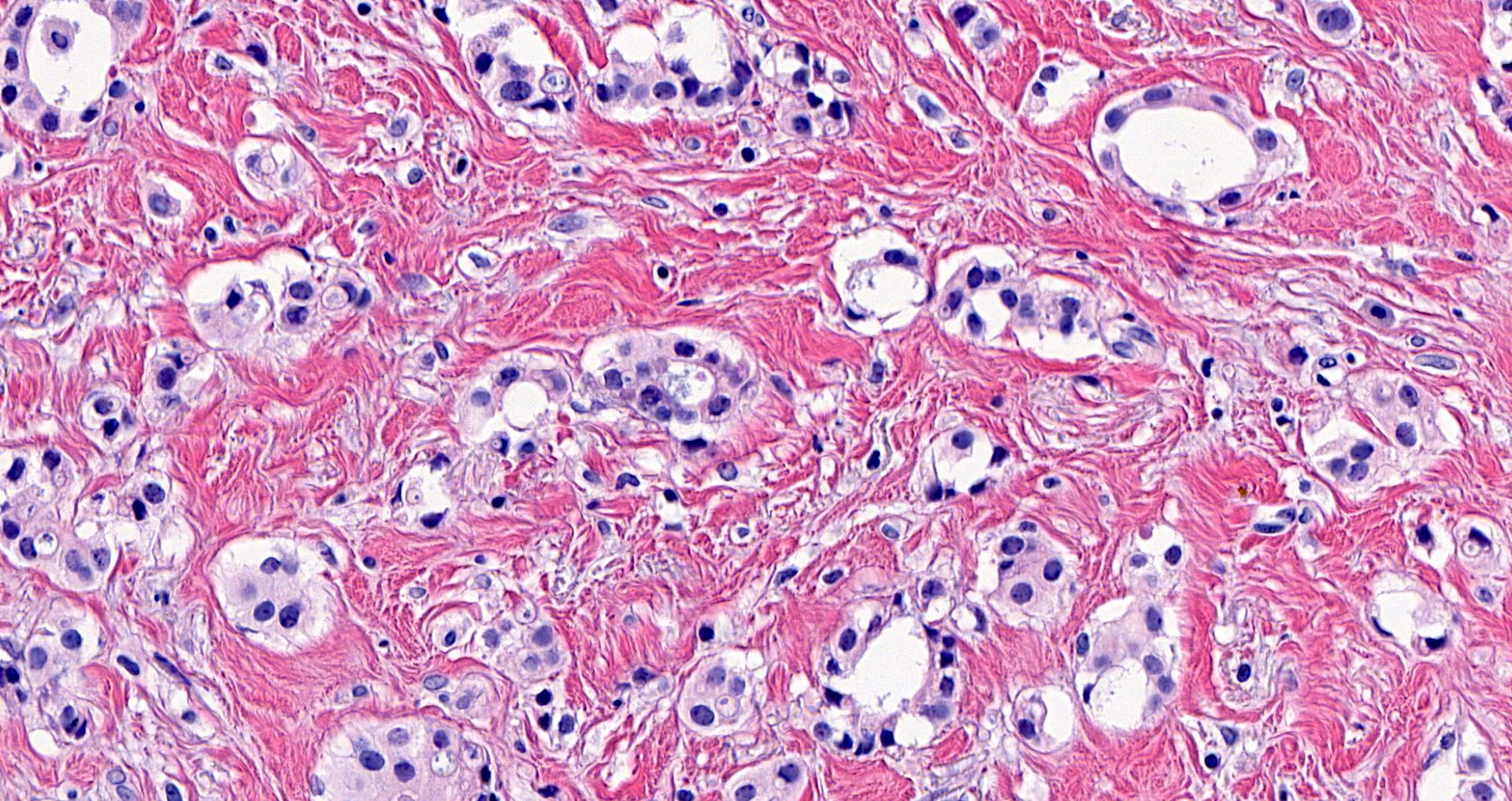
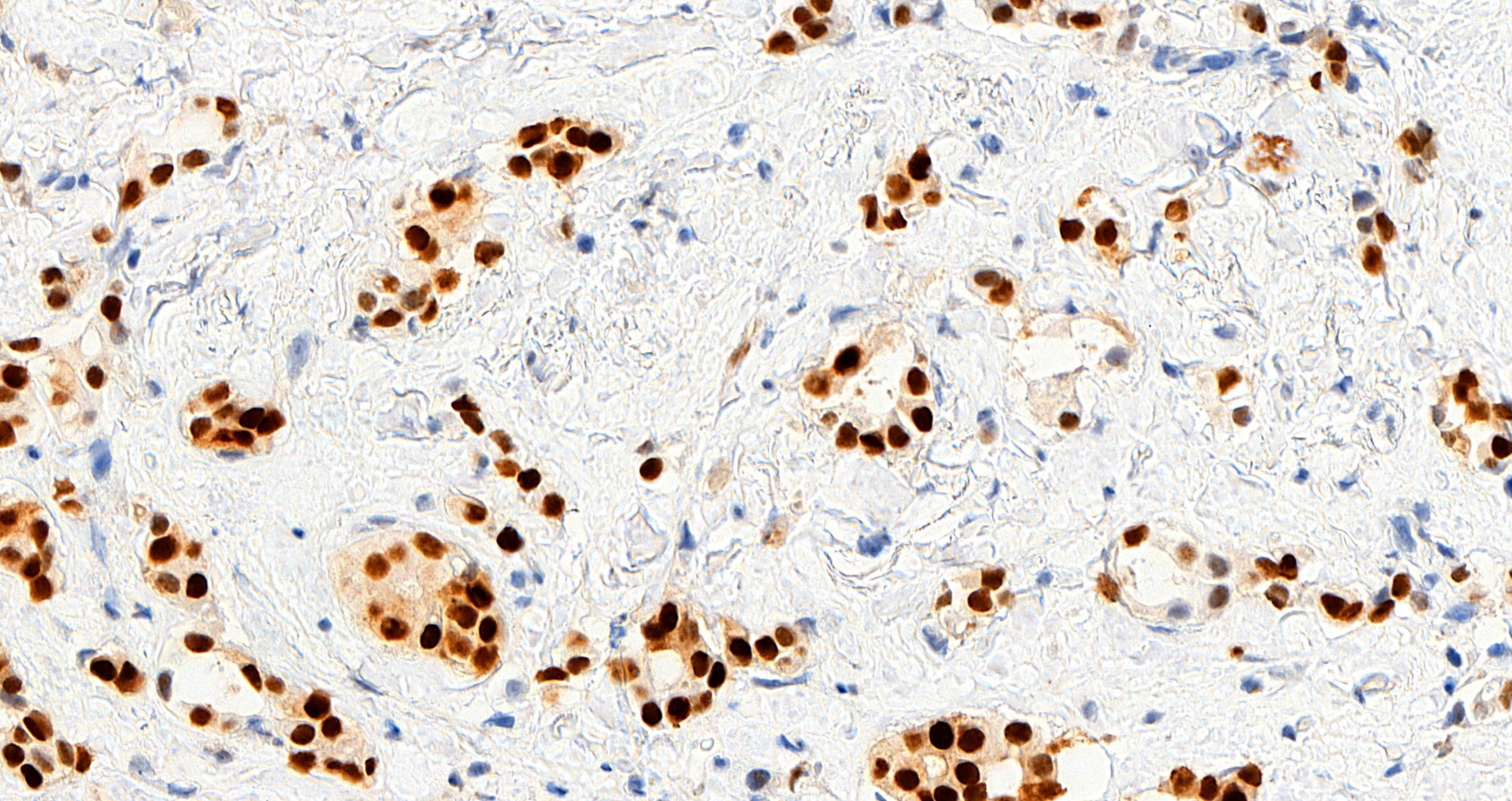
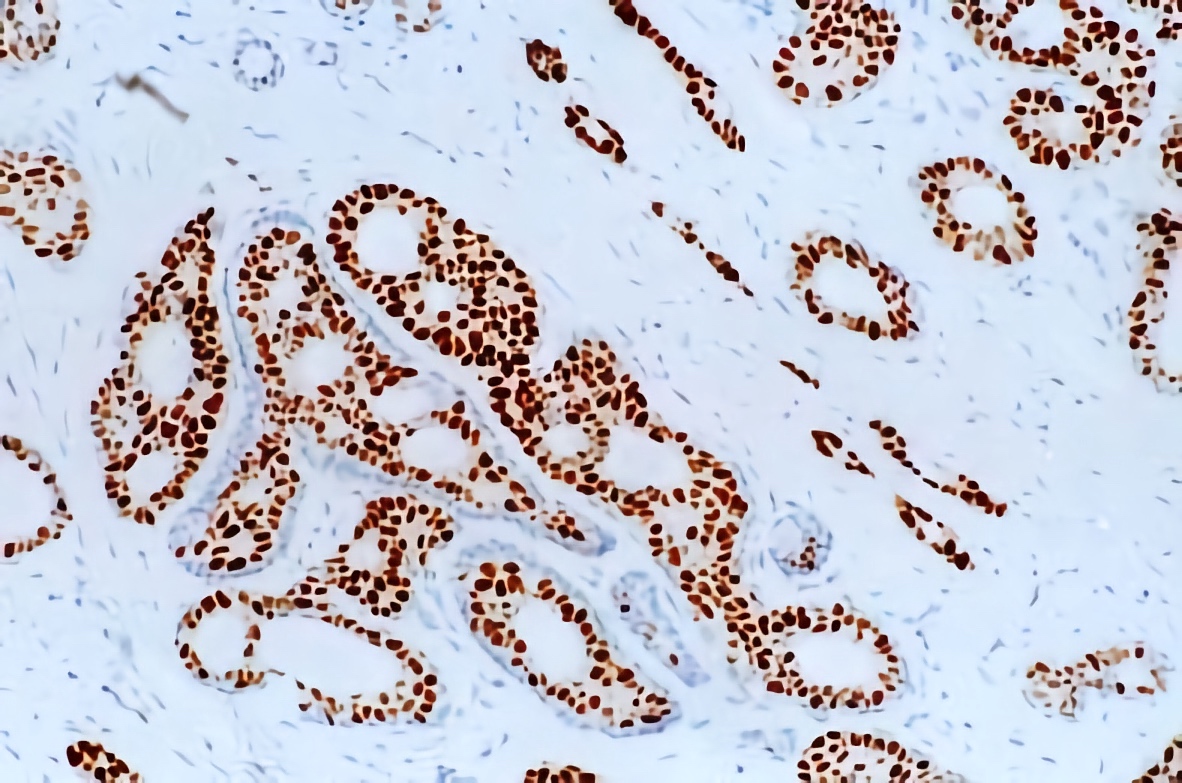
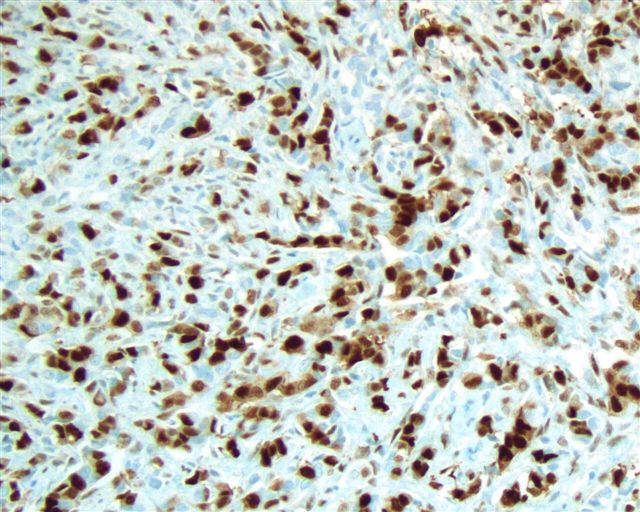
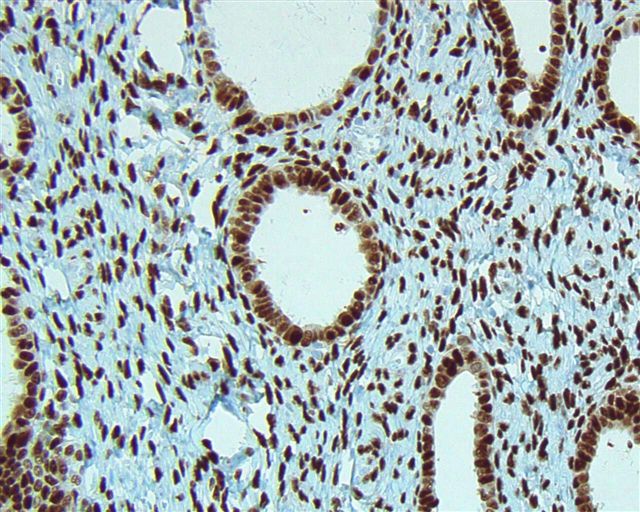
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Julie M. Jorns, M.D., Andrey Bychkov, M.D., Ph.D., Leica Microsystems and
Mowafak Hamodat, M.B.Ch.B., M.Sc. (Case #125)
Virtual slides
Positive staining - normal
- Breast epithelial cells, Toker cells
- Ovarian stroma
- Endocervical epithelial and stromal cells
- Islets of Langerhans of pancreas (Anal Cell Pathol (Amst) 2022;2022:6412148)
- Stromal cells of prostate (Anal Cell Pathol (Amst) 2022;2022:6412148)
- Stromal cells of seminal vesicle (Anal Cell Pathol (Amst) 2022;2022:6412148)
- Smooth muscle, including smooth muscle containing blood vessels (Circulation 1999;99:2688)
Positive staining - disease
- Breast: fibroadenoma (stromal cells), myofibroblastoma, phyllodes tumors (epithelial cells), pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia, intraductal papilloma, columnar cell lesion
- Breast carcinoma (usually well differentiated tumors, including lobular, mucinous, papillary and tubular subtypes)
- Endometrial adenocarcinoma (75 - 96%)
- Cervical carcinoma: endometrioid, minimal deviation
- Endometriosis (glands and stroma)
- Uterus: endometrial carcinoma, endometrial stromal tumors, leiomyoma, smooth muscle tumor of uncertain malignant potential (STUMP); epithelioid leiomyosarcoma (54%) (Anal Cell Pathol (Amst) 2022;2022:6412148, Am J Surg Pathol 2022;46:464)
- Ovarian tumors: endometrioid carcinoma (64.2%), ependymoma, fibromatosis (88%), granulosa cell (juvenile), mucinous borderline endocervical type, high grade serous (50%) (Gynecol Oncol 2005;96:671, Biosci Rep 2021;41:BSR20210478)
- Kidney: mixed epithelial and stromal tumor
- Liver: biliary cystadenoma (stroma), hepatic adenoma
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
- Soft tissue aggressive angiomyxoma, angiomyofibroblastoma, cellular angiofibroma
- Solitary fibrous tumor
- Meningioma (fibrous, myxoid and secretory) (39 - 88%) (Front Oncol 2021;11:611218)
- Pancreas: solid pseudopapillary neoplasm (63%)
Negative staining
- Breast: apocrine metaplasia and carcinomas, microglandular adenosis, myoepithelium and myoepithelial tumors, cylindroma, fibromatosis
- Breast carcinomas - various (triple negative, including adenosquamous, basal-like, BRCA1 related, medullary, mucinous cystadenocarcinoma, metaplastic; also lipid rich)
- Endocervical adenocarcinoma
- Ovary: clear cell carcinoma, Leydig cell tumor, Sertoli cell tumor, steroid cell tumor
- Salivary gland intraductal and other carcinomas
- Uterus: serous carcinoma, endometrial clear cell carcinoma (Anal Cell Pathol (Amst) 2022;2022:6412148)
Sample pathology report
- Left breast, 3 o'clock, 3 cm from the nipple, core biopsy:
- Invasive ductal carcinoma, preliminary modified Bloom Richardson (Nottingham) grade 1 (2+1+1) (see comment)
- Comment: immunohistochemical stains show invasive carcinoma to be
- Estrogen receptor (91 - 100%, strong) positive
- Progesterone receptor (91 - 100%, strong) positive
- HER2 / neu (1+) negative for overexpression
- Controls are appropriate
Additional references
Practice question #1
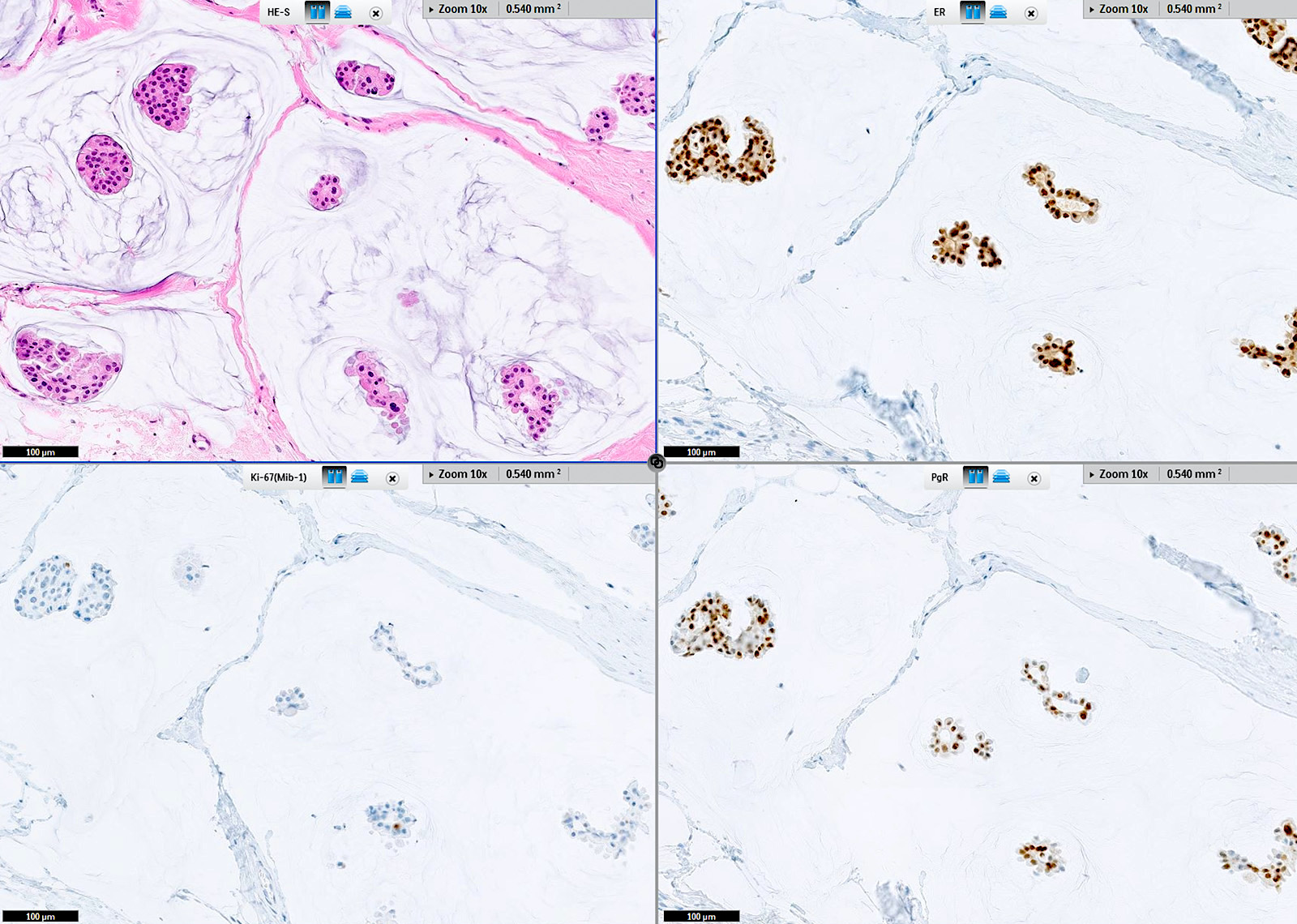
A middle aged woman presents with a 1 cm breast mass detected on breast imaging screening. Progesterone receptor staining is shown. How should this immunohistochemical stain be interpreted?
- Low positive, good prognosis
- Low positive, poor prognosis
- Negative, poor prognosis
- Positive, good prognosis
- Positive, poor prognosis
Practice answer #1
D. Positive, good prognosis. Answer D is correct because positive PR expression is associated with a better prognosis than negative expression in invasive ductal breast carcinomas. Answer E incorrect because the biopsy of the breast mass shows a low grade invasive ductal carcinoma with diffuse, strong PR positivity, which is a favorable prognostic feature. Answers A, B and C are incorrect because the carcinoma is not low positive (1 - 10%, a category currently used for ER but not PR) or negative (< 1%) for PR.
Comment Here
Reference: Progesterone receptor (PR)
Comment Here
Reference: Progesterone receptor (PR)