Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Pathophysiology | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Dusenbery A, Wick MR. Transducin-like enhancer of split 1 (TLE1). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainstle1.html. Accessed May 13th, 2024.
Definition / general
- TLE1 (transducin-like enhancer of split 1) is one member of a family of genes (J Clin Pathol 2021;74:137)
- Located at chromosome 9q21.32 (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2013;21:408)
Essential features
- TLE1 immunohistochemical staining is most commonly used when synovial sarcoma is a diagnostic consideration; in this setting, nuclear expression should be observed
- Sensitivity and specificity are reasonable for this purpose; however, an increasing number of entities have demonstrated TLE1 expression with varying frequency
- Should be interpreted in the appropriate context of histomorphologic, molecular and other immunohistochemical features (Ann Diagn Pathol 2014;18:369)
Pathophysiology
- The protein product of this gene, TLE1, is a transcriptional corepressor, homologous to the corepressor groucho in Drosophila
- Affects signaling pathways relating to embryogenesis, hematopoiesis and differentiation; specifically, lateral inhibition, segmentation, sex determination, eye development and neuronal differentiation (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:106, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2013;21:408)
- Ultimately involved in modulating several signaling pathways, including the WNT / beta catenin pathway, NOTCH pathway and sonic hedgehog pathway (J Clin Pathol 2021;74:137)
- Functions as either an oncogene or tumor suppressor in various cancer types (Oncotarget 2017;8:15971)
- Repression by TLE1 involves histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity
- Research involving HDAC inhibitors and synovial sarcoma supports the premise that, through this connection, TLE1 may be involved in the pathophysiology of synovial sarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:240)
- Therefore it may be a therapeutically useful target in the future (Mol Cancer Ther 2017;16:2656, Eur J Cancer 2010;46:1170)
Interpretation
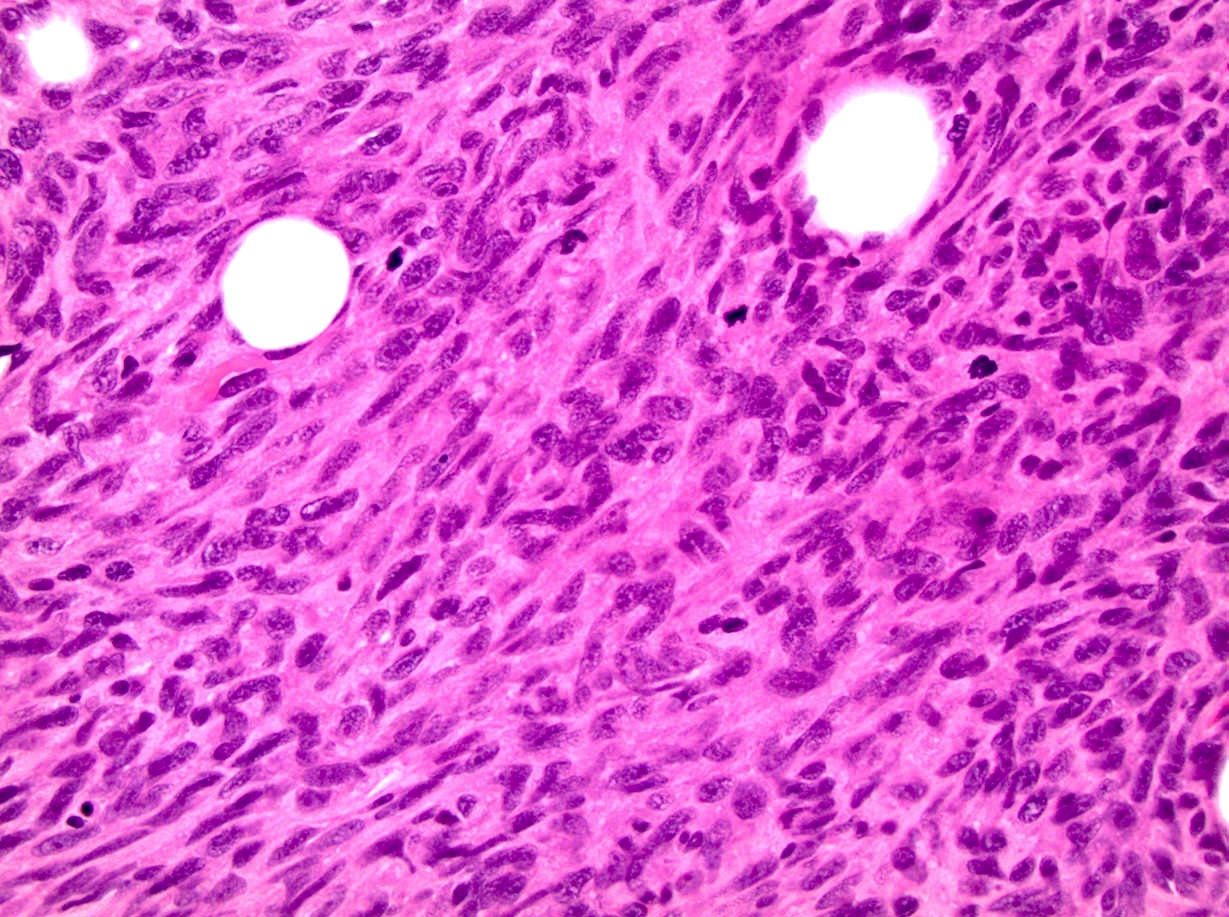
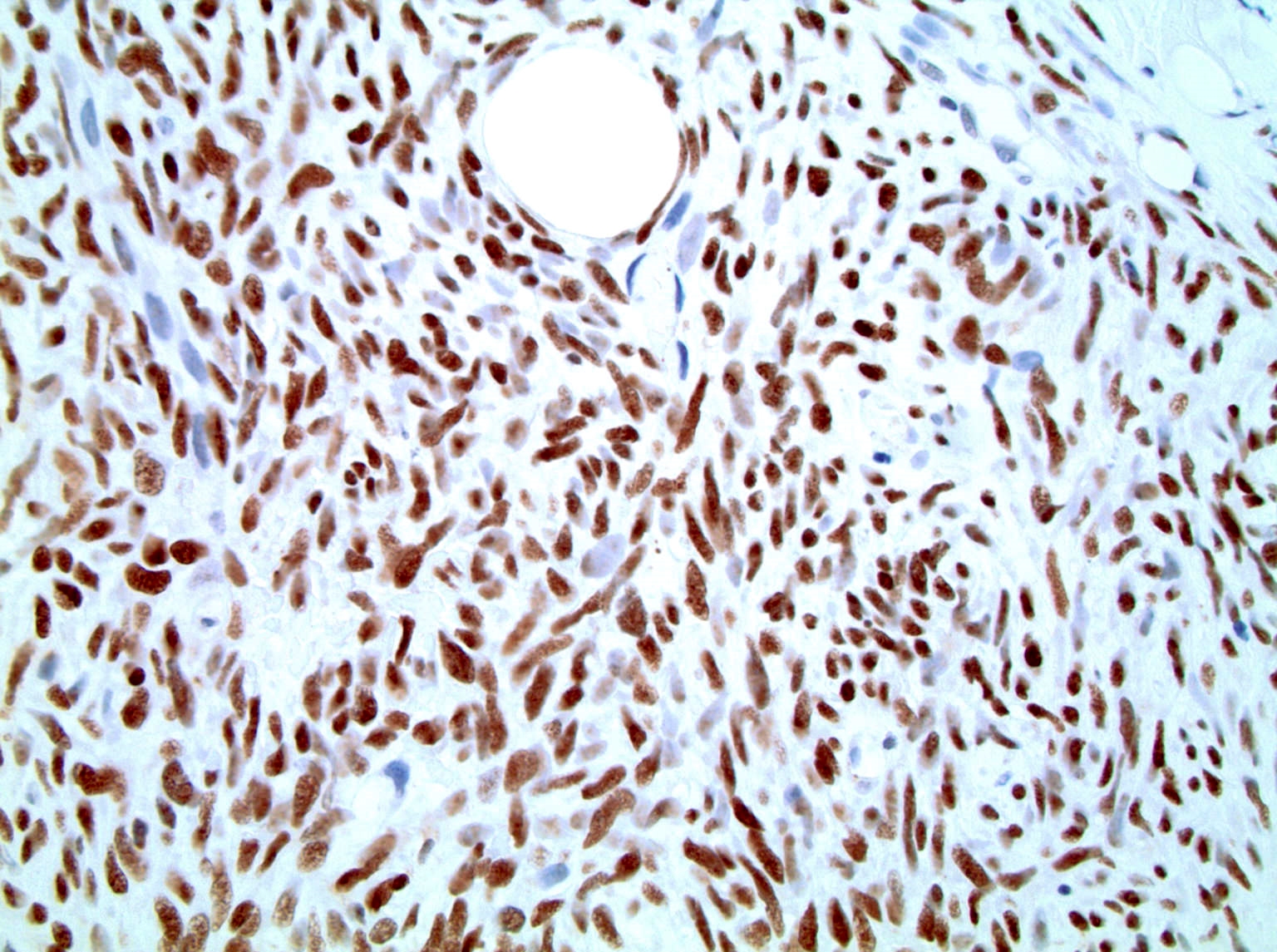
- Intense, diffuse nuclear staining (with only rare background or cytoplasmic labeling) is typically seen in synovial sarcoma, including in all of its histologic subtypes (Ann Diagn Pathol 2014;18:369, Am J Clin Pathol 2011;135:839, Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1743, Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:240)
- However, in biphasic tumors stronger staining has been noted in the glandular component than in the spindled component in some studies; in one study, biphasic tumors were more likely than other subtypes to demonstrate only weak nuclear staining (Mod Pathol 2009;22:872, Am J Clin Pathol 2011;135:839)
- To qualify as positive staining, a 2+ cut off has been advocated for in one meta analysis (Sarcoma 2020;2020:7192347)
Uses by pathologists
- Reasonably sensitive and specific for synovial sarcoma within the appropriate context; this includes its monophasic, biphasic and poorly differentiated forms
- One meta analysis demonstrated the following mean values for detection of synovial sarcoma with TLE1: 94% sensitivity, 81% specificity, 75% positive predictive value and 96% negative predictive value (Sarcoma 2020;2020:7192347)
- Sensitivity ranged from 85 - 100% and specificity ranged from 75 - 96% (Mod Pathol 2009;22:872, Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1743)
- In a study, 22/28 (79%) of monophasic, 18/23 (78%) of biphasic and 20/22 (91%) of poorly differentiated synovial sarcomas demonstrated nuclear immunoreactivity for TLE1 (Am J Clin Pathol 2011;135:839)
- Exact sensitivity and specificity has varied in several publications (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:106)
- Some pathologists prefer using antibodies against the SS18-SSX fusion protein to TLE1 because of its superior specificity (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:922)
- Laboratory considerations:
- One study demonstrated a better overall immunohistochemistry performance profile with a monoclonal TLE1 antibody, as opposed to a polyclonal TLE1 antibody (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2019;27:174)
- Another study demonstrated fairly similar performance of both a monoclonal pan-TLE antibody and a polyclonal TLE1 antibody; there were only 8 discrepancies in scoring among 177 cases, all of which demonstrated staining with the monoclonal pan-TLE antibody but not with the polyclonal TLE1 antibody (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:240)
Prognostic factors
- Within specific tumor types, there is limited literature available regarding the prognostic significance of TLE1 gene expression levels or immunohistochemical staining (Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2021;22:1653, Transl Lung Cancer Res 2021;10:3251, Leuk Res 2018;74:42, Front Oncol 2020;10:576, J Breast Cancer 2017;20:45, J Gastric Cancer 2016;16:21)
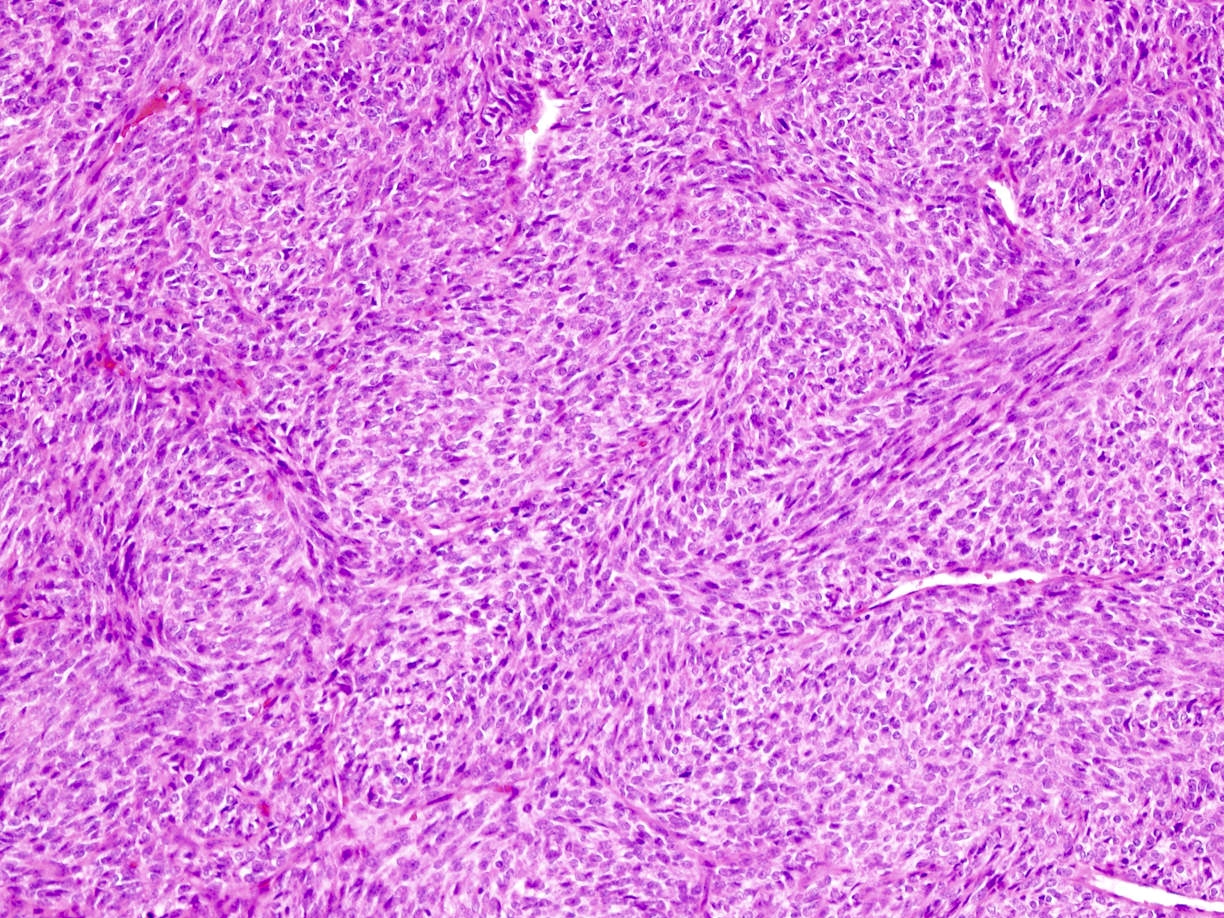
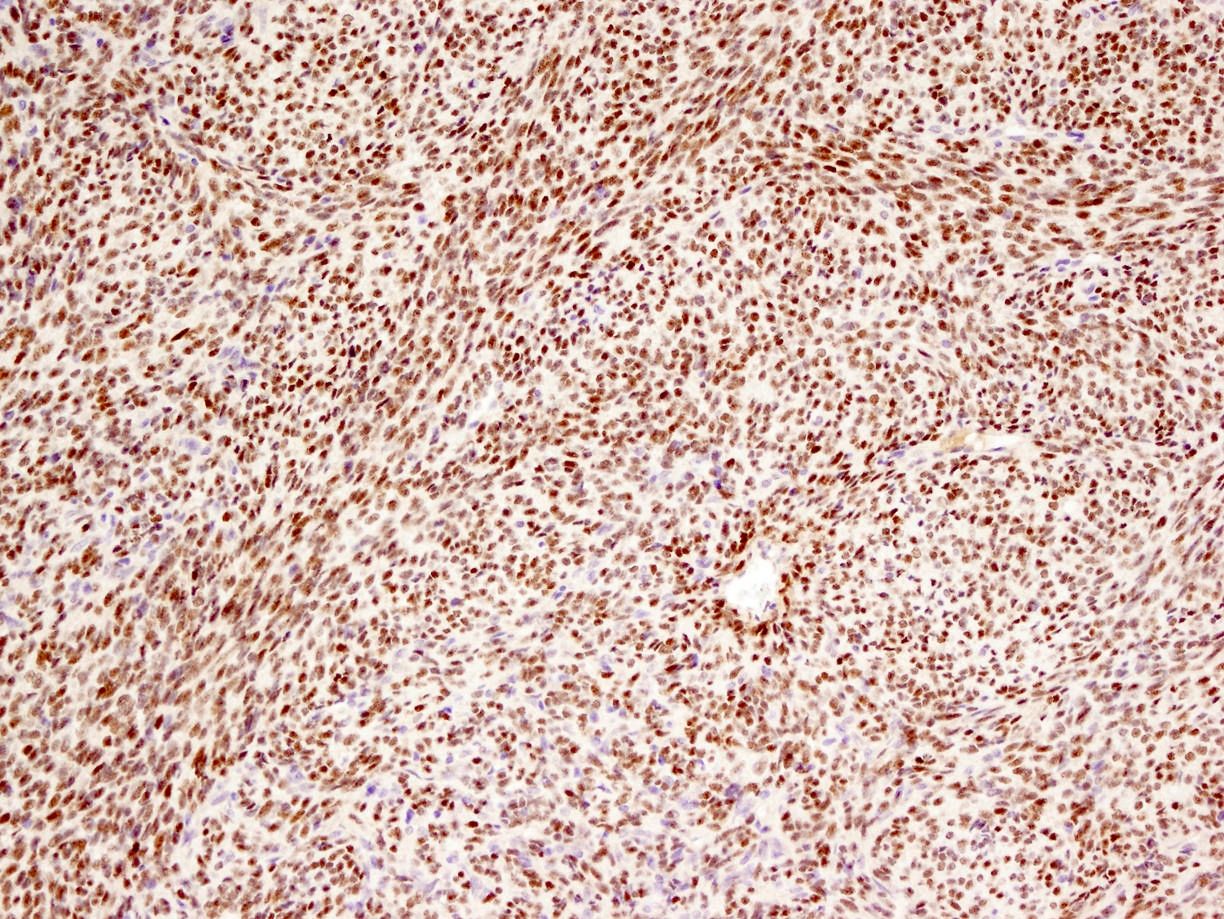
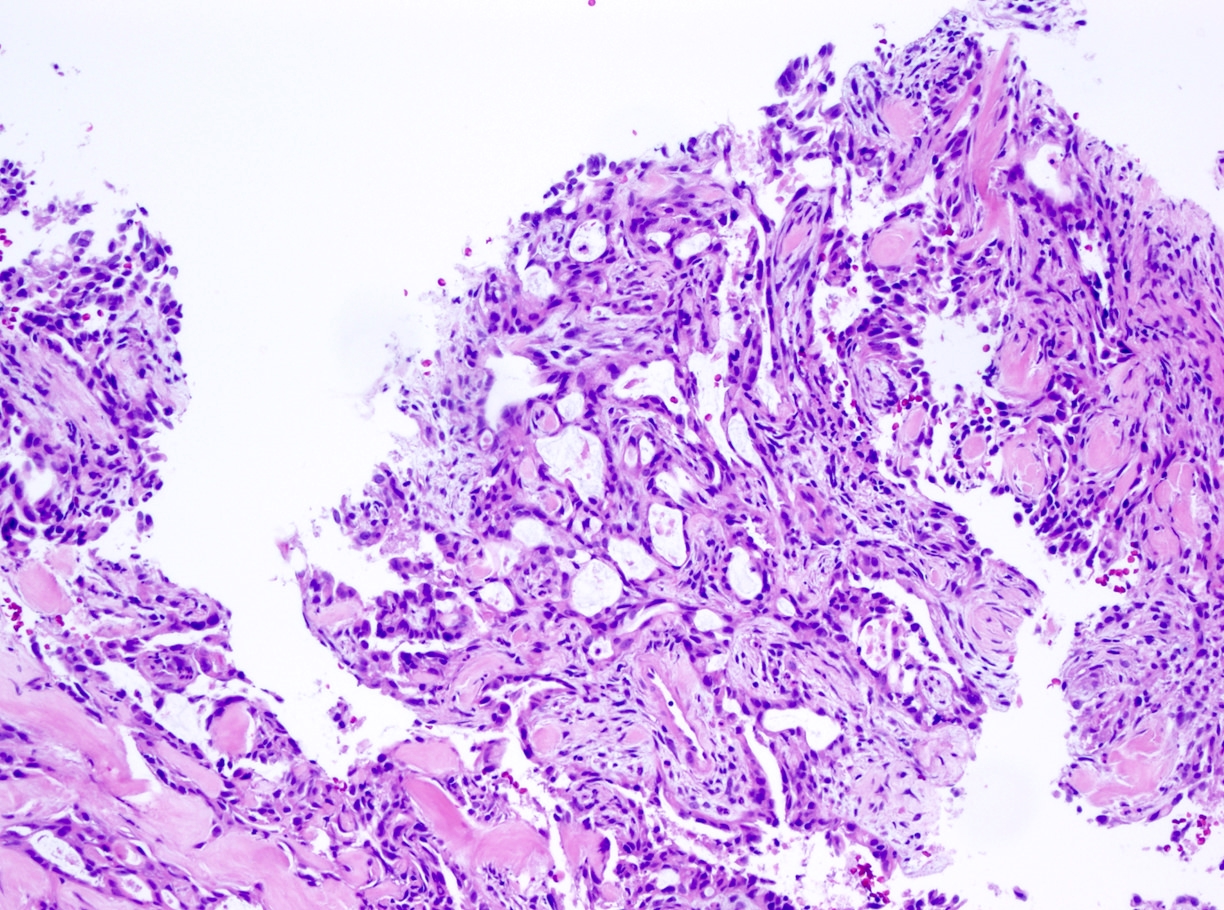
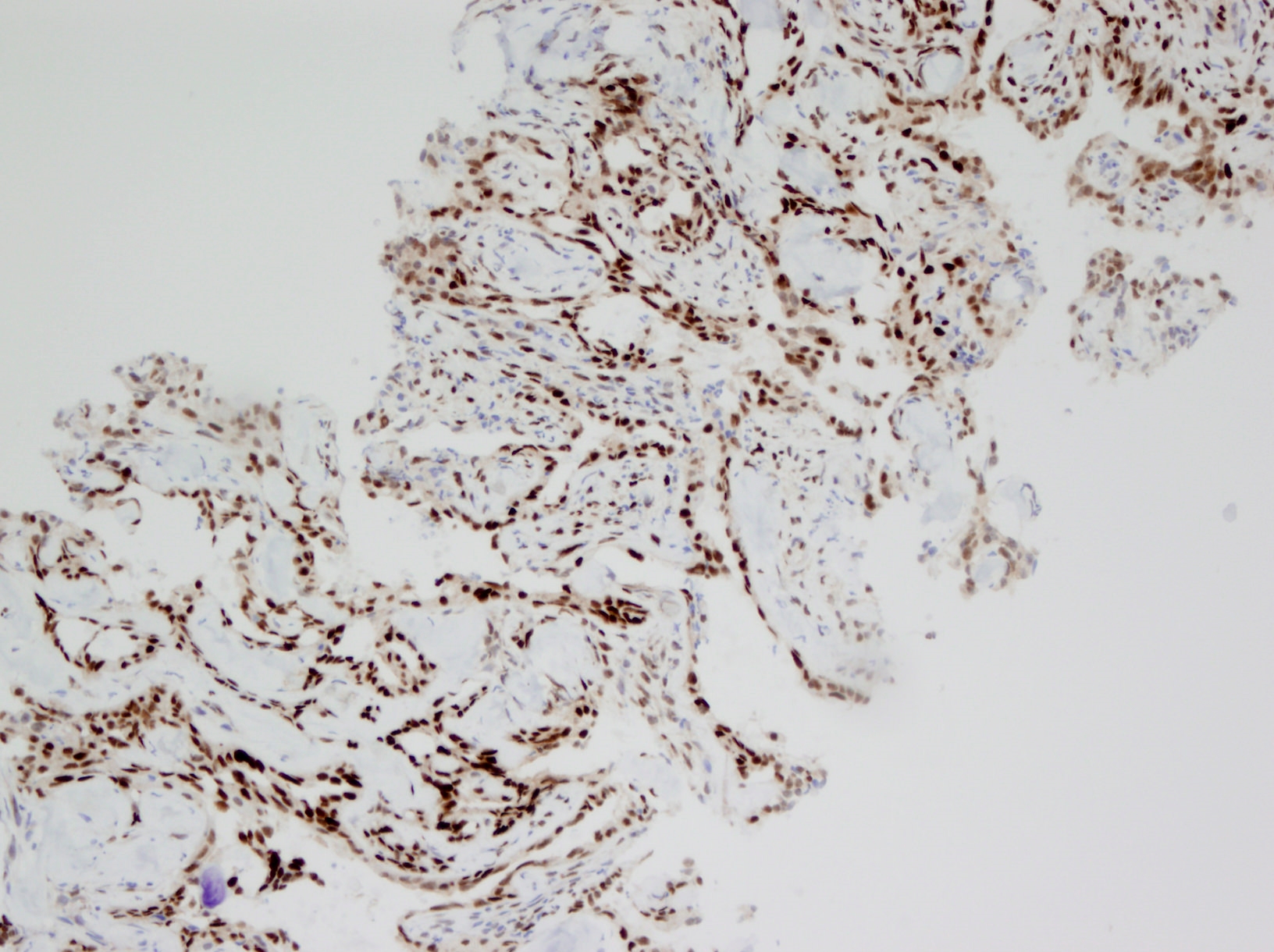
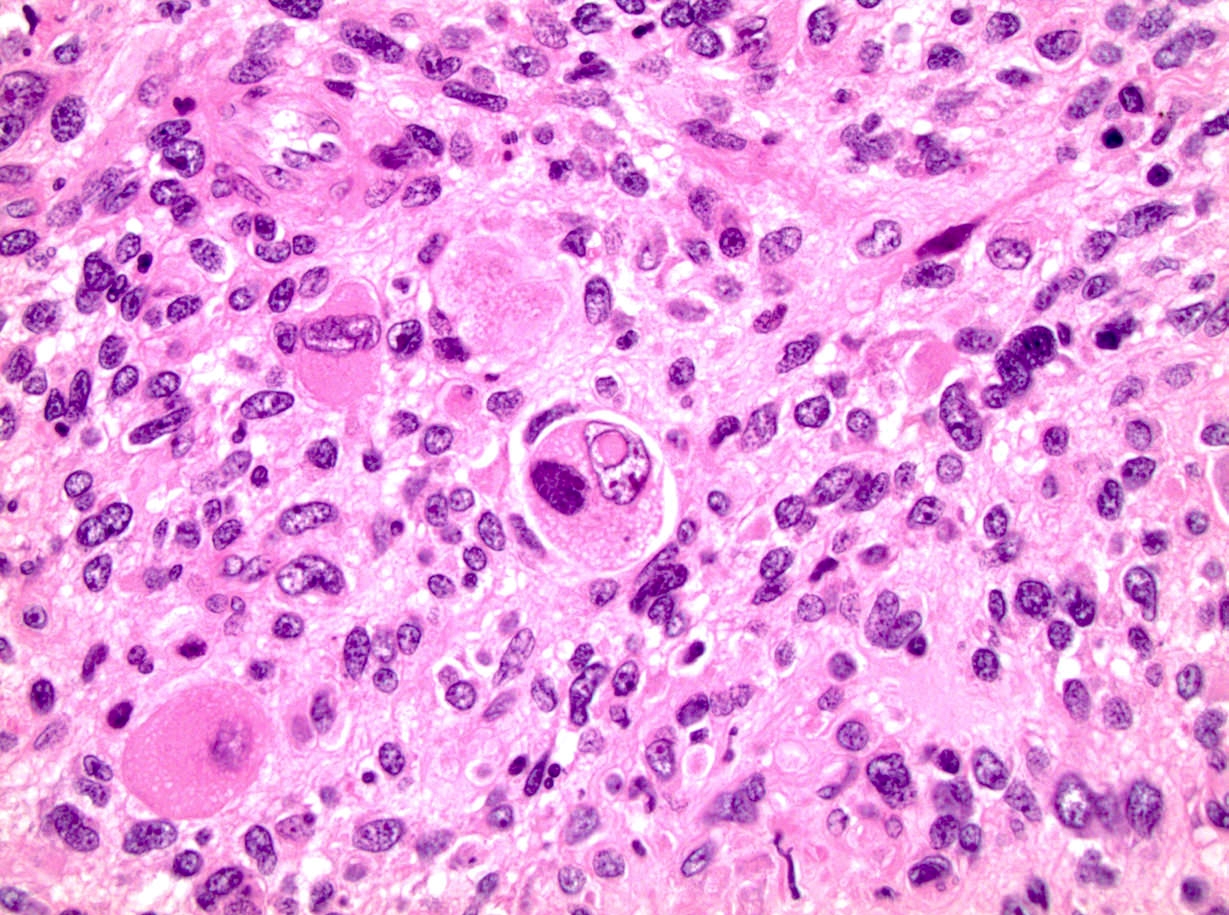
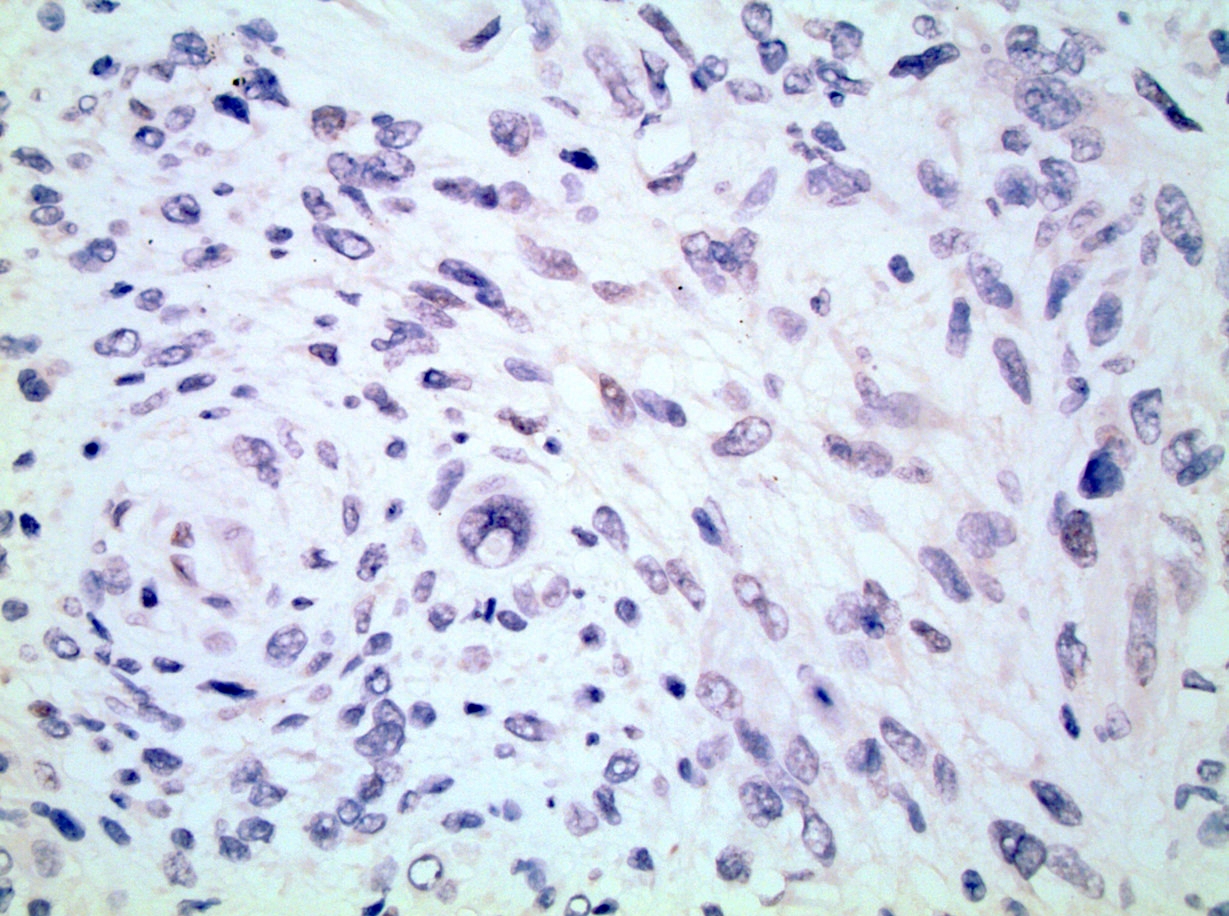
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Mark R. Wick, M.D.
Contributed by Debra L. Zynger, M.D.
Positive staining - normal
- Variably present in basal keratinocytes, adipocytes, perineurial cells, endothelial cells, mesothelial cells and chondrocytes, as well as sebaceous glands and follicular epithelium (Am J Clin Pathol 2011;135:839, Mod Pathol 2009;22:872, Int J Surg Pathol 2019;27:259)
Positive staining - disease
- Intense, diffuse nuclear staining with only rare background or cytoplasmic labeling is typically seen in synovial sarcoma, including all of its histologic subtypes (Ann Diagn Pathol 2014;18:369, Am J Clin Pathol 2011;135:839, Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1743, Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:240)
- In biphasic tumors, however, stronger staining has been noted in the glandular component than in the spindled component in some studies; in one study, biphasic tumors were more likely than other subtypes to demonstrate only weak nuclear staining (Mod Pathol 2009;22:872, Am J Clin Pathol 2011;135:839)
- TLE1 was previously regarded as both highly sensitive and specific for synovial sarcoma but further testing has shown instances of reactivity in other diagnostic entities as well
- Those lesions include some that are in the morphologic differential diagnosis of synovial sarcoma and others that are not
- Many, but not all, TLE1+ tumors besides synovial sarcoma show weak to moderate or heterogeneous labeling as opposed to strong, diffuse nuclear reactivity in synovial sarcoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:106, Mod Pathol 2009;22:872)
- Among the most commonly noted non synovial sarcoma lesions that may stain for TLE1 are peripheral nerve sheath tumors (including neurofibroma, schwannoma and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor) and solitary fibrous tumor / hemangiopericytoma (Am J Clin Pathol 2011;135:839, Mod Pathol 2009;22:872)
- TLE1 expression has also been noted in cutaneous neoplasms at a high frequency, including 100% of atypical fibroxanthomas, 96% of sebaceous adenomas, 80% of sebaceomas, 90% of sebaceous carcinomas, 57% of melanoma with spindle cell morphology, 95% of basal cell carcinomas, 94% of basal cell adenomas and 63% of squamous cell carcinomas (J Cutan Pathol 2020;47:135, Am J Dermatopathol 2019;41:1, Int J Surg Pathol 2019;27:259, Diagn Pathol 2018;13:48)
- Other diagnostic entities that are noted to be positive for TLE1 in > 50% of cases include but may not be limited to:
- Sinonasal glomangiopericytoma: 100% based on 6 total cases (Pathol Res Pract 2019;215:983)
- Primary intracranial sarcoma, DICER1 mutant: 100% based on 6 total cases (Histopathology 2021;78:265)
- BCOR rearranged tumors: 60 - 100% (Diagn Pathol 2021;16:50, Virchows Arch 2017;470:373, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1713, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1702)
- Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma (AFH), including pulmonary primary AFH: 100%, based on a limited number of cases (Thorac Cancer 2021;12:314, Pathology 2020;52:722, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2019;27:e1)
- Biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma: 100%, although this is based on a limited number of cases and noted to be patchy (Virchows Arch 2018;473:615)
- Clear cell sarcoma of the kidney (CCSK): 94% with some variability noted (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2020;23:345)
- Glomus tumor (subcutaneous): approximately 92% with a mixture of strongly positive cases and weak medium positive cases (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:524)
- CIC associated sarcomas: approximately 89% based on 9 total cases and noted to be weak (Virchows Arch 2017;470:373)
- Malignant rhabdoid tumor / atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor: 78% with ≥ 2+ nuclear staining (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2018;21:522)
- Mesothelioma: 69%, with 2+ or 3+ positivity (Virchows Arch 2010;457:577)
- Endometrial stromal sarcoma: 66%, based on 3 total cases (Mod Pathol 2009;22:872)
- Ewing-like sarcomas: 60% (Diagn Pathol 2021;16:50)
- Melanoma with spindle cell morphology: 57% (Int J Surg Pathol 2019;27:259)
Negative staining
- Diagnostic entities that are noted to occasionally demonstrate TLE1 expression but are more commonly found to be negative (strongly positive in < 50% of cases collectively in the reviewed publications; some entities based on a limited number of evaluated cases): rhabdomyosarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, Ewing sarcoma, chondrosarcoma, clear cell sarcoma, carcinosarcoma, SETTLE (spindle epithelial tumor with thymus-like differentiation), GIST (gastrointestinal stromal tumor), undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma, liposarcoma, lipoma, epithelioid sarcoma, and sarcomatoid carcinoma (Int J Gen Med 2021;14:9173, Virchows Arch 2017;470:373, Mod Pathol 2009;22:872, Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1179, Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:240)
- TLE1 expression has been seen to varying degrees in carcinomas, including those of the breast, stomach and lung; most tumor types demonstrated strong positivity in < 50% of cases in the reviewed publications, however some tumor types demonstrated positivity within only a small total number of cases precluding confident characterization of immunophenotype based on this data (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2018;26:368, J Breast Cancer 2017;20:45, J Gastric Cancer 2016;16:21, Cancer Res 2006;66:1294)
- See Positive staining - disease regarding cutaneous neoplasms
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Synovial sarcoma is classically characterized by t(X;18), which leads to SS18-SSX gene fusions, for which fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) has been shown to have a sensitivity of 86 - 97% and a specificity of up to 100%
- TLE1 immunostains can be useful in identifying a specific subpopulation of tumor cells for FISH analysis or in cases with cryptic X;18 rearrangement (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1743)
Sample pathology report
- Soft tissue, right anterior thigh, biopsy:
- Synovial sarcoma, monophasic type (see comment)
- Comment: Microscopic examination demonstrates a monotonous spindle cell proliferation with a fascicular to storiform architecture. Up to 8 mitoses per 10 high power fields are noted. Immunohistochemical stains demonstrate that the tumor cells strongly and diffusely express BCL2 (cytoplasmic) and TLE1 (nuclear). There is very focal EMA expression. The tumor cells are negative for S100, myogenin, myoD1, CD34, MUC4 and ERG. Fluorescence in situ hybridization for SS18 demonstrates a gene rearrangement (see addendum report for full details). These findings support the diagnosis of synovial sarcoma.
Board review style question #1
Which of the following pathways is inhibited by TLE1?
- IGF signaling pathway
- JAK / STAT signaling pathway
- MAPK signaling pathway
- VEGF signaling pathway
- WNT / beta catenin signaling pathway
Board review style answer #1
E. WNT / beta catenin signaling pathway
Comment Here
Reference: Transducin-like enhancer of split 1 (TLE1)
Comment Here
Reference: Transducin-like enhancer of split 1 (TLE1)
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2