Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Less common usage | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Morelli L, Luchini C. CD71. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cdmarkerscd71.html. Accessed May 8th, 2024.
Definition / general
- CD71 is an integral membrane protein that mediates the uptake of transferrin iron complexes
- In human tissues, CD71 is more highly expressed in placental syncytiotrophoblast, myocytes, hepatocytes, basal keratinocytes, endocrine cells of the pancreas, spermatocytes and erythroid precursors
- CD71 is present on actively proliferating cells, essential for iron transport into proliferating cells (benign and malignant)
- Can be expressed by tumor cells; for example, in breast cancers and squamous cell carcinomas of the esophagus
- Level of transferrin receptor is higher in early erythroid precursors during the intermediate normoblast phase, after which expression decreases through the reticulocyte phase
Essential features
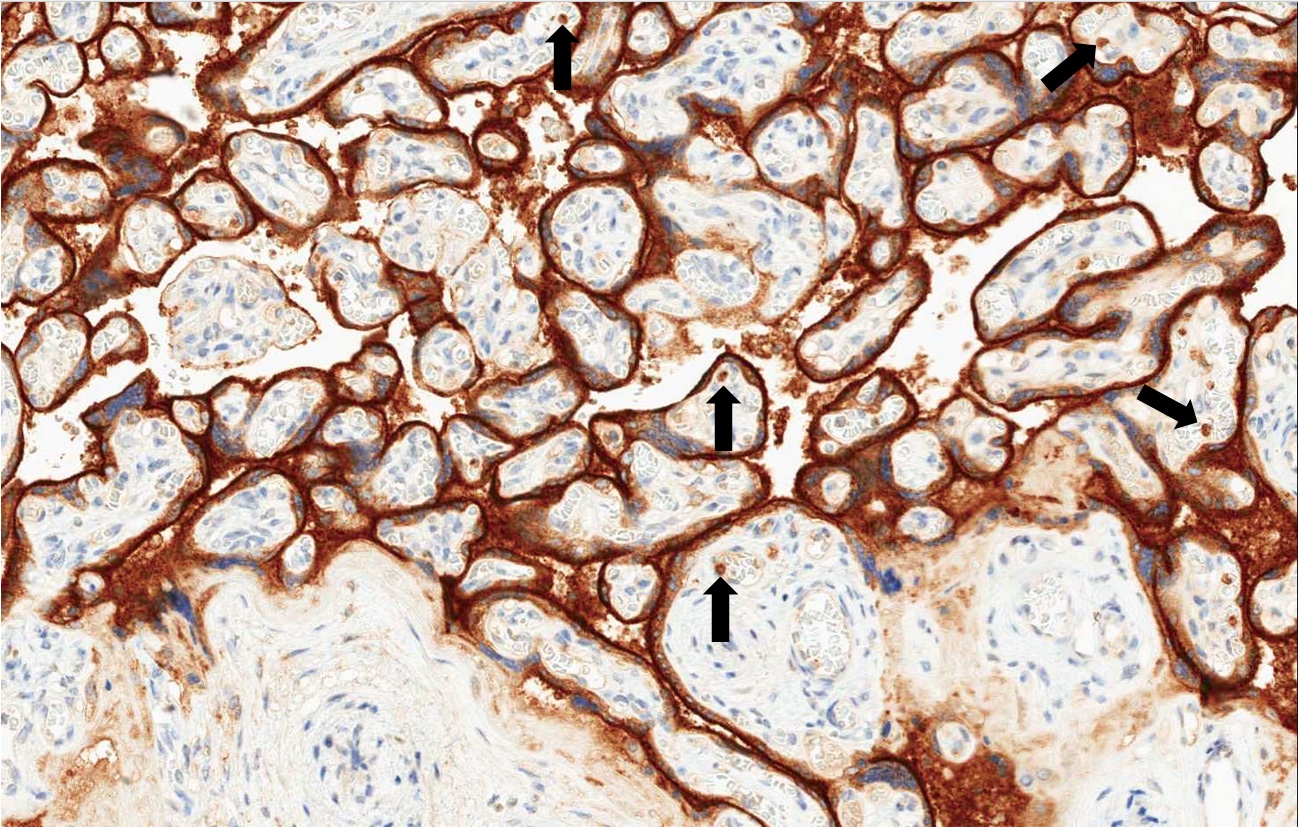
- CD71 is a robust immunohistochemical marker in gestational pathology, used for identifying nucleated red blood cells that can help in excluding a complete mole, and for identifying chorionic villi to demonstrate gestation even in the case of massive necrotic hemorrhagic modifications
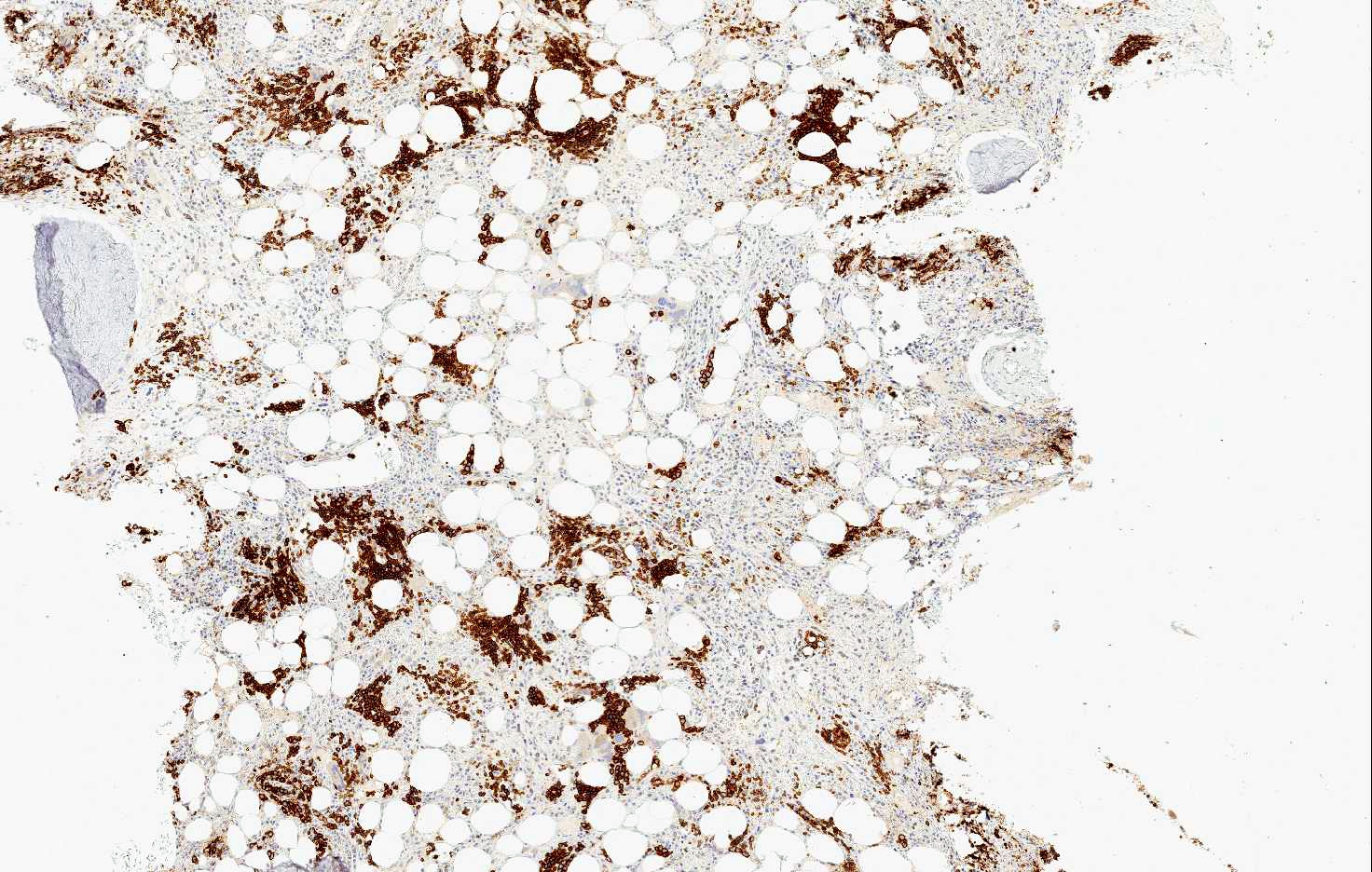
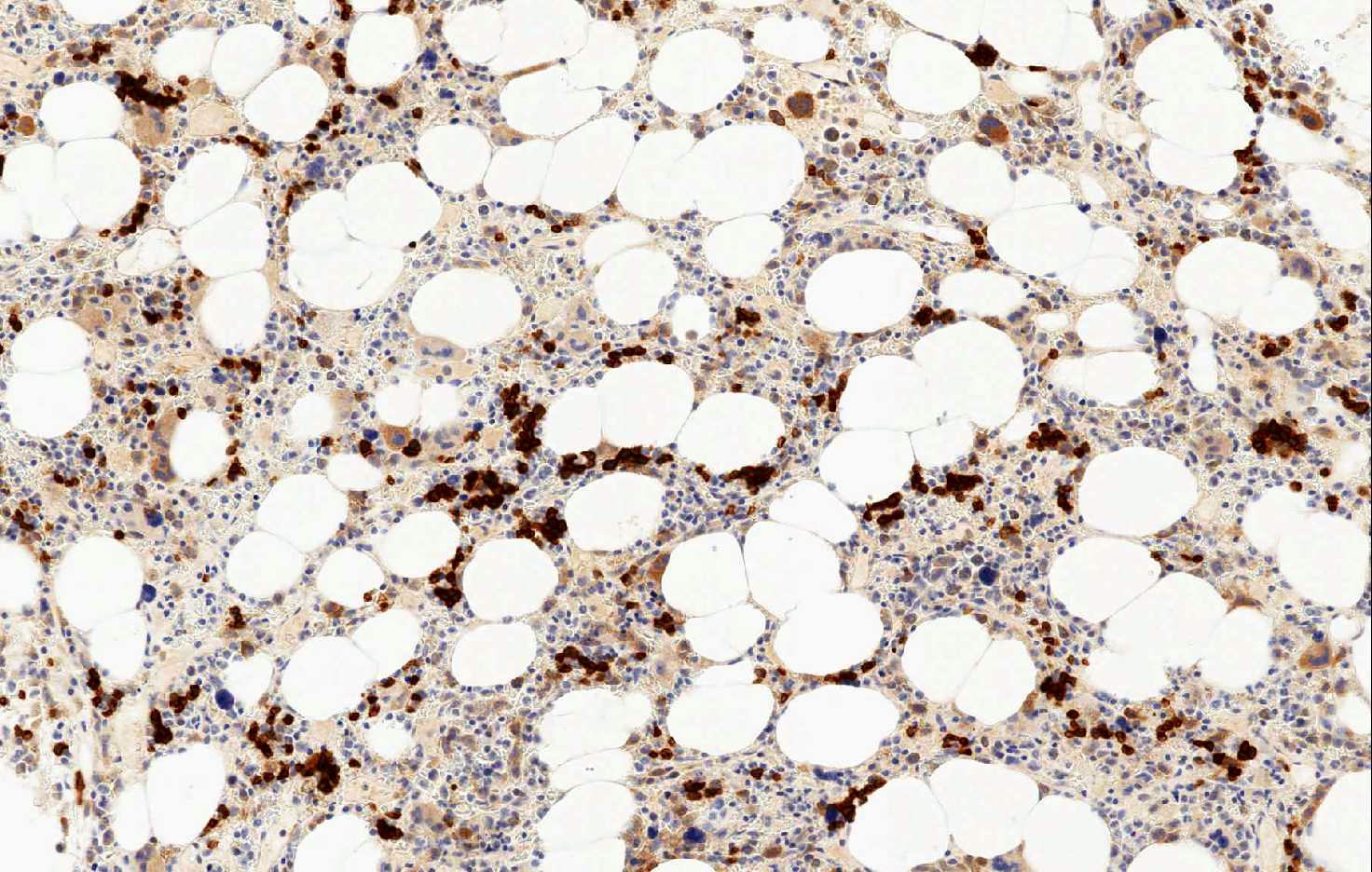
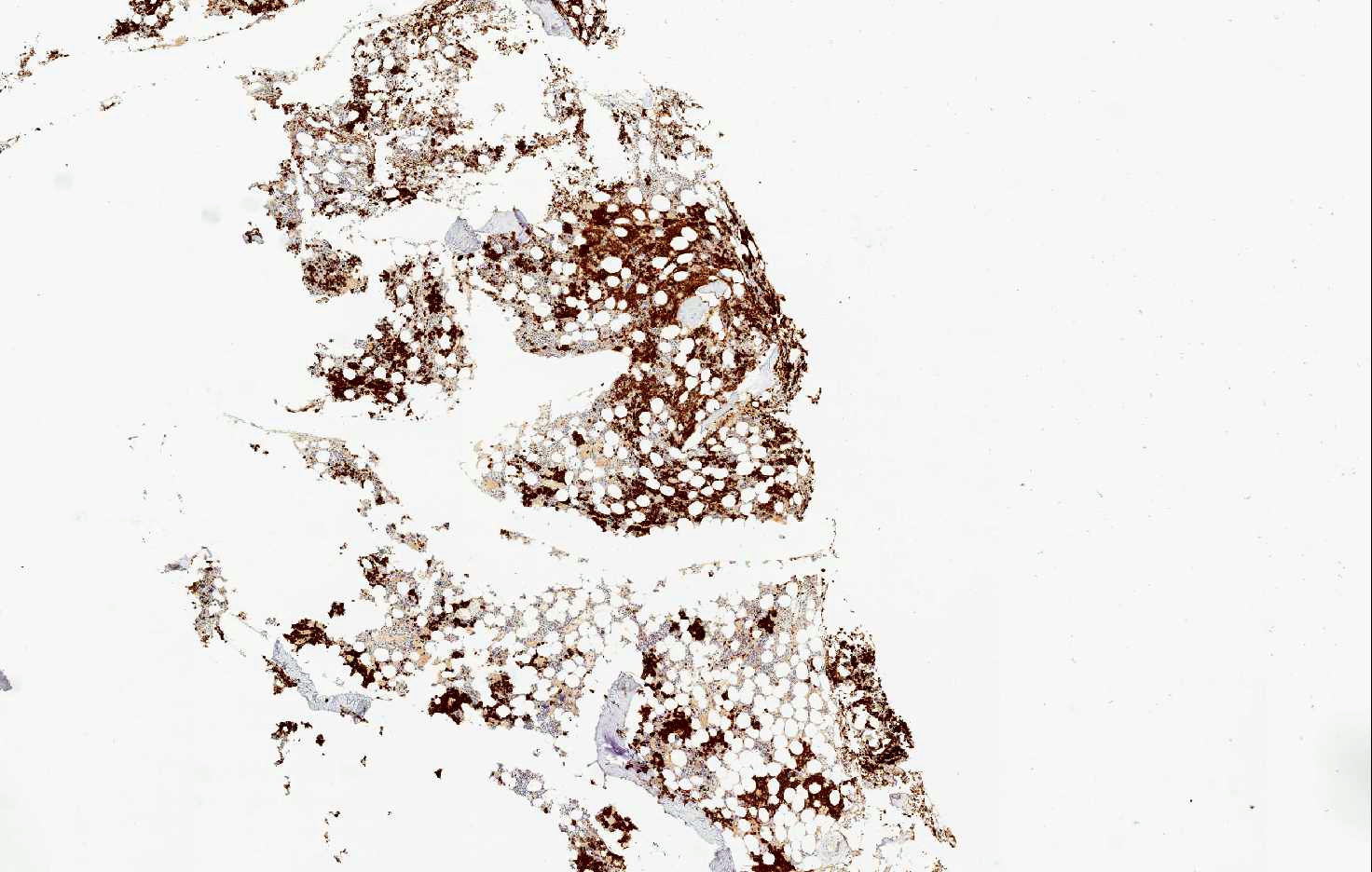
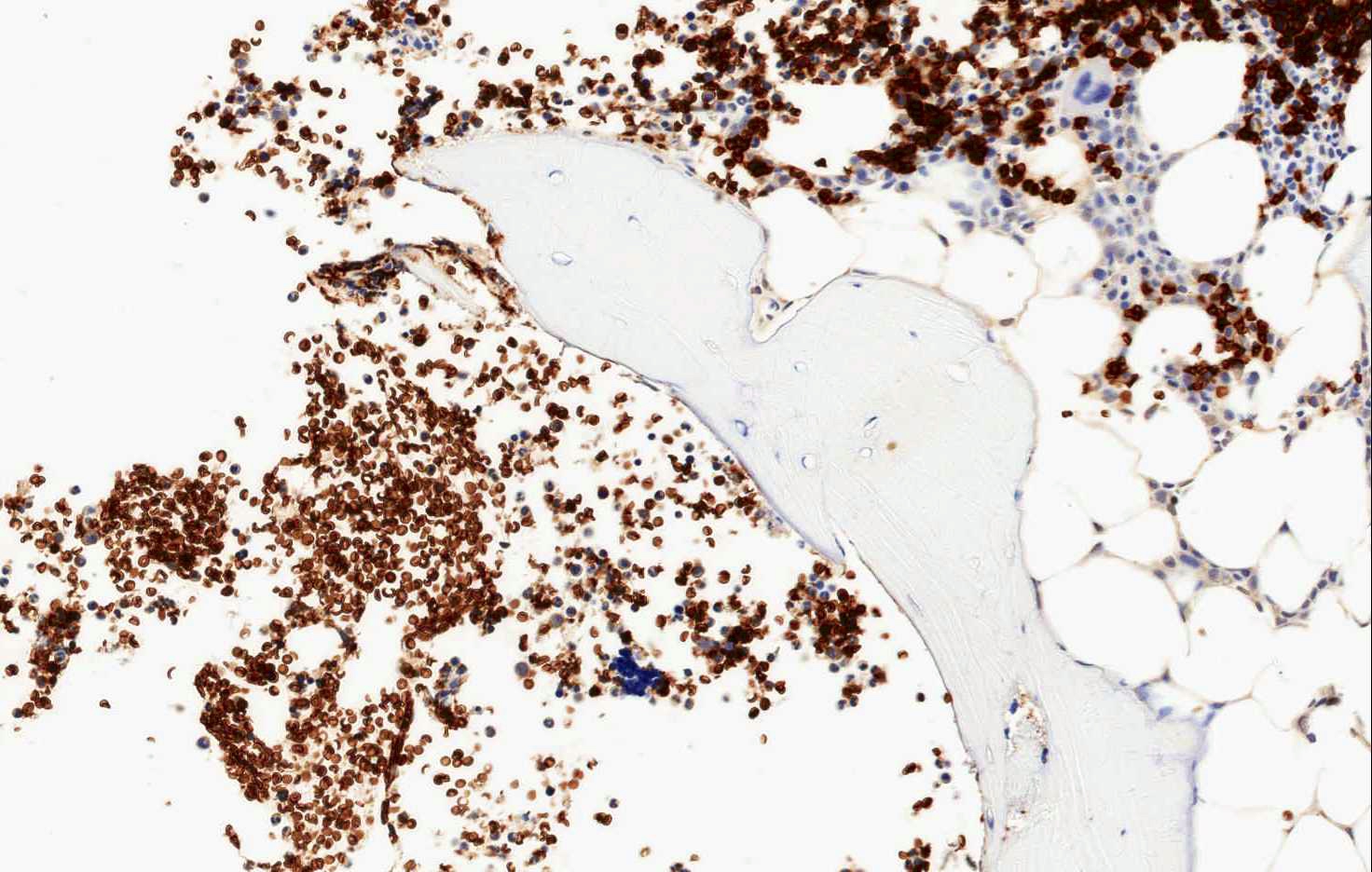
- In hematopathology, CD71 is very useful because it is expressed only by erythroid precursors within the normal hematopoietic marrow and spleen and can aid in the correct identification of all erythroid precursors
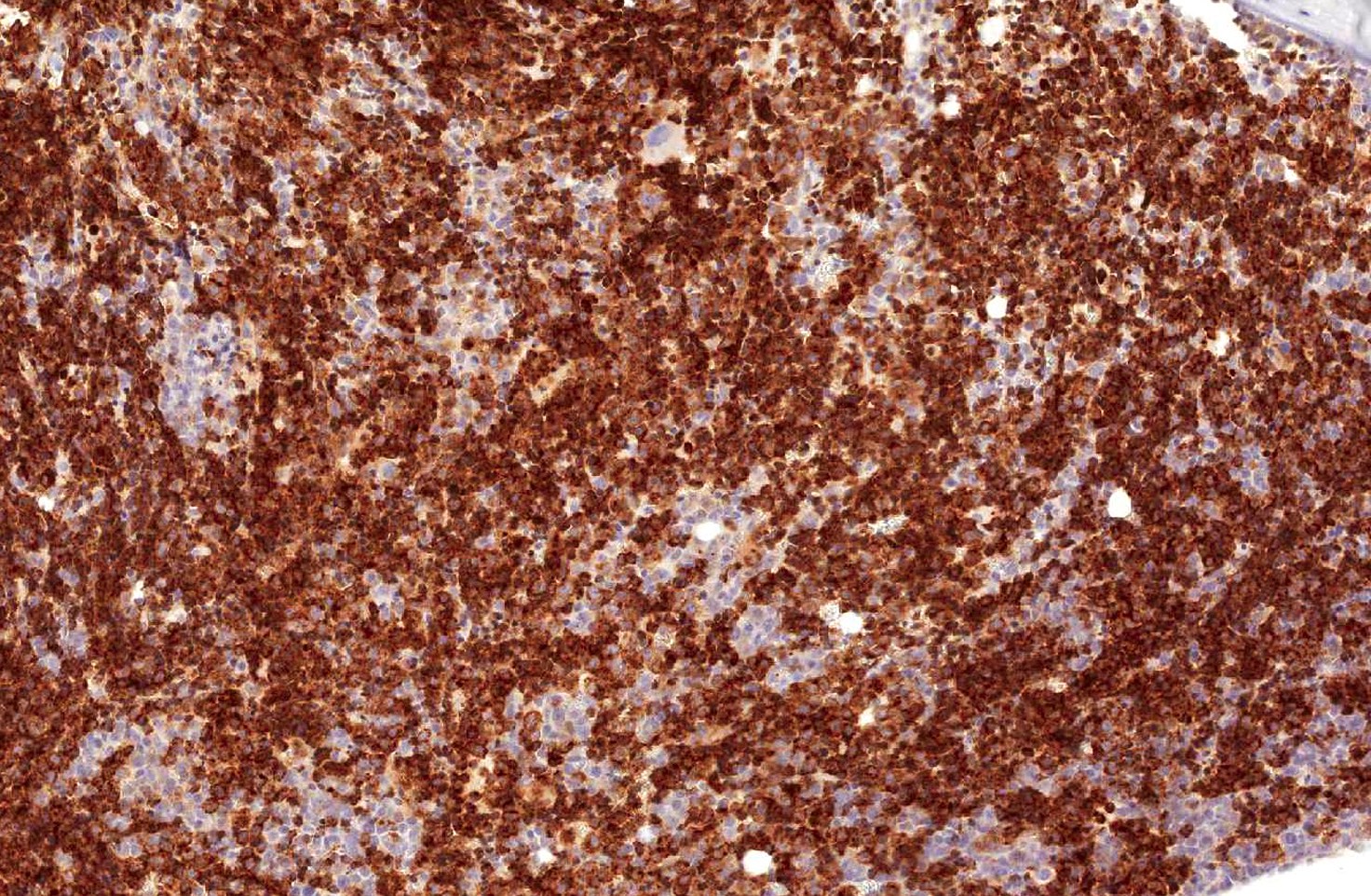
- CD71 expression is important for the diagnosis of the acute myeloid leukemia M6 (acute erythroleukemia)
Terminology
- Also known as transferrin receptor
Pathophysiology
- It is a homodimeric glycoprotein of 760 amino acids that binds to diferric transferrin at the cell surface
- Binding is followed by the internalization, a mechanism partially regulated by hereditary hemochromatosis protein; diferric iron is subsequently released from transferrin owing to endosomal acidification
Interpretation
- To be considered positive, immunohistochemistry for CD71 must stain cell membrane
- Other locations of staining (e.g. nucleus) are considered not reliable
Uses by pathologists
- CD71 is a robust immunohistochemical marker for the detection of nucleated red blood cells and chorionic villi, especially in presence of necrosis (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2016;24:215)
- Demonstration of nucleated red blood cells can be important in molar pathology, helping to exclude a complete mole (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2016;24:215)
- Used to detect micronucleated reticulocytes / Howell-Jolly bodies by flow cytometry, also used to test for erythropoietin doping by athletes (Mutat Res 2003;542:77)
- In hematopathology, CD71 is very useful because it is expressed only by erythroid precursors within the normal hematopoietic marrow and spleen
- CD71 has particular utility for identification of erythroid precursors, differently from glycophorin that marks all types of red blood cells
- In hematopathology, it is useful in identifying erythroid precursors in red blood cell hypoplasia and hyperplasia, with or without dyspoietic features (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:723)
Less common usage
- CD71 is also useful in the cytometry evaluation of childhood acute lymphoid leukemia, giving potential information regarding patient survival (Folia Histochem Cytobiol 2012;50:304)
- In lymph node neoplastic pathology, using flow cytometry, CD71 may be a useful tool in the differential diagnosis between primary mediastinal large B cell lymphoma and diffuse large B cell lymphoma, NOS and in the differential diagnosis between Burkitt lymphoma and CD10+ diffuse large B cell lymphoma, NOS (Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2018;94:459, Am J Clin Pathol 2012;137:665)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Erythroid precursors, placental syncytiotrophoblast, myocytes, hepatocytes, basal keratinocytes, endocrine cells of the pancreas, spermatocytes and capillary endothelium in the brain
- Tumor cells may express this marker
Positive staining - disease
- CD71 is an essential marker in the diagnosis of myeloproliferative neoplasms and myelodysplastic syndromes, using both flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry (Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2015;88:125, Haematologica 2017;102:308, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2016;24:51)
- CD71 could be useful in flow cytometry to discriminate between follicular lymphoma (FL) and CD10+ large B cell lymphomas (LBCL), because its fluorescence intensity is higher in LBCL (Am J Clin Pathol 2006;126:39, Am J Clin Pathol 2012;137:665)
- Another useful application of CD71 in flow cytometry regards its determination for the diagnosis of acute lymphoid leukemia (Folia Histochem Cytobiol 2012;50:304, Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 2018;18:610)
- Its expression is important for the diagnosis of the acute myeloid leukemia M6 (acute erythroleukemya) (Leuk Lymphoma 2014;55:892)
- CD71 can be also detected by flow cytometry in neoplastic cells of primary effusion lymphoma (APMIS 2009;117:222)
- CD71 could be useful in the diagnosis of breast implant associated ALK anaplastic large cell lymphoma, which shows positivity in the neoplastic cells (Clin Cancer Res 2012;18:4549)
Board review style question #1
- In gestational pathology, what can CD71 be used for?
- CD71 is a useful marker in gestational pathology only in addition with beta HCG immunohistochemistry
- CD71 is not a useful marker in gestational pathology
- For staining chorionic villi, also in case of necrotic hemorrhagic modifications and for staining nucleated red blood cells
- Only for highlighting nucleated red blood cells
- Only for highlighting the presence chorionic villi
Board review style answer #1
C. For staining chorionic villi, also in case of necrotic hemorrhagic modifications and for staining nucleated red blood cells. CD71 is a very useful marker in gestational pathology. It stains chorionic villi, even in case of massive necrotic hemorrhagic modifications. In these cases, CD71 is of great help since hematoxylin eosin staining cannot always permit their identification. It is also useful since it stains nucleated red blood cells that can help in excluding the presence of a complete mole in gestational pathology.
Comment Here
Reference: CD71
Comment Here
Reference: CD71
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
B. Erythroid precursors. CD71 is a very helpful marker for staining erythroid precursors.
Comment Here
Reference: CD71
Comment Here
Reference: CD71