Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Gonzalez RS. Stercoral ulcer. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colonstercoralulcer.html. Accessed May 13th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Ulceration of colonic mucosa secondary to impacted feces
Essential features
- Inspissated feces can cause rectosigmoid ulceration in elderly patients
- May perforate and lead to death
Sites
- Usually in rectosigmoid
Etiology
- Impacted feces stagnate, eventually eroding and ulcerating underlying mucosa
Clinical features
- Acute gastrointestinal bleeding in an elderly or bedridden patient
- Patients usually have a history of constipation and hypertension and, possibly, dialysis (Open J Gastroenterol 2012:2;45, Clin Nephrol 2012;77:75)
- Mortality rate may exceed 50% if ulceration leads to perforation (Am Surg 1982;48:20)
Diagnosis
- Proposed criteria for stercoral perforation: round / ovoid antimesenteric perforation > 1 cm, associated with fecaloma, showing necrosis / ulcer / chronic inflammation microscopically (Dis Colon Rectum 2000;43:991)
Case reports
- 85 year old man with lower gastrointestinal bleeding (CMAJ 2011;183:E134)
Gross description
- Sharply demarcated ulcer(s)
- Perforation may be present
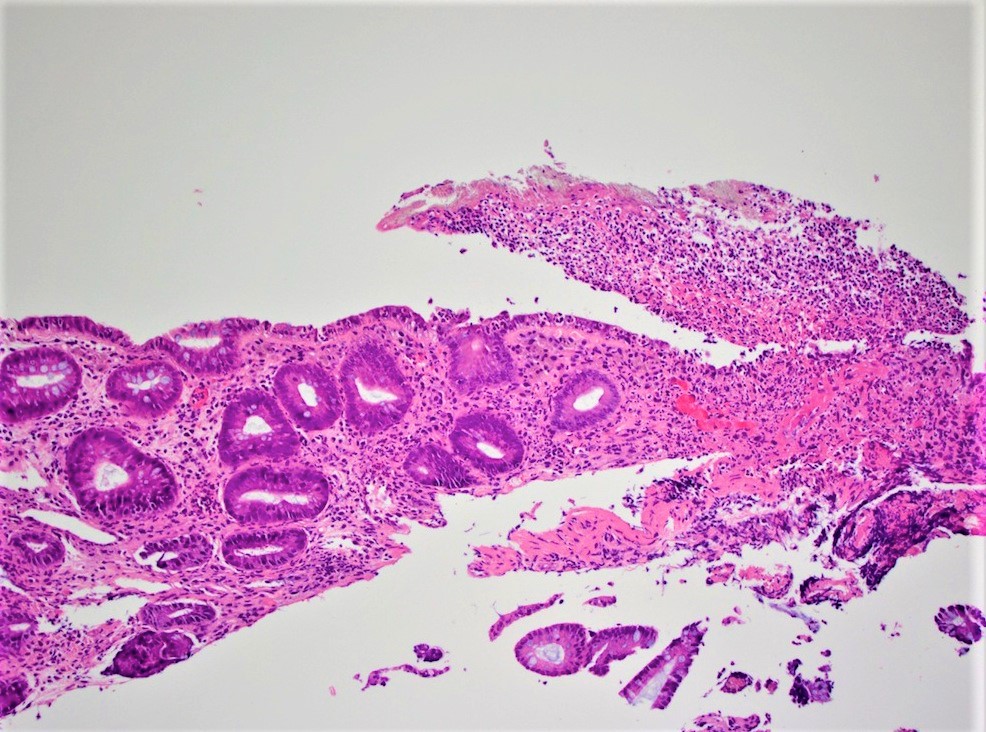
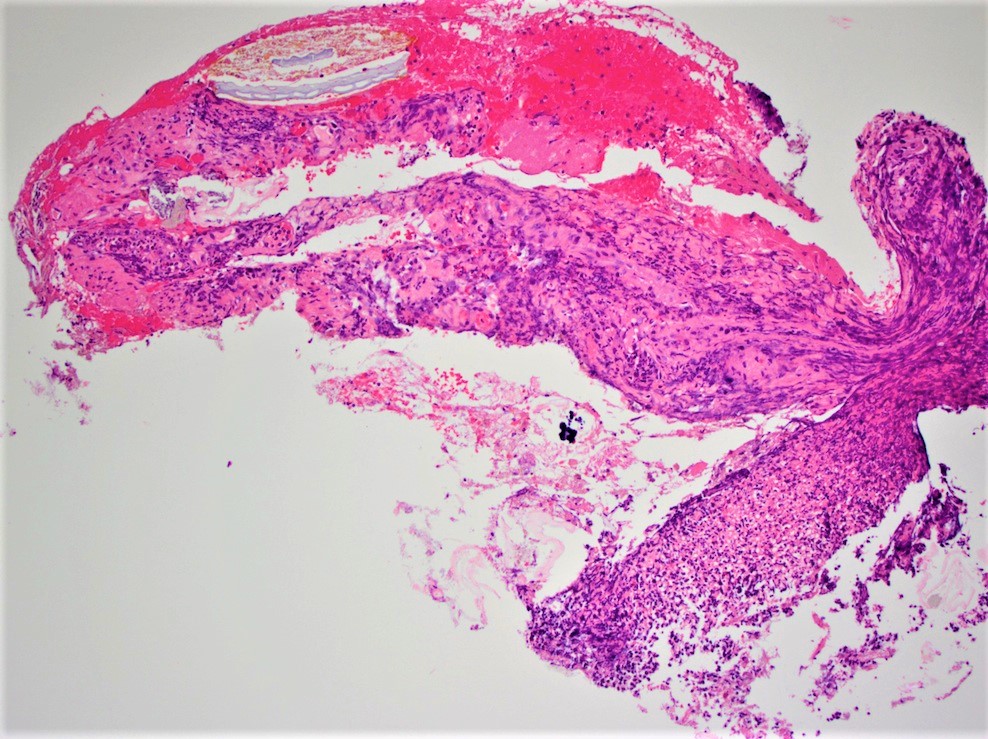
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Colonic ulceration / perforation
- Fecal material may or not may be observable microscopically
Sample pathology report
- Transverse colon, ulcer, biopsy:
- Colonic mucosa with ulceration and embedded fecal material (see comment)
- Comment: The findings are suggestive of a stercoral ulcer.
Differential diagnosis
- Other causes of colonic ulceration / perforation include:
- Colorectal carcinoma:
- Malignant cells present
- Solitary rectal ulcer syndrome:
- Prolapse type changes visible
- Ischemic colitis:
- Background ischemic type changes present
- Inflammatory bowel disease:
- Background nonulcerated mucosa inflamed
- Diverticular disease related colitis:
- Diverticuli also present
- NSAID colitis:
- Difficult to confirm based on histopathology alone
- Colorectal carcinoma:
Additional references
- Overview of stercoral perforation (Sao Paulo Med J 1996;114:1317)
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1